Jan 26, 2026
Your cells are dying. Not dramatically. Not all at once. But with every division, with every passing month, the protective caps on your chromosomes grow shorter. Telomeres, they are called. And when they get too short, the cell stops dividing entirely. This is cellular aging at its most fundamental level, and it is happening inside you right now.
Epitalon offers something remarkable. A four-amino-acid sequence that may actually reverse this process.
But here is the problem. Getting the dosage wrong means getting the results wrong. Too little and nothing happens. Too much and you are wasting peptide while potentially adding unnecessary risk. The difference between a protocol that works and one that fails often comes down to precise numbers, timing, and administration methods that most guides completely ignore.
This guide covers everything researchers need to know about epitalon dosing. We will examine the research-backed protocols that actually produce results, the cycling strategies that maximize effectiveness while minimizing exposure, the reconstitution methods that preserve potency, and the administration techniques that ensure proper absorption. Whether you are new to bioregulator peptides or looking to optimize an existing protocol, the specific numbers and schedules here come directly from published research and clinical experience.
SeekPeptides has compiled this comprehensive resource because longevity research demands precision. General advice is not good enough when you are working with compounds that affect gene expression at the cellular level.
What is epitalon and why does dosage matter so much
Epitalon is a synthetic tetrapeptide with the amino acid sequence Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly. Originally developed by Russian scientist Vladimir Khavinson at the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology, it represents decades of research into longevity peptides and their effects on aging.
The peptide works by activating telomerase, an enzyme that adds length to telomeres. In a landmark study, Khavinson demonstrated that epitalon increased telomerase activity in human fibroblast cells, extending their proliferative lifespan from 34 passages to beyond 44 passages. That represents a 42.5 percent increase in cellular division capacity.
But here is what makes dosage so critical. Unlike many compounds where more equals better, epitalon operates on a different principle entirely.
Clinical studies have found that low, cyclical dosing is sufficient to activate telomerase, restore melatonin secretion, and reduce age-related biomarkers. Increasing the dose does not appear to increase benefits and may only add unnecessary risk. Some trials experimented with doses up to 50 mg per day. These did not demonstrate stronger or longer-lasting results compared to the standard 5 to 10 mg per day range.
This means precision matters more than quantity. The goal is triggering the right cellular response, not flooding the system with excess peptide.
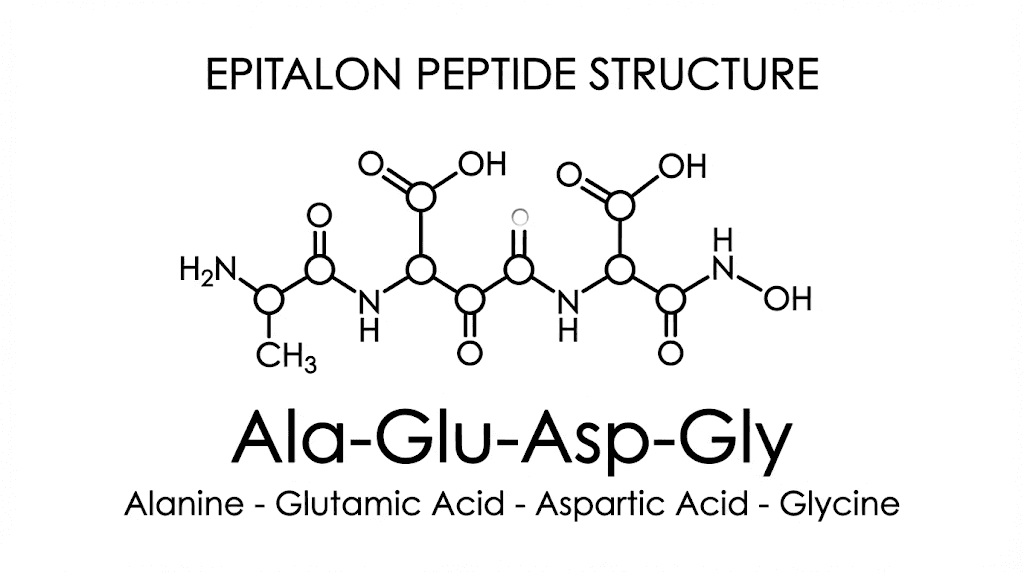
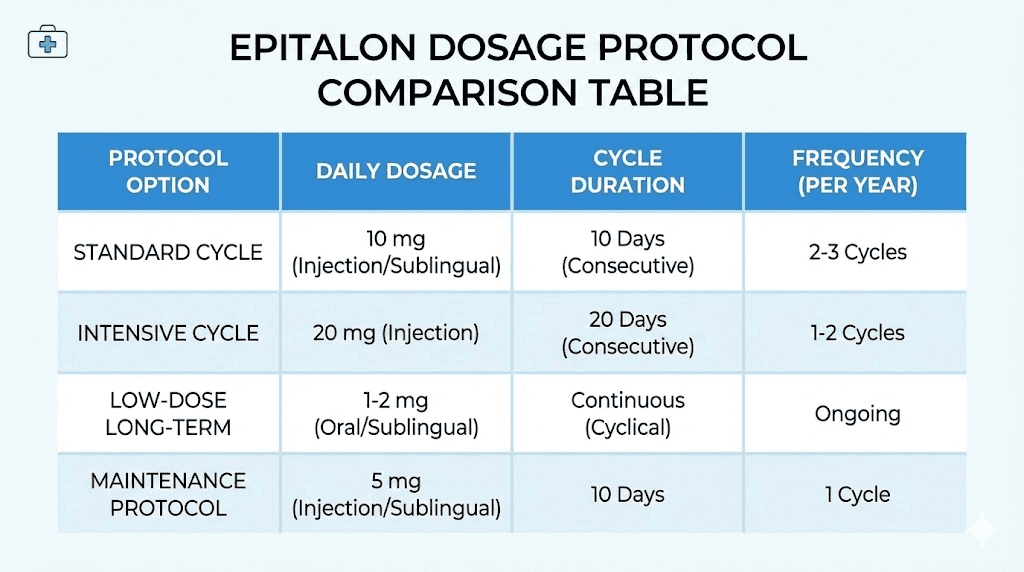
Standard epitalon dosage protocols from research
Research has established several validated dosing protocols for epitalon. Each targets the same fundamental mechanism but differs in intensity and duration. Understanding these options allows researchers to select the approach best suited to their specific goals and circumstances.
The 20-day standard protocol
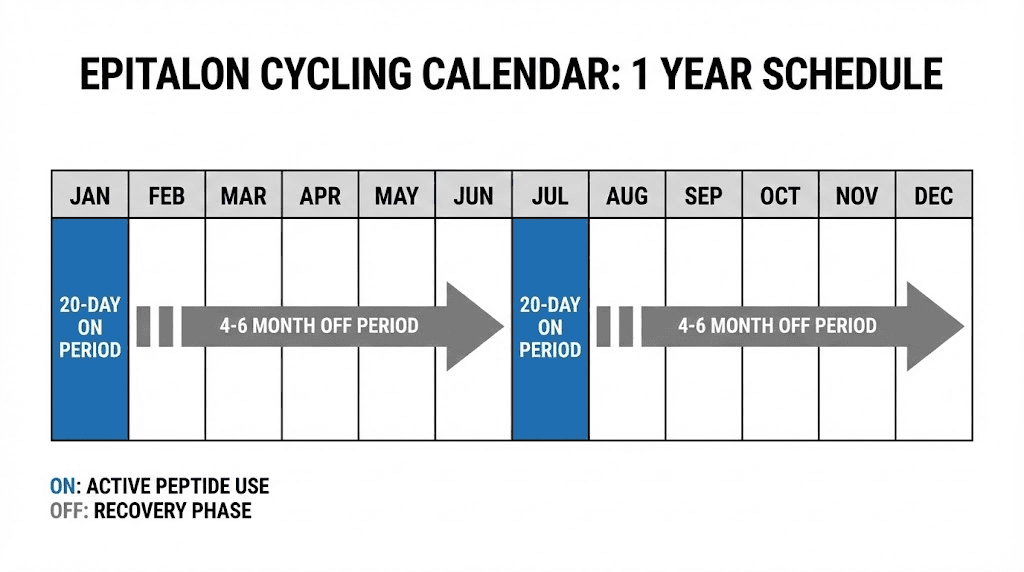
This represents the most commonly cited approach in published research and clinical practice. The protocol calls for 5 mg of epitalon administered subcutaneously once daily for 20 consecutive days. Evening administration is recommended, typically at bedtime, to align with natural circadian rhythms and support the peptide's effects on sleep regulation.
After completing the 20-day cycle, researchers observe a washout period of 4 to 6 months before the next cycle. This cyclical approach is not arbitrary. Epitalon's effects come from short-term courses that reset cellular and circadian mechanisms rather than continuous exposure.
The total cycle dose under this protocol is 100 mg of epitalon. Many researchers consider this the gold standard for peptide dosing in longevity applications.
The 10-day intensive protocol
An alternative approach compresses the same total dose into a shorter timeframe. Researchers administer 10 mg daily for 10 consecutive days, achieving the same 100 mg cycle dose in half the time.
Some clinicians prefer this approach for its convenience and the potential for more concentrated telomerase activation. However, the research comparing outcomes between 10-day and 20-day protocols remains limited.
The every-other-day protocol
A third variation involves administering 10 mg every other day for 10 doses, extending the cycle over 20 days but with intermittent dosing. This approach may reduce injection frequency while maintaining overall exposure levels.
One documented protocol recommends epitalon at 20 mg per mL concentration, with 10 mg doses administered subcutaneously at bedtime every other day for a total of 10 administrations.
Dosage by body weight considerations
Unlike many hormone-related peptides where body weight significantly affects dosing, epitalon protocols typically use fixed doses regardless of individual body mass. The 5 to 10 mg daily range appears effective across a wide range of body weights.
This differs substantially from compounds like BPC-157 and TB-500 where weight-based calculations are standard practice. Researchers should note this distinction when transitioning between different peptide protocols.
Understanding epitalon cycle length and timing
Cycling is not optional with epitalon. It is fundamental to how the peptide works.
The rationale behind cyclical dosing connects directly to epitalon's mechanism of action. Short bursts of telomerase activation appear sufficient to produce lasting effects on telomere length and cellular function. Continuous administration does not seem to provide additional benefit and may actually diminish the compound's effectiveness over time.
Why cycles matter for epitalon
Consider how peptide cycling works at the cellular level. Epitalon activates telomerase gene expression, triggering a cascade of cellular responses. Once activated, these responses continue even after the peptide is cleared from the system. The cells do not need constant stimulation, they need periodic reactivation.
This explains why researchers observe sustained benefits during the off-cycle period. The cellular changes persist even without ongoing epitalon administration.
Optimal cycle frequency
Most protocols recommend one to two complete cycles per year for general anti-aging applications. More aggressive approaches might use three cycles annually, though research supporting increased frequency remains sparse.
The minimum recommended gap between cycles is four months. Six months between cycles is more commonly suggested and allows for complete washout while maintaining benefits from the previous cycle.
Seasonal considerations
Some researchers align their epitalon cycles with seasonal transitions, particularly the shift into winter when natural melatonin production changes and circadian disruption becomes more common. This approach takes advantage of epitalon's effects on pineal gland function and sleep-related hormone regulation.
Others prefer spring and fall cycles to support cellular health during periods of metabolic transition. No definitive research establishes optimal timing, leaving this decision to individual preference and circumstance.
Reconstitution and preparation for epitalon dosing
Proper reconstitution directly affects the potency and safety of any peptide research. Epitalon requires careful handling to maintain stability and ensure accurate dosing.
Choosing your reconstitution solution
Bacteriostatic water remains the standard choice for epitalon reconstitution. The benzyl alcohol preservative inhibits bacterial growth and allows for multiple withdrawals over an extended period, typically up to 28 days when properly refrigerated.
For detailed guidance on bacteriostatic water and peptides, researchers should understand that the 0.9 percent benzyl alcohol concentration is both effective for preservation and well-tolerated at typical injection volumes.
Some sources note that epitalon may exhibit limited solubility in bacteriostatic water alone. For improved reconstitution, researchers sometimes begin with a small volume of 0.6 percent acetic acid to aid dissolution, followed by bacteriostatic water to reach the final volume.
Reconstitution ratios for accurate dosing
With a standard 10 mg vial of epitalon, adding 2.0 mL of bacteriostatic water produces a concentration of 5 mg per mL. This makes dosing straightforward. Each 1 mL (100 units on a standard insulin syringe) delivers 5 mg of epitalon.
For 5 mg doses, researchers would draw 1 mL or 100 units. For 10 mg doses, 2 mL would be needed, though this may require a larger syringe or two separate injections.
Alternative reconstitution with 1.0 mL produces a 10 mg per mL concentration. This allows for smaller injection volumes but requires more precise measurement. Each 0.5 mL or 50 units delivers 5 mg.
The peptide reconstitution calculator can help determine exact volumes based on vial size and desired concentration.
Step-by-step reconstitution process
Begin by allowing both the lyophilized epitalon and the bacteriostatic water to reach room temperature. Cold solutions can cause the peptide to precipitate improperly.
Clean the rubber stopper of the peptide vial with an alcohol swab. Draw the calculated volume of bacteriostatic water into a sterile syringe. Insert the needle through the rubber stopper at an angle, directing the stream of liquid against the glass wall of the vial rather than directly onto the powder cake.
Allow the bacteriostatic water to flow gently into the vial. Do not force it or inject rapidly. Let the peptide dissolve naturally over one to two minutes. If needed, gently swirl the vial, never shake it. Shaking can denature the peptide and reduce its effectiveness.
Once fully dissolved, the solution should be clear and free of particles. Any cloudiness or visible debris indicates contamination or degradation.
Storage after reconstitution
Reconstituted epitalon requires refrigeration at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius. The solution remains stable for approximately six weeks under these conditions, though many researchers prefer to use it within four weeks for maximum potency.
For unreconstituted lyophilized powder, freezer storage at minus 20 degrees Celsius extends stability to three years or more. Refrigerator storage maintains potency for approximately two years.
Understanding proper peptide storage is essential for maintaining research integrity. Temperature fluctuations significantly reduce peptide stability, so avoid storing vials in refrigerator door compartments where temperatures vary with each opening.
For more on storage duration, see our guide on how long reconstituted peptides last in the fridge.
Administration methods and bioavailability comparison
How you deliver epitalon significantly affects how much reaches systemic circulation and produces effects. Research has examined multiple administration routes with varying levels of success.
Subcutaneous injection: the gold standard
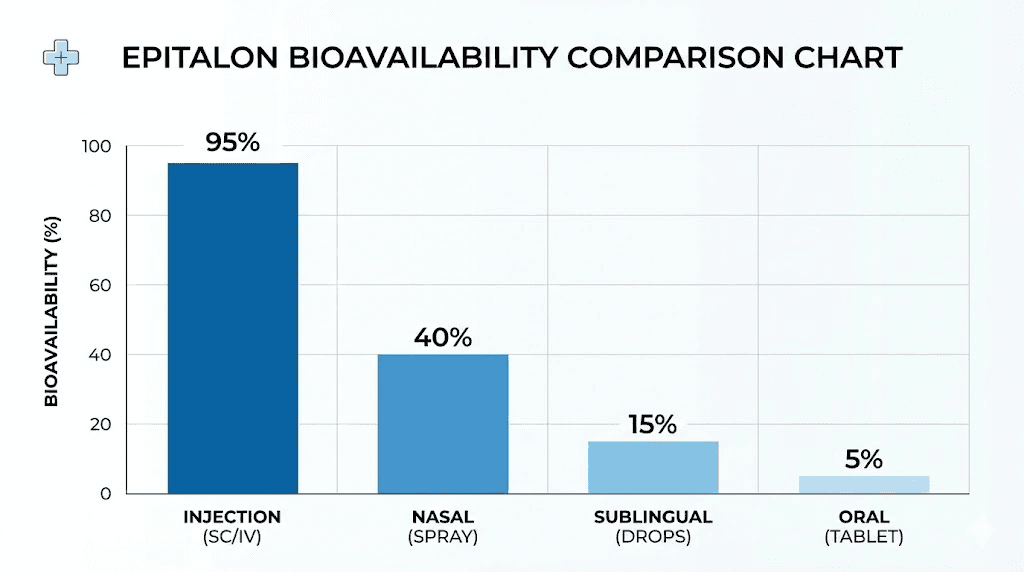
Subcutaneous injection remains the most researched and recommended delivery method for epitalon. The peptide enters the bloodstream efficiently with minimal degradation, and the technique is simple enough for most researchers to perform independently.
Injection sites should rotate systematically through the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms. This rotation prevents lipohypertrophy, the formation of fatty lumps at repeated injection sites, and ensures consistent absorption.
For those new to peptide injections, the process involves pinching a fold of skin, inserting the needle at a 45 to 90 degree angle depending on body composition, and injecting slowly. A complete peptide injection guide can provide detailed visual instruction.
Intramuscular injection
Some protocols specify intramuscular rather than subcutaneous administration. The absorption profile differs slightly, with potentially faster uptake but similar overall bioavailability.
Intramuscular injections typically target the deltoid or gluteal muscles. The technique requires longer needles than subcutaneous injections and carries slightly higher discomfort potential.
Nasal spray delivery
Nasal administration offers a needle-free alternative that some researchers prefer. The nasal mucosa provides reasonably good peptide absorption, bypassing digestive degradation while offering convenience.
However, bioavailability through nasal delivery is lower than injection. The International Peptide Society notes that epitalon administered intranasally would require two to three times the injectable dosage to achieve comparable effects.
For those exploring nasal spray peptides, this means a 5 mg injectable dose might require 10 to 15 mg when administered nasally. Cost considerations become significant at these higher doses.
One approach involves dissolving epitalon in saline solution with 3 percent DMSO, which reportedly increases absorption through the nasal mucosa.
Sublingual administration
Sublingual delivery places the peptide solution under the tongue, allowing absorption through the oral mucosa. This bypasses the digestive system while avoiding injections.
A randomized clinical study involving 75 women found that sublingual epitalon at 0.5 mg per day for 20 days produced measurable increases in melatonin synthesis. Urinary 6-sulfatoxymelatonin, a melatonin metabolite, increased 1.6-fold compared to placebo.
While promising, the doses required for sublingual delivery and the optimal formulation remain less established than injectable protocols.
Oral capsules: limited effectiveness
Oral administration of epitalon faces significant challenges. Enzymatic degradation in the digestive tract substantially reduces bioavailability, often to the point where clinical benefits become questionable.
Research on peptide capsules generally shows that tetrapeptides like epitalon fare poorly when taken orally without specialized delivery systems designed to protect against gastric breakdown.
Epitalon mechanism of action at research doses
Understanding how epitalon works at the cellular level helps explain why specific dosing protocols produce better results than others.
Telomerase activation pathway
Epitalon's primary mechanism involves activating telomerase through upregulation of the hTERT gene, which codes for the catalytic subunit of telomerase. In cell culture studies, addition of epitalon to telomerase-negative human fetal fibroblasts induced expression of this catalytical subunit, enzymatic telomerase activity, and subsequent telomere elongation.
The effect is dose-dependent but plateaus at relatively low concentrations. Studies show that increasing epitalon beyond optimal levels does not produce proportionally greater telomerase activation. This explains why standard protocols use moderate doses rather than attempting to maximize peptide exposure.
Effects on pineal gland function
Epitalon exerts direct influence on the pineal gland and melatonin synthesis. Research in elderly subjects demonstrated that epitalon can normalize hormone circadian rhythms and improve both the quality and duration of sleep.
The pineal gland becomes less efficient with age, reducing melatonin output by up to 75 percent in older individuals. This decline affects sleep quality, circadian regulation, and downstream hormonal systems. Epitalon appears to partially restore pineal function, acting as a true circadian regulator capable of re-entraining disrupted biological rhythms.
For researchers interested in peptides for energy and vitality, this restoration of circadian function may contribute significantly to improved daytime alertness and overall well-being.
Epigenetic and DNA binding effects
Beyond telomerase activation, epitalon has been shown to bind preferentially to methylated cytosine in DNA and to interact with linker histone proteins H1.3 and H1.6. These interactions influence epigenetic regulation and gene expression more broadly.
This suggests epitalon's effects extend beyond simple telomere maintenance to affect how genes are expressed across multiple cellular systems. The implications for cognitive function and systemic health are significant, though research continues to clarify the full scope of these effects.
Antioxidant enzyme activation
Studies in aging rats found that epitalon increased the activities of antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase, glutathione peroxidase, and glutathione-S-transferase. These enzymes protect cells from oxidative damage, a major contributor to aging and disease.
This antioxidant effect may work synergistically with telomerase activation to protect cellular health from multiple angles. Researchers exploring anti-inflammatory peptides may find epitalon offers complementary benefits through oxidative stress reduction.
Epitalon side effects and safety at standard doses
Understanding potential adverse effects helps researchers make informed decisions about protocol design and risk management.
Reported side effects in research
Epitalon has demonstrated a favorable safety profile across both animal and human studies. The most commonly reported side effects are minor and short-lived. These include local irritation or redness at injection sites, mild headaches or dizziness, and occasional fatigue or nausea.
Some individuals notice vivid dreams, lighter sleep, or difficulty adjusting as their circadian system responds to the peptide's effects on melatonin regulation. This typically resolves within the first few days of administration.
Fatigue or drowsiness may occur due to epitalon's role in regulating melatonin and circadian rhythms. Administering doses at bedtime rather than during the day can help manage this effect.
Long-term safety data
The most compelling safety evidence comes from a 15-year follow-up study on long-term epithalamin treatment. This research found no significant adverse effects among treated elderly patients. Additionally, the treatment group showed decreased overall mortality compared to controls.
This extended observation period represents strong evidence of epitalon's favorable safety profile and relative absence of notable side effects over time.
Theoretical concerns about telomerase activation
Because epitalon influences telomerase activity and gene expression, theoretical concerns exist about potential unintended consequences such as abnormal cell proliferation. The logic follows that if telomerase extends cell lifespan, it might also promote cancer development.
However, existing studies have not confirmed any increase in cancer risk from epitalon. In some cases, epitalon appeared to reduce tumor incidence in animal models. Research suggests that epitalon may activate different pathways in normal versus cancer cells, with normal cells showing telomerase upregulation while cancer cells show alternative lengthening of telomeres through different mechanisms.
Still, researchers with active malignancy are generally advised to avoid telomerase-activating compounds until more definitive safety data becomes available.
Hormonal effects
Unlike growth hormone secretagogues or compounds affecting testosterone and hormonal systems, epitalon does not appear to significantly alter hormone levels or cause endocrine disruption beyond its effects on melatonin.
This makes it potentially suitable for stacking with other peptides without concerns about hormonal interference or the need for post-cycle therapy typically associated with hormone-affecting compounds.
Comparing epitalon to epithalamin dosage approaches
Researchers sometimes encounter both epitalon and epithalamin in longevity research. Understanding their relationship helps clarify dosing comparisons.
Origins and composition differences
Epithalamin is a crude polypeptide extract of bovine pineal glands containing multiple peptide fractions. Epitalon is the synthetic tetrapeptide Ala-Glu-Asp-Gly, identified as the putative active component of epithalamin.
Think of it this way. Epithalamin is like crude oil, containing many compounds. Epitalon is like refined gasoline, a specific isolated component.
The distinction matters for dosing because epithalamin preparations vary in composition between batches. Different extractions might contain different amounts of the active component. Epitalon, being synthetic and standardized, offers consistent potency from vial to vial.
Comparative efficacy
In human clinical studies, epitalon and epithalamin both significantly increased telomere lengths in elderly patients aged 60 to 65 and 75 to 80. Their efficacy was comparable to one another for telomere elongation and melatonin restoration.
This suggests that researchers can expect similar outcomes from either compound when using equivalent dosing approaches. The practical advantage of epitalon lies in its standardization and reproducibility.
Regulatory status differences
Epithalamin is approved in Russia for treatment of menopause-related symptoms, anovulatory infertility, and hormone-dependent tumors. It is not approved for medical uses outside of Russia.
Epitalon remains a research compound worldwide, not approved by the FDA or equivalent regulatory agencies for medical treatment. Both compounds fall into similar regulatory categories in most jurisdictions, available for research purposes but not as approved therapeutics.
Stacking epitalon with other peptides
Epitalon's unique mechanism makes it a candidate for combination with other bioregulator peptides and therapeutic compounds. Several stacking approaches have gained attention in longevity research.
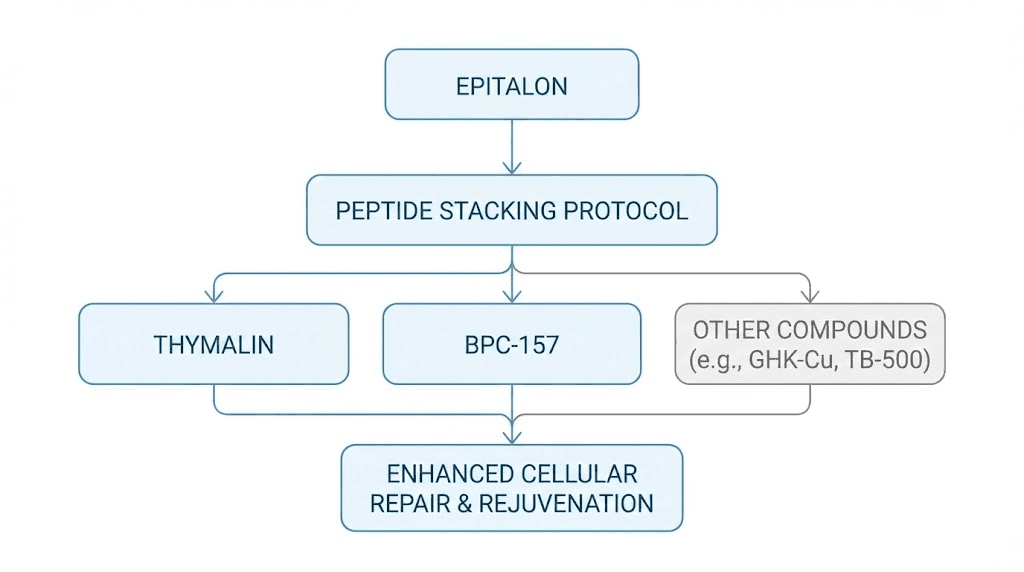
Epitalon plus thymalin stack
The combination of epitalon with thymalin represents what some call the Soviet anti-aging protocol, still used in longevity clinics today. This pairing leverages epitalon's telomerase activation and circadian regulation alongside thymalin's immune system support.
In studies performed at the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation, female rats exposed to both peptides experienced longer lifespans compared to control groups. The combination produced stronger anti-aging and antioxidant effects than either peptide alone.
Typical stacking protocols run both peptides concurrently during the same 10 to 20 day cycle, with thymalin administered at 5 to 10 mg daily via intramuscular or subcutaneous injection.
Epitalon plus BPC-157 for recovery
For researchers focused on tissue repair alongside longevity, combining epitalon with BPC-157 offers complementary mechanisms. BPC-157 supports wound healing and tissue regeneration while epitalon addresses cellular aging at the telomere level.
These peptides operate through entirely different pathways, making adverse interactions unlikely. Researchers often run BPC-157 at standard healing doses during epitalon cycles without apparent interference.
Epitalon with GH secretagogues
Some longevity protocols combine epitalon with growth hormone releasing peptides like ipamorelin or CJC-1295. The rationale involves addressing multiple aspects of aging simultaneously through cellular protection via telomerase and metabolic support via growth hormone optimization.
Timing considerations apply here. GH secretagogues typically work best when administered on an empty stomach and may have optimal timing different from epitalon's bedtime administration. Staggering doses throughout the day can accommodate both protocols.
Combining bioregulators
Beyond thymalin, other bioregulator peptides from the Russian research tradition can complement epitalon. These include cardiogen for cardiovascular support, cortagen for neurological function, and vesugen for vascular health.
Each targets specific tissue systems through gene expression modulation, potentially creating synergistic anti-aging effects when combined thoughtfully. For more on this approach, see our guide on peptide stacking strategies.
Dosing for specific applications and populations
While the standard protocols apply broadly, certain research contexts may benefit from adjusted approaches.
Longevity and anti-aging protocols
For general anti-aging applications, the standard 5 mg daily for 20 days, repeated once or twice annually, represents the most validated approach. This conservative protocol prioritizes long-term safety while still achieving meaningful telomerase activation.
Some longevity clinics use slightly higher doses of 10 mg daily for 10 days, achieving the same total cycle dose in compressed timeframes. Research comparing these approaches head-to-head remains limited, leaving the choice to researcher preference and practical considerations.
Sleep and circadian restoration
Researchers specifically targeting sleep improvement might emphasize bedtime administration and potentially start with lower doses to assess individual sensitivity to melatonin-related effects.
Beginning with 3 mg daily for the first few days before increasing to 5 mg can help identify those who experience excessive drowsiness or circadian disruption from standard doses.
Research in older populations
The majority of human research on epitalon has been conducted in elderly populations, typically ages 60 to 80. Standard protocols appear well-tolerated in this demographic, with the 15-year follow-up study providing reassurance about long-term use in older individuals.
For researchers in younger demographics, the same protocols apply, though the necessity of telomerase activation in individuals with adequate telomere length remains an open question.
Women and menopause considerations
Epithalamin, the crude extract from which epitalon was derived, received approval in Russia specifically for menopause-related symptoms. This suggests potential applications for peptides and menopause.
The connection likely relates to epitalon's effects on pineal function and circadian regulation, both of which become disrupted during the menopausal transition. Standard dosing protocols apply, with bedtime administration potentially supporting sleep quality during this challenging period.
Monitoring and assessing epitalon effectiveness
Determining whether a protocol is working requires appropriate biomarkers and realistic expectations about timelines.
Telomere length measurement
Direct telomere length testing provides the most specific measure of epitalon's intended effect. Several commercial laboratories offer telomere length analysis through blood samples.
Baseline testing before starting an epitalon protocol, followed by repeat testing 3 to 6 months after completing a cycle, can document changes. Research has shown statistically significant telomere elongation in treated versus control groups, though individual results vary.
Sleep quality metrics
Given epitalon's effects on melatonin synthesis, sleep quality often improves measurably during and after protocols. Subjective improvements in sleep onset time, sleep duration, and sleep quality commonly appear within the first week of administration.
Sleep tracking devices can provide objective data on sleep architecture changes, though these consumer devices vary in accuracy.
Expected timelines for results
Unlike some fast-acting peptides, epitalon's effects on cellular aging manifest gradually. Researchers should not expect dramatic changes within days or weeks.
Sleep and energy improvements often appear during the active dosing cycle. Effects on biological aging markers and cellular health emerge over months and may continue improving during off-cycle periods as activated cellular processes continue operating.
The most compelling research endpoints involve mortality and disease incidence tracked over years, as demonstrated in the long-term follow-up studies showing reduced mortality in treated groups.
Signs the protocol may need adjustment
If no improvements in sleep quality, energy, or subjective well-being occur after completing a full cycle, researchers might consider whether reconstitution was performed correctly, whether the peptide source is legitimate, or whether administration technique is adequate.
Excessive drowsiness, prolonged headaches, or other persistent side effects may indicate individual sensitivity requiring dose reduction or timing adjustments.
Sourcing and quality considerations for dosing accuracy
The peptide you use must contain what the label claims at the purity stated. Otherwise, all dosing calculations become meaningless.
Purity requirements
Research-grade epitalon should have purity of at least 98 percent as verified by HPLC testing. Lower purity products contain impurities that may affect both safety and efficacy. They also make accurate dosing impossible since part of the measured powder consists of non-peptide material.
Certificates of analysis from independent peptide testing laboratories provide verification of purity claims. Reputable vendors make these available upon request or include them with shipments.
Storage during shipping
Lyophilized peptides are relatively stable during shipping but can degrade if exposed to excessive heat for extended periods. Summer shipping to warm climates presents particular risks.
Cold pack shipping and expedited delivery minimize temperature exposure. Receiving packages promptly and transferring to appropriate storage reduces degradation risk.
Avoiding counterfeit products
The peptide market includes both legitimate research suppliers and problematic vendors selling mislabeled or underdosed products. Researching vendor reputation, requesting testing documentation, and starting with small orders to verify quality before committing to larger purchases helps protect against counterfeits.
Our guide on grey market peptides provides additional context on sourcing considerations and risk factors.
Protocol examples and practical schedules
Translating the above information into concrete protocols helps researchers plan their approach systematically.
Protocol 1: standard longevity cycle
Goal: General anti-aging and telomere maintenance
Duration: 20 days active, then 4-6 months off
Schedule:
Days 1-20: 5 mg epitalon subcutaneously, once daily at bedtime
Days 21-180: Off cycle, no epitalon
Repeat cycle 1-2 times per year
Reconstitution: 10 mg vial plus 2 mL bacteriostatic water equals 5 mg/mL. Draw 1 mL (100 units) for each dose. Two vials needed per cycle.
Total cycle dose: 100 mg
Expected timeline: Sleep improvements within 1-2 weeks. Cellular effects measured over months. Full benefits assessed over years.
Protocol 2: intensive 10-day cycle
Goal: Concentrated telomerase activation with reduced injection frequency
Duration: 10 days active, then 4-6 months off
Schedule:
Days 1-10: 10 mg epitalon subcutaneously, once daily at bedtime
Days 11-180: Off cycle
Repeat cycle 1-2 times per year
Reconstitution: 10 mg vial plus 1 mL bacteriostatic water equals 10 mg/mL. Draw 1 mL (100 units) for each dose. One vial per cycle.
Total cycle dose: 100 mg
Protocol 3: epitalon plus thymalin stack
Goal: Combined anti-aging and immune support
Duration: 10-20 days active, then 4-6 months off
Schedule:
Days 1-10 (or 1-20): 5-10 mg epitalon subcutaneously at bedtime
Days 1-10 (or 1-20): 5-10 mg thymalin subcutaneously in morning
Remainder of period: Off both peptides
Repeat 1-2 times per year
Notes: Separating administration times (morning thymalin, evening epitalon) may improve individual assessment of each peptide's effects.
Protocol 4: nasal spray approach
Goal: Needle-free administration with acceptable bioavailability trade-off
Duration: 20 days active, then 4-6 months off
Schedule:
Days 1-20: 10-15 mg epitalon intranasally, divided into 2-3 daily doses
Days 21-180: Off cycle
Repeat 1-2 times per year
Formulation: Reconstitute in saline with 3 percent DMSO for improved nasal absorption. Concentration and spray volume depend on delivery device specifications.
Notes: Higher doses compensate for reduced nasal bioavailability compared to injection. Cost per cycle increases accordingly.
Troubleshooting common dosing issues
Even with careful protocol design, researchers may encounter challenges that require adjustment.
No noticeable effects after completing a cycle
If subjective improvements in sleep, energy, or well-being do not appear after a full 20-day cycle, consider the following possibilities.
The peptide may have degraded before or during reconstitution. Check storage conditions and consider sourcing from a different vendor with verifiable purity testing.
Reconstitution technique may have compromised potency. Shaking rather than gently swirling, using non-sterile water, or injecting directly onto the powder cake can all reduce effectiveness.
Individual response varies. Some researchers may require higher doses or longer cycles to achieve noticeable effects, though increasing beyond standard protocols should be approached cautiously.
Expectations may be unrealistic. Epitalon's primary effects on cellular aging occur at molecular levels that may not produce immediately perceptible changes. Trust the research showing objective improvements in telomere length and mortality even when subjective experience seems unchanged.
Excessive drowsiness or fatigue
Strong drowsiness suggests individual sensitivity to melatonin modulation. Reducing the dose to 3 mg daily or administering earlier in the evening rather than at bedtime may help.
The effect typically diminishes after the first few days as the body adjusts. Persistence through initial drowsiness often leads to improved sleep quality and daytime energy once adaptation occurs.
Injection site reactions
Redness, swelling, or itching at injection sites occurs in some individuals. Rotating sites systematically helps prevent accumulation of local reactions. Allowing the injection solution to reach room temperature before administration may reduce discomfort.
Persistent or severe reactions may indicate sensitivity to benzyl alcohol in bacteriostatic water. Reconstituting with sterile water for single-use sessions can determine whether the preservative causes the problem.
Difficulty achieving dissolution during reconstitution
If epitalon does not dissolve completely with standard bacteriostatic water reconstitution, adding a small amount of 0.6 percent acetic acid before the bacteriostatic water may aid dissolution. The acetic acid helps break down the lyophilized cake, while the bacteriostatic water provides the final volume and preservation.
Undissolved particles should not be injected. If complete dissolution proves impossible, the peptide may have degraded and should be discarded.
Research context and regulatory considerations
Understanding the current state of epitalon research helps frame expectations and responsibilities.
Evidence quality assessment
Most epitalon research has been conducted by the St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology, primarily under the direction of Vladimir Khavinson. While this work has produced compelling findings, the concentration of research in a single institution limits independent replication.
Cell culture and animal studies provide strong mechanistic evidence for telomerase activation and telomere elongation. Human studies, while smaller in scale, support both efficacy and safety over extended periods.
Large-scale randomized controlled trials meeting Western regulatory standards have not been conducted. This represents a gap in the evidence base that researchers should acknowledge when making decisions about protocol adoption.
Current regulatory status
Epitalon is not approved by the FDA for the treatment, mitigation, or prevention of any disease. It remains a research compound in most jurisdictions, available for purchase as a research chemical but not as a regulated medication.
Researchers should understand the legal framework in their jurisdiction regarding peptide purchase and use. Regulations vary significantly by country and region.
Informed decision making
Anyone considering epitalon should understand both the promising research findings and the limitations of current evidence. Consulting with healthcare providers familiar with peptide research can help contextualize individual risks and benefits.
SeekPeptides provides educational resources to support informed decision-making. We emphasize that information about dosing protocols does not constitute medical advice or recommendation for self-treatment.
Frequently asked questions
What is the standard epitalon dosage for anti-aging research?
The standard protocol involves 5 to 10 mg daily via subcutaneous injection for 10 to 20 consecutive days, repeated once or twice per year with 4 to 6 months between cycles. Most research validates the 5 mg daily for 20 days approach, totaling 100 mg per cycle.
Can I take epitalon orally instead of injecting it?
Oral administration significantly reduces bioavailability due to enzymatic degradation in the digestive tract. While some oral and sublingual formulations exist, injection remains the gold standard with the most research support. Nasal spray offers a middle ground with moderate bioavailability and no needles, though higher doses are required.
How long do epitalon effects last after a cycle?
Effects on telomere length and cellular health appear to persist for months after completing a cycle, which is why extended off-cycle periods work within the protocol design. Sleep improvements may diminish more quickly but often remain improved compared to baseline.
Is it safe to stack epitalon with other peptides?
Epitalon has been combined with thymalin, BPC-157, and various other peptides without reported adverse interactions. Its unique mechanism of action does not interfere with hormone-related peptides or tissue repair compounds. However, any combination should be approached thoughtfully with consideration of individual factors.
What are the signs that epitalon is working?
Common early indicators include improved sleep quality, more vivid dreams, and increased morning energy. Long-term effects require laboratory measurement of telomere length or biomarkers of cellular aging. Absence of subjective effects does not necessarily mean the peptide is not producing cellular benefits.
Do I need to take epitalon with food or on an empty stomach?
For injectable administration, food timing does not affect absorption. The peptide enters the bloodstream directly regardless of digestive state. For sublingual or oral formulations, absorption may be better on an empty stomach, though specific research is limited.
How should I store reconstituted epitalon?
Reconstituted epitalon requires refrigeration at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius and remains stable for approximately 4 to 6 weeks. Protect from light and avoid temperature fluctuations. Never freeze reconstituted peptide solution as this degrades the compound. For more details, see our guide on peptide storage.
Can women use epitalon during perimenopause or menopause?
The original epithalamin extract received approval in Russia specifically for menopause-related symptoms, suggesting relevance for women during hormonal transitions. Standard epitalon protocols apply regardless of sex. The peptide's effects on circadian regulation and sleep may provide particular benefit during perimenopause when these systems become disrupted. Our guide on peptides for perimenopause provides additional context.
External resources
For researchers serious about optimizing their longevity protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available. Evidence-based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions provide support at every stage of your research journey.



