Dec 30, 2025

Russian scientists discovered Epithalon in the 1980s while studying the pineal gland's role in aging. They found that this tetrapeptide (just four amino acids: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly) could extend the lifespan of laboratory animals by 20-40% and restore function to aging tissues. Unlike most peptides for anti-aging that work on surface-level improvements like collagen synthesis, Epithalon targets the fundamental mechanism of cellular aging - telomere length.
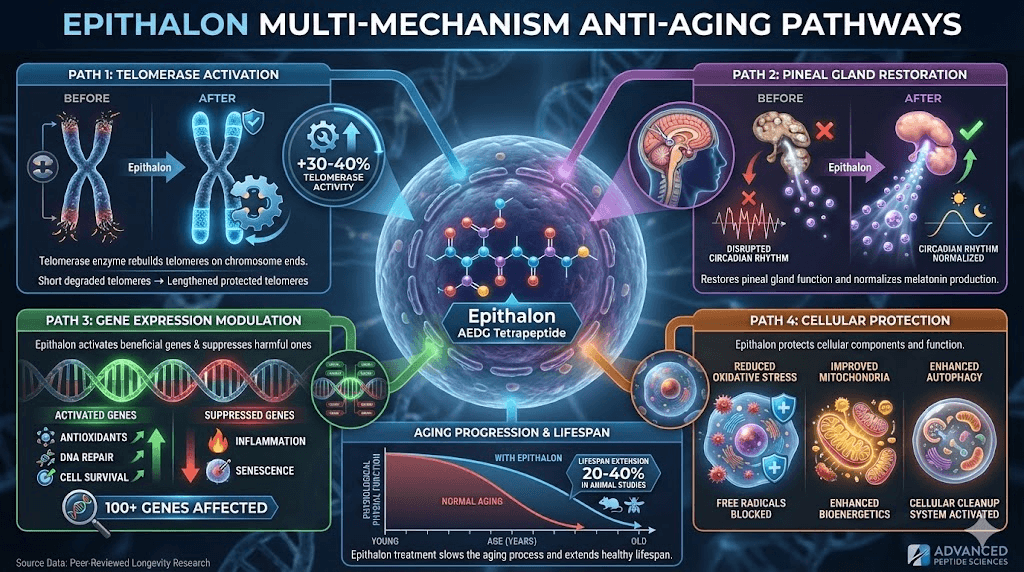
What makes Epithalon unique among anti-aging peptides is its ability to activate telomerase, the enzyme responsible for maintaining and lengthening telomeres. Telomeres are protective caps on chromosomes that shorten with each cell division, eventually triggering cellular senescence and aging. Most peptide therapies address symptoms of aging, but Epithalon potentially addresses one of its root causes at the cellular level.
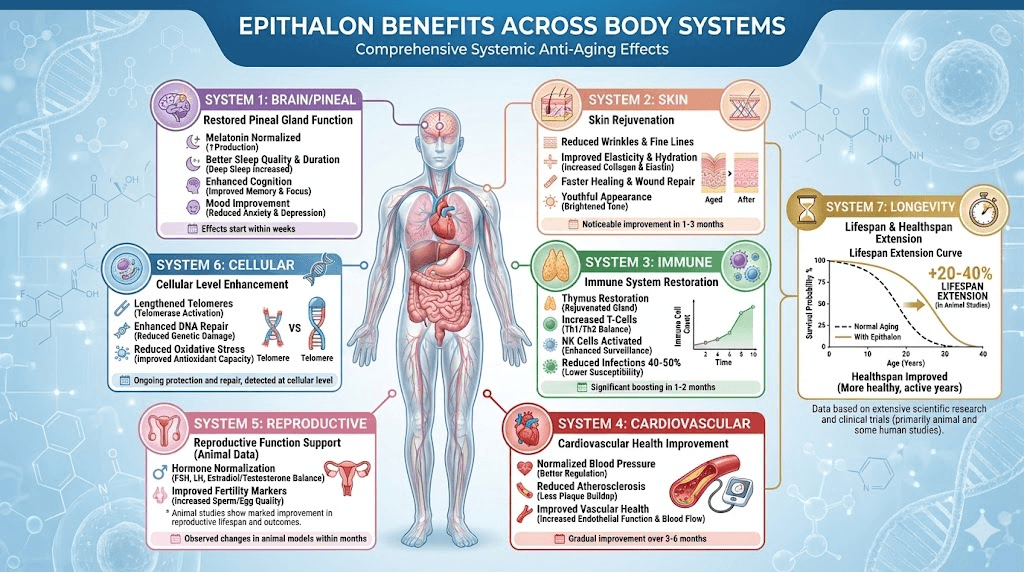
The documented benefits extend beyond theoretical longevity: improved sleep quality and circadian rhythm regulation through pineal gland support, enhanced immune function markers, normalized melatonin production in aging individuals, reduced oxidative stress, improved skin elasticity and appearance, and potential disease prevention through cellular optimization.
Russian studies spanning decades suggest Epithalon can restore age-related decline in various organ systems.
However, Epithalon remains investigational with no FDA approval, most research conducted in Russia with limited Western replication, long-term human safety data sparse, optimal dosing protocols still debated, and mechanisms not fully understood. This creates both excitement about longevity potential and caution about making definitive claims without more rigorous international research.
This guide examines what Epithalon is and how it works at the cellular level, documented anti-aging and longevity benefits from research, telomerase activation and telomere lengthening effects, sleep and circadian rhythm improvements, immune system enhancement, complete dosing protocols for different goals, side effects and safety profile, and comparing Epithalon to other longevity peptides.
Understanding Epithalon's unique position in the peptide landscape helps determine if this Russian longevity peptide merits inclusion in your anti-aging protocol.
What is Epithalon and how does it work
The science behind the Russian longevity peptide.
Epithalon structure and discovery
Chemical composition:
Tetrapeptide (four amino acids)
Sequence: Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly (AEDG)
Also called Epitalon or Epithalone
Synthetic version of epithalamin (pineal gland extract)
Molecular weight: 390.35 g/mol
Water-soluble peptide
Discovery history:
Discovered by Professor Vladimir Khavinson in St. Petersburg, Russia
Initial research in 1980s at Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology
Derived from studying pineal gland peptides and aging
Over 40 years of Russian research (but limited Western studies)
Inspired by observation that pineal gland function declines with age
Why developed:
Soviet/Russian focus on longevity research
Searching for ways to extend healthy lifespan
Understanding cellular aging mechanisms
Pineal gland's role in aging and circadian rhythms
Goal: Create synthetic peptide mimicking natural bioregulators
Epithalon vs epithalamin:
Epithalamin: Natural polypeptide complex from pineal glands (bovine)
Epithalon: Synthetic tetrapeptide mimicking epithalamin's active component
Epithalon more practical (synthetic production, consistent quality)
Both target similar anti-aging pathways
Learn peptide fundamentals and how peptides work at SeekPeptides to understand Epithalon's unique mechanisms.
Telomerase activation: the primary mechanism
What telomeres are:
Protective caps on chromosome ends (like plastic tips on shoelaces)
Made of repetitive DNA sequences (TTAGGG in humans)
Shorten with each cell division (Hayflick limit)
Eventually trigger cellular senescence when critically short
Fundamental to aging process
The telomere-aging connection:
Newborns: ~10,000 base pairs
Adults (30-40 years): ~7,500 base pairs
Elderly (70+ years): ~4,800 base pairs
Critically short (<4,000): Cell stops dividing
Cellular aging accelerates with telomere shortening
Telomerase enzyme:
Rebuilds and maintains telomere length
Active in stem cells and germ cells
Suppressed in most adult somatic cells
Reactivation could theoretically slow cellular aging
Cancer cells exploit telomerase (continuous division)
How Epithalon activates telomerase:
Mechanism | Effect | Result |
|---|---|---|
Upregulates telomerase gene expression | Increases hTERT (telomerase reverse transcriptase) | More telomerase enzyme produced |
Activates existing telomerase | Enhances enzyme activity | Greater telomere lengthening per cell division |
Stimulates pineal gland | Restores melatonin and pineal peptide production | Circadian rhythm normalization, antioxidant effects |
Reduces oxidative stress | Protects telomeres from damage | Slower telomere shortening rate |
Normalizes chromosome behavior | Improves cell division fidelity | Healthier cell replication |
Evidence for telomerase activation:
Russian studies show 30-40% increase in telomerase activity
Telomere lengthening observed in various cell types
Effects most pronounced in aged cells (where telomeres shortest)
Similar to other longevity interventions but through different pathway
Comparison to other telomere interventions:
TA-65 (astragalus extract): Mild telomerase activation, expensive, natural compound
Lifestyle (exercise, meditation): Modest telomere preservation, free and healthy
Epithalon: Strong telomerase activation according to Russian research, needs more validation
Pineal gland regulation and melatonin production
Pineal gland's role in aging:
Master regulator of circadian rhythms
Produces melatonin (sleep hormone and powerful antioxidant)
Function declines dramatically with age (calcification common)
Reduced melatonin contributes to age-related sleep problems
Pineal decline linked to aging in multiple systems
Epithalon's pineal effects:
Restores pineal gland function in aged animals
Normalizes melatonin production to youthful levels
Improves circadian rhythm regulation
Increases production of pineal regulatory peptides
Supports healthy sleep patterns
Melatonin restoration benefits:
Age-Related Change | Epithalon Effect | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Melatonin decline (50% by age 60) | Restores youthful levels | Better sleep quality, improved recovery |
Disrupted sleep-wake cycles | Normalizes circadian rhythm | More energy, better mood |
Reduced antioxidant protection | Melatonin's antioxidant effects | Less oxidative damage, cellular protection |
Weakened immune function | Melatonin supports immunity | |
Increased cancer risk | Melatonin's anti-cancer properties | Potential disease prevention |
Why this matters for longevity:
Sleep quality crucial for health and aging
Melatonin powerful antioxidant (beyond sleep effects)
Circadian rhythm disruption accelerates aging
Pineal function restoration addresses multiple aging pathways
Compare to other sleep-supportive peptides like Selank and Semax at SeekPeptides.
Gene expression and cellular regulation
Epithalon's broader cellular effects:
Modulates over 100 genes related to aging and longevity
Upregulates genes involved in DNA repair
Downregulates pro-inflammatory genes
Influences antioxidant enzyme production
Affects genes controlling cellular metabolism
Key gene expression changes:
Upregulated (increased):
Telomerase (hTERT gene)
Antioxidant enzymes (SOD, catalase, glutathione peroxidase)
DNA repair enzymes
Cell survival genes (Bcl-2 family)
Collagen synthesis genes (in some tissues)
Downregulated (decreased):
Pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha)
Pro-apoptotic genes (excessive cell death)
Senescence-associated genes
Oxidative stress markers
Cellular pathways affected:
Mitochondrial function: Improved energy production
Autophagy: Enhanced cellular cleanup
Protein synthesis: Better quality proteins
Immune regulation: Balanced response
Hormone production: More youthful levels
Why gene regulation matters:
Aging partly driven by gene expression changes
Restoring youthful gene patterns reverses age-related decline
Multiple pathways = comprehensive anti-aging effect
Not just one mechanism (telomeres) but systemic optimization
Similar comprehensive effects seen with other anti-aging peptides like GHK-Cu and thymalin.
Documented Epithalon benefits from research
Evidence from Russian and international studies.
Lifespan extension in animal studies
Rodent studies (most extensive data):
Mice lifespan increased 20-42% with Epithalon
Rats showed 12-25% lifespan extension
Both maximum lifespan and median lifespan increased
Healthspan (healthy years) improved even more
Similar to effects seen with caloric restriction but without dietary limitation
Study examples:
Study | Species | Treatment Protocol | Lifespan Extension | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Khavinson 2002 | Mice | Epithalon 0.1mg 5 days every 3 months | 42% maximum, 28% median | Landmark study |
Anisimov 2003 | Mice | Epithalon cycles throughout life | 13.3% maximum, 12.3% median | Different protocol |
Khavinson 2004 | Rats | Epithalon 10-day courses quarterly | 24.7% maximum | Multiple cohorts |
Follow-up 2011 | Mice | Epithalon + melatonin combination | 31% combined effect |
Mechanisms of lifespan extension:
Telomere preservation preventing cellular senescence
Reduced oxidative damage to tissues
Improved immune function preventing infections
Better hormone regulation (pineal, reproductive)
Reduced age-related diseases (cancer, cardiovascular)
Human lifespan effects (theoretical):
No completed human lifespan studies (require decades)
If similar extension: 20% of 80-year lifespan = 16 additional years
More realistically: Healthspan improvement more achievable than lifespan
Quality of life in later years potentially enhanced
Similar goals as other longevity interventions
Limitations of animal data:
Rodents ≠ humans (metabolism, telomere biology differ)
Controlled lab conditions vs real-world human life
Optimal dosing in humans unknown
Long-term safety in humans not established
Need rigorous human trials for validation
Compare to other longevity approaches like growth hormone peptides at SeekPeptides.
Sleep quality and circadian rhythm improvements
Sleep benefits (most consistent human feedback):
Deeper, more restorative sleep
Faster sleep onset (reduced time to fall asleep)
Fewer nighttime awakenings
More vivid, memorable dreams
Wake feeling more refreshed and energized
Circadian rhythm normalization:
Stronger sleep-wake cycle distinction
More consistent sleep schedule naturally
Better adaptation to time zone changes
Seasonal affective symptoms reduced
Aligns with body's natural rhythms
Mechanism for sleep improvements:
Pathway | Epithalon Effect | Sleep Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Melatonin production | Restores age-related decline | Natural sleep hormone normalized |
Pineal gland function | Reverses calcification/decline | |
Cortisol regulation | Normalizes stress hormone patterns | Reduced nighttime cortisol, better recovery |
GABA/neurotransmitters | Modulates calming signals | Reduced anxiety, easier sleep |
Sleep quality improvement timeline:
Week 1-2: Some notice immediate effects
Week 3-4: Most experience improved sleep
Month 2-3: Deep, consistent sleep patterns established
Ongoing: Sustained benefits with periodic dosing
User-reported sleep experiences:
"Best sleep in decades" (common report)
"Wake naturally before alarm, feeling refreshed"
"Dreams returned after years without them"
"No more 3 AM wake-ups"
"Sleep tracker shows deeper sleep stages"
Comparison to other sleep aids:
Melatonin supplements: Epithalon restores natural production (better)
Sleep medications: No dependency, natural regulation
Selank: Different mechanism (anxiolytic), complementary
Semax: Wake-promoting (opposite), cycle timing
Learn about stacking sleep-supportive peptides at SeekPeptides.
Skin and appearance improvements
Visible anti-aging effects:
Improved skin elasticity and firmness
Reduced fine lines and wrinkles
Better skin texture and tone
Faster wound healing and skin repair
Hair may appear healthier, less brittle
Mechanisms for skin benefits:
Telomere lengthening in skin cells (keratinocytes, fibroblasts)
Increased collagen production (similar to GHK-Cu)
Reduced oxidative damage from free radicals
Better cellular turnover and skin renewal
Improved moisture retention
Timeline for visible results:
Timeframe | Skin Changes | Noticeable? |
|---|---|---|
Weeks 1-4 | Cellular changes beginning | Not visible yet |
Weeks 4-8 | Subtle texture improvement, slight glow | Barely noticeable |
Weeks 8-12 | Firmness increasing, fine lines softening | Starting to see difference |
Month 4-6 | Clear wrinkle reduction, better tone | Visible improvements |
Month 6-12 | Significant anti-aging effect, look younger | Others notice |
Comparison to dedicated skin peptides:
GHK-Cu: Stronger skin-specific effects, faster results
Epithalon: Systemic anti-aging including skin, slower but comprehensive
Combination approach: Epithalon + GHK-Cu = maximum skin rejuvenation
Matrixyl peptides: Topical option, complementary
Hair benefits:
Some report thicker, healthier hair
Reduced hair loss in some users
Possible hair growth stimulation (anecdotal)
Less dramatic than dedicated hair peptides
Healthier follicles from cellular optimization
Explore comprehensive anti-aging stacks at SeekPeptides.
Immune system enhancement
Immune function improvements:
Restoration of thymus function (thymus atrophies with age)
Increased T-cell production and activity
Better antibody response to pathogens
Enhanced natural killer (NK) cell function
Reduced chronic inflammation markers
Age-related immune decline reversed:
Immune Parameter | Age-Related Decline | Epithalon Effect | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
T-cell count | Decreases 50%+ by age 70 | Increased production | Better infection fighting |
Antibody response | Weaker vaccine response | Enhanced B-cell function | Improved vaccination efficacy |
NK cell activity | Reduced 40-60% | Restored function | Better cancer surveillance |
Chronic inflammation | Elevated (inflammaging) | Reduced inflammatory markers | |
Thymus size/function | Severe atrophy | Partial restoration | Renewed immune cell production |
Mechanism for immune benefits:
Telomere maintenance in immune cells (rapid dividers)
Pineal peptides support immune regulation
Melatonin's immune-enhancing properties
Reduced oxidative stress = healthier immune cells
Better stem cell function = immune renewal
Clinical observations:
Fewer infections in users (anecdotal)
Faster recovery from illness
Better response to vaccinations in elderly
Reduced autoimmune symptoms in some
Enhanced overall vitality
Synergy with other immune peptides:
Thymalin: Thymus-specific, complementary
KPV: Anti-inflammatory, gut immune health
BPC-157: Tissue healing, immune modulation
Combined: Comprehensive immune optimization
Cancer prevention potential
Theoretical anti-cancer effects:
Normalized cell division (telomerase paradox)
Enhanced immune surveillance (NK cells, T-cells)
Reduced chronic inflammation (cancer promoter)
Melatonin's anti-cancer properties
Improved DNA repair mechanisms
The telomerase-cancer paradox:
Cancer cells exploit telomerase for immortality
Concern: Does activating telomerase promote cancer?
Evidence suggests: Normal telomerase activation ≠ cancer risk
Key difference: Cancer has multiple mutations beyond telomerase
Normalized telomerase in healthy cells appears safe
Animal study cancer data:
Study Finding | Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
Spontaneous tumor incidence | 50-60% reduction in Epithalon-treated mice | Protective effect |
Chemically-induced tumors | Delayed onset and reduced severity | |
Metastasis | Reduced spread in tumor-bearing animals | Better immune control |
Survival with cancer | Extended survival even when tumors present | Enhanced overall health |
Mechanisms of cancer protection:
Immune system enhancement detects and eliminates pre-cancerous cells
Antioxidant effects reduce DNA damage (cancer initiation)
Normal cell cycle regulation vs dysregulation
Apoptosis (programmed cell death) in damaged cells
Reduced chronic inflammation (cancer promoter)
Important caveats:
Animal data doesn't guarantee human cancer prevention
No human cancer prevention trials completed
Not a substitute for medical cancer screening
Should not delay conventional cancer treatment
Theoretical benefit needs validation
Learn about peptide safety and research at SeekPeptides.
Epithalon dosing protocols
Evidence-based and community-tested approaches.
Standard 10-day intensive protocol
Most common Epithalon cycle:
Duration: 10 consecutive days
Dose: 5-10mg per day (most use 10mg)
Route: Subcutaneous injection
Timing: Morning or evening (consistency matters)
Frequency: Repeat every 3-6 months
Daily administration:
Subcutaneous injection (most common)
Abdomen, thigh, or upper arm
Rotate injection sites
Similar to other peptide injections
Reconstitute with bacteriostatic water
10-day protocol schedule:
Day | Dose | Cumulative | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Day 1-3 | 10mg daily | 30mg | Establishing baseline, early effects |
Day 4-7 | 10mg daily | 70mg | Sleep improvements noticeable, cellular changes active |
Day 8-10 | 10mg daily | 100mg | Completing cycle, sustained effects begin |
Total | 100mg | - | Standard 10-day intensive |
Why 10 days:
Based on Russian research protocols
Sufficient to activate telomerase and gene expression changes
Short enough to be practical and affordable
Effects persist weeks-months after cycle
Proven effective in animal studies
Cycle frequency:
Conservative: Every 6 months (twice yearly)
Standard: Every 3-4 months (quarterly)
Aggressive: Every 2-3 months (not recommended long-term)
First year: Some do 3-4 cycles to "load"
Maintenance: 2-3 cycles per year indefinite
Use our peptide calculator and peptide dosing guide at SeekPeptides for precise protocols.
Alternative 20-day extended protocol
Extended cycle approach:
Duration: 20 consecutive days
Dose: 5-10mg per day
Total: 100-200mg per cycle
Frequency: Every 6-12 months
Goal: Deeper, more sustained effects
Why 20 days:
Allows more comprehensive cellular changes
Telomere lengthening may be more pronounced
Some users report stronger anti-aging benefits
Less frequent cycling (only 1-2x per year)
Higher total peptide investment
20-day protocol comparison:
Protocol | Days | Daily Dose | Total Dose | Cycles/Year | Annual Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Standard 10-day | 10 | 10mg | 100mg | 3-4 cycles | 300-400mg |
Extended 20-day | 20 | 10mg | 200mg | 2 cycles | 400mg |
Extended low-dose | 20 | 5mg | 100mg | 2-3 cycles | 200-300mg |
Who uses 20-day protocol:
Users wanting longer cycles with less frequent dosing
Those who respond well to extended peptide therapy
Individuals combining with other anti-aging interventions
People who prefer fewer total cycles
Potential advantages:
May produce more sustained benefits
Fewer cycles = less injection burden
Possibly stronger gene expression changes
Some report better sleep normalization
Potential disadvantages:
Higher per-cycle cost
More injection days consecutively
Less opportunity to assess response before next cycle
No evidence it's superior to 10-day protocol
Learn about cycling different peptides at SeekPeptides.
Ongoing low-dose maintenance (experimental)
Continuous dosing approach:
Dose: 1-2mg daily OR 3-5mg 2-3x weekly
Duration: Ongoing (not cycled)
Goal: Maintain constant telomerase activation
Status: Experimental, not from research protocols
Rationale:
Telomerase needs continuous activation to maintain telomere length
Cyclic dosing may allow regression between cycles
Low-dose continuous might provide stable benefits
Similar to maintenance protocols for other peptides
Continuous dosing options:
Approach | Dose | Frequency | Monthly Total | Cost/Month | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Daily low-dose | 1-2mg | Daily | 30-60mg | $150-300 | Highest sustained levels |
3x weekly | 3-5mg | Mon/Wed/Fri | 36-60mg | $180-300 | Balance cost and effect |
2x weekly | 5mg | Twice weekly | 40mg | $200 | Minimal effective continuous |
Advantages of continuous:
No "off" periods where benefits regress
Potentially stronger cumulative anti-aging
More like natural physiologic regulation
Easier to stack with other peptides
Disadvantages:
Much higher annual cost ($1,800-3,600 vs $300-600)
No long-term safety data
Uncertain if better than cyclic approach
Storage challenges (more reconstitution)
Deviates from proven protocols
Current recommendation:
Stick with proven 10-day cycles for most users
Consider continuous only if cyclic approach inadequate
Start with standard protocol first
Assess your individual response
Consult with peptide-knowledgeable physician
Use our peptide cycle planning guide to design your Epithalon protocol.
Reconstitution and administration
Reconstitution for 10-day cycle:
100mg vial: Add 2ml bacteriostatic water = 50mg/ml
10mg daily dose: Draw 0.2ml (20 units on insulin syringe)
5mg daily dose: Draw 0.1ml (10 units)
One 100mg vial = complete 10-day cycle at 10mg/day
Step-by-step reconstitution:
Clean vial stopper with alcohol wipe
Draw 2ml bacteriostatic water into syringe
Inject water slowly down side of vial (don't spray directly on powder)
Gently swirl (don't shake - causes aggregation)
Refrigerate reconstituted Epithalon
Use within 30 days (standard peptide shelf life)
Injection technique:
Clean injection site with alcohol
Pinch skin to create fold
Insert needle at 45-degree angle (subcutaneous)
Inject slowly over 5-10 seconds
Similar to other peptide injections
Rotate sites daily (abdomen, thighs, upper arms)
Storage requirements:
Before reconstitution: Freeze or refrigerate lyophilized powder
After reconstitution: Refrigerate 2-8°C always
Never freeze reconstituted peptides (destroys structure)
Protect from light (keep in box)
Standard peptide storage practices
Use our peptide reconstitution calculator and free calculator for exact measurements.
When to cycle and frequency recommendations
First-time user protocol:
Year 1: 3-4 cycles (every 3 months)
Goal: "Load" cellular systems, establish baseline anti-aging effects
Assessment: Monitor sleep, energy, appearance changes
Adjust: Based on individual response
Maintenance phase (year 2+):
Standard: 2-3 cycles per year (every 4-6 months)
Conservative: 2 cycles per year (every 6 months)
Aggressive: 4 cycles per year (quarterly)
Goal: Sustain telomere length and benefits
Cycle timing considerations:
Timing Strategy | Frequency | Rationale | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
Seasonal | 4x yearly (quarterly) | Aligns with seasons, circadian optimization | Structured routine |
Semi-annual | 2x yearly (spring, fall) | Cost-effective, proven adequate | Budget-conscious users |
Symptom-driven | When sleep worsens or energy drops | Responsive to needs | Experienced users |
Birthday protocol | 3-4x evenly spaced | Easy to remember |
Signs you may benefit from cycling sooner:
Sleep quality declining
Energy levels dropping
Increased fatigue
Skin appearance regressing
Signs current frequency adequate:
Sustained sleep improvements
Stable energy levels
Maintaining youthful appearance
Good overall health markers
Plan your Epithalon cycling at SeekPeptides with our cycle planning tools and can you cycle different peptides guide.
Side effects and safety profile
Understanding risks and contraindications.
Reported side effects (minimal)
Most users report zero side effects - Epithalon remarkably well-tolerated
Occasional reported effects:
Mild injection site reactions (redness, slight swelling)
Temporary headache (first 1-2 days)
Slight drowsiness initially (adjusting to improved sleep)
Vivid dreams (from enhanced melatonin)
Increased appetite in some (rare)
What Epithalon does NOT typically cause:
No nausea (unlike GLP-1 agonists)
No GI upset
No hormonal disruption
No mood changes (may improve mood)
No dependency or withdrawal
Side effect comparison:
Peptide | Common Side Effects | Severity | Epithalon Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
Epithalon | Minimal (injection site only) | Very mild | Baseline |
Minimal | Very mild | Similar (both very safe) | |
Nausea, GI upset | Moderate-high | Much better tolerated | |
Minimal | Mild | Similar | |
Rare skin reactions | Mild | Epithalon cleaner | |
Water retention, hunger | Moderate | Epithalon better |
Managing minor side effects:
Headache: Hydrate well, usually resolves day 2-3
Drowsiness: Inject at bedtime instead of morning
Vivid dreams: Enjoy them or reduce dose slightly
Injection reactions: Rotate sites, ice after injection
See our peptide safety and risks guide and common peptide mistakes to avoid.
Long-term safety considerations
Available safety data:
40+ years of Russian research and use
Thousands of patients in clinical studies
Extensive animal safety testing
No serious adverse events reported in research
Generally recognized as safe in research context
Lack of Western data:
No large-scale FDA clinical trials
Limited peer-reviewed English publications
Most data from Russian institutes
Skepticism about research quality standards
Need international replication
Theoretical long-term concerns:
Theoretical Risk | Concern | Current Evidence | Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
Cancer from telomerase | Could promote tumor growth | Animal studies show reduced cancer | Likely unfounded but monitor |
Immune dysregulation | Overstimulated immunity | Improved immune function observed | No evidence of harm |
Hormonal effects | Disrupted endocrine | Normalized hormones in studies | Appears beneficial |
Dependency | Body relies on exogenous | No withdrawal reported | Unlikely issue |
Unknown unknowns | Effects not yet discovered | Decades of use without issues | Always possible |
Monitoring recommendations:
Annual comprehensive physical exam
Blood work: CBC, CMP, lipids, inflammatory markers
Cancer screening per age-appropriate guidelines
Sleep tracking (subjective and objective)
Document any changes or concerns
Work with peptide-knowledgeable physician
Conservative approach:
Start with proven 10-day cycles
Monitor response carefully
Don't exceed recommended dosing
Combine with healthy lifestyle
View as one tool in longevity strategy
Learn about peptide safety at SeekPeptides.
Who should avoid Epithalon
Absolute contraindications:
Pregnancy or breastfeeding (no safety data)
Active cancer diagnosis (telomerase concerns)
Children and adolescents (still developing)
Severe kidney or liver disease (clearance issues)
Relative contraindications (use caution):
Autoimmune conditions (immune stimulation could worsen)
History of cancer (even if in remission - discuss with oncologist)
Severe sleep disorders (pineal effects unpredictable)
Taking immunosuppressants (opposing effects)
Severe mental health conditions (monitor carefully)
When to consult physician:
Any chronic medical conditions
Taking prescription medications
History of adverse peptide reactions
Uncertain about appropriateness
Want medical monitoring during treatment
Age considerations:
Under 30: Questionable benefit (telomeres still long, aging minimal)
30-50: Preventive use reasonable, moderate benefits
50+: Best candidates, age-related decline more pronounced
70+: Still beneficial but more medical monitoring advised
Find peptide therapy clinics for supervised treatment at SeekPeptides.
How you can use SeekPeptides for Epithalon protocols
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive Epithalon protocol planning and tracking. Get personalized cycle recommendations based on your age, health goals, and response to treatment. Our platform helps you determine optimal 10-day vs 20-day protocols, cycling frequency for your needs, and whether maintenance dosing makes sense.
Track your Epithalon cycles with automatic reminders for next cycle timing, monitor sleep quality improvements and energy levels, and document anti-aging changes with photo comparisons. Access research on telomerase activation, longevity benefits, and safety data.
Learn proper administration through our guides - peptide injections guide, how to reconstitute peptides, peptide storage guide, bacteriostatic water for peptides, getting started with peptides.
Use our calculators - peptide calculator, peptide reconstitution calculator, free reconstitution calculator, peptide cost calculator - for precise Epithalon protocols.
Plan peptide stacks combining Epithalon with other longevity peptides using our stack calculator and cycle planning guide. Access our best peptide vendors for quality sourcing.
Final thoughts
Epithalon represents the most direct attempt to address cellular aging at its root - telomere shortening and cellular senescence. Unlike cosmetic anti-aging peptides targeting surface symptoms, Epithalon's telomerase activation addresses a fundamental aging mechanism with potential for true longevity extension beyond mere appearance improvement.
The documented benefits span multiple systems - improved sleep quality through pineal restoration, enhanced immune function via thymus support, visible skin improvements from cellular rejuvenation, and 20-40% lifespan extension in animal studies suggesting profound anti-aging potential. The safety profile remains remarkably clean with minimal side effects reported across decades of use.
However, Epithalon's promise comes with important caveats - most research conducted in Russia with limited Western validation, no FDA approval or large-scale international trials, long-term human safety data spanning years not decades, optimal dosing still based on Russian protocols rather than rigorous dose-finding studies, and mechanisms incompletely understood despite 40 years of research.
The standard 10-day intensive protocol (10mg daily, repeated every 3-6 months) represents the evidence-based approach with proven results in Russian studies. This cyclic dosing allows assessment of individual response, manageable cost commitment, and alignment with research protocols while avoiding unproven continuous administration strategies.
Your decision to use Epithalon should weigh the compelling longevity potential against the limited Western research validation, understanding this remains an investigational anti-aging intervention rather than established medical treatment. For those comfortable with this risk-benefit profile, Epithalon offers a unique approach to cellular rejuvenation unavailable through any other peptide class or pharmaceutical intervention.
Helpful resources for Epithalon
Peptide calculator - Calculate doses
Peptide reconstitution calculator - Mix correctly
Free peptide reconstitution calculator - Alternative calculator
Peptide cost calculator - Budget planning
Peptide cycle planning guide - Cycle planning
Take care of yourself, join us