Feb 2, 2026
Some researchers see results in two weeks. Others wait months. The difference is not luck. It is not genetics. It is not even the specific peptide they choose. The difference comes down to understanding how hormones actually work, which pathways need support, and how to match the right peptide to the right problem at the right time.
Hormonal balance is not a single switch you flip. It is a symphony of interconnected systems, each one influencing the others in ways that most people never consider. The hypothalamus talks to the pituitary. The pituitary talks to the gonads, the thyroid, the adrenals. And every one of those conversations happens through chemical messengers, many of which are peptides themselves. When one system falls out of rhythm, the others compensate. Sometimes they overcompensate. Sometimes they simply give up. That is when you feel it. The fatigue that coffee cannot fix. The weight that exercise cannot shift. The mood changes that seem to come from nowhere. The sleep that never quite refreshes. These are not isolated symptoms. They are signals from a hormonal network under strain. Peptides offer something unique in this landscape.
Unlike synthetic hormones that override natural production, peptides work with the body own signaling systems. They nudge. They amplify. They restore conversations between glands that have gone quiet. This guide covers every major hormonal axis, the peptides that influence each one, and the practical protocols that researchers use to bring the whole system back into balance.
Whether you are exploring how peptides work for the first time or looking to refine an existing protocol, the information here draws from clinical studies, established research, and real-world observations.
How the hormonal system actually works
Before diving into specific peptides, you need to understand the architecture. The endocrine system is not a collection of independent glands. It is a hierarchy. A chain of command. And at the top of that chain sits the hypothalamus.
The hypothalamus receives information from everywhere. Blood sugar levels. Stress signals. Sleep-wake cycles. Temperature. Inflammation markers. It processes all of this and sends instructions downward through releasing hormones. These releasing hormones travel a short distance to the pituitary gland, which acts as the master amplifier. The pituitary then sends its own hormones into the bloodstream, reaching target glands throughout the body. Those target glands produce the hormones you actually feel: testosterone, estrogen, cortisol, thyroid hormone, growth hormone. This is the basic feedback loop that governs nearly every aspect of how you feel, perform, and age.
Four major axes control hormonal balance. Understanding them is essential for anyone researching peptide safety and risks or considering a hormone-supportive protocol.
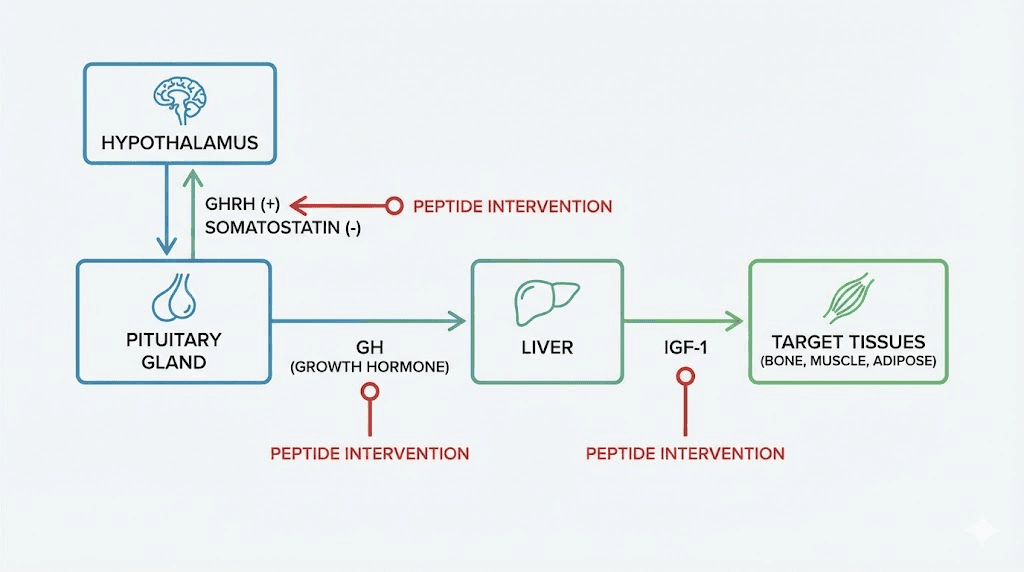
The growth hormone axis
The hypothalamus releases growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH). This triggers the pituitary to secrete growth hormone. GH then travels to the liver and other tissues, stimulating production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1). IGF-1 does much of the actual work: building muscle, burning fat, repairing tissue, supporting bone density. A counterbalancing hormone called somatostatin puts the brakes on GH release, ensuring the system does not overshoot. As you age, GHRH output declines. Somatostatin does not. The result is a steady drop in GH and IGF-1, sometimes called somatopause. By age 40, most adults have lost 50% or more of their youthful GH output. This is where GH-supporting peptides enter the picture, and they remain one of the most researched categories in peptide science.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis
This axis controls reproductive hormones. The hypothalamus releases gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) in a pulsatile pattern. Pulsatile is the key word. The timing matters as much as the amount. GnRH stimulates the pituitary to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). In men, LH drives testosterone production in the Leydig cells. FSH supports sperm production. In women, these same hormones orchestrate the menstrual cycle, ovulation, and the production of estrogen and progesterone. When this axis weakens, men experience low testosterone. Women enter perimenopause and eventually menopause. Both face declining quality of life. Peptides like kisspeptin sit at the very top of this cascade, acting as the master switch for GnRH release.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
Stress. This axis manages it. The hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) in response to perceived threats, whether physical, psychological, or inflammatory. CRH tells the pituitary to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). ACTH tells the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. Cortisol is not inherently bad.
You need it. It mobilizes energy, reduces inflammation acutely, and keeps you alert. The problem is chronic activation. When the HPA axis stays turned on, cortisol remains elevated. This suppresses the HPG axis, impairs thyroid function, disrupts sleep, promotes fat storage, and degrades muscle tissue. Managing cortisol is therefore not just about stress. It is about protecting every other hormonal axis from collateral damage. Research into peptides for anxiety and stress response has expanded significantly in recent years.
The thyroid axis
The hypothalamus releases thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). The pituitary responds with thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). The thyroid gland produces T4, which converts to the active form T3 in peripheral tissues. Thyroid hormones set the metabolic rate for every cell in your body. Too little and everything slows down: metabolism, cognition, mood, digestion. Too much and the system races unsustainably. Thyroid function is exquisitely sensitive to cortisol levels, inflammation, gut health, and immune status. This is why thyroid problems rarely exist in isolation, and why bioregulator peptides that target multiple systems simultaneously have attracted research attention.
These four axes do not operate independently. They cross-talk constantly. Elevated cortisol suppresses GnRH. Low thyroid hormone impairs GH secretion. Poor sleep disrupts all four. This interconnection is precisely why peptides hold such promise for hormonal balance. They can address multiple axes simultaneously, restoring the conversations that aging and stress have silenced.
Peptides that target growth hormone balance
The growth hormone axis is the most extensively studied target for peptide-based interventions. There is good reason for this. GH decline affects everything: body composition, energy, recovery, cognitive function, skin quality, and even immune response. The peptides in this category work through two primary mechanisms. Some mimic GHRH, telling the pituitary to release more GH. Others mimic ghrelin, activating a different receptor that also stimulates GH release. The most sophisticated protocols combine both.
CJC-1295
CJC-1295 is a modified GHRH analog with 30 amino acids. What makes it remarkable is its half-life. Native GHRH lasts minutes in the bloodstream. CJC-1295, through a modification called Drug Affinity Complex (DAC), extends that to 5.8 to 8.1 days. A single dose produces dose-dependent GH increases of 2 to 10 fold that persist for six or more days. IGF-1 levels rise 1.5 to 3 fold and remain elevated for 9 to 11 days. These are not theoretical numbers. They come from published research in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
The practical significance is substantial. Rather than requiring multiple daily injections, CJC-1295 with DAC can be administered once or twice weekly. It preserves the natural pulsatile pattern of GH release rather than creating a single artificial spike. This is important because GH pulsatility itself carries biological information. The body responds differently to pulses than to a steady stream. For those new to this peptide, the CJC-1295 dosage calculator provides a useful starting reference, and the CJC-1295 complete guide covers the pharmacology in detail.
CJC-1295 without DAC (sometimes called modified GRF 1-29) has a much shorter half-life of about 30 minutes. This version requires more frequent dosing but gives more precise control over GH pulses. Some researchers prefer it for this reason. The choice between the two depends on protocol goals and practical considerations around dosing frequency.
Ipamorelin
Ipamorelin holds a unique position among growth hormone secretagogues. It was the first truly selective GH secretagogue identified. What does selective mean in this context? It means ipamorelin stimulates GH release without affecting ACTH, cortisol, FSH, LH, prolactin, or TSH. Even at doses 200 times higher than the effective dose for GH release, these other hormones remain unchanged.
This selectivity matters enormously for hormone balance. Many older GH secretagogues like GHRP-6 and GHRP-2 also increase cortisol and prolactin. When you are trying to balance hormones, the last thing you want is to fix one axis while disrupting another. Ipamorelin avoids this problem entirely. It releases GH cleanly. The ipamorelin benefits profile reflects this clean action: improved body composition, better sleep quality, enhanced recovery, and support for overall well-being without the side effect burden of less selective compounds.
Researchers commonly pair ipamorelin with CJC-1295 without DAC. The combination creates a synergistic effect. CJC-1295 mimics GHRH at one receptor. Ipamorelin mimics ghrelin at a different receptor. Together, they produce a GH pulse significantly larger than either one alone. The ipamorelin versus CJC-1295 comparison explains how these two peptides complement rather than compete with each other. Understanding ipamorelin side effects is also important for anyone planning a protocol.
Sermorelin
Sermorelin is a 29-amino-acid GHRH analog that has been used clinically since the 1990s. It has the longest track record of any GH-stimulating peptide. Clinical studies show improvements in skin thickness after 16 weeks of use, significant increases in insulin sensitivity in men, and restoration of more youthful GH pulsatility patterns.
What makes sermorelin particularly relevant for hormone balance is its effect on insulin sensitivity. Insulin resistance is both a cause and consequence of hormonal imbalance. When cells become resistant to insulin, blood sugar rises, inflammation increases, and the resulting metabolic stress impairs every other hormonal axis. By improving insulin sensitivity, sermorelin addresses a root cause rather than just a symptom. The sermorelin benefits profile extends beyond GH release to include these broader metabolic improvements.
For men specifically, sermorelin has shown particular promise. The sermorelin-ipamorelin blend for men has become one of the most popular GH-stimulating protocols, combining the GHRH action of sermorelin with the ghrelin-mimetic action of ipamorelin. Results documented in sermorelin before and after reports typically show improvements in body composition, energy, and sleep within 8 to 12 weeks. For those considering this option, the sermorelin cost guide provides practical budgeting information.
Tesamorelin
Tesamorelin is the most potent GHRH analog available. It holds FDA approval for reducing visceral adipose tissue in HIV-associated lipodystrophy, making it one of the few peptides with formal regulatory endorsement. In clinical trials, tesamorelin produced approximately 20% reduction in visceral fat over six months. Visceral fat is not cosmetic. It is metabolically active tissue that produces inflammatory cytokines, disrupts insulin signaling, and directly impairs hormonal balance.
The potency of tesamorelin compared to sermorelin is well-documented. It produces larger GH pulses and more significant IGF-1 elevation. However, this increased potency also means more careful monitoring is appropriate. For researchers evaluating their options, understanding the differences between these GHRH analogs helps inform protocol design. The broader landscape of peptides for weight loss often includes tesamorelin as a primary consideration for its proven effect on visceral fat specifically.
Hexarelin
Hexarelin is the most potent ghrelin-mimetic GH secretagogue. It produces the largest acute GH spikes of any peptide in this class. However, it is not selective like ipamorelin. Hexarelin also increases cortisol and prolactin, which is a significant consideration for anyone focused on overall hormone balance. There is another issue. Hexarelin is prone to desensitization. With continued use, GH response diminishes, sometimes substantially. This has led most researchers to favor ipamorelin for sustained protocols, reserving hexarelin for short-term or intermittent use. The hexarelin benefits are real but come with trade-offs that must be weighed carefully.
One area where hexarelin stands apart is cardioprotection. Research suggests it has direct protective effects on cardiac tissue independent of GH release, mediated through a specific cardiac receptor subtype. For researchers interested in this unique property, hexarelin remains an important peptide to understand even if it is not the first choice for broad hormonal support.
Across this entire category, the peptide stack calculator can help researchers plan combinations, and the peptide stacks guide provides detailed combination strategies. Those evaluating GH peptides specifically should also review the IGF peptide guide to understand the downstream effects of increased GH on IGF-1 and its various isoforms.
Peptides for reproductive hormone regulation
The HPG axis governs fertility, sexual function, body composition, mood, bone density, and much more. When it declines, whether from aging, stress, or medical conditions, the effects ripple through every aspect of life. The peptides targeting this axis work at different levels of the cascade, from the very top (kisspeptin, which activates GnRH neurons) to downstream modulators that influence LH, FSH, and sex steroid production directly.
Kisspeptin
Kisspeptin is the master regulator of reproductive hormone signaling. Encoded by the KISS1 gene, this peptide activates GnRH neurons in the hypothalamus, essentially serving as the on-switch for the entire HPG axis. Without kisspeptin, there is no puberty. Without kisspeptin, GnRH pulses become disorganized or absent. Without kisspeptin, reproductive function shuts down.
Research has revealed that kisspeptin does more than just turn GnRH on or off. It modulates the pulse frequency and amplitude of GnRH release. This matters because different pulse patterns produce different downstream effects. Rapid GnRH pulses favor LH production. Slower pulses favor FSH. By influencing the pattern rather than just the amount, kisspeptin has the potential to fine-tune reproductive hormone output rather than simply amplify it.
Clinical studies have explored kisspeptin administration in both men and women. In men with functional hypogonadism, kisspeptin infusion restored LH pulsatility and increased testosterone levels. In women, it has been investigated as a potential trigger for ovulation in fertility protocols, offering an alternative to traditional hCG triggers. The kisspeptin benefits extend across both sexes and represent a fundamentally different approach to supporting reproductive hormones, one that works with the body highest-level regulatory signals rather than bypassing them.
Kisspeptin also influences metabolic signaling. Kisspeptin neurons receive input about energy availability, which is why severe caloric restriction and excessive exercise can shut down reproductive function. The body, through kisspeptin, prioritizes survival over reproduction when resources are scarce. This connection between metabolism and reproduction is mediated at the kisspeptin level, making it a uniquely integrative target for hormone balance.
Enclomiphene
Enclomiphene is the trans-isomer of clomiphene citrate, a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). While not technically a peptide, it is frequently included in peptide-oriented protocols for hormone balance because of how directly it influences the HPG axis. Enclomiphene blocks estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus and pituitary. This removes negative feedback, causing the brain to perceive lower estrogen levels and respond by increasing GnRH, LH, and FSH output.
The result in men is increased testosterone production from their own testes. Unlike exogenous testosterone, which shuts down the HPG axis through negative feedback, enclomiphene actually stimulates it. This preserves testicular function and fertility, a critical consideration for many men. The enclomiphene testosterone guide details the specific mechanisms by which this compound supports endogenous testosterone production.
For researchers comparing approaches to testosterone support, the distinction between exogenous replacement and endogenous stimulation is fundamental. The peptides versus TRT comparison explores this distinction in depth. While TRT delivers testosterone directly, peptide-based and SERM-based approaches aim to restore the body own production capacity. Each approach has its place, and the right choice depends on individual circumstances, goals, and baseline hormonal status. The peptides for testosterone guide covers the full range of available options.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hCG mimics LH structurally and functionally. When administered to men, it directly stimulates the Leydig cells to produce testosterone, bypassing the hypothalamus and pituitary entirely. This makes it useful in specific contexts: maintaining testicular function during TRT, supporting fertility, and providing a more physiological testosterone stimulus than pure exogenous testosterone.
In women, hCG is used extensively in fertility medicine to trigger ovulation. It mimics the natural LH surge that causes a mature follicle to release an egg. The hCG peptide guide covers both male and female applications in detail.
The limitation of hCG is that it does not address the upstream problem. If kisspeptin or GnRH signaling is impaired, hCG can compensate at the gonadal level but does not fix the underlying regulatory dysfunction. This is why many researchers view hCG as a bridge or adjunct rather than a standalone long-term solution for hormonal imbalance.
Testagen
Testagen is a bioregulator peptide from the Khavinson peptide research tradition. It consists of a short amino acid sequence (typically a tetrapeptide) that targets testicular tissue specifically. The theory behind bioregulator peptides is that these short sequences, derived from the organs they target, can restore gene expression patterns associated with youthful function.
The research on testagen, while earlier-stage than that on kisspeptin or enclomiphene, suggests it may support testosterone production through a completely different mechanism: epigenetic regulation of testicular cells rather than hormonal stimulation. The testagen complete guide examines the available evidence. For context on the broader category, the Khavinson peptides guide provides essential background on how bioregulator peptides were developed and how they differ from traditional hormone-stimulating peptides.
Building a reproductive hormone protocol often involves combining agents that work at different levels of the axis. A kisspeptin analog at the top, an SERM like enclomiphene in the middle, and possibly hCG or testagen at the gonadal level. The peptide cycle planning guide discusses how to structure such multi-target approaches, and understanding how many peptides can be taken simultaneously is essential before building complex stacks.
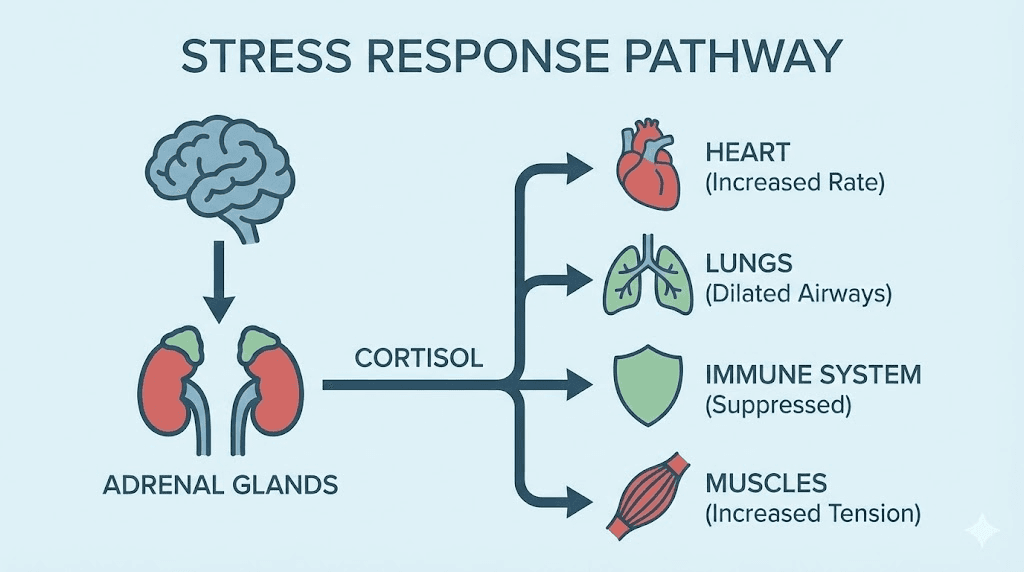
Peptides that influence cortisol and the stress response
Cortisol is the hormone that derails everything else. Elevated cortisol suppresses GnRH (lowering testosterone and estrogen). It impairs TSH release (weakening thyroid function). It promotes insulin resistance (disrupting metabolic hormones). It interferes with GH secretion (accelerating aging). Managing cortisol is therefore not just about feeling less stressed. It is about protecting every other hormonal axis in the body.
The peptides in this section do not block cortisol directly. That would be dangerous. Instead, they modulate the stress response through different mechanisms: calming neural circuits, supporting neurotransmitter balance, improving sleep quality, and enhancing the body ability to return to baseline after stress.
DSIP (delta sleep-inducing peptide)
DSIP was first isolated from the blood of rabbits during electrically induced sleep. Its name describes its most well-known effect, but DSIP does far more than promote sleep. Research suggests it modulates cortisol rhythms, potentially inhibiting nighttime cortisol elevations that disrupt sleep architecture and prevent proper recovery.
The connection between sleep and hormones is not subtle. It is massive. Growth hormone is primarily released during deep sleep. Testosterone production peaks during sleep. Cortisol is supposed to drop to its lowest point around midnight, then rise gradually to wake you in the morning. When this pattern is disrupted, whether by stress, screen exposure, shift work, or other factors, every hormone suffers. DSIP aims to restore proper sleep architecture, and by extension, the hormonal processes that depend on it.
The DSIP benefits include not only improved sleep onset and maintenance but also stress adaptation and cortisol modulation. Detailed dosing information is available in the DSIP dosage guide. For those exploring sleep-focused peptide strategies, the pineal peptide for sleep article provides complementary approaches.
Selank
Selank is a synthetic peptide based on the naturally occurring immunomodulatory peptide tuftsin, with additional modifications to extend its half-life and enhance its neurological effects. Developed at the Institute of Molecular Genetics in Russia, selank has been studied for its anxiolytic (anti-anxiety) properties.
How does an anti-anxiety peptide relate to hormone balance? Through the HPA axis. Anxiety and chronic stress keep the HPA axis activated. Cortisol stays elevated. And elevated cortisol, as we have established, suppresses virtually every other hormonal system. By reducing anxiety at the neurological level, selank may help normalize HPA axis activity, allowing cortisol to return to healthy patterns.
Research suggests selank modulates GABA, serotonin, and dopamine systems. It appears to increase BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor) expression and influence the enkephalin system. These are not simple sedating effects. Selank seems to enhance the brain ability to process stress without overreacting to it. The selank dosage guide covers the practical aspects of this peptide, and the broader anxiety peptide guide places it in context alongside other neurologically active peptides.
Semax
Semax is a synthetic analog of ACTH (4-10), the fragment of adrenocorticotropic hormone that influences brain function without stimulating cortisol production. This is a crucial distinction. Semax provides the cognitive and neuroprotective benefits associated with ACTH-related signaling without activating the adrenal cortisol response. The semax dosage guide provides practical protocol information, and for researchers interested in cognitive-hormonal connections, the best peptides for brain function overview covers the full landscape of nootropic peptides. The nootropic peptides guide goes even deeper into the mechanisms.
BPC-157 and the gut-brain-hormone connection
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound-157) is primarily known for tissue repair. It accelerates healing of tendons, ligaments, muscle, and gut tissue. But its relevance to hormone balance goes deeper than repair alone.
The gut produces more than 30 hormones. It contains hundreds of millions of neurons. The gut-brain axis directly influences HPA axis activity, serotonin production, and inflammatory signaling. BPC-157 supports gut barrier integrity and accelerates healing of damaged intestinal tissue. The BPC-157 overview and BPC-157 mechanisms explain its actions in detail. For dosing guidance, the BPC-157 dosage calculator is a practical resource. The BPC-157 and TB-500 stacking guide covers one of the most popular combinations.
The gut health peptides guide provides broader context. The inflammation peptides guide covers additional options for managing the inflammatory component.
Thyroid-supporting peptides
Thyroid disorders affect an estimated 20 million Americans, with up to 60% unaware of their condition. The thyroid sets the metabolic pace for every cell. When it underperforms, everything slows. Weight gain. Fatigue. Brain fog. Cold sensitivity. Depression. Hair loss.
Thymosin alpha-1
Thymosin alpha-1 is a 28-amino-acid peptide originally isolated from the thymus gland. Its connection to thyroid health comes through the immune system. The most common cause of hypothyroidism in developed countries is Hashimoto thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition. By modulating immune function, thymosin alpha-1 may help reduce the autoimmune attack on thyroid tissue. The thymalin peptide guide covers a related thymic peptide. The best peptides for immune system provides a comprehensive overview. The peptides for autoimmune diseases guide directly addresses autoimmune thyroid conditions.
Cortagen
Cortagen is a bioregulator peptide targeting the adrenal cortex. Elevated cortisol impairs T4-to-T3 conversion and increases reverse T3. By supporting healthier adrenal function, cortagen may indirectly improve thyroid hormone utilization. The cortagen complete guide details the research. The bioregulator peptides guide covers the broader framework.
Other bioregulator approaches
The Khavinson peptides guide provides a comprehensive overview. The livagen peptide guide covers liver-targeted bioregulation. The vilon peptide and chonluten peptide articles address related applications.
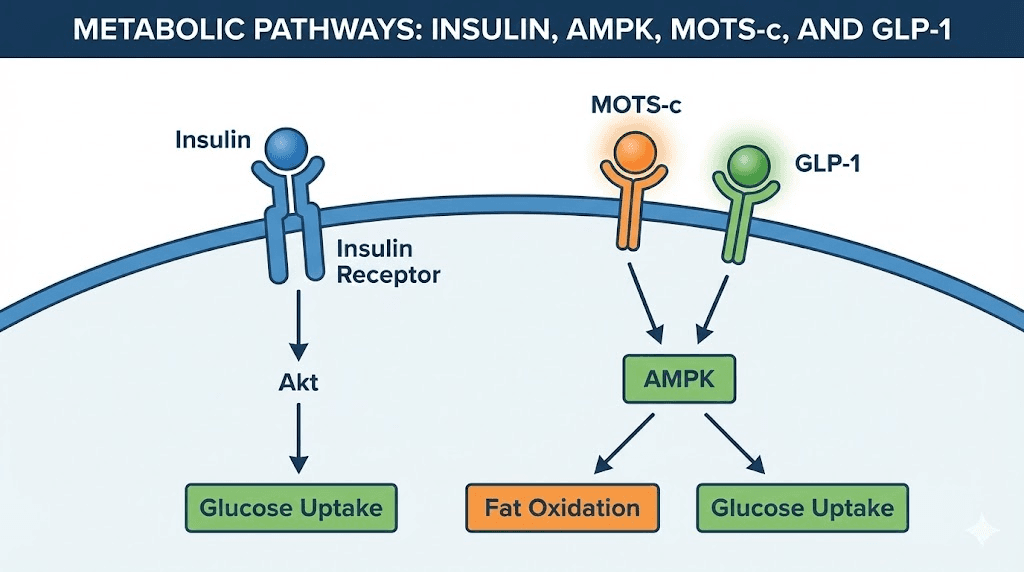
Metabolic peptides and insulin sensitivity
Insulin resistance promotes inflammation. Inflammation elevates cortisol. Cortisol suppresses sex hormones and thyroid function. This is the metabolic-hormonal vicious cycle.
MOTS-c
MOTS-c is encoded by mitochondrial DNA. It activates AMPK, improves glucose uptake, enhances fatty acid oxidation, and increases insulin sensitivity. The MOTS-c benefits guide provides comprehensive coverage. The MOTS-c dosage chart offers specific protocols. The MOTS-c side effects guide addresses safety.
GLP-1 receptor agonists
The semaglutide versus tirzepatide comparison examines key differences. The semaglutide dosage calculator helps with planning. The best peptides for weight loss guide covers full options. Peptides for weight loss and muscle gain addresses recomposition. The GLP-3 peptide and cagrilintide represent the next frontier.
AOD-9604
The AOD-9604 guide covers the research. The HGH fragment calculator provides dosing support. The best fat burning peptides and fat burning peptides for men offer context.
The pancreatic peptide hormones guide provides a detailed overview. The peptide formula guide covers structural chemistry. Understanding C-peptide levels provides a practical marker for pancreatic function.
Circadian rhythm and sleep hormone peptides
Sleep is not passive rest. It is an active hormonal event. GH pulses during slow-wave sleep. Testosterone peaks during REM. Cortisol drops to its nadir around midnight. Disrupt sleep, and you disrupt all of them.
Epitalon
The epitalon benefits span circadian restoration, anti-aging effects, and hormonal support. The epitalon dosage guide provides protocols. The longevity peptides guide places epitalon in broader context. The anti-aging peptides overview covers circadian-support peptides.
Pineal peptide bioregulators
The pineal peptide for sleep article covers these in detail. The best peptides for energy and energy peptide guide address daytime alertness.
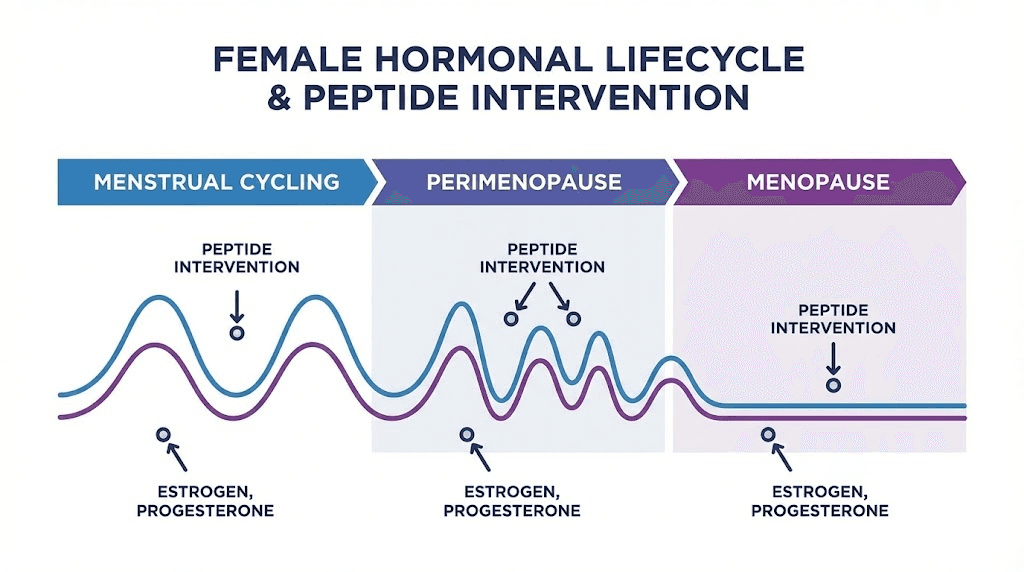
Peptides for hormone balance in women
Women face unique hormonal challenges at every life stage. Peptides offer the ability to support endogenous hormone production rather than replace it.
The best peptides for perimenopause guide addresses the transitional period. The peptides for menopause article covers full menopause. The safest peptides for women prioritizes safety. The peptides for women over 40 guide breaks down priorities. The best peptides for women overview covers all goals. The peptides for weight loss in women addresses female metabolism. The lipo-C peptide covers body composition. The oxytocin peptide guide covers reproductive and emotional health.
Peptides for hormone balance in men
Male hormonal health centers on testosterone but requires addressing the entire system. The peptides for testosterone guide covers full options. The testosterone peptide overview focuses on key compounds. The complete guide for men addresses all categories. The peptides versus TRT compares approaches. The best peptides for libido and PT-141 guide cover sexual function. The hCG guide covers fertility preservation.
Building a hormone-balancing peptide protocol
The getting started guide provides foundational advice. Understanding common mistakes prevents errors. The combining peptides guide addresses stacking.
The stacking guide covers combinations. The stack calculator helps with logistics. The dosing guide covers timing. The dosage chart provides quick reference. The injection guide covers technique. The injection pen guide discusses convenience. The cycling guide addresses timing. The cycle planning guide provides frameworks. The reconstitution guide provides instructions. The reconstitution calculator determines concentrations. The bacteriostatic water guide and mixing guide cover preparation. The storage guide provides recommendations. The lyophilized versus liquid comparison explains powder form.
What to expect and realistic timelines
The timeline guide provides granular expectations. The before and after results documents real outcomes.
Safety, side effects, and monitoring
The safety guide provides comprehensive risk mitigation. Understanding peptide legality is important. The research versus pharmaceutical peptides distinction matters. The ipamorelin side effects profile is the mildest. The cost guide addresses economics. The online therapy guide covers providers. The injectable versus oral comparison helps choose delivery. The injectable list provides a catalog. The peptides versus SARMs and benefits and risks guide provide context. The research guide contextualizes evidence.
Frequently asked questions
What are the best peptides for hormone balance?
The best peptide depends on which system is most impaired. For GH decline, CJC-1295 and ipamorelin. For testosterone, enclomiphene and kisspeptin. For cortisol, DSIP and selank. For metabolism, MOTS-c and GLP-1 agonists. The complete peptide list covers all options.
How long do peptides take to balance hormones?
Noticeable improvements take 6 to 12 weeks. Full remodeling requires 3 to 6 months. The timeline guide provides specific expectations.
Can peptides replace hormone replacement therapy?
Sometimes yes, sometimes no. The peptides versus TRT comparison addresses this.
Are peptides safe for long-term use?
Safety varies by peptide. Regular monitoring and cycling are essential. The safety guide covers risks.
What peptides help with menopause symptoms?
GH secretagogues, DSIP, epitalon, and BPC-157. The menopause guide and perimenopause guide cover protocols.
Do peptides affect thyroid function?
Some influence thyroid indirectly through immune modulation and cortisol management. The Khavinson guide covers thyroid-targeted formulations.
Can men and women use the same peptides?
Many work for both sexes. Differences arise in reproductive-axis peptides. See the women guide and men guide.
How do I know which hormones are out of balance?
Comprehensive blood work is the only reliable method. Test testosterone, estradiol, cortisol, TSH, free T4, free T3, IGF-1, and fasting insulin at minimum.
What is the difference between peptides and steroids?
Peptides signal the body to produce hormones. Steroids are the hormones themselves. The peptides versus SARMs comparison and peptide introduction explain the biology.
Can peptides help with cortisol levels?
Yes. DSIP influences nighttime cortisol. Selank reduces HPA axis activation. Semax provides cognitive benefits without cortisol elevation. BPC-157 reduces gut-mediated inflammation.
Hormonal balance is not a destination. It is a dynamic equilibrium that requires ongoing attention, periodic reassessment, and willingness to adjust.
SeekPeptides members gain access to detailed protocols, dosing frameworks, stacking strategies, and the latest research updates for every peptide discussed in this guide. Whether you are navigating perimenopause, addressing declining testosterone, managing stress-related hormonal disruption, or building a comprehensive anti-aging protocol, the SeekPeptides platform provides the structured guidance that transforms information into action. Explore the peptide calculator tools, review the stacking protocols, and connect with a community of informed researchers who approach hormone optimization with the seriousness it deserves.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Join us here.



