Jan 19, 2026

Your testosterone levels have been dropping for years. You have tried the supplements. You have optimized your sleep. You have lifted heavy things and eaten your cruciferous vegetables. And yet, the numbers keep sliding downward, taking your energy, your drive, and your recovery capacity with them. Traditional testosterone replacement therapy sits on the table as an option, but you know the tradeoffs: potential fertility impacts, dependency, and the complexity of managing exogenous hormones for life.
There is another path. One that works with your body's existing regulatory systems rather than overriding them entirely.
Testagen represents a fundamentally different approach to hormonal optimization. Developed by Russian gerontologist Vladimir Khavinson over decades of research, this tetrapeptide bioregulator does not simply flood your system with hormones. It speaks directly to your DNA, modulating gene expression in ways that help restore natural function to tissues that have lost their youthful efficiency. The concept sounds almost too elegant to be true. And yet, the research, while limited to preclinical models, shows intriguing patterns of restoration rather than replacement.
This guide examines everything currently known about Testagen: its molecular mechanisms, its effects on both testosterone and thyroid function, the dosing protocols that researchers use, how it compares to other testosterone-supporting peptides, and the critical limitations you need to understand before considering it.
Whether you are researching bioregulators for the first time or evaluating whether Testagen fits into an existing peptide protocol, the information here will help you make informed decisions based on what the science actually shows.
What is Testagen and how does it work
Testagen belongs to a class of compounds called peptide bioregulators, developed primarily through the work of Professor Vladimir Khavinson at the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology. These short peptides, typically just two to seven amino acids in length, represent a different paradigm from most peptide therapeutics. Rather than binding to cell surface receptors to trigger immediate effects, bioregulators penetrate cells and interact directly with DNA to influence gene expression.
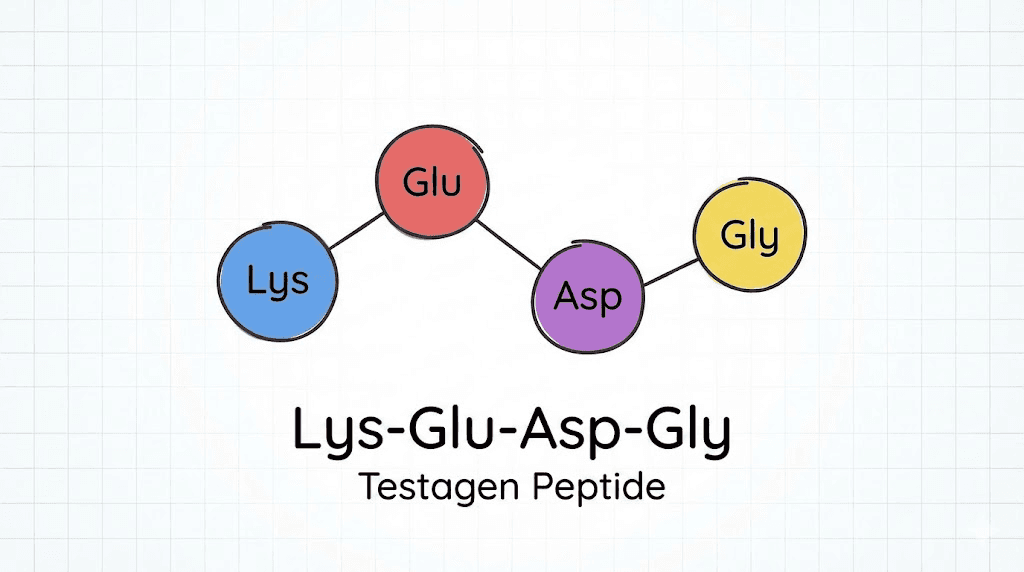
The molecular structure of Testagen is elegantly simple: just four amino acids arranged in a specific sequence.
Lysine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine combine to form what researchers call KEDG. This tetrapeptide was originally isolated from testicular tissue extracts, where it appears to play a role in regulating the genetic programs that control steroidogenesis, the process by which your body produces steroid hormones including testosterone.
What makes Testagen particularly interesting is its proposed mechanism of action. Unlike growth hormone secretagogues that stimulate pituitary release of hormones, or direct hormone replacement that bypasses natural production entirely, Testagen appears to work at the epigenetic level.
Research suggests it can cross both cellular and nuclear membranes, reaching the DNA itself where it may influence which genes get expressed and at what levels.
The epigenetic mechanism
Think of your DNA as a vast library of instructions. Every cell contains the complete set, but only certain books get pulled from the shelves depending on the cell's function and current needs. Epigenetic regulation determines which books are accessible and which remain locked away. As we age, this regulatory system can become dysregulated, with important genes getting silenced and less useful ones becoming overactive.
Testagen, according to the research conducted by Khavinson and colleagues, may help restore more youthful patterns of gene expression in specific tissues. Studies have shown that short peptides like Testagen can interact with histone proteins, the scaffolding around which DNA wraps, potentially making certain genes more or less accessible for transcription.
This is a fundamentally different approach than simply adding more of a hormone. Instead of overriding your body's regulatory systems, Testagen theoretically helps those systems function more like they did when you were younger.
The peptide is not doing the work of producing testosterone.
It is helping the tissues responsible for testosterone production remember how to do their job properly.
Target tissues and pathways
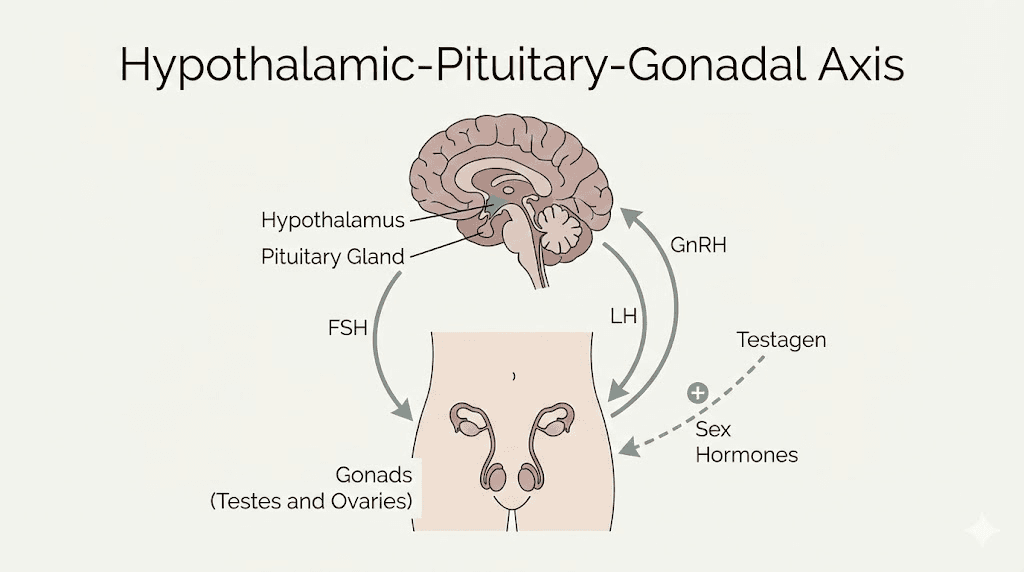
Testagen's effects center on two primary systems: the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis that controls testosterone production, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis that regulates metabolic hormones.
Effects on the HPG axis:
The HPG axis is your body's testosterone thermostat. The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which signals the pituitary to release luteinizing hormone (LH). LH then travels to the testes, where it stimulates Leydig cells to produce testosterone. When this axis becomes dysregulated, whether through aging, chronic stress, or other factors, testosterone production suffers.
Research suggests Testagen may help normalize function at multiple points along this axis. Some studies indicate effects on the anterior pituitary gland itself, potentially improving its responsiveness to hypothalamic signals. Other research points to direct effects on testicular tissue, where Testagen may influence gene expression patterns associated with steroidogenesis.
Effects on thyroid function:
Perhaps surprisingly, Testagen also appears to influence thyroid hormone production. Studies in hypophysectomized chicken models showed that Testagen could stimulate the anterior pituitary to increase release of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), ultimately raising levels of the active thyroid hormones T3 and T4.
This connection makes biological sense. Thyroid function and testosterone production are intimately linked. Hypothyroidism commonly causes low testosterone levels, and normalizing thyroid function often improves testosterone status.
By supporting both systems simultaneously, Testagen may address hormonal dysfunction more comprehensively than single-target interventions.
Research on Testagen benefits
Understanding what Testagen can and cannot do requires careful examination of the existing research. Most studies have been conducted in animal models or cell cultures, with limited human data available.
This limitation is crucial to keep in mind when evaluating claims about the peptide's benefits.
Testosterone and reproductive function
The most relevant research for those interested in testosterone optimization comes from studies examining Testagen's effects on male reproductive function.
One significant study examined men with chronic abacterial prostatitis, a condition often associated with hormonal dysfunction. Treatment with Testagen led to improvements in uroflowmetry indicators (measuring urinary flow), reduction in prostatic inflammation, and notably, elevation in serum testosterone levels. While this represents a specific clinical population rather than general testosterone optimization, it demonstrates that the peptide can influence testosterone production in human subjects.
Animal studies have shown more detailed mechanistic effects. In aged animal models, Testagen treatment appeared to reverse some age-related changes in testicular tissue at the cellular level. Researchers observed increased telomerase activity, reduced DNA damage markers, and expression of genes typically associated with younger, more functional tissue.
These findings suggest that Testagen may help restore testicular function rather than simply masking dysfunction.
Thyroid function restoration
The thyroid research on Testagen provides some of the most compelling mechanistic data available. Studies using hypophysectomized chickens, which is birds with surgically removed pituitary glands, examined whether Testagen could restore thyroid function even without normal pituitary signaling.
Hypophysectomy caused predictable changes: decreased body weight, reduced thyroid gland weight, enlarged thyroid follicles, and flattened thyrocytes (the cells that produce thyroid hormone). Treatment with Testagen partially reversed these changes, suggesting the peptide can influence thyroid tissue directly as well as through pituitary pathways.
Interestingly, researchers noted that restoration was more pronounced in younger animals compared to older ones. This suggests that while Testagen may help restore function, the degree of benefit may depend on the baseline health of the target tissues. Severely damaged or atrophied tissue may respond less robustly than tissue with milder dysfunction.
Anti-aging and cellular rejuvenation
Khavinson's broader research program has focused on peptide bioregulators as geroprotectors, compounds that may slow aging at the cellular level. Testagen fits into this framework through several proposed mechanisms.
Telomerase activation: Some research suggests Testagen may increase telomerase activity in target tissues. Telomerase is the enzyme that maintains telomeres, the protective caps on chromosome ends that shorten with each cell division. Shortened telomeres are associated with cellular aging and dysfunction. By potentially supporting telomerase activity, Testagen might help maintain cellular youth in reproductive tissues.
Gene expression normalization: Aging involves broad changes in gene expression patterns, with some beneficial genes becoming silenced and others becoming overactive. Testagen, like other bioregulators, may help restore more youthful expression patterns in its target tissues. This represents a fundamentally different approach than simply replacing hormones that decline with age.
Stem cell differentiation: Early research by Khavinson suggested that Testagen may influence stem cell differentiation, potentially helping maintain the pool of regenerative cells that support tissue repair and renewal. If confirmed, this could have significant implications for long-term tissue health.
Immune system effects
While not its primary application, Testagen may also influence immune function.
Research on Khavinson peptides broadly has shown anti-inflammatory effects, including reduced expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF and IL-6. For men dealing with chronic low-grade inflammation, which is common with aging and associated with testosterone decline, these effects could provide additional benefit beyond direct hormonal effects.
Hemostasis and blood clotting
Dr. Boris Kuznik, who collaborated with Khavinson on early bioregulator research, examined Testagen's effects on hemostasis.
Preliminary findings suggested the peptide may help normalize blood clotting function in certain disease states.
While this is not a primary reason most people would consider Testagen, it highlights the peptide's broad regulatory effects on multiple physiological systems.
Testagen dosage protocols
Dosing information for Testagen comes primarily from research protocols and clinical experience rather than formal dose-finding studies. As with all research peptides, these protocols should be understood as experimental rather than clinically validated.
Standard dosing range
For subcutaneous injection, the typical dose range falls between 100-300mcg daily. Most protocols suggest starting at the lower end of this range and adjusting based on response and tolerability.
Conservative starting protocol:
Dose: 100mcg daily
Administration: Subcutaneous injection
Timing: Morning administration preferred
Duration: 4-6 weeks initially
Standard optimization protocol:
Dose: 200-300mcg daily
Administration: Subcutaneous injection
Timing: Once daily, morning
Cycle length: 1-2 months
Break: 1-3 months between cycles
The cycling approach reflects how bioregulators are typically used. Rather than continuous administration, most protocols involve defined treatment periods followed by breaks. This pattern may help prevent receptor adaptation and allows assessment of sustained benefits.
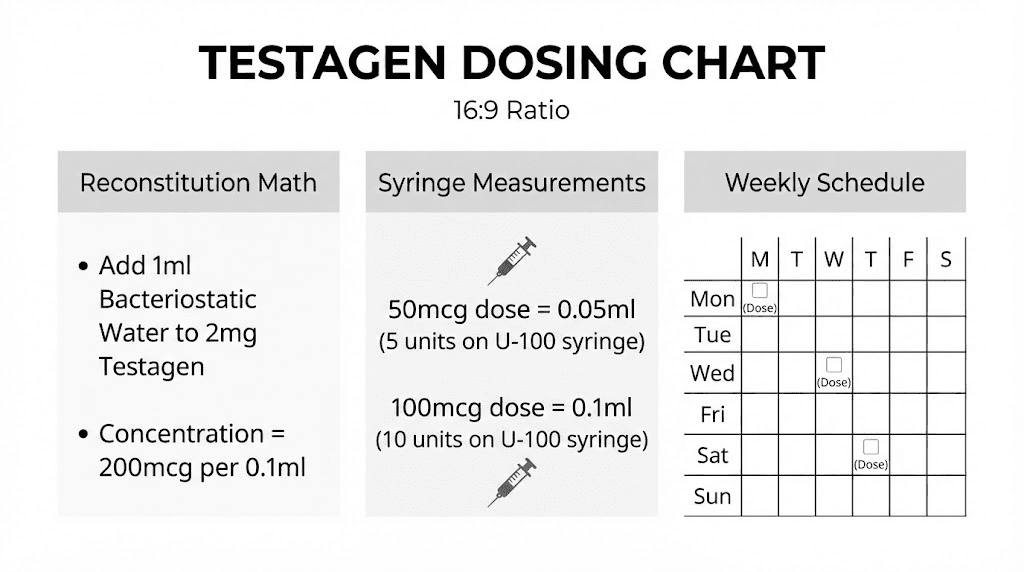
Reconstitution for injectable Testagen
Testagen typically comes in 20mg vials as lyophilized powder. Proper reconstitution ensures accurate dosing and peptide stability.
Standard reconstitution:
Add 3.0ml bacteriostatic water to a 20mg vial
Resulting concentration: approximately 6.67mg/ml (6670mcg/ml)
For 100mcg dose: draw approximately 0.015ml (1.5 units on U-100 insulin syringe)
For 200mcg dose: draw approximately 0.03ml (3 units)
The small volumes involved with Testagen dosing make accurate measurement challenging. Using a U-100 insulin syringe with fine gradations helps ensure precision. Some researchers prefer reconstituting with larger volumes to make measurement easier, though this reduces overall vial life.
Oral bioregulator protocols
Testagen is also available in capsule form as part of the Khavinson Cytogen product line.
Research suggests bioregulator peptides maintain some oral bioavailability despite their peptide structure, potentially due to their small size and specific amino acid composition.
Oral protocols typically recommend 2 capsules once or twice daily before meals, continued for one month. Some practitioners suggest repeating courses every 3-6 months for maintenance. Following oral Testagen, some protocols recommend transitioning to Testoluten, a natural testicular peptide extract, for continued support.
The relative bioavailability of oral versus injectable Testagen has not been precisely determined in humans. For those prioritizing reliability and potency, subcutaneous injection remains the preferred route.
Storage and stability
Proper peptide storage ensures Testagen maintains its activity throughout use.
Lyophilized powder: Store frozen at -20°C for maximum long-term stability. Protect from light and moisture.
Reconstituted solution: Refrigerate at 2-8°C and use within 3-4 weeks. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles, which can damage peptide structure.
Administration techniques
Testagen can be administered through several routes, each with distinct characteristics.
Subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous injection provides the most reliable absorption and is the best-documented administration route for bioregulator peptides.
Injection technique:
Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and allow to dry
Pinch a fold of skin at the abdomen (avoiding 2 inches around navel), thigh, or upper arm
Insert needle at 45-90 degree angle into the skin fold
Inject slowly and steadily
Withdraw needle and apply light pressure if needed
Rotate injection sites systematically to prevent tissue irritation or lipohypertrophy. A simple rotation through left abdomen, right abdomen, left thigh, right thigh provides adequate site variation for typical protocols.
Subcutaneous administration bypasses first-pass metabolism and delivers the peptide directly to systemic circulation.
For a small peptide like Testagen, this route provides excellent bioavailability.
Oral administration
Oral Testagen capsules offer convenience at the potential cost of reduced bioavailability. The exact oral bioavailability in humans remains undetermined, but animal studies suggest meaningful absorption is possible.
For oral use, take capsules before meals when stomach acid is lowest. The peptide's small size may allow some intact absorption before digestive breakdown. However, those seeking maximum effect typically prefer the injectable route.
Testagen compared to other testosterone peptides
Understanding how Testagen fits within the broader landscape of testosterone-supporting peptides helps clarify when it might be appropriate to consider.
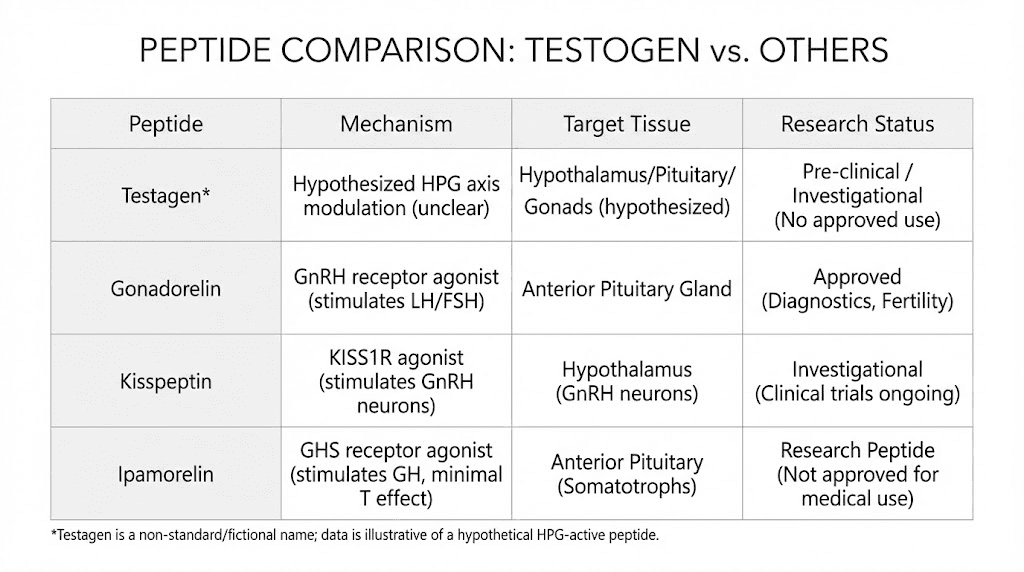
Testagen vs growth hormone secretagogues
Growth hormone secretagogues like Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 work by stimulating pituitary release of growth hormone, which indirectly supports testosterone through IGF-1 mediated effects. These peptides have more robust human research supporting their use but work through entirely different mechanisms than Testagen.
GH secretagogues may be more appropriate when growth hormone deficiency is the primary concern, with testosterone benefits being secondary.
Testagen targets the reproductive axis more directly and may be preferable when testosterone and thyroid optimization are the primary goals.
Testagen vs Gonadorelin
Gonadorelin (GnRH) directly stimulates the pituitary to release LH and FSH, providing a pharmacological push to the HPG axis. This approach is more aggressive than Testagen, essentially forcing increased output from the pituitary.
Testagen's bioregulatory approach is gentler, theoretically helping normalize function rather than override it. Gonadorelin may be appropriate for acute intervention, while Testagen's mechanism suits longer-term optimization goals.
Testagen vs Kisspeptin
Kisspeptin sits upstream of GnRH in the HPG axis, stimulating the hypothalamus to release GnRH.
Like Gonadorelin, it provides a pharmacological stimulus to the hormonal cascade rather than the epigenetic modulation proposed for Testagen.
Testagen vs other Khavinson bioregulators
Epithalon is probably the most well-known Khavinson peptide, targeting the pineal gland to support melatonin production and potentially telomerase activation. While both are bioregulators, they target different tissues: Epithalon focuses on circadian rhythm and general anti-aging, while Testagen targets reproductive and thyroid function specifically.
Many practitioners combine multiple bioregulators to address different organ systems simultaneously. Testagen stacks well with Epithalon (for sleep and anti-aging), Pinealon (for cognitive support), and Thymalin (for immune function).
Stacking Testagen with other peptides
Combining Testagen with complementary peptides may enhance overall results, though such combinations add complexity and should be approached thoughtfully.
Testagen + Epithalon stack
This combination addresses hormonal and anti-aging goals simultaneously. Epithalon supports melatonin production and circadian rhythm, which indirectly affects testosterone production since testosterone synthesis peaks during deep sleep.
The two bioregulators work through different pathways, potentially providing synergistic benefit.
Example protocol:
Testagen: 100-200mcg morning
Epithalon: 100-200mcg evening
Cycle: 4-6 weeks on, 4-6 weeks off
Testagen + Thymalin stack
For those concerned about both hormonal and immune function, combining Testagen with Thymalin (a thymus bioregulator) may provide broader support.
This combination has been suggested for chronic prostatitis cases where both endocrine and immune dysfunction contribute to symptoms.
Testagen + BPC-157 stack
While BPC-157 is not a bioregulator, combining it with Testagen might support both hormonal optimization and tissue healing. Men dealing with chronic inflammation or injury alongside testosterone concerns might consider this combination, though it represents a more complex protocol requiring careful consideration.
Safety, side effects, and contraindications
Testagen's safety profile appears favorable based on available research, though human clinical trial data remains limited.
Reported side effects
The most commonly reported effects include:
Injection site reactions: Minor redness, swelling, or itching at injection sites. These typically resolve quickly and can be minimized by proper injection technique and site rotation.
Increased appetite: Some users report increased hunger, potentially related to effects on metabolic signaling. Managing dietary intake during Testagen use may be necessary to avoid unintended weight gain.
Mild headache or fatigue: Occasionally reported, though rare. These effects typically resolve with continued use or dose adjustment.
Mood changes: As with any intervention affecting hormonal systems, some users report shifts in mood or libido. These are generally positive (improved mood, increased libido) but can occasionally present as irritability or restlessness.
Notably, some sources claim Testagen produces no side effects or allergic reactions. However, any bioactive compound has potential for individual reactions, and such absolute claims should be viewed skeptically.
Contraindications
Testagen should be avoided in certain situations:
Known hypersensitivity: Anyone with allergic reactions to Testagen's component amino acids should avoid use.
Active malignancies: Due to potential effects on cell proliferation and gene expression, Testagen is contraindicated in those with active cancer.
Thyroid cancer or hyperthyroidism: Given Testagen's effects on thyroid function, those with thyroid malignancy or overactive thyroid should not use it.
Hormone-sensitive conditions: Prostate cancer, breast cancer (in those with male breast tissue concerns), or other hormone-sensitive conditions warrant extreme caution.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Insufficient safety data exists for use during pregnancy or lactation.
Drug interactions
Specific drug interaction studies for Testagen have not been conducted. However, theoretical interactions warrant consideration:
Thyroid medications: If you take levothyroxine or other thyroid medications, Testagen's effects on TSH could alter your requirements. Close monitoring would be essential.
Hormone therapies: Those on testosterone replacement therapy or other hormone treatments should consult their provider before adding Testagen, as effects could be additive or interfering.
Immunosuppressants: Given potential immune-modulating effects, those on immunosuppressive medications should exercise caution.
What Testagen cannot do
Honest assessment of Testagen's limitations is essential for realistic expectations.
It is not testosterone replacement
Testagen does not directly increase testosterone levels the way TRT does. If your testosterone production machinery is severely compromised, Testagen's gene-regulatory approach may not produce the dramatic increases seen with direct hormone replacement. The peptide works best when supporting underperforming but still functional tissue.
Human research is limited
Most Testagen research has been conducted in animal models or cell cultures. While the available human data is promising, it comes from specific clinical populations rather than general testosterone optimization studies. Extrapolating results from prostatitis patients or elderly subjects to healthy men seeking optimization involves uncertainty.
Effects may be subtle
Bioregulators work through gentle modulation rather than dramatic intervention. Users expecting rapid, obvious changes may be disappointed. Benefits often emerge gradually over weeks to months and may be more noticeable as sustained function rather than acute improvement.
Quality varies significantly
As a research peptide without FDA approval, Testagen quality control depends entirely on vendor standards.
Underdosed, contaminated, or degraded product is possible from less reputable sources.
Verification of peptide purity through third-party testing certificates is essential.
Who might benefit from Testagen
Based on its proposed mechanisms and available research, certain profiles may be better candidates for Testagen than others.
Good candidates
Men with mild to moderate testosterone decline: Those whose levels have declined but whose testicular function is not severely compromised may respond well to Testagen's supportive approach.
Those seeking natural optimization: Men who prefer working with their body's systems rather than overriding them with exogenous hormones may find Testagen's bioregulatory mechanism appealing.
Thyroid-testosterone connection: Men whose testosterone decline appears related to suboptimal thyroid function might benefit from Testagen's dual-axis support.
Post-cycle recovery: Some bodybuilders use Testagen as part of post-cycle therapy to help restore natural hormonal function after anabolic steroid use.
Anti-aging focused individuals: Those interested in Khavinson's broader longevity research may include Testagen as part of a comprehensive bioregulator protocol.
Less suitable candidates
Severe hypogonadism: Men with severely compromised testosterone production may need more aggressive intervention than Testagen provides.
Those seeking rapid results: Testagen's gradual, regulatory mechanism is not suited for those wanting dramatic, quick changes.
Primary testicular failure: If the testes themselves are damaged beyond restoration, supporting their gene expression may have limited benefit.
Practical considerations for researchers
For those considering Testagen research protocols, several practical factors warrant attention.
Sourcing quality peptide
Testagen should come from vendors providing third-party certificates of analysis confirming purity and identity. Look for:
Purity testing (HPLC) showing 98%+ purity
Mass spectrometry confirming molecular identity
Proper cold-chain shipping
Appropriate packaging protecting from light and moisture
Baseline testing
Establishing baseline hormone levels before starting allows objective assessment of any changes. Relevant tests include:
Total and free testosterone
LH and FSH
TSH, free T3, and free T4
SHBG (sex hormone binding globulin)
Retesting at 4-6 weeks and again after completing a cycle provides data for evaluating response.
Realistic timeline
Bioregulator effects typically emerge gradually. Subjective improvements in energy, mood, or libido might appear within 2-4 weeks, but measurable hormone changes often take longer. Plan protocols of at least 4-6 weeks for meaningful assessment.
Frequently asked questions
What is Testagen peptide used for?
Testagen is a bioregulatory peptide researched for its potential to support testosterone production and thyroid function through epigenetic mechanisms. It belongs to the Khavinson peptide family developed for anti-aging and organ-specific support. Unlike direct hormone replacement, Testagen theoretically works by modulating gene expression in target tissues to restore more youthful function patterns.
How does Testagen work?
Testagen (KEDG) is a tetrapeptide that may cross cellular and nuclear membranes to interact directly with DNA. Research suggests it influences gene expression patterns associated with steroidogenesis and thyroid hormone production.
Rather than adding hormones directly, it may help tissues produce hormones more efficiently by restoring optimal genetic programs.
Effects on the anterior pituitary may influence both the testosterone and thyroid axes.
What is the proper Testagen dosage?
Research protocols typically use 100-300mcg daily via subcutaneous injection. Starting at 100mcg and adjusting based on response is the conservative approach.
For reconstitution, adding 3ml bacteriostatic water to a 20mg vial creates approximately 6.67mg/ml concentration. Use the peptide calculator for precise measurements. Cycles typically run 4-6 weeks followed by equal break periods.
Is Testagen safe?
Available research suggests Testagen is well-tolerated with minimal side effects. Reported effects include injection site reactions, increased appetite, and occasional headache or fatigue. However, human clinical trial data is limited, and long-term safety has not been established. Testagen is contraindicated in those with active malignancy, thyroid cancer, hyperthyroidism, or hormone-sensitive conditions. Consult a healthcare provider before use.
Can Testagen replace TRT?
Testagen works through different mechanisms than testosterone replacement therapy and should not be considered equivalent. While TRT directly provides exogenous testosterone, Testagen theoretically supports natural production through gene regulatory effects. For severe hypogonadism, TRT may be necessary.
Testagen may be more appropriate for mild decline or as supportive therapy. Some men use it as part of post-cycle recovery protocols.
How long until Testagen shows results?
Bioregulators typically work gradually rather than producing immediate effects. Subjective improvements in energy or mood might appear within 2-4 weeks. Measurable hormone changes may take 4-6 weeks or longer to manifest. The peptide results timeline varies individually. Plan protocols of at least 4-6 weeks minimum, with follow-up testing to objectively assess changes.
Can I stack Testagen with other peptides?
Testagen combines reasonably well with other bioregulators like Epithalon (anti-aging, sleep), Thymalin (immune support), and Pinealon (cognitive function). Some also combine it with other peptide stacks for broader effects. However, combining multiple compounds adds complexity. Start with single compounds to understand individual responses before adding combinations.
Where can I get Testagen?
Testagen is available from research peptide vendors as a research chemical. It is not FDA-approved for human use. Quality varies significantly between sources, so verification of purity through third-party testing certificates is essential. Look for vendors with established reputations, proper cold-chain shipping, and transparent quality documentation.
External resources
PubMed: Peptides of pineal gland and thymus prolong human life
Springer: Peptide bioregulators, a new class of geroprotectors
For researchers exploring bioregulator peptides and hormonal optimization, SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources including protocol guides, stacking recommendations, and access to a community of experienced practitioners.
The platform offers evidence-based information that helps you navigate the complex landscape of peptide research safely and effectively.
Hormonal optimization is a marathon, not a sprint. Testagen represents one tool among many for those seeking to support their body's natural function rather than override it. Whether it proves right for your situation depends on your specific goals, baseline function, and willingness to work with a compound that offers promise but limited clinical validation.
Approach with appropriate skepticism, track your results objectively, and adjust based on what your body actually tells you.