Jan 19, 2026

You bought the vial, watched the reconstitution videos, set an alarm for bedtime dosing. And yet, three weeks into your DSIP protocol, you are still staring at the ceiling at 2am wondering what went wrong. Sound familiar?
The frustrating truth is that most DSIP failures have nothing to do with the peptide itself. They stem from dosing mistakes that sabotage results before the first injection even happens.
Delta sleep-inducing peptide operates differently than melatonin or prescription sleep aids. It does not knock you out. It does not make you groggy. What it does, when dosed correctly, is shift your sleep architecture toward deeper, more restorative phases. The kind of sleep where your body actually repairs itself. The kind where you wake up feeling like a different person.
But here is the problem. The optimal DSIP dosage varies wildly depending on your goals, your current sleep patterns, and how your body metabolizes this particular peptide. Clinical studies used vastly different protocols. Online forums contradict each other constantly. And vendor recommendations prioritize selling more product over achieving results. This guide cuts through that noise with evidence-based dosing strategies that actually work, drawn from published research, clinical protocols, and documented user experiences across thousands of administrations.
What follows is the most comprehensive DSIP dosage resource available anywhere.
You will learn exact microgram amounts, precise timing windows, reconstitution ratios that preserve potency, cycling strategies that prevent tolerance, and troubleshooting protocols for when things go wrong. Whether you are a first-time user trying to figure out where to start or an experienced researcher optimizing an existing protocol, the information here will transform how you approach this fascinating sleep peptide.
Understanding DSIP before you dose
Before calculating your first injection, you need to understand what makes DSIP fundamentally different from other sleep interventions. This is not academic trivia.
It directly impacts how you should dose.
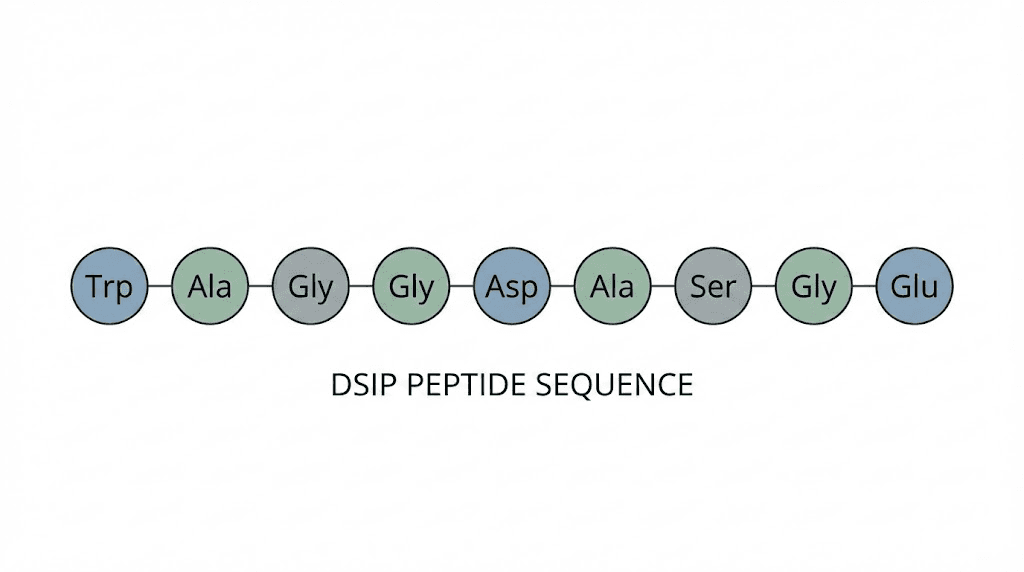
DSIP, or delta sleep-inducing peptide, consists of just nine amino acids arranged in a specific sequence: Trp-Ala-Gly-Gly-Asp-Ala-Ser-Gly-Glu. Swiss researchers first isolated it in 1974 from rabbit cerebral venous blood during induced sleep states. The discovery sparked decades of research into how this small peptide influences sleep architecture, stress response, and hormonal regulation.
Unlike melatonin, which primarily signals sleep timing to your circadian system, DSIP appears to modulate sleep depth and quality. It enhances GABA-activated currents in key brain regions while simultaneously blocking NMDA receptor responses in cortical areas. This dual action creates conditions favorable for slow-wave sleep, the deepest and most restorative sleep phase.
The peptide also interacts with your hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, the system controlling stress hormones. Research shows DSIP can decrease basal corticotropin levels and block excessive cortisol release. For anyone whose sleep problems stem partly from stress, this mechanism matters enormously. High cortisol at night destroys sleep quality regardless of what else you do.
Here is what this means for dosing. DSIP works through subtle neurochemical modulation rather than brute-force sedation. You cannot simply take more to sleep harder. In fact, excessive doses often produce the opposite effect, causing paradoxical insomnia or next-day grogginess.
The goal is finding the minimum effective dose that shifts your sleep architecture without overwhelming the delicate receptor systems involved.
Why generic dosing advice fails
Most DSIP dosing recommendations you will find online range from 100-500mcg administered before bed. That range is technically accurate but practically useless. It is like saying the correct driving speed is somewhere between 15 and 90 miles per hour. True, but unhelpful.
The wide variance exists because clinical research used wildly different protocols. Early human studies by Schneider-Helmert administered 25 nanomoles per kilogram intravenously. Later research used fixed microgram amounts subcutaneously. Animal studies employed still different approaches scaled by body weight. Synthesizing this data into actionable dosing protocols requires understanding the context behind each number.
Your individual response also matters more than with most peptides. Some people experience profound sleep improvements at 50mcg. Others need 250mcg to notice anything. Factors like body composition, baseline sleep quality, concurrent medications, and even your natural GABA receptor density all influence optimal dosing.
What works perfectly for someone else may fail completely for you.
DSIP dosage protocols by experience level
Rather than giving you a single number that may or may not work, here are structured protocols based on your experience and goals. Start with the protocol matching your situation and adjust based on response.
First-time user protocol
If you have never used DSIP before, conservative initial dosing prevents wasted product and unwanted side effects. Your goal for the first two weeks is assessment, not optimization.
Week 1:
Dose: 50mcg
Frequency: Once, on a night when you can sleep in the next morning
Timing: 2-3 hours before intended sleep
Purpose: Assess basic tolerance and response
Week 2:
Dose: 75-100mcg
Frequency: 2-3 times during the week
Timing: 1-2 hours before bed
Purpose: Establish baseline effective dose
During this assessment phase, track sleep quality subjectively and, if possible, with a wearable device that measures sleep stages. Look for increased deep sleep percentage, reduced time to fall asleep, and improved morning alertness. If you experience grogginess, headaches, or paradoxical insomnia, the dose is too high for your neurochemistry.
Most first-time users find their sweet spot between 75-150mcg.
Some respond well at just 50mcg.
Others need the full 200mcg range.
The assessment protocol helps you identify where you fall without wasting product or suffering unnecessary side effects.
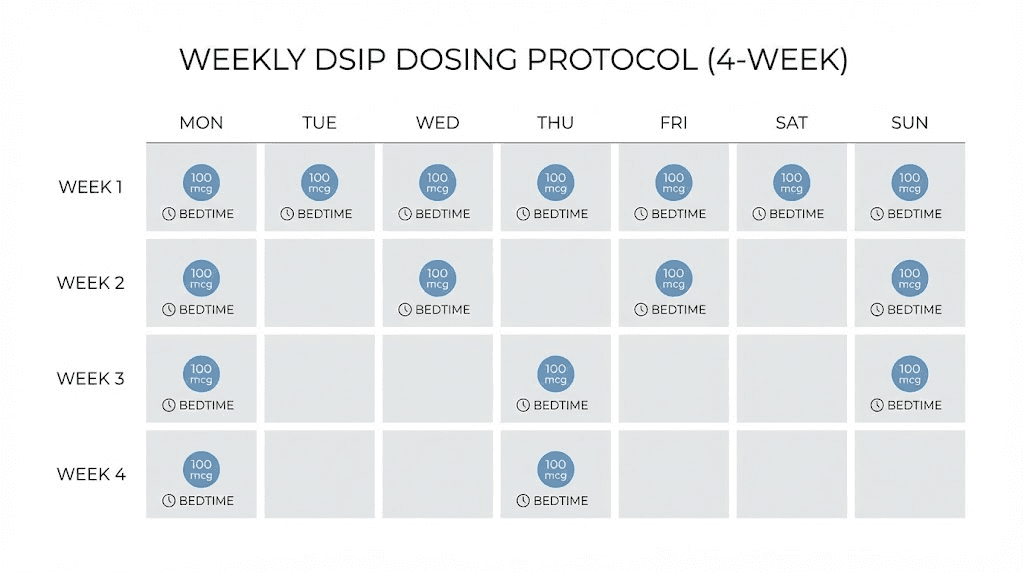
Standard optimization protocol
Once you have established basic tolerance and found a dose that produces noticeable effects, you can move into optimization. This protocol maximizes benefits while minimizing tolerance development.
Typical protocol structure:
Dose: 100-200mcg based on individual response
Frequency: 3-5 times per week
Timing: 1-3 hours before bed (experiment to find your optimal window)
Cycle length: 4-8 weeks
Break period: 2-4 weeks between cycles
The frequency debate generates significant discussion. Some researchers advocate daily use for consistent sleep architecture modification. Others prefer every-other-day or three-times-weekly dosing to prevent receptor adaptation. The evidence is mixed, with some studies suggesting DSIP does not induce tolerance while user reports sometimes indicate diminishing returns with daily use.
A practical compromise involves starting with every-other-day dosing and adjusting based on your response. If effects remain strong after two weeks of alternate-day use, you can increase frequency. If you notice diminishing benefits, reduce to three times weekly or add rest days.
Advanced sleep optimization protocol
For experienced users who have established their effective dose and want to maximize results, advanced protocols incorporate additional variables like timing precision, peptide stacking, and targeted cycling.
Precision timing approach:
DSIP has a very short plasma half-life, estimated around 7-15 minutes in some studies. This means timing matters more than with longer-acting compounds. Rather than using a fixed pre-bedtime interval, advanced users often experiment with different timing windows.
Some find administering DSIP 3 hours before bed, allowing the initial effects to settle before sleep attempt, produces the best results. Others prefer 30-60 minutes pre-sleep for more immediate effect.
Your optimal timing depends on individual metabolism and how quickly you typically fall asleep.
Stacking considerations:
DSIP combines reasonably well with certain other peptides and supplements, though caution is warranted. Common stacking approaches include:
Selank for additional anxiolytic benefits that complement DSIP's sleep effects. The two peptides work through different mechanisms, with Selank modulating anxiety pathways while DSIP focuses on sleep architecture.
Epithalon for enhanced melatonin production combined with DSIP's sleep depth effects. This stack addresses both sleep timing and sleep quality through complementary mechanisms.
BPC-157 when recovery optimization is the primary goal. Deep sleep facilitates physical repair, and combining these peptides may enhance athletic recovery protocols.
Avoid stacking DSIP with other sedating compounds, alcohol, or prescription sleep medications. The combined effects can produce excessive sedation or unpredictable interactions. If you take any medications affecting GABA, serotonin, or dopamine systems, consult a healthcare provider before adding DSIP.
Reconstitution and concentration calculations
Accurate dosing requires proper reconstitution. Many DSIP failures trace back to incorrect mixing that either destroys the peptide or makes precise dosing impossible.
Standard reconstitution protocol
DSIP typically comes in lyophilized (freeze-dried) form in 5mg or 10mg vials. The powder appears as a small white or off-white cake at the bottom of the vial. Before reconstitution, store these vials in the freezer at -20°C for maximum stability.
For a 5mg vial:
Add 2.5ml bacteriostatic water
Resulting concentration: 2mg/ml (2000mcg/ml)
For a 100mcg dose: draw 0.05ml (5 units on a standard insulin syringe)
For a 200mcg dose: draw 0.10ml (10 units)
For a 10mg vial:
Add 3.0ml bacteriostatic water
Resulting concentration: 3.33mg/ml (3333mcg/ml)
For a 100mcg dose: draw 0.03ml (3 units)
For a 200mcg dose: draw 0.06ml (6 units)
Alternatively, for easier math with a 5mg vial, you can add 5ml of bacteriostatic water to create a 1mg/ml (1000mcg/ml) concentration. This makes dosing calculations simple: 0.1ml equals 100mcg, 0.15ml equals 150mcg, and so on. The tradeoff is that larger volumes per injection can be slightly less comfortable.
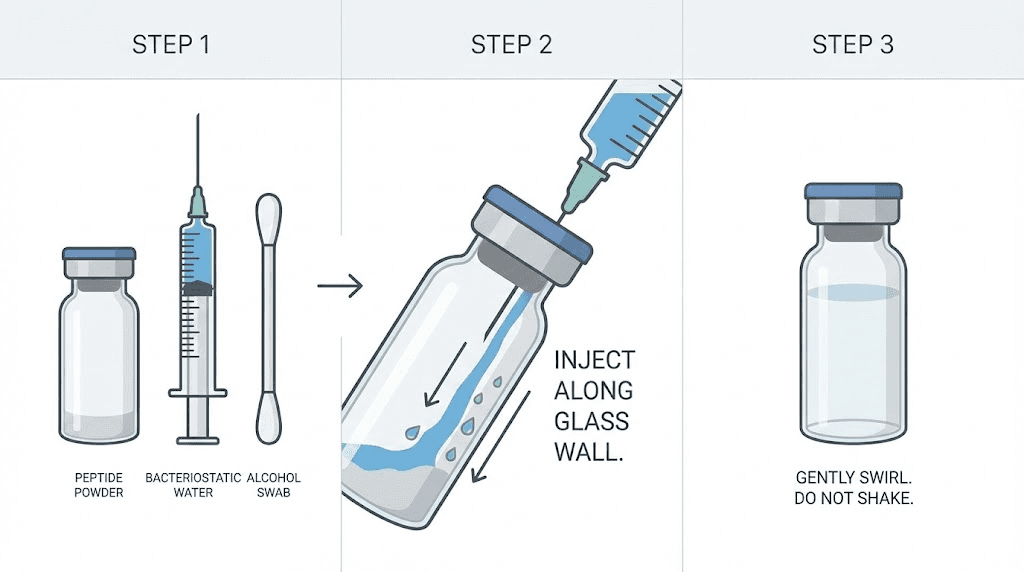
Reconstitution technique
How you add the water matters as much as how much you add. Peptides are delicate molecules that can denature (lose their structure and effectiveness) if handled roughly.
Never inject the bacteriostatic water directly onto the powder cake. Instead, aim the needle at the inside wall of the vial and let the water run down the glass slowly. The liquid will gradually dissolve the lyophilized peptide without the mechanical stress of direct impact.
After adding the water, do not shake the vial. Vigorous shaking introduces air bubbles and can damage the peptide through mechanical agitation. Instead, gently roll the vial between your palms or let it sit at room temperature for a few minutes. The DSIP will dissolve on its own, producing a clear, colorless solution.
If the reconstituted solution appears cloudy, contains particles, or looks discolored, do not use it. These signs indicate contamination or peptide degradation. Discard the vial and start fresh with a new one.
Storage after reconstitution
Once reconstituted, DSIP stability decreases significantly.
Store the mixed solution in your refrigerator at 2-8°C (36-46°F).
Keep it away from light, ideally in a drawer or wrapped in foil.
Use reconstituted DSIP within 3-4 weeks for optimal potency. While some degradation studies suggest longer stability windows, practical experience indicates noticeable potency loss beyond one month. For a standard protocol using 150mcg five times weekly, a 5mg vial reconstituted in 2.5ml provides approximately 66 doses, more than enough to complete within the recommended timeframe.
Never freeze reconstituted peptide solutions. The freeze-thaw cycle can damage molecular structure and reduce effectiveness. If you cannot use all the reconstituted DSIP within a month, consider smaller vial sizes or split your reconstitution to maintain fresh supply.
Administration routes and techniques
DSIP can be administered through multiple routes, each with distinct advantages and considerations. Your choice affects onset time, bioavailability, and practical convenience.
Subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous injection remains the most common and well-studied administration route for DSIP. You inject the peptide into the fatty tissue layer just beneath the skin, where it absorbs gradually into systemic circulation.
Injection technique:
Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and let it dry completely
Pinch a fold of skin at your chosen site (abdomen, upper thigh, or upper arm work well)
Insert the needle at a 45-90 degree angle into the pinched skin fold
Inject slowly and steadily over several seconds
Withdraw the needle and apply light pressure if needed
Rotate injection sites to prevent lipohypertrophy (tissue buildup from repeated injections in the same spot). A simple rotation pattern using left abdomen, right abdomen, left thigh, right thigh gives each site a week to recover between injections.
Subcutaneous administration provides reliable absorption and consistent effects. Most clinical research used this route, making it the best-validated approach for DSIP dosing protocols.
Nasal spray administration
Intranasal DSIP has gained popularity as a needle-free alternative. The nasal mucosa is highly vascularized, allowing absorption directly into circulation, and some evidence suggests nasal administration may provide more direct central nervous system access via the olfactory pathway.
Nasal spray considerations:
Typically lower bioavailability than injection, requiring somewhat higher doses
Faster onset in some users due to direct CNS access
More convenient and less intimidating for needle-averse individuals
Requires properly calibrated spray bottles for accurate dosing
Converting from injectable to nasal dosing is not straightforward. Some users report needing 20-50% higher nasal doses to achieve equivalent effects, though individual variation is substantial. If transitioning from subcutaneous to nasal administration, start at your established injectable dose and adjust based on response rather than assuming a specific conversion ratio.
Nasal spray preparation requires additional equipment and technique. The solution concentration, spray bottle calibration, and administration technique all affect dosing accuracy. For most users seeking reliable, research-backed protocols, subcutaneous injection remains the preferred route.
Timing optimization for maximum benefit
When you take DSIP matters almost as much as how much you take. The peptide's short half-life and mechanism of action create specific timing considerations that can make or break your results.
The timing window debate
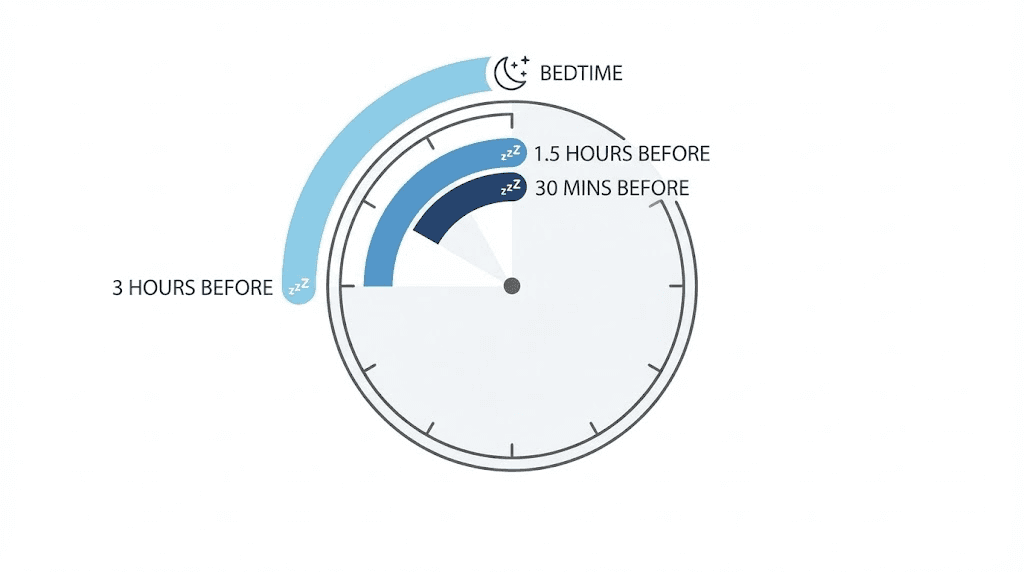
Recommendations for pre-bedtime DSIP administration range from 30 minutes to 3 hours before sleep. This variance reflects genuine uncertainty in the literature combined with significant individual variation in response.
Dr. William Seeds, author of Peptide Protocols, recommends 100mcg administered approximately 3 hours before bedtime. This earlier timing allows the peptide's effects to establish before you attempt sleep, potentially creating more natural-feeling drowsiness rather than sudden sedation.
Ben Greenfield's protocol suggests 150mcg administered 1 hour before bed, three times weekly. This closer-to-bedtime approach may work better for those who fall asleep quickly once the peptide takes effect.
The research supports both approaches depending on what you are optimizing for. Earlier administration (2-3 hours) tends to produce gradual sleep pressure that builds naturally. Later administration (30-60 minutes) creates more immediate effects but may feel more drug-like to some users.
Finding your optimal timing
Rather than adopting someone else's timing protocol, experiment systematically to find what works for your physiology.
Week 1 experiment:
Administer DSIP 3 hours before intended sleep
Track time to fall asleep, sleep quality, morning alertness
Note any grogginess or sleep disturbance
Week 2 experiment:
Administer DSIP 1.5 hours before intended sleep
Track the same variables
Compare results to week 1
Week 3 experiment:
Administer DSIP 30-45 minutes before intended sleep
Track and compare
Identify which timing produced the best results
Some users find their optimal timing changes over a cycle. Initial doses may work better with earlier administration, while established protocols tolerate closer-to-bedtime dosing. Stay flexible and adjust based on ongoing results rather than locking into a fixed timing regardless of how it performs.
Cycling strategies to prevent tolerance
Whether DSIP actually produces tolerance remains scientifically debated. Some research suggests the peptide does not induce receptor adaptation, while user reports occasionally describe diminishing effects with prolonged daily use. A prudent approach assumes some tolerance potential and incorporates cycling to maintain effectiveness.
Standard cycling protocol
The most common cycling approach involves 4-8 weeks of active use followed by 2-4 weeks off. This pattern allows any potential receptor adaptation to normalize while preventing dependence on the peptide for sleep.
8-week on, 4-week off example:
Weeks 1-2: Assessment and dose finding (every other day)
Weeks 3-6: Optimization phase (3-5 times weekly)
Weeks 7-8: Maintenance (3 times weekly)
Weeks 9-12: Complete break, no DSIP
During the off period, focus on sleep hygiene fundamentals: consistent wake times, light exposure management, temperature optimization, and stress reduction. These foundational practices often improve independently of peptide use, making subsequent DSIP cycles even more effective.
Alternative cycling approaches
Some users prefer shorter, more frequent cycles rather than extended periods followed by long breaks.
5-on/2-off weekly pattern:
Use DSIP Sunday through Thursday nights
Take Friday and Saturday off
Continue indefinitely with monthly full-week breaks
This approach maintains consistent sleep support on work nights while allowing regular receptor recovery. The weekend break often coincides with more flexible sleep schedules anyway, making it practically convenient.
As-needed protocol:
Use DSIP only during periods of elevated stress or sleep difficulty
Maintain for 2-4 weeks as needed
Discontinue when sleep normalizes
This conservative approach treats DSIP as a targeted intervention rather than ongoing supplementation. It naturally prevents tolerance by limiting exposure and may be appropriate for those with generally good sleep who experience periodic difficulties.
Dosage adjustments for specific goals
DSIP research suggests benefits beyond basic sleep improvement, including stress reduction, pain management, and potential effects on hormonal systems.
Different goals may benefit from different dosing approaches.
Sleep quality optimization
For pure sleep quality improvement, the standard dosing protocols described earlier apply. Focus on finding the minimum effective dose that increases deep sleep without causing grogginess. Track results over multiple weeks, as sleep architecture changes often take time to manifest in subjective improvements.
Key metrics to track:
Time to fall asleep (sleep latency)
Number of nighttime awakenings
Deep sleep percentage (if using a wearable)
Morning alertness and energy
Daytime cognitive performance
Stress and cortisol management
DSIP's effects on the HPA axis and cortisol regulation suggest potential benefits for stress-related sleep problems. If your sleep issues stem primarily from elevated evening cortisol or chronic stress, slightly different dosing may help.
Consider earlier administration (3+ hours before bed) to allow cortisol-modulating effects to establish before sleep pressure builds. Some practitioners report that lower, more frequent doses (75-100mcg nightly) produce better stress-related benefits than higher intermittent doses.
Combining DSIP with other anxiety-modulating peptides like Selank may enhance stress-related benefits, though this adds complexity to the protocol and increases the importance of proper medical guidance.
Athletic recovery enhancement
Deep sleep is when your body does most of its physical repair and muscle growth. Athletes and those focused on physical performance may benefit from DSIP protocols timed around training demands.
Consider using DSIP on nights following intense training sessions when recovery demands are highest. The enhanced deep sleep may accelerate muscle repair, reduce inflammation, and improve next-day performance readiness.
Some athletes combine DSIP with recovery-focused peptides like BPC-157 or TB-500 for comprehensive recovery protocols.
If pursuing this approach, understand that you are working with multiple compounds and should ideally have guidance from a practitioner familiar with peptide therapies.
Side effects and how to minimize them
DSIP appears to be well-tolerated in research settings, with no major toxicity identified even at high doses. However, side effects can occur, particularly with inappropriate dosing.
Common side effects
Headaches: The most frequently reported side effect, usually indicating the dose is too high for your neurochemistry. Reduce dose by 25-50% and reassess.
Grogginess: Morning grogginess suggests either excessive dosing or poor timing. Try lower doses or earlier administration to allow effects to dissipate before wake time.
Paradoxical insomnia: Some users experience worse sleep at certain doses, particularly when starting too high. This counterintuitive response resolves with dose reduction.
Injection site reactions: Minor redness or discomfort at injection sites is common with any subcutaneous administration. Rotate sites and ensure proper injection technique to minimize this.
Mood fluctuations: Rarely, users report emotional changes during DSIP use. If significant mood effects occur, discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider.
Minimizing side effects
Most DSIP side effects result from excessive dosing. The solution is simple: start lower than you think necessary and increase gradually. A conservative starting dose of 50mcg may feel like a waste of time if you have read about 300mcg protocols online, but finding your minimum effective dose prevents unnecessary side effects and conserves expensive peptide.
Timing optimization also reduces side effects. Morning grogginess often resolves by moving administration earlier in the evening. Headaches may improve with better hydration around dosing times. Systematic experimentation with timing variables often solves problems without requiring dose changes.
If side effects persist despite dose and timing adjustments, DSIP may not be the right peptide for your goals. Individual neurochemistry varies significantly, and some people simply do not respond well to DSIP regardless of protocol optimization.
Alternative sleep peptides or conventional approaches may work better for these individuals.
Drug interactions and contraindications
While DSIP has not been extensively studied for drug interactions, its mechanism of action suggests several important precautions.
Known interactions
Naloxone: Research suggests naloxone may block DSIP's effects. If you use naloxone or naltrexone for any reason, DSIP protocols will likely be ineffective.
Sedatives and sleep medications: Combining DSIP with prescription sleep medications, benzodiazepines, or other sedatives risks excessive sedation. Do not combine without medical supervision.
Alcohol: Avoid alcohol on DSIP dosing nights. Both substances affect GABAergic systems, and combining them may produce unpredictable sedation.
Peptidase inhibitors: DSIP degrades via amino-peptidases. Medications that inhibit these enzymes (like certain blood pressure medications) may alter DSIP metabolism.
Contraindications
Do not use DSIP if you:
Are pregnant or breastfeeding (insufficient safety data)
Have sleep apnea or other breathing-related sleep disorders (sedation risk)
Take prescription sedatives or sleep medications
Have a history of severe reactions to injected peptides
Are under 18 years old
If you have any chronic medical condition or take regular medications, consult a healthcare provider familiar with peptide therapies before starting DSIP. The peptide's effects on hormonal systems, particularly growth hormone and cortisol, may have implications for certain conditions.
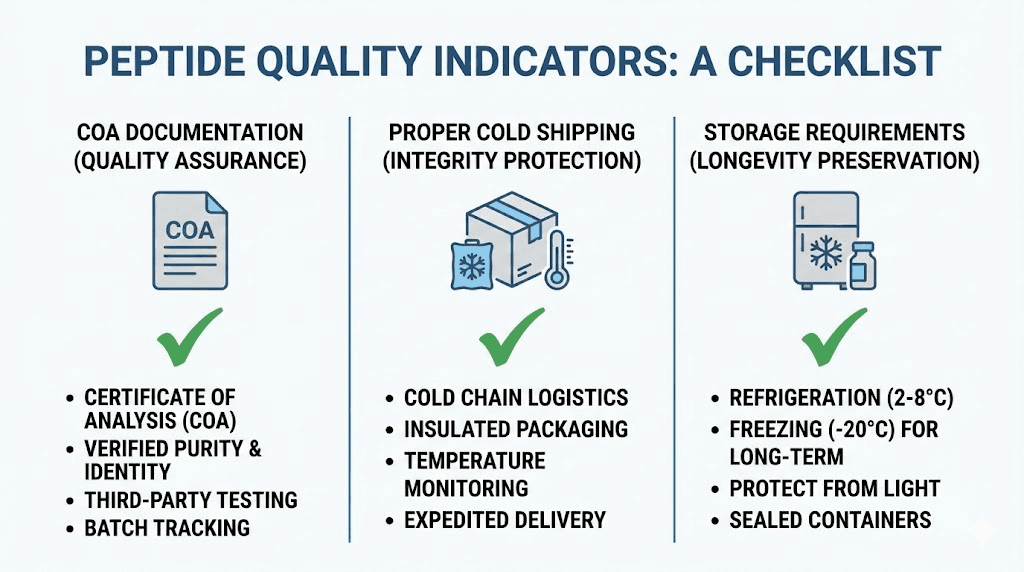
Quality and sourcing considerations
DSIP is not FDA-approved and exists in a regulatory gray area as a research chemical. This means quality varies dramatically between sources, and poor-quality product is one of the most common reasons for protocol failure.
What to look for in a source
Third-party testing: Reputable vendors provide certificates of analysis from independent laboratories confirming purity, typically 98%+ for research-grade peptides. Without this documentation, you have no way to verify what you are actually getting.
Proper handling: Peptide storage matters. Vendors should ship lyophilized product with appropriate cold packs and packaging. Peptides that arrive warm or improperly packaged may have degraded significantly.
Reputation: Established vendors with long track records and positive community feedback generally provide more reliable products than new or unknown sources. Research vendor reputation before purchasing.
Avoiding common quality problems
Underdosed product is common in the peptide market. If you use a consistent protocol that suddenly stops working, consider whether your new batch may be underdosed rather than assuming tolerance has developed.
Contamination is another concern with research peptides. Bacterial contamination can cause injection site infections or systemic illness. Always use proper sterile technique and discard any reconstituted solution that appears cloudy or develops visible particles.
Storage degradation affects even high-quality product. If you purchased DSIP months ago and stored it improperly, potency may have declined significantly. Fresh product stored correctly provides the most reliable results.
Troubleshooting common problems
Even with proper protocols, DSIP users sometimes encounter problems. Here are solutions to the most common issues.
Problem: No noticeable effect
Possible causes:
Dose too low for your neurochemistry
Product quality issues (underdosed or degraded)
Timing not optimal for your sleep patterns
Individual non-response to DSIP
Solutions:
Increase dose by 25-50% increments over several days
Try a different vendor or batch
Experiment with different timing windows
If no response at 250mcg with confirmed quality product, DSIP may not work for you
Problem: Initial effects that faded
Possible causes:
Tolerance development from excessive frequency
Product degradation over time
Changes in baseline sleep (improvement making DSIP less noticeable)
Solutions:
Take a 2-4 week break and reassess
Check reconstitution date and prepare fresh solution
Reduce frequency to prevent tolerance
Consider whether improved sleep fundamentals may have reduced DSIP's relative impact
Problem: Inconsistent results
Possible causes:
Variable timing or dosing
Lifestyle factors interfering (stress, caffeine, irregular schedule)
Injection technique inconsistency
Solutions:
Standardize protocol: same dose, same time, same technique
Address confounding factors: caffeine cutoff 8+ hours before bed, consistent wake times
Ensure consistent subcutaneous depth and injection sites
Problem: Too much sedation or next-day grogginess
Possible causes:
Dose too high
Timing too close to bedtime
Interaction with other substances
Solutions:
Reduce dose by 25-50%
Administer earlier in the evening (2-3 hours before bed)
DSIP dosage compared to other sleep peptides
Understanding how DSIP compares to other sleep-promoting peptides helps you choose the right tool for your situation.
DSIP vs Selank
Selank primarily targets anxiety and mood, with sleep benefits occurring secondary to reduced anxiety. If your sleep problems stem primarily from racing thoughts or anxiety, Selank may address the root cause more directly than DSIP.
DSIP works more directly on sleep architecture, enhancing deep sleep phases regardless of baseline anxiety levels. For straightforward sleep optimization without significant anxiety component, DSIP is the more targeted option.
Some users combine both peptides: Selank during the day for anxiety management, DSIP in the evening for sleep optimization. This combination requires careful timing and may benefit from professional guidance.
DSIP vs melatonin
Melatonin signals sleep timing to your circadian system but does not directly enhance sleep depth. It helps you fall asleep but does not necessarily improve sleep quality once you are asleep.
DSIP appears to enhance sleep architecture itself, potentially increasing deep sleep percentage regardless of circadian timing. For those who fall asleep fine but wake unrefreshed, DSIP may address the actual problem while melatonin would not.
The two can be combined, as they work through different mechanisms.
However, start with one or the other to understand individual effects before adding complexity.
DSIP vs prescription sleep medications
Prescription medications like zolpidem (Ambien), eszopiclone (Lunesta), or benzodiazepines work through different mechanisms than DSIP, typically enhancing GABAergic activity more broadly.
These medications often produce more immediate, powerful sedation but can disrupt normal sleep architecture, reduce deep sleep, and cause dependency with regular use. DSIP's gentler mechanism may preserve more natural sleep patterns, though its effects are less dramatic.
Never combine DSIP with prescription sleep medications without medical supervision.
The overlapping mechanisms create risk of excessive sedation and respiratory depression.
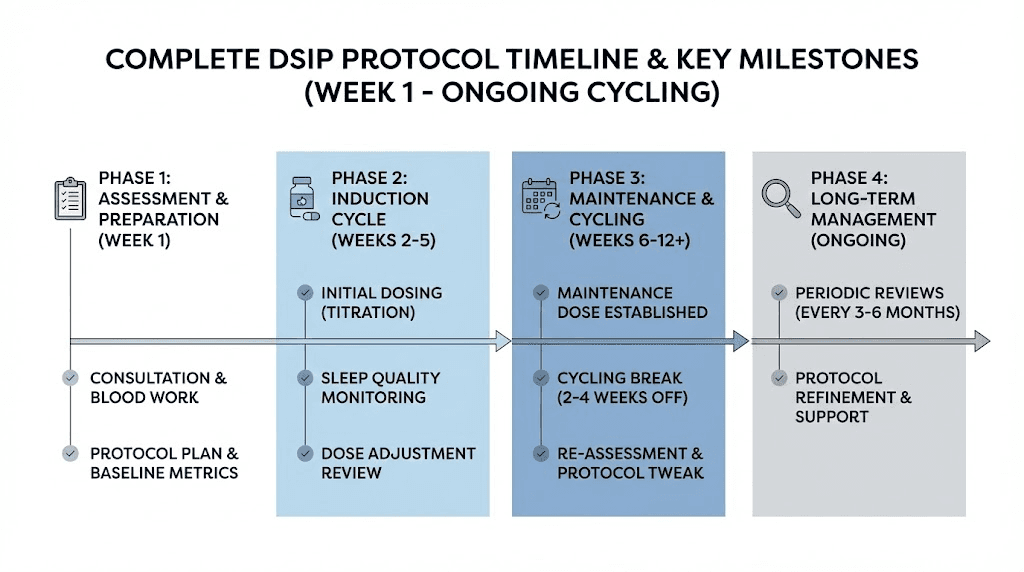
Building your complete DSIP protocol
With all the variables covered, here is how to assemble everything into a practical protocol you can implement.
Step 1: Preparation
Before your first dose:
Obtain quality DSIP from a reputable vendor with third-party testing
Get appropriate bacteriostatic water, insulin syringes, and alcohol swabs
Plan your assessment schedule (which nights you will dose, when you will evaluate)
Establish baseline sleep tracking (subjective or with wearable device)
Clear any potential interactions (medications, supplements, alcohol plans)
Step 2: Assessment phase (weeks 1-2)
Reconstitute your DSIP according to the protocols described earlier. Start with 50mcg on a low-pressure night when you can sleep in the next morning. Note your response across all relevant variables.
Gradually increase to 75-100mcg over the next week, dosing 2-3 times.
By the end of week 2, you should have a sense of your approximate effective dose range.
Step 3: Optimization phase (weeks 3-8)
Based on assessment results, establish your working protocol:
Dose: Your minimum effective dose (typically 75-200mcg)
Frequency: 3-5 times weekly based on tolerance observations
Timing: Your optimal pre-bedtime window
Track results weekly and make minor adjustments as needed. Most optimization happens in the first 2-3 weeks of this phase.
Step 4: Maintenance and cycling (ongoing)
After your initial 6-8 week cycle, take 2-4 weeks off completely. Use this break to:
Assess baseline sleep quality without DSIP
Allow any potential receptor adaptation to normalize
Evaluate whether continued use is necessary or beneficial
If returning to DSIP after the break, you may find your effective dose has changed. Repeat a brief assessment before resuming your full protocol.
Step 5: Long-term management
With consistent cycling, DSIP can be used long-term for sleep optimization. Most users eventually establish a sustainable pattern: perhaps 4-6 weeks of active use followed by 2-3 weeks off, repeated as needed based on sleep quality and life demands.
Some find they need DSIP less over time as their overall sleep quality improves. Others maintain regular use indefinitely with good results. Your long-term approach should be guided by ongoing assessment of benefits versus any diminishing returns.
Frequently asked questions
What is the best DSIP dosage for beginners?
Start with 50mcg administered once, preferably on a night when you can sleep in the next morning. This conservative approach allows you to assess basic tolerance without wasting product or experiencing unnecessary side effects. Most beginners find their effective dose between 75-150mcg after a 2-week assessment period using our peptide calculator to ensure accurate measurements.
How long does it take for DSIP to work?
DSIP has a very short plasma half-life, with effects beginning within 10-30 minutes of subcutaneous injection for most users. However, sleep architecture improvements may take several nights to become noticeable. Many users report the most significant benefits emerging after 1-2 weeks of consistent use as cumulative effects on deep sleep patterns develop.
Can I take DSIP every night?
While daily use is possible, most protocols recommend 3-5 times weekly to reduce potential tolerance development. Some users employ daily dosing during particularly stressful periods but cycle off regularly. Monitor for diminishing effects, which may indicate the need for reduced frequency or a complete break from DSIP.
Is DSIP safe to use long-term?
Long-term DSIP safety has not been established through clinical trials. The peptide appears well-tolerated in research settings with no major toxicity identified. However, most practitioners recommend cycling protocols (4-8 weeks on, 2-4 weeks off) rather than continuous indefinite use. Consult a healthcare provider familiar with peptide therapies for personalized guidance.
What happens if I take too much DSIP?
Excessive DSIP dosing typically causes headaches, grogginess, or paradoxical insomnia rather than dangerous effects. No lethal dose has been established in animal studies, and the peptide appears to have wide safety margins. If you experience adverse effects, simply reduce your dose. Severe or concerning symptoms warrant medical attention and discontinuation of use.
Can I combine DSIP with other peptides?
DSIP combines reasonably well with certain other peptides. Common stacks include Selank for anxiety reduction, Epithalon for enhanced melatonin production, and recovery peptides like BPC-157. Avoid combining with sedating substances or prescription sleep medications. Review the peptide stacking calculator for compatibility guidance.
How should I store DSIP?
Lyophilized (powder) DSIP should be stored in the freezer at -20°C for maximum stability. After reconstitution with bacteriostatic water, store in the refrigerator at 2-8°C and use within 3-4 weeks. Never freeze reconstituted solutions. Protect from light by storing in a dark location or wrapping vials in foil. Review our complete peptide storage guide for detailed instructions.
Does DSIP affect hormones?
Research suggests DSIP interacts with several hormonal systems. It may stimulate growth hormone release, modulate cortisol levels through HPA axis effects, and influence luteinizing hormone.
These hormonal effects contribute to its potential anti-aging and stress-reduction benefits but also warrant caution for those with hormone-sensitive conditions. Baseline hormonal testing before starting DSIP may be advisable.
External resources
PubMed: Effects of delta sleep-inducing peptide on sleep of chronic insomniac patients
European Journal of Anaesthesiology: Delta sleep-inducing peptide review
For researchers serious about optimizing their sleep protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available. Members get access to detailed dosing calculators, evidence-based protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions. The platform provides personalized guidance that generic information cannot match.
Sleep is not optional. It is when your body repairs, your mind consolidates, and your hormones regulate. Getting it right with DSIP requires understanding the nuances covered in this guide.
Apply these protocols systematically, track your results honestly, and adjust based on what your body tells you.
The path to restorative sleep is individual, but the principles that guide it are consistent.
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Join SeekPeptides.