Jan 20, 2026

Some researchers lose fat. Others build muscle. But achieving both simultaneously? That requires a completely different approach, and it's where most peptide protocols fall short.
The difference between spinning your wheels and achieving genuine body recomposition often comes down to peptide selection, timing, and understanding which compounds actually support dual goals versus those optimized for only one. People chase weight loss peptides or muscle building peptides separately, never realizing that the intersection of both goals demands specific strategies most guides completely ignore.
This isn't another generic overview. This guide breaks down exactly which peptides work for simultaneous fat loss and muscle preservation, the specific protocols that support body recomposition, why certain popular choices actually undermine dual goals, and how to structure a comprehensive approach based on your individual starting point. Whether you're researching growth hormone secretagogues, exploring GLP-1 agonists, or considering combination stacks, the information here will help you make informed decisions backed by actual research rather than marketing claims.
SeekPeptides has compiled protocols from thousands of researchers pursuing body recomposition, and the patterns that separate success from frustration are remarkably consistent. The right peptides matter. But so does everything else surrounding them.
Understanding body recomposition and why it's different from simple weight loss
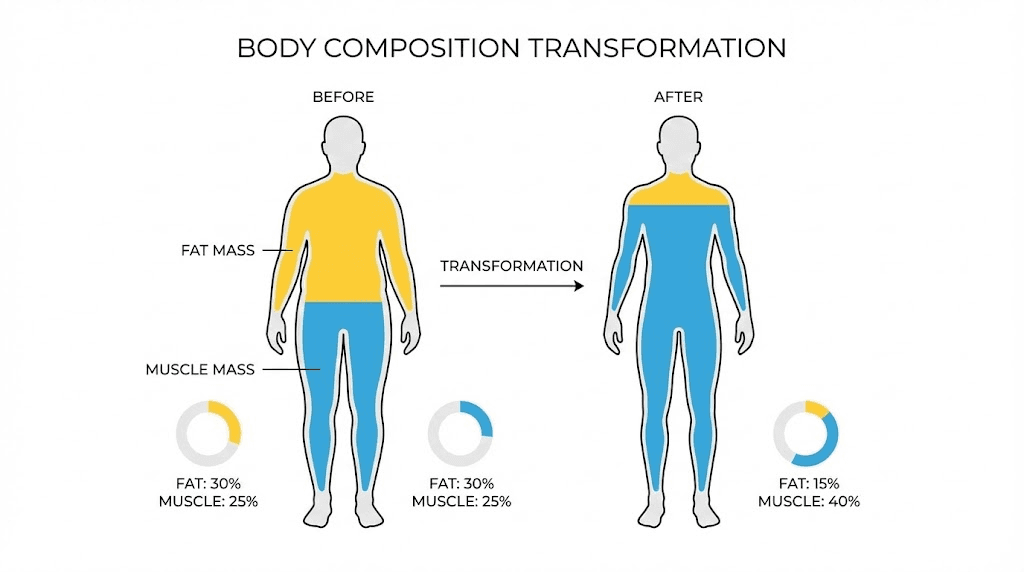
Body recomposition represents the holy grail of physique transformation. You're not just losing weight. You're fundamentally reshaping your body composition by reducing fat mass while simultaneously building or preserving lean muscle tissue.
This is hard.
Traditional weight loss creates a caloric deficit that triggers fat burning, but that same deficit often compromises muscle protein synthesis. Your body, facing energy restriction, may catabolize muscle tissue for fuel. The scale drops. But so does your metabolic rate, your strength, and ultimately your ability to maintain results long-term.
Body recomposition demands a different metabolic environment entirely. You need signals that tell your body to spare muscle while preferentially burning fat. You need hormonal support that enhances protein synthesis even during energy restriction. You need compounds that improve fat oxidation without the muscle-wasting effects of aggressive dieting alone.
This is precisely where peptides become valuable tools.
Certain peptides, particularly growth hormone secretagogues, create metabolic conditions favorable for body recomposition. They elevate growth hormone and IGF-1, hormones that simultaneously promote muscle preservation and fat metabolism. Other peptides target appetite regulation, making caloric deficits more sustainable without the metabolic compensation that typically derails progress. Still others support recovery, allowing more frequent and intense training that drives both muscle stimulus and caloric expenditure.
But here's what most guides miss: not all weight loss peptides support muscle retention, and not all muscle-building peptides enhance fat loss. The peptides optimal for pure weight loss, for instance, may actually accelerate lean mass loss if used without complementary strategies. Understanding these distinctions is critical before selecting any protocol.
Growth hormone secretagogues: the foundation of recomposition peptides
If body recomposition had a peptide class designed specifically for the task, it would be growth hormone secretagogues. These compounds stimulate your pituitary gland to produce more of your own natural growth hormone, triggering a cascade of metabolic effects that simultaneously favor muscle anabolism and fat catabolism.
Growth hormone doesn't just build muscle. It fundamentally shifts how your body partitions nutrients.
Elevated GH levels increase lipolysis, the breakdown of stored fat into fatty acids your body can use for energy. Simultaneously, GH enhances protein synthesis in muscle tissue, directing amino acids toward muscle building rather than other metabolic pathways. This dual action is precisely what body recomposition requires: preferential fat burning while maintaining or building lean mass.
CJC-1295 and ipamorelin: the gold standard combination
The CJC-1295 and ipamorelin combination has emerged as the most widely used stack for body recomposition, and the reasoning is sound. These two peptides work through complementary mechanisms that create synergistic effects greater than either alone.
CJC-1295 is a growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) analog with an extended half-life. After a single injection, research shows dose-dependent increases in plasma growth hormone concentrations of 2 to 10 times baseline levels, sustained for 6 days or more. IGF-1 levels rise 1.5 to 3 times baseline and remain elevated for 9 to 11 days. This sustained elevation creates a consistent anabolic environment rather than the brief spikes that characterize natural GH secretion.
Ipamorelin works differently. It's a ghrelin mimetic, a growth hormone releasing peptide (GHRP) that triggers sharp GH pulses from the pituitary. Unlike older GHRPs, ipamorelin provides clean GH release with minimal impact on cortisol, prolactin, or appetite. This selectivity makes it ideal for recomposition, where you want anabolic signaling without hormonal disruption that could compromise results.
Together, CJC-1295 amplifies the amplitude and frequency of GH release while ipamorelin triggers precise pulses. The result is a robust, sustained elevation in growth hormone that supports both muscle protein synthesis and fat oxidation.
Standard dosing protocol for body recomposition
Most protocols use a 1:1 ratio of CJC-1295 to ipamorelin, with dosing based on body weight. The standard recommendation is approximately 1 mcg per kilogram of body weight for each peptide per dose.
For practical application:
Under 150 lbs: 100-150 mcg of each peptide
150-200 lbs: 200 mcg of each peptide (standard protocol)
200-250 lbs: 250-300 mcg of each peptide
Over 250 lbs: 300 mcg of each peptide
Timing matters significantly. Taking this combination before bed capitalizes on your body's natural growth hormone release during deep sleep, amplifying an existing physiological process. Alternatively, morning dosing in a fasted state may better support daytime fat oxidation and energy levels. Some researchers use both timing approaches, splitting daily doses between morning and evening administration.
Use the peptide calculator to determine exact amounts based on your reconstitution method and dosing requirements.
Critical protocol note: eating within 2 hours of injection significantly blunts the growth hormone response. Proper fasting protocols are essential for maximum benefit. Insulin elevation from food intake directly suppresses GH release, undermining the primary mechanism of these peptides.
Cycling recommendations
Continuous daily dosing leads to receptor desensitization over time. The most common approach uses a 5-days-on, 2-days-off schedule to maintain receptor sensitivity. Full cycles typically run 12 weeks followed by 4-week breaks before resuming.
For comprehensive guidance on cycling different peptides and structuring your peptide cycle planning, these factors significantly impact long-term results.
Expected timeline for results
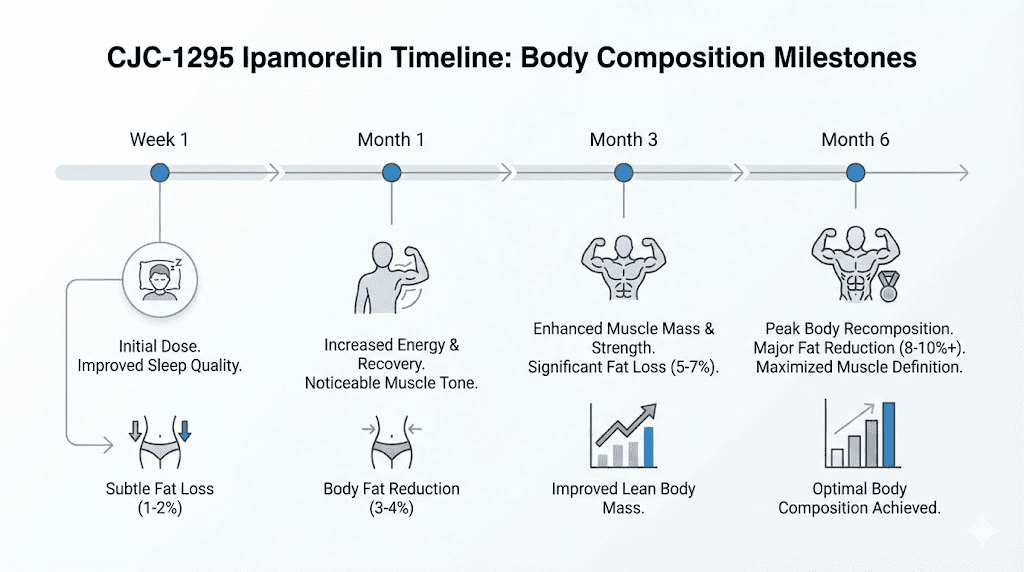
Body recomposition isn't fast. But the CJC-1295/ipamorelin combination produces consistent, measurable changes on a predictable timeline.
Weeks 1-4: Subtle improvements in sleep quality, faster recovery between training sessions, and initial fat mobilization. The scale may not change dramatically, but body composition shifts begin.
Months 2-3: Visible belly fat reduction becomes apparent. Muscle definition sharpens. Recovery times continue improving, allowing more training volume.
Months 4-6: Noticeable lean muscle gains alongside continued fat loss. Skin quality often improves. The full metabolic effects become clearly visible.
Most researchers report meaningful body composition changes by weeks 8-12, with continued improvements through month 6. This aligns with the time required for sustained GH elevation to produce measurable tissue changes.
MK-677 (ibutamoren): the oral alternative for sustained GH elevation
For researchers seeking the benefits of growth hormone elevation without injectable peptides, MK-677 (ibutamoren) offers a compelling option. This orally active growth hormone secretagogue stimulates the pituitary gland to increase GH production, sustaining elevated levels around the clock.
MK-677 isn't technically a peptide, but it functions similarly to GHRP compounds. It binds to ghrelin receptors, triggering GH release that persists throughout the day rather than producing isolated pulses. Research shows MK-677 can increase growth hormone secretion by up to 97%, with corresponding elevations in IGF-1 to levels typical of healthy young adults.
For body recomposition specifically, MK-677 offers several advantages.
First, oral administration eliminates injection requirements, improving compliance and convenience. Second, the sustained GH elevation supports consistent anabolic signaling, beneficial for muscle preservation during caloric restriction. Third, many users report significantly improved sleep quality, which itself supports recovery and body composition optimization.
Clinical evidence supports modest but meaningful body composition effects. One 12-month randomized controlled trial found that subjects taking MK-677 gained 1.1 kg of fat-free mass compared to a 0.5 kg loss in the placebo group. While not dramatic, this preservation effect during what would otherwise be muscle-losing conditions demonstrates the compound's recomposition potential.
MK-677 dosing for body recomposition
Dosing typically ranges from 10 to 30 mg daily, with most recomposition protocols settling around 20-25 mg.
Beginners: 10-15 mg daily for 1-2 weeks to assess tolerance
Standard recomposition dose: 20-25 mg daily
Advanced users: Up to 30 mg daily (increased side effect risk)
Timing depends on goals. For bulking and maximum GH elevation, morning dosing on an empty stomach works well. For cutting or recomposition where appetite control matters, evening dosing before bed helps manage the appetite increase MK-677 typically causes through ghrelin activation.
Cycles commonly run 8-24 weeks. Beginners should start with 8-12 week cycles, while experienced researchers may extend to 16-20 weeks for continued recomposition effects. Peak benefits for body composition typically appear after 8-12 weeks of consistent use.
Important considerations
MK-677 does increase appetite significantly in many users, particularly in the first few weeks. This ghrelin activation can challenge caloric restriction goals. Managing this requires strategic timing, increased fiber and protein intake for satiety, and potentially combining with appetite-suppressing compounds.
Water retention commonly occurs early in cycles, temporarily obscuring body composition changes. This typically resolves within 2-4 weeks as the body adjusts.
Prolonged high-dose use may impact insulin sensitivity. This risk is minimized through moderate dosing, regular physical activity, and attention to diet quality. Periodic blood glucose monitoring is advisable during extended cycles.
Unlike injectable peptides, MK-677 hasn't received FDA approval and remains investigational. Its long-term safety profile in healthy populations isn't fully established, though existing research hasn't identified serious adverse effects at standard doses.
Tesamorelin: FDA-approved fat reduction with muscle preservation
Tesamorelin holds a unique position among recomposition peptides: it's the only growth hormone releasing hormone analog with FDA approval specifically for reducing abdominal fat. Developed for HIV-associated lipodystrophy, tesamorelin demonstrates selective effects on visceral adipose tissue while preserving lean mass.
The clinical evidence is robust.
A 2010 clinical trial found subjects receiving tesamorelin achieved an average 18% decrease in visceral fat compared to placebo. Importantly, this visceral fat reduction occurred without proportional loss of lean muscle tissue. A 2019 analysis of trial data concluded tesamorelin was "effective in increasing skeletal muscle area and density," directly demonstrating its recomposition potential.
Tesamorelin's mechanism differs subtly from other GH secretagogues. Rather than broadly elevating growth hormone, it specifically stimulates pulsatile GH release that mimics natural secretion patterns. This may explain its favorable effects on body composition without some side effects associated with sustained GH elevation.
Tesamorelin protocol
The FDA-approved dosage is 2 mg injected subcutaneously once daily. The newer Egrifta WR formulation delivers 1.28 mg daily with equivalent efficacy but smaller injection volume.
For body recomposition, consistent daily administration is essential. Unlike some peptides that benefit from cycling, tesamorelin protocols typically continue for extended periods to maintain results. Clinical studies used 12-month durations with good tolerability.
Results require patience. Meaningful visceral fat reduction typically requires 3-6 months of consistent use, with optimal results appearing after 6+ months. The effects specifically target deep abdominal fat rather than subcutaneous fat, which may explain why some users report belt-notch changes before scale changes.
Tesamorelin and ipamorelin stacking
Some protocols combine tesamorelin with ipamorelin to enhance overall GH output while leveraging tesamorelin's fat-targeting specificity. This stack aims to maximize both muscle preservation and fat loss beyond what either peptide achieves alone.
When stacking these compounds, dosing considerations change. A common approach uses full-dose tesamorelin (2 mg) with reduced ipamorelin (100-150 mcg) to avoid excessive GH stimulation while gaining synergistic benefits.
Important limitations
Tesamorelin's effects are not permanent. Fat levels typically return after discontinuation, requiring either continued use or lifestyle modifications to maintain results. Additionally, tesamorelin specifically targets visceral fat, so those seeking subcutaneous fat reduction may find other options more effective.
For those exploring peptide stacking for recomposition, understanding how tesamorelin complements other compounds helps optimize protocol design.
GLP-1 agonists for weight loss: the muscle preservation challenge
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide have revolutionized weight loss with unprecedented efficacy. Clinical trials show average weight reductions of 15-25% of body weight, outcomes previously achievable only through bariatric surgery.
But for body recomposition specifically, GLP-1 agonists present a significant challenge.
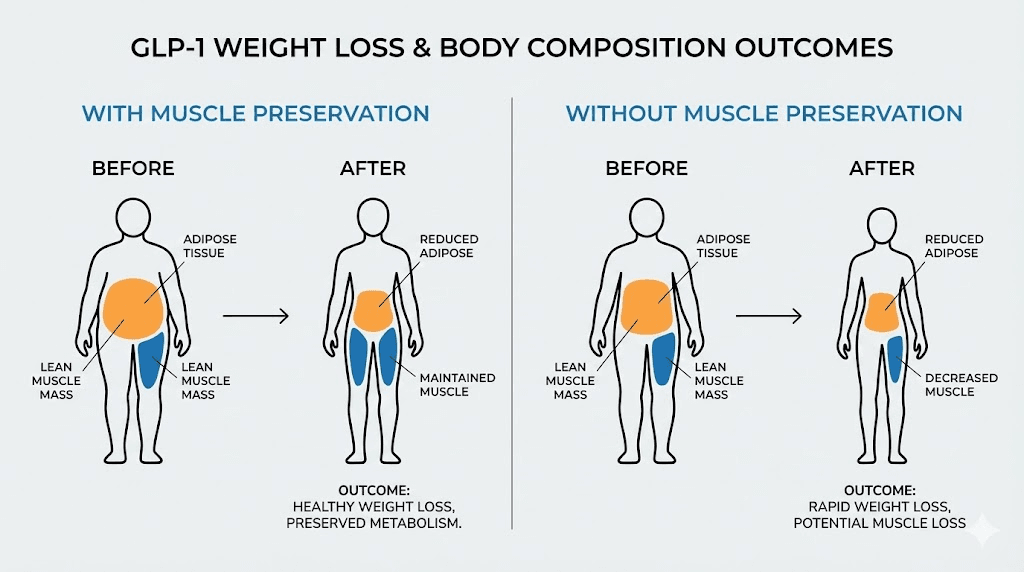
Research indicates approximately 40% of weight lost from semaglutide comes from lean mass, including muscle tissue. Major trials estimated skeletal muscle loss of 10% or more during 68-72 weeks of treatment, approximating the average muscle decline that would normally occur over 20 years of aging. This accelerated lean mass loss directly conflicts with recomposition goals.
The mechanism makes sense when you understand how GLP-1 agonists work. They dramatically reduce appetite and food intake, creating substantial caloric deficits. Without specific interventions to preserve muscle, the body will catabolize lean tissue alongside fat to meet energy demands. The more aggressive the caloric deficit, the greater the muscle loss risk.
This doesn't mean GLP-1 agonists can't support body recomposition. It means they require deliberate strategies to mitigate lean mass loss.
Strategies for muscle preservation during GLP-1 therapy
Research has identified three critical interventions that significantly reduce muscle loss during GLP-1 treatment.
High protein intake: Target protein consumption of 1.2-1.6 g per kg of body weight daily, minimum. For those engaged in resistance training, 1.6-2.2 g/kg may further enhance muscle preservation. Distributing approximately 25-40 g protein per meal helps optimize muscle protein synthesis throughout the day. Research found that in semaglutide groups, consuming more protein was directly linked to reduced muscle loss.
Resistance training: This is non-negotiable for anyone using GLP-1 agonists while pursuing recomposition. Systematic reviews confirm resistance training helps preserve muscle mass during caloric restriction. Training 2-3 times weekly minimum, focusing on compound movements that stimulate large muscle groups, provides the mechanical loading signals that protect against catabolism.
Consistent exercise participation: A case series demonstrated remarkable results when patients combined GLP-1 therapy with comprehensive exercise programs. Individuals exercising 4-7 days weekly, including resistance training 3-5 days per week, with adequate protein intake achieved outcomes that seem almost impossible: one patient lost 33% body weight with only 6.9% lean mass loss, while two others actually gained lean mass while losing significant fat.
These interventions transform GLP-1 agonists from weight loss tools into potential recomposition aids, but only when implemented consistently.
Combining GLP-1 agonists with growth hormone secretagogues
An emerging strategy uses GLP-1 agonists for their appetite suppression and metabolic benefits while simultaneously running growth hormone secretagogues to protect lean mass. The theory is sound: GLP-1 handles the fat loss side while GH peptides provide the anabolic signals that preserve muscle.
This combination isn't extensively studied, but the individual mechanisms suggest potential synergy. Combining peptides with GLP-1 medications requires careful attention to dosing, timing, and monitoring, but represents a promising approach for true body recomposition.
Consider using the peptide stack calculator when planning combined protocols.
AOD-9604: targeted fat metabolism without hormonal disruption
AOD-9604 takes a different approach to fat loss. Rather than broadly stimulating growth hormone release, this peptide is a modified fragment of human growth hormone specifically designed to target fat metabolism without the other effects of full GH.
The peptide works by activating lipolysis in adipose tissue, encouraging fat breakdown and oxidation. Critically, AOD-9604 doesn't elevate IGF-1 levels or impair glucose metabolism, distinguishing it from full-length GH and making it potentially suitable for those who need to avoid these effects.
Clinical evidence for AOD-9604 is mixed but informative. In a 12-week randomized trial, subjects receiving 1 mg daily lost an average of 2.6 kg compared to 0.8 kg in the placebo group. The 1 mg group lost more than triple the weight of placebo, demonstrating real fat loss effects. However, a larger 24-week trial with 536 participants failed to show statistically significant weight loss, leading to termination of pharmaceutical development.
This inconsistency suggests AOD-9604 may provide modest fat loss support rather than dramatic effects. For body recomposition purposes, it might serve better as a supportive compound rather than a primary intervention.
AOD-9604 protocols
Common dosing ranges from 250-500 mcg daily via subcutaneous injection. Administration in a fasted state, typically before breakfast, maximizes fat oxidation potential. Research established that doses above 1 mg (1000 mcg) provide no additional benefits.
Cycle lengths typically run 12-24 weeks for body composition protocols. The compound is generally well-tolerated with minimal reported side effects in human studies.
For those specifically targeting stubborn fat while using other compounds for muscle building, AOD-9604 may complement a broader protocol without adding hormonal complexity.
Recovery peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500 for training support
Body recomposition requires training. Intense, consistent, progressive training that provides both the stimulus for muscle growth and the caloric expenditure for fat loss. Recovery peptides don't directly cause fat loss or muscle gain, but they enable the training intensity and frequency that drives both.
BPC-157 demonstrates remarkable healing and regenerative properties, primarily through promoting angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation). Studies show accelerated healing of musculoskeletal injuries, particularly tendon-to-bone damage. For researchers pushing training limits, BPC-157 may support faster recovery from the inevitable minor injuries that accumulate during aggressive protocols.
TB-500 similarly accelerates tissue repair and reduces inflammation. Together, these peptides form the foundation of many recovery stacks, allowing more training volume and intensity over time. The BPC-157 vs TB-500 comparison helps determine which might better serve specific recovery needs, while many researchers use both simultaneously for comprehensive support.
The BPC-157 TB-500 stacking guide provides detailed protocols for combining these recovery-focused compounds with recomposition goals.
Why recovery matters for recomposition
Consider the math of body recomposition. Building muscle requires progressive overload, consistently challenging muscles beyond their current capacity. Losing fat requires caloric deficits and sufficient activity to maintain elevated energy expenditure. Both goals benefit from training frequently and intensely.
But training while in a caloric deficit for fat loss already compromises recovery. You're asking your body to repair and grow with fewer resources available. Add the accumulated fatigue of high training frequency, and injuries become increasingly likely. An injury that sidelines training for weeks can derail months of recomposition progress.
Recovery peptides address this vulnerability. By potentially accelerating tissue repair and reducing inflammation, they may allow sustainable training intensity during the caloric restriction that recomposition requires.
Explore injury healing peptide options and how they integrate with body composition goals.
Optimal peptide stacks for different body recomposition goals
Not all recomposition goals are identical. Someone starting with significant fat to lose needs a different approach than someone already lean who's trying to gain muscle without adding fat. Your starting point determines which peptide combinations make sense.
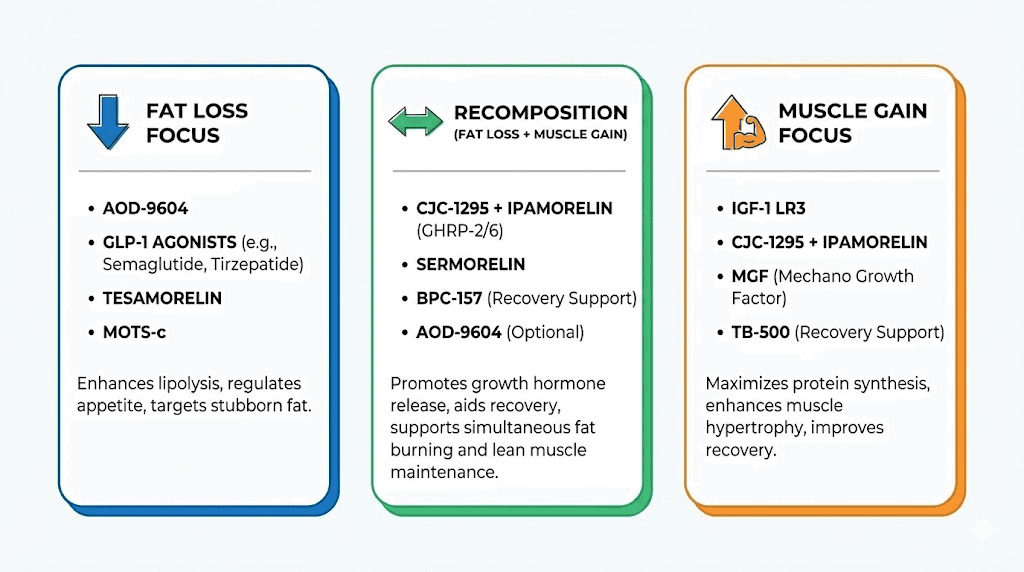
Stack 1: High body fat, primary goal fat loss with muscle preservation
For researchers starting with significant fat mass, the priority is substantial fat loss while protecting existing muscle from catabolism.
Primary compounds:
Semaglutide or tirzepatide at standard therapeutic doses for appetite suppression and metabolic effects
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin (200 mcg each, evening dose) for GH-mediated muscle preservation
Support compounds:
BPC-157 (250-500 mcg daily) for training recovery
Critical requirements:
Protein intake 1.6-2.0 g/kg body weight daily
Resistance training 3-4x weekly minimum
Progressive overload focus despite caloric deficit
This stack leverages GLP-1 agonists for their powerful appetite control and fat loss effects while using growth hormone secretagogues to provide anabolic signals that protect lean tissue. The combination directly addresses the muscle loss concern associated with aggressive GLP-1 weight loss.
Stack 2: Moderate body fat, true body recomposition
For those at intermediate body fat levels seeking genuine recomposition, simultaneous fat loss and muscle gain, the approach balances both goals.
Primary compounds:
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin (200-300 mcg each, twice daily: morning and evening)
MK-677 (20-25 mg daily, evening) for sustained GH elevation
Support compounds:
Tesamorelin (2 mg daily) for targeted visceral fat reduction
BPC-157 + TB-500 for comprehensive recovery support
Critical requirements:
Slight caloric deficit (10-15% below maintenance)
Protein intake 1.8-2.2 g/kg body weight
Resistance training 4-5x weekly with progressive overload
Cardio for additional caloric expenditure without excessive volume
This comprehensive stack provides multiple pathways to elevated growth hormone, supporting both muscle building and fat oxidation simultaneously. The moderate caloric deficit allows muscle growth while still promoting fat loss, true recomposition territory.
Stack 3: Already lean, adding muscle without fat gain
For lean researchers focused primarily on muscle accrual while staying lean, the stack emphasizes anabolic signaling.
Primary compounds:
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin (300 mcg each, twice daily)
MK-677 (25 mg daily) for sustained IGF-1 elevation
Support compounds:
BPC-157 + TB-500 for aggressive training recovery
AOD-9604 (300-400 mcg daily) for fat metabolism support during surplus
Critical requirements:
Slight caloric surplus (10-15% above maintenance)
Protein intake 2.0-2.4 g/kg body weight
High volume resistance training
Limited cardio to avoid caloric deficit
When already lean, the challenge shifts from fat loss to clean gains. This stack maximizes anabolic signaling to support muscle growth while AOD-9604 provides some protection against fat accumulation during the necessary caloric surplus.
For detailed guidance on combining multiple compounds, the guide on taking multiple peptides addresses safety and practical considerations.
The critical role of diet and training in peptide-supported recomposition
Peptides are tools. Powerful tools. But tools without proper application achieve nothing.
No peptide stack will produce body recomposition without appropriate nutrition and training. This isn't marketing disclaimers; it's metabolic reality. Peptides modulate hormonal signals, but those signals require raw materials (protein), mechanical stimulation (training), and appropriate energy balance (diet) to produce results.
Protein requirements: the non-negotiable foundation
Protein intake during recomposition isn't just important. It's the primary determinant of whether you preserve muscle or lose it alongside fat.
Research consistently shows that higher protein intake during caloric restriction dramatically reduces lean mass loss. For individuals using peptides and engaging in resistance training, minimum targets of 1.6-2.2 g protein per kg body weight daily are standard recommendations. Some protocols push to 2.4 g/kg for aggressive recomposition phases.
Protein timing matters too. Distributing intake across 4-6 meals with 25-40 g protein each maximizes muscle protein synthesis signaling throughout the day. Pre-sleep protein may be particularly valuable given that GH-elevating peptides are often dosed before bed, creating a favorable hormonal environment for overnight muscle protein synthesis.
Resistance training: the stimulus that matters
You cannot build muscle without mechanically loading muscle tissue. Peptides provide hormonal support, but without the stimulus of resistance training, that support goes unused.
For recomposition, training protocols should emphasize:
Compound movements that stimulate large muscle groups (squats, deadlifts, rows, presses)
Progressive overload, consistently increasing demands on muscle tissue
Sufficient volume to drive hypertrophy signaling
Frequency that allows stimulating each muscle group 2-3x weekly
The combination of high protein intake with structured resistance training creates the conditions where peptide-elevated growth hormone actually translates to preserved or increased lean mass.
Energy balance: the recomposition sweet spot
True body recomposition typically occurs in a slight caloric deficit, usually 10-20% below maintenance.
This deficit provides the energy restriction that mobilizes fat stores while the combination of training stimulus, protein intake, and hormonal support from peptides protects lean tissue.
Aggressive deficits accelerate fat loss but also increase muscle loss risk, even with peptide support. Patience with moderate deficits produces better long-term body composition outcomes than aggressive approaches that sacrifice muscle for faster scale movement.
Tracking body composition rather than just weight becomes essential during recomposition. The scale may stay stable while body fat decreases and muscle increases. Without body composition measurements, you might mistake successful recomposition for failed weight loss.
Realistic timelines and managing expectations
Body recomposition takes time. Longer than most people expect. And peptides, while helpful, don't dramatically accelerate the fundamental biological processes involved.
Building muscle happens at a rate of roughly 0.5-1 lb per month under optimal conditions. That's with perfect nutrition, perfect training, perfect sleep, and adequate hormonal support. Losing fat sustainably happens at roughly 1-2 lbs per week. The math suggests that meaningful body recomposition, gaining several pounds of muscle while losing substantial fat, requires months of consistent effort.
What peptides actually accelerate
Peptides don't dramatically speed muscle building or fat loss beyond natural rates. What they do is:
Improve the favorability of metabolic conditions for simultaneous goals
Support better recovery, enabling more training volume
Provide appetite control that makes caloric deficits sustainable
Create hormonal environments that favor muscle preservation during fat loss
Potentially improve sleep quality, which impacts recovery and metabolism
These effects are meaningful but not magical. Someone using well-designed peptide protocols might achieve in 3-4 months what would take 6-8 months naturally. But they won't achieve in 4 weeks what naturally requires months.
Tracking progress appropriately
Weekly scale measurements are nearly useless for tracking recomposition. Water retention, food volume, and daily fluctuations easily mask changes in fat and muscle mass.
Better tracking methods include:
Monthly body composition assessments (DEXA, bioimpedance, skinfolds)
Progress photos under consistent lighting and conditions
Measurements (waist, chest, arms, thighs)
Strength progression in key lifts
How clothes fit over time
For those wanting to see typical results, the peptides before and after results provide realistic examples of what well-designed protocols achieve over appropriate timeframes.
Safety considerations and monitoring
Peptide protocols for body recomposition involve compounds with varying safety profiles. Understanding risks and implementing appropriate monitoring protects both health and results.
Growth hormone secretagogue concerns
Compounds that elevate GH and IGF-1 carry theoretical risks related to these hormones:
Water retention and joint discomfort, typically temporary
Potential blood glucose impacts with extended high-dose use
Theoretical concerns about long-term IGF-1 elevation
Interaction with certain health conditions
Periodic blood work monitoring glucose, HbA1c, and IGF-1 levels provides useful data during extended protocols. Most issues are dose-dependent and resolve with dosage reduction or discontinuation.
GLP-1 agonist considerations
These compounds carry well-documented side effects including:
Gastrointestinal effects (nausea, constipation, diarrhea)
Potential gallbladder issues with rapid weight loss
Muscle loss without appropriate countermeasures
Rare but serious concerns like pancreatitis
Using GLP-1 agonists under medical supervision is strongly recommended given their potency and side effect profile.
Source quality matters
The peptide market includes both research-grade and pharmaceutical-grade products. Quality varies dramatically between suppliers, and contaminated or mislabeled products create risks beyond the compounds themselves.
Peptide testing labs can verify product identity and purity. Reputable peptide sourcing and verification practices significantly reduce risks associated with product quality.
For storage considerations that affect potency, understand how long peptides last in the fridge and at room temperature. Proper peptide storage maintains compound integrity throughout your protocol.
Professional guidance
Working with healthcare providers experienced in peptide therapy offers significant advantages. They can monitor relevant biomarkers, adjust protocols based on individual response, and identify potential issues before they become serious. Finding peptide therapy providers in your area may be worthwhile for comprehensive protocols.
The guide on doctors prescribing research peptides explains the current landscape of medical peptide access.
Comparing peptide approaches to alternatives
Peptides aren't the only tools available for body recomposition. Understanding how they compare to alternatives helps inform decisions.
Peptides vs steroids for recomposition
The peptides vs steroids comparison is relevant for body recomposition goals. Anabolic steroids directly increase muscle protein synthesis at rates peptides cannot match. For pure muscle building, steroids are more potent.
However, peptides offer advantages for recomposition specifically:
GH-mediated fat loss that steroids don't provide
Less hormonal disruption and easier recovery
Lower side effect profiles at effective doses
Legal status in many jurisdictions
Sustainable long-term use without cycling requirements
For those prioritizing health alongside results, peptides present a more moderate approach that still supports meaningful body composition changes.
Peptides vs SARMs
Comparing peptides to SARMs reveals different mechanisms for similar goals. SARMs directly stimulate androgen receptors in muscle tissue, promoting protein synthesis.
They're effective for muscle building but don't offer the fat loss benefits of GH-elevating peptides.
For pure recomposition, GH secretagogues likely have advantages due to their dual effects on muscle and fat metabolism. SARMs may be more effective for pure muscle building goals.
Natural alternatives
It's worth noting that body recomposition is achievable naturally, just more slowly. Optimized training, nutrition, and sleep can produce meaningful body composition changes over time. Peptides accelerate and enhance these processes but don't replace the fundamentals.
For those exploring options, comparing testosterone boosters to peptides may also be relevant depending on individual circumstances.
Advanced considerations for experienced researchers
For those with peptide experience seeking to optimize recomposition protocols, several advanced strategies merit consideration.
Periodized peptide protocols
Rather than running identical protocols continuously, periodized approaches align peptide selection with training phases:
Fat loss emphasis phase (8-12 weeks):
Higher emphasis on GLP-1 agonists or AOD-9604
GH secretagogues for muscle preservation
Moderate caloric deficit
Muscle building emphasis phase (8-12 weeks):
Maximum GH secretagogue dosing
Caloric surplus or maintenance
Reduced or eliminated GLP-1 use
Maintenance phase (4-8 weeks):
Reduced peptide doses or break periods
Maintenance calories
Training maintenance volume
This periodization prevents receptor desensitization, allows metabolic recovery, and may produce better long-term results than continuous aggressive protocols.
Timing optimization
Advanced timing strategies attempt to maximize the metabolic environment at key moments:
Pre-workout GH secretagogue dosing to elevate fat oxidation during training
Post-workout protein plus GH elevation for enhanced recovery
Pre-sleep dosing to capitalize on natural GH release during deep sleep
Fasted morning dosing for maximum fat oxidation
These strategies may provide marginal benefits beyond basic protocols, though individual response varies.
Emerging compounds
The peptide landscape continues evolving. Retatrutide, a triple agonist targeting GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors, shows unprecedented weight loss efficacy in trials. Though not yet FDA-approved, it represents the direction of next-generation metabolic peptides.
Combination therapies pairing GLP-1 agonists with muscle-preserving compounds like bimagrumab are under active investigation. These approaches directly address the lean mass loss concern while maintaining GLP-1 weight loss benefits.
Understanding how long peptides take to work helps calibrate expectations when experimenting with newer compounds.
Special considerations for specific populations
Women and body recomposition peptides
Peptides for women require consideration of different hormonal contexts. Growth hormone secretagogues work similarly in both sexes, but women may be more susceptible to certain side effects like water retention.
The guide to safe peptides for women addresses female-specific considerations including menstrual cycle timing, pregnancy precautions, and dosing adjustments.
For women approaching or in menopause, peptides for menopause discusses how hormonal changes affect peptide selection and efficacy.
Men and testosterone support
Some men combine body recomposition peptides with testosterone-supporting peptides.
While GH secretagogues don't directly affect testosterone, optimizing multiple hormonal axes may enhance overall results.
The complete peptide guide for men addresses male-specific considerations including testosterone interactions and sexual health peptides like PT-141.
Older adults
Age-related muscle loss (sarcopenia) makes body recomposition both more important and more challenging for older adults. GH secretagogues may be particularly valuable given natural GH decline with age.
However, older adults may face increased risks with aggressive GLP-1 use. Research notes that older age, combined with disease severity, may influence appropriate candidate selection due to sarcopenia risk. Muscle preservation strategies become even more critical in this population.
The peptides for anti-aging page discusses compounds relevant for age-related concerns beyond pure body composition.
Practical implementation guide
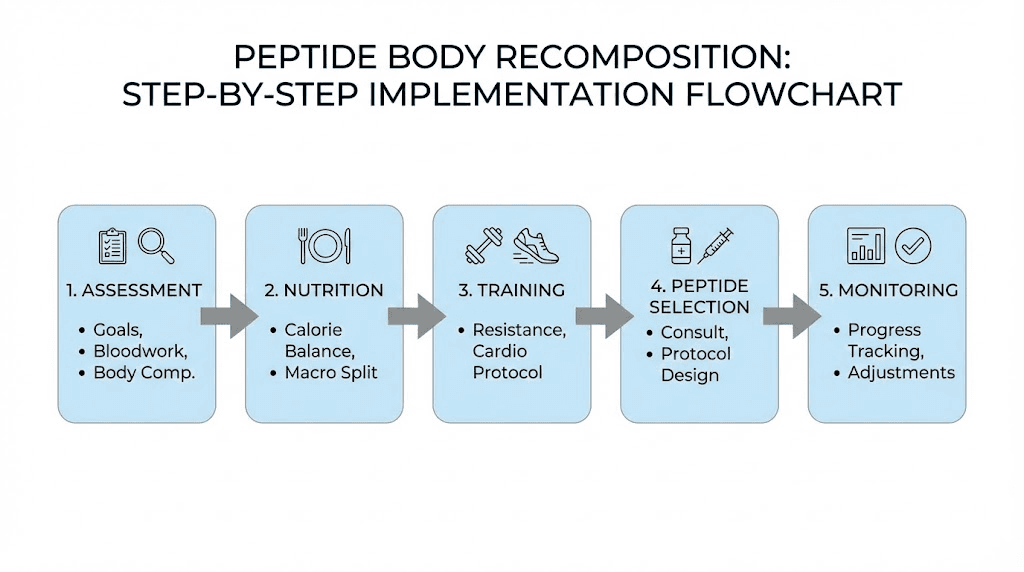
Theory without practice produces nothing. Here's a step-by-step implementation framework for body recomposition peptide protocols.
Step 1: Assess your starting point
Get baseline measurements before starting any protocol:
Body weight
Body composition (DEXA, bioimpedance, or skinfolds)
Key measurements (waist, chest, arms, thighs)
Progress photos (front, side, back)
Baseline blood work (optional but valuable)
Current strength levels on key lifts
These baselines allow objective progress assessment rather than subjective impressions.
Step 2: Establish nutrition foundation
Before adding peptides, get nutrition dialed in:
Calculate maintenance calories
Set appropriate deficit (10-20% for recomposition)
Establish protein targets (1.6-2.2 g/kg minimum)
Plan meal timing, especially around training and peptide dosing
Prepare for tracking intake accurately
Nutrition failures undermine even optimal peptide protocols. Get this foundation solid first.
Step 3: Establish training foundation
Ensure training program supports recomposition goals:
Resistance training 3-5x weekly
Compound movement focus
Progressive overload tracking
Appropriate volume for recovery capacity
Cardio as needed for caloric goals without excessive volume
Again, establish this before peptides. Peptides enhance good training; they don't replace it.
Step 4: Select appropriate peptide protocol
Based on your starting point and goals, select from the stacks outlined above or design a custom approach. Consider:
Primary goal (fat loss priority vs muscle priority vs balanced)
Starting body composition
Budget and access to compounds
Comfort with injectable vs oral administration
Risk tolerance and monitoring capacity
Use the complete peptide list to understand available options and the peptide cost calculator for budget planning.
Step 5: Acquire quality peptides
Source peptides from reputable suppliers. Understand lyophilized vs liquid peptides and injectable vs oral options. Acquire necessary supplies including bacteriostatic water for reconstitution.
Learn proper reconstitution techniques before starting. Improper preparation can destroy expensive peptides or create contamination risks.
Step 6: Implement and monitor
Begin protocol with careful monitoring:
Start at lower doses and titrate up as tolerated
Track subjective markers (energy, sleep, appetite, recovery)
Monitor for side effects
Maintain nutrition and training consistency
Monthly body composition assessments
Periodic blood work as appropriate
Step 7: Adjust based on response
Individual response varies. Be prepared to:
Adjust doses based on effects and tolerability
Modify nutrition if progress stalls
Increase or decrease training volume based on recovery
Switch compounds if response is poor
Extend or shorten cycles based on results
Body recomposition is an iterative process.
Initial protocols rarely survive contact with individual physiology unchanged.
Frequently asked questions
What is the best single peptide for body recomposition?
No single peptide optimally addresses both fat loss and muscle gain simultaneously. The CJC-1295/ipamorelin combination is widely considered the best starting point because it elevates growth hormone through complementary mechanisms, supporting both fat oxidation and muscle protein synthesis. For those preferring oral administration, MK-677 provides similar GH elevation without injections.
Can I achieve body recomposition with semaglutide alone?
Semaglutide alone typically produces weight loss with significant lean mass loss, not true body recomposition.
To achieve recomposition with semaglutide, you must combine it with resistance training 3-5x weekly and protein intake of 1.6-2.2 g/kg daily minimum. Adding GH secretagogues may further protect lean mass. Without these interventions, expect approximately 40% of weight lost to come from muscle.
How long until I see results from body recomposition peptides?
Expect subtle changes (improved sleep, better recovery) within 2-4 weeks. Visible body composition changes typically begin around weeks 8-12 with optimal nutrition and training. Significant recomposition, meaning clearly visible muscle gain alongside fat loss, generally requires 4-6 months of consistent protocol adherence. The timeline for peptide effects varies by compound and individual response.
Do I need to cycle body recomposition peptides?
Most GH secretagogues benefit from cycling to prevent receptor desensitization. Common approaches include 5 days on, 2 days off weekly, or 12-week cycles with 4-week breaks. GLP-1 agonists don't require cycling and are typically used continuously. Recovery peptides like BPC-157 can be used as needed without strict cycling requirements. See the peptide cycle planning guide for detailed protocols.
Can women use the same body recomposition peptides as men?
Yes, most body recomposition peptides work similarly in both sexes. Women may use slightly lower doses and should monitor for water retention more carefully. GH secretagogues don't affect sex hormones directly and are appropriate for women. The guide to peptides for women provides female-specific dosing considerations and safety information.
What's the minimum training required for peptide-supported recomposition?
Resistance training 3x weekly hitting all major muscle groups is the minimum for meaningful results. Progressive overload must occur over time. Without this training stimulus, even optimal peptide protocols won't build muscle, they can only help preserve existing tissue during fat loss. For best results, 4-5x weekly training with compound movements is recommended.
Are body recomposition peptides safe long-term?
Long-term safety data varies by compound. Tesamorelin has 12-month safety data in medical populations. MK-677 has been studied up to 2 years. CJC-1295 and ipamorelin have less long-term data but no identified chronic safety concerns at standard doses. GLP-1 agonists have extensive safety data as FDA-approved medications. Periodic blood work monitoring and breaks between cycles provide additional safety margins.
Can I use peptides while on other medications?
Interactions vary by compound and medication. GLP-1 agonists have known interactions with diabetes medications and may affect absorption of oral medications due to slowed gastric emptying. GH secretagogues may impact blood glucose in diabetics. Always consult healthcare providers about potential interactions with current medications before starting any peptide protocol.
For researchers serious about optimizing their peptide protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who've navigated these exact questions.