Jan 8, 2026

Immune-modulating peptides represent a distinct category within the broader peptide landscape, requiring clear terminology and regulatory context before meaningful discussion of specific compounds can proceed.
Unlike growth hormone secretagogues or healing peptides that work through relatively straightforward receptor interactions, immune peptides interface with one of the body's most complex and tightly regulated systems, the adaptive and innate immune response networks that determine everything from infection clearance to autoimmune balance to cancer surveillance.
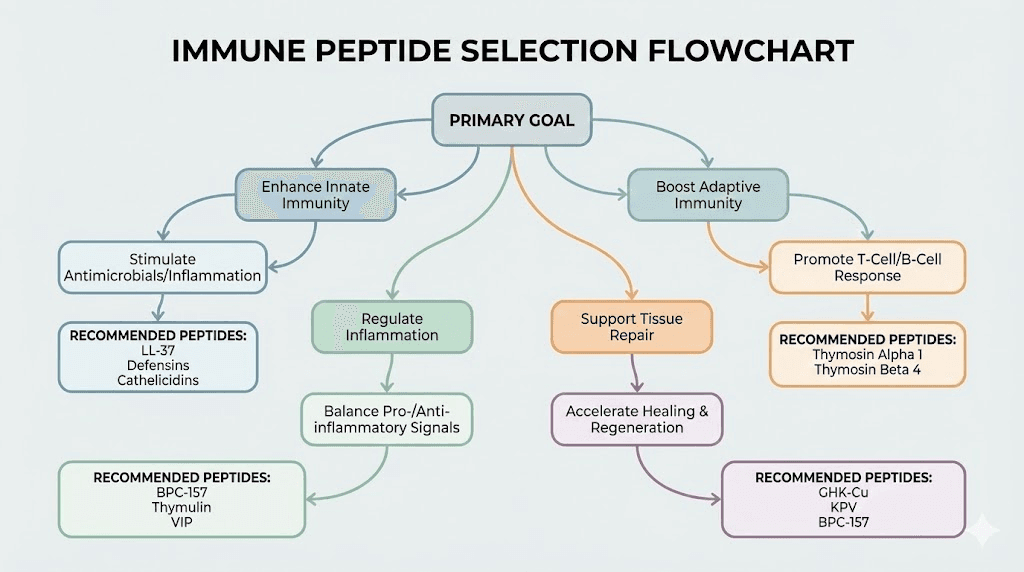
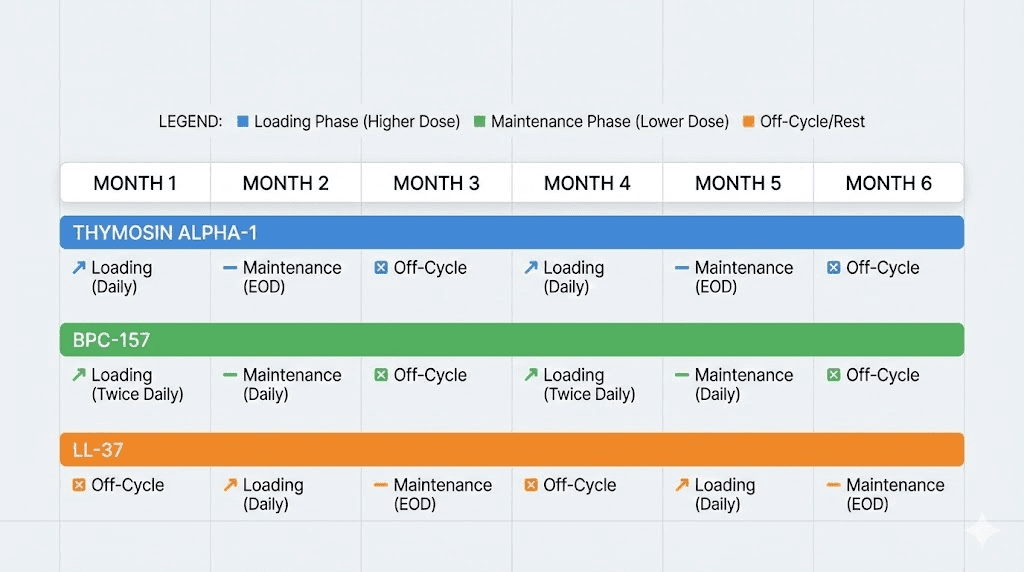
Thymosin Alpha-1 stands as the most extensively researched immune peptide with decades of clinical documentation across viral infections, immunodeficiency states, and adjunctive cancer therapy, while newer compounds like LL-37, Selank, and KPV offer different mechanisms ranging from direct antimicrobial activity to cytokine modulation to gut-immune axis optimization.
SeekPeptides provides personalized guidance for navigating these complex immunological decisions with evidence-based protocols tailored to individual situations.
Understanding immune system peptides
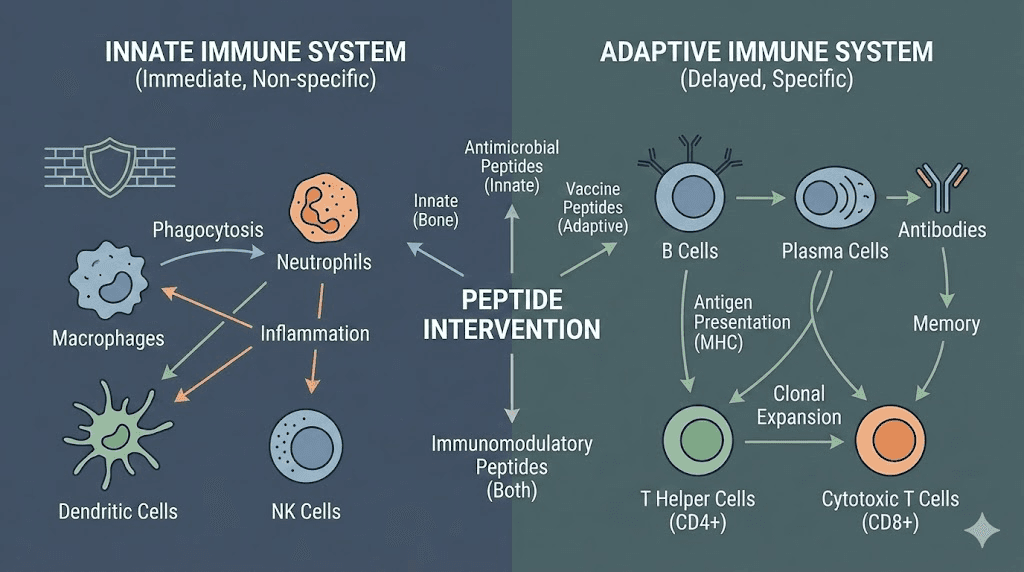
The immune system operates through two interconnected arms that must maintain careful balance. The innate immune system provides immediate, non-specific defense through physical barriers, inflammatory responses, and cells like neutrophils and macrophages that attack anything recognized as foreign. The adaptive immune system develops specific responses through T cells and B cells that learn to recognize particular pathogens and create immunological memory for faster future responses.
Peptides influence both arms through various mechanisms. Some peptides act directly as antimicrobial agents, physically disrupting bacterial membranes or interfering with viral replication. Others modulate immune cell activity, either enhancing function when immunity needs boosting or calming overactive responses in inflammatory or autoimmune conditions. The best immune peptides demonstrate this dual capacity, what researchers call immunomodulation rather than simple immunostimulation.
This distinction matters enormously for practical application. Pure immunostimulants can be dangerous in autoimmune conditions or when fighting infections that trigger excessive inflammatory responses. True immunomodulators help the immune system find appropriate balance, enhancing weak responses while tempering overactive ones. Most peptides covered in this guide demonstrate modulatory rather than purely stimulatory effects.
Understanding your specific immune goals determines which peptides make sense. Someone with frequent infections and poor immune response benefits from different peptides than someone managing autoimmune inflammation or recovering from immunosuppressive treatments. Getting started with peptides provides foundational context for newcomers to peptide research.
Thymosin Alpha-1: the gold standard immune peptide
Thymosin Alpha-1 represents the most extensively documented immune peptide with over three decades of research and clinical application across dozens of countries. Originally isolated from thymus tissue extracts, this 28-amino-acid peptide plays essential roles in T cell development, maturation, and function. The thymus gland produces Thymosin Alpha-1 naturally, though production declines significantly with age, contributing to the immunosenescence that makes older individuals more vulnerable to infections and cancers.
Mechanism of action
Thymosin Alpha-1 works through multiple immunological pathways that collectively enhance immune surveillance and response capacity. The peptide promotes differentiation of T cell precursors into mature, functional T cells capable of recognizing and responding to threats. It enhances dendritic cell function, improving antigen presentation so the immune system can better identify what requires attack. Thymosin Alpha-1 also modulates cytokine production, shifting the immune balance toward appropriate responses rather than simply amplifying all immune activity.
The toll-like receptor pathways represent key intervention points for Thymosin Alpha-1. These receptors serve as immune system sentinels, detecting pathogen-associated molecular patterns and initiating appropriate responses. By enhancing toll-like receptor signaling, Thymosin Alpha-1 improves the immune system's ability to detect and respond to viral, bacterial, and fungal threats.
Natural killer cell activity increases significantly with Thymosin Alpha-1 administration. These cells provide crucial defense against virus-infected cells and early-stage cancer cells that might otherwise escape immune detection. The enhancement of NK cell function contributes substantially to Thymosin Alpha-1's antiviral and anticancer properties.
Clinical evidence and applications
Thymosin Alpha-1 holds regulatory approval in over 35 countries for various indications including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and as adjunctive therapy for certain cancers. This regulatory status reflects substantial clinical evidence beyond typical peptide research compounds.
Chronic hepatitis B: Multiple clinical trials demonstrate Thymosin Alpha-1 enhances sustained viral suppression rates when combined with interferon or nucleoside analogs. The peptide helps the immune system recognize and clear hepatitis B infected cells that might otherwise persist indefinitely.
Hepatitis C: Before direct-acting antivirals revolutionized hepatitis C treatment, Thymosin Alpha-1 combined with interferon showed improved sustained virologic response rates compared to interferon alone. While less relevant now that curative oral medications exist, this research established Thymosin Alpha-1's antiviral immune enhancement credibly.
Cancer immunotherapy: Thymosin Alpha-1 demonstrates synergy with various cancer treatments including chemotherapy, radiation, and checkpoint inhibitors. The peptide helps restore immune function suppressed by cancer itself and by immunosuppressive treatments. Some oncologists use Thymosin Alpha-1 to help patients tolerate more aggressive treatment regimens with fewer infectious complications.
Vaccine enhancement: Thymosin Alpha-1 improves vaccine responses, particularly in elderly or immunocompromised individuals who typically respond poorly to vaccination. This adjuvant effect holds particular relevance for influenza vaccines and other immunizations where adequate response proves challenging in vulnerable populations.
Dosing protocols for Thymosin Alpha-1
Standard immune enhancement protocol:
1.6mg subcutaneously two to three times weekly for 12-16 weeks provides typical immune optimization. Some researchers use higher frequency during acute immune challenges, then reduce to maintenance dosing. The peptide calculator helps determine appropriate dosing adjustments based on individual factors.
Acute infection support:
1.6mg daily for 5-7 days during active infections, then returning to two to three times weekly. Higher frequency addresses acute immune demands while avoiding long-term daily dosing that might reduce receptor sensitivity.
Post-treatment immune recovery:
Following chemotherapy, surgery, or other immunosuppressive events, 1.6mg three times weekly for 4-8 weeks helps restore immune function. Timing typically begins once acute treatment recovery allows.
Response monitoring includes tracking infection frequency, duration when infections occur, inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein, and lymphocyte subset analysis when available. Most users report reduced infection susceptibility within 4-8 weeks of consistent administration.
LL-37: the antimicrobial defender
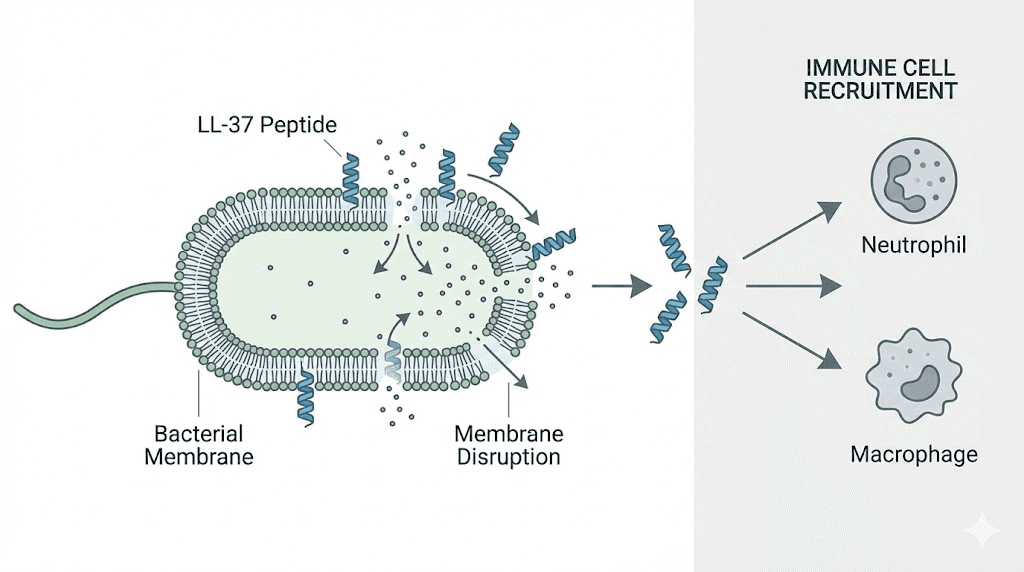
LL-37 belongs to the cathelicidin family of antimicrobial peptides, representing one of the few human-derived peptides with direct pathogen-killing activity. Unlike immunomodulatory peptides that enhance immune cell function, LL-37 directly attacks bacteria, fungi, and enveloped viruses through membrane disruption and other mechanisms. This dual role as both antimicrobial agent and immune modulator makes LL-37 unique among research peptides.
Direct antimicrobial mechanisms
LL-37's antimicrobial activity stems primarily from its cationic, amphipathic structure. The positively charged peptide interacts with negatively charged bacterial membranes, inserting itself and creating pores that disrupt membrane integrity. Bacteria cannot easily develop resistance to this mechanism since it targets fundamental membrane properties rather than specific enzymes or metabolic pathways.
The peptide demonstrates activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, including antibiotic-resistant strains like MRSA and certain Pseudomonas species. This broad-spectrum activity makes LL-37 potentially valuable as antibiotic resistance continues growing globally.
Antiviral activity extends to enveloped viruses including influenza, herpes simplex, and HIV. LL-37 disrupts viral envelopes similarly to bacterial membranes, preventing viral entry into host cells. This mechanism differs from most antiviral drugs that target specific viral enzymes.
Antifungal effects target Candida and other pathogenic fungi through similar membrane-disrupting mechanisms. Biofilm disruption represents another valuable property, as LL-37 can penetrate and help break down bacterial biofilms that otherwise resist both immune attack and antibiotic treatment.
Immunomodulatory effects
Beyond direct antimicrobial activity, LL-37 significantly influences immune cell behavior. The peptide recruits immune cells to infection sites through chemotactic effects, essentially calling in reinforcements when needed. It modulates inflammatory responses, initially promoting appropriate inflammation to fight infection, then helping resolve inflammation once the threat passes.
Wound healing acceleration occurs through LL-37's effects on epithelial cell migration and angiogenesis. The peptide supports tissue repair alongside its infection-fighting properties, making it particularly relevant for infected wounds or surgical sites at risk for infection.
Vitamin D status significantly affects natural LL-37 production. Vitamin D receptor activation upregulates cathelicidin expression, explaining part of why vitamin D deficiency correlates with increased infection susceptibility. Supplemental LL-37 can compensate for insufficient endogenous production in vitamin D deficient individuals.
LL-37 applications and protocols
Recurring infections:
Individuals experiencing frequent bacterial or viral infections may benefit from LL-37's direct antimicrobial and immune-enhancing effects. Typical protocols involve 50-100mcg subcutaneously daily during acute infections, then two to three times weekly for prevention.
Wound healing:
Local application or subcutaneous injection near wound sites can accelerate healing while preventing infection. This application parallels natural LL-37 release at wound sites. Learn more about healing peptides in the fast injury healing guide.
Biofilm-associated conditions:
Chronic infections involving biofilms, including certain sinus infections, prostatitis, and chronic UTIs, may respond to LL-37's biofilm-disrupting properties. These applications remain investigational but show promise for conditions that resist conventional antibiotic treatment.
Combination with BPC-157 addresses both antimicrobial needs and tissue healing, representing a comprehensive approach to infected tissue recovery.
Selank: immune modulation meets anxiolysis
Selank represents a synthetic peptide derived from the naturally occurring immunomodulatory peptide tuftsin, modified for enhanced stability and additional neurological effects. Russian researchers developed Selank specifically to combine immune enhancement with anxiolytic and nootropic properties, creating a compound that addresses the well-documented connection between stress, anxiety, and immune dysfunction.
Dual mechanism profile
The immune effects of Selank center on modulating cytokine expression and immune cell activity. The peptide influences interleukin production, shifting the immune balance in ways that enhance appropriate responses while dampening excessive inflammation. T cell and B cell function improves under Selank administration, strengthening both cellular and humoral immune responses.
Simultaneously, Selank modulates GABA, serotonin, and dopamine systems in the brain, producing anxiolytic effects without sedation or cognitive impairment. This makes Selank particularly valuable when stress and anxiety contribute to immune dysfunction, addressing both the psychological stressor and its physiological consequences.
The stress-immune connection warrants emphasis. Chronic stress and anxiety demonstrably suppress immune function through elevated cortisol and altered cytokine profiles. By reducing anxiety and stress responses, Selank indirectly supports immune function even beyond its direct immunomodulatory effects. The peptides for anxiety complete guide covers Selank's anxiolytic mechanisms in greater detail.
Research evidence
Russian clinical research, where Selank holds regulatory approval for anxiety disorders, provides the most substantial evidence base. Studies demonstrate improved immune parameters alongside psychological benefits in patients using Selank for anxiety treatment.
Immunological studies show enhanced phagocytic activity of neutrophils and macrophages, improved antibody production, and modulated cytokine responses that favor appropriate immune activation. These effects appear without the overstimulation risks associated with pure immunostimulants.
Neurological benefits include improved memory and cognitive function, reduced anxiety without sedation, and enhanced stress resilience. For individuals whose immune dysfunction connects to chronic stress, these cognitive and emotional benefits may prove as important as direct immune effects.
Selank dosing protocols
Intranasal administration:
200-400mcg per nostril, two to three times daily represents standard dosing. Intranasal delivery provides rapid absorption and direct access to CNS effects while also delivering systemic immune benefits. The nasal spray peptides guide covers proper intranasal technique.
Subcutaneous injection:
250-500mcg daily or every other day provides consistent systemic levels for immune modulation. Some researchers prefer injection for more reliable dosing compared to nasal spray variability.
Cycling considerations:
Most protocols recommend 2-4 week cycles followed by equal break periods. This prevents potential receptor desensitization and maintains effectiveness for long-term use. Some users run Selank continuously at lower doses without apparent tolerance issues, though evidence for this approach remains limited.
KPV: the anti-inflammatory tripeptide
KPV represents the C-terminal tripeptide fragment of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone, concentrated down to just three amino acids, lysine-proline-valine, that retain significant anti-inflammatory activity without the melanogenic effects of the full hormone. This makes KPV particularly relevant for inflammatory conditions where immune calming rather than stimulation serves the goal.
Mechanism and inflammation control
KPV exerts anti-inflammatory effects through multiple pathways. The peptide inhibits NF-kappaB activation, one of the master switches controlling inflammatory gene expression. By reducing NF-kappaB activity, KPV decreases production of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-alpha, IL-1, and IL-6.
The melanocortin system represents KPV's primary target, specifically the MC1R receptor expressed on immune cells and epithelial tissues. Activation of this receptor initiates anti-inflammatory signaling cascades that resolve rather than perpetuate inflammatory responses.
Gut-specific effects make KPV particularly valuable for intestinal inflammation. The peptide demonstrates protective effects against colitis in animal models, reducing inflammatory infiltration and tissue damage. This gut-immune axis modulation connects to broader systemic immune effects given the intestine's role as the body's largest immune organ. The peptides for gut health page covers intestinal peptide applications comprehensively.
Applications for KPV
Inflammatory bowel conditions:
The most compelling evidence for KPV involves intestinal inflammation. Oral administration delivers the peptide directly to gut tissue where it can exert local anti-inflammatory effects. Doses of 200-500mcg orally, one to two times daily, represent typical protocols for gut-focused applications.
Systemic inflammation:
For broader anti-inflammatory effects, subcutaneous administration at 200-500mcg daily provides systemic delivery. This approach suits conditions involving generalized inflammation rather than specifically gut-localized issues.
Autoimmune support:
KPV's anti-inflammatory mechanisms may benefit certain autoimmune conditions where excessive inflammation drives tissue damage. However, autoimmune applications require careful consideration and ideally professional guidance given the complexity of immune dysregulation in these conditions.
The KPV peptide benefits article provides additional mechanism details, and the KPV peptide dosage guide covers administration specifics.
BPC-157: indirect immune support through healing
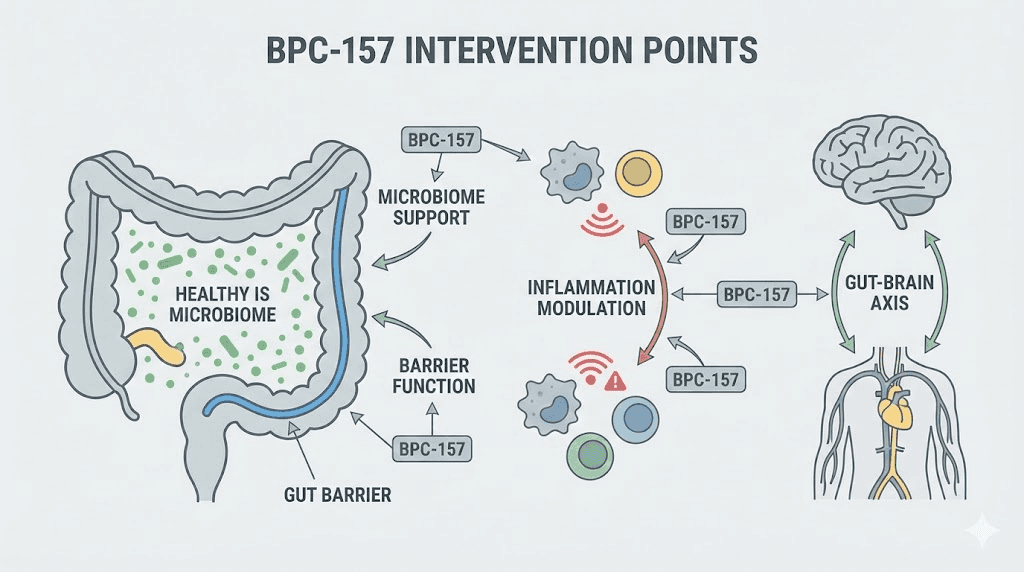
While not primarily classified as an immune peptide, BPC-157 significantly influences immune function through its tissue-healing and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. The peptide's effects on gut health, blood vessel formation, and inflammatory modulation create an environment conducive to optimal immune function even though BPC-157 doesn't directly target immune cells.
Gut-immune connection
The gastrointestinal tract contains approximately 70% of the body's immune cells and serves as a primary interface between external environment and internal systems. BPC-157's profound gut-protective and gut-healing effects support immune function by maintaining intestinal barrier integrity and healthy gut immune tissue.
Leaky gut, where intestinal permeability allows inappropriate immune activation against food particles and gut bacteria, contributes to both local and systemic inflammation. BPC-157 tightens intestinal junctions and heals damaged gut epithelium, reducing the antigenic load that drives chronic immune activation.
Gut microbiome health also influences immune function substantially. By supporting healthy gut tissue and reducing inflammation, BPC-157 creates conditions favorable for beneficial bacterial populations that themselves support immune balance.
Anti-inflammatory mechanisms
BPC-157 modulates inflammatory pathways including nitric oxide systems that influence immune cell activity. The peptide promotes resolution of inflammation rather than simply suppressing it, allowing appropriate immune responses while preventing chronic inflammatory states that exhaust immune resources.
Tissue healing accelerated by BPC-157 reduces the inflammatory burden associated with ongoing tissue damage. Faster healing means less time for immune resources to focus on repair rather than defense against pathogens.
Integration with immune protocols
BPC-157 combines effectively with primary immune peptides. Adding BPC-157 to Thymosin Alpha-1 or LL-37 protocols addresses the foundational gut health that supports optimal immune function. Standard BPC-157 dosing of 250-500mcg twice daily integrates smoothly with immune-focused protocols.
The BPC-157 vs TB-500 comparison helps determine which healing peptide best suits specific situations, though both offer indirect immune benefits through tissue healing.
TB-500: systemic healing with immune benefits
TB-500, the synthetic version of Thymosin Beta-4, offers immune relevance through its healing and anti-inflammatory effects. While related to Thymosin Alpha-1 in origin (both derive from thymus tissue research), TB-500 works through different mechanisms focusing on cell migration, tissue repair, and inflammation modulation rather than direct T cell enhancement.
Immune-relevant mechanisms
TB-500 promotes actin polymerization and cell migration, enabling immune cells to reach infection or injury sites more effectively. Macrophages and other immune cells require motility to survey tissues and respond to threats. Enhanced migration capacity improves immune surveillance throughout the body.
Anti-inflammatory effects reduce the tissue damage caused by excessive inflammation while still allowing appropriate immune responses. This anti-inflammatory activity helps prevent the collateral damage that occurs when inflammation persists beyond its useful purpose.
Tissue regeneration supported by TB-500 maintains the physical barriers (skin, mucous membranes, gut lining) that represent the first line of immune defense. Intact barriers prevent pathogen entry more effectively than any internal immune mechanism.
TB-500 for immune support
TB-500 serves best as a supportive rather than primary immune peptide. Its value lies in maintaining tissue integrity, reducing inflammatory burden, and supporting immune cell function rather than directly enhancing immune parameters.
Standard TB-500 dosing of 2-2.5mg twice weekly during loading phases, then 2mg weekly for maintenance, integrates with immune protocols without timing conflicts. The TB-500 benefits article covers broader applications beyond immune support.
Semax: neuroprotection with immune modulation
Semax, a synthetic analog of ACTH (4-10), primarily serves nootropic and neuroprotective purposes but demonstrates meaningful immune-modulating effects that warrant inclusion in immune peptide discussions. Like Selank, Semax addresses the brain-immune connection, though through different mechanisms.
Immune effects of Semax
Semax influences gene expression related to immune function, particularly genes involved in inflammation and immune cell development. Research shows altered expression of multiple immune-related genes following Semax administration, suggesting broad immunomodulatory capacity.
Anti-inflammatory effects through reduced IL-6 and TNF-alpha expression provide immune support similar to other anti-inflammatory peptides. This inflammation reduction benefits both brain health (Semax's primary application) and systemic immune balance.
Stress response modulation through Semax's effects on the HPA axis indirectly supports immune function. Like Selank, Semax helps maintain appropriate stress responses that don't chronically suppress immunity.
Semax applications
Semax suits situations where cognitive enhancement, neuroprotection, and immune modulation all serve beneficial purposes. The peptide works well for individuals experiencing stress-related cognitive decline alongside immune dysfunction.
Dosing typically involves 200-600mcg intranasally, one to three times daily. The Semax peptide dosage guide provides comprehensive administration information.
Thymalin: thymus extract peptide
Thymalin consists of peptide fractions extracted from bovine thymus tissue, representing a more complex preparation than single-peptide compounds like Thymosin Alpha-1. This mixture contains multiple thymic peptides that collectively support thymus function and T cell development.
Mechanism and effects
Thymalin works by providing thymic peptides that support T cell maturation and function. The thymus gland involutes (shrinks and becomes less functional) with age, reducing natural production of these peptides. Supplemental thymic peptides may partially compensate for this age-related decline.
Effects include enhanced T cell counts, improved T cell subset ratios (helper vs suppressor cells), increased thymic hormone levels, and better vaccine responses. These effects prove most pronounced in older individuals with demonstrable thymic insufficiency.
Clinical applications
Thymalin has been used clinically in Eastern Europe and Russia for immune enhancement in various conditions including post-surgical recovery, chronic infections, and cancer adjunctive therapy. The evidence base, while substantial in Russian literature, remains less accessible to Western researchers.
Dosing typically involves 5-10mg intramuscularly daily for 5-10 days, then maintenance dosing monthly or as needed. Cycling prevents continuous thymic stimulation that might reduce effectiveness.
Comparison: immune peptide selection guide
Different immune goals require different peptide selections. This comparison helps match peptides to specific situations.
Peptide | Primary Mechanism | Best For | Evidence Quality | Administration | Cost Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Thymosin Alpha-1 | T cell enhancement | General immune support, viral infections | Extensive clinical | Subcutaneous | High |
LL-37 | Direct antimicrobial | Bacterial/viral infections, biofilms | Strong preclinical | Subcutaneous/local | Medium |
Selank | Immunomodulation + anxiolysis | Stress-related immune dysfunction | Clinical (Russia) | Intranasal/SC | Low-Medium |
KPV | Anti-inflammatory | Gut inflammation, autoimmune support | Moderate preclinical | Oral/SC | Medium |
BPC-157 | Gut healing, anti-inflammatory | Gut-immune dysfunction | Strong preclinical | Oral/SC | Low |
TB-500 | Tissue healing | Barrier maintenance, inflammation | Moderate preclinical | Subcutaneous | Medium |
Semax | Neuro + immune modulation | Cognitive + immune goals | Clinical (Russia) | Intranasal | Low-Medium |
Thymalin | Thymic support | Age-related immune decline | Clinical (Russia/EU) | Intramuscular | Medium |
Evidence quality ratings consider both quantity and accessibility of research. "Clinical" indicates human trials exist, while "preclinical" indicates primarily animal and in vitro research.
Immune peptide protocols by situation
Specific immune situations benefit from tailored peptide combinations and dosing strategies.
Protocol 1: general immune optimization (preventive)
Goal: Enhance overall immune function in generally healthy individuals
Primary peptide: Thymosin Alpha-1 1.6mg subcutaneously twice weekly
Supporting peptide: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily for gut-immune support
Optional addition: Selank 200mcg intranasal daily if stress affects immunity
Duration: 12-16 weeks initial optimization, then maintenance dosing as needed
Expected outcomes:
Weeks 1-4: Subtle improvements in energy and recovery
Weeks 4-8: Reduced frequency of minor infections
Weeks 8-16: Improved overall resilience, better vaccine responses if applicable
Cost estimate: $300-500/month depending on Thymosin Alpha-1 source
Protocol 2: acute infection support
Goal: Support immune response during active viral or bacterial infection
Primary peptide: Thymosin Alpha-1 1.6mg daily for 5-7 days, then twice weekly
Secondary peptide: LL-37 100mcg daily during active infection for antimicrobial support
Supporting peptide: BPC-157 500mcg twice daily for tissue protection and healing
Duration: Acute phase (daily dosing) 5-10 days, then transitioning to maintenance
Considerations: Begin at first sign of infection for best results. Not a replacement for necessary medical care with serious infections.
Cost estimate: Higher during acute phase due to daily dosing, approximately $100-200/week
Protocol 3: post-illness immune recovery
Goal: Restore immune function following significant illness, surgery, or immunosuppressive treatment
Primary peptide: Thymosin Alpha-1 1.6mg three times weekly for 8-12 weeks
Healing support: TB-500 2.5mg twice weekly for 4 weeks, then weekly
Gut restoration: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily throughout protocol
Duration: 8-12 weeks active recovery, longer if starting from significant immunocompromise
Monitoring: Consider bloodwork including CBC with differential and inflammatory markers at baseline and every 4 weeks
Cost estimate: $400-600/month during active recovery phase
Protocol 4: autoimmune support
Goal: Modulate immune function to reduce autoimmune inflammation without further immunosuppression
Primary peptide: KPV 300-500mcg daily, oral for gut-focused or SC for systemic
Supporting peptide: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily for anti-inflammatory support
Stress modulation: Selank 200-400mcg intranasal daily if anxiety present
Caution: Avoid strong immunostimulants like Thymosin Alpha-1 in autoimmune conditions unless under professional guidance. The goal is modulation, not stimulation.
Duration: 8-12 weeks minimum, often longer for chronic conditions
Cost estimate: $200-400/month
Protocol 5: aging immune support (immunosenescence)
Goal: Address age-related immune decline in individuals over 50
Primary peptide: Thymosin Alpha-1 1.6mg twice weekly ongoing
Thymic support: Thymalin 10mg IM for 10 days, repeat every 3-6 months
Cellular support: GHK-Cu for tissue maintenance, see GHK-Cu dosage guide
Gut health: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily
Duration: Ongoing with periodic Thymalin cycles
Additional support: Consider Epithalon for telomere support as part of comprehensive anti-aging approach. See peptides for anti-aging for complete longevity protocols.
Cost estimate: $400-700/month during active phases
Safety considerations for immune peptides
Immune system modulation requires careful consideration of individual circumstances. What benefits one person may harm another depending on their specific immune status.
Contraindications and cautions
Organ transplant recipients: Immunostimulating peptides like Thymosin Alpha-1 could theoretically increase rejection risk by enhancing immune function against the transplanted organ. Transplant recipients should avoid immune peptides without explicit approval from their transplant team.
Active autoimmune flares: During active autoimmune attacks, adding immune stimulation can worsen symptoms. Anti-inflammatory peptides like KPV may help, but immunostimulants should be avoided during flare periods.
Cancer treatment considerations: Some cancers benefit from enhanced immunity (immunotherapy-responsive tumors), while others might theoretically progress with immune enhancement. Cancer patients should work with oncologists familiar with immune peptides before use.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Insufficient safety data exists for most immune peptides during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Avoid unless specifically cleared by healthcare providers.
Monitoring recommendations
Regular blood work helps track immune peptide effects and safety. Consider baseline and periodic testing of:
Complete blood count with differential to monitor white blood cell populations
Comprehensive metabolic panel for organ function
Inflammatory markers (CRP, ESR) to track inflammation changes
Lymphocyte subsets (CD4/CD8 ratio, NK cells) when available for detailed immune assessment
Thyroid function, as some immune modulation can affect thyroid activity
The peptide safety and risks guide covers general peptide safety principles.
Interaction considerations
Immune peptides can interact with immunosuppressive medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Those on immunosuppressants (prednisone, methotrexate, biologics, etc.) should coordinate peptide use with prescribers.
Vaccine timing may matter. Enhancing immune function around vaccination could improve responses, but timing immune peptides with live vaccines requires careful consideration.
Concurrent infection treatment should continue, peptides support but don't replace antibiotics or antivirals when medically indicated.
Sourcing and quality for immune peptides
Immune peptide quality matters enormously given the critical nature of immune function. Contaminated, underdosed, or mislabeled products carry significant risks when the goal is immune health.
Quality indicators
Third-party testing: Reputable vendors provide certificates of analysis from independent laboratories showing purity, identity, and absence of contamination. Learn to read peptide testing results for quality verification.
Proper storage: Immune peptides require proper cold chain handling. Vendors should ship with cold packs and clearly indicate storage requirements. The peptide storage guide covers proper handling practices.
Reconstitution requirements: Most immune peptides require reconstitution with bacteriostatic water. Use the peptide reconstitution calculator for proper preparation. The bacteriostatic water guide covers appropriate diluents.
Vendor considerations
The best peptide vendors guide evaluates sources for research peptides. For immune peptides specifically, consider vendors with demonstrated experience in these compounds and transparent quality documentation.
Pharmaceutical-grade Thymosin Alpha-1 (Zadaxin) exists in countries where it holds approval, representing the gold standard for this peptide. Research-grade alternatives vary in quality depending on source.
Combining immune peptides with other protocols
Immune peptides integrate with other peptide protocols for comprehensive health optimization.
With healing peptides
The BPC-157 and TB-500 stack complements primary immune peptides by maintaining tissue integrity and reducing inflammatory burden. This combination addresses both direct immune enhancement and the foundational tissue health that supports immune function.
With growth hormone peptides
Growth hormone influences immune function, and GH-releasing peptides like CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin may provide indirect immune support through improved tissue repair and reduced inflammation. The peptide stack calculator helps plan multi-peptide protocols.
With anti-aging protocols
Immune function declines with age, making immune peptides natural components of comprehensive anti-aging strategies. Combining Thymosin Alpha-1 with anti-aging peptides like Epithalon and GHK-Cu addresses multiple aging mechanisms simultaneously.
Timing and scheduling
Most immune peptides don't have strict timing requirements like growth hormone peptides. They can be administered at convenient times without food timing concerns. When combining with GH peptides that require fasted administration, immune peptides can be given at different times without conflict.
The peptide stacking guide covers general principles for combining multiple compounds.
Lifestyle factors affecting immune peptide effectiveness
Peptides work within the context of overall health practices. Optimizing lifestyle factors enhances immune peptide results.
Sleep and immune function
Sleep deprivation severely impairs immune function regardless of peptide use. Adequate, quality sleep supports T cell function, cytokine production, and immune memory formation. Immune peptides cannot fully compensate for chronic sleep deficiency.
Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep when running immune protocols. Some immune peptides, particularly those with neurological effects like Selank and Semax, may improve sleep quality as an additional benefit.
Stress management
Chronic stress elevates cortisol and shifts immune function toward inflammatory and away from adaptive responses. Stress management practices, meditation, exercise, social connection, and adequate rest, support immune peptide effectiveness.
Peptides like Selank directly address the stress-immune connection, but external stress management remains important regardless of peptide protocol.
Nutrition for immune support
Adequate protein provides amino acid building blocks for immune cell production and peptide utilization. Micronutrients including vitamin D, zinc, vitamin C, and selenium support various immune functions.
Gut health through fiber, fermented foods, and avoidance of inflammatory triggers supports the gut-immune axis that BPC-157 and KPV help optimize.
Exercise considerations
Moderate exercise enhances immune function while excessive exercise can temporarily suppress immunity. Balance training intensity when running immune protocols, avoiding overtraining that would counteract peptide benefits.
The peptides for athletic performance page covers balancing training stress with recovery optimization.
Frequently asked questions
Can immune peptides cure autoimmune conditions?
No peptide cures autoimmune conditions. Immune-modulating peptides may help manage symptoms and reduce inflammatory burden, but autoimmune conditions require comprehensive management strategies. Peptides like KPV and BPC-157 offer supportive anti-inflammatory effects rather than curative treatment.
How long before immune peptides show effects?
Most users notice subtle effects within 2-4 weeks, with more substantial improvements developing over 8-12 weeks. Acute infection support may show faster effects during active illness. Long-term immune optimization requires consistent use over months rather than weeks.
Can I use immune peptides while taking prescription medications?
This depends on the specific medications involved. Immunosuppressive drugs may interact with immunostimulating peptides. Always discuss peptide use with prescribing physicians, particularly for immunosuppressants, chemotherapy agents, or biologics.
Are immune peptides safe for elderly individuals?
Immune peptides, particularly Thymosin Alpha-1 and Thymalin, show particular benefit for age-related immune decline. However, elderly individuals often have multiple health conditions and medications that warrant careful evaluation. Start with conservative doses and monitor closely.
How do immune peptides compare to supplements like vitamin D or zinc?
Immune peptides work through different mechanisms than nutritional supplements. They are not replacements for adequate vitamin D, zinc, or other nutrients essential for immune function. Optimal results come from combining peptides with adequate nutrition rather than using peptides to compensate for deficiencies.
Can immune peptides prevent COVID-19 or other viral infections?
No peptide has been proven to prevent specific viral infections. Enhanced immune function may improve general resistance to infections and potentially reduce severity when infections occur, but this doesn't constitute prevention. Vaccines remain the proven approach for specific viral prevention.
How SeekPeptides supports immune optimization
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for navigating immune peptide research with confidence and clarity.
Personalized protocol guidance helps match immune goals with appropriate peptide selections. The complex landscape of immune peptides benefits from structured approaches tailored to individual situations.
Educational resources including peptide research guides and mechanism explanations build understanding necessary for informed decisions.
Dosing tools including the peptide calculator, reconstitution calculator, and cost calculator support practical implementation.
SeekPeptides remains committed to evidence-based guidance for immune optimization through peptide research.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your immune system stay balanced, your infections stay rare, and your recovery stay swift. Join SeekPeptides for personalized immune optimization guidance and evidence-based peptide protocols.