Jan 20, 2026
Your body already produces peptides that regulate performance. Every single day.
These short amino acid chains signal muscles to repair, tell your brain to focus, and instruct cells to generate energy. The question isn't whether peptides affect performance. They do. The question is whether you can optimize these pathways deliberately.
Most people stumble into peptide research looking for a single solution. They want faster recovery. Sharper focus. Better endurance. And they find one peptide that promises everything. This approach fails. Different performance goals require different peptide mechanisms, different protocols, and different expectations about what's actually achievable.
The landscape of performance-enhancing peptides spans athletic recovery, cognitive enhancement, metabolic optimization, and even sexual function. Understanding which peptides target which systems, and how they interact with your body's existing processes, separates productive research from expensive experimentation that leads nowhere.
This guide breaks down performance peptides by category, mechanism, and practical application. You'll learn which compounds have actual research backing them, what realistic protocols look like, and which combinations make scientific sense. Whether you're exploring options for faster injury recovery or investigating cognitive enhancement, the information here will guide your research toward compounds that match your specific goals.
What makes a peptide a "performance" peptide?
The term "performance peptide" gets thrown around loosely.
Supplement companies use it for marketing. Forums use it for anything that isn't a basic health compound. But scientifically, performance peptides share specific characteristics that distinguish them from general wellness peptides or therapeutic compounds.
Performance peptides enhance output beyond baseline levels. That's the defining feature. They don't just restore function or fix deficiencies. They push capacity higher, whether that capacity is muscular endurance, cognitive processing, recovery speed, or energy production. This distinction matters because it determines research expectations.
A peptide that helps you recover from injury faster than normal qualifies. One that simply returns you to normal function does not. A peptide that improves cognitive performance beyond your genetic baseline qualifies. One that only corrects a deficiency does not. The line isn't always clean, but the concept matters for setting realistic goals.
Most peptides exert their effects through one of several mechanisms. They bind to specific receptors that trigger cellular responses. They modulate hormone secretion patterns. They influence gene expression in target tissues. Or they provide building blocks that cells use for specific functions.
SeekPeptides members often ask about the difference between research peptides and pharmaceutical compounds. The primary distinction lies in regulatory status. Pharmaceutical peptides have completed human clinical trials and received approval for specific medical conditions. Research peptides show promise in preclinical studies but haven't cleared the regulatory pathway for human therapeutic use.
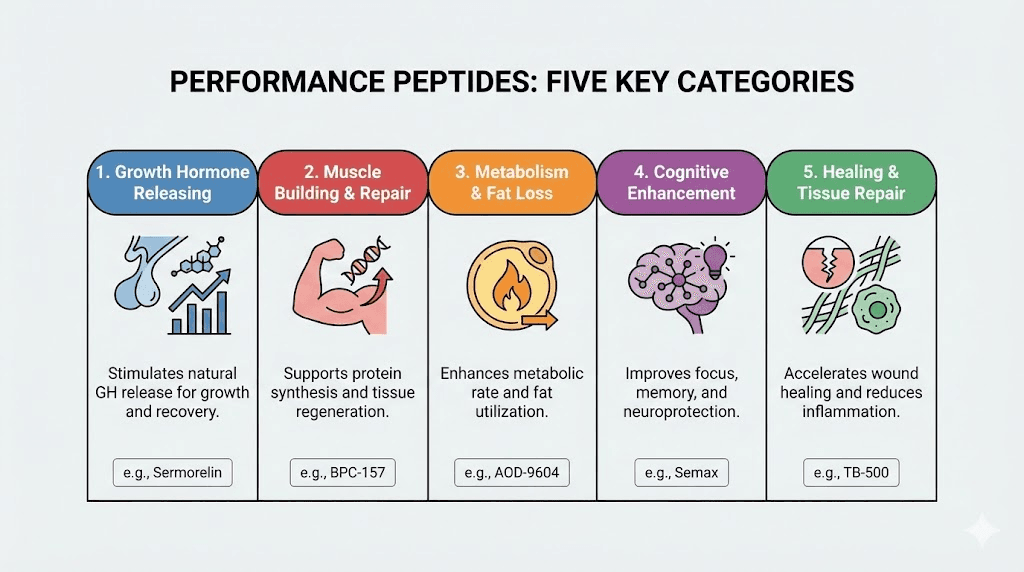
Categories of performance peptides
Performance peptides fall into distinct categories based on their primary mechanism and target system. Understanding these categories helps you identify which compounds align with your research goals and which combinations might work synergistically.
Growth hormone secretagogues stimulate your pituitary gland to release more growth hormone naturally. Compounds like ipamorelin and CJC-1295 fall into this category. They don't introduce external hormones. They amplify your body's own hormone production, which influences muscle growth, fat metabolism, and recovery.
Tissue repair peptides accelerate healing in specific tissues. BPC-157 and TB-500 represent the most researched options here. They work through different mechanisms but both promote faster recovery from injuries and intense training stress.
Metabolic modulators influence how cells generate and use energy. MOTS-c stands out in this category for its effects on mitochondrial function and metabolic flexibility.
Nootropic peptides enhance cognitive function. Semax and Selank have decades of research behind them and clear mechanisms of action in the brain.
Sexual function peptides modulate desire and physical response through central nervous system pathways. PT-141 works differently than traditional approaches because it targets the brain rather than peripheral vasculature.
Each category requires different research approaches, different dosing strategies, and different expectations about onset and duration of effects.
Athletic performance peptides: recovery, endurance, and muscle
Athletes drive most of the interest in performance peptides.
The appeal is obvious. Faster recovery means more training. More training means better adaptation. Better adaptation means improved performance. The logic is sound. The execution requires understanding specific compounds and their mechanisms.
Athletic performance peptides generally work through tissue repair acceleration, growth hormone pathway stimulation, or metabolic enhancement. Most serious protocols combine multiple approaches because peak performance requires optimization across several systems simultaneously.
BPC-157: the tissue repair standard
BPC-157, or Body Protection Compound-157, emerged from research into gastric juice proteins. This 15-amino-acid peptide demonstrates remarkable effects on tissue healing across multiple tissue types, from tendons and ligaments to muscles and even the gut lining.
The mechanism involves multiple pathways. BPC-157 upregulates growth factors including VEGF, which promotes blood vessel formation in damaged tissue. It modulates the nitric oxide system. It appears to influence the FAK-paxillin pathway involved in cell migration during wound healing. The result is accelerated repair across connective tissues that normally heal slowly.
For athletic recovery, the implications are significant. Tendon injuries that typically require months of recovery show faster healing in animal studies. Ligament damage, muscle tears, and joint injuries all respond to BPC-157 in preclinical research.
Dosing protocols typically range from 200 to 500 micrograms daily. Some researchers prefer injection near the injury site for localized effects. Others use systemic administration through subcutaneous injection in the abdominal area. Both approaches show benefits in the research, though injection protocols dominate serious research applications.
The comparison between BPC-157 and TB-500 comes up constantly. Both promote healing. But BPC-157 appears stronger for localized tissue repair, particularly tendons and the gut. TB-500 shows broader systemic effects and better flexibility improvements. Many protocols combine both for comprehensive recovery support.
Cycle length varies by research goal. Acute injury recovery might involve 4 to 6 weeks of daily administration. Some researchers use shorter cycles of 2 to 3 weeks followed by breaks. The compound doesn't appear to cause tolerance or require cycling for safety, but periodic breaks help assess response and adjust protocols.
TB-500: systemic repair and flexibility
TB-500 represents a synthetic fragment of Thymosin Beta-4, a naturally occurring protein involved in tissue repair and cell migration.
The 43-amino-acid parent compound regulates actin, a critical protein for cell structure and movement.
TB-500 captures the active region responsible for most therapeutic effects.
The mechanism centers on actin regulation. By modulating actin, TB-500 influences how cells move through damaged tissue, how new blood vessels form, and how quickly wounds close. It also appears to have anti-inflammatory properties that reduce damage from oxidative stress.
Athletes report improvements in flexibility that go beyond injury recovery. The compound seems to improve tissue suppleness and range of motion even in undamaged tissue. This makes it popular among researchers interested in muscle performance and injury prevention rather than just treatment.
Typical protocols use 2 to 2.5 milligrams twice weekly during loading phases, reducing to weekly or bi-weekly maintenance doses. The longer half-life compared to BPC-157 allows for less frequent dosing. Most research cycles run 4 to 8 weeks.
Reconstitution requires bacteriostatic water and careful technique. TB-500 is relatively stable once reconstituted but should be refrigerated and used within a few weeks. The proper handling of peptide solutions matters significantly for maintaining potency.
Stacking BPC-157 and TB-500 creates what many consider the gold standard for recovery peptide protocols. The complementary mechanisms target different aspects of tissue repair. BPC-157 handles localized healing while TB-500 provides systemic anti-inflammatory and flexibility benefits.
Growth hormone secretagogues for athletic performance
Growth hormone influences nearly every aspect of athletic performance. It promotes muscle protein synthesis, accelerates fat metabolism, supports connective tissue integrity, and enhances recovery from training stress. The problem is that natural GH production declines with age and doesn't always keep pace with intense training demands.
Growth hormone secretagogues offer an alternative to direct GH administration. Rather than introducing external hormone, they stimulate your pituitary gland to produce and release more GH naturally. This maintains the pulsatile release pattern that matters for optimal effects.
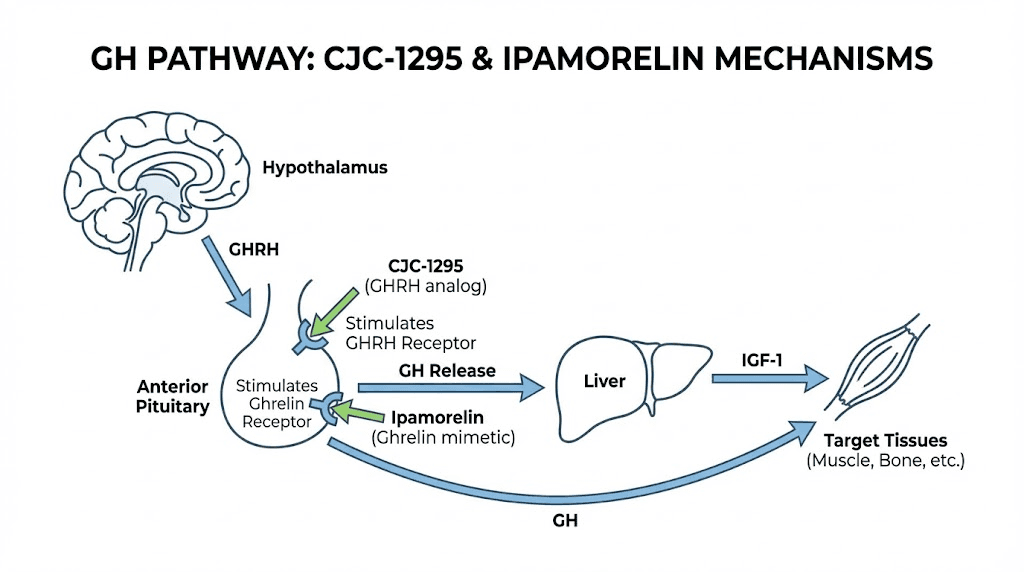
CJC-1295 is a modified growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) analog. The modification extends its half-life from minutes to days, allowing for less frequent dosing while maintaining elevated GH levels. Studies show that a single injection can increase GH secretion for 6 days or more and IGF-1 levels for 9 to 11 days.
Ipamorelin works through a different pathway. It's a growth hormone releasing peptide (GHRP) that mimics ghrelin, the hunger hormone that also stimulates GH release. Ipamorelin is popular because it stimulates GH release without significantly affecting cortisol or prolactin, unlike some other GHRPs.
The combination of CJC-1295 and ipamorelin creates a synergistic effect. CJC-1295 increases the frequency of GH pulses while ipamorelin increases their amplitude. Together, they produce more pronounced and sustained GH elevation than either alone.
Standard protocols use 100 to 300 micrograms of each peptide daily, typically administered before sleep to align with natural GH release patterns. Cycles run 8 to 12 weeks followed by breaks to prevent receptor desensitization.
The effects on athletic performance manifest across several domains. Enhanced recovery between training sessions. Improved lean body composition from accelerated fat oxidation. Better sleep quality, which itself supports recovery. Stronger connective tissues that resist injury. These benefits accumulate over weeks of consistent use.
Athletes exploring these compounds should understand the regulatory landscape. Growth hormone secretagogues are prohibited by WADA for competitive athletes. They remain research compounds without FDA approval for performance enhancement. The decision to research these compounds requires careful consideration of individual circumstances.
MOTS-c: the mitochondrial performance peptide
MOTS-c stands apart from other performance peptides because of its origin. Rather than being derived from nuclear DNA like most peptides, MOTS-c is encoded by mitochondrial DNA. This makes it a mitochondrial-derived peptide, or MDP, with unique effects on cellular energy production.
The primary mechanism involves AMPK activation. AMPK, or AMP-activated protein kinase, serves as the master regulator of cellular energy balance. When AMPK activates, cells shift from energy storage to energy utilization. Fat oxidation increases. Glucose uptake improves. Mitochondrial biogenesis accelerates.
For endurance athletes, these effects translate to improved metabolic flexibility. The ability to switch efficiently between fuel sources, from glucose to fat and back, determines performance in extended efforts. MOTS-c appears to enhance this switching capacity.
Research in mice shows remarkable effects on physical performance. Old mice treated with MOTS-c matched the running capacity of young mice. The peptide improved muscle metabolism and preserved function against age-related decline. While human data remains limited, these preclinical results generated significant interest.
MOTS-c also influences insulin sensitivity. Better insulin sensitivity means more efficient glucose utilization, which matters for both endurance performance and body composition. Athletes concerned with fat loss while maintaining performance often research this compound.
Dosing protocols vary widely in the research community. Some use 5 to 15 milligrams per week split into multiple injections. Others prefer lower doses of 0.5 to 1 milligram several times weekly. Treatment cycles typically span 4 to 8 weeks followed by rest periods.
The compound requires careful handling and storage. MOTS-c is sensitive to temperature and light exposure. Reconstitution should use bacteriostatic water, and the solution should be refrigerated and used within recommended timeframes.
Collagen peptides for athletic performance
Collagen peptides represent a different category within performance research. Unlike the injectable peptides discussed above, collagen peptides typically come as oral supplements. They consist of hydrolyzed collagen broken into smaller peptide fragments that the gut can absorb.
The athletic application centers on joint health and connective tissue support. Collagen forms the primary structural protein in tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and skin. Supplementing with collagen peptides may provide the specific amino acids needed for tissue maintenance and repair.
Research shows promising results for joint pain in athletes. A 24-week study found that athletes taking collagen hydrolysate experienced reduced joint pain compared to placebo. The effects appeared most significant in those with activity-related joint discomfort.
The distinction between collagen hydrolysate and collagen peptides matters for research purposes. Both terms describe hydrolyzed collagen, but peptide size and processing methods vary between products. Generally, smaller peptides show better absorption.
Effective doses range from 10 to 15 grams daily. Taking collagen peptides with vitamin C may enhance absorption and collagen synthesis. Many athletes consume their collagen 30 to 60 minutes before training to time amino acid availability with exercise-induced collagen synthesis.
The effects on athletic performance are indirect but meaningful. Healthier joints mean more consistent training. Stronger tendons mean reduced injury risk. Better recovery from connective tissue stress means greater training volume over time. These cumulative benefits compound across months and years.
Collagen peptides complement injectable recovery peptides rather than replacing them. BPC-157 and TB-500 accelerate healing. Collagen peptides provide the structural building blocks for that healing. Using both creates a comprehensive approach to connective tissue support.
Cognitive performance peptides: focus, memory, and mental clarity
Physical performance gets most attention in peptide discussions. But cognitive performance determines success in many domains. The ability to focus intensely, remember accurately, and think clearly under pressure often matters more than pure physical capacity.
Cognitive peptides, often called nootropic peptides, enhance brain function through various mechanisms. Some increase neurotransmitter availability. Others promote neuroplasticity. Still others protect neurons from damage and degeneration. Understanding these mechanisms helps match peptides to specific cognitive goals.
The best peptides for brain function share a common characteristic: they work with the brain's existing systems rather than overriding them. This creates enhancement without the crash or dependency associated with stimulants.
Semax: the focus and memory peptide
Semax emerged from Soviet research in the 1980s as a synthetic analog of ACTH, the adrenocorticotropic hormone. Specifically, Semax replicates the ACTH(4-10) fragment and adds a modification that improves stability and bioavailability.
The mechanism involves multiple neurotransmitter systems. Semax increases dopamine and serotonin activity, which influences motivation, mood, and focus. It also modulates acetylcholine, the primary neurotransmitter for learning and memory. Perhaps most importantly, Semax upregulates BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, which supports neuroplasticity and long-term cognitive function.
Users report heightened focus and mental clarity that differs from stimulant effects. Rather than the jittery alertness of caffeine or amphetamines, Semax creates calm concentration. Thoughts flow more easily. Distractions fade. Complex problems become more manageable.
Memory improvements manifest in both formation and recall. Information sticks better during learning. Retrieval becomes faster and more reliable. These effects appear particularly pronounced under stress, when cognitive function normally degrades.
Semax comes in different concentrations for different applications. The 0.1% solution suits cognitive enhancement and mild neuroprotection. The 1% solution, reserved for neurological conditions, packs ten times the concentration. Most cognitive researchers use the lower concentration.
Administration is typically intranasal. The nasal mucosa provides direct access to the brain while bypassing the digestive system that would break down oral peptides. Two to three drops per nostril, one to three times daily, represents a common protocol. Cycles run 5 to 14 days followed by breaks.
Semax pairs well with other nootropics. Combining it with racetams or choline sources may enhance effects. However, starting with Semax alone helps establish baseline response before adding complexity.
Selank: cognitive enhancement through anxiety reduction
Selank developed alongside Semax in Russian research programs. Where Semax emphasizes focus and memory directly, Selank approaches cognitive enhancement through anxiety modulation. The logic is simple: anxiety impairs cognition. Reduce anxiety, and cognitive function improves.
The structure derives from tuftsin, an immunomodulatory peptide, with modifications that enhance brain penetration and anxiolytic effects. Selank modulates serotonin and dopamine systems similarly to Semax but with a stronger influence on anxiety-related pathways.
Clinical studies show anxiolytic effects comparable to benzodiazepines but without the sedation, cognitive impairment, or dependency. This makes Selank attractive for researchers seeking anxiety reduction that enhances rather than impairs performance.
Cognitive benefits emerge from reduced anxiety interference. When worry and stress don't consume mental resources, more capacity remains for productive thinking. Focus improves not through stimulation but through removal of obstacles.
The effects on anxiety extend beyond acute stress. Selank appears to modulate baseline anxiety levels with regular use. Researchers dealing with chronic stress or generalized anxiety often prefer it over Semax.
Administration mirrors Semax. Intranasal delivery, typically 200 to 400 micrograms per dose, provides reliable brain uptake. Dosing two to three times daily during 2 to 4 week cycles maintains consistent effects.
Many researchers alternate between Semax and Selank or use them together at different times of day. Semax in the morning supports focus during productive work. Selank in the afternoon or evening promotes relaxed clarity without interfering with sleep.
Dihexa: the neurogenesis peptide
Dihexa represents a newer entry in cognitive peptides with an unusually potent mechanism. This small peptide, derived from angiotensin IV, promotes neurogenesis and synaptogenesis with remarkable efficiency. Some researchers describe it as seven times more potent than BDNF at promoting new neural connections.
The mechanism involves the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) system. Dihexa prevents the breakdown of HGF, allowing this growth factor to stimulate neural repair and new neuron formation. The result is enhanced neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to form new connections and reorganize existing ones.
Cognitive effects center on learning and memory consolidation. Information processing improves. New skills develop faster. Memory encoding and retrieval both benefit. The effects accumulate over time as new neural connections form and stabilize.
Dosing remains experimental given limited human research. Most protocols use very small doses in the range of 5 to 20 milligrams orally or even lower doses through other administration routes. The compound's potency means that effective doses are orders of magnitude smaller than typical nootropics.
Dihexa attracts researchers interested in long-term cognitive enhancement rather than acute performance gains. The neurogenesis effects take time to manifest. Benefits accumulate over weeks and months of consistent use.
Caution is warranted given the limited human safety data. Promoting neural growth sounds positive, but uncontrolled growth carries risks. Researchers typically use conservative doses and monitor carefully for any concerning effects.
Cerebrolysin: the neuroprotective complex
Cerebrolysin differs from single-peptide nootropics. It's a complex of multiple peptides derived from pig brain tissue, used clinically in parts of Europe and Asia for neurological conditions including stroke recovery and dementia.
The mechanism encompasses multiple pathways. The peptide mixture provides neurotrophic factors that support neuron survival and growth. It modulates neurotransmitter systems. It protects against oxidative stress and inflammation that damage neural tissue.
For cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals, Cerebrolysin offers neuroprotection alongside performance benefits. The compound may preserve cognitive function during aging while also enhancing current performance.
Administration requires injection, typically intravenous or intramuscular. Clinical protocols use doses ranging from 10 to 30 milliliters depending on the condition being treated. Enhancement-focused researchers typically use lower doses.
Availability varies by country due to regulatory differences. In some regions, Cerebrolysin is a prescription medication. In others, it's available through research channels. Understanding local regulations matters for anyone considering this compound.
Sexual performance peptides: desire and function
Sexual performance represents a distinct domain that performance peptides can address. Unlike other aspects of performance that respond to training and lifestyle optimization, sexual function often requires different interventions. Peptides offer mechanisms distinct from traditional pharmaceutical approaches.
The key insight driving peptide research in this area is that sexual function has both peripheral and central components. Traditional treatments like PDE5 inhibitors address peripheral blood flow. Peptides can address central nervous system factors including desire, arousal, and reward pathways.
PT-141: the central desire peptide
PT-141, also known as bremelanotide, emerged from research on melanotan peptides originally developed for sunless tanning. Researchers noticed that these melanocortin receptor agonists produced unexpected effects on sexual arousal. PT-141 was refined to maximize sexual effects while minimizing tanning and other side effects.
The mechanism differs fundamentally from PDE5 inhibitors. PT-141 activates melanocortin receptors in the brain, specifically MC3R and MC4R, which influence sexual desire and arousal at the neurological level. It increases dopamine signaling in pathways associated with reward and motivation.
The FDA approved bremelanotide in 2019 as Vyleesi for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in premenopausal women. This represents rare regulatory validation for a peptide in the sexual performance space.
Effects differ from traditional erectile dysfunction treatments. PT-141 increases both desire and physical response. Users report enhanced arousal, stronger sensations, and more satisfying experiences overall. The psychological component matters as much as the physical.
The PT-141 protocol for men typically uses 1 to 2 milligrams via subcutaneous injection 45 to 60 minutes before anticipated activity. Effects last 6 to 12 hours. The compound should not be used more than once in 24 hours or more than 8 times per month according to prescribing guidelines.
Side effects include nausea, flushing, and headache. Nausea is most common, particularly with first use. Some researchers use anti-nausea medication prophylactically. The effects typically diminish with subsequent uses.
PT-141 offers an option for individuals who don't respond to PDE5 inhibitors or who experience desire issues rather than purely mechanical dysfunction. It can also be combined with traditional treatments for enhanced effects, though combination use should be approached carefully.
SeekPeptides provides detailed protocols for researchers exploring PT-141 and other compounds affecting sexual function. The membership resources include dosing calculators and guidance on managing potential side effects.
Energy and metabolism peptides
Energy production underlies all performance. Athletic output requires ATP. Cognitive function depends on neural energy. Even recovery processes consume substantial metabolic resources. Peptides that enhance cellular energy production affect performance across all domains.
Metabolic peptides work at the cellular level, influencing how mitochondria generate ATP and how cells utilize glucose and fatty acids. These effects are foundational rather than superficial. Optimizing cellular energy production creates benefits that cascade through every system.
MOTS-c revisited: the exercise mimetic
MOTS-c deserves extended discussion because its effects on energy metabolism make it relevant to virtually every performance goal. Beyond the athletic applications discussed earlier, MOTS-c influences metabolic health in ways that support both physical and cognitive performance.
The "exercise mimetic" label reflects how MOTS-c activates pathways normally triggered by physical exercise. AMPK activation improves insulin sensitivity, increases fat oxidation, and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis. These are the same adaptations that occur with endurance training.
For researchers unable to train optimally due to injury, time constraints, or other limitations, MOTS-c may help maintain metabolic adaptations. This doesn't replace exercise, but it may reduce the fitness loss during periods of reduced activity.
The effects on body composition follow from metabolic improvements. Better fat oxidation means more efficient use of fat stores for energy. Improved insulin sensitivity means better glucose handling. Together, these create favorable conditions for fat loss while maintaining or building lean tissue.
Cognitive benefits stem from improved brain energy metabolism. The brain consumes enormous amounts of glucose. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurons contributes to cognitive decline and neurodegeneration. MOTS-c's effects on mitochondrial function may translate to better neural energy production.
The relationship between exercise and MOTS-c is bidirectional. Exercise increases endogenous MOTS-c production. Supplemental MOTS-c may enhance exercise adaptations. This suggests potential synergy between physical training and peptide research.
AOD-9604: the GH fragment for fat metabolism
AOD-9604 represents a fragment of growth hormone, specifically amino acids 177-191 of the GH molecule. This fragment retains the fat-metabolizing properties of growth hormone without its effects on blood sugar or IGF-1 levels.
The mechanism involves beta-3 adrenergic receptor activation and direct effects on fat cells. AOD-9604 stimulates lipolysis, the breakdown of stored fat, and inhibits lipogenesis, the formation of new fat. It also reduces appetite through central nervous system effects.
Research in humans shows modest fat loss effects. A 12-week study found that AOD-9604 produced statistically significant reductions in body weight compared to placebo. The effects weren't dramatic but were consistent and meaningful.
For performance applications, AOD-9604 offers body composition benefits without the blood sugar disruption that full GH or GH secretagogues can cause. Athletes concerned about metabolic effects during periods of caloric restriction may find this particularly relevant.
Dosing typically ranges from 200 to 500 micrograms daily, usually administered in the morning before food. Cycles run 4 to 12 weeks depending on goals and response.
The complete guide to AOD-9604 covers dosing, timing, and combination strategies in detail. Understanding how this peptide fits within a broader fat loss approach matters more than the peptide itself.
SS-31: mitochondrial protection
SS-31, also known as elamipretide, represents cutting-edge mitochondrial peptide research. This small peptide targets the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it stabilizes cardiolipin and optimizes electron transport chain function.
Mitochondria are the power plants of cells, generating ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. When mitochondria function suboptimally, energy production drops and reactive oxygen species increase. This affects every cell in the body but impacts high-energy-demand tissues like muscle, heart, and brain most severely.
SS-31 concentrates in mitochondrial membranes at very low doses. Once there, it improves electron flow through the respiratory chain and reduces electron leakage that generates damaging free radicals. The result is more efficient energy production with less oxidative damage.
Athletic performance benefits stem from improved muscular energy production. Fatigue resistance increases when mitochondria generate ATP more efficiently. Recovery improves when oxidative damage decreases. These effects particularly benefit endurance athletes who depend on aerobic metabolism.
The benefits of SS-31 extend to cardiac function and neuroprotection. The heart depends entirely on mitochondrial ATP production. Neurons have minimal glycolytic capacity and rely heavily on mitochondria. Optimizing mitochondrial function in these tissues creates system-wide benefits.
Research protocols typically use subcutaneous injection at doses ranging from 0.1 to 1 milligram per kilogram body weight. The compound is still in clinical trials for various conditions, so human dosing guidance continues to evolve.
Peptide stacking for performance optimization
Single peptides rarely optimize performance across all desired domains. Most researchers eventually explore combinations, or stacks, that address multiple mechanisms simultaneously. Strategic stacking amplifies benefits while managing complexity.
The principles of effective stacking include mechanistic complementarity, timing coordination, and risk management. Complementary mechanisms mean the peptides work through different pathways that don't interfere with each other. Coordinated timing ensures peptides reach peak effect when needed. Risk management means not combining peptides with overlapping side effect profiles.
The recovery stack: BPC-157 + TB-500
This combination represents the most established performance peptide stack. BPC-157 provides localized tissue repair through growth factor upregulation. TB-500 delivers systemic anti-inflammatory effects and flexibility improvements through actin modulation.
The synergy is clear. Different mechanisms target different aspects of recovery. BPC-157 excels at healing specific injuries. TB-500 improves overall tissue quality and resilience. Together, they create comprehensive recovery support.
Standard protocols run BPC-157 at 250 to 500 micrograms daily with TB-500 at 2 to 2.5 milligrams twice weekly. Some researchers inject both near injury sites. Others use systemic administration. The peptide stack calculator helps determine appropriate doses based on individual factors.
This stack suits athletes dealing with injury, those in heavy training phases, and anyone seeking to minimize the tissue damage that accumulates with intense physical activity. The compounds are well-tolerated and don't appear to interfere with each other.
The GH enhancement stack: CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin
Combining a GHRH analog with a GHRP creates multiplicative effects on growth hormone secretion. CJC-1295 increases pulse frequency while Ipamorelin increases pulse amplitude. The combined effect exceeds what either compound achieves alone.
Dosing typically uses 100 to 300 micrograms of each peptide daily. Administration before sleep aligns with natural GH rhythms. Some protocols add a second dose in the morning to maintain elevated GH throughout the day.
This stack supports muscle growth, fat loss, recovery, and sleep quality. The effects take weeks to manifest fully as GH levels elevate and downstream adaptations occur. Cycles of 8 to 12 weeks followed by breaks prevent receptor desensitization.
Athletes should understand the regulatory implications. Both compounds are prohibited in competitive sports. The decision to research them involves weighing potential benefits against rules and regulations that apply to individual circumstances.
The cognitive enhancement stack: Semax + Selank
Combining the focus-enhancing effects of Semax with the anxiolytic effects of Selank creates balanced cognitive enhancement. Focus improves without anxiety increase. Calm emerges without sedation. The combination addresses both activation and relaxation components of optimal mental performance.
Timing strategies vary. Some researchers use Semax in the morning and Selank in the afternoon. Others use both together for specific high-demand situations. The compounds share administration routes (intranasal) and don't appear to interfere pharmacologically.
This stack suits knowledge workers, students, and anyone whose performance depends on sustained mental effort. The lack of stimulant side effects makes it suitable for extended use during demanding periods.
The comprehensive performance stack
Advanced researchers sometimes combine peptides across categories for system-wide optimization. A comprehensive stack might include:
Recovery peptides (BPC-157, TB-500) for tissue repair and injury prevention. GH secretagogues (CJC-1295, Ipamorelin) for anabolic support and body composition. MOTS-c for metabolic optimization. Semax for cognitive enhancement during training and competition.
Such stacks require careful management. Timing must be coordinated. Side effects must be monitored. Costs add up quickly. But for serious researchers pursuing peak performance across multiple domains, comprehensive stacking represents the logical extension of single-peptide research.
SeekPeptides members access detailed stacking protocols developed from aggregated research outcomes. The community shares what works, what doesn't, and how to troubleshoot common issues.
Practical considerations for peptide research
Understanding peptide mechanisms matters. But practical execution determines whether research succeeds or fails. Storage, reconstitution, administration, and sourcing all affect outcomes. Getting these details right is as important as choosing the right compounds.
Storage and handling
Peptides are sensitive molecules. Heat, light, moisture, and contamination all degrade them. Proper storage preserves potency and ensures consistent research results.
Lyophilized (freeze-dried) peptides should remain frozen or refrigerated until reconstitution. Most maintain stability for months when stored at -20°C. Refrigerator storage at 2-8°C works for shorter periods. Room temperature storage accelerates degradation significantly.
Once reconstituted, peptides require refrigeration and should be used within weeks. Bacteriostatic water provides preservative protection that extends usable life compared to sterile water. The stability of reconstituted peptides varies by compound, but few last more than 4 weeks even with proper storage.
Light exposure degrades many peptides. Store vials in their original packaging or wrap them in aluminum foil. Avoid leaving reconstituted solutions in direct light even briefly.
Contamination introduces bacteria that multiply in peptide solutions. Always use sterile technique when reconstituting and drawing doses. Wipe stoppers with alcohol. Use fresh needles for each draw. Never touch the needle or stopper with bare hands.
Reconstitution protocols
Converting lyophilized peptides to injectable solutions requires precision. The amount of diluent determines concentration. Concentration determines injection volume. Getting this right ensures accurate dosing.
Standard reconstitution uses bacteriostatic water. Inject the water along the vial wall rather than directly onto the peptide cake. This gentle approach prevents damage to the peptide structure. Let the water dissolve the peptide gradually. Gentle swirling is acceptable. Shaking is not.
Calculate concentration based on peptide amount and water volume. For example, 5mg of peptide reconstituted with 2mL of water creates a concentration of 2.5mg/mL. Each 0.1mL (10 units on an insulin syringe) delivers 250mcg.
The reconstitution calculator handles these calculations automatically. Input the peptide amount and desired dose, and it outputs the water volume and injection amount. This eliminates math errors that could lead to incorrect dosing.
Administration techniques
Most performance peptides use subcutaneous injection. This deposits the peptide in the fat layer just beneath the skin, where it absorbs gradually into the bloodstream.
Common injection sites include the abdomen (1-2 inches from the navel), the thigh (front or outer), and the upper arm (back area with adequate fat). Rotating sites prevents irritation and scar tissue buildup.
Use insulin syringes with fine needles (29-31 gauge) for comfortable injections. Draw the dose, expel air bubbles, pinch the skin, insert at 45-90 degrees, inject slowly, and withdraw. Apply gentle pressure to the site afterward.
Intranasal peptides like Semax and Selank use spray bottles or droppers. The nasal mucosa absorbs peptides directly into circulation and provides access to the brain. Proper technique involves tilting the head slightly, aiming the spray toward the outer nostril wall, and breathing gently.
Some peptides offer oral administration options. Bioavailability is typically lower than injection, but convenience may outweigh potency concerns for certain applications. Comparing administration routes helps determine what makes sense for specific research goals.
Sourcing quality peptides
Peptide quality varies dramatically between sources. Underground labs may sell degraded, contaminated, or mislabeled products. Even seemingly legitimate sources sometimes fail quality testing.
Quality indicators include third-party testing with published results, proper packaging and storage, clear labeling with batch numbers, and established reputation within the research community. Price alone doesn't indicate quality, though suspiciously cheap peptides warrant skepticism.
Testing services can verify peptide identity and purity. HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography) and mass spectrometry confirm that the peptide matches its label and hasn't degraded. While testing adds cost, it provides assurance for serious researchers.
The guide to peptide testing labs covers how to evaluate and use third-party testing services. Understanding what tests reveal, and what they don't, helps interpret results correctly.
Community knowledge helps identify reliable sources. Peptide forums and research communities share experiences with different vendors. Aggregated feedback reveals patterns that individual purchases might miss.
Legal and regulatory considerations
Performance peptides exist in a complex regulatory landscape that varies by compound, country, and intended use. Understanding these considerations is essential for responsible research.
In the United States, most performance peptides are not FDA-approved for human use. They're available as "research chemicals" intended for scientific investigation rather than personal consumption. This status creates a gray area that individual researchers must navigate.
The legality of peptides depends on how they're classified. Some peptides have achieved prescription drug status for specific medical conditions. Others remain research compounds. A few have been explicitly banned or restricted.
For athletes, competitive regulations add another layer. WADA prohibits most growth hormone secretagogues, many metabolic modulators including MOTS-c, and various other performance peptides. Testing methods continue to improve, and detection windows extend beyond active use periods.
The regulatory landscape continues evolving. Compounds that are accessible today may become restricted tomorrow. Staying current on regulations matters for anyone conducting peptide research.
Medical supervision adds legitimacy and safety to peptide research. Physicians can monitor health markers, adjust protocols based on individual response, and intervene if problems arise. Some clinics specialize in peptide therapy and can provide guidance within appropriate medical contexts.
Expected timelines and realistic expectations
Peptide effects unfold over different time scales. Understanding these timelines helps set appropriate expectations and evaluate whether protocols are working.
Acute effects occur immediately or within hours. PT-141's effects on arousal manifest within an hour of administration. Semax's focus enhancement appears within 15-30 minutes of intranasal dosing. These immediate effects are noticeable from the first dose.
Short-term effects develop over days to weeks. BPC-157's tissue healing accelerates within the first week but continues improving over 4-6 weeks. TB-500's flexibility improvements emerge over 2-4 weeks of consistent use. Recovery from specific injuries follows individual timelines.
Long-term effects require weeks to months. GH secretagogue benefits on body composition manifest over 2-3 months. MOTS-c's metabolic improvements accumulate over similar timeframes. Cognitive peptides that promote neuroplasticity show compounding benefits over extended use.
How long peptides take to work depends on the specific compound, the outcome being measured, and individual factors including age, health status, and concurrent interventions. Patience is essential. Abandoning protocols before effects have time to manifest wastes resources and provides no useful information.
Realistic expectations matter as much as patience. Peptides optimize existing systems. They don't transform poor genetics, compensate for inadequate training, or overcome fundamentally unhealthy lifestyles. The researchers who see the best results are those who have everything else optimized and use peptides to push beyond what lifestyle optimization alone achieves.
Safety monitoring and risk management
Peptide research carries inherent risks that responsible researchers must manage. Most compounds lack extensive human safety data. Individual responses vary. Interactions with medications or health conditions can create unexpected problems.
Baseline testing before starting any peptide protocol provides reference points for monitoring. Basic blood work including metabolic panels, hormone levels, and markers of organ function establishes what "normal" looks like for each individual. Subsequent testing reveals whether peptides are causing concerning changes.
Specific peptides warrant specific monitoring. GH secretagogues can affect blood sugar and insulin sensitivity, so monitoring fasting glucose and HbA1c makes sense. Compounds affecting liver metabolism may warrant liver function tests. Heart-related peptides justify cardiovascular monitoring.
Side effect awareness enables early intervention. Understanding what side effects to expect, which warrant concern, and which indicate problems helps researchers respond appropriately. Most peptide side effects are mild and transient. A few signal the need to stop immediately.
Documentation supports both safety and optimization. Logging doses, timing, effects, and any adverse reactions creates a record for troubleshooting. If something goes wrong, documentation helps identify the cause. If something works well, documentation enables replication.
Medical supervision provides additional safety layers. Physicians can order comprehensive testing, interpret results accurately, and provide guidance when problems arise. For researchers conducting anything beyond basic protocols, medical involvement makes sense.
Frequently asked questions
What are the best peptides for overall athletic performance?
The most effective combination for overall athletic performance includes BPC-157 and TB-500 for recovery, paired with CJC-1295 and ipamorelin for GH support. This stack addresses tissue repair, inflammation, muscle growth, and body composition. Adding MOTS-c can enhance metabolic efficiency and endurance. Individual goals should guide specific choices within this framework.
Can peptides be used together safely?
Most performance peptides can be combined safely because they work through different mechanisms. Combining multiple peptides requires understanding each compound's effects and potential interactions. Start with single peptides to establish individual response before adding complexity. Monitor carefully when introducing new combinations.
How do performance peptides compare to steroids?
Peptides work through different mechanisms than anabolic steroids. Peptides vs steroids represents a fundamental choice in approach. Peptides typically enhance natural processes while steroids introduce external hormones. Effects are generally milder with peptides but with potentially fewer long-term consequences. The choice depends on individual goals, risk tolerance, and regulatory considerations.
Do peptides show up on drug tests?
Many performance peptides are prohibited by WADA and subject to testing in competitive sports. Detection methods continue to improve. Some peptides can be detected for days or weeks after use. Athletes subject to drug testing should assume that peptide use will be detected and plan accordingly.
Are there peptides specifically for women?
Most performance peptides work similarly in men and women. However, some compounds have been studied more in one sex than the other. PT-141 has FDA approval specifically for women. Safe peptides for women include BPC-157, TB-500, Semax, and collagen peptides, which have good safety profiles across sexes.
What's the difference between research peptides and pharmaceutical peptides?
Research peptides are compounds available for scientific investigation that haven't completed regulatory approval for human therapeutic use. Pharmaceutical peptides have completed clinical trials and received approval for specific medical conditions. The distinction affects availability, quality assurance, and legal status.
How should peptides be stored to maintain potency?
Lyophilized peptides should be stored frozen or refrigerated away from light. Reconstituted peptides require refrigeration and should be used within weeks. Peptide expiration depends on storage conditions, with proper storage extending usable life significantly.
Can peptides help with injury recovery?
BPC-157 and TB-500 specifically target tissue repair and have substantial research supporting their use for injury recovery. Effects on tendons, ligaments, muscles, and joints are documented in preclinical studies. Many researchers report faster recovery from injuries with these compounds.
External resources
PubMed - National Library of Medicine database for peptide research
WADA Prohibited List - Current status of peptides in competitive sports
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night.