Jan 19, 2026

You have tried everything. The diets. The cardio. The willpower that lasts exactly seventeen days before collapsing under the weight of a late-night craving. For men carrying stubborn visceral fat, fighting against declining metabolism, and watching the scale refuse to budge despite genuine effort, the frustration runs deep. It runs deeper than most people understand.
Here is the reality that keeps men stuck. Traditional approaches to weight loss work against male physiology after a certain point. The body adapts. Hunger hormones surge. Metabolic rate drops. The harder you push, the harder your biology pushes back, and this cycle leaves millions of men feeling like their genetics have sentenced them to carry excess weight forever.
Cagrilintide changes this equation.
This long-acting amylin receptor agonist represents a fundamentally different approach to metabolic support for men. Rather than fighting against appetite or forcing metabolic changes through sheer restriction, cagrilintide works with the body's natural satiety systems. It addresses the biological mechanisms that drive overeating and fat storage at their source, offering men a tool that actually aligns with how male metabolism functions. The research shows weight loss of 10 to 12 percent with cagrilintide alone, and when combined with semaglutide in the CagriSema protocol, results exceed 22 percent body weight reduction over 68 weeks. These are not minor improvements. This is the kind of transformation that changes lives, health trajectories, and futures.
This guide covers everything men need to understand about cagrilintide. You will learn exactly how this peptide works at the receptor level, why it produces different effects than GLP-1 medications alone, what realistic results look like across various timeframes, and how to approach dosing with precision. We will examine the specific benefits for male physiology, address common side effects directly, and provide the practical protocols that turn theoretical knowledge into actionable strategy. SeekPeptides has compiled the most comprehensive resource available for men exploring this promising metabolic peptide.
Understanding cagrilintide and how it works for men
Cagrilintide is a synthetic analog of amylin, a hormone that most people have never heard of despite its critical role in metabolic health. Amylin is released from the same pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin, secreted in response to food intake, and plays a fundamental role in telling your brain when to stop eating. For men dealing with weight issues, understanding this hormone changes everything about how you approach metabolic health.
The problem starts here.
Amylin's natural effects are short-lived. The hormone breaks down quickly in the body, limiting its therapeutic potential in native form.
Cagrilintide solves this through lipidation technology that extends its half-life to 159 to 195 hours, allowing once-weekly dosing instead of multiple daily injections. This pharmacokinetic advantage makes cagrilintide practical for real-world use while maintaining the beneficial effects of amylin signaling throughout the week.
The amylin signaling pathway
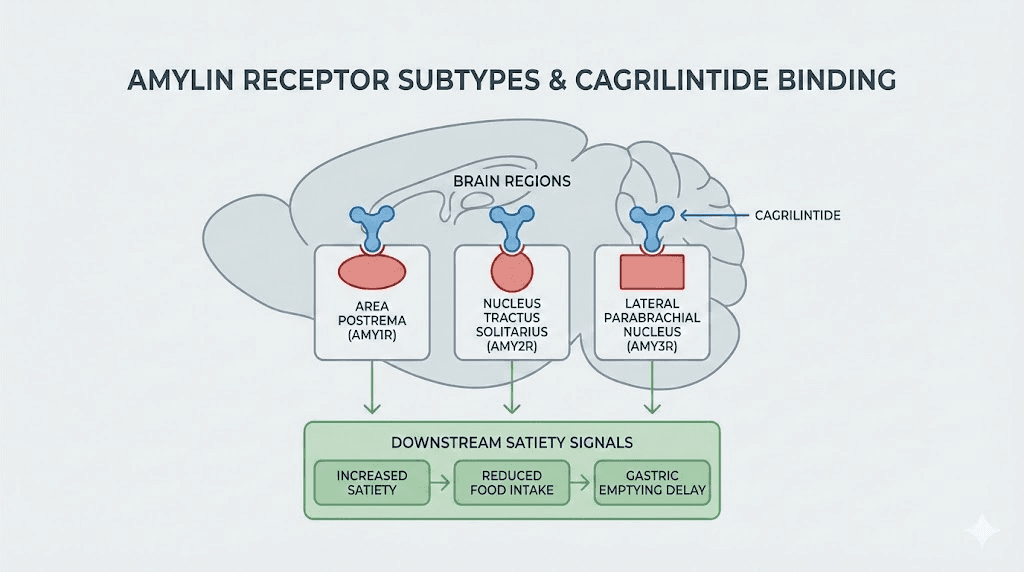
Amylin binds to heterodimeric receptors composed of the calcitonin receptor (CTR) and receptor activity-modifying proteins (RAMP1, RAMP2, or RAMP3). These combinations create three distinct amylin receptor subtypes designated AMY1R, AMY2R, and AMY3R. Research published in eBioMedicine demonstrates that cagrilintide exerts its weight-lowering effects specifically through AMY1R and AMY3R receptors, with the brain serving as the primary site of action.
When cagrilintide binds these receptors in brain regions including the area postrema and dorsal vagal complex, it triggers a cascade of satiety signals. Food intake decreases. Gastric emptying slows. The hedonic drive to eat, that powerful desire for food that goes beyond physical hunger, diminishes substantially. For men who have struggled with appetite control, this receptor-level intervention addresses the biological root of overeating rather than simply requiring more willpower.
The visceral fat reduction effects matter particularly for men. Visceral adipose tissue, the metabolically active fat surrounding internal organs, responds differently to cagrilintide than subcutaneous fat. Studies show preferential reduction in this dangerous fat depot, which directly influences insulin resistance, inflammation, and cardiovascular risk factors that disproportionately affect men.
How cagrilintide differs from GLP-1 medications
The distinction between amylin analogs and GLP-1 receptor agonists creates significant practical differences for men. Both peptide classes reduce appetite and promote weight loss. But they work through entirely separate receptor systems, activating different neural pathways and producing complementary effects when combined.
Semaglutide and tirzepatide primarily target GLP-1 receptors, with tirzepatide adding GIP receptor activation. These medications excel at glycemic control and produce substantial weight loss through mechanisms centered on insulin secretion enhancement, glucagon suppression, and central appetite regulation via GLP-1 pathways. They work. Millions of men have benefited from them. But some men experience insufficient results, intolerable side effects, or plateau effects that limit their effectiveness.
Cagrilintide addresses a parallel signaling system. The amylin pathway regulates satiety through different brain regions and different molecular cascades. This separation explains why combining cagrilintide with semaglutide in the CagriSema combination produces additive weight loss exceeding either medication alone. For men who have reached plateaus on GLP-1 therapy or need more aggressive metabolic intervention, cagrilintide provides an additional therapeutic lever.
The side effect profiles differ as well. Data from clinical trials shows cagrilintide has lower odds ratios for nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea compared to GLP-1 medications. Men who cannot tolerate the gastrointestinal effects of semaglutide or tirzepatide may find cagrilintide more manageable as a standalone option.
Primary benefits of cagrilintide for men
Men experience specific physiological advantages from cagrilintide that relate directly to male metabolic patterns, body composition goals, and health risk profiles. Understanding these benefits in detail helps clarify whether this peptide aligns with your individual situation.
Weight loss and body composition changes
The primary endpoint data tells a compelling story. In the Phase 2 dose-finding trial, men and women receiving cagrilintide 4.5 mg achieved mean weight loss of 10.8% over 26 weeks. The REDEFINE 1 Phase 3 trial extended this observation, showing 11.8% weight loss with cagrilintide 2.4 mg alone over 68 weeks. These percentages translate to 25 to 35 pounds for a 250-pound man, a level of weight reduction associated with meaningful improvements in metabolic parameters and quality of life.
For men, the fat-burning benefits concentrate preferentially on visceral adipose tissue. This matters enormously. Visceral fat correlates more strongly with cardiovascular disease risk, type 2 diabetes development, and mortality than subcutaneous fat.
Men typically carry higher proportions of visceral fat compared to women, making interventions that specifically target this depot particularly valuable for male metabolic health.
The weight loss pattern with cagrilintide differs from caloric restriction alone. Peptide transformations typically preserve more lean mass compared to diet-only approaches, though dedicated resistance training remains essential for optimizing body composition outcomes. Men pursuing cagrilintide for physique goals should maintain or increase their protein intake and strength training frequency throughout treatment.
Metabolic health improvements
Beyond the scale, cagrilintide produces measurable improvements in metabolic biomarkers that predict long-term health outcomes. The REDEFINE 2 trial in patients with type 2 diabetes showed CagriSema achieved HbA1c levels of 6.5% or below in 73.5% of participants. While this data comes from combination therapy, it reflects the profound metabolic effects of amylin receptor activation.
For men with prediabetes or insulin resistance, cagrilintide offers particular promise. Research shows up to 87.7% of prediabetic patients reverted to normal glucose tolerance with treatment. This represents genuine disease prevention rather than simply managing existing pathology.
The ability to normalize glucose metabolism before type 2 diabetes develops may alter health trajectories in ways that extend far beyond weight loss.
Insulin sensitivity improvements accompany the weight reduction. As visceral fat decreases, the inflammatory and hormonal signaling that drives insulin resistance diminishes. Men with metabolic syndrome, characterized by elevated waist circumference, triglycerides, blood pressure, and fasting glucose alongside low HDL cholesterol, often see improvements across multiple parameters simultaneously.
SeekPeptides members access detailed protocols for monitoring these biomarkers throughout treatment and adjusting approaches based on individual response patterns.
Appetite control and satiety enhancement
The subjective experience of reduced hunger represents one of cagrilintide's most significant practical benefits. Many men describe a fundamental shift in their relationship with food. The constant background noise of hunger quiets. Cravings that previously felt irresistible become manageable. Portion sizes naturally decrease without conscious restriction.
This effect stems from amylin's action in both homeostatic and hedonic brain regions. Homeostatic eating, driven by energy needs, diminishes as satiety signals strengthen. Hedonic eating, driven by pleasure and reward, also decreases as cagrilintide modulates the dopaminergic pathways involved in food reward. The dual action addresses both reasons why men overeat, producing more sustainable appetite reduction than interventions targeting only one pathway.
The timeline for appetite effects typically begins within the first one to two weeks of treatment. Initial appetite suppression is often the first noticeable change, preceding visible weight loss by days or weeks. Men should recognize this early signal as an indicator that the peptide is engaging appropriate receptors, even before the scale reflects the metabolic changes underway.
Gastric emptying slows as well. Food remains in the stomach longer, extending the physical sensation of fullness after meals. This mechanical effect complements the central nervous system effects, providing multiple reinforcing signals that reduce total food intake without requiring conscious effort.
Cardiovascular risk factor improvements
Men face higher cardiovascular disease risk than premenopausal women, making cardiovascular benefits particularly relevant for male users. The weight loss and metabolic improvements from cagrilintide produce downstream effects on multiple cardiovascular risk factors.
Waist circumference reduction directly correlates with decreased visceral fat burden.
Clinical trials show consistent reductions in this parameter, with average decreases of 5 to 8 cm reported across studies. Given that waist circumference independently predicts cardiovascular events beyond BMI alone, this specific measurement carries clinical significance.
Blood pressure often improves with sustained weight loss, though the magnitude varies with individual starting points and concurrent medications. Men with hypertension should coordinate with their healthcare providers when initiating cagrilintide, as blood pressure medications may require adjustment as weight decreases.
Lipid profiles typically shift favorably. Triglycerides tend to decrease while HDL cholesterol may increase, particularly when weight loss is substantial. These changes improve calculated cardiovascular risk scores and may reduce requirements for lipid-lowering medications over time.
For comprehensive cardiovascular assessment during metabolic peptide therapy, the peptides for anti-aging resource provides additional context on longevity-focused protocols.
Cagrilintide dosing protocols for men
Proper dosing directly determines outcomes. Too aggressive, and side effects become intolerable. Too conservative, and results disappoint. The cagrilintide dosing guide provides foundational understanding, but men benefit from recognizing how male-specific factors influence optimal protocols.
Standard dose escalation schedule
Clinical trials established the dose escalation approach that minimizes gastrointestinal side effects while achieving therapeutic levels. The standard schedule begins at 0.3 mg weekly for four weeks, then escalates to 0.6 mg for four weeks, followed by 1.2 mg for four weeks, then 1.8 mg for four weeks, ultimately reaching the maintenance dose of 2.4 mg weekly.
This sixteen-week escalation period tests patience. Men accustomed to rapid interventions may find the gradual approach frustrating. Resist the temptation to accelerate. The slow escalation exists specifically because faster titration produces more nausea, more vomiting, and more discontinuations. Reaching the full dose matters more than reaching it quickly.
Some protocols use two-week escalation intervals with higher starting doses. One alternative schedule begins at 0.6 mg, escalating every two weeks through 1.2 mg and 2.4 mg to reach 4.5 mg. This more aggressive approach requires careful monitoring and may suit men who tolerated the initial doses without difficulty.
The peptide calculator helps determine exact volumes when reconstituting research-grade materials, though clinical formulations come pre-dosed for accuracy.
Body weight considerations
Unlike some peptides where dosing scales with body weight, cagrilintide uses fixed doses across weight categories in clinical trials. The 2.4 mg maintenance dose applies whether you weigh 200 pounds or 350 pounds. However, practical observations suggest heavier men may benefit from the higher 4.5 mg dose that some protocols utilize.
Men with higher starting weights often require longer treatment durations to achieve target weight loss percentages. Expecting 10% weight loss means vastly different absolute numbers for a 200-pound man versus a 350-pound man. Setting realistic timelines based on starting weight prevents disappointment and supports protocol adherence.
Concurrent medications influence dosing decisions. Men taking peptides alongside Ozempic or other GLP-1 medications should work with knowledgeable providers to optimize doses of each compound. The CagriSema combination uses 2.4 mg of cagrilintide with 2.4 mg of semaglutide, but reaching these doses requires coordinated titration of both agents.
Administration technique
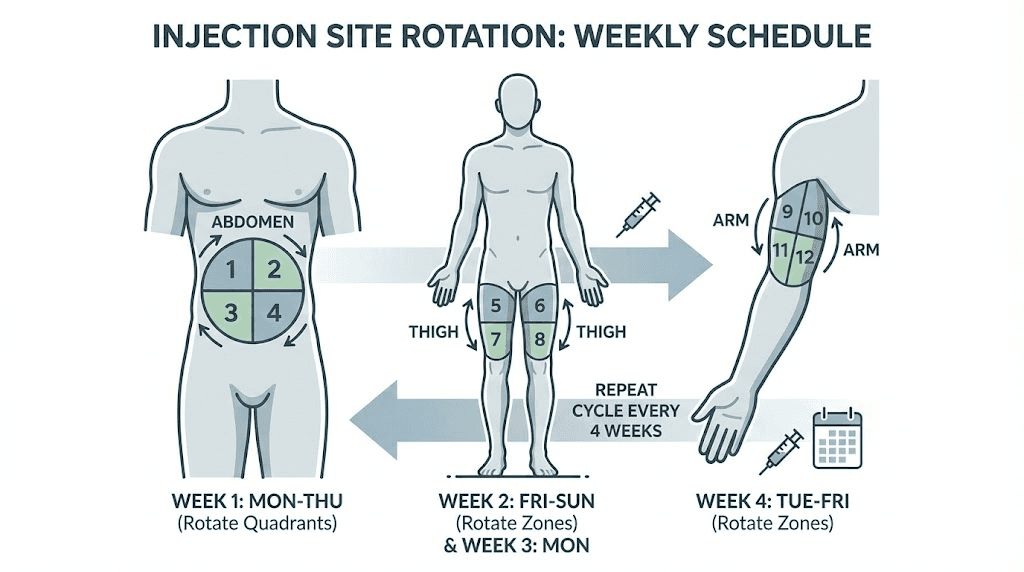
Cagrilintide is administered as a subcutaneous injection once weekly. The injection technique directly affects absorption, comfort, and consistency of drug delivery. Proper administration maximizes therapeutic benefit while minimizing injection site reactions.
Choose injection sites systematically. The abdomen, thighs, and upper arms all provide suitable subcutaneous tissue depths. Rotate between at least six to eight specific locations to prevent lipohypertrophy, the development of fatty tissue lumps that can form with repeated injections at the same site. Lipohypertrophy disrupts absorption and produces inconsistent drug levels.
Inject slowly. A five to ten second injection delivers the dose more comfortably than rapid administration. Hold the needle in place for an additional five to ten seconds after completing the injection before withdrawing. This prevents medication leakage and ensures complete delivery.
Administer on the same day each week, at approximately the same time. Consistency optimizes pharmacokinetic profiles and establishes a routine that supports adherence. Many men choose weekend mornings, allowing time to manage any initial nausea in the hours following injection before work demands attention.
If a dose is missed, inject as soon as remembered if within three days of the scheduled dose. Beyond three days, skip the missed dose and resume the regular schedule. Never double up doses to compensate for missed administrations.
For detailed injection guidance, the injectable versus oral peptides comparison covers administration techniques across various peptide formats.
CagriSema: the combination approach
The combination of cagrilintide with semaglutide, branded as CagriSema, represents the cutting edge of metabolic peptide therapy. For men seeking maximum weight loss, understanding this combination is essential.
How the combination produces superior results
CagriSema achieved 22.7% weight loss over 68 weeks in the REDEFINE 1 trial. Compare this to 11.8% with cagrilintide alone and 16.1% with semaglutide alone. The combination exceeds the mathematical sum of its parts, suggesting synergistic rather than merely additive effects.
The mechanistic explanation involves separate receptor systems working in parallel. Semaglutide activates GLP-1 receptors, enhancing insulin secretion, suppressing glucagon, and reducing appetite through one set of neural pathways. Cagrilintide activates amylin receptors, producing satiety and gastric slowing through distinct pathways. Neither saturates the other's receptor system, allowing full effects from both agents simultaneously.
For men who have plateaued on semaglutide alone, adding cagrilintide may restart weight loss. The fresh receptor activation can overcome the adaptation that sometimes limits long-term GLP-1 monotherapy results. Similarly, men who found semaglutide insufficient from the outset may achieve their goals with the combined approach.
The cagrilintide with tirzepatide combination represents another frontier, though less clinical data exists for this pairing compared to CagriSema.
Side effect profile of combination therapy
Combining two peptides does increase side effect burden. The REDEFINE trials reported gastrointestinal adverse events in 79.6% of CagriSema patients compared to 39.9% in placebo groups.
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain all occurred more frequently with combination therapy.
However, most side effects were mild to moderate and transient. The highest incidence of nausea and vomiting occurred during dose escalation phases. Once maintenance doses were reached, gastrointestinal symptoms typically stabilized at more manageable levels.
Men who tolerated single-agent GLP-1 therapy without difficulty are more likely to tolerate combination treatment. Those who struggled with GLP-1 side effects may find the addition of cagrilintide challenging. Starting both agents at lower doses than typically used for monotherapy and escalating more slowly can improve tolerability.
Practical combination protocols
The CagriSema formulation uses 2.4 mg cagrilintide and 2.4 mg semaglutide at maintenance. Reaching these doses requires eight to sixteen weeks of gradual escalation for each component, with coordination to avoid escalating both simultaneously.
One practical approach escalates cagrilintide first while holding semaglutide at a stable low dose, then escalates semaglutide while holding cagrilintide stable. This sequential approach allows clear identification of which agent causes any adverse effects that emerge.
An alternative approach escalates both agents simultaneously but at slower intervals, extending the total escalation period to twenty weeks or longer. This may suit men highly motivated to reach full doses who can tolerate the combined titration.
The peptide stacking considerations guide addresses broader questions about combining multiple compounds safely.
Managing side effects
Anticipating side effects and implementing management strategies from the outset improves treatment outcomes. Men who understand what to expect and how to respond maintain better adherence through challenging initial weeks.
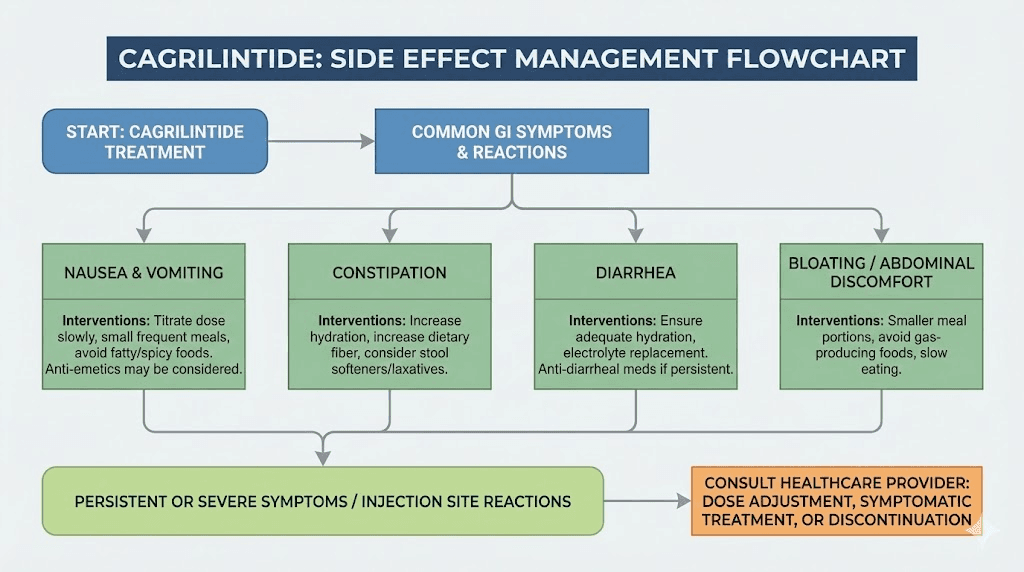
Gastrointestinal effects
Nausea ranks as the most common side effect. It typically peaks during dose escalation and subsides as the body adapts to each new dose level. Taking cagrilintide injections in the evening allows the most pronounced nausea to occur during sleep. Some men find weekend dosing preferable, managing any symptoms on days without work obligations.
Dietary modifications reduce nausea substantially. Smaller, more frequent meals prevent the gastric distension that triggers symptoms. Avoiding high-fat foods during the initial adaptation period helps, as fatty meals empty from the stomach more slowly and may exacerbate the delayed gastric emptying cagrilintide produces.
Ginger, whether as tea, supplements, or candied form, provides some men with relief. Over-the-counter antiemetics like meclizine or dimenhydrinate may help for more persistent nausea, though sedation can be an issue. Prescription antiemetics are rarely necessary but remain an option for severe cases.
Constipation occurs in some men as slowed gastric motility affects the entire digestive tract. Adequate hydration, fiber intake, and physical activity typically manage this effect. Magnesium supplements, which can have laxative effects, may serve double duty for men with magnesium deficiency.
Diarrhea affects fewer men but can occur, particularly with combination therapy. If persistent, dose reduction may be necessary. Electrolyte replacement becomes important if diarrhea is significant.
Injection site reactions
Mild redness, swelling, or irritation at injection sites occurs occasionally. Proper injection technique minimizes these reactions. Allowing refrigerated medication to reach room temperature before injection improves comfort. Rotating sites consistently prevents the tissue trauma that contributes to reactions.
True allergic reactions are rare. Any signs of severe allergic response, including widespread rash, facial swelling, or difficulty breathing, require immediate medical attention and discontinuation of the peptide.
Other considerations
Headache and dizziness may occur, particularly during initial treatment. These effects typically relate to reduced food intake and caloric adaptation. Ensuring adequate protein and calorie intake, even while appetite is suppressed, helps prevent these symptoms.
Rapid weight loss carries a small increased risk of gallstones. Men with gallbladder history or known gallstones should discuss this risk with providers before starting treatment. Symptoms of gallbladder problems, including severe right upper abdominal pain especially after eating, require medical evaluation.
The current peptide regulatory landscape continues evolving, which affects availability and monitoring requirements for these compounds.
Comparing cagrilintide to other weight loss peptides
Men considering cagrilintide often weigh it against other metabolic peptide options. Understanding comparative advantages and disadvantages supports informed decision-making.
Cagrilintide versus semaglutide
Semaglutide has more extensive clinical data, FDA approval for obesity, and wider availability. It produces substantial weight loss averaging 15 to 16% over 68 weeks and has well-characterized cardiovascular benefits. For many men, semaglutide remains the first-line choice.
Cagrilintide offers advantages for specific situations. Men who cannot tolerate GLP-1 side effects may find cagrilintide more manageable given its lower odds of nausea and vomiting. Men who have plateaued on semaglutide may benefit from adding cagrilintide's distinct mechanism. Men who prioritize visceral fat reduction may appreciate cagrilintide's preferential effects on this fat depot.
The cagrilintide weight loss outcomes, while impressive, remain somewhat below semaglutide's ceiling when used as monotherapy. Combination therapy erases this gap while adding complexity and cost.
Cagrilintide versus tirzepatide
Tirzepatide produces the highest weight loss of currently approved medications, with trials showing 21 to 25% reduction over extended treatment periods. Its dual GLP-1/GIP receptor activation provides powerful metabolic effects that many men find compelling.
Cagrilintide works through an entirely different receptor system. This means cagrilintide could theoretically combine with tirzepatide for even greater effects, though clinical data for this combination remains limited. Men already on tirzepatide who want additional support might consider cagrilintide as an adjunct.
Tirzepatide's side effect profile resembles semaglutide's, with gastrointestinal effects common during escalation. Men who tolerate tirzepatide well typically tolerate it better than semaglutide.
The choice between these options often comes down to availability, cost, and individual response.
Cagrilintide versus retatrutide
Retatrutide adds glucagon receptor activation to GLP-1 and GIP agonism, creating a triple-agonist profile. Early trial data shows remarkable weight loss approaching 25% with the highest doses tested. The retatrutide complete guide and retatrutide dosing information provide detailed coverage.
Cagrilintide's amylin mechanism is entirely separate from retatrutide's triple-agonist profile.
Like with tirzepatide, this separation suggests combination potential, though no clinical trials have evaluated this pairing. Men interested in frontier metabolic approaches may eventually have access to amylin analogs combined with triple agonists.
For now, retatrutide remains in clinical trials with uncertain approval timeline. Cagrilintide has advanced further toward approval in the form of CagriSema, which may reach the market sooner.
Cagrilintide versus tesofensine
The tesofensine compound works through neurotransmitter reuptake inhibition rather than peptide receptor activation. This creates a fundamentally different mechanism addressing dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine systems involved in appetite and reward.
Tesofensine may combine with cagrilintide since they work through completely separate pathways.
Men exploring aggressive metabolic interventions sometimes consider multi-mechanism approaches. However, combining compounds increases complexity and requires careful oversight.
Realistic expectations and timelines
Setting accurate expectations prevents disappointment and supports long-term adherence. Men achieve better outcomes when they understand typical trajectories and individual variation patterns.
What to expect in the first month
Week one brings noticeable appetite reduction for most men. Food thoughts decrease. Portion sizes shrink naturally. The constant pull toward snacking weakens. Weight may not change dramatically, as adaptation and water shifts complicate early measurements.
By week two, scale weight typically begins decreasing. One to two pounds per week represents a healthy pace during early treatment. More rapid losses often reflect water rather than fat and may not persist. Men should focus on consistent downward trends rather than daily fluctuations.
Week three and four consolidate these changes. The body adapts to reduced caloric intake. Energy levels stabilize after any initial dip. Side effects, if present, begin improving. Men who reached their first dose escalation may experience temporary symptom recurrence that then resolves.
By month's end, expect three to six pounds of weight loss depending on starting weight and caloric deficit achieved. Some men see more dramatic results, others less. The trajectory matters more than any single data point.
Medium-term expectations
Months two through six encompass the primary weight loss phase for most men. Weight drops steadily, typically averaging two to four pounds weekly during aggressive caloric deficits or one to two pounds weekly with more moderate approaches.
By month three, most men have reached maintenance cagrilintide doses. The full appetite-suppressing effect is established. Body composition changes become visible. Clothes fit differently. Face shape changes. Energy improves as metabolic burden decreases.
The six-month mark typically shows 8 to 12% total body weight reduction. A 250-pound man might weigh 220 to 230 pounds. Metabolic parameters including fasting glucose, triglycerides, and blood pressure typically show meaningful improvements by this point.
Plateaus occur. Most men experience one or more periods where weight loss stalls despite continued compliance. These plateaus usually resolve spontaneously within two to four weeks. Patience during plateaus prevents counterproductive behaviors like excessive restriction or abandoning the protocol.
Long-term outcomes
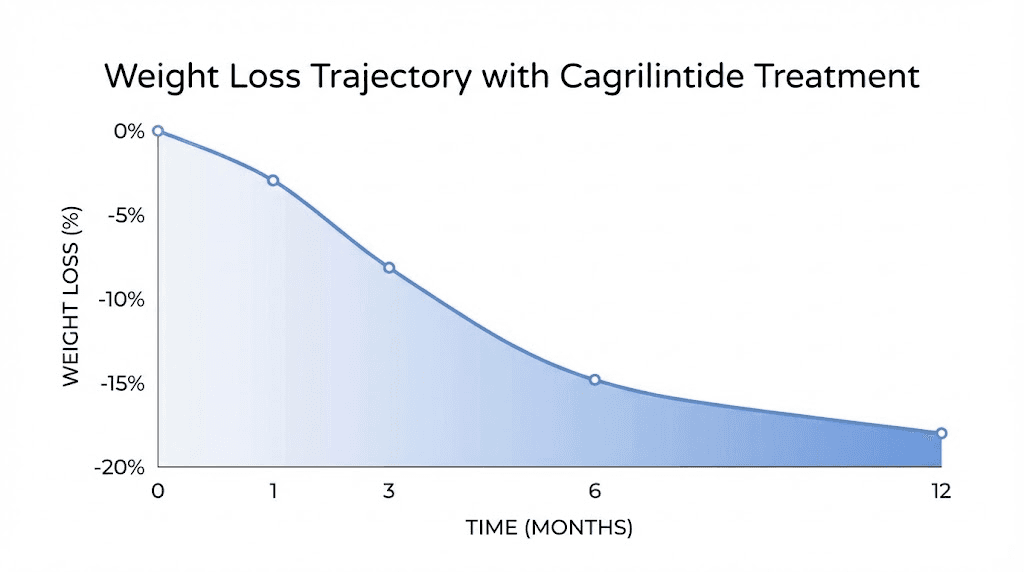
The 68-week clinical trial data provides the best window into long-term expectations. Cagrilintide alone produces approximately 12% weight loss. CagriSema produces 22 to 23%. These represent average outcomes, with individual variation around these means.
Weight maintenance after initial loss requires ongoing treatment for most men. Unlike some interventions where you complete a course and maintain results independently, metabolic peptides typically require continued use to prevent regain. The biological drives that caused weight gain persist, and removing the peptide support allows them to reassert themselves.
The peptide transformation examples show what sustained commitment can achieve. Men who maintain protocols for twelve months and beyond often achieve results exceeding clinical trial averages.
Optimizing results with lifestyle factors
Cagrilintide provides powerful metabolic support, but lifestyle factors determine how much of that potential translates into actual results. Men who optimize nutrition, exercise, and recovery achieve outcomes substantially exceeding those who rely on the peptide alone.
Protein intake requirements
Protein becomes even more important during peptide-supported weight loss. The appetite suppression cagrilintide produces makes eating feel less urgent, which can lead to inadequate protein intake if not consciously addressed. Insufficient protein during weight loss accelerates muscle loss, which undermines body composition goals and metabolic rate.
Target 1.0 to 1.2 grams of protein per pound of goal body weight daily. For a man targeting 200 pounds, this means 200 to 240 grams of protein daily. Space this across four to six eating occasions to optimize muscle protein synthesis. Prioritize complete protein sources including meat, fish, eggs, and dairy, or carefully combine plant proteins to ensure complete amino acid profiles.
Protein shakes can help meet targets when appetite is suppressed.
A shake does not require the same appetite that a large meal demands.
Men struggling to consume adequate protein often find liquid sources more manageable during the initial high-suppression period.
Exercise programming
Resistance training is non-negotiable for optimal body composition during weight loss.
Weight training signals the body to preserve muscle mass even in caloric deficit.
Without this signal, the body readily sacrifices muscle as part of the weight loss process, leaving men lighter but not meaningfully leaner.
Train major muscle groups two to three times weekly. Compound movements like squats, deadlifts, presses, rows, and pull-ups provide efficient stimulus. Progressive overload, gradually increasing weights or repetitions over time, maintains the adaptation signal even as body weight decreases.
Cardiovascular exercise supports caloric deficit and cardiovascular health without the muscle-preserving benefits of resistance training. Moderate amounts, perhaps 150 to 200 minutes of low-to-moderate intensity cardio weekly, complement strength training without interfering with recovery. Excessive cardio can impair muscle retention and may be counterproductive for body composition goals.
The peptides for cardio endurance guide addresses compounds that may support cardiovascular training adaptations.
Sleep and recovery
Sleep deprivation undermines weight loss through multiple mechanisms.
Poor sleep increases hunger hormones, decreases satiety hormones, impairs insulin sensitivity, and reduces motivation for healthy behaviors. Cagrilintide cannot fully compensate for chronically inadequate sleep.
Target seven to nine hours of quality sleep nightly. Consistent sleep and wake times support circadian rhythm regulation. Cool, dark sleeping environments optimize sleep quality. Limiting screens before bed reduces sleep-disrupting blue light exposure.
Stress management similarly affects outcomes. Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which promotes visceral fat storage and muscle breakdown. Stress-driven eating, even when appetite is suppressed by cagrilintide, can undermine caloric deficits. Identifying stressors and implementing management strategies supports metabolic goals.
Special considerations for men
Male physiology creates specific considerations when using metabolic peptides. Understanding these factors helps men optimize their approaches and anticipate issues that may affect their individual responses.
Testosterone and metabolic peptides
Men with low testosterone may experience attenuated weight loss responses. Testosterone supports lean mass maintenance, and low levels predispose toward muscle loss during weight loss. If testosterone deficiency exists, addressing it may improve outcomes from metabolic peptide therapy.
Weight loss itself often improves testosterone levels. Visceral fat produces aromatase, which converts testosterone to estrogen. As visceral fat decreases, this conversion diminishes, and testosterone levels may rise. Some men find that significant weight loss normalizes previously low testosterone without requiring hormone replacement.
The peptides for testosterone and testosterone peptide resources address compounds that specifically target testosterone support, which may complement metabolic peptides in men with documented deficiency.
Libido and sexual function
Weight loss typically improves sexual function in overweight men. Improved blood flow, better hormone profiles, increased confidence, and reduced inflammation all contribute to enhanced libido and erectile function. Many men report these improvements as among the most valued benefits of weight loss.
Cagrilintide has no known direct effects on sexual function. It does not appear to impair libido or erectile capacity. The indirect effects of weight loss are generally positive for sexual health.
The best peptides for libido and peptides for erectile dysfunction guides address compounds specifically targeting these concerns for men who need additional support.
Muscle preservation strategies
Men often prioritize maintaining or building muscle alongside fat loss. This goal requires deliberate strategy when using metabolic peptides that suppress appetite and reduce caloric intake.
Slower weight loss rates preserve more muscle. Targeting 0.5 to 1% body weight loss per week rather than aggressive deficits protects lean mass. This may mean partially countering cagrilintide's appetite suppression to ensure adequate caloric intake.
Protein timing around training matters. Consuming protein within one to two hours of resistance training optimizes the muscle protein synthesis response. A post-workout meal or shake containing 30 to 50 grams of protein supports training adaptations.
Some men consider growth hormone secretagogues like sermorelin or ipamorelin alongside metabolic peptides to support lean mass retention. These combinations increase complexity but may benefit men with specific body composition goals.
The peptide stacking guide addresses multi-peptide protocols.
Current status and future availability
Understanding cagrilintide's regulatory status and availability helps men plan appropriately. The landscape continues evolving.
Regulatory approval status
Cagrilintide is not currently FDA-approved as a standalone medication. Clinical trials are ongoing, and Novo Nordisk has indicated plans to file for approval. The CagriSema combination represents the most likely initial approval pathway, with regulatory submissions expected.
Outside clinical trials, cagrilintide exists primarily in the research chemical space. This creates challenges around purity, authenticity, and consistency that men must navigate carefully.
The peptide regulation updates track changes in this landscape.
Research peptide considerations
Men accessing research-grade cagrilintide face quality control challenges.
Third-party testing provides some assurance of purity and identity. Reputable suppliers provide certificates of analysis. Even with precautions, research peptides carry inherent uncertainties.
Reconstitution requirements add complexity. Lyophilized peptides require proper reconstitution with bacteriostatic water. Storage conditions affect stability. The peptide storage guide and room temperature stability information help maintain potency.
SeekPeptides provides members with detailed guidance on evaluating sources, interpreting testing results, and maintaining proper storage protocols.
When approved options may arrive
CagriSema may reach the market within the next one to two years based on current trial timelines and regulatory trajectories. FDA approval would provide standardized, quality-controlled formulations with proper dosing guidance.
Insurance coverage for approved weight loss medications has expanded considerably. GLP-1 agonists initially faced coverage challenges that have progressively improved. CagriSema may follow similar patterns, eventually becoming accessible through standard medical channels for men who meet criteria.
Frequently asked questions
How quickly will I see weight loss results with cagrilintide?
Most men notice appetite changes within the first one to two weeks. Visible weight loss typically begins by week two to three. Meaningful changes, where clothes fit differently and others notice, generally occur by six to eight weeks. The full effect develops over four to six months as you reach maintenance doses and establish consistent patterns.
Can I use cagrilintide without exercise?
Weight loss occurs even without exercise due to reduced caloric intake. However, body composition outcomes suffer significantly without resistance training. Muscle loss accelerates, metabolic rate drops faster, and long-term maintenance becomes harder.
For optimal results, combine cagrilintide with regular strength training two to three times weekly.
Is cagrilintide safe for long-term use?
Clinical trials extending 68 weeks show acceptable safety profiles with no unexpected serious adverse events. However, very long-term data spanning years to decades does not yet exist. The safety profile appears similar to other peptide medications in the metabolic class. Ongoing monitoring for liver function, kidney function, and other parameters is prudent during extended use.
Will I regain weight if I stop taking cagrilintide?
Most men regain weight after discontinuing metabolic peptides, similar to patterns seen with semaglutide and tirzepatide.
The biological drives that caused initial weight gain persist and reassert themselves when pharmacological support is removed. Long-term weight maintenance typically requires ongoing treatment or aggressive lifestyle modifications that most people find difficult to sustain.
How does cagrilintide compare to bariatric surgery?
Bariatric surgery produces greater average weight loss, with gastric bypass achieving 25 to 30% and sleeve gastrectomy achieving 20 to 25% total body weight reduction. CagriSema approaches surgical outcomes with 22 to 23% weight loss. Surgery carries surgical risks and requires permanent dietary modifications.
Peptides require ongoing administration.
The right choice depends on individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and access to each option.
Can I combine cagrilintide with other peptides?
Combining cagrilintide with semaglutide (as CagriSema) has clinical trial support. Combining with other peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500 for healing, MOTS-c for metabolic support, or growth hormone secretagogues lacks formal study but is practiced in some protocols. The multi-peptide guidance addresses practical considerations.
What happens if I miss a dose?
If you miss a dose and remember within three days, inject immediately. If more than three days have passed, skip the missed dose and resume your regular weekly schedule. Do not double doses. Occasional missed doses have minimal impact on overall outcomes. Consistent weekly dosing produces the best results.
Should I eat even when I'm not hungry on cagrilintide?
Yes, ensuring adequate nutrition remains important even with suppressed appetite. Focus particularly on protein intake to preserve muscle mass. Aim for minimum caloric floors based on your goals, typically no lower than 1,200 to 1,500 calories daily for men, even if appetite would allow less. Severe caloric restriction accelerates muscle loss and may impair hormonal function.
External resources
For researchers serious about optimizing their metabolic protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions.
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Join us.