Dec 30, 2025

Cognitive enhancement through peptide therapy typically involves well-known compounds like Semax, Selank, or Pinealon. But a lesser-known peptide called PDA (Phosphodiesterase Activator) offers a unique approach to brain optimization through mechanisms distinct from these more popular nootropic peptides. While research remains limited compared to established cognitive enhancers, PDA's phosphodiesterase modulation presents intriguing possibilities for memory, learning, and neuroprotection.
PDA peptide works by influencing cyclic nucleotide metabolism - specifically affecting cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate) and cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate) signaling pathways critical for neuronal function.
Unlike Semax's direct BDNF upregulation or Selank's GABAergic modulation, PDA targets the enzymes (phosphodiesterases) that break down these critical second messengers, potentially extending their beneficial effects on cognition and memory.
The theoretical benefits include enhanced long-term potentiation (the cellular basis of learning and memory), improved synaptic plasticity, neuroprotection against age-related cognitive decline, enhanced cerebral blood flow, and optimization of neuronal energy metabolism. These effects position PDA as a potential brain health and cognitive optimization tool, though human clinical data remains sparse.
However, PDA faces significant limitations - minimal human clinical trials (most data from animal studies), unclear optimal dosing protocols, limited availability from peptide vendors, mechanisms not fully elucidated despite theoretical promise, and uncertain safety profile for long-term use.
This makes PDA an experimental option requiring careful consideration versus established alternatives.
This guide examines what PDA peptide is and its phosphodiesterase mechanism, theoretical benefits for cognitive enhancement and neuroprotection, available research and animal study data, dosing protocols from limited human use, comparing PDA to Semax, Selank, and Pinealon, side effects and safety considerations, and whether PDA merits inclusion in cognitive enhancement stacks.
Understanding PDA's unique but under-researched mechanisms helps determine if this experimental nootropic peptide warrants consideration for brain optimization or if more established options provide better risk-benefit profiles.
What is PDA peptide and how does it work
The science behind phosphodiesterase activation.
PDA peptide structure and discovery
Chemical identity:
Full name: Phosphodiesterase Activator peptide
Short peptide sequence (exact structure varies by formulation)
Synthetic compound (not naturally occurring)
Designed to modulate PDE enzymes
Part of experimental nootropic peptide class
Discovery and development:
Developed through rational drug design
Based on understanding PDE role in cognition
Less publicized than Russian peptides
Limited commercial development
Primarily research/experimental use
Why "phosphodiesterase activator":
Named for its primary mechanism
Activates certain PDE isoforms
Modulates cyclic nucleotide levels
Affects cAMP/cGMP pathways
Different from PDE inhibitors (like caffeine)
Classification:
Cognitive enhancer
Neuroprotective agent (theoretical)
Research chemical status
Not FDA approved for any use
Limited information challenges:
Sparse published research
Proprietary formulations exist
Mechanism not fully characterized
Dosing protocols largely anecdotal
Learn about what peptides are and how they work at SeekPeptides.
Phosphodiesterase enzyme system
What phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are:
Enzymes that break down cyclic nucleotides
cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate)
Critical for cellular signaling
11 PDE families (PDE1-PDE11)
Role in brain function:
Control duration/intensity of cAMP/cGMP signals
Regulate synaptic plasticity
Affect memory formation
Modulate neuronal excitability
Influence cerebral blood flow
PDE families relevant to cognition:
PDE Family | Location | Substrate | Cognitive Role |
|---|---|---|---|
PDE4 | Widespread in brain | cAMP | Memory consolidation, long-term potentiation |
PDE5 | Hippocampus, cortex | cGMP | Memory formation, synaptic plasticity |
PDE9 | Striatum, cortex | cGMP | Learning, motor function |
PDE10 | Striatum | cAMP and cGMP | Striatal signaling, motor learning |
Why modulating PDEs matters:
Inhibiting PDEs → increased cAMP/cGMP → enhanced signaling
PDE inhibitors (like caffeine for PDE4) boost cognition
But PDA is an activator (opposite effect?)
Paradoxically, both approaches may benefit brain function
Context-dependent effects
PDE inhibitors vs PDA (activator):
Most research on PDE inhibitors (increase cAMP/cGMP)
PDA as "activator" seems contradictory
Possible explanations:
Selective PDE isoform targeting
Biphasic dose-response
Nomenclature confusion
Proprietary mechanism claims
Limited data makes mechanism unclear
Compare to other nootropic mechanisms at SeekPeptides.
Cyclic nucleotide signaling and memory
How cAMP/cGMP affect memory:
Second messengers in neurons
Activated by neurotransmitters
Trigger protein kinases (PKA for cAMP, PKG for cGMP)
Lead to gene expression changes
Essential for long-term memory formation
cAMP pathway in cognition:
Activated by dopamine, norepinephrine
PKA phosphorylates CREB (transcription factor)
CREB drives memory-related genes
Critical for long-term potentiation (LTP)
Enhances synaptic strength
cGMP pathway in cognition:
Activated by nitric oxide (NO)
PKG affects synaptic transmission
Modulates neuroplasticity
Important for memory consolidation
Affects cerebral blood flow
Long-term potentiation (LTP):
Cellular basis of learning and memory
Strengthening of synapses
Requires cAMP/cGMP signaling
Enhanced by elevated cyclic nucleotides
Similar to Pinealon's neuroplasticity effects
Theoretical PDA mechanism:
Proposed Effect | Mechanism | Cognitive Result |
|---|---|---|
Modulate cAMP levels | PDE4 targeting | Enhanced memory consolidation |
Optimize cGMP signaling | PDE5 targeting | Improved neuroplasticity |
Enhance LTP | Sustained cyclic nucleotides | Better learning capacity |
Increase cerebral blood flow | cGMP-mediated vasodilation | More brain oxygenation |
Uncertainty remains:
Exact PDA mechanism poorly documented
"Activator" label contradicts typical nootropic approaches
May work through indirect pathways
More research needed for clarity
Neuroprotective mechanisms (theoretical)
How PDA might protect neurons:
Cyclic nucleotides have neuroprotective roles
Anti-apoptotic effects (prevent cell death)
Antioxidant signaling pathways
Mitochondrial support
Similar to other neuroprotective peptides
Potential protective effects:
Against oxidative stress:
cAMP activates antioxidant enzymes
Reduces free radical damage
Protects neuronal membranes
Similar to SS-31 mitochondrial effects
Against excitotoxicity:
Modulates glutamate signaling
Prevents calcium overload
Protects from overstimulation damage
Important for brain injury recovery
Against neuroinflammation:
cAMP reduces inflammatory cytokines
Modulates microglial activation
Protects blood-brain barrier
Similar to KPV anti-inflammatory effects
Against age-related decline:
Supports synaptic function
Enhances neuroplasticity
May slow cognitive aging
Complementary to Pinealon's bioregulator effects
Evidence level:
Mostly theoretical (cyclic nucleotide biology)
Animal studies show promise
Human data extremely limited
Can't make definitive claims
Unlike proven neuroprotective peptides
See peptides for brain health and neuroprotection.
Theoretical benefits and limited evidence
What PDA might do based on mechanism.
Cognitive enhancement potential
Theoretical cognitive benefits:
Enhanced memory formation and consolidation
Improved learning capacity
Better focus and attention
Increased mental clarity
Enhanced working memory
Basis for cognitive claims:
Cyclic nucleotides essential for LTP
PDE inhibitors improve cognition in studies
cAMP pathway critical for memory
Extrapolation from mechanism
But: PDA-specific data lacking
Anecdotal reports (limited):
Some users report subtle cognitive boost
Improved mental stamina
Better information retention
Effects described as mild/moderate
Less dramatic than Semax
Comparison to established nootropics:
Cognitive Effect | PDA (Theoretical) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
Memory enhancement | Possibly moderate | Strong, proven | Moderate-strong |
Focus/attention | Unknown | Very strong | Moderate |
Mental energy | Possibly mild | Strong | Mild-moderate |
Neuroprotection | Theoretical | Moderate | Strong |
Evidence level | Very low (animal) | High (human trials) | Moderate (Russian trials) |
Realistic expectations:
Likely subtle effects at best
Not a powerful nootropic like Semax
May support brain health long-term
Experimental with unclear benefit
Consider proven alternatives first
Memory and learning improvements
How PDA might enhance memory:
Long-term potentiation support
Enhanced synaptic plasticity
Better memory consolidation during sleep
Improved pattern recognition
Faster learning acquisition
Animal study evidence (limited):
Some rodent studies show improved maze learning
Enhanced object recognition memory
Better spatial memory tasks
Neuroprotection in injury models
But: Dosing, protocols not well-documented
Human evidence:
Essentially absent
No published clinical trials
Only anecdotal reports
Unclear optimal dosing
Major limitation vs proven peptides
Who might benefit (theoretical):
Students seeking cognitive edge
Older adults with mild cognitive decline
People seeking brain optimization
Those intolerant to stimulating nootropics
Experimental biohackers
Uncertainty acknowledgment:
Can't make strong claims
Theoretical benefits ≠ proven effects
Individual variation likely high
More research desperately needed
Consider established alternatives first
Learn about proven cognitive peptides at SeekPeptides.
Cerebral blood flow and brain energy
Potential vascular benefits:
cGMP mediates vasodilation
Could increase cerebral blood flow
More oxygen and glucose to brain
Enhanced mental energy
Similar to PDE5 inhibitors (Viagra)
Metabolic support:
cAMP affects mitochondrial function
Could enhance ATP production
Better neuronal energy
Reduces mental fatigue
Complementary to SS-31's mitochondrial effects
Evidence:
PDE inhibitors do increase cerebral blood flow
cGMP pathway well-established for this
But PDA-specific data lacking
Theoretical extrapolation only
Age-related cognitive decline prevention
Theoretical preventive benefits:
Supports neuroplasticity as brain ages
Protects synaptic connections
Enhances memory formation capacity
May slow cognitive aging
Neuroprotective effects
Why cyclic nucleotides matter for aging:
cAMP/cGMP signaling declines with age
Reduced neuroplasticity in elderly
Impaired memory formation
PDA theoretically counteracts this
But: No long-term human data
Comparison to proven options:
Approach | Evidence Level | Age-Related Benefit | Safety Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
PDA | Very low | Theoretical only | Unknown long-term |
Moderate | Proven in Russian trials | Good (decades use) | |
High | Proven cognitive support | Excellent | |
Lifestyle (exercise, diet) | Very high | Strongly proven | Best |
Reality check:
PDA unproven for aging prevention
Better options exist
Could be part of comprehensive stack
But not first-line choice
More research needed
PDA peptide dosing protocols
Experimental protocols from limited use.
Reported dosing ranges (anecdotal)
Typical doses reported:
Low dose: 50-100mcg daily
Standard dose: 100-250mcg daily
High dose: 250-500mcg daily
Route: Usually subcutaneous injection
Frequency: Once daily
Important caveats:
No clinical trials establishing optimal dose
Anecdotal reports only
Individual variation high
Start low if experimenting
Comparison to other cognitive peptides:
Peptide | Typical Dose | Route | Frequency | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PDA | 100-250mcg | SubQ | Daily | Very low (anecdotal) |
200-600mcg | Intranasal or SubQ | 1-2x daily | High (clinical) | |
250-750mcg | Intranasal or SubQ | 1-2x daily | Moderate (clinical) | |
20mg | SubQ | 10 days cyclic | Moderate (Russian) |
Duration of use:
Short-term: 2-4 weeks trial
Medium-term: 1-3 months
Long-term: Unknown safety
Cycling not established
More conservative than continuous
Use our peptide calculator and dosing guide at SeekPeptides.
Administration methods
Subcutaneous injection:
Most common method reported
Similar to other peptides
Abdomen, thigh injection sites
Standard peptide injection technique
Intranasal (unconfirmed):
Some report nasal administration
Bioavailability unknown
May or may not work
Injection likely more reliable
Timing:
Morning: Most common (for mental energy)
Before cognitive tasks
Consistent daily timing
Effects likely subtle, gradual
Not immediate like Semax
Side effects and safety concerns
Reported side effects (rare, anecdotal):
Mild headache (occasional)
Slight jitteriness (rare)
Injection site reactions (normal for peptides)
Insomnia if dosed too late
Generally well-tolerated
Major safety concerns:
No long-term safety data
Unknown effects of chronic use
Potential for cyclic nucleotide imbalance
Cardiovascular effects unknown
May interact with medications (PDE drugs)
Who should avoid:
People with cardiovascular conditions
Those on PDE inhibitor medications
Pregnancy / breastfeeding
Unknown medical conditions
Anyone seeking proven interventions
Monitoring recommendations:
Start very low dose
Track subjective effects carefully
Monitor cognitive function
Watch for any adverse reactions
Discontinue if concerns arise
See peptide safety guide and common mistakes.
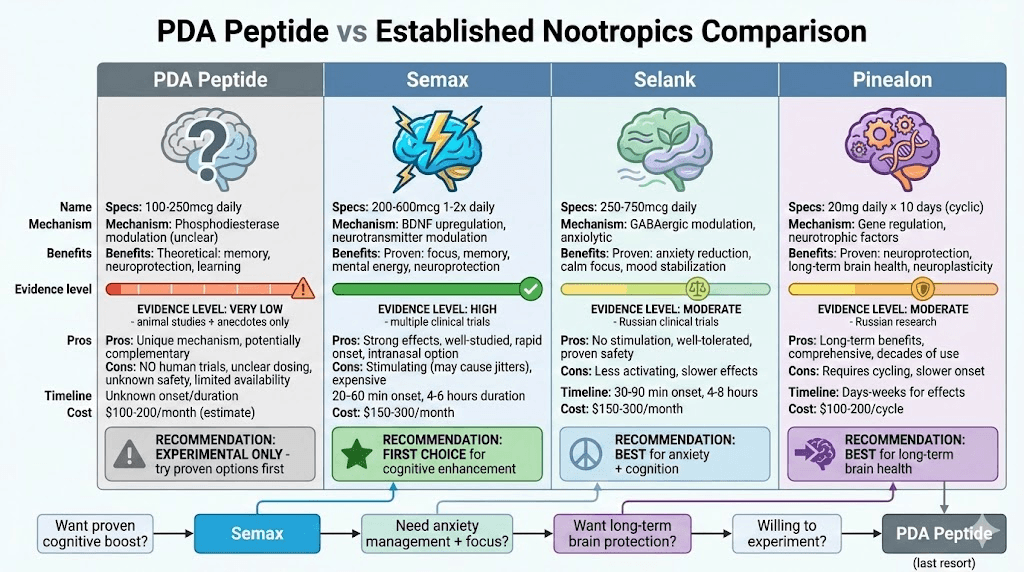
Comparing PDA to established cognitive peptides
Better alternatives with proven efficacy.
PDA vs Semax
Semax advantages:
Extensive clinical research
Proven cognitive enhancement
Well-established dosing protocols
Rapid, noticeable effects
Intranasal option convenient
PDA advantages:
Different mechanism (potentially complementary)
Possibly less stimulating
Theoretical long-term neuroprotection
May be cheaper (if available)
When to choose Semax over PDA:
Want proven cognitive boost
Need focus and energy
Value safety data
Seeking reliable results
First-time nootropic peptide user
See complete Semax dosage guide for protocols.
PDA vs Selank
Selank advantages:
Proven anxiolytic effects
Good safety profile
Calm mental clarity
Well-studied dosing
Intranasal convenient
PDA theoretical advantages:
Different pathway (cyclic nucleotides vs GABA)
Potentially more metabolic support
May enhance memory more directly
But: Unproven claims
When to choose Selank over PDA:
Anxiety + cognitive needs
Want proven effects
Prefer non-stimulating approach
Need mood stabilization
Value established protocols
See Selank injection dosage guide for complete information.
PDA vs Pinealon
Pinealon advantages:
Decades of Russian use
Proven neuroprotection
Long-term brain health benefits
Established 10-day protocol
Part of bioregulator family
PDA theoretical advantages:
Daily use vs cyclic (more consistent?)
Different mechanism
Potentially more immediate cognitive effects
May be complementary
But: All theoretical
When to choose Pinealon over PDA:
Age-related cognitive concerns
Value established protocols
Seeking proven neuroprotection
Prefer cyclic approach
See Pinealon peptide benefits complete guide.
Stacking PDA with other nootropics
Potential combinations (all theoretical):
PDA + Semax:
Different pathways (cyclic nucleotides + BDNF)
Could be synergistic
Semax provides immediate boost
PDA supports long-term plasticity (theory)
No data on combination
PDA + Selank:
PDA for cognition, Selank for anxiety
Balanced mental state
Complementary mechanisms
Both well-tolerated individually
Combination unstudied
PDA + Pinealon:
Both target brain health
Different timeframes (daily vs cyclic)
Could support each other
Comprehensive neuroprotection
But: PDA adds uncertainty
Recommendation:
Try established peptides first
Add PDA only if inadequate response
Don't start multiple unknowns together
Monitor effects carefully
Simpler stacks usually better
Learn about peptide stacking strategies at SeekPeptides.
Availability and sourcing
Finding PDA peptide (challenges).
Limited vendor availability
Why PDA hard to find:
Not widely produced
Low demand (unknown compound)
Most peptide vendors don't stock
Proprietary formulations exist
Research-only status
Where PDA might be found:
Specialized research chemical vendors
Some nootropic peptide suppliers
International sources (quality uncertain)
May be sold under alternative names
Limited, sporadic availability
Quality concerns:
No regulatory oversight
Testing questionable
Purity uncertain
May be misidentified compound
Higher risk than established peptides
Pricing (if available):
Highly variable
$100-300+ per vial (estimated)
Unknown amount needed
May not be cost-effective
Established peptides similar price with proven benefits
See best peptide vendors for quality sourcing of proven compounds.
Legal and regulatory status
Regulatory classification:
Research chemical (not approved drug)
Not FDA approved for any use
"Not for human consumption" label
Gray area legal status
Similar to other research peptides
Legal considerations:
Personal use likely legal (not scheduled)
Import/customs variable
No prescription possible
Vendors selling "research use only"
Standard peptide legality issues
How you can use SeekPeptides for cognitive optimization
SeekPeptides focuses on proven cognitive enhancement peptides with established safety and efficacy. Learn about Semax for powerful cognitive boost, Selank for anxiety-free focus, and Pinealon for long-term brain health.
Use our calculators - peptide calculator, cost calculator, stack calculator - for cognitive protocol planning.
Access comprehensive guides - best peptide for energy and focus, peptides for anxiety, peptide stacks guide.
Find peptide therapy clinics for supervised treatment and access best peptide vendors for quality sourcing.
Final thoughts
PDA peptide represents an interesting theoretical approach to cognitive enhancement through phosphodiesterase modulation and cyclic nucleotide signaling. The mechanisms involving cAMP/cGMP pathways suggest potential for memory enhancement, neuroprotection, and cognitive optimization.
However, PDA suffers from critical limitations - essentially no human clinical trials, unclear optimal dosing protocols, limited availability from peptide vendors, unknown long-term safety profile, and mechanisms not fully characterized despite theoretical promise. This relegates PDA to experimental status unsuitable for first-line cognitive enhancement attempts.
Established alternatives offer dramatically better risk-benefit profiles - Semax provides proven rapid cognitive enhancement with extensive clinical data, Selank delivers anxiety-free focus with decades of research, and Pinealon supports long-term brain health through bioregulator mechanisms.
These proven options should always precede experimental compounds like PDA.
Your cognitive optimization strategy should prioritize evidence-based interventions - PDA's theoretical mechanisms don't justify use when proven nootropic peptides with established dosing, safety profiles, and clinical efficacy exist as superior alternatives.
Helpful resources for cognitive enhancement
Best peptide for energy and focus - Cognitive peptides overview
Semax peptide dosage guide - Proven nootropic
Selank peptide injection dosage - Anxiety + focus
Pinealon peptide benefits - Brain health
Peptide calculator - Dosing tool
In case I don’t see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Take care of yourself.