Jan 6, 2026

Peptide stability at room temperature represents one of the most misunderstood aspects of peptide handling, with consequences ranging from reduced efficacy to complete compound degradation.
The molecular structure of peptides makes them inherently sensitive to environmental conditions, and temperature plays a decisive role in determining shelf life.
Understanding whether peptides expire requires examining the complex interplay between amino acid sequences, moisture content, and thermal energy. Most lyophilized peptides maintain stability for days to weeks at room temperature, while reconstituted peptides degrade within hours without refrigeration.
This guide covers the science behind peptide degradation at ambient temperatures, specific timeframes for different peptide types, proper storage protocols that preserve potency, warning signs indicating compromised compounds, and recovery strategies when temperature exposure occurs. SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for understanding peptide stability and maximizing the value of your research compounds through evidence-based storage practices.
Understanding peptide molecular stability
Peptides consist of amino acid chains connected by peptide bonds, and these bonds possess specific vulnerabilities to environmental stress. Temperature affects the kinetic energy within molecules, accelerating chemical reactions that break down peptide structures. The degradation process involves multiple pathways including hydrolysis, oxidation, deamidation, and aggregation. Each pathway responds differently to temperature changes, creating complex stability profiles that vary between peptide compounds.
The chemistry of peptide degradation
Hydrolysis represents the primary degradation mechanism for peptides exposed to moisture at elevated temperatures. Water molecules attack peptide bonds, cleaving the amino acid chain into smaller fragments. This reaction accelerates dramatically with temperature, roughly doubling in rate for every 10°C increase. Injectable peptides face particular hydrolysis risk once reconstituted because the aqueous environment provides abundant water molecules for the reaction.
Oxidation affects peptides containing methionine, cysteine, tryptophan, and histidine residues. Oxygen reacts with these amino acids, altering their structure and potentially destroying biological activity. Room temperature storage exposes peptides to atmospheric oxygen, and higher temperatures increase oxidation rates. Many popular peptides contain oxidation-sensitive residues, making proper storage essential for maintaining potency.
Deamidation occurs when asparagine and glutamine residues lose their amide groups, converting to aspartic and glutamic acid respectively. This modification changes the peptide's charge and can significantly impact receptor binding. Deamidation proceeds faster at higher temperatures and represents a major stability concern for peptides stored at room temperature for extended periods.
Aggregation happens when peptide molecules stick together, forming larger complexes that may precipitate from solution or lose biological activity. Temperature fluctuations particularly promote aggregation as peptides unfold and refold repeatedly. Peptide injection protocols emphasize avoiding aggregated solutions because they may cause injection site reactions and deliver unpredictable doses.
Lyophilized versus reconstituted stability
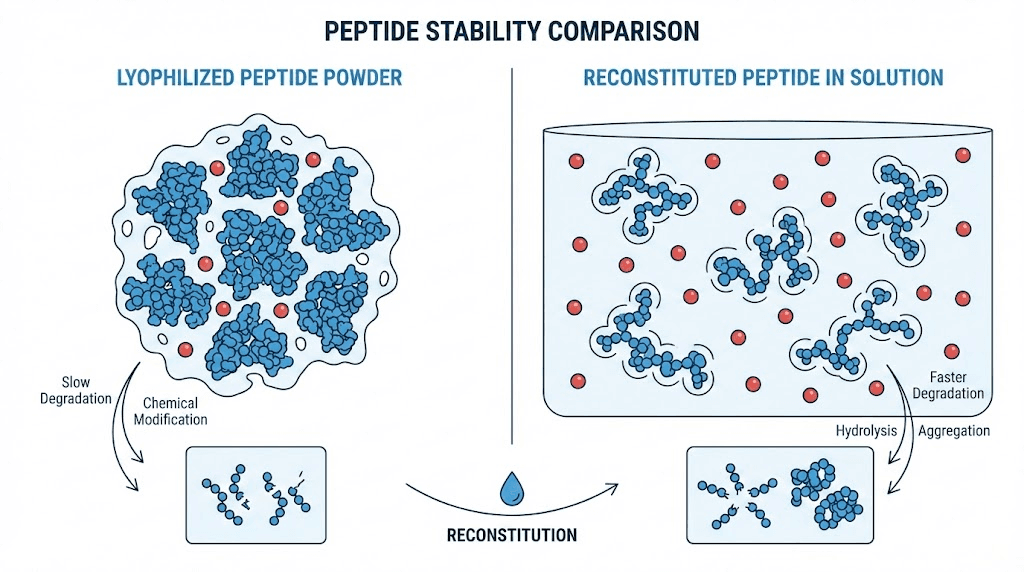
The physical state of a peptide dramatically influences its room temperature stability. Lyophilized peptides exist as dry powders with minimal moisture content, which removes water as a reactant for hydrolysis. This freeze-dried state provides substantial protection against degradation, allowing many peptides to survive weeks or even months at room temperature without significant potency loss.
Reconstituted peptides present a completely different stability profile. Once dissolved in bacteriostatic water or another solvent, peptides become vulnerable to all aqueous degradation pathways. The clock starts ticking immediately upon reconstitution, and room temperature storage accelerates the countdown dramatically. Reconstituted peptide storage guidelines universally recommend refrigeration, and room temperature exposure should be minimized to the time required for preparation and administration.
Room temperature timeframes by peptide type
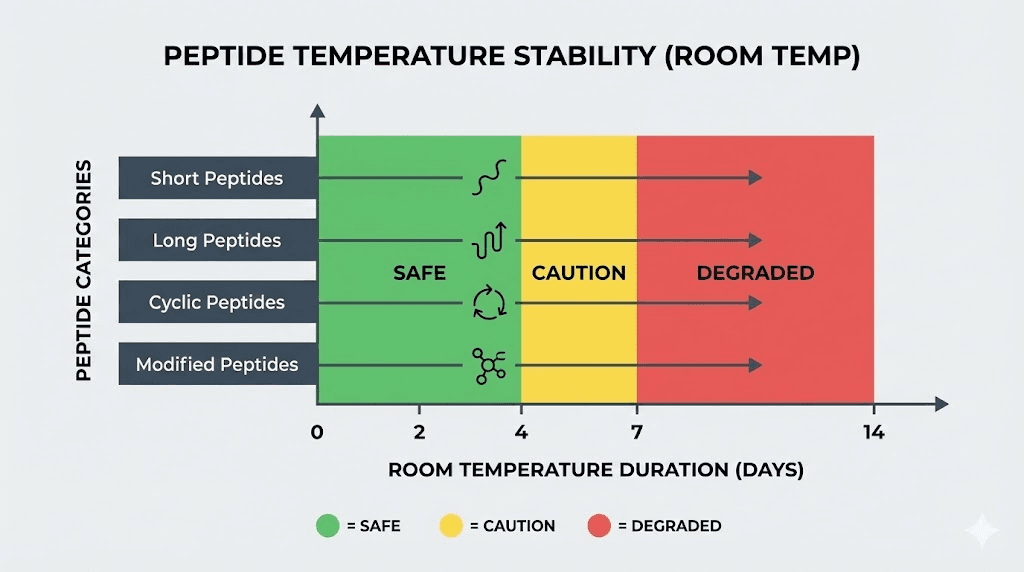
Different peptides exhibit varying stability profiles based on their amino acid composition, molecular weight, and structural features. Understanding these differences helps researchers and users make informed decisions about storage and handling. The following sections detail specific timeframes for major peptide categories when exposed to room temperature conditions.
Healing and recovery peptides
BPC-157 demonstrates relatively good stability among therapeutic peptides. Lyophilized BPC-157 typically maintains potency for 2-4 weeks at room temperature, though refrigeration extends this significantly. Once reconstituted, BPC-157 should not remain at room temperature for more than 1-2 hours during use. The pentadecapeptide structure provides moderate stability, but the compound still degrades through standard pathways when exposed to heat and moisture.
Peptides for tissue repair generally share similar stability characteristics. TB-500 shows comparable room temperature tolerance in lyophilized form, lasting 2-3 weeks under typical conditions. The TB-500 dosing protocols recommend preparing only what will be used within a short timeframe to minimize stability concerns.
Fast injury healing applications often combine multiple peptides, and the stability of these combinations depends on the least stable component. When stacking healing peptides, storage decisions should account for the most temperature-sensitive compound in the mixture.
Growth hormone secretagogues
Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 represent commonly used growth hormone releasing peptides with distinct stability profiles. Ipamorelin demonstrates moderate stability, maintaining potency for approximately 2-3 weeks at room temperature in lyophilized form. CJC-1295 shows similar characteristics, though the DAC (Drug Affinity Complex) modified version may exhibit slightly different degradation kinetics.
HGH Fragment 176-191 requires more careful handling due to its shorter amino acid sequence. Smaller peptides often degrade faster because they have fewer stabilizing intramolecular interactions. This fragment should not remain at room temperature for more than 1-2 weeks in powder form, and reconstituted solutions demand immediate refrigeration.
Muscle growth peptides as a category tend toward moderate stability, but users should err on the side of caution. The investment in these compounds justifies proper storage practices that maximize potency retention.
Metabolic peptides
Semaglutide benefits from structural modifications that enhance stability compared to native GLP-1. The fatty acid chain attachment and amino acid substitutions reduce degradation susceptibility. Lyophilized semaglutide can tolerate room temperature for 3-4 weeks, making it more forgiving than many peptides. However, comparing semaglutide to tirzepatide reveals that both compounds still benefit from refrigerated storage.
Cagrilintide combined with semaglutide creates additional stability considerations. Cagrilintide as an amylin analog has its own degradation profile, and combination products require storage conditions that protect both components. The CagriSema dosing protocols specify storage requirements that account for the stability of each peptide.
Weight loss peptides often represent significant financial investments, making proper storage economically important. The cost of replacing degraded peptides typically exceeds the minimal effort required for appropriate temperature control.
Copper peptides and skincare compounds
GHK-Cu copper peptide presents unique stability challenges due to the copper ion coordination. The metal-peptide complex can dissociate at elevated temperatures, releasing free copper and reducing efficacy. GHK-Cu longevity depends heavily on storage conditions, with room temperature exposure limited to 1-2 weeks for lyophilized material.
Copper peptide refrigeration is strongly recommended for maintaining the metal coordination essential for biological activity. Understanding GHK-Cu effects includes recognizing that degraded product may not deliver expected results.
Natural skin peptides vary widely in stability based on their source and structure. Syn-Ake and similar cosmetic peptides typically include stabilizing excipients in commercial formulations that extend room temperature tolerance.
Scientific factors affecting room temperature stability
Multiple variables beyond temperature influence how long peptides remain viable at ambient conditions. Understanding these factors enables better storage decisions and helps predict stability under various circumstances.
The interaction between temperature and other environmental conditions creates complex degradation scenarios that require comprehensive management.
Humidity and moisture exposure
Ambient humidity dramatically affects lyophilized peptide stability at room temperature. High humidity environments allow moisture absorption into supposedly dry peptide powders, initiating hydrolysis reactions even in unopened vials. Improperly sealed containers expose peptides to atmospheric moisture, accelerating degradation beyond what temperature alone would cause.
The relationship between humidity and degradation rate follows predictable patterns. Below 30% relative humidity, most lyophilized peptides maintain reasonable stability at room temperature. Above 60% humidity, degradation accelerates substantially even at moderate temperatures. Tropical and coastal climates pose particular challenges for peptide storage.
Desiccants can mitigate humidity effects when proper refrigeration is unavailable. Silica gel packets placed with peptide vials absorb moisture and extend room temperature viability. However, desiccants represent a secondary measure and cannot substitute for appropriate temperature control.
Light exposure considerations
Ultraviolet and visible light accelerate peptide degradation through photochemical reactions. Aromatic amino acids including tyrosine, tryptophan, and phenylalanine absorb UV radiation, leading to structural modifications. Peptide transformation under light exposure can convert active compounds to inactive or potentially problematic variants.
Room temperature storage often coincides with light exposure because refrigerators provide dark environments while countertops and shelves do not. Amber vials offer protection against light-induced degradation, and peptides stored at room temperature should always remain in light-protective containers.
The combination of room temperature and light exposure creates synergistic degradation effects. Studies show that peptides exposed to both conditions degrade faster than predicted by either factor alone. Dark, temperature-controlled storage remains the gold standard for peptide preservation.
Oxygen and oxidative stress
Atmospheric oxygen reacts with susceptible amino acid residues, particularly during extended room temperature storage. Oxidation reactions produce modified peptides with altered or absent biological activity. Injectable peptide formulations often include antioxidants to combat oxidative degradation, but these protective agents have limited capacity.
Vial headspace management affects oxidation rates at room temperature.
Vials with large air pockets above the peptide provide more oxygen for degradation reactions. Proper reconstitution techniques minimize headspace and reduce oxidative exposure.
Nitrogen flushing represents a professional-grade protection method.
Replacing air with inert nitrogen removes oxygen from the storage environment. Some research-grade peptides arrive in nitrogen-flushed vials, and maintaining this atmosphere during storage extends room temperature viability.
pH and solution chemistry
Reconstituted peptide stability depends heavily on solution pH. Most peptides exhibit optimal stability within specific pH ranges, typically between 4 and 7. Deviations from optimal pH accelerate degradation, and this effect intensifies at room temperature.
Peptide reconstitution with appropriate diluents helps maintain favorable pH conditions.
Bacteriostatic water typically has near-neutral pH, supporting stability.
Acidic or alkaline reconstitution solutions may provide antimicrobial benefits but can accelerate peptide breakdown.
Buffer systems in peptide formulations help resist pH changes that occur during storage. Phosphate, acetate, and citrate buffers appear in many commercial peptide products. These buffers provide stability insurance but cannot overcome the thermodynamic drive toward degradation at elevated temperatures.
Practical storage guidelines and best practices
Converting stability science into actionable protocols requires practical guidelines suitable for various storage scenarios. The following recommendations address real-world situations where room temperature exposure may be unavoidable while minimizing degradation risk.
Shipping and transit considerations
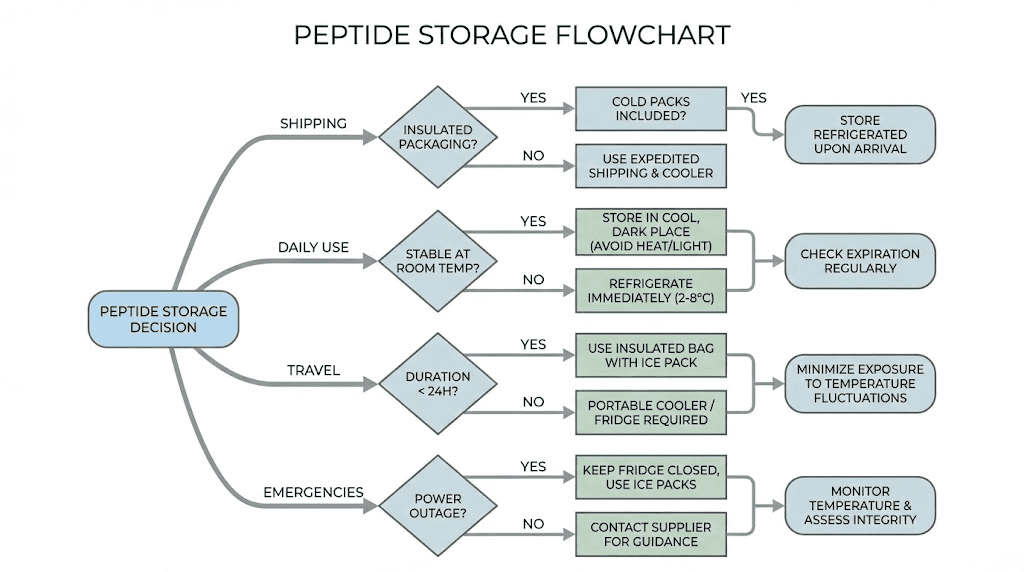
Peptide shipments often experience room temperature exposure during transit. Lyophilized peptides generally tolerate shipping conditions lasting 1-3 days without significant degradation. Most reputable vendors ship with appropriate packaging to minimize temperature excursions.
Legal peptide sourcing through established suppliers typically includes cold chain management. Insulated packaging with ice packs maintains reduced temperatures during transit. Summer shipments may require expedited delivery to minimize heat exposure.
Upon receipt, peptides should be refrigerated immediately.
Even if packaging feels cool, transferring products to controlled temperature storage maximizes remaining shelf life. Delayed refrigeration after delivery wastes some of the room temperature tolerance that protected the peptide during shipping.
Reconstitution and handling protocols
Peptide calculators help determine appropriate reconstitution volumes, minimizing waste from unused material. Reconstitute only what will be used within the refrigerated storage window rather than preparing large quantities that may degrade.
During reconstitution, peptides should remain at room temperature only as long as necessary for the process. Allow refrigerated peptides to equilibrate briefly before opening to prevent condensation, but complete the reconstitution process efficiently. Injection preparation should occur immediately before administration rather than hours in advance.
The BPC-157 calculator and similar tools help optimize dose preparation to avoid excess reconstituted material. Calculating exact amounts needed reduces waste and ensures each dose comes from freshly prepared solution.
Emergency and travel scenarios
Travel situations may necessitate temporary room temperature storage. For trips lasting 1-2 days, lyophilized peptides in sealed vials generally survive without refrigeration. Longer travel requires portable cooling solutions such as insulated bags with ice packs or mini refrigerators.
Power outages present unexpected room temperature exposure scenarios. Keeping refrigerator doors closed maintains cold temperatures for 4-6 hours. Peptides near the back of the refrigerator stay coldest longest. After extended outages, evaluate peptide appearance before use.
Tracking peptide results helps identify whether storage compromises affected potency. Users maintaining detailed logs can correlate outcomes with storage conditions, identifying problems early.
Signs of peptide degradation
Recognizing degraded peptides prevents administration of ineffective or potentially problematic compounds.
Visual inspection, physical characteristics, and functional assessment all contribute to degradation detection. Learning these warning signs protects users from wasted doses and unexpected outcomes.
Visual indicators
Color changes often signal oxidative degradation. Clear solutions turning yellow, brown, or pink suggest chemical modifications have occurred. Copper peptide concerns particularly manifest through color shifts as the copper coordination changes.
Cloudiness or precipitation indicates aggregation or insolubility of degradation products. Originally clear reconstituted peptides should remain clear. Hazy solutions or visible particles suggest the peptide has undergone structural changes incompatible with remaining dissolved.
Clumping in lyophilized powder reveals moisture absorption. Dry peptide powder should flow freely when the vial is gently shaken. Caked or clumped powder has likely absorbed humidity and begun degrading even before reconstitution.
Physical property changes
Reconstitution difficulties may indicate degradation. Fresh lyophilized peptides typically dissolve readily in appropriate diluents. Peptides requiring excessive agitation, extended dissolution times, or failing to fully dissolve have likely degraded.
Unusual foam or bubbles during reconstitution can signal degradation products that affect surface tension. Some foaming is normal, but excessive or persistent bubbling warrants caution.
Odor changes occasionally accompany peptide degradation, particularly oxidative breakdown. While most peptides have minimal scent, strong or unusual odors suggest chemical changes have occurred.
Functional assessment
Reduced efficacy represents the most reliable degradation indicator but requires prior experience with functional product. Peptide protocols for men and safe peptides for women both emphasize consistent sourcing and storage to enable meaningful comparison between doses.
Unexpected responses may indicate degradation products with different biological activities. Some peptide breakdown products retain partial activity while others become inactive. Occasionally, degradation creates compounds with different receptor interactions than the parent peptide.
Analytical testing methods provide definitive degradation assessment but require specialized equipment. Mass spectrometry, HPLC, and other analytical techniques can quantify intact peptide remaining after storage. These methods serve research applications where precise potency determination is essential.
Comparing peptide storage methods
Understanding the relative merits of different storage approaches helps optimize peptide preservation. Room temperature represents just one option on a spectrum from frozen storage to elevated temperature stress. Each method offers different balances of convenience, cost, and stability.
Storage Method | Temperature Range | Lyophilized Duration | Reconstituted Duration | Cost | Convenience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Frozen (-20°C) | -20 to -10°C | 2-3 years | 3-6 months | Medium | Low |
Refrigerated (2-8°C) | 2-8°C | 1-2 years | 2-4 weeks | Low | High |
Cool Room Temperature | 15-20°C | 1-3 months | 8-24 hours | None | Very High |
Standard Room Temperature | 20-25°C | 2-4 weeks | 2-8 hours | None | Very High |
Warm Room Temperature | 25-30°C | 1-2 weeks | 1-2 hours | None | Very High |
The table above provides general guidelines, but individual peptides may vary significantly from these estimates. Research-grade versus pharmaceutical peptides may contain different stabilizers affecting storage duration. Always defer to manufacturer recommendations when available.
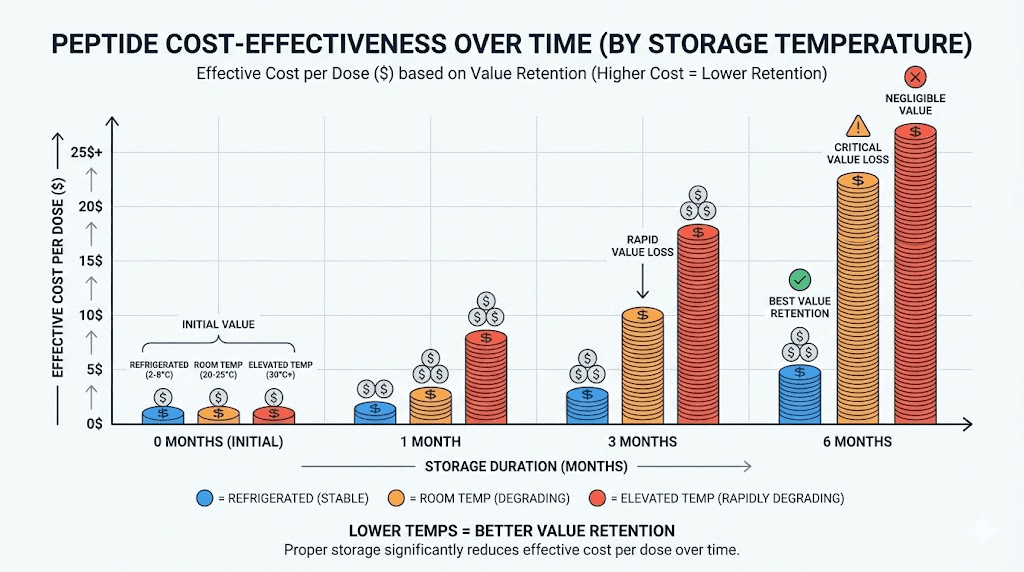
Cost-benefit analysis of storage options
Refrigeration represents the optimal balance for most peptide users. Standard household refrigerators maintain appropriate temperatures with minimal operating cost. The stability extension compared to room temperature storage typically justifies any minor inconvenience.
Peptide cost calculations reveal that storage-related degradation represents a significant expense category. A peptide losing 50% potency effectively costs twice as much per effective dose. Proper storage investment pays for itself through maintained potency.
Frozen storage makes sense for long-term inventory but introduces freeze-thaw concerns for reconstituted materials. Repeated freezing and thawing damages peptides through ice crystal formation. Reserve frozen storage for unopened lyophilized vials and long-term stockpiling.
Specific peptide stability profiles
Individual peptides warrant specific consideration based on their unique stability characteristics. The following profiles detail room temperature tolerance for commonly used compounds, enabling informed storage decisions.
BPC-157 stability specifics
BPC-157 contains 15 amino acids in a sequence that provides moderate inherent stability. The pentadecapeptide lacks highly oxidation-sensitive residues, contributing to reasonable room temperature tolerance. Lyophilized BPC-157 typically maintains 90%+ potency for 2-3 weeks at controlled room temperature (20-25°C).
BPC-157 regulatory status varies by jurisdiction, but storage recommendations remain consistent regardless of legal classification. The compound benefits from dark, dry storage conditions. Comparing BPC-157 to TB-500 reveals similar stability profiles for these healing peptides.
Reconstituted BPC-157 requires refrigeration and should not remain at room temperature beyond the preparation and administration window. Most protocols suggest discarding reconstituted BPC-157 left unrefrigerated for more than 2 hours.
Semaglutide and GLP-1 analogs
Semaglutide incorporates structural modifications specifically designed to improve stability. The acylated side chain and amino acid substitutions extend half-life in vivo and also improve storage stability. Lyophilized semaglutide shows excellent room temperature tolerance, often maintaining potency for a month or more.
Cagrilintide and retatrutide represent newer metabolic peptides with varying stability profiles. Cagrilintide combined with tirzepatide requires storage conditions that protect both components.
Commercial GLP-1 products often include proprietary stabilizers enabling room temperature storage for specified periods.
Compounded or research-grade materials may lack these additives and require more conservative storage practices.
Growth hormone peptides
Safe muscle growth peptides in the growth hormone secretagogue category show variable room temperature stability. Ipamorelin versus CJC-1295 comparisons reveal slightly better stability for CJC-1295 DAC due to its larger molecular weight and additional protective features.
HGH Fragment 176-191 requires more careful handling than full-length growth hormone peptides. The shorter sequence provides less structural stability, making refrigeration particularly important. Room temperature exposure should not exceed 1 week for lyophilized fragment peptides.
Athletic performance peptides often face storage challenges during competition travel. Planning ahead with appropriate cooling solutions prevents compromising expensive peptide investments.
Specialty and niche peptides
Selank and anxiety-targeting peptides typically show moderate room temperature stability. These nootropic compounds benefit from standard refrigeration practices.
PT-141 (bremelanotide) and PT-141 nasal spray formulations have specific stability requirements depending on formulation. Nasal spray preparation may include stabilizers extending room temperature viability.
KPV peptide and timing protocols should account for stability when determining storage between doses. Gut health applications may require frequent dosing, making stability particularly relevant.
Epitalon, Pinealon, Cartalax, and other anti-aging peptides vary in stability based on their specific sequences. Chonluten, Ovagen, and Pancragen from the Khavinson peptide family share similar short-sequence characteristics affecting stability.
Recovery and damage assessment protocols
When peptides experience unintended room temperature exposure, systematic assessment helps determine whether the product remains viable. Not all temperature excursions result in complete degradation, and proper evaluation prevents unnecessary waste.
Assessing exposure severity
Duration matters significantly. Brief exposure (under 1-2 hours) rarely causes substantial degradation for lyophilized peptides. Extended exposure (days to weeks) progressively reduces potency. Knowing exactly how long the peptide remained at elevated temperature enables better assessment.
Temperature specifics affect outcomes. Air-conditioned room temperature (20-22°C) causes less damage than summer heat (30°C+). If possible, determine the actual temperature the peptide experienced rather than assuming worst-case scenarios.
Peptide state influences vulnerability. Lyophilized peptides tolerate temperature excursions much better than reconstituted solutions. An unopened vial left out overnight faces lower risk than a reconstituted vial in the same conditions.
Visual and physical inspection
After temperature exposure, carefully examine the peptide before use. Check lyophilized powder for caking, discoloration, or unusual appearance. Assess reconstituted solutions for clarity, color, and any precipitation.
Compare current appearance to the peptide's original state when received. Significant changes suggest degradation has occurred. Subtle or no changes indicate the peptide may have survived exposure intact.
When in doubt, start with a reduced dose to assess response before committing to a full protocol. Gradual dose escalation helps identify whether the peptide retains expected activity.
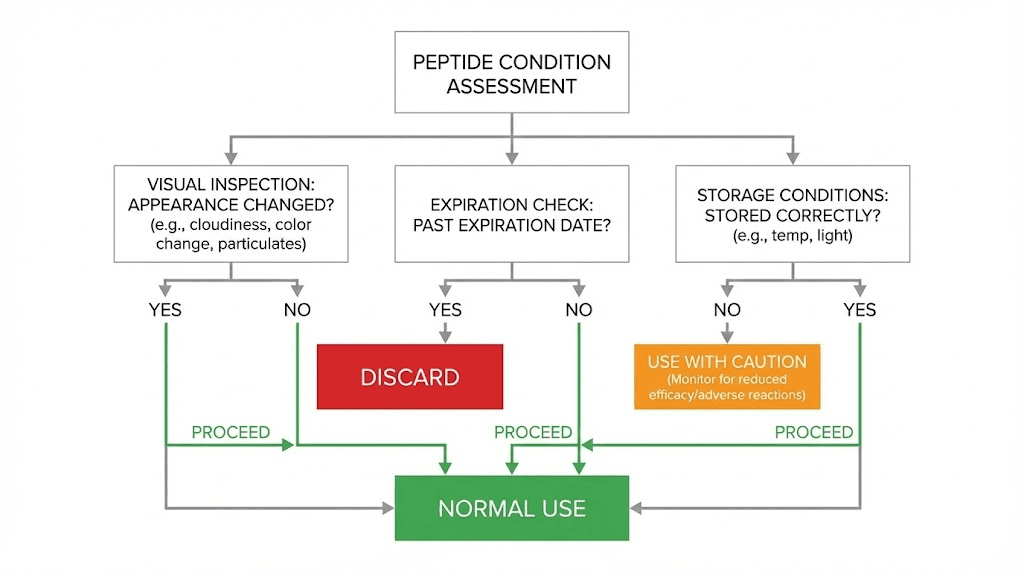
Decision framework for compromised peptides
Definitely discard if: visible precipitation, significant color change, unusual odor, reconstituted solution left at room temperature more than 4 hours, or lyophilized peptide at warm temperature for more than 2 weeks.
Probably safe to use if: sealed lyophilized vial at controlled room temperature for less than 1 week, brief reconstituted exposure under 2 hours, no visible changes, and peptide responds normally on initial test dose.
Use with caution if: intermediate exposure duration, minor changes in appearance, or storage conditions unknown. Consider reduced dosing and careful monitoring of response.
Peptide stacking and combination storage
Many protocols involve multiple peptides stored and used together. Peptide stacking introduces additional storage considerations because different peptides in a stack may have different stability requirements.
Storage compatibility in stacks
When storing multiple peptides, organize by stability requirements. Group peptides with similar temperature needs together. Store the most temperature-sensitive compound at appropriate conditions, as this protects the entire stack.
Strength protocols often combine growth hormone peptides with healing compounds. Both categories tolerate standard refrigeration well, making combined storage straightforward.
Fat loss stacks may include metabolic peptides with excellent stability alongside more sensitive compounds. Default to conditions required by the least stable component.
Combined reconstitution considerations
Some users reconstitute multiple peptides in the same vial for convenience. This practice introduces cross-contamination and stability risks. If combining peptides, use immediately rather than storing the mixture.
Injectable preparations require sterile technique regardless of storage duration. Contaminated vials degrade faster and pose additional risks beyond peptide degradation.
Keep detailed records of reconstitution dates for each peptide in a stack. Different reconstitution times mean different expiration windows. Track each vial individually to avoid using degraded products.
Regional and environmental considerations
Storage challenges vary significantly based on geographic location and local conditions. Users in different climates face distinct obstacles to peptide preservation.
Hot climate storage
Tropical and desert regions present severe peptide storage challenges. Summer temperatures exceeding 30°C dramatically accelerate degradation. Air conditioning becomes essential rather than optional for peptide storage.
Power reliability affects storage planning in some regions. Backup cooling solutions, including insulated containers with ice packs, provide protection during outages. Freezing water bottles in advance creates emergency cooling capacity.
Peptide therapy in Houston, Austin, Scottsdale, Las Vegas, Miami Beach, and Atlanta all involve hot climate considerations that affect storage planning.
Cold climate advantages
Northern climates offer natural cooling potential during winter months. However, freezing temperatures pose their own risks for reconstituted peptides. Ice crystal formation damages protein structure.
Insulated storage prevents both overheating and freezing. Temperature-stable locations within buildings provide consistent conditions year-round. Interior closets or cabinets often maintain more stable temperatures than exterior walls or garages.
Humidity management
Coastal and tropical regions experience high humidity that threatens lyophilized peptide stability. Dehumidifiers in storage areas help control moisture levels. Desiccant packets inside storage containers provide additional protection.
Sealed containers with fresh desiccant offer superior humidity protection compared to original vial packaging alone. Consider transferring peptides to airtight secondary containers for long-term storage in humid environments.
Vendor quality and initial stability
Peptide quality at purchase significantly affects room temperature tolerance. Properly manufactured and handled peptides arrive with full potency to draw upon during storage. Compromised products may have reduced stability reserves from the start.
Recognizing quality indicators
Prime Peptides reviews, Polaris Peptides reviews, Nexaph reviews, and comparisons of vendors like Integrity Research Peptides, Profound Peptides, NextGen Peptides, Elite Research Peptides, Purest Peptide, Power Peptides, Planet Peptides, Transcend Peptides, Lean Peptides, Revive Peptides, and RPO Peptides help identify reliable sources.
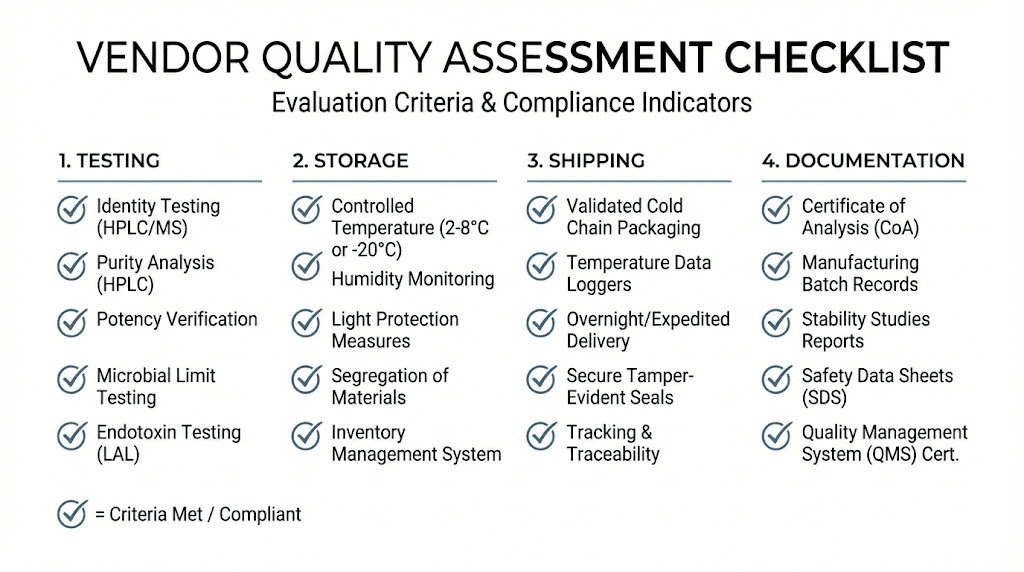
Quality vendors provide certificates of analysis documenting purity and potency. Third-party testing verification adds credibility. Understanding analytical reports enables informed vendor assessment.
Shipping practices reflect vendor commitment to quality. Appropriate packaging, cold packs for temperature-sensitive items, and expedited shipping options indicate serious quality management.
Storage before purchase
Vendor storage practices before shipment affect the peptide's stability budget. Properly stored inventory arrives with maximum remaining shelf life. Products stored poorly before purchase may have reduced room temperature tolerance.
Purchase from vendors with appropriate storage facilities. Ask about inventory management practices. Fast-moving products from popular vendors spend less time in storage before reaching customers.
Manufacturing date information, when available, helps assess remaining stability. Fresher products provide longer useful life. Avoid deeply discounted peptides that may be near expiration.
How SeekPeptides supports peptide storage education
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for understanding peptide stability and implementing proper storage practices. The platform offers tools and guides addressing every aspect of peptide handling from purchase through administration.
The reconstitution calculator helps determine appropriate dilution volumes, minimizing waste from excess preparation. Proper reconstitution supports stability by avoiding unnecessarily dilute solutions. The peptide calculator enables precise dose calculations, ensuring prepared amounts match actual needs.
Educational guides covering peptide expiration and reconstituted storage duration provide detailed information beyond this overview. Specific peptide storage requirements receive dedicated coverage.
SeekPeptides remains committed to evidence-based peptide education, helping users maximize value from their peptide investments through proper handling and storage practices.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night.
May your peptides stay potent, your storage stay cool, and your protocols stay effective. Join SeekPeptides.