Jan 26, 2026
You have been researching peptides for weeks. Maybe months. You understand the mechanisms. You know which peptide targets your specific goal. But when you start looking at prices, confusion sets in fast. One website lists BPC-157 at $35. Another charges $400 for what looks like the same thing. A clinic quotes you $600 per month while someone on a forum mentions spending $50. What is actually going on with peptide pricing?
The answer is not simple, and that frustrates people.
Peptide costs vary dramatically based on source, purity, quantity, and whether you are going through a clinic or purchasing research-grade compounds. The same peptide that costs $30 from one supplier might run $500 from a compounding pharmacy. Neither price is wrong. They represent completely different products, quality standards, and legal frameworks. Understanding these differences means the difference between wasting money and getting actual results from your peptide protocols.
This guide breaks down exactly what peptides cost across every category. We cover individual peptide pricing, monthly protocol expenses, clinic versus research grade comparisons, and strategies to reduce costs without sacrificing quality. By the end, you will know precisely what to budget for any peptide therapy approach you choose.
SeekPeptides members access detailed cost breakdowns, protocol calculators, and budget optimization guides that go far beyond what we can cover here. But this foundation will give you the knowledge to make informed decisions about your peptide investment.
Understanding the peptide pricing landscape
Peptide pricing confuses people because there is no single market. Instead, multiple parallel markets exist, each with its own pricing logic, quality standards, and legal considerations. Grasping this landscape is essential before you spend a single dollar.
The research peptide market operates differently from the clinical peptide market. Compounding pharmacies charge different rates than online suppliers. Domestic sources price differently than international ones. And pharmaceutical-grade peptides exist in an entirely separate category from everything else.
Think of it like coffee. You can buy instant coffee for $3, decent beans for $12, specialty roast for $25, or single-origin from a micro-roaster for $50. All technically coffee. All provide caffeine. But the experience, quality, and results differ substantially. Research peptides versus pharmaceutical peptides work similarly.
Research peptide pricing
Research peptides represent the most accessible entry point for most people. These compounds are sold explicitly for laboratory research, not human use. This legal framework allows suppliers to sell peptides without the regulatory overhead that pharmaceutical companies face.
The result? Dramatically lower prices.
A 5mg vial of BPC-157 from a research supplier typically costs $25 to $80. The exact same quantity from a compounding pharmacy runs $200 to $400. Same peptide sequence. Same molecular weight. But different manufacturing standards, testing protocols, and legal classifications create the price gap.
Research peptide suppliers operate on volume. They synthesize large batches and sell to researchers, academic institutions, and individuals conducting personal research. Margins stay tight because competition is fierce. Dozens of suppliers compete for the same customer base, and price becomes a primary differentiator.
Quality varies significantly in this market. Some suppliers maintain rigorous purity testing with third-party verification. Others cut corners. The price difference between a 95% pure peptide and a 99% pure peptide might only be $10 to $20 per vial, but that 4% difference can mean contamination, degradation products, or synthesis errors that affect both safety and efficacy.
Peptide testing labs provide certificates of analysis that verify purity. Reputable suppliers publish these certificates. If a supplier cannot provide third-party testing results, consider that a major red flag regardless of how attractive the pricing looks.
Clinical and compounding pharmacy pricing
Clinical peptides come through healthcare providers and compounding pharmacies. These follow pharmaceutical manufacturing standards with extensive quality control, sterility testing, and regulatory compliance. The cost reflects this additional oversight.
Monthly clinical peptide therapy typically runs $200 to $800 for standard protocols. Complex multi-peptide regimens can exceed $1,500 monthly. These prices include not just the peptides themselves but professional oversight, dosing guidance, and access to medical support if issues arise.
Compounding pharmacies customize peptide preparations to individual prescriptions. A physician evaluates your health status, determines appropriate peptides and dosages, then sends the prescription to a licensed compounding facility. The pharmacy synthesizes or reconstitutes the peptides according to strict protocols, then ships directly to you.
This system adds cost but also adds safety. Compounding pharmacies face FDA oversight. They must maintain sterile facilities, test for contamination, and document every step of production. When something goes wrong with a compounded medication, there are legal frameworks for accountability and recourse.
The price premium for clinical peptides ranges from 200% to 800% compared to research-grade equivalents. Is that premium worth it? The answer depends on your priorities, risk tolerance, and how much you value professional medical guidance in your peptide therapy journey.
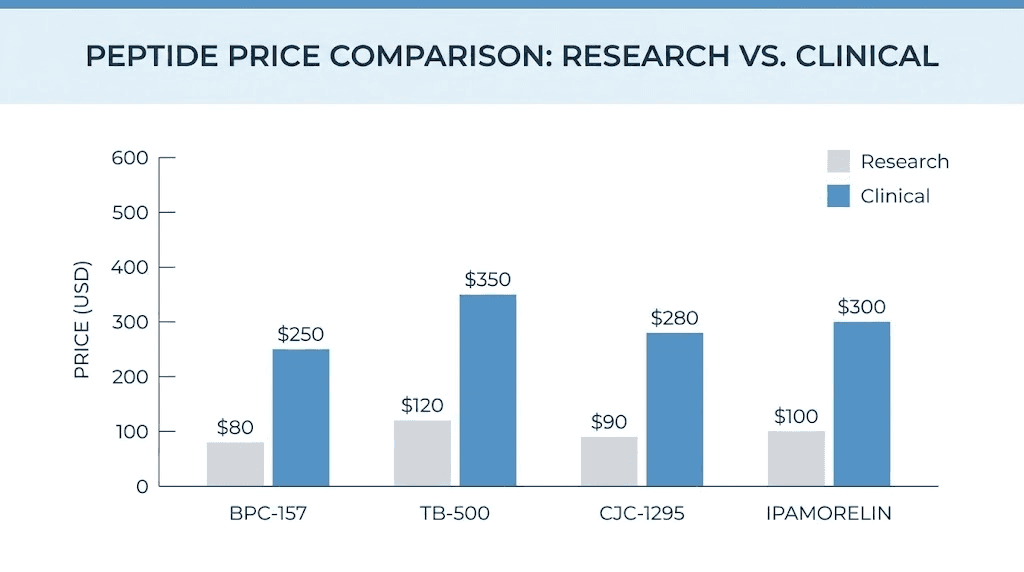
Individual peptide pricing breakdown
Let us get specific. Below you will find current pricing for the most popular peptides across both research and clinical markets. These figures represent typical ranges based on current market conditions and may fluctuate based on supply, demand, and regulatory changes.
BPC-157 costs
BPC-157 remains one of the most sought-after peptides for tissue repair and injury healing. Pricing reflects its popularity and relatively straightforward synthesis.
Research grade BPC-157 costs $25 to $80 for a 5mg vial. A 10mg vial runs $45 to $120. These prices assume 98% or higher purity from reputable suppliers. Budget options at 95% purity cost slightly less but sacrifice quality.
Clinical BPC-157 from compounding pharmacies ranges $200 to $400 for a one-month supply. This typically includes enough peptide for twice-daily dosing at therapeutic levels, plus the reconstitution solution and syringes.
A standard BPC-157 protocol runs 4 to 8 weeks. Using research-grade peptides, a complete cycle costs $75 to $250 depending on dosage and duration. The same protocol through clinical channels runs $400 to $800.
Many researchers combine BPC-157 with TB-500 for enhanced healing effects. The BPC-157 and TB-500 stack increases total cost but may provide synergistic benefits that justify the additional investment.
TB-500 costs
TB-500 pricing runs slightly higher than BPC-157 due to its longer amino acid sequence and more complex synthesis requirements.
Research-grade TB-500 costs $40 to $100 for a 5mg vial. Clinical-grade runs $250 to $450 monthly. The loading phase of TB-500 protocols requires higher initial doses, which increases first-month costs compared to maintenance phases.
A typical TB-500 cycle involves loading doses of 4 to 8mg weekly for the first 4 to 6 weeks, then maintenance doses of 2 to 4mg weekly thereafter. Research-grade cost for a 12-week protocol ranges $200 to $500. Clinical protocols run $750 to $1,400 for the same duration.
Growth hormone releasing peptides
The growth hormone peptide category includes multiple compounds with varying price points.
Ipamorelin represents the budget-friendly option in this category. Research grade costs $35 to $75 for a 5mg vial. Clinical Ipamorelin runs $150 to $300 monthly. Its clean side effect profile makes it popular for those new to GH peptides.
CJC-1295 costs slightly more. Research pricing sits at $50 to $100 for 5mg. Clinical pricing ranges $200 to $400 monthly. The DAC (Drug Affinity Complex) version costs more than non-DAC due to extended half-life properties.
The Sermorelin and Ipamorelin combination has gained popularity for its synergistic effects on growth hormone release. Blended products cost $100 to $200 research-grade or $400 to $700 monthly clinical.
Sermorelin alone runs $50 to $90 research-grade for a standard vial. Clinical sermorelin pricing ranges $175 to $400 monthly depending on provider and dosing requirements.
Tesamorelin sits at the premium end of GH peptides. Research grade costs $100 to $200 for a 2mg vial. Clinical tesamorelin runs $800 to $1,500 monthly due to its specific FDA approval for HIV-associated lipodystrophy and the higher dosing requirements.
Weight loss peptides
The weight loss peptide category has experienced explosive growth, which affects both availability and pricing.
Semaglutide pricing varies dramatically based on source. Brand-name Ozempic and Wegovy cost $900 to $1,300 monthly without insurance. Compounded semaglutide from licensed pharmacies runs $200 to $500 monthly. Research-grade availability has become limited due to patent enforcement.
Tirzepatide faces similar dynamics. Brand-name Mounjaro costs $1,000 to $1,500 monthly retail. Compounded versions range $300 to $600 monthly where available. Research availability is extremely limited.
AOD-9604 offers a more accessible alternative. Research grade costs $40 to $90 for a 5mg vial. Clinical AOD-9604 runs $200 to $400 monthly. This fat-burning peptide works through different mechanisms than GLP-1 agonists and remains more widely available.
Retatrutide represents the newest generation of weight loss peptides. Still limited in availability, research pricing when available runs $150 to $300 for standard vials. ZLZ peptide retatrutide has shown promising results in trials but remains difficult to source.
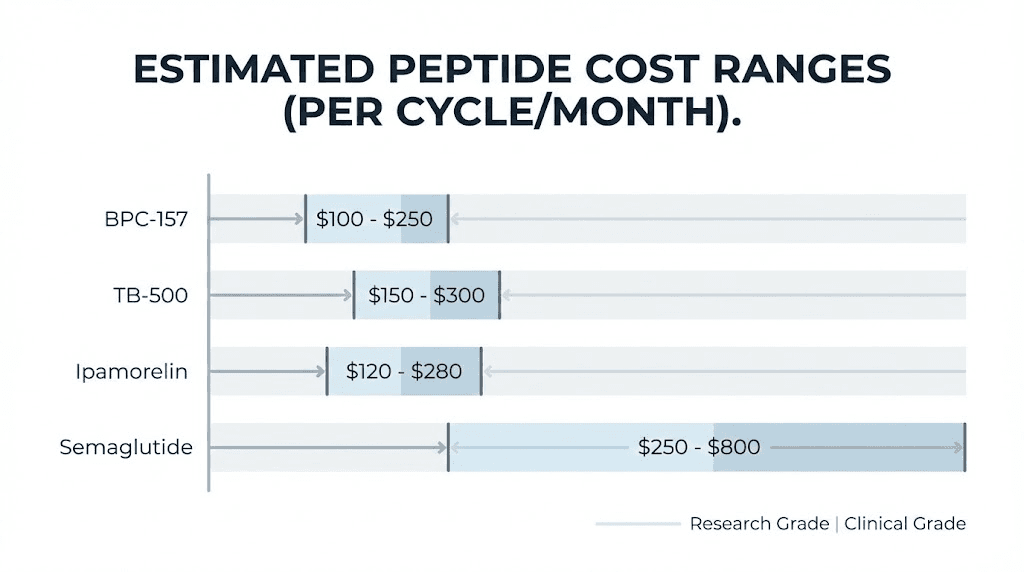
Copper peptides and skin health
GHK-Cu copper peptides serve dual purposes in healing and skin health applications.
Research-grade GHK-Cu costs $50 to $120 for a 50mg vial. Injectable preparations run higher than topical formulations. GHK-Cu injection dosing requires careful calculation due to the higher concentrations involved.
Clinical GHK-Cu preparations range $300 to $600 monthly depending on delivery method and concentration. Copper peptide serums for topical use cost $30 to $150 retail, positioning them as more accessible entry points for skin health applications.
The Glow stack combines BPC-157, TB-500, and GHK-Cu into a single protocol. Glow peptide protocols cost $150 to $400 research-grade for a complete cycle, or $600 to $1,200 clinical.
Cognitive and neuroprotective peptides
Semax leads the cognitive peptide category. Research pricing runs $40 to $80 for standard preparations. Nasal spray formulations cost slightly more due to additional processing requirements. Clinical Semax ranges $150 to $350 monthly.
Selank costs similar to Semax. Research grade runs $40 to $90 per vial. Both peptides are often used together for combined anxiolytic and cognitive effects, which doubles the cost but may provide enhanced benefits for anxiety management and focus.
Dihexa represents the premium cognitive peptide. Research pricing ranges $100 to $200 for small quantities. Its extreme potency means tiny doses suffice, which partially offsets the higher per-milligram cost.
Adamax and other brain-focused peptides vary widely in price. Most fall in the $50 to $150 range for research-grade supplies.
Longevity and anti-aging peptides
The longevity peptide category commands premium pricing due to specialized applications and limited supply.
Epitalon costs $80 to $150 for a standard research vial. Epitalon dosing protocols typically run 10 to 20 days, making individual cycles relatively affordable despite higher per-vial costs.
Thymalin runs $60 to $120 research-grade. The bioregulator peptide category includes multiple compounds at similar price points, including Vesugen, Cardiogen, and Cortagen.
SS-31 represents cutting-edge mitochondrial support. Research pricing runs $100 to $200 for standard quantities. Limited availability can push prices higher during supply constraints.
MOTS-c similarly costs $100 to $200 research-grade. MOTS-c dosing charts help calculate protocol costs based on individual requirements.
Immune and inflammation peptides
KPV peptide costs $50 to $100 research-grade. Its applications for inflammatory conditions and gut health have increased demand and stabilized pricing.
Thymosin Alpha-1 runs $70 to $150 research-grade. Clinical preparations cost significantly more, ranging $400 to $800 monthly for therapeutic protocols.
LL-37 and other antimicrobial peptides cost $80 to $180 research-grade. These specialized compounds serve niche applications but command stable pricing due to consistent demand.
Monthly protocol costs by goal
Individual peptide pricing only tells part of the story. Most people run protocols combining multiple peptides over extended timeframes. Understanding total monthly costs requires looking at complete protocol expenses.
Injury recovery protocols
A basic injury healing protocol using BPC-157 alone costs $50 to $150 monthly research-grade or $200 to $400 clinical. This represents the entry-level approach for pain management and tissue repair.
Enhanced recovery stacks combining BPC-157 and TB-500 run $100 to $300 monthly research-grade or $450 to $900 clinical. This combination targets both joint healing and soft tissue repair simultaneously.
Premium recovery protocols adding GHK-Cu to the BPC-157 and TB-500 stack cost $150 to $450 monthly research-grade or $700 to $1,400 clinical. The Wolverine stack represents one popular version of this comprehensive approach.
Muscle growth and performance protocols
Muscle building peptides typically involve growth hormone secretagogues, which sit in the mid-to-premium price range.
A basic GH peptide protocol using Ipamorelin alone costs $75 to $200 monthly research-grade or $200 to $400 clinical. This provides baseline growth hormone support for muscle growth and recovery.
Standard performance stacks combining CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin run $150 to $350 monthly research-grade or $400 to $800 clinical. This combination provides sustained GH release throughout the day.
Advanced protocols adding peptides like Hexarelin or IGF-1 LR3 push monthly costs to $250 to $600 research-grade or $800 to $1,800 clinical. These intensive protocols target serious athletic performance goals.
Weight loss protocols
Weight loss peptide protocols vary dramatically based on peptide selection.
Budget-friendly options using AOD-9604 cost $80 to $200 monthly research-grade or $250 to $500 clinical. This approach works well for those seeking fat loss support without premium pricing.
Mid-range protocols using compounded semaglutide run $200 to $500 monthly through legitimate clinical channels. Brand-name GLP-1 medications cost $900 to $1,500 monthly without insurance coverage.
Premium weight loss stacks combining multiple mechanisms can exceed $500 monthly research-grade or $1,500 monthly clinical. These comprehensive approaches target metabolic optimization from multiple angles.
Anti-aging and longevity protocols
Anti-aging peptide protocols range from modest to premium depending on comprehensiveness.
Basic longevity support using a single bioregulator peptide costs $50 to $120 monthly research-grade or $200 to $400 clinical. Epitalon-only protocols fall in this range.
Comprehensive anti-aging stacks combining multiple bioregulators, GH peptides, and NAD+ support run $200 to $500 monthly research-grade or $600 to $1,500 clinical.
Premium longevity protocols incorporating cutting-edge peptides like SS-31 and MOTS-c push costs to $300 to $700 monthly research-grade or $1,000 to $2,500 clinical.
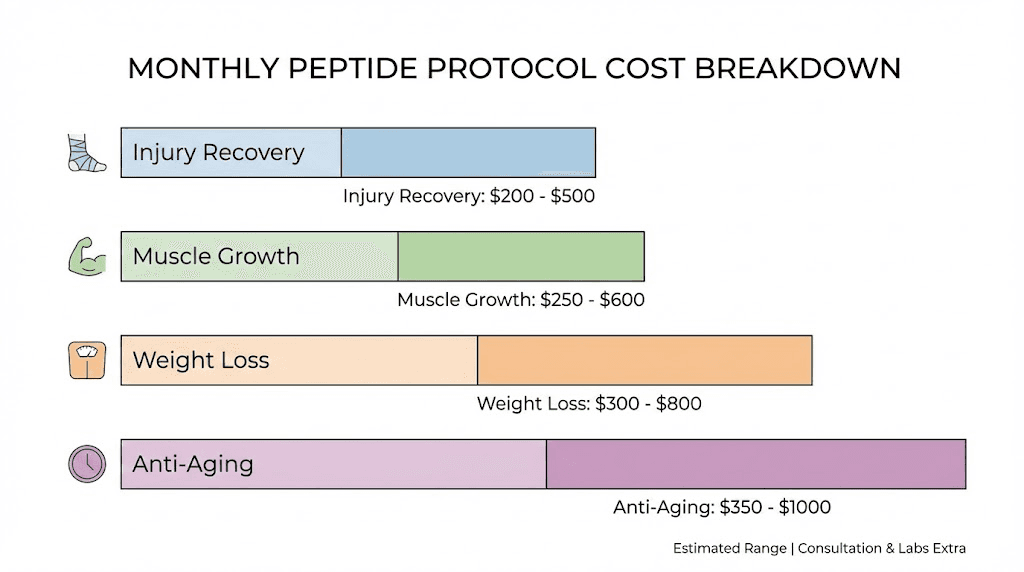
Factors affecting peptide costs
Understanding why peptides cost what they do helps you make smarter purchasing decisions and identify fair pricing versus price gouging.
Manufacturing complexity
Peptide synthesis requires specialized equipment and expertise. Longer amino acid chains cost more to produce because each additional amino acid adds synthesis steps, purification requirements, and potential failure points.
A 15-amino-acid peptide like BPC-157 is relatively simple to synthesize. A 44-amino-acid peptide requires substantially more processing. This explains why some peptides cost dramatically more than others despite serving similar functions.
Synthesis method also affects pricing. Solid-phase peptide synthesis dominates the industry, but newer recombinant production methods can reduce costs for certain peptides. As manufacturing technology improves, prices generally trend downward over time.
Purity levels
Purity dramatically affects both cost and effectiveness. The difference between 95% and 99% purity might seem small, but that 4% represents impurities that can include unreacted precursors, truncated sequences, degradation products, and synthesis byproducts.
Higher purity requires more extensive purification steps, typically involving high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Each purification pass adds cost but removes contaminants that could affect safety or efficacy.
Premium suppliers charging $10 to $30 more for 99%+ purity peptides often represent better value than budget options with lower purity. The peptide testing process verifies these purity claims through third-party analysis.
Supply and demand dynamics
Peptide markets respond to demand fluctuations like any other market. When a peptide gains popularity through social media attention or new research publications, prices often spike before stabilizing as supply catches up.
Semaglutide and tirzepatide pricing exemplifies this dynamic. Massive demand following weight loss coverage in mainstream media created supply constraints that persist today. Compounding pharmacies face ingredient shortages. Research suppliers have largely exited these markets due to patent concerns.
Conversely, established peptides with stable demand and multiple suppliers tend toward competitive pricing. BPC-157, TB-500, and Ipamorelin have reached market maturity where price competition keeps costs reasonable.
Regulatory factors
Legal status significantly impacts peptide pricing. FDA-approved peptides like semaglutide carry premium pricing that reflects R&D investment, clinical trial costs, and regulatory compliance expenses.
Research peptides operate in a gray area that allows lower pricing but comes with trade-offs in quality assurance and legal clarity. The legal status of peptides continues evolving, and regulatory changes can rapidly affect availability and pricing.
International sourcing adds another layer of complexity. Peptides manufactured overseas may cost less but face quality variability and customs concerns. Chinese peptide sources dominate certain market segments with aggressive pricing that domestic suppliers struggle to match.
Quantity and bulk purchasing
Volume discounts apply throughout the peptide supply chain. Research suppliers typically offer 10% to 20% discounts for orders of 5 to 20 vials. Larger quantities can push discounts higher.
Clinical programs often reduce per-month costs for longer commitments. A 3-month program might cost less per month than month-to-month pricing. Six-month commitments offer even better rates at many providers.
These discounts make sense from both supplier and buyer perspectives. Suppliers benefit from predictable demand and reduced transaction costs. Buyers benefit from lower per-unit pricing on peptides they plan to use anyway.
Comparing sourcing options
Where you buy peptides matters as much as which peptides you buy. Each sourcing option offers different trade-offs between cost, quality, convenience, and legal clarity.
Research peptide suppliers
Online research peptide suppliers offer the lowest pricing but require the most buyer diligence. Prices run 60% to 80% lower than clinical alternatives. Quality varies from excellent to concerning.
Reputable research suppliers provide certificates of analysis from independent testing labs. They maintain proper storage and shipping protocols. They respond professionally to quality concerns. These suppliers have built reputations over years of consistent service.
Less reputable suppliers cut corners that affect both safety and efficacy. Common issues include underdosed vials, contamination, degradation from improper storage, and fraudulent purity claims. The peptide research community helps identify reliable sources through user reports and testing results.
Key questions when evaluating research suppliers include whether they provide third-party testing, how they handle shipping temperature control, what their return policy covers, and how long they have operated. Grey market peptide purchasing requires careful vetting.
Compounding pharmacies
Licensed compounding pharmacies represent the middle ground between research suppliers and pharmaceutical products. Prices run higher than research grade but lower than brand-name medications.
Compounding pharmacies must register with state boards of pharmacy and follow strict manufacturing protocols. They face regular inspections and must maintain sterile facilities. Medications are prepared to individual prescriptions from healthcare providers.
Quality assurance is substantially higher than research peptide suppliers. However, compounding pharmacies are not identical to pharmaceutical manufacturers. Recent regulatory attention has highlighted quality issues at some facilities, leading to increased oversight.
Accessing compounding pharmacy peptides requires a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. This adds cost through consultation fees but also provides medical oversight for your peptide use. Many online peptide therapy providers now offer telemedicine consultations that streamline this process.
Pharmaceutical products
FDA-approved peptide medications offer the highest quality assurance and clearest legal status. They also carry the highest prices.
Pharmaceutical peptides undergo extensive clinical testing before approval. Manufacturing facilities face rigorous FDA inspection. Every batch undergoes quality testing before release. Consistency is guaranteed.
The trade-off is cost. Brand-name semaglutide costs $900 to $1,300 monthly. That price reflects billions in R&D investment, clinical trial expenses, and the marketing infrastructure pharmaceutical companies maintain.
Insurance coverage can dramatically change this equation. If your insurance covers peptide medications, out-of-pocket costs may drop to $25 to $100 monthly, making pharmaceutical options the best value. Without insurance, they remain the most expensive option.
International sources
Overseas peptide suppliers, particularly from Asia, offer dramatically lower pricing. The same peptide that costs $50 domestically might run $15 to $25 internationally.
Quality varies enormously. Some international manufacturers maintain standards equivalent to domestic suppliers. Others operate with minimal quality control. Without physical inspection or verified testing, buyers cannot easily distinguish between these options.
Customs and import regulations add uncertainty. While small personal-use quantities typically pass through without issue, shipments may be seized or delayed. International shipping also exposes peptides to temperature fluctuations that can cause degradation.
The cost savings must be weighed against quality uncertainty, shipping risks, and the hassle of potential customs issues. For some peptides and buyers, international sourcing makes sense. For others, domestic options provide better overall value despite higher pricing.
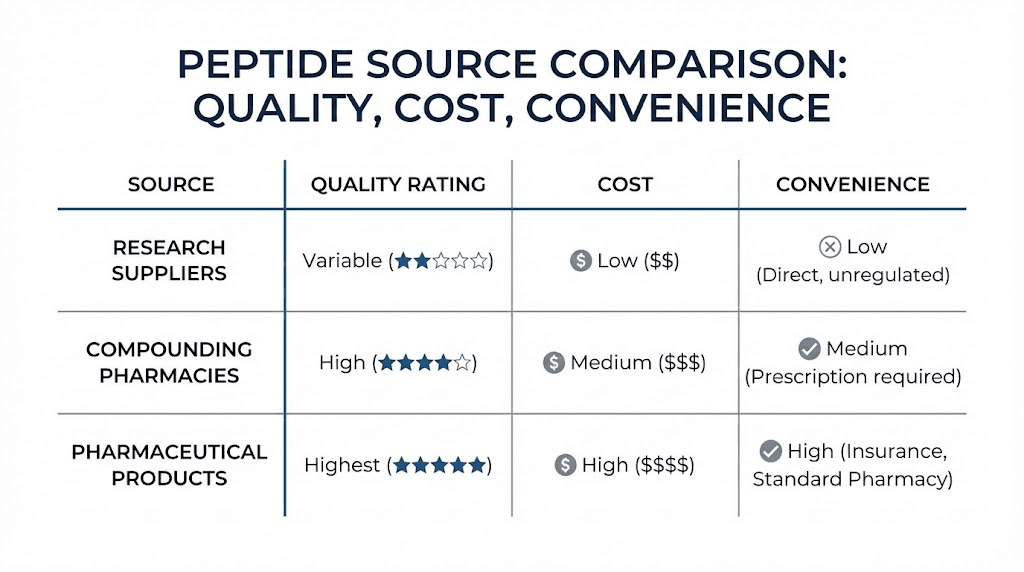
Calculating your actual protocol costs
Theoretical pricing only matters when translated into actual protocol expenses. The peptide cost calculator helps with precise calculations, but understanding the methodology helps you verify results and plan budgets.
Determining dosage requirements
Protocol costs depend primarily on dosage. Higher doses consume more peptide per week, increasing costs proportionally. The peptide dosing guide provides standard ranges for common peptides.
Body weight influences dosing for most peptides. A 200-pound person may require twice the dose of a 100-pound person to achieve equivalent effects. Calculate your dose based on current body weight, not target weight.
Protocol phase also matters. Loading phases typically use higher doses than maintenance phases. Front-loading costs may be 2x to 3x higher than ongoing maintenance costs. Factor this into total protocol budgeting.
Calculating vials needed
Once you know your daily or weekly dose, calculate total peptide requirements for your planned protocol duration.
Example calculation for BPC-157:
Protocol: 250mcg twice daily for 8 weeks
Daily dose: 500mcg (0.5mg)
Weekly dose: 3.5mg
8-week total: 28mg
Vials needed: 6 x 5mg vials or 3 x 10mg vials
At $40 per 5mg vial, total cost = $240
At $70 per 10mg vial, total cost = $210
Larger vial sizes typically offer better value per milligram. However, reconstituted peptides have limited stability. If you cannot use a 10mg vial before it degrades, smaller vials waste less peptide despite higher per-milligram costs. Reconstituted peptide stability guides these decisions.
Adding reconstitution supplies
Peptide protocols require more than just peptides. Bacteriostatic water for reconstitution, insulin syringes for injection, alcohol swabs for sterilization, and proper storage containers all add to total protocol costs.
Reconstitution supplies typically cost $20 to $50 for a full protocol. This includes a 30mL vial of bacteriostatic water ($10 to $20), a box of insulin syringes ($8 to $15), and alcohol swabs ($5 to $10).
These supplies are reusable across multiple peptides and protocols. Once you have established a supply kit, ongoing costs drop to essentially just peptide replacement.
Accounting for waste and errors
Real-world protocols rarely achieve 100% efficiency. Some peptide is lost during reconstitution. Some is lost when drawing from vials. Occasional errors require discarding compromised doses.
Budget approximately 10% to 15% additional peptide beyond theoretical requirements. This buffer accounts for normal losses and provides flexibility if you decide to extend your protocol or adjust dosing.
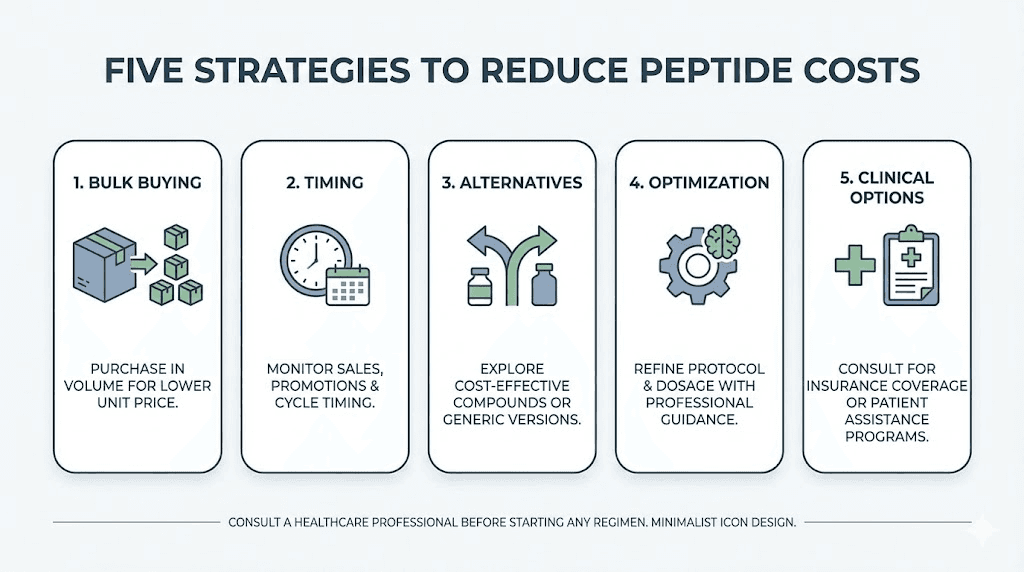
Strategies to reduce peptide costs
Smart purchasing strategies can reduce peptide expenses by 20% to 50% without sacrificing quality. These approaches require more planning but deliver meaningful savings.
Buying in bulk
Volume purchases offer the most straightforward savings. Most suppliers discount 10% to 20% for orders of 5 or more vials. Some offer even deeper discounts for larger quantities.
This strategy works best for peptides you plan to use long-term. BPC-157, TB-500, and growth hormone peptides often become staples in ongoing optimization protocols. Buying a 6-month supply upfront locks in savings and ensures you have stock available.
Bulk buying risks include peptide degradation if storage is suboptimal and tying up cash in inventory. Proper peptide storage mitigates degradation concerns. Only bulk buy amounts you can use within the peptide stability window.
Timing purchases strategically
Peptide suppliers run sales around holidays and during slower business periods. Black Friday, end-of-year clearances, and summer slowdowns often bring 15% to 30% discounts.
Signing up for supplier newsletters provides advance notice of sales. Some suppliers offer loyalty programs with ongoing discounts for repeat customers. These small savings compound over time.
Avoid panic buying during supply crunches. When a peptide becomes temporarily scarce, prices spike and quality often suffers as marginal suppliers enter the market. If possible, maintain buffer inventory to ride out supply disruptions.
Choosing cost-effective alternatives
Multiple peptides often address similar goals at different price points. Selecting more affordable options that still meet your needs reduces costs without compromising results.
For growth hormone support, Ipamorelin costs less than Tesamorelin while providing solid GH release for most users. Unless you specifically need Tesamorelin for its FDA-approved indication, Ipamorelin offers better value.
For healing support, BPC-157 alone may suffice for minor injuries. Adding TB-500 makes sense for more significant tissue damage. Adding GHK-Cu further enhances results but also increases cost. Match protocol intensity to actual need rather than defaulting to maximum stacks.
For weight loss, AOD-9604 costs a fraction of semaglutide. It works through different mechanisms and may not produce equivalent results, but for some users it provides meaningful support at dramatically lower cost.
Optimizing protocol efficiency
Maximizing results from each dollar spent involves more than just buying cheaper peptides. Protocol optimization ensures you extract full value from your investment.
Proper storage prevents degradation that wastes peptide. Correct reconstitution avoids losses. Optimal injection technique ensures full dose delivery. Each improvement in protocol execution translates to better results per dollar spent.
Timing peptide administration for maximum effect also improves efficiency. Growth hormone peptides work best on an empty stomach. Peptide timing protocols optimize the body response to each dose.
Stacking synergistic peptides can improve cost-efficiency even when total spending increases. Two peptides that enhance each other results may deliver more value than higher doses of a single peptide at the same total cost.
Exploring clinical alternatives
For some users, clinical peptide programs offer better value despite higher sticker prices.
Telemedicine peptide clinics have compressed costs dramatically. Initial consultations that once required in-person visits now happen via video call for $50 to $150. Prescription peptides ship directly to your door.
Insurance coverage, where available, transforms the value equation. If your plan covers semaglutide, your $25 copay beats any research peptide alternative. Check with your insurer about peptide coverage before assuming you must pay out of pocket.
HSA and FSA funds can cover peptide therapy expenses. Using pre-tax dollars effectively provides a 25% to 35% discount depending on your tax bracket. These accounts represent underutilized resources for peptide budgeting.
Hidden costs to consider
Sticker prices tell only part of the story. Several hidden costs affect total peptide investment. Accounting for these ensures accurate budgeting.
Consultation and monitoring
Clinical peptide programs include professional oversight in their pricing. Self-directed protocols require separate arrangements for medical guidance.
Initial consultations with peptide-knowledgeable physicians cost $100 to $300. Some users skip this step, but having medical input on protocol design and monitoring provides valuable safety and optimization guidance.
Ongoing blood work to monitor peptide effects adds $100 to $500 per test depending on panel comprehensiveness. Growth hormone peptides warrant IGF-1 testing. Weight loss peptides warrant metabolic panels. Testing ensures peptides are working and not causing unintended effects.
Supplies and equipment
Beyond basic reconstitution supplies, some protocols require additional equipment.
Proper refrigeration for peptide storage matters if your standard refrigerator experiences temperature fluctuations. A dedicated mini-fridge with stable temperatures costs $50 to $150 but protects your peptide investment.
Sharps disposal containers run $10 to $20 and represent both a safety and legal requirement in many jurisdictions. Used syringes cannot go in regular trash.
Travel cases for peptide transport cost $20 to $50 if you need to maintain protocols while away from home.
Time investment
Peptide protocols require time that carries implicit cost. Reconstitution, injection preparation, and actual administration take 5 to 15 minutes per dose. Multiple daily doses add up.
Research time is substantial for self-directed protocols. Understanding mechanisms, optimal dosing, timing, and potential interactions requires hours of reading and learning. SeekPeptides members access curated information that reduces this research burden significantly.
Protocol tracking and adjustment adds ongoing time commitment. Monitoring results, tweaking doses, and troubleshooting issues requires consistent attention over protocol duration.
Opportunity costs
Money spent on peptides cannot be spent elsewhere. Consider what else those funds could accomplish.
Sometimes basic interventions provide better value than peptides. Optimizing sleep, nutrition, and exercise often delivers more results per dollar than any peptide. Peptides work best as enhancement to already-solid fundamentals, not as substitutes for them.
Some users would benefit more from professional coaching, gym membership upgrades, or nutrition consulting than from additional peptides. Evaluate your complete optimization portfolio, not just peptide spending in isolation.
Cost comparison by peptide category
The following tables summarize typical costs across peptide categories. Use these as reference points when planning protocols and comparing options.
Healing and recovery peptides
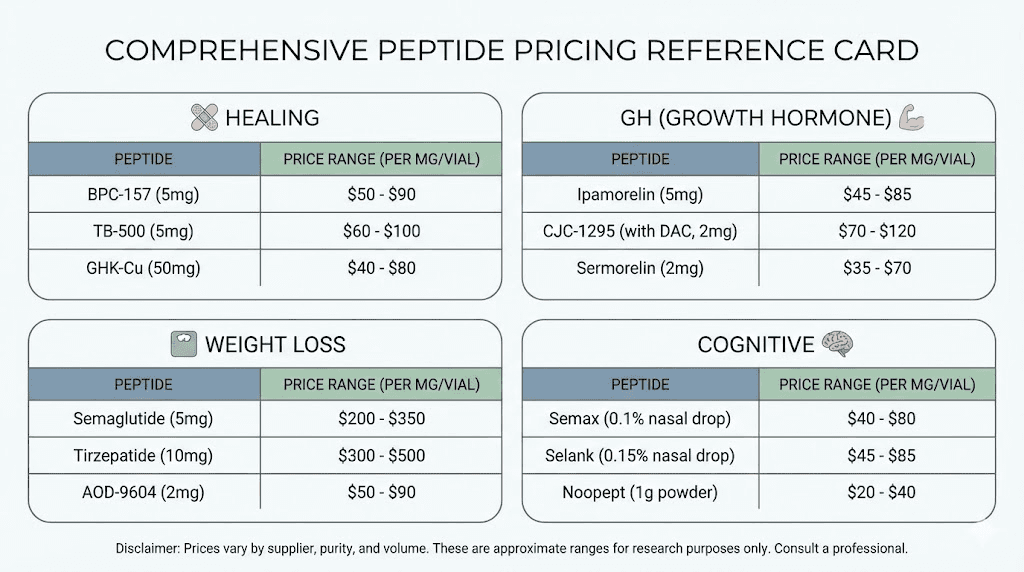
Peptide | Research Price (per vial) | Clinical Price (monthly) | Typical Protocol Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
$25-$80 (5mg) | $200-$400 | 4-8 weeks | |
TB-500 | $40-$100 (5mg) | $250-$450 | 8-12 weeks |
$50-$120 (50mg) | $300-$600 | 4-12 weeks | |
$50-$100 | $200-$400 | 4-8 weeks | |
Thymosin Alpha-1 | $70-$150 | $400-$800 | 4-12 weeks |
Growth hormone peptides
Peptide | Research Price (per vial) | Clinical Price (monthly) | Typical Protocol Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
$35-$75 (5mg) | $150-$300 | 3-6 months | |
$50-$100 (5mg) | $200-$400 | 3-6 months | |
$50-$90 | $175-$400 | 3-6 months | |
Tesamorelin | $100-$200 (2mg) | $800-$1,500 | 3-6 months |
$40-$90 | $200-$400 | 4-8 weeks |
Weight loss peptides
Peptide | Research Price | Clinical/Rx Price (monthly) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Semaglutide | Limited availability | $200-$500 (compounded) / $900-$1,300 (brand) | Insurance may cover |
Tirzepatide | Limited availability | $300-$600 (compounded) / $1,000-$1,500 (brand) | Supply constrained |
$40-$90 (5mg) | $200-$400 | Widely available | |
Retatrutide | $150-$300 | Not yet widely available | Emerging option |
Cognitive and longevity peptides
Peptide | Research Price (per vial) | Clinical Price (monthly) | Typical Protocol Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
$40-$80 | $150-$350 | Ongoing or cycled | |
Selank | $40-$90 | $150-$350 | Ongoing or cycled |
$80-$150 | $200-$400 | 10-20 day cycles | |
$100-$200 | $400-$800 | Variable | |
$100-$200 | $400-$800 | Variable |
Frequently asked questions
What is the cheapest way to get peptides?
Research-grade peptides from reputable online suppliers offer the lowest prices. A budget approach using research-grade compounds costs 60% to 80% less than clinical alternatives. However, cheaper is not always better. Quality verification through third-party testing is essential regardless of price point. The cheapest option that fails to deliver results provides no value. Balance cost against quality assurance.
Why do clinical peptides cost so much more than research peptides?
Clinical peptides include pharmaceutical-grade manufacturing, sterility testing, quality assurance protocols, medical oversight, and regulatory compliance. These add substantial costs that research suppliers do not bear. Clinical pricing also reflects the convenience of having peptides prepared to your prescription, shipped ready to use, with professional support available if issues arise. The premium pays for safety infrastructure and accountability.
Does insurance cover peptide therapy?
Most insurance plans do not cover peptide therapy for general wellness purposes. However, FDA-approved peptides prescribed for specific medical conditions may receive partial or full coverage. Semaglutide for diabetes or weight management may be covered. Growth hormone for documented deficiency may be covered. Check with your specific insurance carrier about coverage for your intended peptide use. HSA and FSA funds can typically be used for peptide expenses regardless of insurance coverage status.
How much does a typical peptide cycle cost?
Costs vary enormously based on peptide selection and protocol duration. A basic BPC-157 healing cycle runs $75 to $250 research-grade over 8 weeks. A comprehensive growth hormone peptide stack runs $300 to $700 research-grade over 3 months. Weight loss protocols using compounded semaglutide run $600 to $1,500 for 3 months. Anti-aging stacks can exceed $1,000 for comprehensive protocols. Use the peptide cost calculator for personalized estimates.
Are expensive peptides better than cheap ones?
Price alone does not determine quality. Some expensive peptides are overpriced. Some budget peptides maintain excellent quality. The key factors are purity verification through third-party testing, proper storage and shipping protocols, and supplier reputation within the research community. A $40 vial from a reputable supplier with verified 99% purity beats a $30 vial from an unknown source with no testing documentation. Focus on quality indicators rather than price alone.
How can I verify peptide quality before buying?
Request certificates of analysis showing third-party purity testing. Check supplier reputation in peptide research forums. Look for detailed product information including synthesis method and storage requirements. Reputable suppliers welcome questions about their quality control. Red flags include unwillingness to provide testing documentation, prices dramatically below market rates, and lack of professional customer service. When in doubt, independent testing through peptide testing services can verify what you receive.
Should I buy peptides in bulk to save money?
Bulk buying makes sense for peptides you plan to use long-term at stable doses. The 10% to 20% bulk discount compounds into meaningful savings over time. However, only buy quantities you can use within the peptide stability window. Lyophilized peptides typically remain stable for 2 to 3 years with proper storage. Reconstituted peptides last 4 to 8 weeks refrigerated. Do not bulk buy beyond what you can use before degradation occurs.
What hidden costs should I budget for?
Beyond peptide costs, budget for bacteriostatic water ($10-$20), insulin syringes ($8-$15), alcohol swabs ($5-$10), and proper storage if needed. Blood work for monitoring adds $100-$500 depending on panel comprehensiveness. Initial medical consultation runs $100-$300 if you seek professional guidance. Total ancillary costs typically add 15% to 25% to base peptide expenses.
Making informed peptide investment decisions
Peptide costs represent an investment in your health optimization goals. Like any investment, returns depend not just on what you spend but on how strategically you allocate resources.
Start by clarifying your actual goals. Vague objectives lead to unfocused spending. Specific goals enable targeted protocols that maximize results per dollar. Someone wanting faster injury recovery needs different peptides than someone pursuing longevity. Someone with $200 monthly budget needs different strategies than someone with $1,000.
Match protocol intensity to goal importance and timeline. Aggressive protocols make sense for acute needs. Maintenance protocols work for ongoing optimization at lower cost. Periodizing between intensive and maintenance phases optimizes both results and expenses.
Track your results systematically. Subjective improvements matter, but objective measurements provide clearer feedback on what is working. Blood markers, body composition measurements, performance metrics, and recovery times all provide data points. If expensive peptides are not producing measurable improvements, reassess rather than continuing to spend.
Build knowledge that reduces future costs. Understanding mechanisms helps you select appropriate peptides. Understanding protocol optimization helps you extract maximum value from each purchase. Understanding your individual response patterns helps you refine protocols over time. SeekPeptides members accelerate this learning through comprehensive educational resources and community knowledge sharing.
Consider peptides as one component of your overall optimization strategy. The most effective approach integrates peptides with nutrition, training, sleep, and stress management. Spending $500 monthly on peptides while neglecting $50 worth of basic supplements or $100 monthly on quality food undermines your investment. Optimize the foundation before adding advanced interventions.
Peptide costs will likely decrease over time as manufacturing improves and competition increases. Prices that seem high today may look reasonable in five years. At the same time, regulatory changes could restrict availability or increase costs for certain peptides. Build protocols around compounds with stable supply chains when possible.
The right peptide investment is one that delivers meaningful results within your budget constraints while maintaining appropriate quality and safety standards. Neither the cheapest option nor the most expensive option is automatically correct. The optimal choice balances efficacy, cost, quality, and personal priorities in ways unique to your situation.
For researchers serious about optimizing their peptide protocols while managing costs effectively, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available. Members access detailed cost calculators, budget optimization guides, vendor comparisons, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions.
External resources
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your peptide investments stay strategic, your protocols stay optimized, and your results stay measurable.



