Jan 7, 2026

Peptide stacking represents one of the most frequently misunderstood aspects of peptide research, with newcomers often defaulting to either extreme caution, running single peptides in isolation, or dangerous overconfidence, combining five or six compounds without understanding receptor competition, timing conflicts, or synergistic amplification risks.
Most experienced researchers successfully run two to four peptides simultaneously, though the optimal number varies based on which peptides you choose, whether they compete for similar receptors, how their timing windows align, and what physiological systems you want to target.
This small guide covers everything from basic stacking principles to advanced multi-peptide protocols, receptor competition science, timing optimization strategies, safety monitoring requirements, and specific combination recommendations for different goals including fat loss, muscle growth, injury healing, anti-aging, and athletic performance. SeekPeptides provides personalized protocol guidance to help navigate these complex decisions with confidence.
The direct answer: how many peptides at once
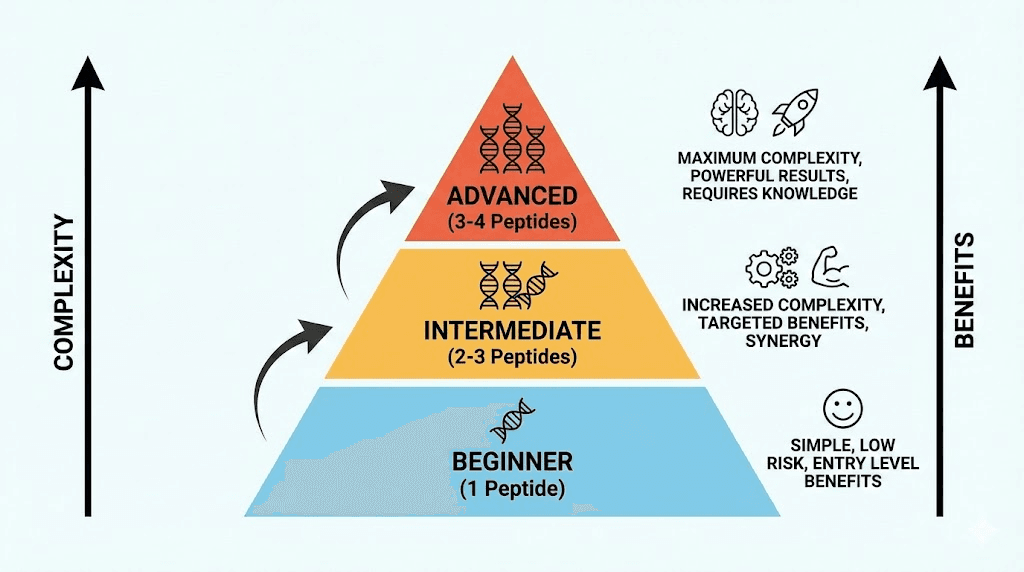
Before diving into the science, here is the straightforward answer most researchers need. Two to three peptides represents the optimal range for most people. This allows targeting multiple physiological pathways without creating unmanageable complexity or overwhelming receptor systems.
Beginners should start with a single peptide. Learn how your body responds before adding complexity. One peptide for four to eight weeks gives you baseline data about your individual response patterns, potential side effects, and effective dosing ranges.
Intermediate researchers typically run two to three peptides targeting complementary goals. A BPC-157 and TB-500 healing stack represents the classic example, two peptides working through different mechanisms to accelerate tissue repair. Similarly, combining a growth hormone secretagogue like CJC-1295 with Ipamorelin creates synergistic GH release without receptor competition.
Advanced users sometimes run four peptides, occasionally five, but more rarely produces better results. Beyond four peptides, complexity increases exponentially while marginal benefits diminish. You also face practical challenges: more injections, more reconstitution, more timing coordination, more variables making it difficult to identify what is actually working.
Understanding peptide receptor competition
The primary factor limiting how many peptides you can take simultaneously involves receptor competition. Peptides work by binding to specific cellular receptors, triggering downstream signaling cascades. When two peptides compete for the same receptor, they do not produce additive effects. Instead, they compete for binding sites, potentially reducing the effectiveness of both.
Growth hormone secretagogues and receptor types
Growth hormone releasing peptides illustrate receptor competition clearly. GHRPs like GHRP-2 and GHRP-6 bind to ghrelin receptors (GHS-R1a) in the pituitary gland. Running two different GHRPs simultaneously means both compounds compete for the same ghrelin receptors. You do not get double the growth hormone release. You get receptor competition that may actually reduce overall effectiveness.
However, combining a GHRP with a GHRH analog like CJC-1295 produces genuine synergy because they work through different receptor systems. CJC-1295 binds to GHRH receptors while Ipamorelin binds to ghrelin receptors. Together, they amplify GH release beyond what either achieves alone. This represents intelligent stacking, using compounds that complement rather than compete.
Understanding which receptors your chosen peptides target helps determine safe combinations. The peptide stack calculator can help identify potential receptor conflicts before you begin.
Healing peptides and tissue specificity
BPC-157 and TB-500 represent the gold standard healing combination precisely because they work through distinct mechanisms. BPC-157 acts primarily through local tissue effects, upregulating growth factors at injury sites, modulating nitric oxide systems, and protecting against NSAID-induced damage. TB-500 works systemically, promoting cell migration, reducing inflammation throughout the body, and supporting tissue remodeling.
These peptides enhance each other without competition. BPC-157 provides targeted local healing while TB-500 creates a systemic pro-healing environment. Researchers consistently report faster recovery with the combination than either peptide alone. Learn more about peptides for bone and cartilage repair for specific healing applications.
GLP-1 agonists and metabolic receptors
Semaglutide and tirzepatide both act on GLP-1 receptors, though tirzepatide also activates GIP receptors. Running both simultaneously makes no pharmacological sense. You would have two compounds competing for GLP-1 binding sites while potentially amplifying side effects like nausea beyond tolerable levels.
If using a GLP-1 agonist for fat loss, choose one compound rather than stacking multiple GLP-1 agonists. The cagrilintide and semaglutide combination represents an exception, as cagrilintide targets amylin receptors rather than GLP-1, creating complementary appetite suppression through different pathways.
Timing windows and administration scheduling
Beyond receptor competition, practical timing constraints affect how many peptides you can realistically manage. Different peptides have different optimal administration times, and some timing requirements conflict with each other.
Fasted administration requirements
Growth hormone secretagogues require fasted administration for optimal effectiveness. Food, particularly carbohydrates and fats, blunts the GH response to these peptides. Most researchers administer GH peptides first thing in the morning before breakfast or before bed, at least two to three hours after eating.
This creates specific timing windows. If you want to run multiple GH-releasing peptides, they need to fit within the same fasted windows. Fortunately, you can combine CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin in the same injection since they work synergistically. The peptide reconstitution calculator helps determine proper mixing ratios.
Flexible timing peptides
Not all peptides require fasted administration. BPC-157 demonstrates stable effectiveness regardless of food intake. You can administer it with meals, between meals, or during fasted periods without significantly impacting results. This flexibility makes BPC-157 easy to incorporate into any multi-peptide protocol.
TB-500 similarly shows timing flexibility, though most researchers prefer consistent administration schedules for tracking purposes. Twice-weekly dosing works well for TB-500, fitting around other peptide schedules without conflict.
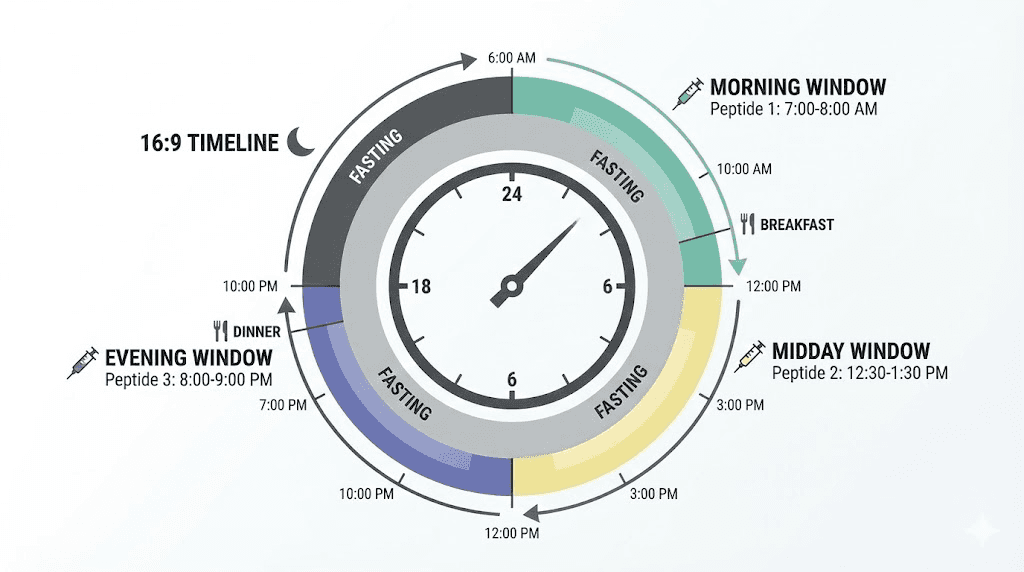
Sample multi-peptide timing schedule
A three-peptide healing and growth stack might follow this daily schedule:
Morning (fasted, immediately upon waking):
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin combined injection, 100mcg each. Wait 20-30 minutes before eating breakfast. BPC-157 250mcg at injury site or subcutaneously.
Evening (before bed, 2+ hours after dinner):
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin second dose (optional, 100mcg each). BPC-157 second dose, 250mcg.
Twice weekly (any time):
TB-500 2.5mg per injection, Monday and Thursday or similar spacing.
This schedule manages three peptides efficiently without timing conflicts. The peptide dosage calculator helps determine appropriate doses for your situation.
Peptide stacking by goal
Your research goals determine which peptides to combine. Different objectives require different combinations. Here are evidence-based stacks for common goals.
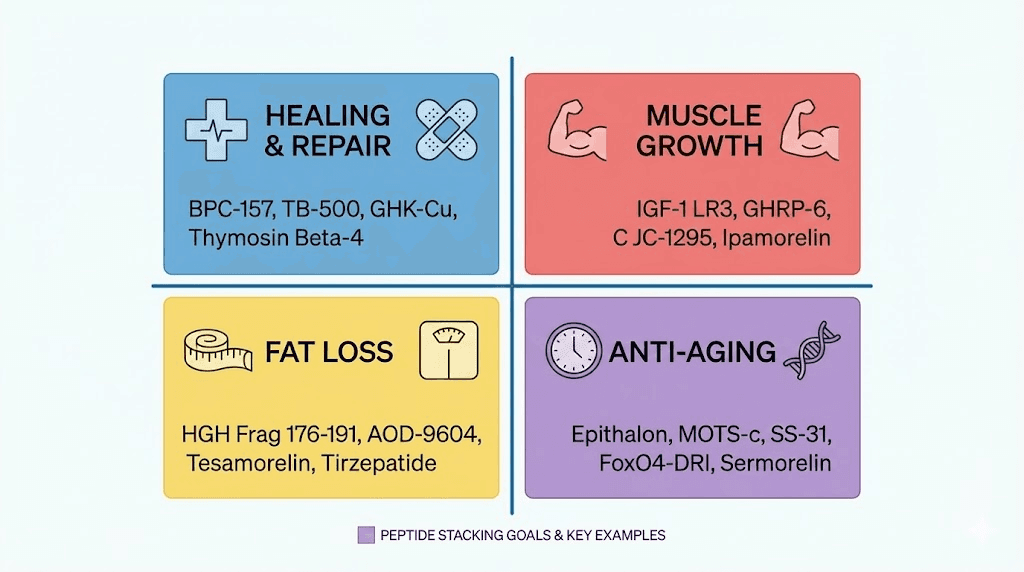
Protocol 1: injury healing and recovery (2 peptides)
Goal: Accelerate tissue repair, reduce recovery time from injuries or surgery
Peptides:
BPC-157: 250-500mcg twice daily, near injury site when possible
TB-500: 2-2.5mg twice weekly for loading, then 2mg weekly for maintenance
Why this works: BPC-157 provides localized healing acceleration through growth factor upregulation and angiogenesis at injury sites. TB-500 creates systemic healing support through enhanced cell migration and reduced inflammation. Together they address both local and systemic aspects of tissue repair.
Duration: 4-8 weeks depending on injury severity. Acute injuries may heal within 4 weeks. Chronic conditions or surgical recovery may require 8-12 weeks.
Expected timeline:
Week 1-2: Reduced inflammation and pain at injury site
Week 2-4: Accelerated tissue remodeling, improved range of motion
Week 4-8: Significant structural healing, return to normal function
Cost estimate: $150-300 per month depending on sources and dosing
Read more about fast injury healing protocols and peptide strength protocol benefits.
Protocol 2: growth hormone optimization (2-3 peptides)
Goal: Increase natural GH production for body composition, recovery, and anti-aging benefits
Peptides:
CJC-1295 DAC: 2mg weekly (or CJC-1295 no DAC 100mcg twice daily)
Ipamorelin: 100-200mcg twice daily, fasted
Optional third: MK-677 (not technically a peptide) 12.5-25mg daily
Why this works: CJC-1295 provides sustained GHRH activity, extending the duration of GH release. Ipamorelin triggers pulsatile GH secretion through ghrelin receptor activation. The combination produces more natural GH release patterns than either alone.
Duration: 12-16 weeks typical cycle, some researchers run continuously at lower doses
Expected timeline:
Week 1-4: Improved sleep quality, subtle recovery improvements
Week 4-8: Noticeable body composition changes, improved skin quality
Week 8-16: Significant lean mass improvement, fat reduction, enhanced recovery
Cost estimate: $200-400 per month
The safest peptides for muscle growth guide provides additional context.
Protocol 3: fat loss and body recomposition (2-3 peptides)
Goal: Maximize fat loss while preserving or building lean mass
Peptides:
Semaglutide: Start 0.25mg weekly, titrate to 1-2.4mg weekly over 8-16 weeks
BPC-157: 250mcg twice daily (protects gut health during GLP-1 use)
Optional third: Ipamorelin 100mcg twice daily (supports lean mass preservation)
Why this works: Semaglutide provides powerful appetite suppression and improved insulin sensitivity for fat loss. BPC-157 protects against GLP-1-induced gut motility issues and supports overall tissue health. Ipamorelin maintains GH levels to preserve muscle during caloric deficit.
Duration: 16-24 weeks for significant fat loss, can extend longer with medical supervision
Expected timeline:
Week 1-4: Appetite reduction, initial weight loss beginning
Week 4-12: Consistent fat loss of 1-2 pounds weekly
Week 12-24: Significant body composition transformation
Cost estimate: $300-600 per month depending on semaglutide source
See the peptides for weight loss guide for comprehensive information.
Protocol 4: anti-aging and longevity (3-4 peptides)
Goal: Comprehensive age-management targeting multiple systems
Peptides:
Epithalon: 5-10mg daily for 10-20 days, cycle 2-3 times yearly
GHK-Cu: 1-2mg daily or topically for skin and tissue support
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin: Standard GH-releasing protocol
Optional fourth: Pinealon for neurological support
Why this works: Epithalon extends telomeres and reactivates telomerase in somatic cells. GHK-Cu supports tissue regeneration, collagen synthesis, and wound healing. The GH-releasing combination maintains youthful hormone levels. Together they address multiple aging mechanisms.
Duration: Ongoing with cycling patterns, typically 10-20 day Epithalon bursts 2-3 times per year, other peptides continuous or cycled quarterly
Expected timeline:
Month 1-3: Improved skin quality, better sleep, enhanced recovery
Month 3-6: Visible anti-aging effects, improved energy and cognition
Month 6-12: Cumulative benefits across multiple systems
Cost estimate: $400-800 per month during active phases
The peptides for anti-aging page covers this topic extensively.
Peptide combination comparison table
This table compares common peptide stacks across key factors to help guide your selection:
Stack | Peptide Count | Complexity | Cost/Month | Best For | Experience Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BPC-157 + TB-500 | 2 | Low | $150-250 | Injury healing | Beginner |
CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin | 2 | Low | $150-300 | GH optimization | Beginner |
Semaglutide + BPC-157 | 2 | Medium | $300-500 | Fat loss | Intermediate |
Healing + GH Stack | 4 | Medium | $300-450 | Recovery + Growth | Intermediate |
Recomp Stack | 3 | Medium | $350-550 | Body recomposition | Intermediate |
Full Anti-Aging | 4 | High | $500-800 | Longevity | Advanced |
Performance Stack | 3-4 | High | $400-600 | Athletic performance | Advanced |
The complexity rating reflects not just the number of peptides but also timing requirements, potential interactions, and monitoring needs. Higher complexity stacks require more experience to manage effectively.
Safety considerations for multi-peptide protocols
Running multiple peptides simultaneously requires understanding both individual compound safety profiles and potential interaction risks. Most peptides have favorable safety profiles when used responsibly, but combinations introduce additional variables.
Side effect amplification
Some side effects amplify when multiple peptides affecting similar systems combine. Water retention represents a common example. Individual GH-releasing peptides cause mild water retention in some users. Combining multiple GH-active compounds can increase this effect significantly.
GLP-1 agonists cause gastrointestinal side effects including nausea, reduced appetite, and altered motility. Running multiple compounds affecting gut function simultaneously can amplify these effects beyond tolerable levels. This is why stacking semaglutide with tirzepatide makes no sense, you would likely experience severe GI distress without additional benefit.
The peptides legality guide covers regulatory considerations for researchers.
Blood sugar considerations
Growth hormone releasing peptides can affect blood sugar regulation. GH promotes insulin resistance as part of its fat-mobilizing effects. Running multiple GH-active compounds, especially alongside MK-677 which significantly elevates GH and IGF-1, requires monitoring blood glucose response.
Conversely, GLP-1 agonists improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar. Combining strong GH secretagogues with GLP-1 agonists creates opposing forces on glucose metabolism. This is not necessarily dangerous, but requires understanding that blood sugar effects may be unpredictable.
Cardiovascular monitoring
Several peptides affect blood pressure and heart rate. PT-141 can cause transient blood pressure changes and flushing. Some GH peptides affect fluid balance and blood pressure. Thymosin peptides rarely cause cardiovascular effects but remain a consideration.
If running multiple peptides with cardiovascular effects, baseline blood pressure monitoring becomes important. Track readings before starting and periodically during your protocol.
Injection site management
Practical safety includes injection site rotation. Multiple daily injections across several peptides means many subcutaneous injections weekly. Proper rotation prevents lipohypertrophy, local reactions, and injection site scarring.
Consider these injection site rotation strategies: alternate between left and right sides of the abdomen, include outer thighs and upper arms in rotation, keep injection sites at least one inch apart, and track injection locations to ensure proper rotation.
The peptide injections guide provides detailed administration techniques.
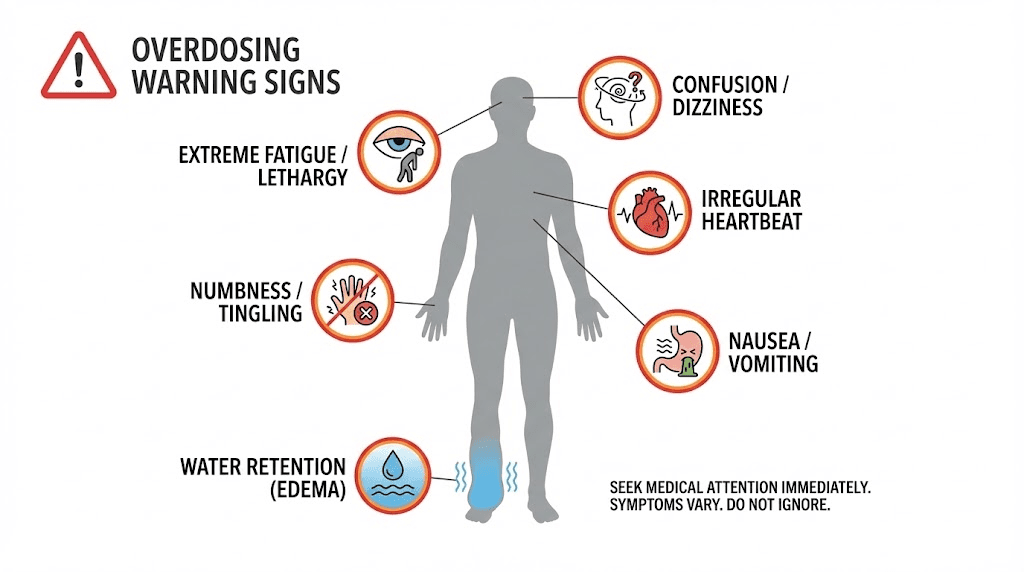
Signs you are running too many peptides
Your body provides signals when peptide protocols become excessive. Recognizing these signs helps optimize your approach.
Excessive water retention
Mild water retention represents a normal response to GH-active peptides. Excessive water retention, puffy face, swollen hands and feet, rapid weight gain that is clearly not fat or muscle, suggests you are pushing GH activity too high. This might mean too high doses, too many GH-active peptides, or individual hypersensitivity.
Response: Reduce doses or eliminate one GH-active compound. Consider whether you actually need multiple GH secretagogues.
Persistent fatigue or lethargy
Peptides should generally improve energy and recovery. If you feel persistently fatigued, especially during the day when you should feel alert, something may be off. This can indicate blood sugar dysregulation, excessive GH affecting sleep architecture, or simply too many compounds stressing your system.
Response: Check blood glucose. Ensure GH peptides are not affecting sleep quality. Consider reducing protocol complexity.
Numbness or tingling in extremities
Carpal tunnel symptoms, including hand numbness and tingling, represent a classic sign of elevated growth hormone. If you experience these symptoms, your GH activity is likely too high. This can occur with aggressive GH peptide dosing, especially multiple compounds.
Response: Reduce or eliminate GH secretagogues. Symptoms typically resolve within days to weeks of dose reduction.
Diminishing returns despite increasing doses
If you keep adding peptides or increasing doses without seeing proportional results, you have likely hit receptor saturation or are experiencing diminishing returns. More is not always better with peptides. At some point, additional compounds provide no benefit while increasing cost, complexity, and potential side effects.
Response: Consider whether simpler protocols might actually work better. Return to basics with well-designed two-peptide stacks.
Starting your first peptide stack
If you are new to peptide stacking, following a structured approach prevents problems and optimizes results.
Step 1: establish single-peptide baselines
Before stacking, run individual peptides alone to understand your personal response. If you eventually want to run BPC-157, TB-500, and a GH peptide together, start with just BPC-157 for four weeks. Note how you feel, any side effects, and effectiveness.
Then try TB-500 alone for a period. Then your GH peptide. This approach takes longer but provides crucial information. When you eventually combine them, you will know exactly what each peptide does for you individually.
Step 2: add peptides sequentially
When starting a stack, introduce one new peptide every one to two weeks. This allows you to identify any adverse reactions to specific compounds. If you start three peptides simultaneously and experience problems, you will not know which compound is responsible.
Example sequence for a healing + GH stack: Week 1-2 BPC-157 only to establish dosing and response, Week 3-4 add TB-500 and observe combined healing effects, Week 5-6 add CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin to complete the stack.
Step 3: start with conservative doses
When combining peptides, start at the lower end of dose ranges. Synergistic effects mean combined peptides may produce stronger effects than the same doses run individually. You can always increase doses based on response. Starting too high risks side effects and wastes product.
The peptide calculator and peptide cost calculator help plan appropriate starting doses and budget.
Step 4: maintain detailed logs
Track everything when running multi-peptide protocols. Record doses, timing, injection sites, subjective effects, measurable outcomes, and any side effects. This data helps optimize your protocol over time and troubleshoot any issues.
Key variables to track: daily doses administered, injection times and sites, subjective energy and mood, weekly body composition measurements, sleep quality ratings, recovery assessments, monthly progress photos, strength metrics, overall protocol evaluation.
Common peptide stacking mistakes
Learning from common errors helps optimize your approach. These mistakes appear frequently among peptide researchers.
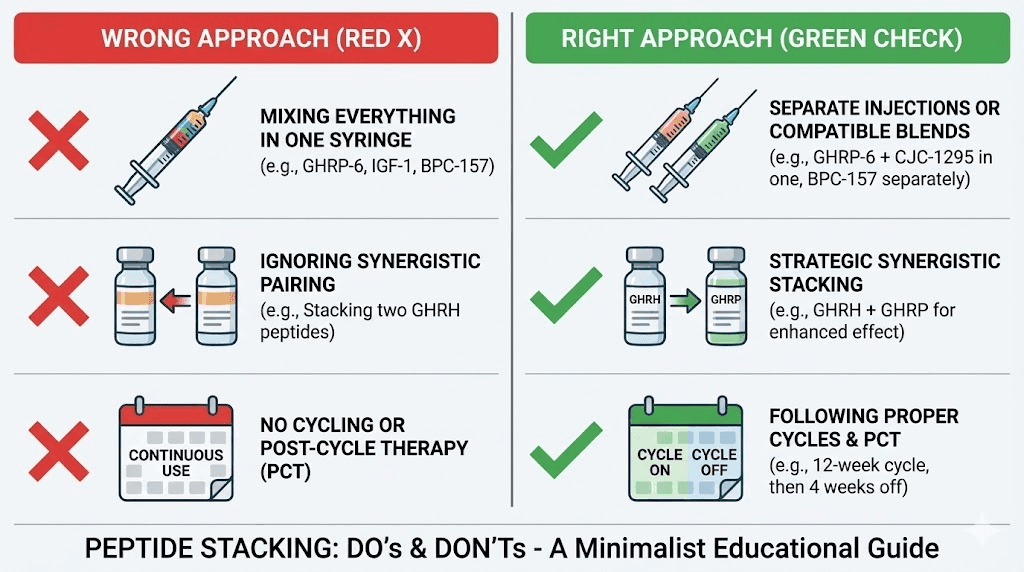
Mistake 1: stacking similar mechanisms
Running multiple GHRPs simultaneously rarely makes sense. GHRP-2, GHRP-6, Ipamorelin, and Hexarelin all bind to ghrelin receptors. Stacking two or three GHRPs means receptor competition, not synergy.
Better approach: Choose one GHRP and combine it with a GHRH analog like CJC-1295 for true synergy. The Ipamorelin vs CJC-1295 comparison explains why these combine well.
Mistake 2: ignoring timing requirements
GH secretagogues administered with food produce blunted responses. Some researchers add GH peptides to their stack without adjusting eating schedules, then wonder why results disappoint. Timing matters.
Better approach: Design your protocol around timing requirements first. Identify fasted windows and schedule peptides accordingly. If your lifestyle does not allow fasted administration, choose peptides without food timing restrictions.
Mistake 3: too much too soon
Enthusiasm often leads beginners to start with complex multi-peptide stacks. They want maximum results immediately. Instead, they get confusion about what is working, potential side effects from unknown sources, and wasted money on compounds they may not need.
Better approach: Start simple. A well-designed two-peptide stack often outperforms a poorly-designed five-peptide stack. Master basics before adding complexity.
Mistake 4: inconsistent administration
Peptides require consistent administration for optimal results. Sporadic dosing, skipping doses frequently, or constantly changing protocols prevents achieving steady-state effects. Some peptides like BPC-157 require twice-daily dosing for optimal tissue levels.
Better approach: Choose protocols you can actually maintain consistently. A simpler stack you administer perfectly outperforms a complex stack you follow inconsistently.
Mistake 5: ignoring quality considerations
Stacking multiple peptides from questionable sources multiplies risk. If one peptide is underdosed, contaminated, or mislabeled, your entire stack becomes compromised. Quality matters exponentially more with multi-peptide protocols.
Better approach: Source peptides from reputable suppliers with third-party testing. The Prime Peptides review comparison and vendor guides help identify reliable sources. Learn to read peptide testing results for quality verification.
Advanced stacking strategies
Experienced researchers employ sophisticated strategies to optimize multi-peptide protocols.
Cycling vs continuous use
Some peptides benefit from cycling, periods of use alternating with periods off. Others work best with continuous administration. Understanding which approach suits each peptide helps design optimal long-term protocols.
Peptides favoring cycling: Epithalon works best in 10-20 day bursts, 2-3 cycles per year. Continuous use may reduce effectiveness through receptor downregulation. Some GH secretagogues show reduced effectiveness over months of continuous use, though this is debated.
Peptides suitable for continuous use: BPC-157 shows stable effectiveness with long-term use, no significant tolerance development. Semaglutide and other GLP-1 agonists are designed for continuous use, maintaining effectiveness indefinitely. TB-500 can be used continuously at maintenance doses after initial loading.
Loading and maintenance phases
Some peptides benefit from loading phases with higher initial doses, followed by reduced maintenance dosing. TB-500 commonly follows this pattern: 2-2.5mg twice weekly for four to six weeks, then 2mg weekly for maintenance.
This approach can be applied to stacks. During an initial healing phase, run higher doses of healing peptides. Once acute healing completes, reduce to maintenance doses while potentially adding other peptides for different goals.
Goal-based phase shifting
Advanced researchers shift peptide focus based on phases. A body recomposition protocol might look like:
Phase 1 (weeks 1-8): Fat loss focus with Semaglutide titrated up, BPC-157 for gut protection, possibly thyroid-supporting compounds.
Phase 2 (weeks 9-16): Lean mass focus maintaining lower semaglutide dose, adding CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin for GH support, continuing BPC-157.
Phase 3 (weeks 17-24): Optimization focus reducing or eliminating semaglutide, emphasizing GH peptides, adding healing peptides if needed for training recovery.
This approach keeps total peptide count manageable at any given time while addressing multiple goals across the protocol duration.
Peptide storage when running multiple compounds
Managing multiple reconstituted peptides requires attention to storage. Peptides degrade over time, especially once reconstituted. Running five peptides simultaneously means five vials to track, each with different reconstitution dates and stability windows.
Stability considerations
Most reconstituted peptides remain stable for 3-4 weeks when refrigerated properly. Some peptides like BPC-157 show excellent stability, maintaining potency for 6+ weeks refrigerated. Others degrade faster.
The reconstituted peptide storage guide and refrigerator storage duration article provide specific stability data. Room temperature storage accelerates degradation significantly.
Labeling and organization
With multiple peptides, proper labeling becomes critical. Each vial should clearly indicate peptide name and concentration after reconstitution, reconstitution date, volume of bacteriostatic water added, and dose per unit volume for easy calculation.
Consider a dedicated peptide refrigerator section or container to keep compounds organized and prevent confusion during administration.
Reconstitution planning
Rather than reconstituting all peptides simultaneously, stagger reconstitution based on usage rates. If you use BPC-157 daily but TB-500 only twice weekly, reconstitute amounts appropriate to each usage pattern. This minimizes waste from peptide degradation.
The peptide reconstitution calculator helps plan appropriate reconstitution volumes.
Monitoring and adjusting multi-peptide protocols
Ongoing monitoring helps optimize results and catch problems early. Multi-peptide protocols require more attention than single compounds.
Subjective monitoring
Track how you feel daily. Note energy levels, sleep quality, appetite, mood, recovery from training, and any unusual symptoms. Changes in these parameters help identify both positive effects and potential problems.
Rate key variables on a 1-10 scale daily for trend analysis over weeks and months.
Objective measurements
Depending on your goals, track relevant objective metrics:
Body composition: Weight, body fat percentage, circumference measurements, progress photos
Performance: Strength numbers, endurance metrics, recovery indicators
Health markers: Blood pressure, fasting glucose, HbA1c if using GH or GLP-1 peptides
Healing: Range of motion, pain scales, functional capacity tests
The peptides before and after article shows what realistic progress looks like.
Blood work considerations
Periodic blood work provides insight into metabolic effects of multi-peptide protocols. Consider testing basic panel including complete metabolic panel and complete blood count, hormone panel with IGF-1 to reflect GH activity plus fasting insulin and thyroid function, and metabolic markers like fasting glucose, HbA1c, and lipid panel.
Test at baseline before starting, then every 3-6 months during extended protocols.
When to adjust your stack
Consider modifying your protocol when side effects persist beyond initial adaptation of 1-2 weeks, expected results are not materializing after appropriate timeframe, blood work shows concerning changes, goals shift and current peptides no longer align, or cost becomes unsustainable for the benefits received.
Adjustments might include dose changes, eliminating one peptide, substituting alternatives, or simplifying the overall protocol.
Frequently asked questions
Can you inject multiple peptides in the same syringe?
Some peptides can be combined in the same syringe for a single injection. CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin are commonly combined this way since they work synergistically. However, not all peptides should be mixed. Check compatibility before combining, some peptides may degrade or interact negatively when mixed. When uncertain, administer separately. The injectable peptides guide provides more administration details.
How long should you wait between starting new peptides?
Wait at least one to two weeks between introducing new peptides to your stack. This allows you to identify any adverse reactions to specific compounds and assess individual effects before adding complexity. Rushing to add multiple peptides simultaneously makes troubleshooting difficult if problems arise.
Is there a maximum number of peptides you should never exceed?
While no absolute maximum exists, practical considerations limit reasonable stacks to four or five peptides maximum. Beyond this, complexity becomes unmanageable, timing windows conflict, potential interactions multiply, and diminishing returns make additional peptides not worthwhile. Most researchers achieve optimal results with two to three well-chosen peptides.
Can peptide stacks cause long-term health issues?
Individual peptides generally show favorable safety profiles in research. However, long-term effects of multi-peptide combinations remain less studied. Conservative approaches include periodic breaks from protocols, regular health monitoring, and avoiding aggressive dosing. If you experience persistent negative effects, reduce or discontinue peptides and consult healthcare professionals. Read about peptide expiration and storage safety.
Should women use different peptide stacks than men?
Most peptide stacks work similarly for both sexes, though some considerations differ. Women may be more sensitive to GH effects and should start with lower doses. Certain peptides like PT-141 work differently based on sex. The best peptides for women and peptides for women over 40 guides cover sex-specific considerations.
Do peptides from different categories always stack safely?
Peptides from different categories, such as healing peptides, GH secretagogues, and metabolic peptides, generally combine more safely than multiple peptides within the same category. However, different category does not guarantee safety. Always research specific compound interactions and start conservatively. The peptides vs SARMs comparison provides related safety context.
How SeekPeptides supports peptide stacking decisions
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for optimizing multi-peptide protocols tailored to individual goals and circumstances.
The peptide stack calculator helps plan combinations with appropriate dosing, timing, and reconstitution calculations. Input your chosen peptides and receive guidance on administration schedules.
Individual peptide calculators including the BPC-157 calculator, TB-500 calculator, semaglutide calculator, and CJC-1295 calculator provide compound-specific dosing guidance.
The peptide cost calculator helps budget multi-peptide protocols, important when running several compounds simultaneously adds up quickly.
Comparison guides like BPC-157 vs TB-500, semaglutide vs tirzepatide, and Ipamorelin vs CJC-1295 help select between similar options when building stacks.
SeekPeptides remains committed to providing evidence-based peptide guidance helping researchers make informed stacking decisions.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your stacks stay synergistic, your timing stay optimal, and your results stay progressive. Join SeekPeptides for personalized protocol guidance and comprehensive peptide research support.