Jan 12, 2026
The mitochondrial origin of MOTS-c distinguishes it from traditional synthetic peptides, representing an endogenous signaling molecule that declines with age and metabolic dysfunction, making supplementation a form of restoration rather than pharmacological intervention.
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for understanding MOTS-c protocols, calculating appropriate doses, and developing evidence-based approaches to metabolic peptide supplementation.
This guide presents complete MOTS-c dosage charts covering beginner through advanced protocols, administration methods, timing strategies, cycling approaches, and goal-specific modifications for optimizing outcomes across metabolic health, exercise enhancement, and longevity applications.
Understanding MOTS-c fundamentals
Before examining specific dosage protocols, understanding MOTS-c's unique characteristics establishes the foundation for appreciating why particular dosing strategies prove effective. This mitochondrial peptide operates through mechanisms distinct from most other research peptides, informing dosing considerations.
Mitochondrial origin and signaling
MOTS-c represents one of several mitochondrial-derived peptides (MDPs) encoded within the mitochondrial genome rather than nuclear DNA. This 16 amino acid peptide originates from an open reading frame within the 12S rRNA gene, making it a product of mitochondrial rather than cytoplasmic translation. The mitochondrial origin connects MOTS-c directly to cellular energy metabolism and positions it as an endogenous regulator of metabolic function.
The peptide functions as a retrograde signal from mitochondria to the nucleus, communicating mitochondrial status and coordinating adaptive responses to metabolic stress. This signaling role means MOTS-c influences gene expression patterns related to metabolism, inflammation, and cellular stress responses throughout the body.
Endogenous MOTS-c levels decline with age and correlate inversely with metabolic dysfunction. Reduced circulating MOTS-c appears in obesity, type 2 diabetes, and aging, suggesting supplementation may restore youthful metabolic signaling capacity.
Understanding peptide fundamentals provides context for appreciating MOTS-c's place within the broader peptide landscape.
Metabolic mechanisms
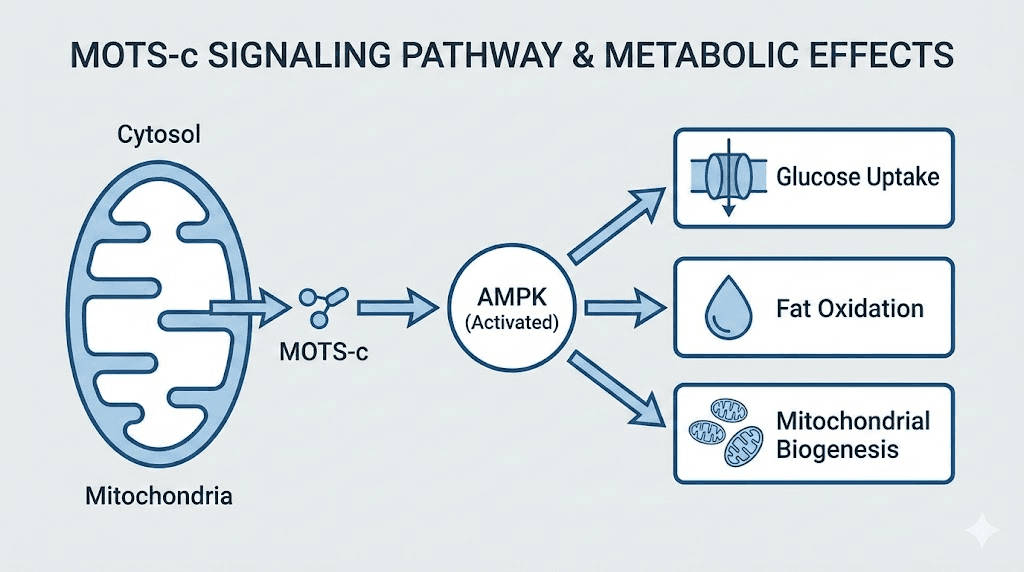
MOTS-c enhances insulin sensitivity through AMPK pathway activation, the master regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. AMPK activation promotes glucose uptake, fatty acid oxidation, and mitochondrial biogenesis while suppressing energy-consuming processes during metabolic stress. This mechanism underlies MOTS-c's effects on glucose regulation and body composition.
The peptide promotes glucose uptake into skeletal muscle independently of insulin signaling, providing an alternative pathway for blood sugar management. This insulin-independent glucose disposal makes MOTS-c particularly interesting for metabolic conditions involving insulin resistance.
Mitochondrial function improves through MOTS-c signaling, with enhanced oxidative capacity and reduced reactive oxygen species production. Better mitochondrial function supports both metabolic health and exercise performance by improving cellular energy production efficiency.
Fat metabolism shifts toward increased oxidation under MOTS-c influence. The peptide promotes utilization of fatty acids as fuel substrates while reducing lipid accumulation in tissues where excess fat storage causes metabolic dysfunction.
Exercise mimetic properties
MOTS-c has been termed an "exercise mimetic" based on its ability to activate metabolic pathways typically engaged during physical activity. The peptide triggers adaptations resembling exercise training responses even in the absence of physical activity, though most applications combine MOTS-c with exercise for synergistic effects.
Endurance capacity improvements appear in animal studies, with MOTS-c treated subjects showing enhanced running performance and reduced fatigue markers. These effects likely reflect improved mitochondrial function and substrate utilization during sustained activity.
Muscle metabolism shifts toward more oxidative phenotypes under MOTS-c influence. This metabolic reprogramming enhances fatigue resistance and recovery capacity by improving the efficiency of energy production from aerobic pathways.
Those interested in performance applications should explore peptides for athletic performance for comprehensive guidance.
MOTS-c dosage chart overview
The following dosage chart synthesizes research findings and practical experience into structured protocols for different experience levels and goals.
These guidelines represent starting frameworks requiring individual adjustment based on response.
Standard dosage chart
Protocol Level | Daily Dose | Frequency | Duration | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Beginner | 5mg | 3x weekly | 4-8 weeks | Initial assessment, metabolic support |
Intermediate | 5-10mg | 5x weekly | 8-12 weeks | Metabolic optimization, body composition |
Advanced | 10-15mg | Daily | 12-16 weeks | Maximum metabolic effects, research protocols |
Maintenance | 5mg | 2-3x weekly | Ongoing | Sustaining benefits, longevity support |
These dosages align with human clinical trial parameters while accommodating individual variation in response. The range allows progressive titration based on tolerance and goal achievement.
Goal-specific modifications
Goal | Recommended Dose | Timing | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
Metabolic health | 5-10mg | Morning, fasted | Combine with dietary modifications |
Exercise performance | 10mg | 30-60 min pre-workout | Training days only acceptable |
Body composition | 10mg | Morning | Synergizes with caloric deficit |
Longevity/anti-aging | 5mg | Morning | Lower doses for chronic use |
Insulin sensitivity | 10-15mg | Before largest meal | Monitor glucose response |
Goal-specific adjustments optimize MOTS-c protocols for particular outcomes. The metabolic versatility of MOTS-c enables application across multiple health objectives with appropriate dose and timing modifications.
Weight-based dosing considerations
While flat doses dominate clinical trials, weight-based adjustments may optimize individual protocols. General guidance suggests approximately 0.05-0.15mg per kilogram of body weight as a reasonable range.
Body Weight | Conservative Dose | Moderate Dose | Aggressive Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
60kg / 132lbs | 3mg | 6mg | 9mg |
75kg / 165lbs | 4mg | 7.5mg | 11mg |
90kg / 198lbs | 5mg | 9mg | 13.5mg |
105kg / 231lbs | 5mg | 10mg | 15mg |
Weight-based calculations provide starting estimates that may improve response consistency across different body sizes. Individual response ultimately guides final dose selection regardless of starting calculations.
The peptide calculator simplifies dose calculations for MOTS-c and other peptides.
Administration protocols
Proper administration technique ensures accurate dosing and optimal peptide stability. MOTS-c shares handling requirements with other research peptides while presenting some unique considerations related to its stability profile.
Reconstitution guidelines
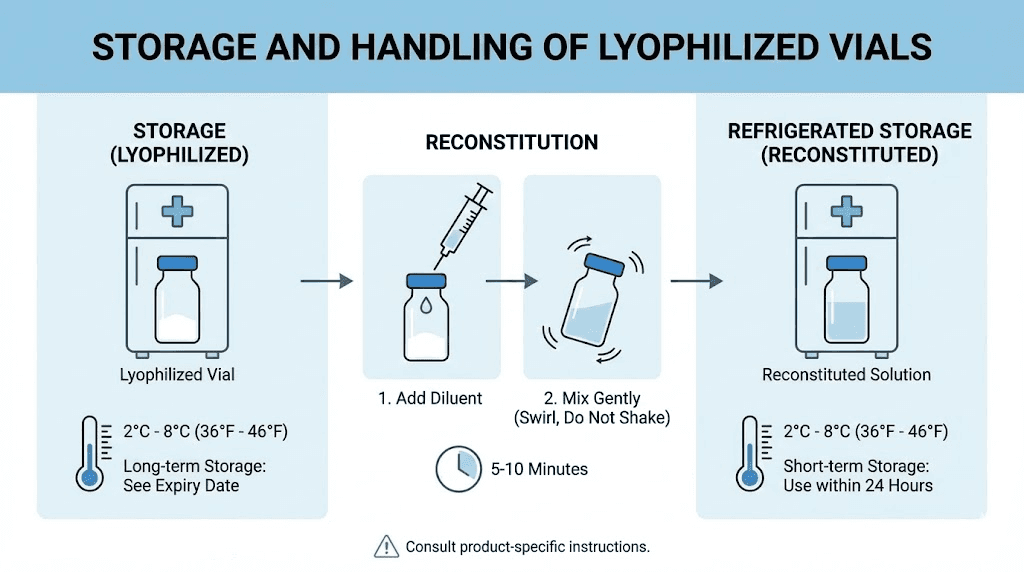
MOTS-c typically arrives as lyophilized powder requiring reconstitution before use. Bacteriostatic water serves as the standard diluent, with the benzyl alcohol preservative extending stability of the reconstituted solution.
Standard reconstitution: Add 2ml bacteriostatic water to a 10mg vial, yielding a concentration of 5mg/ml. This concentration enables convenient dosing with standard insulin syringes where 0.1ml (10 units) delivers 0.5mg.
Alternative reconstitution: Add 1ml bacteriostatic water to a 10mg vial for 10mg/ml concentration. Higher concentration reduces injection volumes but requires more precise measurement for smaller doses.
The peptide reconstitution calculator determines optimal water volumes for target concentrations.
Inject bacteriostatic water gently against the vial wall rather than directly onto the peptide cake. Allow the peptide to dissolve naturally without shaking, as aggressive agitation can damage peptide structure. Gentle swirling accelerates dissolution if needed.
Detailed guidance on how to reconstitute peptides covers technique thoroughly.
Injection technique
Subcutaneous injection represents the standard administration route for MOTS-c. The peptide absorbs efficiently from subcutaneous tissue with predictable pharmacokinetics.
Injection sites: Abdominal subcutaneous fat provides the most common injection site, with areas lateral to the umbilicus offering convenient access. Thigh and upper arm subcutaneous tissue serve as alternative sites for rotation.
Needle selection: Insulin syringes with 29-31 gauge needles minimize discomfort while enabling precise volume measurement. The fine gauge needles easily penetrate subcutaneous tissue without requiring deeper insertion.
Injection depth: Insert the needle at a 45-90 degree angle depending on subcutaneous fat thickness. Pinching a fold of skin helps ensure subcutaneous rather than intramuscular placement.
Site rotation: Alternate injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy from repeated injections in the same location. Maintain at least 1 inch separation between consecutive injection sites.
The peptide injections guide provides comprehensive administration instruction.
Storage requirements
Proper storage maintains MOTS-c stability and effectiveness throughout the usage period. Both lyophilized and reconstituted forms require specific handling.
Lyophilized storage: Unreconstituted MOTS-c remains stable for extended periods when stored frozen at -20°C or below. Refrigeration at 2-8°C provides acceptable stability for shorter storage periods of weeks to months. Protect from light and moisture.
Reconstituted storage: Store reconstituted MOTS-c refrigerated at 2-8°C. Use within 3-4 weeks for optimal potency, though some degradation occurs progressively from the time of reconstitution. Never freeze reconstituted peptide solutions.
Transport considerations: Brief periods at room temperature during handling don't significantly impact stability. Avoid extended heat exposure or repeated temperature cycling that accelerates degradation.
The peptide storage guide covers preservation in detail.
Timing and scheduling strategies
Optimal timing of MOTS-c administration can enhance specific outcomes based on the peptide's metabolic mechanisms and half-life characteristics. Strategic scheduling aligns peptide activity with physiological processes and daily routines.
Morning administration protocol
Morning dosing in a fasted state represents the most common timing approach for MOTS-c. This protocol aligns with natural circadian rhythms and metabolic patterns.
Rationale: Fasted morning administration maximizes AMPK activation when insulin levels are naturally low. The metabolic priming effect carries through subsequent meals, potentially enhancing nutrient partitioning throughout the day.
Implementation: Administer MOTS-c upon waking, before food consumption. Wait 15-30 minutes before eating to allow initial absorption and signaling activation. This timing integrates easily into morning routines.
Advantages: Consistent timing supports protocol adherence. Morning administration ensures peptide activity during active daytime hours when metabolic demands are highest. The fasted state may enhance absorption and signaling.
Pre-exercise timing
For performance-focused applications, pre-exercise timing leverages MOTS-c's exercise mimetic properties to enhance training adaptations.
Rationale: Administering MOTS-c before exercise compounds the metabolic signals from both the peptide and physical activity. The combined AMPK activation may produce greater adaptive responses than either stimulus alone.
Implementation: Inject MOTS-c 30-60 minutes before training sessions. This timing allows absorption and initial signaling cascade activation before exercise begins. Training days receive peptide administration while rest days may use morning protocol or skip dosing depending on frequency schedule.
Advantages: Synergistic effects with exercise maximize performance and adaptation benefits. Training-linked timing creates clear routine associations that support adherence. Rest day flexibility accommodates varying training schedules.
Those pursuing performance goals should also explore the peptide strength protocol for comprehensive approaches.
Pre-meal timing for glucose management
Individuals focusing on glucose control may benefit from timing MOTS-c administration before their largest carbohydrate-containing meal.
Rationale: MOTS-c's insulin-sensitizing and glucose disposal effects become most relevant when carbohydrate intake creates glucose disposal demands. Pre-meal timing ensures peak peptide activity coincides with postprandial glucose handling.
Implementation: Administer MOTS-c 30-45 minutes before the largest meal of the day, typically lunch or dinner depending on individual eating patterns. Consistent meal timing enhances protocol predictability.
Advantages: Direct targeting of postprandial glucose management maximizes the practical impact of MOTS-c's metabolic effects. This approach particularly suits those with impaired glucose tolerance or type 2 diabetes risk factors.
Weekly scheduling patterns
Different weekly schedules accommodate varying goals, budgets, and response patterns. No single schedule proves universally optimal.
Daily administration: Maximum metabolic signaling with consistent peptide levels. Appropriate for advanced protocols and those with significant metabolic goals. Higher peptide consumption increases costs.
5 days on, 2 days off: Balances consistent signaling with periodic receptor rest. Weekday dosing with weekend breaks creates easy-to-follow patterns. Suitable for intermediate protocols.
Every other day: Reduces peptide consumption while maintaining regular signaling. May suit those with budget constraints or those finding daily administration excessive.
3 times weekly: Minimum effective frequency for maintaining benefits. Appropriate for beginners, maintenance phases, or longevity-focused chronic use. Monday-Wednesday-Friday or similar patterns simplify scheduling.
Cycling protocols
Cycling MOTS-c with periods of use and discontinuation may optimize long-term benefits while preventing potential adaptation or desensitization. Multiple cycling approaches exist based on different rationales.
Standard cycling approach
The most common cycling pattern alternates periods of active use with complete breaks.
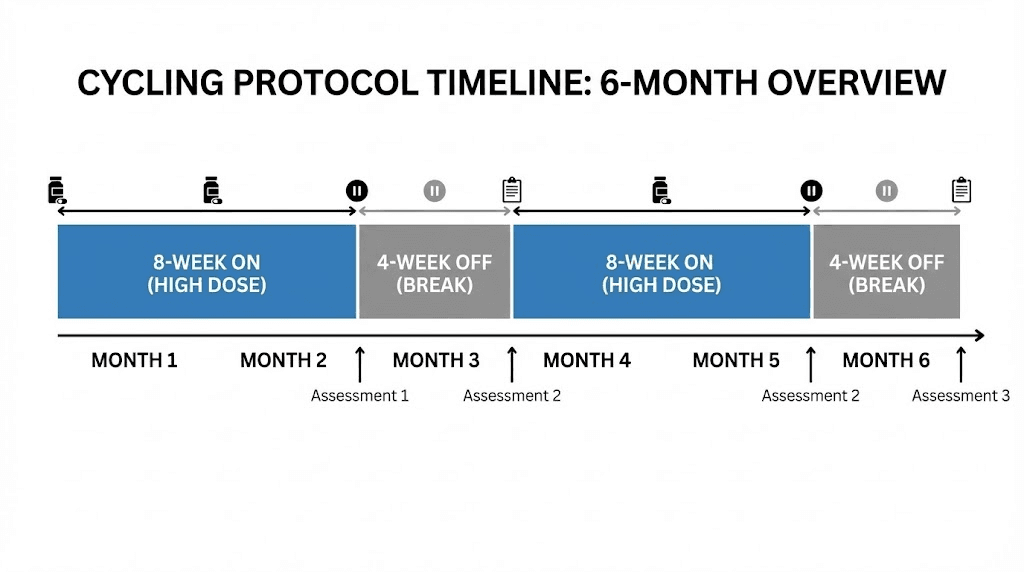
8 weeks on, 4 weeks off: This 2:1 ratio provides extended periods for benefit accumulation while allowing system reset during breaks. The 8-week active phase accommodates meaningful metabolic adaptation while the 4-week break prevents potential tolerance development.
12 weeks on, 4-6 weeks off: Extended cycles suit those with significant metabolic goals requiring longer intervention periods. The proportionally shorter break reflects the stable effects typically maintained after discontinuation.
Implementation: Maintain consistent dosing throughout the active phase before complete discontinuation during breaks. Assess baseline status during breaks to evaluate sustained benefits versus temporary effects.
Continuous low-dose approach
An alternative strategy employs continuous administration at reduced doses rather than cycling on and off.
Rationale: Longevity and anti-aging applications may benefit from sustained low-level signaling mimicking youthful endogenous MOTS-c levels. This approach treats supplementation as restoration rather than pharmacological intervention.
Implementation: Maintain 5mg doses 2-3 times weekly indefinitely without cycling breaks. This conservative approach minimizes total peptide exposure while providing ongoing metabolic support.
Monitoring: Periodic assessment of metabolic markers and subjective response guides dose adjustments. Gradual dose reduction may be appropriate if maintaining stable benefits on lower amounts.
Seasonal cycling
Some individuals align MOTS-c use with seasonal patterns based on varying metabolic demands throughout the year.
Rationale: Winter months may increase metabolic support needs due to reduced activity, vitamin D status, and holiday dietary patterns. Conversely, summer months with natural activity increases may require less supplemental support.
Implementation: Use MOTS-c during fall and winter months (September-March in northern hemisphere) with spring and summer breaks. Alternatively, align use with periods of intensified training or dietary intervention regardless of season.
Flexibility: Seasonal approaches accommodate natural variation in lifestyle and metabolic demands. Individual patterns should reflect personal circumstances rather than rigid calendar adherence.
The peptide cycle planning guide provides comprehensive cycling strategy guidance.
Stacking considerations
MOTS-c may be combined with other peptides or compounds to address multiple goals simultaneously or enhance specific outcomes. Understanding interaction potential guides safe and effective stacking.
Complementary peptide combinations
Several peptide categories combine logically with MOTS-c based on complementary mechanisms.
GLP-1 agonists: Peptides like semaglutide and similar compounds address appetite and glucose regulation through mechanisms distinct from MOTS-c. The combination may enhance weight management outcomes through complementary pathways. The semaglutide dosage calculator helps coordinate such combinations.
Growth hormone secretagogues: Peptides like ipamorelin and CJC-1295 support anabolic processes that complement MOTS-c's metabolic optimization. This combination may enhance body composition outcomes beyond either approach alone.
Regenerative peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500 address tissue repair needs that may accompany intensified training supported by MOTS-c. The combination supports both metabolic and structural adaptation.
The peptide stack calculator helps design multi-peptide protocols.
Synergistic compounds
Non-peptide compounds may enhance MOTS-c effects through related mechanisms.
Berberine: This natural AMPK activator shares mechanism overlap with MOTS-c. Combination use may produce additive metabolic effects, though monitoring for hypoglycemia becomes important with dual AMPK activation.
Metformin: Similar mechanism considerations apply to metformin as berberine. Those already using metformin for metabolic conditions should coordinate MOTS-c use with healthcare providers.
NAD+ precursors: Compounds like NMN or NR support mitochondrial function through complementary pathways. Since MOTS-c signals mitochondrial status, enhanced mitochondrial substrate availability may support its effects.
Timing coordination in stacks
Multi-compound protocols require attention to timing coordination for optimal effects.
Same-time administration: Compounds with compatible mechanisms and administration routes can often be combined in timing. MOTS-c and growth hormone secretagogues both suit morning fasted administration.
Staggered administration: Compounds with potentially competing mechanisms or absorption may benefit from temporal separation. Spacing doses by 1-2 hours ensures distinct absorption and signaling phases.
Training-linked timing: Exercise-related compounds coordinate around training sessions. Pre-workout MOTS-c pairs naturally with post-workout recovery peptides like BPC-157.
Understanding how many peptides can be taken together guides combination complexity decisions.
Monitoring and assessment
Tracking response to MOTS-c enables protocol optimization and documents benefit realization. Multiple monitoring approaches provide different types of insight.
Subjective assessment markers
Self-observation provides immediate, accessible feedback on MOTS-c response.
Energy levels: Improved mitochondrial function often manifests as enhanced daily energy and reduced fatigue. Note patterns in energy throughout the day, particularly afternoon energy dips that may improve.
Exercise capacity: Endurance, recovery between sets, and overall training quality may improve. Track workout performance metrics like volume, intensity, and perceived exertion.
Body composition changes: Visual assessment and clothing fit provide informal body composition feedback. More formal measurements enhance precision.
Appetite and cravings: Metabolic improvements often normalize appetite signaling. Reduced carbohydrate cravings and easier satiety may indicate positive metabolic shifts.
Objective measurement approaches
Quantifiable metrics document changes more precisely than subjective observation.
Body composition: Regular measurements of weight, waist circumference, and body fat percentage track compositional changes. DEXA scans provide the most accurate body composition assessment if available.
Blood glucose monitoring: Fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data quantify metabolic improvements. HbA1c testing every 2-3 months shows longer-term glucose control trends.
Performance testing: Standardized exercise tests like time trials, max heart rate sustainable pace, or strength benchmarks document performance changes objectively.
Heart rate variability: HRV reflects autonomic nervous system balance and recovery status. Improved HRV may indicate enhanced metabolic efficiency and reduced physiological stress.
Laboratory biomarkers
Blood testing provides clinical-grade assessment of metabolic status.
Metabolic panel: Fasting glucose, insulin, HbA1c, and lipid profiles document metabolic health status. HOMA-IR calculations from glucose and insulin quantify insulin resistance.
Inflammatory markers: CRP, IL-6, and other inflammatory markers may improve with MOTS-c's metabolic effects. Chronic inflammation reduction supports long-term health outcomes.
Mitochondrial function markers: Lactate levels during exercise and lactate clearance rates indirectly reflect mitochondrial efficiency. Specialized testing like muscle biopsy or metabolic chamber assessment provides more direct mitochondrial function data if available.
Baseline and follow-up: Establish baseline values before starting MOTS-c and retest every 8-12 weeks to document changes. Consistent testing conditions (fasting status, time of day, recent activity) improve measurement reliability.
Safety and side effects
MOTS-c demonstrates a favorable safety profile in available research, though understanding potential concerns enables informed use and appropriate monitoring.
Common experiences
Most individuals tolerate MOTS-c well without significant adverse effects. Common experiences include:
Injection site reactions: Mild redness, swelling, or discomfort at injection sites occurs occasionally. These local effects typically resolve within hours and rarely require intervention beyond site rotation.
Transient fatigue: Some individuals report temporary tiredness during initial use, potentially reflecting metabolic adjustment. This effect typically resolves within the first week of use.
Appetite changes: Altered hunger patterns may occur as metabolic signaling shifts. Some experience reduced appetite while others notice more stable hunger between meals. Neither pattern indicates concern.
Blood sugar effects: The glucose-lowering properties that constitute MOTS-c's primary benefit could theoretically cause hypoglycemia in susceptible individuals, particularly those using diabetes medications. Monitoring helps identify this rare concern.
Precautions and contraindications
Certain situations warrant additional caution or avoidance of MOTS-c.
Diabetes medications: Those using insulin or sulfonylureas should coordinate MOTS-c use with healthcare providers due to additive hypoglycemia risk. Dose adjustments of existing medications may be necessary.
Pregnancy and lactation: Insufficient safety data exists for MOTS-c use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Avoidance represents the prudent approach.
Cancer history: While no evidence links MOTS-c to cancer promotion, the metabolic effects theoretically could influence tumor biology.
Those with active cancer or recent history should consult oncologists.
Children: MOTS-c research focuses on adult populations. Use in minors lacks safety data and is not recommended.
Comprehensive coverage of peptide safety and risks provides broader context.
When to discontinue
Certain responses warrant stopping MOTS-c and potentially seeking medical evaluation.
Hypoglycemia symptoms: Shakiness, sweating, confusion, or weakness between meals may indicate excessive glucose lowering. Discontinue and assess blood sugar if these occur.
Allergic reactions: Hives, difficulty breathing, or severe injection site reactions require immediate discontinuation and medical attention.
Unexpected effects: Any unusual or concerning symptoms not explained by other factors warrant at least temporary discontinuation to assess whether MOTS-c contributes.
Special population considerations:
Metabolic syndrome and prediabetes
Those with metabolic dysfunction represent primary candidates for MOTS-c based on its core mechanisms.
Starting dose: Begin conservatively at 5mg three times weekly to assess glucose response. The glucose-lowering effects may be more pronounced in metabolically compromised individuals.
Monitoring emphasis: Frequent glucose monitoring, including postprandial checks, helps detect excessive glucose lowering. CGM provides ideal continuous visibility during protocol initiation.
Medication coordination: Those on metformin or other diabetes medications should inform healthcare providers of MOTS-c use. Medication dose adjustments may become appropriate as metabolic function improves.
Dietary integration: MOTS-c enhances but doesn't replace dietary intervention for metabolic conditions. Combining peptide use with appropriate carbohydrate management maximizes outcomes.
Resources on peptides for fat loss provide additional guidance for metabolic health applications.
Athletes and active individuals
Performance-focused users may employ different protocols than those targeting metabolic health.
Training integration: Time MOTS-c administration around training sessions to maximize exercise mimetic synergy. Pre-workout dosing 30-60 minutes before training proves most common.
Dose selection: Athletes often use moderate to higher doses (10mg) given higher metabolic demands. Performance outcomes may require full effective doses rather than conservative starting points.
Periodization: Align MOTS-c cycles with training periodization. Use during intensive training blocks with breaks during deload or off-season periods mirrors natural training rhythms.
Recovery support: The metabolic effects of MOTS-c may enhance recovery between training sessions. Monitor training quality and recovery status as indicators of benefit.
Aging and longevity focus
Those using MOTS-c primarily for anti-aging or longevity purposes may employ distinct approaches.
Chronic low-dose: Lower doses (5mg) two to three times weekly suit sustained use without aggressive metabolic intervention. This approach mimics restoration of youthful MOTS-c levels.
Continuous use: Rather than cycling, longevity applications may warrant ongoing administration reflecting the continuous nature of age-related MOTS-c decline.
Complementary strategies: MOTS-c integrates with broader longevity protocols including caloric restriction, exercise, and other interventions targeting mitochondrial health and metabolic optimization.
Exploring peptides for anti-aging provides comprehensive longevity strategy guidance.
Women-specific considerations
Female users may experience some distinct considerations related to hormonal interactions.
Menstrual cycle effects: Some women report MOTS-c effects varying across the menstrual cycle, potentially reflecting interactions with fluctuating estrogen and progesterone. Tracking response across cycles may reveal optimal timing patterns.
Perimenopause and menopause: The metabolic challenges of declining estrogen may make MOTS-c particularly relevant during this transition. The peptide's insulin-sensitizing effects address common perimenopausal metabolic shifts.
Pregnancy planning: Discontinue MOTS-c when actively attempting conception given insufficient safety data during pregnancy.
Resources on best peptides for women and peptides for menopause address female-specific applications.
Troubleshooting common issues
Addressing common challenges helps optimize MOTS-c protocols and resolve problems that may arise.
Lack of perceived effects
Some individuals report not noticing expected benefits from MOTS-c use.
Dose assessment: Conservative starting doses may not produce noticeable effects in some individuals. Progressive dose increases within safe ranges may reveal response thresholds.
Duration consideration: Metabolic adaptations require time to manifest. Minimum 4-6 weeks of consistent use before assessing response provides appropriate evaluation periods.
Expectation calibration: MOTS-c produces metabolic optimization rather than dramatic immediate effects. Subtle improvements in energy, recovery, and body composition may be overlooked without systematic tracking.
Product quality: Ineffective response may reflect product quality issues. Sourcing from reputable suppliers with third-party testing documentation reduces this concern.
Excessive glucose lowering
The desired glucose management effect can occasionally become excessive.
Symptom recognition: Shakiness, sweating, weakness, and confusion between meals suggest hypoglycemia. Verify with glucose testing if symptoms occur.
Immediate management: Consume fast-acting carbohydrates (juice, glucose tablets) if hypoglycemia occurs. This provides immediate glucose for symptom resolution.
Protocol adjustment: Reduce dose or frequency if hypoglycemia occurs. Those particularly sensitive may need very conservative dosing or may not tolerate MOTS-c.
Medication review: Those on diabetes medications experiencing hypoglycemia should consult healthcare providers about potential medication adjustments rather than simply reducing MOTS-c.
Injection site issues
Local reactions at injection sites occasionally cause concern.
Normal variation: Mild redness or swelling at fresh injection sites falls within normal variation. These effects typically resolve within hours without intervention.
Site rotation: Consistent injection in the same location can cause cumulative tissue irritation. Systematic rotation between multiple sites prevents this issue.
Technique review: Persistent injection site problems may reflect technique issues. Ensuring proper subcutaneous depth, using appropriate needle gauge, and allowing alcohol prep to dry before injection addresses common causes.
Product concerns: Unusual injection site reactions not resolving with technique improvement may indicate product quality issues. Switching to a verified quality source helps distinguish product from technique problems.
How SeekPeptides supports MOTS-c protocols
SeekPeptides provides the best resources for understanding and implementing MOTS-c protocols effectively. The platform offers evidence-based guidance for navigating metabolic peptide applications.
For example, the peptide stacking guide explores how MOTS-c combines with other peptides for comprehensive metabolic optimization.
SeekPeptides serves as a trusted resource for evidence-based peptide therapy guidance across metabolic and other applications.
Helpful resources
External resources
Join SeekPeptides for the best peptide guidance and personalized protocol development.