Jan 31, 2026
Testosterone replacement therapy and peptide therapy look almost identical on paper. Both promise higher testosterone. Both target men who feel sluggish, weak, and frustrated by declining hormone levels. Both involve injections, protocols, and lab work. But in practice? The outcomes diverge in ways that matter enormously for your long-term health, your fertility, and your ability to walk away from treatment without consequence.
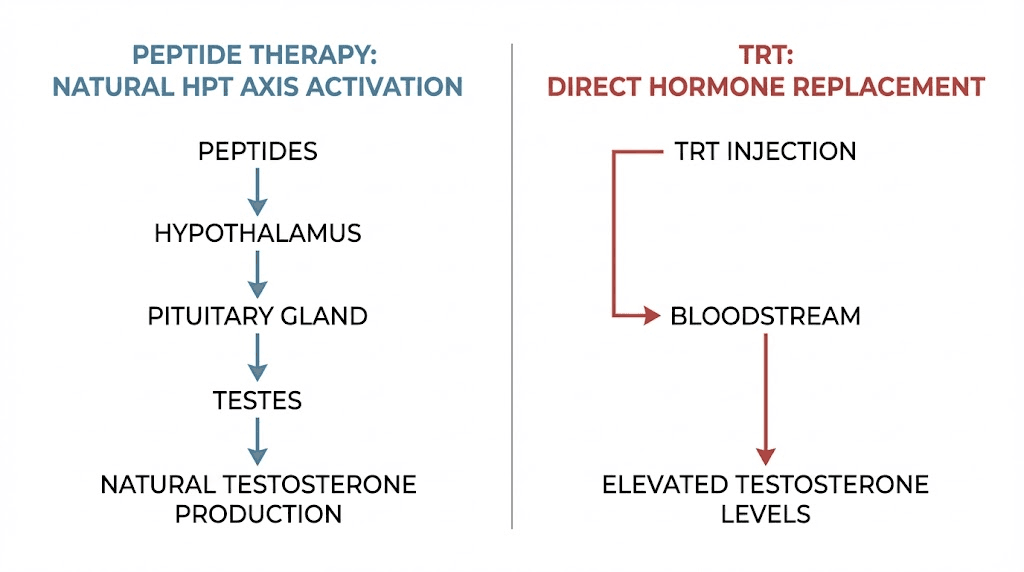
Here is the core difference. TRT replaces your testosterone from the outside. Peptides signal your body to make more of its own. That single distinction ripples outward into every decision you will face: how fast you see results, what side effects you risk, whether you can still have children, and whether stopping treatment leaves you worse off than when you started. One approach hands you the hormone directly. The other hands your body the instructions to build it.
This is not a simple "which is better" debate. Some men genuinely need TRT. Their testes have failed. Their levels sit in the basement despite every lifestyle intervention. For them, exogenous testosterone is not optional. It is medical necessity. But for the growing number of men in their 30s and 40s experiencing mild to moderate decline, peptides offer something TRT simply cannot: preservation. Preservation of natural production. Preservation of fertility. Preservation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis that keeps your entire endocrine system functioning as designed.
The peptide landscape has expanded rapidly. Compounds like sermorelin, ipamorelin, and CJC-1295 now sit alongside traditional testosterone therapies as legitimate tools for hormone optimization. Growth hormone secretagogues, selective estrogen receptor modulators, and synthetic GnRH analogs have created an entirely new category of intervention. Meanwhile, TRT itself has accumulated decades of clinical data, culminating in the landmark TRAVERSE trial of 5,246 men that reshaped how physicians view cardiovascular risk. Both paths have evidence. Both have limitations. And choosing between them, or combining them, requires understanding exactly what each one does inside your body.
This guide covers everything. Mechanisms. Side effects. Fertility implications. Cost. Protocols. Combinations. And the honest truth about who should choose what. If you are weighing peptides for testosterone optimization against conventional TRT, the next several thousand words will give you the clearest picture available anywhere.
How testosterone replacement therapy actually works
TRT is straightforward in concept. Your body is not producing enough testosterone, so you supply it externally. The testosterone enters your bloodstream, binds to androgen receptors, and your tissues respond as though your body made it naturally. Muscle protein synthesis increases. Energy returns. Libido improves. Brain fog lifts.
Simple. Effective. And deceptively incomplete as an explanation.
What happens beneath the surface is far more complex. When exogenous testosterone floods your system, your hypothalamus detects the elevated levels and reduces its output of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. The pituitary gland, receiving less GnRH stimulation, slows its production of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone. Your testes, starved of LH and FSH signaling, gradually reduce their own testosterone production. Over months, they can physically shrink. This cascade is called HPTA suppression, and it is not a rare side effect. It is the expected, inevitable consequence of exogenous testosterone administration.
The delivery methods vary. Intramuscular injections of testosterone cypionate or enanthate remain the most common, typically administered every one to two weeks. Transdermal gels applied daily offer steadier levels but lower peak concentrations. Patches work similarly but cause skin irritation in many users. Subcutaneous pellets implanted every three to six months provide the most consistent release but require a minor surgical procedure for each cycle. Each method delivers the same molecule. The differences lie in pharmacokinetics, convenience, and cost.
Results come fast. Most men notice improved energy and mood within two to three weeks. Libido changes often appear within three to six weeks. Body composition shifts, including increased lean mass and decreased fat mass, become measurable by three to six months. These timelines are well-documented across dozens of clinical trials and represent one of TRT greatest strengths: speed and reliability of response.
But speed has a cost. The TRAVERSE trial, published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2023, followed 5,246 men with hypogonadism and preexisting cardiovascular risk for an average of 33 months. The primary finding was reassuring: TRT was noninferior to placebo for major adverse cardiovascular events, with rates of 7.0% versus 7.3%. That headline calmed decades of cardiovascular fear. However, secondary findings told a more nuanced story. Men on TRT experienced increased rates of non-fatal arrhythmias, venous thromboembolic events, and acute kidney injury. These were not catastrophic risks, but they were real, measurable, and statistically significant.
The side effect profile extends beyond cardiovascular concerns. Erythrocytosis, defined as hematocrit exceeding 52%, occurs in a significant percentage of TRT users and requires regular blood monitoring. Acne, particularly on the back and shoulders, affects many men especially during the initial months. Androgenic alopecia can accelerate in genetically predisposed individuals. Gynecomastia, the development of breast tissue, results from testosterone aromatizing into estrogen. Fluid retention can elevate blood pressure. Sleep apnea may worsen. Each of these effects is manageable with proper medical oversight, but they add complexity and cost to what initially seems like a simple hormone replacement.
The deeper issue is commitment. Once your HPTA shuts down, restarting it is neither quick nor guaranteed. Some men recover natural production within months of stopping TRT. Others require a year or more. A subset never fully recovers. This reality transforms TRT from a treatment into a lifestyle commitment. You are not supplementing a hormone. You are replacing an entire system. And that system, once dormant, may not wake up when you call.
For men exploring their options, understanding TRT peptide alternatives provides critical context before making a decision that could last the rest of their lives.
How peptide therapy works: signaling versus replacing
Peptides take a fundamentally different approach. Instead of delivering testosterone directly, they send signals that encourage your body to produce more of its own hormones. The machinery stays active. The feedback loops stay intact. And the testes keep working.
Think of it this way. TRT is like hiring a contractor to build your house while your construction crew sits idle in the parking lot. Peptides are like giving your crew better blueprints, sharper tools, and a compelling reason to work harder. The house gets built either way. But only one approach leaves you with a functional crew when the project ends.
The peptides relevant to testosterone optimization fall into several categories, each targeting a different node in the hormonal network. Testosterone peptides work through multiple mechanisms, and understanding these mechanisms is essential for choosing the right protocol.
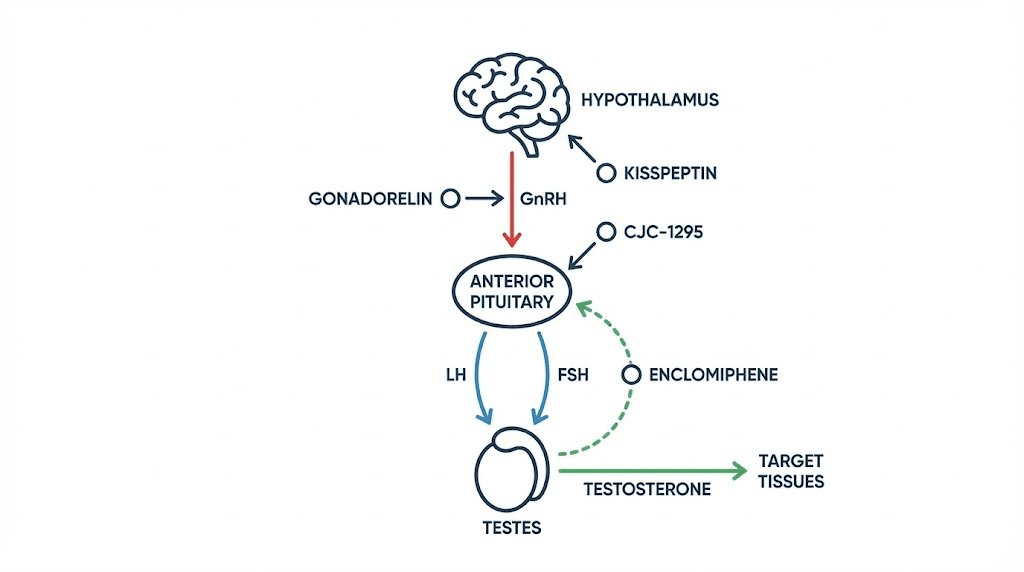
Gonadorelin: the GnRH mimic
Gonadorelin is a synthetic version of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. When administered in pulsatile fashion, it stimulates the pituitary gland to release LH and FSH, the same hormones that tell your testes to produce testosterone and sperm. Unlike TRT, which silences the pituitary, gonadorelin amplifies its signal. This makes it particularly valuable for men who want to boost testosterone while maintaining fertility. Clinicians frequently use it alongside TRT as a protective measure, keeping the testes active even when exogenous testosterone would otherwise shut them down.
Kisspeptin: the master regulator
Kisspeptin sits upstream of GnRH in the hormonal cascade. It is the signal that tells the hypothalamus to release GnRH in the first place. Research has shown that kisspeptin administration can robustly stimulate LH release and subsequent testosterone production. Because it works at the very top of the HPTA, it preserves the entire downstream pathway. Early clinical studies suggest it may also play roles in mood regulation and metabolic health, making it a compound of significant interest for comprehensive male optimization.
Enclomiphene: the selective modulator
Enclomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator that blocks estrogen feedback at the hypothalamus and pituitary. When these tissues cannot detect estrogen, they interpret the situation as low sex hormones and ramp up GnRH, LH, and FSH production. The result is increased testicular testosterone production without any exogenous hormone entering the body. Our enclomiphene peptide testosterone guide covers the clinical evidence in detail. Studies have shown enclomiphene can raise testosterone levels significantly while maintaining or even improving sperm parameters, a combination TRT cannot achieve alone.
Growth hormone secretagogues: the indirect boosters
CJC-1295 and ipamorelin do not directly increase testosterone. Instead, they stimulate growth hormone release, which creates a cascade of downstream benefits that synergize powerfully with testosterone. Published research on CJC-1295 demonstrated dose-dependent growth hormone increases of 2 to 10 times baseline levels sustained for six or more days, with IGF-1 increases of 1.5 to 3 times baseline lasting nine to eleven days. The compound demonstrated a half-life of 5.8 to 8.1 days, making it remarkably long-acting compared to native GHRH.
Ipamorelin, a selective growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist, offers a cleaner stimulation profile. Unlike older secretagogues such as hexarelin, ipamorelin does not significantly stimulate prolactin or cortisol release. This selectivity means fewer side effects and more predictable outcomes. The sermorelin ipamorelin blend has become one of the most popular peptide stacks for men seeking comprehensive hormone optimization.
Sermorelin deserves special mention. As a GHRH analog, it mimics the natural growth hormone releasing hormone your hypothalamus produces. Long-term studies have shown no receptor desensitization with continued use, meaning it remains effective over months and years without requiring dose escalation. The sermorelin before and after results many users report include improved sleep quality, reduced body fat, increased lean mass, and better recovery from exercise.
The timeline for peptide results differs from TRT. Most men notice initial improvements in sleep, energy, and recovery within two to four weeks. Testosterone increases of 30 to 60 percent typically manifest within the first two to three months. Body composition changes follow over three to six months. This is slower than TRT. Noticeably slower. But the trajectory is upward without the same dependency risk, and many men find the trade-off worthwhile.
Peptide therapy also offers flexibility. Unlike TRT, which typically requires continuous use to maintain benefits, many peptide protocols can be cycled. Users can run a peptide protocol for several months, taper off, and often maintain a significant portion of their gains because the underlying production machinery was never shut down. Our guide on cycling different peptides explains how to structure these on-off periods effectively.
The evidence base for peptides, however, is less robust than for TRT. Many findings come from animal studies, preliminary human trials, or clinical observations rather than large randomized controlled trials. This does not mean peptides are ineffective. It means the data is younger and less complete. Men considering peptide therapy should weigh this honestly against the decades of TRT research. For navigating this evolving landscape, SeekPeptides offers comprehensive resources that help separate established evidence from emerging research.
Side effects compared: what each approach costs your body
Every intervention has a price. The question is not whether side effects exist but which ones you can live with and which ones you cannot.
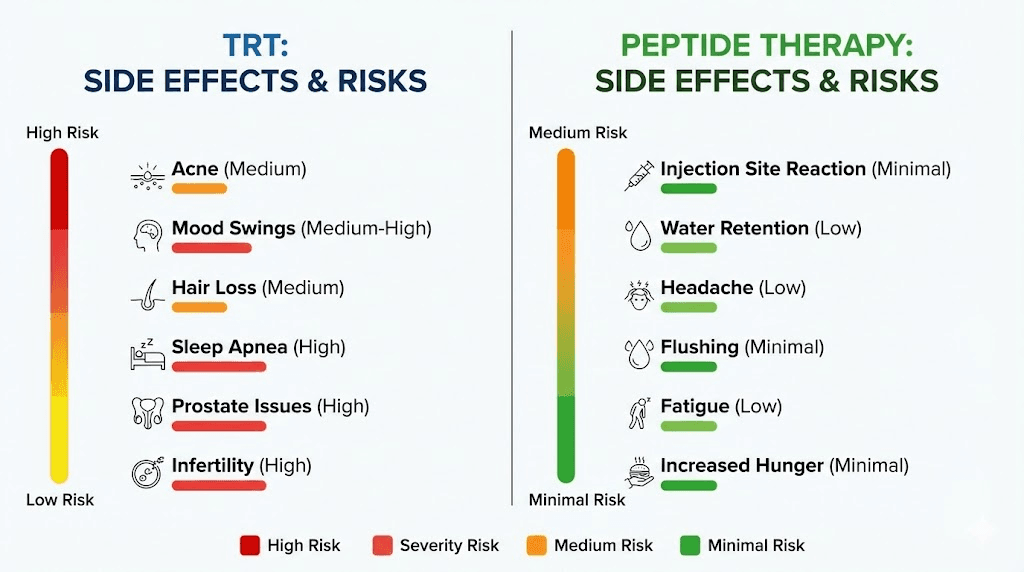
TRT side effects are well-documented across thousands of study participants and decades of clinical use. The most common include acne, which affects roughly 15 to 25 percent of users, particularly during the first three to six months. Androgenic alopecia accelerates in men with genetic predisposition, sometimes noticeably within months. Erythrocytosis, the elevation of hematocrit above 52 percent, requires regular monitoring and may necessitate therapeutic phlebotomy. Gynecomastia occurs when excess testosterone aromatizes into estrogen, and while manageable with aromatase inhibitors, it adds another medication to the protocol. Fluid retention can push blood pressure upward. The TRAVERSE trial added non-fatal arrhythmias, venous thromboembolic events, and acute kidney injury to the known risk profile.
Then there is the big one. HPTA suppression.
This is not a side effect in the traditional sense. It is the mechanism by which TRT works. Your body detects adequate testosterone and stops making its own. Testicular atrophy follows. Intratesticular testosterone drops. Spermatogenesis slows or stops. Recovery after cessation takes months to years, and some men never fully recover. The HCG peptides guide discusses how human chorionic gonadotropin can partially mitigate this shutdown, but prevention is always preferable to rescue.
Peptide side effects, by comparison, tend to be milder and more transient. Injection site reactions, including redness, swelling, and occasional bruising, are the most frequently reported. Some users experience water retention, particularly with growth hormone secretagogues, though this typically resolves within the first few weeks. Headaches occur in a minority of users and usually diminish with continued use. Transient flushing or dizziness can follow gonadorelin administration. The ipamorelin side effects profile is notably clean, which is one reason it has become such a popular choice.
The critical difference is what happens when you stop. Discontinuing peptides does not leave you in a hormonal deficit. Your HPTA was never suppressed. Your testes never went dormant. You may lose some of the enhancement you gained, but you return to your baseline rather than falling below it. Stopping TRT, by contrast, can leave you with lower testosterone than you had before starting, at least temporarily and sometimes permanently.
Side effect comparison at a glance
Side effect | TRT | Peptide therapy |
|---|---|---|
Acne | Common (15-25%) | Rare |
Hair loss acceleration | Common in predisposed | Not reported |
Erythrocytosis | Significant risk, requires monitoring | Not reported |
Gynecomastia | Possible (aromatization) | Not reported |
Fluid retention | Common | Mild, transient with GH peptides |
HPTA suppression | Guaranteed | Does not occur |
Testicular atrophy | Expected without HCG | Does not occur |
Fertility impact | Severe (suppresses spermatogenesis) | Minimal to none |
Cardiovascular risk | Arrhythmias, VTE (TRAVERSE data) | No significant data |
Injection site reactions | Common | Common |
Headaches | Uncommon | Occasional, transient |
Recovery after stopping | Months to years, sometimes permanent | Quick return to baseline |
This table tells a story that numbers alone cannot. TRT carries heavier side effects because it is a heavier intervention. It replaces a system rather than supporting one. For men with genuine hypogonadism, these risks are justified because the alternative, living with severely low testosterone, carries its own serious health consequences including metabolic syndrome, osteoporosis, depression, and cardiovascular disease. But for men with mild to moderate decline, the risk-benefit calculation shifts significantly toward peptides.
Understanding peptide therapy cost is also important in this comparison, as the financial commitment differs substantially between the two approaches.
The fertility question: where the gap becomes a canyon
If you want children, or even think you might someday, this section matters more than everything else combined.
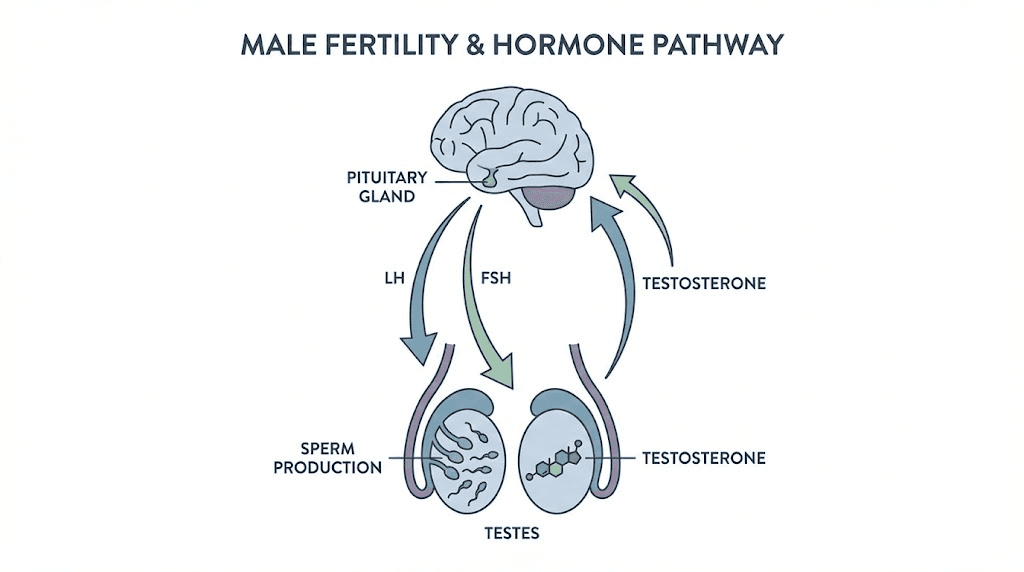
TRT suppresses spermatogenesis. Full stop. When exogenous testosterone shuts down LH and FSH production, the testes lose the signals they need to produce sperm. Intratesticular testosterone, which must be 50 to 100 times higher than serum levels for normal spermatogenesis, plummets. Sperm counts drop. For many men on TRT, counts reach zero. This effect can occur within weeks of starting treatment and may persist for months or years after discontinuation.
The clinical data is unambiguous. Multiple studies have demonstrated that testosterone administration, whether injectable, transdermal, or implanted, reliably suppresses spermatogenesis. The World Health Organization actually investigated testosterone as a male contraceptive in the 1990s, achieving azoospermia in approximately 65 percent of participants and severe oligospermia in most of the remainder. TRT is, in effect, male birth control. Yet many men begin treatment without understanding this, and some physicians prescribe it without adequate fertility counseling.
Peptide therapy preserves fertility because it works through the HPTA rather than around it. Gonadorelin maintains LH and FSH signaling, keeping the testes actively producing both testosterone and sperm. Enclomiphene, by blocking estrogen feedback at the hypothalamus, actually increases LH and FSH output. Studies have shown that enclomiphene can raise testosterone levels while simultaneously improving sperm parameters, a result that is pharmacologically impossible with TRT alone.
Research combining enclomiphene and gonadorelin has demonstrated that these peptides can raise LH and FSH even during concurrent TRT administration. This finding is remarkable because it suggests that the HPTA can be partially reactivated even in the presence of exogenous testosterone. For men who are already on TRT and want to preserve or restore fertility, this combination represents a significant clinical advance.
For men already on TRT who discover they want to conceive, HPTA restart protocols exist. The standard approach involves HCG priming at 1,500 to 3,000 IU administered two to three times weekly, followed by or combined with selective estrogen receptor modulators. Published data suggests success rates of 80 to 90 percent for restoring spermatogenesis in appropriate candidates, though "success" is defined variably across studies and full recovery can take six to twelve months or longer.
HCG itself mimics LH and directly stimulates testicular testosterone and sperm production. Our HCG peptides guide explains how this compound fits into both fertility preservation and post-TRT recovery. The HMG peptide, which contains both LH and FSH activity, can be even more effective for restoring complete spermatogenic function.
The bottom line is stark. A 32-year-old man who starts TRT without fertility protection may spend years trying to reverse the damage when he decides he wants a family. A 32-year-old man who chooses peptide therapy instead never faces that problem. The fertility gap between these two approaches is not a minor difference. It is a canyon.
Testosterone peptides: a closer look at each compound
The phrase "peptide therapy" covers a wide range of compounds with different mechanisms, different targets, and different evidence bases. Lumping them together does a disservice to both the science and the men trying to make informed decisions. Let us examine each one individually.
CJC-1295: the long-acting GH releaser
CJC-1295, whether with or without Drug Affinity Complex modification, is a growth hormone releasing hormone analog that stimulates the pituitary to release growth hormone. The published research is compelling. Dose-dependent GH increases of 2 to 10 times baseline persist for six or more days after a single injection. IGF-1, the downstream mediator of many GH effects, increases 1.5 to 3 times baseline for 9 to 11 days. The half-life of 5.8 to 8.1 days means less frequent dosing compared to native GHRH, which has a half-life of minutes.
While CJC-1295 does not directly raise testosterone, the growth hormone and IGF-1 increases it produces enhance body composition, recovery, and overall metabolic health in ways that complement testosterone optimization. Many clinicians prescribe CJC-1295 alongside testosterone-boosting interventions for a synergistic effect. The CJC-1295 dosage calculator can help determine appropriate starting doses based on individual factors.
Ipamorelin: the clean secretagogue
Ipamorelin binds to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor and triggers GH release from the pituitary. Its distinguishing feature is selectivity. Unlike GHRP-6 and GHRP-2, which also stimulate appetite-regulating ghrelin and stress hormone cortisol, ipamorelin causes minimal changes in prolactin and cortisol levels. This means the GH boost comes without the hunger spikes, cortisol elevation, or prolactin-related side effects that plague older compounds.
The ipamorelin versus CJC-1295 comparison is one of the most common questions in the peptide community. The short answer: they work through different receptors and combine beautifully. CJC-1295 provides the sustained baseline elevation while ipamorelin adds pulsatile peaks that mimic natural GH secretion patterns. Together, they produce results that neither achieves alone.
Sermorelin: the time-tested GHRH analog
Sermorelin has the longest clinical track record of any growth hormone secretagogue. It was FDA-approved for pediatric growth hormone deficiency in the 1990s and has been used off-label for adult GH optimization for decades. Its mechanism is straightforward: it mimics natural GHRH and stimulates the pituitary to release growth hormone in a physiological pulsatile pattern.
One of sermorelin most important advantages is the absence of receptor desensitization with long-term use. Many peptides lose effectiveness over time as receptors downregulate. Sermorelin does not exhibit this problem, making it suitable for extended protocols. The sermorelin cost guide provides current pricing information, and many users find it among the more affordable peptide options. Results documented in sermorelin before and after reports consistently show improvements in sleep quality, body composition, skin elasticity, and subjective well-being.
Enclomiphene: the testosterone-specific SERM
Enclomiphene occupies a unique position in this landscape. As a selective estrogen receptor modulator, it blocks estrogen receptors at the hypothalamus and pituitary, tricking these organs into perceiving low estrogen. The response is increased GnRH, LH, and FSH production, which directly drives testicular testosterone synthesis. The enclomiphene guide covers the clinical evidence showing testosterone increases of 200 to 400 percent in hypogonadal men, with preserved or improved semen parameters.
What makes enclomiphene special is directness. While GH secretagogues support testosterone indirectly through metabolic optimization, enclomiphene targets the testosterone production pathway itself. It tells your body to make more testosterone, and your body complies. For men whose primary goal is raising testosterone without exogenous hormones, enclomiphene may be the single most effective peptide option available.
Supporting peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500
Not all relevant peptides target testosterone directly. BPC-157 and TB-500, detailed in our BPC-157 TB-500 stacking guide, are tissue repair peptides that complement hormone optimization protocols. Men pursuing aggressive training programs alongside TRT or peptide therapy often experience joint pain, tendon strain, and slower recovery. These healing peptides address recovery from a completely different angle.
BPC-157, a pentadecapeptide derived from human gastric juice, has demonstrated remarkable healing properties across tendons, ligaments, muscles, and the gastrointestinal tract. The BPC-157 dosage calculator helps users determine appropriate dosing. TB-500, a synthetic version of thymosin beta-4, promotes angiogenesis and cell migration to damaged tissue. The TB-500 dosage calculator provides similar dosing guidance. Together, they form the popular wolverine stack, named for its remarkable regenerative effects.
For men on TRT or peptide therapy who want accelerated recovery, exploring tissue repair peptides alongside their hormone protocol can yield significant quality-of-life improvements. The fast injury healing resource provides additional context on how these compounds support physical recovery.
Body composition: muscle, fat, and the hormonal intersection
Men do not pursue testosterone optimization in a vacuum. They want to look better. Feel stronger. Perform at a higher level. Both TRT and peptides deliver body composition improvements, but through overlapping yet distinct mechanisms.
TRT directly activates androgen receptors in muscle tissue, increasing muscle protein synthesis and nitrogen retention. The result is measurable. Studies consistently show lean mass increases of 3 to 6 kilograms over six to twelve months of TRT, with concurrent fat mass reductions of 1 to 3 kilograms. These changes occur even without structured exercise, though training amplifies the effect dramatically. For men interested in maximizing these outcomes, our best peptides for muscle growth guide covers compounds that complement testosterone-driven anabolism.
Peptide therapy approaches body composition differently. Growth hormone secretagogues like CJC-1295 and ipamorelin stimulate lipolysis, the breakdown of stored fat, particularly visceral fat surrounding the organs. They also promote lean mass gains, though typically more modest than those seen with supraphysiological testosterone. The peptides for muscle growth overview explains how different peptides contribute to anabolic processes.
The fat loss angle deserves special attention. Many men with low testosterone carry excess visceral fat, which itself suppresses testosterone through aromatase activity and inflammatory cytokine production. This creates a vicious cycle: low testosterone promotes fat gain, and fat gain further suppresses testosterone. Breaking this cycle is essential, and peptides offer targeted tools. The best fat burning peptide options include compounds like AOD-9604 and 5-amino-1MQ, both of which promote fat metabolism without the androgenic side effects of testosterone. The peptides for fat loss resource page covers additional options in detail.
Tesamorelin, a growth hormone releasing hormone analog specifically approved for reducing visceral adipose tissue, represents one of the few FDA-approved peptide therapies. While approved for HIV-associated lipodystrophy, its mechanism of visceral fat reduction applies broadly. Men on TRT who still struggle with belly fat often find that adding a GH secretagogue addresses the adiposity component that testosterone alone cannot.
The peptides for weight loss and muscle gain category is one of the most searched topics in the peptide community, and for good reason. The dual goal of adding muscle while losing fat, the holy grail of body recomposition, is more achievable when multiple hormonal pathways are optimized simultaneously. Our lean peptides guide focuses specifically on compounds that support this recomposition goal.
For men primarily focused on fat loss, the peptides for weight loss guide and the bioactive precision peptides for weight loss article provide deep dives into specific compounds and protocols. Women facing similar challenges can consult the peptides for weight loss women guide for gender-specific considerations.
Energy, mood, and cognitive function
Low testosterone does not just affect muscles and fat. It clouds the mind. Saps motivation. Flattens mood. Many men describe the experience as living behind a fog that they cannot quite identify but that colors everything gray.
TRT clears this fog quickly. Androgen receptors populate the brain extensively, particularly in areas governing mood, motivation, and cognitive function. When testosterone binds these receptors, the subjective experience shifts. Clarity returns. Ambition resurfaces. The world regains its color. This is not placebo. Multiple neuroimaging studies have demonstrated that testosterone modulates brain activity patterns associated with motivation, spatial cognition, and emotional regulation.
Peptides offer their own cognitive benefits, though through different pathways. Growth hormone plays a significant role in brain health, influencing neuroplasticity, memory consolidation, and neuroprotection. The best peptides for brain function include compounds like semax, a synthetic analog of ACTH that enhances cognitive function through brain-derived neurotrophic factor upregulation. SS-31, a mitochondria-targeted peptide, supports cellular energy production in neurons and other high-demand tissues.
For men experiencing anxiety alongside low testosterone, the peptides for anxiety guide explores compounds that address the neurochemical underpinnings of stress and anxiety. DSIP, delta sleep-inducing peptide, can improve sleep architecture, and poor sleep is both a cause and consequence of low testosterone. The DSIP peptide dosage guide covers proper administration for sleep optimization.
Energy is another domain where both approaches deliver but through different mechanisms. TRT raises energy through direct androgen receptor activation and improved mitochondrial function. Peptides like MOTS-c target mitochondrial function directly, acting as exercise mimetics that improve cellular energy production. The MOTS-c peptide dosage chart provides evidence-based dosing protocols. Our broader best peptides for energy guide covers multiple compounds that address fatigue from different angles.
The mood and cognition advantages of combining TRT with targeted peptides can exceed what either achieves alone. A man on TRT who adds semax for cognitive enhancement and DSIP for sleep optimization is addressing hormone levels, brain function, and recovery simultaneously. This multi-target approach represents the cutting edge of male optimization.
Sexual health: libido, function, and satisfaction
Let us address the question that many men think about first but ask about last.
Testosterone is the primary driver of male libido. Low levels reliably reduce desire, arousal, and satisfaction. TRT restores these parameters effectively in most hypogonadal men, with improvements typically noticeable within three to six weeks of starting treatment. Erectile function also improves, though the relationship is more complex. Testosterone influences desire more directly than mechanical function, which also depends on vascular health, nerve integrity, and psychological factors.
Peptides offer unique sexual health advantages. PT-141, also known as bremelanotide, works through melanocortin receptors in the brain rather than through vascular pathways like PDE5 inhibitors. It increases desire and arousal through central nervous system activation, making it effective even in men who do not respond to medications like sildenafil. Our PT-141 peptide guide covers mechanisms, dosing, and what to expect. For men specifically struggling with erectile function, the best peptide for erectile dysfunction guide compares all available options.
The best peptide for libido overview examines how different compounds influence desire through distinct pathways. Some work through testosterone elevation, others through GH optimization, and compounds like PT-141 through direct central nervous system activation. This variety means that if one approach does not produce the desired result, alternatives exist.
For men on TRT who still experience suboptimal libido, which happens more often than many expect, adding PT-141 or optimizing growth hormone through secretagogues can make a meaningful difference. Testosterone is necessary for libido but not always sufficient. The sexual health response depends on a complex interplay of hormones, neurotransmitters, and psychological factors.
The combination approach: when both is better than either
The peptides-versus-TRT framing implies a binary choice. In clinical practice, the most sophisticated protocols often use both.
Consider a common scenario. A 48-year-old man starts TRT for confirmed hypogonadism. His testosterone levels stabilize in the optimal range. Energy improves. Libido returns. But he notices his midsection stubbornly retains fat despite improved training. His sleep quality has not improved as expected. And he wants to ensure his testes remain functional. His physician adds sermorelin and ipamorelin for GH optimization, gonadorelin for testicular preservation, and BPC-157 for the chronic tendinitis that limits his training.
This is not polypharmacy for its own sake. It is targeted intervention at multiple nodes in a complex system. TRT addresses the testosterone floor. GH secretagogues address growth hormone, body composition, and sleep. Gonadorelin preserves testicular function. BPC-157 enables the training that maximizes hormonal benefits. Each component serves a specific, evidence-based purpose.
The peptide stacks guide covers how to combine compounds safely and effectively. Stacking is an art as much as a science, and the peptide stack calculator helps users design protocols based on their specific goals. Whether the goal is athletic performance, anti-aging, or comprehensive hormone optimization, the stacking approach allows customization that monotherapy cannot match.
Common combination protocols include:
TRT + gonadorelin (preserves testicular function during TRT)
TRT + CJC-1295/ipamorelin (adds GH benefits to testosterone base)
TRT + BPC-157/TB-500 (healing support for active individuals)
TRT + PT-141 (addresses libido beyond what testosterone alone achieves)
Enclomiphene + GH secretagogues (full natural optimization without exogenous testosterone)
Sermorelin + ipamorelin + enclomiphene (comprehensive peptide-only protocol)
The performance peptides guide explores how these combinations support men who demand the most from their bodies. For men focused on longevity rather than performance, the longevity peptides guide covers compounds like epitalon, which targets telomere maintenance and may slow biological aging. The epitalon dosage guide provides detailed protocol information.
What matters most is the principle: treat the whole system, not just one number on a lab report. Testosterone is important. It is not everything. Growth hormone, IGF-1, thyroid function, cortisol regulation, sleep quality, inflammation markers, and dozens of other variables all contribute to how a man feels, performs, and ages. Peptides allow clinicians to address multiple targets simultaneously, creating protocols that TRT alone simply cannot replicate.
Practical protocols: what each approach looks like day to day
Theory matters. But so does lived experience. What does each approach actually feel like in daily practice?
A typical TRT protocol
The most common TRT protocol involves intramuscular injection of testosterone cypionate, typically 100 to 200 mg weekly, split into two injections for more stable levels. Some men use subcutaneous injections with insulin syringes for convenience and potentially smoother pharmacokinetics. Blood work is drawn every six to twelve weeks initially, then every three to six months once stable. Key markers include total and free testosterone, estradiol, hematocrit, PSA, and lipid panel.
Additional medications often enter the picture. An aromatase inhibitor like anastrozole may be prescribed if estradiol rises too high. HCG at 500 to 1,000 IU two to three times weekly may be added for testicular preservation. DHEA supplementation is sometimes included as TRT can suppress adrenal androgens. Each additional medication adds cost, complexity, and potential side effects.
The daily experience: inject twice weekly, take oral medications daily, monitor blood work regularly, adjust doses based on labs and symptoms. Most men settle into a routine within the first three months. The ongoing commitment, however, is indefinite.
A typical peptide protocol
Peptide protocols vary more widely because the available compounds address different targets. A comprehensive testosterone-optimization peptide protocol might include CJC-1295/ipamorelin injected subcutaneously before bed five nights per week, enclomiphene taken orally each morning, and gonadorelin injected subcutaneously three times weekly. Some protocols add BPC-157 for healing support, KPV for inflammatory conditions, or MOTS-c for metabolic optimization.
Preparation requires some learning. Most peptides come in lyophilized powder form and must be reconstituted with bacteriostatic water before use. The peptide reconstitution calculator simplifies the math, and the peptide calculator helps determine precise dosing. Proper peptide storage is essential for maintaining potency. Understanding how long peptides last in the fridge, how long reconstituted peptides last, and how long peptides last at room temperature prevents waste and ensures effectiveness.
Blood work on peptide therapy typically monitors testosterone, LH, FSH, IGF-1, fasting glucose, and standard metabolic panels. The monitoring is less intensive than TRT in many cases because the risk of erythrocytosis, dramatic estrogen spikes, and other TRT-specific complications is lower.
The daily experience: reconstitute peptides weekly, inject subcutaneously once or twice daily with small insulin syringes, take any oral compounds as directed, and monitor with periodic blood work. The injection volume is small and the needles are fine, making the process considerably less daunting than intramuscular TRT injections. Understanding what a peptide injection involves can ease the initial apprehension many men feel.
For those who prefer avoiding injections entirely, the peptide capsules guide and nasal spray peptides guide explore alternative delivery methods. The injectable versus oral peptides comparison helps users understand the bioavailability trade-offs of each route.
Cost comparison: what your wallet needs to know
Money matters. Hormone optimization is an ongoing expense, and the financial differences between TRT and peptides are significant.
TRT through a physician typically costs $100 to $250 per month for the testosterone itself, plus $50 to $100 per blood draw, plus the cost of any ancillary medications like aromatase inhibitors or HCG. Insurance may cover some or all of these costs if hypogonadism is clinically diagnosed with qualifying lab values. Annual out-of-pocket costs range from roughly $1,200 to $4,000 depending on insurance coverage and required ancillaries.
Peptide therapy costs vary more widely. Growth hormone secretagogues typically run $150 to $400 per month. Enclomiphene costs $50 to $150 per month. BPC-157 and TB-500 add $100 to $300 per month depending on dosing. Comprehensive multi-peptide protocols can reach $400 to $800 per month. Insurance rarely covers peptide therapy, making the out-of-pocket burden higher. The how much do peptides cost guide provides current market pricing across major suppliers. The peptide cost calculator helps users estimate their specific protocol expenses.
However, the cost calculation is incomplete without considering long-term implications. TRT is typically a lifetime commitment. Peptides can often be cycled, with periods of use followed by periods off treatment during which benefits partially persist. Over a decade, the total cost comparison may favor peptides for men who can maintain results with cycling, while favoring TRT for men who need consistent exogenous replacement. The peptide therapy cost complete guide breaks down these long-term economics in detail.
Access is another cost consideration. TRT requires a physician prescription and is available through traditional medical channels, telehealth clinics, and compounding pharmacies. Peptide therapy occupies a more complex regulatory space. The are peptides legal guide clarifies current regulations, and the peptide regulation news page tracks evolving guidelines. The peptide therapy online resource covers legitimate telemedicine options, while the can doctors prescribe research grade peptides article addresses a common point of confusion.
Who should choose peptides
Peptide therapy is the better starting point for specific populations. Recognizing yourself in these descriptions can simplify what otherwise feels like an overwhelming decision.
Younger men under 40. If you are in your 20s or 30s with declining energy and mildly low testosterone, jumping straight to TRT is premature. Your HPTA still functions. Your testes still produce. Peptides can amplify what your body already does without shutting down systems you will need for decades to come. The peptides for testosterone guide is an excellent starting point for this age group.
Men who want children. Current or future fertility plans make peptides the clear choice. There is no ambiguity here. TRT suppresses spermatogenesis. Peptides preserve it. If fatherhood is anywhere in your future, even as a distant possibility, protect your fertility first and optimize testosterone second.
Men with mild to moderate decline. Total testosterone in the 300 to 500 ng/dL range, with symptoms, represents the sweet spot for peptide therapy. Your body still responds to stimulation. The deficiency is not severe enough to require direct replacement. Peptides can push these levels into the 500 to 800 range in many cases, which is sufficient to resolve symptoms for most men.
Men who value flexibility. If committing to a lifetime of injections gives you pause, peptides offer an exit strategy. You can cycle on and off. You can adjust compounds based on changing goals. You can stop entirely without HPTA recovery concerns. This flexibility appeals to men who view hormone optimization as a tool rather than a permanent lifestyle change.
Men already using other peptides. If you are using BPC-157 for gut health, as explored in the peptides for gut health guide, or GHK-Cu copper peptides for skin and tissue health, adding testosterone-optimizing peptides to your existing protocol is simpler and more synergistic than introducing TRT.
For women experiencing hormonal decline, different considerations apply entirely. The best peptides for women, peptides for perimenopause, and peptides for menopause guides address gender-specific protocols.
Who should choose TRT
Some men need TRT. Not as a preference. As a medical necessity.
Confirmed severe hypogonadism. Total testosterone consistently below 200 to 250 ng/dL on multiple morning fasting blood draws, with clinical symptoms, warrants direct replacement. At these levels, the HPTA is already significantly compromised, and peptide stimulation may not generate a meaningful response. The testes may lack the capacity to respond even with optimal signaling.
Primary hypogonadism. When the problem originates in the testes themselves, whether from injury, surgery, genetic conditions, or age-related Leydig cell failure, no amount of pituitary stimulation will restore adequate production. The factory is broken. Delivering better orders to a broken factory changes nothing. TRT replaces what the factory can no longer make.
Men over 50 with diminished testicular reserve. Age-related decline in testicular function eventually reaches a point where peptide stimulation yields diminishing returns. While some older men respond well to peptides, many find that the magnitude of response does not justify the complexity and cost. TRT provides reliable, predictable testosterone elevation regardless of testicular reserve.
Men who have failed peptide therapy. Three to six months of a well-designed peptide protocol with adequate dosing and compliance should produce measurable results. If labs show minimal testosterone improvement despite adherence, the conclusion is clear: your body needs more than signaling can provide. TRT becomes the logical next step.
Men with severe symptoms affecting quality of life. Profound fatigue, clinical depression secondary to hypogonadism, severe sexual dysfunction, or significant muscle wasting may demand the faster, more predictable response that TRT delivers. Waiting three to six months for peptides to gradually elevate testosterone is not always clinically appropriate when symptoms are severe.
Recovery and exit strategies
Every treatment decision should consider the exit. What happens when you stop? What does recovery look like? How long until you return to baseline?
Stopping TRT initiates a challenging period. With the HPTA suppressed, endogenous testosterone production is minimal. Symptoms of low testosterone, often worse than pre-treatment levels, can emerge within two to four weeks of cessation. This hypogonadal window can last months while the HPTA gradually restarts.
Post-TRT recovery protocols exist and can significantly accelerate the process. The standard approach involves HCG priming at 1,500 to 3,000 IU administered two to three times weekly for four to eight weeks, followed by or overlapping with a SERM like clomiphene or enclomiphene for four to twelve weeks. Published success rates for HPTA restart range from 80 to 90 percent in appropriate candidates, though "restart" may mean recovery to a lower baseline than pre-TRT levels.
Some men never fully recover. Risk factors for poor recovery include extended duration of TRT use, older age, prior anabolic steroid use, and pre-existing testicular pathology. The longer the HPTA remains suppressed, the lower the probability of complete recovery. This reality underscores the importance of the initial treatment decision. Starting TRT is easy. Stopping can be the hardest part.
Stopping peptides is comparatively simple. Since the HPTA was never suppressed, there is no recovery period in the traditional sense. Testosterone levels gradually return to pre-treatment baseline over several weeks as the exogenous stimulation ceases. Some men report minimal decline, suggesting that peptide therapy may have a "training effect" on the HPTA, though this has not been rigorously studied. The transition off peptides is smooth enough that many men cycle deliberately, running protocols for three to six months and then taking one to three months off.
This difference in exit difficulty should weigh heavily in the initial decision. A young man who chooses peptides and later decides he needs TRT has lost nothing. A young man who starts TRT and later wishes he had tried peptides first may face permanent consequences.
The regulatory landscape
Navigating the legal and regulatory dimensions of both approaches requires current information and careful attention to evolving guidelines.
TRT is unambiguously legal and FDA-regulated. Testosterone is a Schedule III controlled substance in the United States, requiring a prescription from a licensed physician. The regulatory framework is clear: diagnosis of hypogonadism, confirmed by laboratory testing and clinical symptoms, justifies a prescription. Insurance coverage varies but is available for qualifying patients. The pharmaceutical supply chain is well-established, with multiple FDA-approved formulations from major manufacturers.
Peptides occupy a more complex position. Some peptides have FDA-approved indications, such as tesamorelin for HIV-associated lipodystrophy. Others are prescribed off-label by physicians through compounding pharmacies. Still others exist primarily as research chemicals. The are peptides legal guide provides a current overview of the regulatory framework, while peptide regulation news tracks changes as they occur.
The FDA has taken increasing interest in the peptide market, with recent actions affecting the availability of certain compounds through compounding pharmacies. Understanding the distinction between research versus pharmaceutical peptides is essential for anyone navigating this space. The grey market peptides guide examines the risks and realities of non-pharmaceutical peptide sources, while the peptide testing labs guide covers how to verify purity and potency.
Quality assurance matters enormously in both spaces. TRT from pharmaceutical manufacturers undergoes rigorous FDA oversight. Peptides from compounding pharmacies operate under different, state-level regulatory frameworks. Research-grade peptides operate with minimal regulation. The peptide solutions guide and the is Peptide Sciences a compounding pharmacy article help users understand the difference between sources and what to look for in a reputable supplier.
Another frequently asked question concerns drug testing. For athletes and professionals subject to workplace testing, the do peptides show up on drug tests guide provides essential information. Both TRT and many peptides can trigger positive results depending on the testing panel used.
Comparing peptides with other alternatives
The peptide-versus-TRT comparison does not exist in isolation. Other interventions compete for attention, and understanding how peptides compare to alternatives beyond TRT provides additional perspective.
SARMs, selective androgen receptor modulators, represent another category that men frequently consider alongside peptides and TRT. Our comprehensive peptides versus SARMs comparison covers mechanisms, efficacy, side effects, and legal status of both categories. SARMs occupy a particularly precarious regulatory position and carry significant liver toxicity risks that neither TRT nor most peptides share.
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide have exploded in popularity for weight management. While not directly related to testosterone optimization, the weight loss they promote can indirectly improve testosterone by reducing aromatase-bearing adipose tissue. The semaglutide versus tirzepatide comparison and the retatrutide guide and cagrilintide for men article cover the latest generation of these compounds.
For men interested in the broader peptide ecosystem beyond testosterone optimization, our world of peptides overview provides comprehensive context. The peptide formula guide covers the science of peptide chemistry, while the bio peptide guide and alpha peptides guide explore specific compound categories.
Building your protocol: a decision framework
With all this information, how do you actually decide? Here is a framework that respects the complexity while providing actionable guidance.
Step 1: Get comprehensive bloodwork. Total testosterone, free testosterone, SHBG, LH, FSH, estradiol, prolactin, thyroid panel, CBC with differential, comprehensive metabolic panel, and lipids at minimum. Test in the morning, fasting, on two separate occasions. No single lab draw should determine your trajectory.
Step 2: Assess the severity. Total testosterone below 250 ng/dL with symptoms: TRT is likely appropriate. Between 250 and 500 ng/dL with symptoms: peptides are the reasonable first approach. Above 500 ng/dL with symptoms: look for causes other than testosterone, as the hormone level is likely not the primary issue.
Step 3: Consider your age and life plans. Under 40 with fertility considerations: peptides first, always. Over 50 with no fertility concerns: TRT is a perfectly reasonable choice if symptoms and labs justify it. Between 40 and 50: this is the zone where individual factors, including symptom severity, lifestyle, personal preference, and risk tolerance, determine the best path.
Step 4: Start and assess. Give any protocol three to six months with consistent compliance and regular lab monitoring before concluding it does or does not work. Hormone optimization is not instant gratification. It is a process of careful titration and observation.
Step 5: Adjust and optimize. The initial protocol is rarely the final protocol. Doses change. Compounds are added or removed. Timing is adjusted. This iterative process is normal and expected. The peptides before and after results page shows the range of outcomes men experience and reinforces that individual variation is the norm rather than the exception.
Resources like the peptide forum guide can help connect you with communities of men navigating similar decisions. While peer experience should never replace medical guidance, hearing from others who have walked the same path provides valuable context. SeekPeptides provides curated resources that help members make informed decisions about their hormone optimization journey.
Pain management, joints, and recovery support
Hormone optimization does not occur in a bubble. Many men pursuing TRT or peptide therapy are also dealing with pain, joint issues, and recovery challenges that affect their ability to train, recover, and maintain the active lifestyle that supports hormonal health.
TRT can improve recovery capacity through enhanced muscle protein synthesis and reduced catabolic signaling. However, it does not directly address joint pain, tendon issues, or inflammatory conditions that limit training. Some men on TRT report increased joint discomfort, possibly due to fluid shifts, altered collagen metabolism, or simply the fact that they are training harder and stressing their joints more.
Peptides offer targeted solutions for these issues. The best peptide for pain guide covers compounds specifically studied for analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Best peptides for joint pain narrows the focus to musculoskeletal applications. BPC-157, already mentioned for its healing properties, also demonstrates significant anti-inflammatory activity in joint tissues. The inflammation peptides guide provides a broader view of how peptides modulate inflammatory pathways.
The BPC-157 versus TB-500 comparison helps users understand which healing peptide best suits their specific condition. Some conditions respond better to BPC-157 systemic administration, while others benefit more from TB-500 localized effects. Many users combine both in the wolverine peptides protocol for comprehensive healing support.
For men dealing with gut health issues, whether from NSAID use, stress, or other factors, the peptides for gut health resource covers how compounds like BPC-157 support gastrointestinal healing. Glutamine peptides offer additional gut support through a different mechanism.
Cosmetic and longevity considerations
Not every man pursuing hormone optimization is focused exclusively on testosterone numbers and gym performance. Increasingly, men are interested in the cosmetic and longevity dimensions of both TRT and peptide therapy.
TRT can improve skin quality through increased collagen synthesis and sebaceous gland activity, though the latter effect also contributes to acne. Hair growth on the body may increase, while scalp hair may thin in genetically predisposed individuals. Overall appearance often improves as body composition shifts toward more muscle and less fat.
Peptides offer more targeted cosmetic applications. GHK-Cu copper peptides stimulate collagen synthesis, promote wound healing, and have demonstrated remarkable skin rejuvenation properties. The how to use GHK-Cu peptide injection guide covers proper administration for systemic benefits beyond topical application.
Hair health is another consideration. The peptides for hair loss guide and peptides for hair growth guide cover compounds that may counteract the androgenic alopecia that TRT can accelerate. For men who want higher testosterone without sacrificing their hairline, peptides that raise testosterone through HPTA stimulation rather than exogenous replacement may cause less androgenic pressure at the hair follicle.
Skin tightening is another area where peptides show promise. The peptides for skin tightening guide explores how GH elevation and targeted peptides improve skin elasticity. Collagen peptides for cellulite and glow peptides cover additional cosmetic applications. The Snap-8 peptide has gained particular attention for its wrinkle-reducing properties.
On the longevity front, the longevity peptides guide covers compounds that may influence biological aging through mechanisms distinct from testosterone optimization. Epitalon targets telomere maintenance through telomerase activation. MOTS-c functions as a mitochondrial-derived peptide that mimics exercise at the cellular level. SS-31 targets mitochondrial cardiolipin to restore cellular energy production. The bioregulator peptides category, including compounds like testagen and pancragen, represents a uniquely Russian contribution to peptide science that focuses on organ-specific rejuvenation.
The peptides for anti-aging resource page provides a centralized overview of all compounds with longevity-relevant mechanisms.
Special considerations and advanced topics
The BNP connection
B-type natriuretic peptide levels can be affected by hormonal interventions, and understanding this marker is important for men on either TRT or peptide therapy. The high BNP level causes and symptoms guide provides context for interpreting this cardiac biomarker in the setting of hormone optimization.
Research quality and sourcing
The quality of any peptide protocol depends heavily on sourcing. The peptide vial research guide covers how to evaluate what you are getting. The peptide testing labs guide explains third-party verification options. And the how long peptides last in powder form article helps users understand shelf life and storage requirements.
Understanding the IGF-1 pathway
Many peptides exert their effects through IGF-1, the primary mediator of growth hormone action. The IGF peptide complete guide and the HGH fragment 176-191 calculator cover specific compounds and dosing within this pathway.
The PDA peptide
For those exploring newer compounds, the PDA peptide guide covers an emerging compound in the research pipeline.
AOD-9604 side effects and safety
Men considering GH-fragment peptides alongside their testosterone protocol should review the AOD-9604 side effects profile and the MOTS-c side effects profile to understand what to monitor during use.
Power peptides and compound categories
The power peptides guide covers the most potent compounds available, while the broader peptide stacks guide helps users combine them strategically for maximum benefit.
Frequently asked questions
Can peptides replace TRT completely?
For men with mild to moderate testosterone decline, yes. Peptides like enclomiphene and gonadorelin can raise testosterone 30 to 60 percent above baseline while preserving natural production and fertility. However, for men with severe hypogonadism or primary testicular failure, peptides may not generate sufficient testosterone to resolve symptoms. The answer depends entirely on the underlying cause and severity of the deficiency. The testosterone peptide guide provides detailed comparison data.
Is it safe to combine peptides with TRT?
Yes, and many clinical protocols do exactly this. The most common combination is TRT with gonadorelin for testicular preservation. Adding GH secretagogues like CJC-1295 and ipamorelin alongside TRT addresses body composition and recovery goals that testosterone alone may not fully achieve. Medical supervision is essential for any combined protocol to monitor for interactions and adjust dosing appropriately.
How long before I see results from peptide therapy?
Sleep and subjective energy improvements often appear within two to four weeks. Measurable testosterone increases typically manifest by six to eight weeks. Body composition changes become visible at three to six months. This timeline is slower than TRT, which often produces noticeable effects within two to three weeks. Patience and consistent compliance are essential for peptide protocols to deliver their full potential.
Will I lose my gains if I stop peptide therapy?
You will lose some of the enhancement but return to your baseline rather than falling below it. This is the critical advantage over TRT. Stopping peptides means your testosterone returns to pre-treatment levels over several weeks. Stopping TRT can leave you temporarily, or in some cases permanently, below your original baseline due to HPTA suppression. Muscle and body composition changes maintained through continued training and nutrition tend to persist better regardless of which therapy is discontinued.
Are peptides safer than TRT?
Peptides generally carry a milder side effect profile and, crucially, do not suppress the HPTA. However, "safer" is relative. TRT has decades of clinical data and well-characterized risks. Many peptides have less extensive human safety data. The risk-benefit calculation depends on individual health status, the specific compounds used, dosing, duration, and quality of medical oversight. Both approaches require proper monitoring and professional guidance.
What is the most common peptide stack for testosterone optimization?
The most popular peptide-only testosterone optimization stack combines CJC-1295 with ipamorelin for GH support and enclomiphene for direct testosterone elevation. Some protocols add gonadorelin for additional LH stimulation. This combination addresses multiple hormonal axes simultaneously. The peptide stack calculator can help determine dosing for multi-peptide protocols.
Can I switch from TRT to peptides?
Yes, though the transition requires careful management. An HPTA restart protocol using HCG and SERMs should precede or overlap the transition to peptides. Abruptly stopping TRT and starting peptides will leave you in a hypogonadal window while your HPTA restarts. Work with a physician experienced in both modalities to plan a smooth transition. Success rates for HPTA restart are 80 to 90 percent, but the process takes weeks to months.
How do I know if my testosterone is low enough to need treatment?
The clinical definition of hypogonadism requires both laboratory evidence (typically total testosterone below 300 ng/dL on two separate morning fasting draws) and clinical symptoms (fatigue, low libido, erectile dysfunction, loss of muscle mass, depression, cognitive fog). Symptoms alone, or low numbers alone, may not justify intervention. The combination of both, evaluated by a qualified physician, determines whether treatment is appropriate and which modality best suits your situation.
External resources
TRAVERSE Trial - New England Journal of Medicine - Landmark cardiovascular safety trial for testosterone therapy in 5,246 men
American Urological Association - Testosterone Deficiency Guidelines - Evidence-based clinical guidelines for diagnosing and treating hypogonadism
CJC-1295 Clinical Study - PubMed - Prolonged stimulation of growth hormone and IGF-1 by CJC-1295 in healthy adults
Endocrine Society - Testosterone Therapy Guidelines - Comprehensive clinical guidance for testosterone prescribing and monitoring
FDA Safety Communication on Testosterone Products - Federal safety guidance and labeling requirements for TRT products
For those who want to go deeper into peptide science, SeekPeptides maintains a continuously updated library of peptide guides, calculators, and protocol resources. Members gain access to detailed protocols, dosage charts, and community discussion that go far beyond what any single article can cover. Whether you are choosing between peptides and TRT, designing a combination protocol, or simply trying to understand what these compounds do inside your body, the SeekPeptides membership provides the tools, education, and community support to make that journey with confidence.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your hormones stay balanced, your protocols stay effective, and your results stay consistent.



