Jan 22, 2026
You have been searching for ways to boost testosterone without shutting down your natural production. Every forum, every peptide community, every hormone optimization discussion eventually lands on the same question. Is there something that actually works without the downsides of traditional testosterone replacement?
Enter enclomiphene.
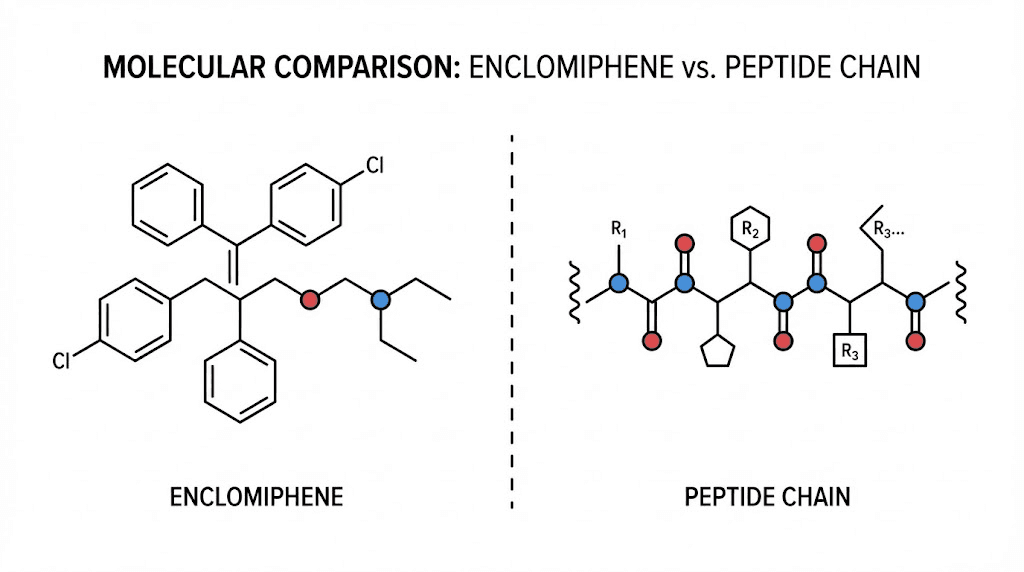
Here is the thing most people get wrong. Enclomiphene is not technically a peptide. It is a selective estrogen receptor modulator, a SERM, that works through a completely different mechanism than the peptides typically used for testosterone optimization. But that distinction matters less than you might think. What matters is whether it works, how it compares to other options, and whether it fits your goals.
The research is clear on several points. Enclomiphene raises testosterone in men with secondary hypogonadism. It preserves fertility when traditional TRT does not. It has a favorable side effect profile compared to its predecessor, clomiphene citrate. These are not small advantages.
This guide covers everything you need to know about enclomiphene for testosterone optimization. You will learn how it works at the molecular level, what the clinical studies actually show, how to dose it properly, what side effects to watch for, and how it compares to both TRT and peptide-based testosterone approaches. Whether you are considering enclomiphene as a standalone treatment, a complement to peptides, or an alternative to traditional hormone replacement, this comprehensive resource will help you make an informed decision.
SeekPeptides has become the trusted resource for thousands navigating testosterone optimization, providing evidence-based protocols and practical guidance for both peptide and non-peptide approaches to hormone health.
What is enclomiphene and why do people call it a peptide?
The confusion around enclomiphene starts with how it entered the conversation about testosterone optimization. Peptide communities discuss it alongside actual peptides because it serves similar goals. People searching for testosterone support naturally encounter enclomiphene in peptide forums, peptide vendor discussions, and peptide protocol threads. The association stuck.
But the chemistry tells a different story.
Enclomiphene is the trans-isomer of clomiphene citrate, the fertility drug marketed as Clomid. Clomiphene contains two isomers: enclomiphene and zuclomiphene. Enclomiphene acts as an estrogen antagonist, blocking estrogen receptors. Zuclomiphene acts as an estrogen agonist, activating estrogen receptors. The two isomers work against each other.
Pure enclomiphene removes the problematic zuclomiphene isomer. This means cleaner estrogen receptor blockade without the estrogenic side effects that plague traditional clomiphene therapy. The molecular weight sits around 406 daltons, far smaller than even the smallest peptides used for peptide therapy.
The SERM classification
Selective estrogen receptor modulators work by binding to estrogen receptors and either activating them or blocking them depending on the tissue. Enclomiphene selectively blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
This blocking action disrupts the negative feedback loop that normally suppresses testosterone production when estrogen levels rise. Your hypothalamus senses estrogen and tells your pituitary to slow down production of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone. Block the estrogen receptors, and that signal never gets through. Your pituitary keeps releasing LH and FSH. Your testes keep producing testosterone.
The mechanism differs fundamentally from TRT or peptide approaches. Exogenous testosterone replaces what your body makes. Peptides like kisspeptin stimulate specific hormone cascades. Enclomiphene removes a brake on your natural production. Same destination, different roads.
Why the peptide community adopted enclomiphene
Several factors explain why enclomiphene became part of the peptide conversation.
First, acquisition. Enclomiphene is not FDA-approved for any indication. Obtaining it requires compounding pharmacies or research chemical suppliers, the same sources many use for peptide procurement. The purchasing experience looks identical.
Second, goals. Men interested in enclomiphene typically want testosterone optimization without fertility compromise. This same population often researches peptides for similar reasons. The Venn diagram of interested parties overlaps significantly.
Third, protocols. Enclomiphene fits into comprehensive hormone optimization protocols alongside growth hormone peptides, healing peptides, and other compounds. Discussing them together makes practical sense even if the biochemistry differs.
Fourth, the injectable versus oral distinction matters less to practical users than to academics. Whether something is technically a peptide matters less than whether it works and how it fits into an overall protocol.
Understanding the distinction still matters. Peptide safety considerations differ from SERM safety considerations. Dosing logic differs. Mechanisms differ. But for practical purposes, enclomiphene earns its place in the testosterone optimization toolkit alongside actual peptides.
How enclomiphene works to boost testosterone
The mechanism of enclomiphene action reveals why it works so well for secondary hypogonadism while failing for primary hypogonadism. Understanding this distinction helps you determine whether enclomiphene fits your situation.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis
Testosterone production follows a cascade. Your hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone. GnRH signals your pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone. LH signals your Leydig cells in the testes to produce testosterone. FSH signals your Sertoli cells to support sperm production.
Multiple feedback loops regulate this cascade. When testosterone rises, it converts partially to estradiol through aromatization. Estradiol binds to estrogen receptors in your hypothalamus and pituitary. This binding signals that hormone levels are sufficient. GnRH release slows. LH and FSH drop. Testosterone production decreases.
This negative feedback loop maintains homeostasis in healthy men. But it becomes problematic when testosterone levels are suboptimal. The feedback loop keeps production suppressed even when you need more testosterone.
Enclomiphene breaks the feedback loop
Enclomiphene competitively binds to estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary without activating them. Estradiol cannot bind. The negative feedback signal never arrives. Your hypothalamus and pituitary interpret this as low estrogen, which correlates with low testosterone in normal physiology.
The response is predictable. GnRH release increases. LH and FSH rise. Testosterone production climbs. Studies show LH increases of 4 to 6 IU/L above baseline. FSH follows a similar pattern. Total testosterone rises by 200 to 400 ng/dL in most responders.
This differs from HCG, which mimics LH directly, or kisspeptin, which stimulates GnRH release at the hypothalamic level. Enclomiphene works by removing inhibition rather than adding stimulation. The distinction matters for understanding how to combine these approaches.
Why secondary hypogonadism responds better
Secondary hypogonadism means your testes can produce testosterone, but signaling from the brain is insufficient. Primary hypogonadism means your testes themselves have reduced capacity regardless of how much LH they receive.
Enclomiphene can only help if your testes respond to stimulation. It increases LH and FSH, but if your Leydig cells cannot respond to elevated LH, testosterone will not rise meaningfully. This is why proper diagnosis matters before choosing any testosterone optimization approach.
Men with primary hypogonadism typically need exogenous testosterone or perhaps regenerative approaches. Men with secondary hypogonadism have more options, including enclomiphene, clomiphene, and various peptide approaches to testosterone optimization.
The persistence effect
One interesting finding from enclomiphene research is that effects on LH and testosterone persist for at least one week after stopping treatment. This suggests the compound does not simply mask a problem but actually resets the feedback set point, at least temporarily.
Longer term data on what happens after extended use is limited. Whether enclomiphene can permanently improve testosterone levels or requires ongoing use remains an open question. Most protocols assume ongoing use for maintained benefits, similar to most hormone optimization approaches.
Clinical evidence for enclomiphene effectiveness
The research on enclomiphene spans multiple phase II and phase III clinical trials, though the compound never achieved FDA approval. Understanding what the studies actually show helps set realistic expectations.
The key clinical trials
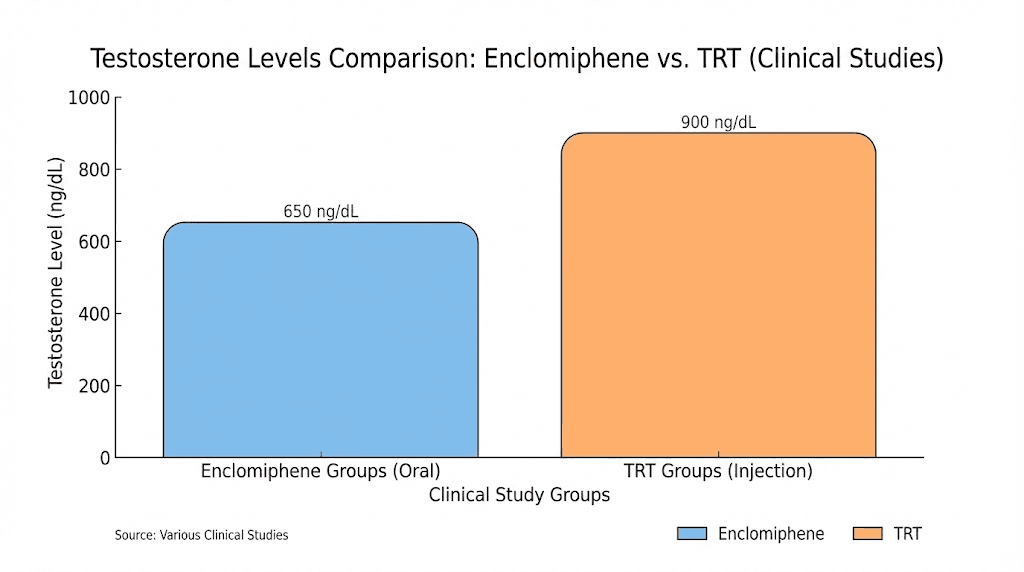
A pivotal study published in BJU International examined three doses of enclomiphene citrate against transdermal testosterone in men with secondary hypogonadism. The doses tested were 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg, and 25 mg daily.
Results after 6 weeks showed mean testosterone of 604 ng/dL in the 25 mg enclomiphene group compared to 500 ng/dL in the transdermal testosterone group. Both treatments effectively raised testosterone into normal ranges. But the downstream effects differed dramatically.
Men receiving testosterone gel showed suppressed LH and FSH, as expected when introducing exogenous testosterone. Men receiving enclomiphene showed elevated LH and FSH, confirming the mechanism of action. This difference has profound implications for fertility preservation.
Fertility outcomes
Perhaps the most compelling finding involves sperm production. In one three-month study comparing enclomiphene to testosterone gel, the fertility outcomes could not have been more different.
Men receiving testosterone gel had sperm concentrations drop below 12 million per milliliter across the board after three months. This level often correlates with significantly impaired fertility.
Men receiving enclomiphene maintained sperm concentrations above 75 million per milliliter. The mean sperm count was 176 million per milliliter. This represents not just fertility preservation but potentially enhanced fertility.
For men who want testosterone optimization without sacrificing reproductive capacity, this finding alone makes enclomiphene worth serious consideration. Traditional TRT comes with significant fertility risks that many men do not fully appreciate until they are trying to conceive.
Speed of response
Another study examined how quickly enclomiphene works by testing 12.5 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg doses over just 14 days. The researchers found significant, dose-dependent increases in total testosterone within two weeks across all doses.
This relatively rapid response compares favorably to some peptide timelines, though slower than the near-immediate effects of testosterone injections.
Men should expect to notice symptomatic improvement within 2 to 4 weeks of starting therapy, with peak effects developing over 6 to 12 weeks.
Comparison to clomiphene citrate
A retrospective study comparing enclomiphene to traditional clomiphene citrate found meaningful differences in both effectiveness and tolerability.
Enclomiphene produced a median testosterone increase of 166 ng/dL with lower estradiol changes compared to clomiphene. More importantly, estradiol actually decreased slightly with enclomiphene while increasing with clomiphene. This difference explains much of the tolerability advantage.
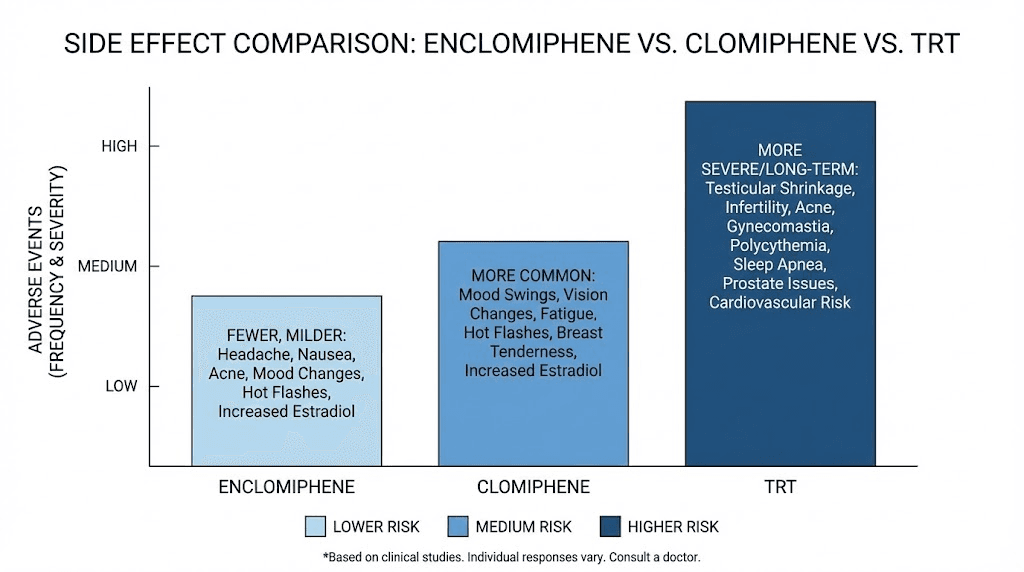
Adverse effects were significantly less frequent with enclomiphene. Decreased libido occurred in far fewer enclomiphene users. Energy reduction was less common. Mood changes were less frequent. These differences reflect the absence of the zuclomiphene isomer and its estrogenic activity.
Meta-analysis findings
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials examining SERMs for male hypogonadism found significant improvements across key markers. Total testosterone increased by an average of 274 ng/dL. LH increased by 4.66 IU/L. FSH increased by 4.59 IU/L.
These findings support SERMs as effective treatments for functional hypogonadism while preserving reproductive function. The review noted that longer and larger trials are needed to confirm long-term safety, a limitation that applies to most hormone optimization approaches.
Enclomiphene dosing protocols
Proper dosing maximizes benefits while minimizing risks. The clinical trial data provides clear guidance, though individual optimization may require adjustment based on response.
Standard dosing ranges
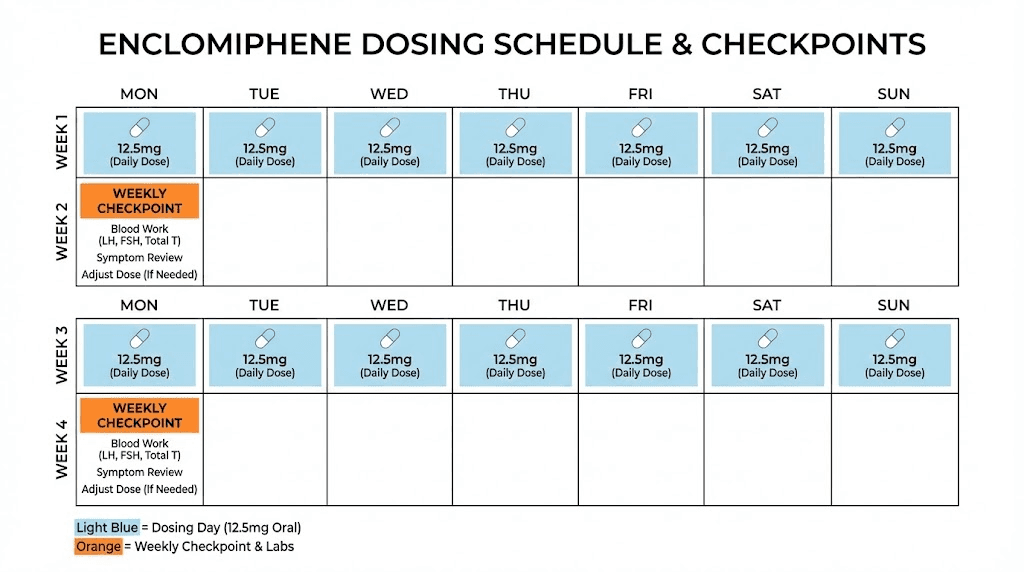
Clinical trials evaluated doses from 6.25 mg to 50 mg daily. The most common protocols use 12.5 mg to 25 mg daily, with most patients responding well to 25 mg daily.
Starting at the lower end makes sense for several reasons. You can always increase if response is insufficient. Starting lower lets you assess tolerance before committing to higher doses. Some men respond excellently to 12.5 mg, making higher doses unnecessary.
A reasonable starting protocol looks like this:
Week 1 to 2: 12.5 mg daily in the morning
Week 3 to 4: Assess response through symptom tracking and blood work
Week 5 onward: Maintain at 12.5 mg if responding well, increase to 25 mg if testosterone remains suboptimal
Some practitioners use intermittent dosing, perhaps 25 mg three to five times weekly rather than daily. This approach may reduce any potential receptor desensitization while maintaining effectiveness. The evidence base for intermittent versus daily dosing remains limited.
Timing considerations
Morning dosing aligns with natural testosterone rhythms and the cortisol awakening response. Taking enclomiphene in the morning means peak drug levels coincide with the period when your hormonal systems are most active.
Some practitioners suggest avoiding food around the dose for optimal absorption, though this is not clearly established in the literature. Taking it with or without food according to your preference and tolerance is reasonable.
Consistency matters more than exact timing. Taking enclomiphene at the same time daily helps maintain stable blood levels and makes it easier to remember. Missing occasional doses is unlikely to cause significant problems given the relatively long biological effects.
Treatment duration
Most protocols run continuously for 3 to 6 months initially.
Blood work at baseline, 4 weeks, and 8 to 12 weeks helps track response and guide adjustments.
The question of long-term continuous use versus cycling remains unsettled. Some practitioners advocate for periodic breaks to prevent any theoretical receptor adaptation. Others maintain patients on continuous therapy indefinitely with good results.
One advantage of enclomiphene over TRT is the relative ease of discontinuation. Effects persist for at least a week after stopping, and natural production is not suppressed the way exogenous testosterone suppresses it. This makes cycling or discontinuation much simpler than with traditional TRT.
Combining with other approaches
Enclomiphene can fit into comprehensive hormone optimization protocols alongside other compounds. Common combinations include:
Enclomiphene plus growth hormone peptides: CJC-1295 combined with Ipamorelin addresses growth hormone optimization while enclomiphene handles testosterone. The mechanisms do not conflict, and the combination targets multiple aspects of hormonal health.
Enclomiphene plus recovery peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500 for healing and recovery complement testosterone optimization by supporting the physical demands that elevated testosterone enables.
Enclomiphene plus sleep peptides: DSIP or other sleep-supporting peptides can enhance natural testosterone production during sleep while enclomiphene removes feedback inhibition.
The key is understanding how each component works and ensuring they complement rather than conflict. Working with knowledgeable practitioners helps design coherent protocols.
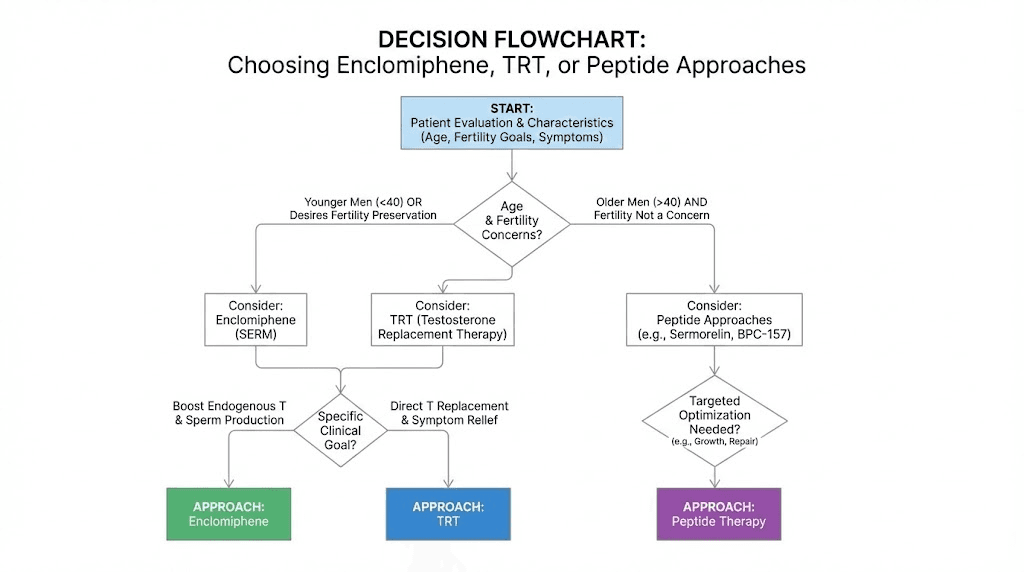
Enclomiphene versus TRT: detailed comparison
The choice between enclomiphene and traditional testosterone replacement therapy depends on individual circumstances, goals, and priorities. Neither approach is universally superior.
Mechanism differences
TRT directly supplies testosterone from external sources. Your body receives the hormone without needing to produce it. This approach is straightforward, predictable, and effective.
Enclomiphene stimulates your body to produce more testosterone by removing feedback inhibition. Your testes do the actual work. This maintains natural production capacity and the downstream benefits that come with it.
The practical implications of this difference are significant. TRT suppresses natural production, sometimes permanently after extended use. Enclomiphene preserves and may even enhance natural production capacity.
Fertility preservation
This represents the clearest advantage for enclomiphene. TRT suppresses sperm production in most men within months. The suppression can be severe and sometimes irreversible.
Enclomiphene maintains or improves sperm production. Men concerned about current or future fertility have a strong reason to prefer enclomiphene over TRT.
Adding HCG to TRT partially addresses the fertility concern, but even with HCG, sperm production often remains below normal. Enclomiphene achieves fertility preservation without requiring additional injections.
Speed and magnitude of testosterone increase
TRT wins on speed. Testosterone levels rise rapidly after starting injections or gels. Symptomatic improvement often occurs within days to weeks.
Enclomiphene works more gradually. Two to four weeks for initial effects, with full optimization taking 6 to 12 weeks.
TRT also typically achieves higher peak testosterone levels. Men can achieve supraphysiological levels if desired, though this carries additional risks. Enclomiphene generally brings levels into the normal-high range but rarely beyond.
For men with severely low testosterone who need rapid symptom relief, TRT may be the better initial choice. For men with moderate deficiency who can accept a slower improvement trajectory, enclomiphene offers advantages.
Side effect profiles
TRT side effects reflect supraphysiological testosterone levels and natural production shutdown. Common issues include testicular atrophy, elevated hematocrit, estrogen imbalances, acne, and hair loss acceleration in predisposed individuals.
Enclomiphene side effects tend to be milder. Headaches occur in about 3 percent of users. Hot flashes affect some. Mood changes can occur but are less common than with clomiphene. Visual disturbances, a concern with clomiphene, appear rare with pure enclomiphene.
Neither approach is risk-free. Both require monitoring and management. But the side effect burden generally favors enclomiphene for most users.
Long-term commitment
TRT typically becomes a lifelong commitment. Stopping after extended use means navigating suppressed natural production, which may never fully recover. The convenience of starting TRT comes with significant long-term implications.
Enclomiphene offers more flexibility. Stopping treatment is simpler because natural production is not suppressed. Men can trial the treatment without committing to permanent hormone replacement.
This flexibility matters especially for younger men or those uncertain about long-term hormone optimization. Starting with enclomiphene allows assessment of whether testosterone optimization improves quality of life before committing to more permanent approaches.
Cost comparison
TRT through clinics typically costs 100 to 300 dollars monthly, including testosterone, supplies, and basic monitoring. More comprehensive programs can exceed 400 to 500 dollars monthly.
Enclomiphene costs vary based on source and dose. Compounding pharmacy prices generally run 50 to 150 dollars monthly. Research chemical sources may be less expensive but come with quality and legal considerations.
Insurance may cover TRT for diagnosed hypogonadism but rarely covers enclomiphene since it lacks FDA approval. Out-of-pocket costs may be similar or favor enclomiphene depending on specific circumstances.
When to choose TRT
TRT makes more sense when testosterone is severely deficient, under 200 ng/dL, when primary hypogonadism has been diagnosed, when rapid symptom relief is needed, when fertility is not a concern, or when age exceeds 50 to 55 with progressive decline.
When to choose enclomiphene
Enclomiphene makes more sense when testosterone is mildly to moderately low (300 to 450 ng/dL), when secondary hypogonadism has been diagnosed, when fertility preservation matters, when flexibility to discontinue is important, or when trying to avoid lifelong hormone replacement.
Side effects and safety considerations
Understanding the side effect profile helps you make informed decisions and know what to monitor. Enclomiphene appears safer than clomiphene but is not without risks.
Common side effects
The most frequently reported side effects in clinical trials include headaches (around 3 percent), hot flashes, and fatigue. These effects are generally mild and often resolve with continued use or dose adjustment.
Some users report mood changes, though less frequently than with traditional clomiphene. The absence of the zuclomiphene isomer reduces estrogenic effects that contribute to mood instability.
Acne can occur as testosterone levels rise, though this reflects the desired effect rather than a drug-specific side effect. Managing skin changes during testosterone optimization follows similar principles regardless of how testosterone is elevated.
Visual concerns
Clomiphene citrate has been associated with visual disturbances, including blurred vision and visual trailing. These effects relate to its impact on certain tissues and raised concerns about long-term eye health.
Pure enclomiphene appears to have a better profile regarding visual effects, though the evidence base is smaller. Monitoring for any visual changes remains prudent, and any significant disturbances warrant discontinuation and medical evaluation.
Cardiovascular and thrombotic risks
SERMs as a class carry some risk of thromboembolic events, including deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This risk is established for tamoxifen and raloxifene and theoretically applies to enclomiphene.
Clinical trials of enclomiphene have not shown significantly elevated rates of these events, but trial durations and sizes limit the ability to detect rare adverse events. Men with personal or family history of blood clots should discuss this risk with their healthcare provider.
Cardiovascular effects require ongoing monitoring. Regular health screenings, attention to cardiovascular risk factors, and prompt evaluation of symptoms like chest pain or leg swelling remain important regardless of which testosterone optimization approach you use.
Estrogen management
Unlike traditional clomiphene, which can raise estradiol due to the zuclomiphene isomer, pure enclomiphene tends to decrease or stabilize estradiol levels while raising testosterone. This represents a significant advantage.
However, testosterone itself converts to estradiol through aromatization. As testosterone rises with enclomiphene treatment, some increase in estradiol may occur. Monitoring both hormones helps identify whether estrogen management becomes necessary.
Signs of elevated estrogen include water retention, mood changes, breast tenderness, and decreased libido despite adequate testosterone. These warrant evaluation and potentially an aromatase inhibitor if estradiol climbs too high.
Bone density considerations
Testosterone supports bone health. Low testosterone contributes to bone loss. Raising testosterone with enclomiphene should theoretically improve bone density, though long-term data specifically on enclomiphene and bone outcomes is limited.
Men with significant bone density concerns should ensure adequate monitoring and consider whether direct testosterone replacement might offer more established bone benefits. The relationship between SERMs and bone in men is less clear than in women, where certain SERMs are actually used to treat osteoporosis.
Interactions and contraindications
Enclomiphene interacts with other medications that affect estrogen receptors or hormone metabolism. Men taking other hormone-affecting medications should discuss potential interactions with their healthcare provider.
Contraindications include active or history of thromboembolic disease, certain hormone-sensitive cancers, and hepatic impairment. The absence of FDA approval means comprehensive prescribing information is not available, making careful medical evaluation even more important.
Monitoring requirements
Regular blood work helps track effectiveness and safety. Recommended monitoring includes total testosterone at baseline and every 4 to 8 weeks until stable, free testosterone or SHBG to assess bioavailable testosterone, LH and FSH to confirm mechanism of action, estradiol to watch for excessive conversion, complete blood count to monitor hematocrit, comprehensive metabolic panel to assess liver and kidney function, and lipid panel to track cardiovascular risk markers.
Monitoring frequency can decrease once levels stabilize, but periodic reassessment remains important for ongoing management.
Combining enclomiphene with peptides
Many men interested in enclomiphene also use various peptides for complementary benefits. Understanding how these approaches work together helps design coherent protocols.
Growth hormone peptides
The combination of testosterone optimization and growth hormone optimization addresses two major hormonal declines that occur with age. Enclomiphene handles the testosterone side while Sermorelin or CJC-1295/Ipamorelin handles growth hormone.
These mechanisms do not conflict. Enclomiphene works on the HPG axis through estrogen receptor blockade. Growth hormone peptides work on the GH axis through GHRH receptor stimulation or ghrelin mimicking. Running both simultaneously is common in comprehensive hormone optimization protocols.
The combination may offer synergistic benefits. Improved sleep from GH peptides can enhance natural testosterone production during sleep. Better body composition from both interventions reduces aromatization of testosterone to estrogen. Enhanced recovery supports the physical activity that naturally elevates testosterone.
Recovery and healing peptides
Men optimizing testosterone often train intensely, creating demand for recovery support. The Wolverine stack of BPC-157 and TB-500 addresses connective tissue stress, inflammation, and recovery in ways that testosterone alone cannot.
Adding healing peptides to an enclomiphene protocol makes sense for active men pushing their physical limits. The enhanced testosterone supports muscle building and recovery capacity, while healing peptides support the tendons, ligaments, and other structures that must handle increased training loads.
Timing does not appear to matter significantly. Taking enclomiphene in the morning and peptide injections in the evening according to their optimal timing works well for most protocols.
Sleep-supporting peptides
Testosterone production occurs primarily during deep sleep. Anything that improves sleep quality indirectly supports natural testosterone. DSIP for sleep optimization can complement enclomiphene by ensuring the conditions for testosterone production are optimal.
Other sleep-supporting peptides like Pinealon work through different mechanisms but serve similar purposes. Men with disrupted sleep patterns may find that addressing sleep improves testosterone response to enclomiphene.
Cognitive peptides
Low testosterone often correlates with cognitive complaints like brain fog and reduced mental sharpness. While raising testosterone typically improves cognition, some men seek additional support through nootropic peptides.
Semax and Selank offer cognitive enhancement through mechanisms unrelated to testosterone. Adding these to an enclomiphene protocol can accelerate cognitive improvement while testosterone levels normalize.
Libido-supporting peptides
Testosterone typically improves libido, but the relationship is not always straightforward. Some men find testosterone optimization does not fully address sexual function concerns.
PT-141 works through melanocortin receptors in the brain to enhance arousal and sexual response. This mechanism complements testosterone action, potentially providing synergistic benefits for sexual health.
Men using enclomiphene who want additional libido support can add PT-141 as needed. The nasal spray form offers convenience for on-demand use.
Protocol integration example
A comprehensive hormone optimization protocol might look like:
Morning: Enclomiphene 25 mg orally
Evening: CJC-1295 100 mcg plus Ipamorelin 100 to 200 mcg subcutaneously before bed
As needed: BPC-157 250 to 500 mcg for injury recovery or chronic tissue support
As needed: PT-141 for enhanced sexual encounters
This type of comprehensive approach addresses multiple aspects of male health optimization simultaneously. The components work through different mechanisms without conflicting, potentially providing benefits greater than any single intervention alone.
Obtaining enclomiphene and quality considerations
Because enclomiphene lacks FDA approval, obtaining it requires navigating a less regulated marketplace. Understanding your options helps ensure safety and quality.
Compounding pharmacies
Compounding pharmacies can legally produce enclomiphene with a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. This route offers the highest assurance of quality and purity.
The challenge is finding a provider willing to prescribe an unapproved compound. Hormone optimization clinics, anti-aging practices, and some urologists familiar with testosterone management may prescribe enclomiphene when appropriate.
Compounding pharmacy costs tend to be higher than research chemical sources, but the quality assurance and legal clarity may justify the premium. Expect to pay 100 to 200 dollars monthly depending on dose and pharmacy.
Research chemical sources
Research chemical suppliers sell enclomiphene for laboratory research purposes. Purchasing for personal use falls into a legal gray area that varies by jurisdiction.
Quality varies significantly between suppliers. Without regulatory oversight, some products may be underdosed, contaminated, or misidentified. Third-party testing becomes especially important when using research chemical sources.
Established suppliers with good reputations and verified third-party testing offer reasonable quality assurance. New or unknown suppliers carry more risk. The price savings compared to compounding pharmacies come with quality and legal trade-offs.
Quality verification
If using research chemical sources, verifying product quality protects your health and investment. Third-party testing services can analyze samples for identity, purity, and contamination.
Look for certificates of analysis from independent laboratories. Reputable suppliers provide this documentation. Claims without verification should be viewed skeptically.
Signs of quality concerns include unusual appearance, inconsistent effects between batches, unexpected side effects, and lack of third-party testing documentation. If something seems wrong, discontinue use and seek alternative sources.
Storage and handling
Enclomiphene capsules or tablets should be stored at room temperature, protected from moisture and light. Proper storage maintains potency and safety throughout the product lifespan.
Typical shelf life is 1 to 2 years when stored properly. Expired product may have reduced potency but is unlikely to be harmful. Still, using fresh product ensures predictable effects.
Who should consider enclomiphene
Enclomiphene is not appropriate for everyone with low testosterone. Understanding the ideal candidate helps determine whether it fits your situation.
Ideal candidates
Men with secondary hypogonadism represent the primary target population. This means the testes can produce testosterone but are receiving insufficient stimulation from the pituitary.
Signs suggesting secondary hypogonadism include low testosterone with low or inappropriately normal LH, intact testicular volume, no history of testicular injury or disease, and symptoms that developed gradually rather than suddenly.
Younger men concerned about fertility preservation are excellent candidates. The ability to raise testosterone without suppressing sperm production offers significant advantages over TRT.
Men wanting to avoid lifelong hormone replacement may prefer trying enclomiphene first. If it works, the flexibility to discontinue without severe consequences provides peace of mind.
Less ideal candidates
Men with primary hypogonadism, where the testes themselves have reduced capacity, are unlikely to respond well to enclomiphene. The mechanism requires functional testes that can respond to increased LH stimulation.
Those needing rapid, dramatic testosterone increases may find enclomiphene too slow or insufficient. Severely symptomatic men or those with very low testosterone may need TRT to achieve adequate levels quickly.
Men with personal or family history of thromboembolic disease face elevated risk with SERMs. The potential benefits may not justify the cardiovascular risks for these individuals.
Those uncomfortable with using non-FDA-approved compounds may prefer approved alternatives even if they come with other trade-offs.
Getting proper evaluation
Before starting any testosterone optimization approach, proper evaluation helps ensure appropriate treatment selection. This typically includes comprehensive blood work with total testosterone, free testosterone, LH, FSH, estradiol, prolactin, thyroid function, and metabolic markers.
Medical history review identifies contraindications and helps determine likely underlying causes. Physical examination may reveal testicular abnormalities or other relevant findings.
Working with practitioners experienced in hormone optimization improves outcomes. Primary care physicians often lack deep expertise in this area. Urologists, endocrinologists, or specialized hormone optimization practitioners may provide more sophisticated evaluation and management.
Troubleshooting common issues
Not everyone responds perfectly to enclomiphene. Understanding common problems and solutions helps optimize your protocol.
Insufficient testosterone response
If testosterone does not rise adequately after 6 to 8 weeks of consistent dosing, several factors may be at play.
First, confirm the dose is adequate. Some men need 25 mg daily to achieve meaningful effects. If starting at 12.5 mg, consider increasing.
Second, verify product quality. Poor quality product may simply not contain adequate active ingredient. Testing or switching sources may be warranted.
Third, consider whether the diagnosis is correct. If primary rather than secondary hypogonadism is present, enclomiphene may not be the right approach regardless of dose.
Fourth, evaluate lifestyle factors. Poor sleep, chronic stress, obesity, and other factors can blunt hormonal responses. Addressing these may improve enclomiphene effectiveness.
Side effects limiting tolerance
If side effects are problematic, dose reduction often helps. Dropping from 25 mg to 12.5 mg or to every-other-day dosing may maintain benefits while improving tolerability.
Headaches sometimes improve with adequate hydration and time. Many side effects diminish as the body adjusts over several weeks.
If specific side effects like visual disturbances occur, discontinuation is prudent. These effects may indicate individual sensitivity that makes enclomiphene inappropriate regardless of dose.
Estradiol issues
If estradiol rises excessively as testosterone increases, symptoms may include water retention, mood changes, breast tenderness, and paradoxically decreased libido despite adequate testosterone.
An aromatase inhibitor like anastrozole can reduce estrogen conversion. However, crashing estrogen too low creates its own problems.
Targeted, careful use guided by blood work works better than aggressive estrogen suppression.
Some men find that enclomiphene alone maintains favorable testosterone to estrogen ratios without needing additional management. Regular monitoring identifies when intervention is needed.
Fertility not improving as expected
While enclomiphene generally preserves or improves fertility, results vary. If semen analysis does not improve, several factors may be involved.
Time may be a factor. Spermatogenesis takes about 74 days, so improvements in sperm production may lag behind testosterone increases by months.
Other fertility factors beyond testosterone may be at play. Semen analysis, hormonal evaluation, and possibly urological consultation help identify whether additional issues need addressing.
Adding HCG to the protocol may provide additional testicular stimulation that enclomiphene alone does not achieve. Some protocols combine both approaches for comprehensive support.
Loss of effectiveness over time
If enclomiphene seems to work initially but effects diminish, receptor adaptation is one possible explanation. Taking periodic breaks may help, though evidence for this approach is limited.
Product quality changes could explain diminishing effects if using research chemical sources. Batch-to-batch variation is a real concern with unregulated products.
Progressive worsening of underlying hypogonadism could also explain declining response. Regular blood work helps distinguish between these possibilities.
Enclomiphene in the broader testosterone optimization landscape
Understanding where enclomiphene fits among the various testosterone optimization options helps you make informed choices.
The testosterone optimization spectrum
Options for men with low testosterone range from conservative lifestyle interventions through progressively more aggressive medical approaches.
Lifestyle optimization includes sleep improvement, stress management, weight loss, exercise, and nutritional optimization. These approaches are safe and beneficial regardless of other interventions but may not suffice for significant testosterone deficiency.
Natural testosterone support includes various supplements claiming to boost testosterone. Evidence for most is limited, but some ingredients like ashwagandha and vitamin D show modest effects in certain populations.
SERMs including enclomiphene remove feedback inhibition to stimulate natural production. They preserve fertility and maintain natural production capacity while achieving meaningful testosterone increases.
Peptide approaches like kisspeptin directly stimulate the hormone cascade at various points. These offer another way to enhance natural production without exogenous hormones.
HCG mimics LH to directly stimulate testicular testosterone production. It can work alone or alongside TRT to preserve testicular function.
Traditional TRT replaces testosterone directly through injections, gels, patches, or pellets. This achieves the highest and most predictable testosterone levels but with fertility and dependency trade-offs.
Where enclomiphene fits
Enclomiphene occupies an intermediate position, more effective than lifestyle and supplements alone, but preserving more natural function than TRT. It represents a reasonable first-line medical intervention for many men with secondary hypogonadism.
For men who want to optimize testosterone while maintaining fertility and avoiding lifelong replacement, enclomiphene offers a compelling option. Those who do not respond adequately can always move to more aggressive approaches.
The future of enclomiphene
Despite promising research, enclomiphene failed to achieve FDA approval. The manufacturer received a Complete Response Letter in 2015 indicating the application could not be approved in its current form. Development has since stalled.
This regulatory limbo means enclomiphene may remain a compounding pharmacy and research chemical product rather than a conventional prescription medication. Access will likely continue through current channels unless regulatory status changes.
The research clearly supports enclomiphene as an effective treatment for secondary hypogonadism. Whether it eventually achieves FDA approval depends on commercial interest in pursuing the costly approval process. Until then, it remains an off-label option requiring careful navigation.
Frequently asked questions
Is enclomiphene actually a peptide?
No. Enclomiphene is a selective estrogen receptor modulator with a molecular weight around 406 daltons. It is a small molecule drug, not a peptide. The association with peptides comes from its popularity in the same communities that use peptides for hormone optimization and similar goals.
How long does it take for enclomiphene to work?
Studies show testosterone increases within two weeks of starting treatment. Symptom improvement typically follows within 2 to 4 weeks. Full optimization may take 6 to 12 weeks. This is slower than TRT but comparable to or faster than many peptide timelines.
Can I take enclomiphene with TRT?
The mechanisms work differently, and combining them does not make sense from a physiological standpoint. TRT suppresses LH, which enclomiphene tries to raise. If you are on TRT, enclomiphene will not help because the feedback loop is already maximally suppressed. HCG is the typical add-on for men wanting testicular support while on TRT.
Does enclomiphene require a prescription?
Technically yes. Enclomiphene is not available over the counter. Compounding pharmacies require a prescription. Research chemical sources sell for laboratory research purposes, with personal use falling into a gray area that varies by jurisdiction.
How does enclomiphene compare to clomiphene for testosterone?
Enclomiphene is the purified trans-isomer of clomiphene without the estrogenic zuclomiphene isomer. Studies show enclomiphene produces similar testosterone increases with fewer side effects, particularly regarding mood, libido, and energy. The estradiol increase seen with clomiphene is reduced or absent with enclomiphene.
Will enclomiphene affect my fertility?
Enclomiphene preserves and may enhance fertility. Unlike TRT, which suppresses sperm production, enclomiphene maintains or increases sperm counts while raising testosterone. This makes it particularly attractive for men who may want children in the future.
What are the main side effects of enclomiphene?
The most common side effects include headaches, hot flashes, and fatigue. These are generally mild and often resolve with time or dose adjustment. Serious risks like blood clots are possible but appear rare in clinical trials. Visual disturbances are less common than with traditional clomiphene.
Can I stack enclomiphene with peptides?
Yes. Enclomiphene works through estrogen receptor blockade, which does not conflict with most peptide mechanisms. Common combinations include enclomiphene with growth hormone peptides, recovery peptides like BPC-157, or sleep-supporting peptides like DSIP.
Is enclomiphene FDA approved?
No. Despite completing phase II and phase III clinical trials, enclomiphene never achieved FDA approval. A Complete Response Letter in 2015 indicated the application could not be approved in its present form. It remains available through compounding pharmacies and research chemical suppliers.
How do I know if enclomiphene is right for me?
Ideal candidates have secondary hypogonadism with low testosterone and low or inappropriately normal LH, intact testicular function, interest in fertility preservation, and willingness to use a non-FDA-approved compound. Men with primary hypogonadism, very low testosterone needing rapid improvement, or history of blood clots may be better served by other approaches.
For researchers serious about optimizing testosterone through evidence-based approaches, SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources covering both peptide and non-peptide protocols for hormone health.



