Jan 10, 2026

Tissue repair mechanisms operate through multiple interconnected pathways that rarely respond optimally to single interventions, with injuries activating inflammatory cascades, angiogenic processes, fibroblast proliferation, and extracellular matrix remodeling simultaneously across damaged regions. BPC-157 and TB-500 represent two of the most extensively researched regenerative peptides, each targeting distinct yet complementary aspects of the healing response through mechanisms that compound rather than compete when administered together.
The rationale for combining these peptides extends beyond simple additive effects, as BPC-157's gastric pentadecapeptide sequence activates growth factor pathways and nitric oxide systems while TB-500's thymosin beta-4 derivative promotes actin regulation, cell migration, and blood vessel formation through separate receptor interactions.
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for understanding peptide stacking strategies, optimizing protocols, and developing evidence-based approaches to regenerative support.
Understanding the individual peptides
Before exploring combination strategies, understanding each peptide's unique properties establishes the foundation for appreciating their synergistic potential. Both peptides have accumulated substantial research documentation demonstrating regenerative effects across multiple tissue types and injury models.
BPC-157 fundamentals
BPC-157, body protection compound-157, consists of a 15 amino acid sequence derived from human gastric juice proteins. This pentadecapeptide demonstrates remarkable stability compared to most peptides, maintaining activity in gastric acid environments that rapidly degrade other protein fragments. The compound's natural origin in protective gastric secretions aligns with its documented tissue-protective and healing-promoting properties.
The mechanism profile of BPC-157 encompasses multiple pathways relevant to tissue repair. Nitric oxide system modulation represents a central mechanism, with BPC-157 influencing both constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase activity depending on tissue context and injury status. This NO modulation affects blood flow, inflammation, and cellular signaling throughout healing tissues.
Growth factor pathway activation contributes significantly to BPC-157's regenerative effects. The peptide upregulates expression of epidermal growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor among others. These growth factors drive the cellular proliferation and tissue remodeling required for structural repair.
Understanding what BPC-157 is and how to take BPC-157 provides essential background for stacking applications.
The BPC-157 dosage calculator helps determine appropriate individual dosing before incorporating combination protocols.
TB-500 fundamentals
TB-500 represents a synthetic version of the active region of thymosin beta-4, a naturally occurring 43 amino acid peptide found in virtually all human cells. The synthetic fragment captures the key functional sequences responsible for TB-500's regenerative properties while offering improved stability and standardized production.
Actin regulation forms the core mechanism of TB-500 activity. The peptide binds to actin monomers and influences polymerization dynamics, affecting cytoskeletal organization crucial for cell migration, division, and structural adaptation. This actin modulation enables the enhanced cellular mobility observed in TB-500 treated tissues.
Angiogenesis promotion through TB-500 establishes new blood vessel networks in healing tissues. The peptide upregulates VEGF expression and promotes endothelial cell migration, creating the vascular infrastructure necessary for sustained tissue repair. Without adequate blood supply, healing stalls regardless of other favorable conditions.
Anti-inflammatory effects complement the regenerative mechanisms, with TB-500 reducing inflammatory cytokine expression and limiting excessive inflammation that can impair healing. This immunomodulatory activity helps transition tissues from acute inflammatory phases to productive repair states.
Exploring TB-500 benefits in depth clarifies the specific advantages this peptide contributes to combination protocols.
The TB-500 dosage calculator ensures accurate individual dosing as the foundation for stack development.
The science of synergy
Combining BPC-157 and TB-500 produces effects exceeding simple addition of individual benefits. True synergy emerges when distinct mechanisms converge on shared outcomes through complementary pathways, amplifying net effects beyond what either compound achieves alone.
Complementary mechanism profiles
BPC-157 and TB-500 approach tissue repair through largely non-overlapping pathways, minimizing redundancy while maximizing coverage of healing requirements. Where BPC-157 emphasizes growth factor signaling and nitric oxide modulation, TB-500 focuses on cytoskeletal dynamics and angiogenesis. This mechanistic complementarity means combining the peptides addresses more healing pathway simultaneously than either alone.
The temporal aspects of healing also favor combination approaches. Different phases of tissue repair require different molecular support. Early inflammatory phases, proliferative phases, and remodeling phases each present distinct requirements. BPC-157's anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects prove particularly valuable early, while TB-500's cell migration and angiogenic promotion become increasingly important as repair progresses.
Tissue type considerations further support synergistic combinations. Some tissues respond more robustly to BPC-157 while others show greater sensitivity to TB-500. Combining both peptides ensures comprehensive coverage regardless of the specific tissue composition of injured areas.
Research evidence for combination effects
While direct head-to-head comparison studies of the combination versus individual peptides remain limited, the mechanistic evidence strongly supports synergistic interactions. Animal studies examining multi-peptide regenerative protocols consistently show enhanced outcomes compared to single-peptide approaches.
Anecdotal reports from the research community describe accelerated healing timelines when both peptides are employed together. Tendon injuries, muscle tears, and ligament damage all reportedly respond more rapidly to combination protocols than to either peptide alone.
The theoretical framework for synergy rests on well-established principles of systems biology. Complex biological processes like tissue repair involve multiple rate-limiting steps. Addressing only one bottleneck leaves others unaffected. Combination approaches simultaneously address multiple bottlenecks, enabling faster overall progress through the repair cascade.
Understanding the broader landscape of peptide stacking strategies provides context for appreciating BPC-157 and TB-500 combination protocols.
Potential interaction considerations
Despite largely complementary mechanisms, some pathway overlap exists between BPC-157 and TB-500. Both influence VEGF expression, though through different upstream regulators. Both affect inflammatory processes, though through distinct mechanisms. These overlapping effects likely produce additive rather than synergistic benefits in specific pathway components.
No documented antagonistic interactions between BPC-157 and TB-500 appear in the research literature. The peptides don't compete for receptors or interfere with each other's mechanisms. This absence of negative interactions supports the safety of combination approaches.
Timing of administration may influence interaction dynamics. Simultaneous versus staggered dosing could theoretically affect how the peptides interact at tissue sites. However, practical experience suggests both approaches produce beneficial outcomes, with the choice often driven by convenience rather than optimization concerns.
Practical stacking protocols
Translating synergy theory into practical protocols requires attention to dosing, timing, duration, and administration methods. Multiple validated approaches exist, with selection depending on specific goals, injury characteristics, and individual response patterns.
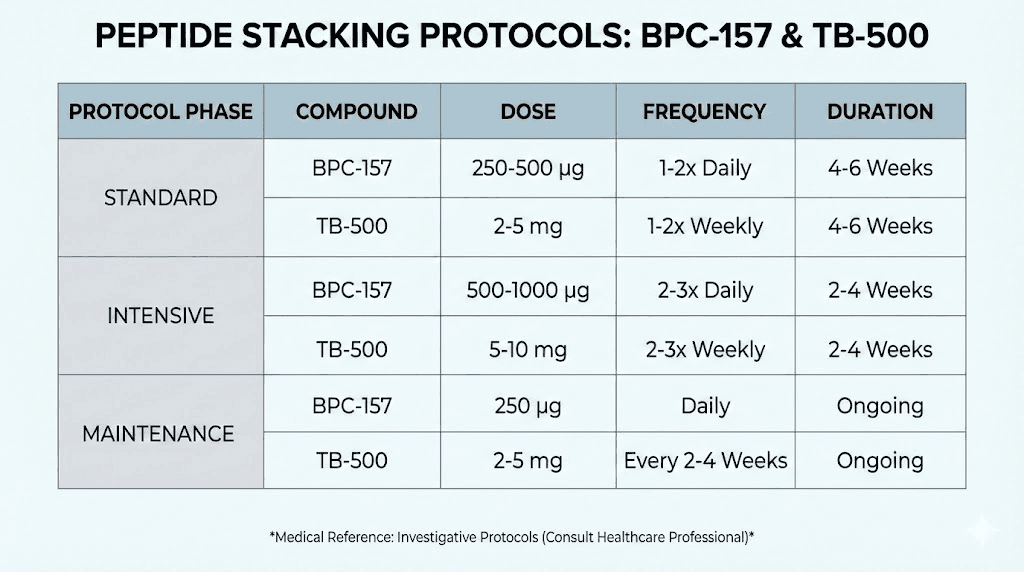
Standard combination protocol
The most commonly employed stack uses moderate doses of both peptides administered daily or near-daily for defined treatment cycles. This approach prioritizes consistency and comprehensive pathway coverage.
BPC-157 component: 250-500mcg daily, divided into one or two doses. Subcutaneous injection near injury sites or systemic administration both show effectiveness. The BPC-157 5mg dosing guide provides detailed calculation methods.
TB-500 component: 2-2.5mg twice weekly during loading phase (first 4-6 weeks), reducing to 2-2.5mg weekly during maintenance. TB-500's longer half-life supports less frequent dosing than BPC-157.
Duration: 6-12 weeks depending on injury severity and response. Significant injuries may benefit from longer protocols while minor tissue stress responds within shorter timeframes.
Administration: Subcutaneous injection represents the standard route for both peptides. Injection sites can be local (near injury) or systemic (abdominal or thigh). Local injection may provide faster onset at specific sites while systemic dosing offers broader distribution.
Intensive healing protocol
More aggressive stacking approaches employ higher doses and more frequent administration for acute or severe injuries requiring rapid intervention.
BPC-157 component: 500-750mcg twice daily (morning and evening). Higher doses accelerate pathway saturation though also increase material costs.
TB-500 component: 5mg twice weekly during intensive phase, maintaining this elevated dose for 2-4 weeks before transitioning to standard maintenance.
Duration: 2-4 weeks intensive phase, followed by 4-8 weeks standard protocol. The intensive period addresses acute healing needs while transition to standard dosing supports continued repair without unnecessary peptide expenditure.
Application: This protocol suits acute injuries, post-surgical recovery, or situations requiring rapid return to function. The higher doses and costs are justified by accelerated timelines in appropriate contexts.
Maintenance and prevention protocol
Lower-dose combination approaches support ongoing tissue health and injury prevention in active individuals with chronic tissue demands.
BPC-157 component: 150-250mcg daily or 250-500mcg every other day. Lower doses provide sustained pathway support without aggressive intervention.
TB-500 component: 2mg weekly or biweekly. Reduced frequency maintains tissue support while minimizing ongoing costs and administration burden.
Duration: Ongoing during periods of high physical demand, with periodic breaks to assess baseline tissue status and response maintenance.
Application: Athletes in demanding training phases, individuals with recurring injury patterns, or those seeking proactive tissue support benefit from maintenance approaches.
The peptide stack calculator helps design personalized combination protocols based on individual parameters and goals.
Application-specific guidance
Different injury types and tissue targets respond optimally to tailored stacking approaches. Understanding tissue-specific considerations enables protocol refinement beyond generic recommendations.
Tendon and ligament injuries
Connective tissue injuries represent one of the most well-established applications for BPC-157 and TB-500 combination therapy. Tendons and ligaments heal slowly due to limited blood supply and high mechanical demands, making them ideal targets for regenerative peptide support.
BPC-157 demonstrates particular affinity for tendon tissue, with multiple studies showing accelerated tendon healing in animal models. The peptide promotes tenocyte proliferation, collagen synthesis, and functional recovery of tendon strength.
TB-500's angiogenic effects address the vascular limitations that slow tendon healing. New blood vessel formation improves nutrient delivery and waste removal, supporting the metabolically demanding repair process.
Local injection near injured tendons may provide advantages over systemic administration for these focal injuries. Subcutaneous injection in proximity to the affected structure delivers peptides directly to the region requiring support.
Exploring the best peptides for tendon repair provides additional context on tendon-focused applications.
Muscle injuries
Muscle tissue responds well to combination peptide support, with both BPC-157 and TB-500 demonstrating pro-regenerative effects in muscle damage models. Muscle strains, tears, and contusions all represent potential applications.
TB-500's actin regulation becomes particularly relevant in muscle tissue, where actin forms a critical component of the contractile apparatus. Supporting cytoskeletal organization aids muscle fiber reconstruction and functional recovery.
BPC-157's growth factor upregulation promotes satellite cell activation and myoblast proliferation, the cellular processes underlying muscle regeneration. Enhanced growth factor signaling accelerates the proliferative phase of muscle healing.
Combination protocols for muscle injuries typically employ systemic administration given the larger tissue volumes often affected. Higher doses may be warranted for extensive muscle damage compared to focal tendon injuries.
Those focused on muscle development should also explore peptides for muscle growth for complementary approaches.
Joint and cartilage support
Articular cartilage presents unique challenges due to its avascular nature and limited regenerative capacity. While complete cartilage regeneration remains beyond current capabilities, peptide support may slow degradation and promote whatever repair potential exists.
BPC-157 demonstrates chondroprotective effects in animal models of osteoarthritis, reducing cartilage degradation markers and preserving joint structure. These protective effects complement any direct regenerative benefits.
TB-500 may support the synovial and subchondral environments surrounding cartilage, improving the overall joint milieu even if direct cartilage effects remain limited.
Systemic administration typically suits joint applications given the difficulty of accessing intra-articular spaces without specialized medical procedures. Periarticular subcutaneous injection offers a middle ground, delivering peptides near joint structures without requiring joint entry.
Understanding best peptides for joint pain and peptides for bone and cartilage repair expands joint-focused options.
Gut and organ healing
BPC-157's gastric origin makes it particularly suited for gastrointestinal applications. The peptide demonstrates protective and healing effects across the entire GI tract, from esophageal to colonic tissue. Oral administration becomes an option for gut-targeted applications, with BPC-157 maintaining activity despite gastric acid exposure.
TB-500 contributes systemic anti-inflammatory effects that may benefit inflammatory bowel conditions, though its primary value lies in tissue applications beyond the gut.
Combination approaches for organ healing typically emphasize BPC-157 while including TB-500 for systemic support. The specific organ affected influences route selection, with oral BPC-157 suiting GI targets while injectable routes address other organ systems.
Exploring peptides for gut health provides comprehensive guidance on gastrointestinal applications.
Dosing precision and calculation
Accurate dosing ensures consistent results and appropriate peptide expenditure. Understanding reconstitution, calculation methods, and administration techniques supports reliable protocol implementation.
Reconstitution fundamentals
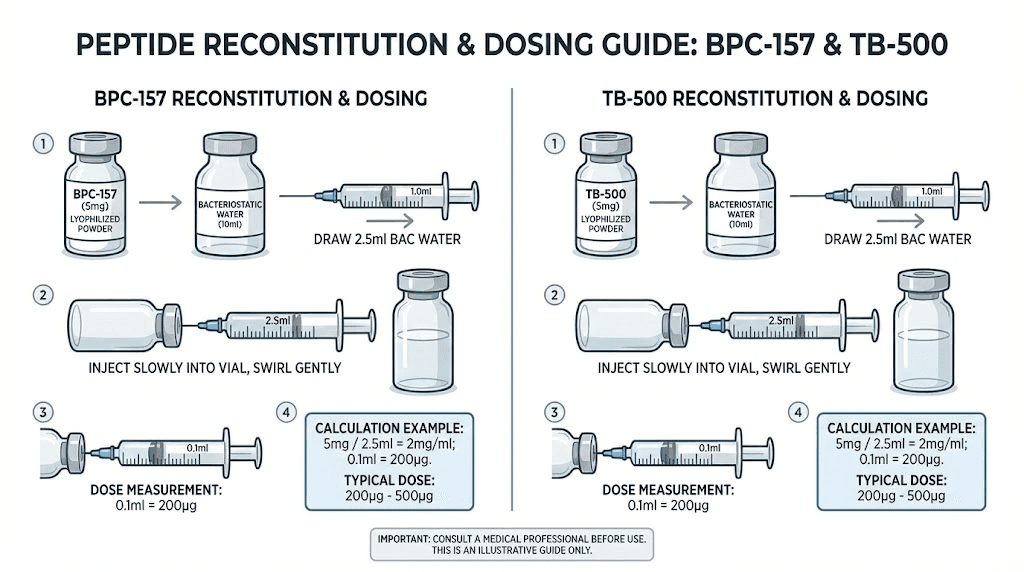
Both BPC-157 and TB-500 typically arrive as lyophilized (freeze-dried) powders requiring reconstitution with bacteriostatic water before use. Proper reconstitution technique preserves peptide integrity and enables accurate dosing.
The peptide reconstitution calculator determines appropriate water volumes for target concentration. Common reconstitution approaches create concentrations enabling convenient dose measurement with insulin syringes.
Bacteriostatic water, containing 0.9% benzyl alcohol as a preservative, extends reconstituted peptide stability compared to sterile water. Bacteriostatic water for peptides provides detailed guidance on diluent selection and handling.
Storage of reconstituted peptides requires refrigeration at 2-8°C to maintain stability. Properly stored, reconstituted BPC-157 and TB-500 remain stable for approximately 3-4 weeks, though some degradation occurs progressively.
Calculation methods
Dose calculation follows straightforward mathematics once reconstitution concentration is established. For a 5mg vial of BPC-157 reconstituted with 2ml bacteriostatic water, the resulting concentration equals 2.5mg/ml or 2500mcg/ml. A 250mcg dose thus requires 0.1ml (10 units on a standard insulin syringe).
TB-500 calculations proceed similarly. A 5mg vial reconstituted with 2ml yields 2.5mg/ml. A 2.5mg dose requires 1ml. The larger TB-500 doses often necessitate larger reconstitution volumes to enable practical measurement.
The peptide calculator automates these calculations, reducing error risk and simplifying protocol implementation.
Detailed guidance on how to calculate peptide dosages provides step-by-step instructions for manual calculation methods.
Administration technique
Subcutaneous injection using insulin syringes represents the standard administration method for both peptides. The 29-31 gauge needles on insulin syringes minimize discomfort while enabling precise volume measurement.
Injection site selection balances convenience with proximity to target tissues. Abdominal subcutaneous fat provides easy access for systemic administration. Perilesional injection near injury sites may enhance local delivery for focal injuries.
Rotation of injection sites prevents lipodystrophy from repeated injections in the same location. Alternating between multiple sites on abdomen, thighs, or other areas distributes tissue stress.
The peptide injections guide covers administration technique in comprehensive detail.
Timeline expectations and monitoring
Setting realistic expectations for healing timelines and monitoring progress enables appropriate protocol adjustments and prevents premature discouragement or excessive optimism.
Early phase response (weeks 1-2)
Initial responses to combination therapy typically manifest as reduced inflammation and pain at injury sites. These early benefits reflect the anti-inflammatory properties of both peptides rather than structural tissue repair, which requires longer timeframes.
Some individuals report subjective improvement within days of initiating protocols. Whether these rapid responses reflect true biological effects or placebo components remains difficult to distinguish. Regardless of mechanism, improved comfort often accompanies early protocol phases.
Structural changes remain minimal during initial weeks. Tendon, ligament, and muscle tissue require extended periods for meaningful collagen deposition and fiber reorganization. Early-phase benefits set the stage for repair rather than constituting repair itself.
Mid-phase progress (weeks 3-6)
Structural healing becomes measurable during mid-protocol phases. Tissue strength gradually increases as new collagen matures and integrates with existing structures. Functional capacity typically expands progressively during this period.
Imaging studies, where employed, may show tissue changes during mid-phase. Reduced inflammation, improved tissue organization, and blood vessel formation become potentially visible on ultrasound or MRI.
Many individuals can resume modified activity during mid-phase, with progressive loading helping direct tissue remodeling along functional lines. Complete restriction typically becomes unnecessary as tissues regain baseline capacity.
Late phase maturation (weeks 7-12+)
Tissue maturation continues beyond acute healing, with collagen cross-linking and fiber organization improving progressively. Full functional recovery often requires the complete protocol duration even when subjective healing feels complete earlier.
Return to full activity becomes appropriate during late phases for most injuries. Progressive loading protocols help tissues adapt to increasing demands while minimizing reinjury risk.
Some chronic or severe injuries require extended protocols beyond typical 12-week durations. Incomplete healing at expected timepoints may warrant protocol extension or reassessment of injury severity and contributing factors.
Understanding general peptide response timelines contextualizes expectations across different applications.
Progress monitoring approaches
Subjective assessment of pain, function, and activity tolerance provides the most accessible progress monitoring. Regular self-assessment at consistent intervals enables trend identification and protocol adjustment.
Functional testing, where appropriate, quantifies progress more objectively. Range of motion, strength testing, or sport-specific performance metrics provide measurable benchmarks for comparison.
Imaging studies offer the most objective assessment but add cost and complexity. Ultrasound can visualize tendon and muscle structure while MRI provides more detailed soft tissue assessment. Imaging typically suits more severe injuries or situations with unclear clinical progress.
Safety and side effect profiles
Both BPC-157 and TB-500 demonstrate favorable safety profiles across research applications and practical use. Understanding potential concerns enables informed decision-making and appropriate monitoring.
BPC-157 safety considerations
BPC-157 shows minimal adverse effects across extensive research use. The peptide's natural origin in gastric secretions suggests inherent biocompatibility with human physiology.
Theoretical concerns regarding growth factor modulation and potential cancer interactions remain unsubstantiated by clinical evidence. The peptide does not appear to promote tumor growth in available research, though long-term human data remains limited.
Injection site reactions including temporary redness, swelling, or discomfort occur occasionally. These local effects typically resolve rapidly and rarely require intervention beyond injection site rotation.
Exploring BPC-157 regulatory status provides context on the legal landscape for this peptide.
TB-500 safety considerations
TB-500 similarly demonstrates a favorable safety profile across research and practical applications. As a fragment of naturally occurring thymosin beta-4, the peptide aligns with endogenous human biology.
Temporary fatigue or flu-like symptoms occasionally accompany TB-500 initiation, particularly at higher doses. These effects typically resolve within days and may reflect immune system modulation during the adjustment period.
Headache represents another occasionally reported effect, potentially related to the peptide's vasodilatory properties. Hydration and gradual dose escalation may minimize this concern.
Reviewing TB-500 alternatives provides options for those seeking different approaches to similar goals.
Combination safety profile
No documented adverse interactions between BPC-157 and TB-500 emerge from available research or community experience. The distinct mechanism profiles minimize potential for negative interactions.
Additive side effects remain theoretically possible, where both peptides contribute to similar adverse effects. In practice, the mild side effect profiles of both peptides make clinically significant additive concerns unlikely.
Starting with lower combination doses and escalating gradually enables individual response assessment before reaching full protocol doses. This conservative approach identifies any unusual sensitivity before significant exposure occurs.
Comprehensive coverage of peptide safety and risks provides broader context for evaluating any peptide protocol.
Optimizing results
Beyond basic protocol implementation, various strategies can enhance outcomes from BPC-157 and TB-500 combination therapy. Attention to supporting factors often determines the difference between good and excellent results.
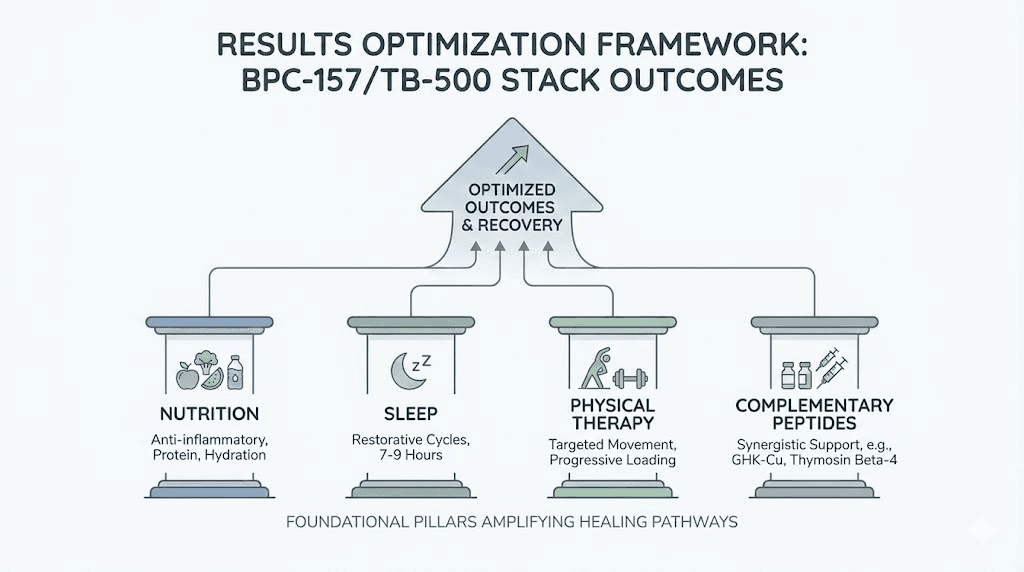
Nutritional support
Adequate protein intake provides the amino acid substrate for tissue repair. Peptide therapy accelerates healing processes that still require raw materials for new tissue construction. Insufficient protein limits repair regardless of signaling optimization.
Vitamin C serves as an essential cofactor for collagen synthesis. Ensuring adequate vitamin C status supports the collagen deposition that constitutes much of connective tissue repair.
Zinc and copper contribute to multiple tissue repair enzymes. These trace minerals often become depleted during healing periods when demands increase.
Anti-inflammatory foods may complement the anti-inflammatory effects of the peptides. Omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil or other sources support favorable inflammatory balance.
Sleep and recovery
Growth hormone release during deep sleep stages supports tissue anabolism. Prioritizing sleep quality and duration enhances the regenerative environment in which peptides operate.
Stress management affects cortisol levels, with chronic stress elevating catabolic hormones that oppose tissue repair. Addressing stress through appropriate interventions supports healing beyond direct physical factors.
Avoiding alcohol and tobacco removes factors that impair tissue repair. Alcohol disrupts protein synthesis while tobacco compromises circulation and oxygen delivery to healing tissues.
Physical therapy integration
Appropriate mechanical loading guides tissue remodeling along functional lines. Complete immobilization produces weak, disorganized repair tissue while progressive loading promotes strong, aligned structures.
Professional physical therapy guidance tailors loading protocols to specific injuries and healing phases. Premature overload risks reinjury while excessive restriction produces suboptimal tissue quality.
Blood flow restriction training may enhance adaptation with lower mechanical loads, potentially valuable during early healing phases when full loading remains inappropriate.
Resources for fast injury healing integrate peptide protocols with comprehensive recovery approaches.
Complementary peptide options
Advanced stacking approaches may incorporate additional peptides beyond the BPC-157/TB-500 foundation. Growth hormone secretagogues like ipamorelin enhance systemic anabolic signaling that supports tissue repair.
Copper peptide GHK-Cu provides additional regenerative support with particular relevance for skin and soft tissue healing.
The wolverine stack concept expands beyond BPC-157 and TB-500 to incorporate additional regenerative peptides for comprehensive healing support.
Complexity increases with additional stack components, requiring careful attention to interactions, timing, and individual response assessment.
Common questions and troubleshooting
Practical implementation of combination protocols raises numerous questions. Addressing common concerns facilitates successful protocol execution.
Can I combine both peptides in one syringe?
Mixing BPC-157 and TB-500 in a single injection syringe appears acceptable based on available evidence. The peptides don't react chemically or interfere with each other's stability. Combined injection reduces injection frequency while delivering both peptides simultaneously.
Some individuals prefer separate injections for flexibility in injection site selection. Local BPC-157 near an injury combined with systemic TB-500 elsewhere enables targeted delivery without mixing constraints.
Should I inject locally or systemically?
Both approaches show effectiveness, with selection depending on injury characteristics. Focal injuries like specific tendon damage may benefit from local perilesional injection. Diffuse injuries or systemic applications suit systemic administration.
Combination approaches using local injection for one peptide and systemic for the other represent another valid strategy. BPC-157 locally at an injury site with systemic TB-500 for comprehensive tissue support exemplifies this hybrid approach.
What if I miss a dose?
Individual missed doses have minimal impact on overall protocol outcomes. Simply resume the regular schedule without attempting to compensate with double doses. Consistency over the full protocol duration matters more than individual dose precision.
Extended interruptions of multiple days warrant protocol reassessment. Brief interruptions require no adjustment while longer gaps may benefit from extended total protocol duration to compensate.
How do I know if it's working?
Subjective improvement in pain, function, and activity tolerance provides the primary effectiveness signal. Gradual progressive improvement over weeks suggests beneficial response. Dramatic overnight changes are unlikely, with healing proceeding incrementally.
Absence of expected improvement by mid-protocol (4-6 weeks) warrants reassessment. Dose adjustment, protocol modification, or reevaluation of injury severity and type may be appropriate.
Can I use this combination long-term?
Extended protocols beyond typical 8-12 week durations appear safe based on available evidence. Chronic or recurring injury patterns may warrant ongoing maintenance protocols at reduced doses.
Periodic breaks from peptide use enable baseline assessment and prevent potential desensitization, though evidence for desensitization with these peptides remains limited. Many individuals cycle through active treatment and maintenance phases over extended periods.
Comparison with alternative approaches
Understanding how BPC-157/TB-500 stacking compares to other regenerative options enables informed selection of appropriate interventions.
Single peptide versus stack
Individual BPC-157 or TB-500 use provides meaningful benefits for many applications. The combination stack offers enhanced effects for more challenging injuries or accelerated timeline requirements.
Cost considerations favor single peptide approaches when budget constraints exist. The stack approximately doubles material costs compared to individual peptide use.
Complexity also increases with stacking, requiring attention to multiple reconstitution, dosing, and timing variables. Simple protocols using one peptide suit individuals preferring straightforward approaches.
The detailed BPC-157 vs TB-500 comparison helps determine when individual peptides suffice versus when stacking adds value.
Peptides versus other regenerative modalities
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections represent the primary clinical alternative for regenerative support. PRP requires blood draw and processing, typically performed in medical settings at considerable cost. Peptides offer self-administered protocols at lower per-treatment cost.
Stem cell therapies represent more aggressive interventional options for severe injuries. These approaches require medical procedures and carry higher costs and risks. Peptides provide less dramatic but more accessible regenerative support.
Conventional therapies including physical therapy, rest, and anti-inflammatory medications form the standard care foundation. Peptides complement rather than replace these approaches, adding regenerative support to conventional recovery strategies.
Broader peptide landscape
Beyond BPC-157 and TB-500, numerous peptides offer regenerative properties. Growth hormone releasing peptides, IGF-1 variants, and other compounds address tissue repair through additional mechanisms.
The best peptides for injury recovery overview surveys the complete regenerative peptide landscape.
Exploring BPC-157 alternatives and TB-500 alternatives identifies options when these primary compounds prove unavailable or unsuitable.
Sourcing and quality considerations
Peptide quality significantly affects protocol outcomes. Understanding sourcing factors enables selection of reliable products.
Quality markers
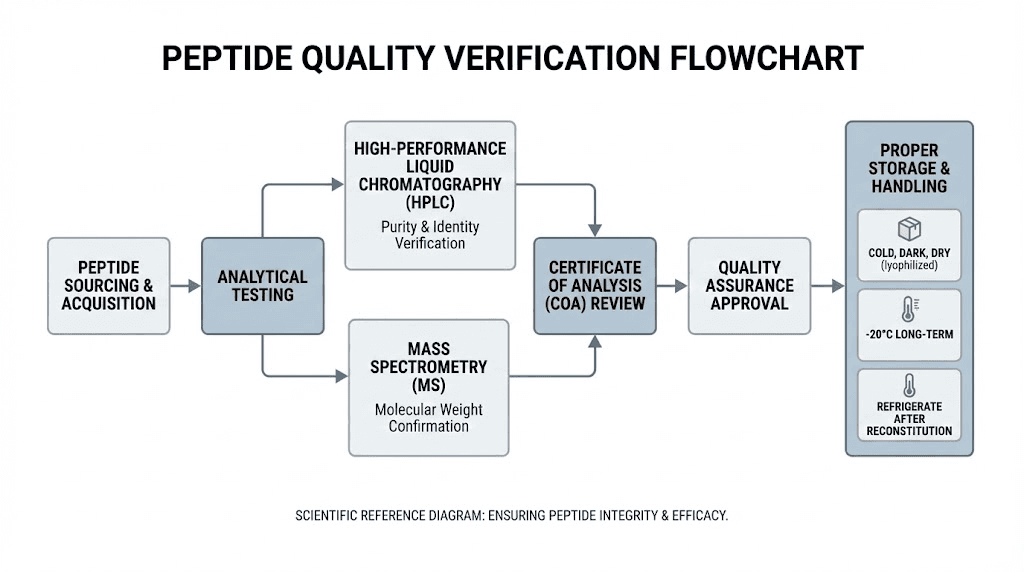
Purity verification through third-party testing provides the primary quality assurance. Certificates of analysis from independent laboratories confirm peptide identity and purity levels, typically targeting greater than 98% purity for research-grade materials.
HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) testing verifies peptide purity and identity. Mass spectrometry confirms molecular weight matching expected values. These analytical methods detect impurities, degradation products, or misidentified compounds.
Understanding peptide testing results enables independent verification of vendor quality claims.
Vendor evaluation
Established vendors with track records in the research community offer greater reliability than unknown sources. Community reputation, longevity, and consistent quality reports support vendor selection.
Transparent testing policies with certificates of analysis available for specific batches indicate quality-focused operations. Vendors unwilling to provide documentation warrant skepticism.
Reviewing best peptide vendor resources provides guidance on source selection.
Storage and handling
Proper storage maintains peptide stability and effectiveness. Lyophilized (unreconstituted) peptides remain stable for extended periods when stored frozen or refrigerated away from light and moisture.
Reconstituted peptides require refrigeration and use within 3-4 weeks for optimal stability. Freezing reconstituted peptides may extend stability though repeated freeze-thaw cycles should be avoided.
The peptide storage guide provides comprehensive handling recommendations.
How SeekPeptides supports regenerative protocols
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for understanding and implementing BPC-157 and TB-500 combination protocols. The platform offers evidence-based guidance for navigating regenerative peptide applications.
The peptide calculator simplifies dosing calculations for both individual and combination protocols. Accurate dosing ensures consistent results across treatment cycles.
Specialized calculators including the BPC-157 dosage calculator and TB-500 dosage calculator provide targeted support for each stack component.
The peptide stack calculator addresses combination protocols specifically, helping design personalized stacking approaches.
Educational resources covering peptide reconstitution and injection technique support proper protocol implementation.
SeekPeptides serves as a trusted resource for evidence-based peptide therapy guidance across regenerative and other applications.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your tissues stay resilient, your healing stay accelerated, and your recovery stay complete. Join SeekPeptides.