Feb 2, 2026
Your muscles have a built-in governor. A molecular brake pedal that decides exactly how much muscle you are allowed to carry. No matter how hard you train, how precisely you eat, how dialed your recovery is, that governor keeps pulling you back toward a biological set point your body has already decided on. The protein responsible? Myostatin. And ACE-031, also known as ramatercept, is the most studied attempt to disable that brake entirely.
The concept sounds almost too good.
Block myostatin, build more muscle. Simple. Except the science behind ACE-031 reveals something far more complex, a story of genuine breakthrough results tangled with unexpected vascular side effects that ultimately shut down clinical development. Understanding what happened, why it happened, and what the data actually showed matters for anyone serious about peptides for muscle growth.
ACE-031 is not just another peptide. It is a recombinant fusion protein that hijacks the activin receptor type IIB signaling pathway. In clinical trials, a single dose produced a 3.3% increase in lean body mass and a 5.1% increase in thigh muscle volume within 29 days. Those numbers came from subcutaneous injection in healthy postmenopausal women, not athletes on stacked protocols. The implications were enormous. The complications were, too.
This guide covers everything researchers need to know about ACE-031. The mechanism. The clinical data. The dosages tested. The side effects that ended the program. The next-generation compounds that followed. And the critical lessons about myostatin inhibition that every serious peptide researcher should understand before exploring this pathway. Whether you are evaluating ACE-031 specifically or trying to understand the broader landscape of peptides for muscle and body composition, the science here matters. SeekPeptides has compiled the most comprehensive breakdown available, drawing from published clinical trial data, preclinical studies, and expert analysis.
What is ACE-031 and how does it work
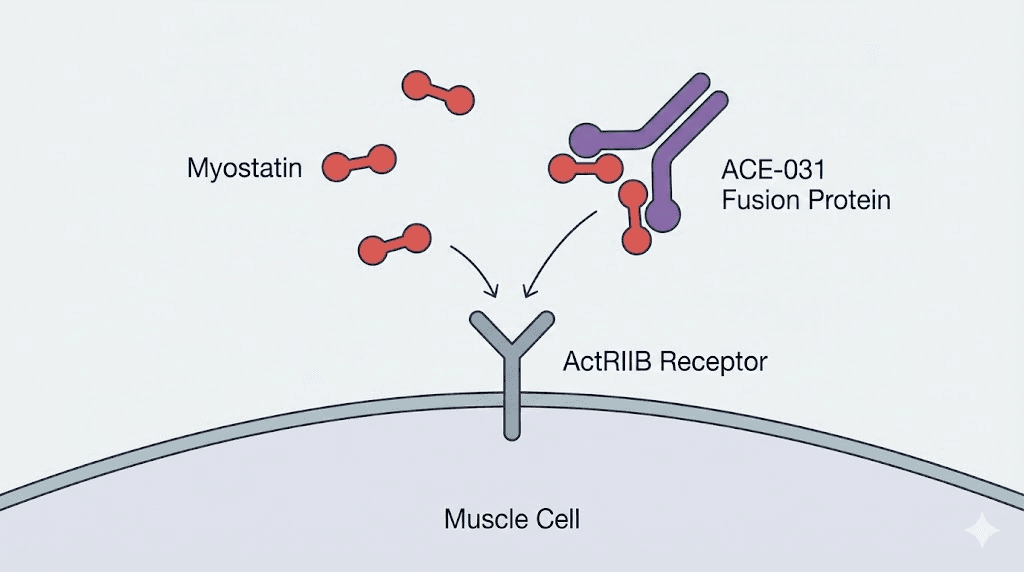
ACE-031 is a soluble form of the activin receptor type IIB fused with the Fc region of human immunoglobulin G1. That technical description matters because it explains exactly what this compound does. It is not a traditional peptide in the way most researchers think about how peptides work. It is a recombinant fusion protein engineered to function as a decoy receptor.
Think of it this way. Myostatin normally circulates through your body, finds its receptor on muscle cells (ActRIIB), binds to it, and sends a signal that says "stop growing." ACE-031 floods the system with fake receptors that grab myostatin before it ever reaches muscle tissue. The myostatin binds to ACE-031 instead. It never delivers its growth-limiting message. Muscle cells never get told to stop. They keep growing.
Developed by Acceleron Pharma in collaboration with Shire Pharmaceuticals, ACE-031 was originally created as a potential treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
The rationale was straightforward: if you could block the signals that limit muscle growth, you could potentially slow or reverse the devastating muscle wasting seen in DMD patients. But the mechanism has implications far beyond rare disease treatment.
The myostatin signaling pathway
Myostatin belongs to the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) superfamily. This family of proteins regulates growth, differentiation, and development across virtually every tissue type. Myostatin specifically targets skeletal muscle. It binds to ActRIIB receptors on muscle cell surfaces, activating downstream signaling cascades (primarily Smad2/3 phosphorylation) that suppress muscle protein synthesis and promote muscle protein breakdown.
Animals with naturally occurring myostatin mutations demonstrate the power of this system. Belgian Blue cattle, for example, carry a myostatin gene deletion that produces what breeders call "double muscling," a dramatic increase in skeletal muscle mass. Whippet dogs with myostatin mutations develop visibly extreme musculature. In humans, a child documented in a 2004 New England Journal of Medicine case report carried a myostatin mutation and displayed unusual muscular development from birth.
The evidence was overwhelming. Block myostatin, get more muscle. The question was how to do it safely and effectively in humans.
Why ACE-031 is different from other myostatin inhibitors
Several approaches to myostatin inhibition exist, and understanding the differences matters for evaluating ACE-031. Monoclonal antibodies like MYO-029 (stamulumab) target myostatin directly, binding the protein itself. These tend to be highly specific but produced disappointing results in early trials, with only modest or no measurable muscle gains.
Follistatin, a naturally occurring protein, acts as a broad antagonist of multiple TGF-beta family members including myostatin and activin. Some researchers describe follistatin as a "biological shotgun" compared to more targeted approaches. It inhibits myostatin and activin simultaneously, removing two brakes on muscle growth at once. But this broad action also means more potential for unintended effects on other peptide signaling pathways.
ACE-031 falls somewhere in between. As a soluble ActRIIB receptor, it binds not just myostatin but also activin A, activin B, GDF-11, and several bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). This broader binding profile is why it produced stronger muscle-building effects than myostatin-specific antibodies in trials. Compounds with broader target specificity produced 5-9% increases in thigh muscle volume, compared to 3-5% with more specific compounds. But that same broadness created the safety issues that ultimately ended the program.
Clinical trial data and results
The clinical evidence for ACE-031 comes from two major trials. Both produced fascinating results. Both also revealed problems that could not be ignored.
Phase 1 trial in healthy postmenopausal women
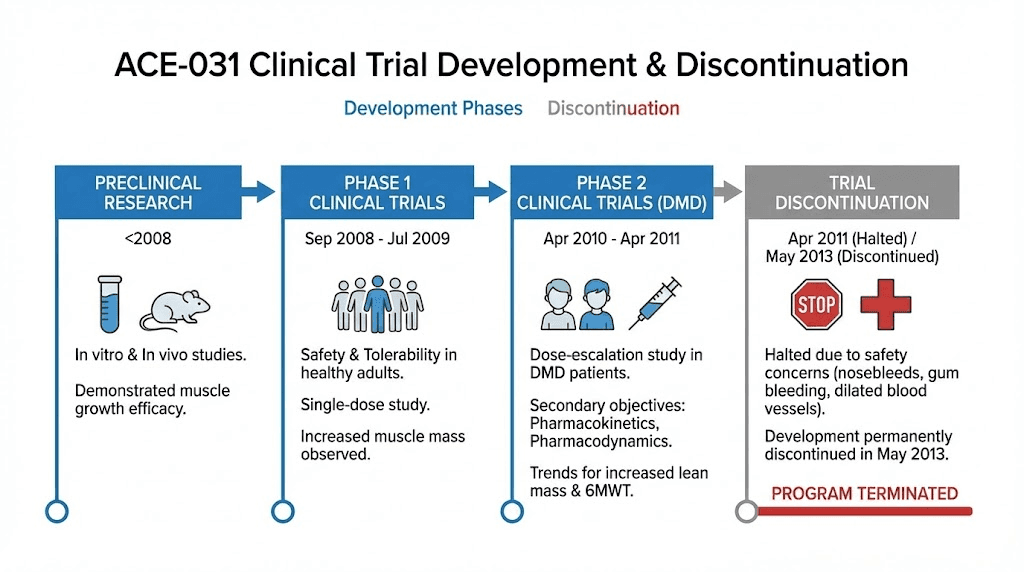
The first human trial (Attie et al., 2013) was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, single ascending-dose study in 48 healthy postmenopausal women. This population was chosen because postmenopausal women naturally experience accelerated bone and muscle loss, making them an ideal population to detect anabolic effects.
Participants received a single subcutaneous injection at doses ranging from 0.02 mg/kg to 3 mg/kg, with a 3:1 randomization ratio (active drug to placebo).
The results at the highest dose (3 mg/kg) were striking:
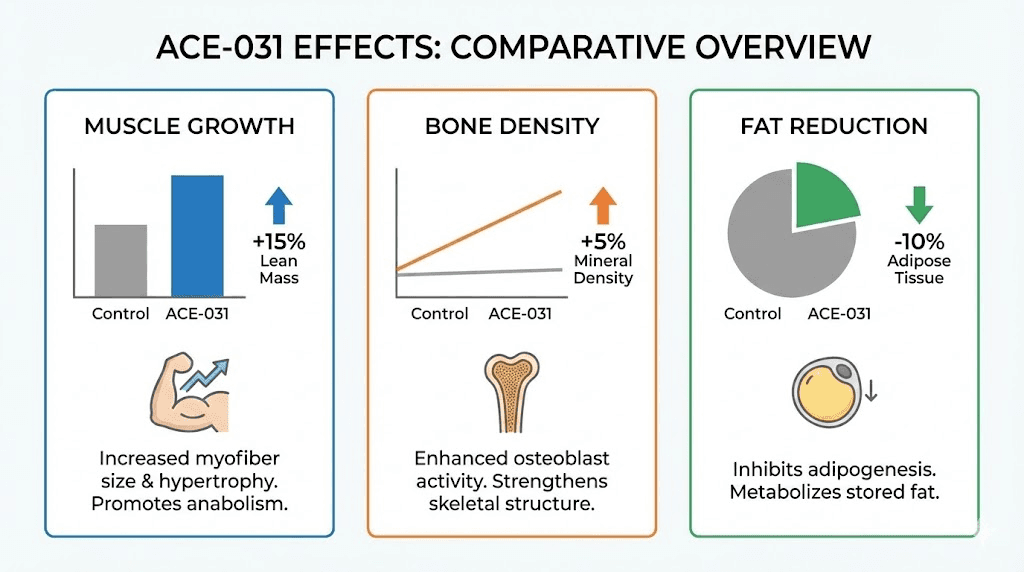
Total body lean mass: 3.3% increase at day 29 (P = 0.03, measured by DXA)
Thigh muscle volume: 5.1% increase at day 29 (P = 0.03, measured by MRI)
Pharmacokinetics: Mean half-life of 10-15 days, with linear dose-proportional exposure
Bone biomarkers: Statistically significant improvements in markers of bone formation
Fat metabolism biomarkers: Favorable changes in adiponectin and leptin levels
A 3.3% increase in lean body mass from a single injection. In 29 days. Without exercise intervention. Without dietary modification. Without any other peptide stacking. That is a remarkable pharmacodynamic signal. For context, the typical rate of muscle gain in trained individuals using optimized nutrition and progressive resistance training is roughly 0.5-1% of body weight per month. ACE-031 achieved over three times that from one injection, in untrained subjects.
The safety profile in this trial was generally favorable. Adverse events included mild injection site erythema. No serious adverse events were reported.
Phase 2 trial in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
The second trial enrolled ambulatory boys with DMD in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study. ACE-031 was administered subcutaneously every 2-4 weeks at doses of 1 mg/kg and 3 mg/kg.
The efficacy signals were encouraging. Trends favored ACE-031 over placebo for several important measures:
6-minute walk test: The ACE-031 group maintained walking distance while the placebo group declined
Lean body mass: Trending increase in the ACE-031 group
Bone mineral density: Trending improvement in the ACE-031 group
None of these trends reached statistical significance, but the trial was not powered or completed to detect efficacy. It was stopped early for safety reasons.
The safety concerns that emerged were epistaxis (nosebleeds), gingival bleeding (gum bleeding), and telangiectasias (dilated blood vessels visible on the skin). While none of these events were classified as serious or severe, the regulatory agencies and sponsoring companies needed to understand the mechanism before proceeding.
Why ACE-031 caused vascular side effects
The vascular issues were traced to ACE-031 binding partners beyond myostatin. Specifically, the compound also trapped BMP9 and BMP10, two ligands critical for maintaining normal endothelial cell function and vascular integrity. When ACE-031 sequestered these BMPs, it disrupted normal blood vessel maintenance, leading to the bleeding and telangiectasia events observed in trials.
This was not a flaw in the myostatin inhibition concept. It was a specificity problem. ACE-031 was too effective at binding TGF-beta family members broadly. The muscle-building effects were genuine and significant. But the compound could not distinguish between the ligands you wanted to block (myostatin) and the ones you needed to leave alone (BMP9, BMP10).
In April 2011, clinical trials were halted. In May 2013, Acceleron Pharma and Shire announced they would not restart development. The collaboration on ACE-031 was permanently concluded.
ACE-031 effects on muscle tissue
Despite the safety concerns that ended clinical development, the muscle-building effects of ACE-031 remain among the most impressive ever documented for any pharmaceutical intervention. Understanding these effects in detail is valuable for researchers evaluating peptides for body composition.
Mechanism of muscle hypertrophy
ACE-031 promotes muscle growth through multiple pathways simultaneously. By trapping myostatin, it removes the primary negative regulator of muscle protein synthesis. But because it also traps activin A and other ActRIIB ligands, the anabolic stimulus is amplified beyond what pure myostatin blockade achieves.
At the cellular level, research suggests ACE-031 may inhibit the ERK1/2 pathway in muscle cells. This mechanism potentially prevents muscle fiber atrophy by impeding programmed cell death pathways. Studies also suggest the compound may preserve mitochondrial function and enhance muscle fiber energy efficiency, meaning the new muscle tissue may be functionally better, not just bigger.
In preclinical mouse models, ACE-031 increased both type 1 (slow-twitch, oxidative) and type 2 (fast-twitch, glycolytic) muscle fiber cross-sectional area. This is notable because many anabolic interventions preferentially affect one fiber type. ACE-031 appeared to grow all muscle equally.
Quantified muscle gains from clinical data
The numbers from published trials paint a clear picture of ACE-031 potency:
Measurement | Change | Timeframe | Population | Dose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Total lean body mass | +3.3% | 29 days | Healthy postmenopausal women | 3 mg/kg single dose |
Thigh muscle volume | +5.1% | 29 days | Healthy postmenopausal women | 3 mg/kg single dose |
Type 1 fiber area | Significant increase | 7 weeks | Mouse models | Weekly dosing |
Type 2 fiber area | Significant increase | 7 weeks | Mouse models | Weekly dosing |
Total body weight (muscle) | Significant increase | 7 weeks | DMD mouse model | Weekly dosing |
Compare these to other anabolic compounds studied in clinical settings. Testosterone replacement therapy in hypogonadal men typically produces 2-5 kg lean mass gains over 6-12 months. Testosterone-stimulating peptides produce more modest effects. ACE-031 achieved comparable lean mass changes in under a month from a single dose. That pharmacological potency is essentially unmatched in the muscle-building compound space.
Implications for sarcopenia and muscle wasting
The postmenopausal women study was particularly relevant for age-related muscle loss. Sarcopenia, the progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength that accompanies aging, affects an estimated 10-16% of adults over 60. It is a major contributor to frailty, falls, fractures, and loss of independence.
Current treatments for sarcopenia are limited to exercise (which many elderly patients cannot perform adequately) and nutritional interventions (which have modest effects). A pharmaceutical that could add 3.3% lean mass from a single injection would represent a transformative treatment option for longevity-focused research.
The DMD trial, though incomplete, also suggested potential for maintaining muscle function in progressive muscular dystrophies. The trend toward preserved 6-minute walk test performance, while not statistically significant, hinted at functional benefit beyond simple mass gain.
Effects beyond muscle: bone density and fat metabolism
One of the most intriguing aspects of ACE-031 research is its multi-tissue effects. Unlike compounds that affect only muscle, ACE-031 demonstrated simultaneous improvements across muscle, bone, and fat compartments. This trifecta of effects made it particularly interesting for researchers studying anti-aging peptides and metabolic health.
Bone mineral density improvements
ACE-031 interacts with ligands involved in skeletal metabolism, not just muscle growth. By trapping activins and other TGF-beta family members that regulate osteoblast and osteoclast activity, ACE-031 appears to shift the balance toward bone building.
The clinical data showed a 3.4% increase in lumbar spine bone mineral density in the Phase 1b study. Preclinical data was even more dramatic. In mouse models, ACE-031 produced:
Femur bone density: 132% increase
Vertebral bone density: 27% increase
Trabecular bone volume fraction: approximately 80% increase
Trabecular number: approximately 70% increase
These bone effects were unique to ACE-031 among myostatin inhibitors. Studies comparing ACE-031 to a strict myostatin-only inhibitor found that while both increased muscle mass, only ACE-031 increased bone density. This suggests the bone benefits came from blocking additional ActRIIB ligands beyond myostatin, specifically those involved in osteoclast regulation.
For researchers interested in peptides for bone health, these findings positioned ACE-031 as potentially valuable for osteoporosis prevention, though the vascular side effects prevented further clinical development.
Fat metabolism changes
The metabolic effects of ACE-031 extended to adipose tissue. Experimental models suggest myostatin inhibition increases fatty acid oxidation and thermogenesis, leading to reduced fat accumulation. Clinical biomarker data from ACE-031 trials showed:
Increased adiponectin levels (associated with improved insulin sensitivity and fat oxidation)
Decreased leptin levels (suggesting reduced fat mass or altered adipocyte metabolism)
Reduced fat cell mass in preclinical observations
Favorable shifts in adipokine secretion profiles
This dual action, building muscle while reducing fat, is the holy grail of body composition research. Few compounds achieve both simultaneously. For anyone researching fat-burning peptides or peptides for fat loss, the ACE-031 data provides compelling evidence for the myostatin inhibition pathway as a dual-action approach.
The metabolic improvements observed with ACE-031 parallel findings from bimagrumab trials. Bimagrumab, a next-generation compound targeting the same receptor pathway, produced a 20% reduction in total body fat mass (7.31 kg) and a 9.5 cm reduction in waist circumference over 48 weeks in obese individuals with type 2 diabetes.
While bimagrumab has a different mechanism (receptor antagonist vs. ligand trap), the shared pathway suggests these metabolic effects are genuine consequences of ActRIIB pathway modulation.
Dosage protocols from clinical trials
Understanding the dosage data from ACE-031 trials is essential for researchers evaluating this pathway. Unlike many peptides where dosing protocols are derived from community experience, ACE-031 dosing comes directly from controlled clinical trials.
Phase 1 dose ranges tested
The Phase 1 ascending-dose study tested the following single subcutaneous doses:
0.02 mg/kg (subtherapeutic, pharmacokinetic assessment)
0.05 mg/kg
0.1 mg/kg
0.3 mg/kg
1 mg/kg
3 mg/kg (highest dose, produced significant muscle and bone effects)
ACE-031 exposure (AUC and Cmax) increased linearly with dose. The mean half-life was 10-15 days across all dose levels, suggesting that once-every-two-weeks or less frequent dosing could maintain therapeutic levels.
Phase 2 DMD dosing
In the DMD trial, participants received ACE-031 at 1 mg/kg or 3 mg/kg subcutaneously every 2-4 weeks. The ascending-dose design meant patients started at lower doses and increased if tolerated. The study was terminated before the full dosing protocol could be evaluated.
Pharmacokinetic profile
Several key pharmacokinetic findings inform how researchers evaluate ACE-031:
Parameter | Value | Clinical significance |
|---|---|---|
Half-life | 10-15 days | Supports infrequent dosing (every 2-4 weeks) |
Dose-response | Linear | Predictable exposure increases with dose |
Route | Subcutaneous injection | Standard peptide administration |
Onset of effects | Within 29 days (single dose) | Rapid muscle and bone effects |
Effect duration | Extended beyond drug clearance | Forum reports suggest ongoing effects 4+ weeks post-dose |
The long half-life and linear pharmacokinetics made ACE-031 straightforward from a dosing perspective. For researchers comparing peptide dosage protocols, ACE-031 stands out for its infrequent dosing requirement and rapid onset of measurable effects. Most peptide protocols require daily or twice-daily dosing. ACE-031 achieved significant results with a single injection every 2-4 weeks.
Important note on reconstitution and stability
ACE-031 is a large fusion protein, not a small peptide. This has important implications for reconstitution and handling. Unlike smaller peptides that remain stable for weeks after reconstitution when stored properly, complex fusion proteins like ACE-031 are more fragile. Forum reports consistently emphasize that reconstituted ACE-031 degrades rapidly and should be used immediately after reconstitution rather than stored. This differs significantly from standard peptide storage protocols.
Side effects and safety profile
The safety data from ACE-031 trials provides critical information for understanding the risks of ActRIIB pathway modulation. This section covers every documented adverse event, the mechanism behind the vascular effects, and how the safety profile compares to other peptide safety considerations.
Documented adverse events from clinical trials
Phase 1 (healthy postmenopausal women):
Injection site erythema (redness at injection site), mild
No serious adverse events
Generally well-tolerated across all dose levels
Significant FSH suppression in female subjects (mechanism and implications unclear)
Phase 2 (DMD boys):
Epistaxis (nosebleeds)
Gingival bleeding (gum bleeding)
Telangiectasias (dilated blood vessels visible through skin)
None classified as serious or severe
Trial stopped as a precautionary measure
Broader reported effects
Beyond clinical trial data, various sources document additional concerns associated with ActRIIB pathway modulation:
Elevated blood pressure: Reported in some contexts, possibly related to vascular effects
Potential cardiac hypertrophy: Theoretically possible given the broad TGF-beta family involvement, though not definitively documented with ACE-031 specifically
Peripheral edema: Swelling in limbs reported by some users
Skin discoloration or rashes: Reported at higher doses over extended periods in non-clinical settings
Headaches: Mild, reported in early days of use
Understanding the BMP9/BMP10 problem
The core safety issue with ACE-031 comes down to selectivity. BMP9 and BMP10 are ligands that maintain normal endothelial cell function, the cells that line blood vessels. When ACE-031 trapped these BMPs alongside myostatin, it effectively disrupted vascular maintenance.
This is not a universal problem with myostatin inhibition. It is specific to the ActRIIB decoy receptor approach. BMP9 and BMP10 bind to ActRIIB in vivo, so any soluble ActRIIB receptor will inevitably capture them. More selective approaches, like monoclonal antibodies targeting myostatin directly, do not have this problem. But they also produce weaker muscle-building effects.
The trade-off became clear. Broader ligand binding equals more muscle growth but also more off-target effects. Narrower targeting equals fewer side effects but less impressive muscle results. This fundamental tension shaped the entire next generation of myostatin inhibitor development.
Comparison to other compound safety profiles
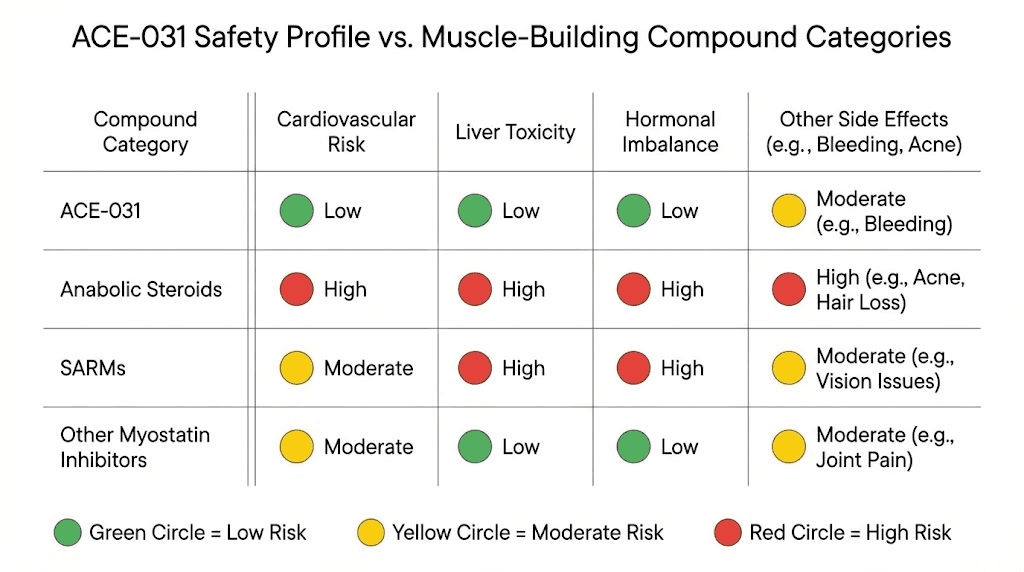
Putting ACE-031 side effects in context helps researchers assess relative risk. Compared to anabolic steroids, the side effect profile is fundamentally different. Steroids produce androgenic effects (acne, hair loss, virilization), hepatotoxicity, cardiovascular strain, and hormonal suppression. ACE-031 side effects were vascular in nature and mechanistically distinct.
Compared to SARMs, which produce their own range of liver and hormonal concerns, ACE-031 represents a completely different risk category. The vascular effects seen with ACE-031 are unique to the ActRIIB pathway and do not occur with other muscle-building approaches.
Compared to growth hormone secretagogues like ipamorelin or CJC-1295, ACE-031 carries higher vascular risk but potentially greater muscle-building efficacy. The risk-benefit calculation differs substantially between these compound classes.
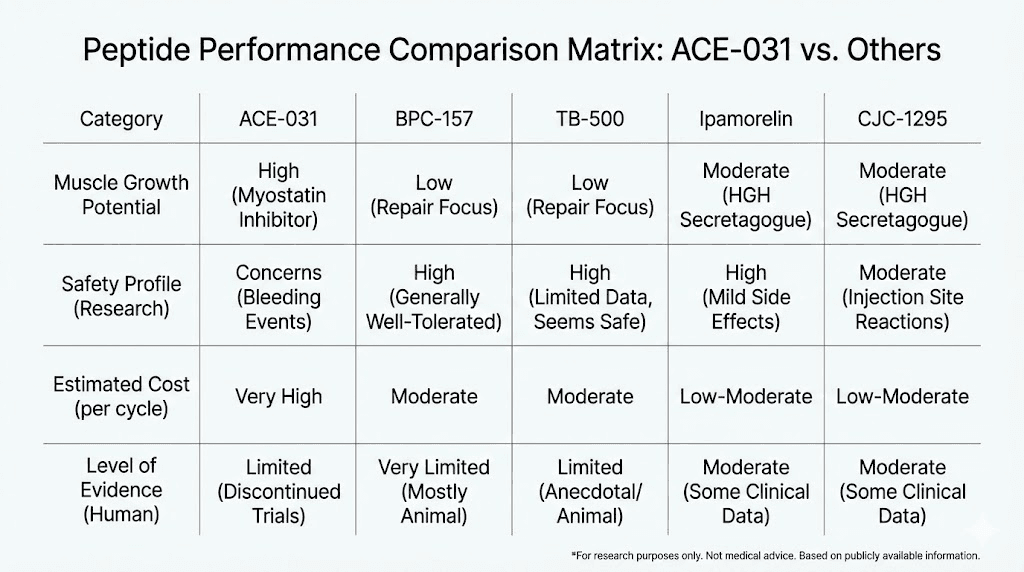
ACE-031 vs. other myostatin inhibitors
The myostatin inhibition landscape includes several distinct approaches. Understanding how ACE-031 compares to alternatives helps researchers evaluate which pathway best suits their goals. This comparison is relevant for anyone exploring peptide research in the muscle growth space.
ACE-031 vs. follistatin 344
Follistatin 344 is often discussed alongside ACE-031 as a myostatin inhibitor, but the mechanisms differ significantly.
Feature | ACE-031 | Follistatin 344 |
|---|---|---|
Type | Soluble ActRIIB-Fc fusion protein | Endogenous glycoprotein |
Target specificity | Broad (myostatin + activins + BMPs + GDF-11) | Very broad ("biological shotgun") |
Muscle growth | 33-46% in animal studies | ~15% over longer periods |
Bone effects | Increased bone density | May reduce bone density (blocks GDF11) |
Administration | Subcutaneous injection | Gene therapy (AAV) or injection |
Clinical status | Discontinued (2013) | Gene therapy trials ongoing |
Half-life | 10-15 days | Variable depending on delivery |
Vascular risk | Documented (BMP9/10 binding) | Less documented but possible |
The bone density difference is particularly notable. ACE-031 increased bone density substantially while follistatin may actually decrease it by blocking GDF11, a factor involved in bone mineralization. For researchers concerned about bone health, this distinction could be significant.
ACE-031 vs. bimagrumab
Bimagrumab (BYM-338) represents a different mechanistic approach to the same pathway. While ACE-031 is a ligand trap (catching myostatin before it reaches receptors), bimagrumab is a monoclonal antibody that directly blocks both ActRII and ActRIIB receptors on cell surfaces.
This distinction matters for safety. Because bimagrumab blocks receptors rather than trapping ligands, circulating levels of BMP9 and BMP10 remain available to bind other receptors. This is why bimagrumab has not shown the same vascular side effects as ACE-031.
Bimagrumab has produced impressive clinical data of its own. In obese individuals with type 2 diabetes, 48 weeks of treatment produced a 20% reduction in body fat mass, a 9.5 cm reduction in waist circumference, and a 4.4% increase in lean body mass. These metabolic results overlap significantly with what ACE-031 appeared capable of based on biomarker data.
ACE-031 vs. ACE-083
ACE-083 was Acceleron Pharma's direct successor to ACE-031, designed specifically to avoid the BMP9/BMP10 problem. ACE-083 is a modified follistatin-Fc fusion protein that traps TGF-beta superfamily ligands locally (at the injection site) rather than systemically.
Critically, ACE-083 does not bind BMP9 or BMP10. This was the key design improvement based on lessons learned from ACE-031. However, in a Phase 2 trial for facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), while MRI showed increased thigh muscle volume, the trial was terminated early for lack of functional efficacy. The muscle grew, but it did not translate to improved strength or mobility.
This raised a deeper question about myostatin inhibition: is more muscle mass always better, or does the quality and functionality of that muscle matter more? The ACE-083 experience suggests that simply growing bigger muscles does not guarantee better performance, a finding with implications for performance-focused peptide research.
Summary comparison table
Compound | Mechanism | Muscle effect | Key safety concern | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
ACE-031 | Soluble ActRIIB (ligand trap) | Strong (+5.1% thigh volume) | Vascular (BMP9/10) | Discontinued 2013 |
ACE-083 | Modified follistatin-Fc (local) | Moderate (MRI increase) | Lack of functional benefit | Discontinued |
Bimagrumab | ActRII/IIB antibody (receptor block) | Moderate (+4.4% lean mass) | Generally well-tolerated | Active trials (metabolic) |
Follistatin 344 | Glycoprotein (broad ligand trap) | Moderate (~15% animal) | Possible bone density loss | Gene therapy trials |
MYO-029 | Anti-myostatin antibody | Weak (no significant gains) | Generally safe | Discontinued (ineffective) |
Domagrozumab | Anti-myostatin antibody | Moderate (MRI increase) | Lack of functional benefit | Discontinued |
Practical considerations for researchers
While ACE-031 is not approved for human use and clinical development has been permanently halted, the compound continues to circulate in research markets. Researchers evaluating this compound face several practical challenges that deserve careful consideration.
Black market product quality concerns
A significant study published in Drug Testing and Analysis (Reichel, 2025) examined 14 black market products sold as ACE-031. The findings were concerning. Of the 14 tested products, only 12 contained any ACVR2B-immunoreactive protein at all. But here is the critical detail: none of those 12 contained an ACVR2B-Fc fusion protein (the actual ACE-031 compound). Instead, they contained full-length activin receptor 2B, a different protein entirely.
This means that most, possibly all, products sold as "ACE-031" on the research market are not actually ACE-031. They are a related but fundamentally different compound. The clinical data, safety profile, dosing parameters, and pharmacokinetics from published trials may not apply to these products at all.
For researchers accustomed to sourcing peptides from research vendors, this is an important cautionary finding. The quality and authenticity issues with ACE-031 exceed what is typically seen with smaller peptides like BPC-157 or TB-500. Manufacturing a recombinant fusion protein requires significantly more sophisticated equipment and expertise than synthesizing standard injectable peptides.
SeekPeptides members access detailed vendor quality guides and third-party testing resources that can help identify legitimate research compounds from counterfeits.
Regulatory and legal status
ACE-031 occupies a complicated regulatory space. Key facts:
FDA status: Granted orphan drug designation for DMD in 2010, but never approved for any indication
WADA status: Prohibited under the 2024 list, classified under S4 "Hormone and metabolic modulators"
No approved pharmaceutical products exist
Available only as research material from peptide vendors, with significant quality concerns
For researchers navigating peptide legality, ACE-031 falls into the grey area of compounds sold for research purposes but prohibited in competitive sports. Understanding these distinctions is important. Peptide regulation is evolving rapidly, and compounds in this category face increasing scrutiny.
Cost considerations
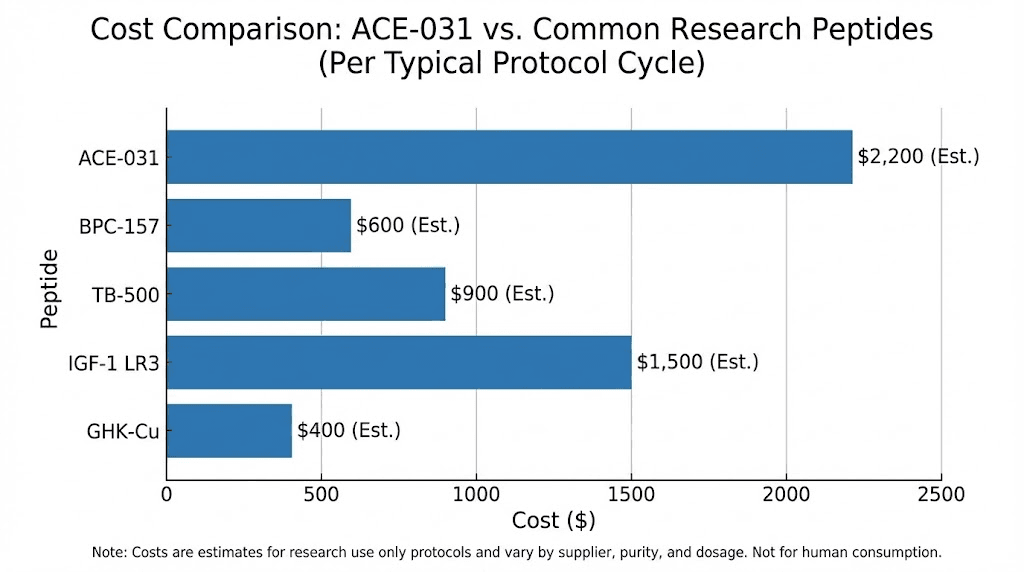
ACE-031 is among the most expensive research peptides available. At approximately $50 per milligram from research sources, a single dose for an 80 kg individual at 1 mg/kg would cost approximately $4,000. At the 3 mg/kg dose that produced the most impressive clinical results, costs would approach $12,000 per dose. This is orders of magnitude more expensive than common research peptides and puts ACE-031 beyond the budget of most individual researchers.
For context on peptide costs and cost calculation, ACE-031 represents the extreme high end of the research peptide market. Combined with the quality concerns noted above, the cost-to-confidence ratio is exceptionally unfavorable.
The broader science of myostatin inhibition
ACE-031 exists within a larger scientific story about myostatin and muscle regulation. Understanding this context is essential for evaluating not just ACE-031 but the entire category of myostatin-targeting compounds.
Why myostatin exists
Myostatin is not a design flaw. It evolved for critical reasons. Muscle tissue is metabolically expensive to maintain. Every kilogram of skeletal muscle burns approximately 13 calories per day at rest, and during activity, energy demands increase dramatically. For organisms evolved in calorie-scarce environments, unlimited muscle growth would be a survival disadvantage.
Myostatin functions as a metabolic efficiency regulator, keeping muscle mass at the minimum level needed for survival while conserving energy. This explains why simply blocking myostatin produces rapid and dramatic muscle growth. The "potential" for larger muscles already exists in every human. Myostatin is just keeping the lid on.
But this also raises important questions about what happens when that lid comes off. Heart tissue can respond to TGF-beta family changes. Reproductive hormones can be affected (the FSH changes seen in ACE-031 trials).
Vascular maintenance relies on related signaling pathways.
The myostatin system is deeply interconnected with other regulatory networks, which is why every attempt at broad inhibition has encountered unexpected consequences.
Myostatin and the TGF-beta superfamily
The challenge of myostatin inhibition comes down to structural similarity. Mature myostatin shares significant sequence and structural homology with other TGF-beta superfamily members including activin A, activin B, GDF-11, and various BMPs. These proteins all signal through related receptors, often the same receptors.
This means that any compound designed to block myostatin risks also blocking its structural cousins. The more potent and broad the blocking mechanism, the more likely off-target effects become. This is the fundamental tension the field has been unable to resolve.
Monoclonal antibodies offer the most specificity (targeting myostatin alone) but produce the weakest effects. Soluble receptors like ACE-031 offer the strongest effects but the worst selectivity. Modified approaches like ACE-083 attempted to split the difference but still could not translate muscle mass into functional improvement.
What the future holds
Despite ACE-031 failure, myostatin inhibition research continues. Several directions show promise:
More selective biologics: Newer antibodies with higher specificity for myostatin over related ligands are in development. The goal is to achieve ACE-031-level muscle effects with antibody-level safety.
Combination approaches: Rather than maximizing myostatin blockade alone, combining moderate myostatin inhibition with other anabolic pathways might achieve better overall results with acceptable safety. Researchers already explore peptide stacking approaches that address multiple pathways simultaneously.
Gene-based therapies: Follistatin gene transfer using AAV vectors has shown promise in animal models and early human trials for muscular dystrophies. This approach provides sustained, local myostatin inhibition without systemic effects.
Metabolic applications: Bimagrumab data showing dramatic fat loss and improved metabolic parameters in obesity and diabetes has revived interest in the pathway. If the metabolic benefits can be captured without unacceptable muscle or vascular effects, this could become a major therapeutic area.
ACE-031 and athletic performance
Given its potent muscle-building effects, ACE-031 has attracted attention from the athletic performance community. Understanding this context is important, particularly regarding drug testing considerations.
WADA prohibition status
ACE-031 is explicitly prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency under section S4 of the prohibited list. This category covers "Hormone and Metabolic Modulators" and specifically includes activin receptor pathway inhibitors. The prohibition applies both in-competition and out-of-competition.
WADA has invested in developing detection methods for myostatin inhibitory peptides. Research published by Walpurgis et al. (2023) describes specific detection methods for six novel myostatin inhibitory peptides from doping control serum samples, achieving detection sensitivity down to 3-9 ng/mL. This suggests anti-doping authorities take the myostatin inhibitor category seriously, even for compounds that are not commercially available as approved pharmaceuticals.
What forum users report
Despite its discontinued clinical status, ACE-031 has been used by some bodybuilders and athletes. Forum reports provide anecdotal data that, while not scientifically rigorous, offers some insight into real-world effects:
Positive reports describe rapid strength increases within the first week of dosing, pronounced muscle fullness and density improvements, continued growth effects extending 4+ weeks after the last injection, and significant pumps during training. One experienced user with over 20 cycles of various compounds described ACE-031 as "a game changer" that produced effects superior to most other anabolic agents.
Negative or skeptical reports note inconsistent results possibly related to product quality (given the counterfeit analysis data), limited effects when compared dose-for-dose to compounds like IGF-1 LR3, and significant cost that may not justify effects relative to other muscle-building peptides.
The community consensus suggests high carbohydrate intake during ACE-031 use enhances results, and that younger users tend to see more pronounced effects. Full-vial immediate use after reconstitution is universally recommended due to stability concerns.
Comparison to established performance peptides
Researchers often want to know how ACE-031 compares to peptides with more established performance track records. The answer depends on what you are trying to achieve.
For raw muscle mass gain, ACE-031 has the most impressive single-dose data of any peptide compound. Nothing else matches a 5.1% increase in thigh muscle volume from one injection.
For recovery and healing, established peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500 offer proven benefits with far better safety profiles and lower cost. The BPC-157/TB-500 stack remains one of the most popular and well-documented healing protocols.
For growth hormone optimization, peptides like ipamorelin, CJC-1295, and sermorelin offer well-characterized benefits with predictable dosing and established safety data.
For fat loss specifically, compounds like AOD-9604, tesofensine, and 5-amino-1MQ have better risk-to-benefit ratios for most researchers. The fat metabolism effects of ACE-031, while interesting, came bundled with vascular risks that simpler fat-loss peptides avoid.
For overall body composition improvement with a good safety profile, SeekPeptides members typically find that well-designed peptide stacks combining growth hormone secretagogues with healing peptides and targeted fat-loss compounds achieve better practical results than any single potent but risky compound.
Reconstitution and handling specifics
For researchers who do work with ACE-031, proper handling is critical. This compound behaves differently from standard peptides during reconstitution and storage.
Why ACE-031 is different from small peptides
Most research peptides (BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu, etc.) are relatively small molecules with 5-40 amino acids. They reconstitute easily in bacteriostatic water, tolerate gentle handling, and remain stable for days to weeks when refrigerated.
ACE-031 is a recombinant fusion protein, orders of magnitude larger and more structurally complex. Its stability depends on maintaining its three-dimensional folded structure. Temperature fluctuations, mechanical stress, and time in solution all contribute to degradation. Once the protein unfolds or aggregates, it loses biological activity.
Handling recommendations based on available data
Reconstitute with sterile water rather than bacteriostatic water (the benzyl alcohol in BAC water may affect protein stability)
Use immediately after reconstitution, do not store reconstituted ACE-031
Store lyophilized (powder) form frozen at -20C or below until ready for use
Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles which damage protein structure
Do not shake or vortex, swirl gently to dissolve
Protect from light during handling and storage
For researchers accustomed to standard peptide mixing protocols, the handling requirements for ACE-031 represent a significant departure. The peptide reconstitution calculator can help determine volumes, but the stability characteristics require more careful attention than typical peptides.
Understanding the research context
ACE-031 teaches several important lessons about peptide research that extend well beyond this specific compound. These principles apply to anyone evaluating novel peptide research compounds.
The specificity-potency tradeoff
ACE-031 demonstrated a principle that recurs across pharmacology: potency and specificity often work against each other. The broadest-acting compounds (ACE-031, follistatin) produced the most dramatic muscle effects but also the most off-target problems. The most specific compounds (MYO-029) were safest but barely worked. Finding the sweet spot remains the central challenge.
This principle applies beyond myostatin inhibitors. When evaluating any new peptide, researchers should ask: what does this compound interact with beyond its primary target? The answer often predicts both the magnitude of desired effects and the likelihood of unwanted ones.
The muscle mass versus function disconnect
Perhaps the most surprising finding across the myostatin inhibitor field is that more muscle does not always mean better function. Both ACE-031 and ACE-083 produced measurable increases in muscle mass (by DXA and MRI), but neither consistently translated those gains into improved functional outcomes like walking distance or muscle strength.
This challenges a fundamental assumption in the muscle-building space: that bigger equals better. The quality of new muscle tissue, its fiber type composition, innervation, vascular supply, and contractile properties, may matter as much as its volume. Researchers evaluating muscle growth peptides should consider functional endpoints alongside mass measurements.
Why clinical trial data matters
ACE-031 stands out in the research peptide world because it has legitimate clinical trial data. Most peptides used in the research community have preclinical (animal) data at best, with human evidence coming primarily from anecdotal reports. The ACE-031 Phase 1 and Phase 2 data provide quantified, placebo-controlled human evidence for both efficacy and safety.
This is both an advantage and a cautionary tale. The data proves the mechanism works in humans. But it also proves the risks are real and specifically documented, not hypothetical. For researchers weighing the evidence base of various compounds, ACE-031 represents a rare case where the official clinical picture is clearer than the usual fog of forum reports and vendor claims.
Stacking and combination considerations
While no clinical data exists for ACE-031 combinations (the compound was never studied alongside other agents), researchers interested in the myostatin pathway often ask about theoretical stacking approaches. Understanding how ACE-031 might interact with other compounds requires considering mechanism-level compatibility.
Theoretical synergies
Growth hormone secretagogues: Compounds like ipamorelin and sermorelin-ipamorelin blends work through an entirely different pathway (GH/IGF-1 axis). Theoretically, combining myostatin inhibition with growth hormone optimization could produce additive or synergistic muscle growth by removing a brake (myostatin) while simultaneously pressing the accelerator (GH/IGF-1). No data exists to confirm this theory.
Healing peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500 promote tissue repair and angiogenesis.
Given that ACE-031 compromises vascular integrity, the angiogenic properties of healing peptides might theoretically offset some vascular concerns. This is purely speculative and has never been studied.
Anti-aging compounds: Epitalon, SS-31, and other longevity peptides target cellular aging mechanisms. The muscle-preserving and bone-building effects of ACE-031 align with anti-aging goals, but the vascular risks conflict with the longevity objective of maintaining cardiovascular health.
Theoretical conflicts
Compounds affecting vascular function: Any compound that influences blood vessel formation, blood pressure, or vascular integrity should be approached with extreme caution alongside ACE-031. The documented BMP9/BMP10 disruption already compromises vascular maintenance. Adding additional vascular stressors could compound the risk.
Compounds affecting TGF-beta pathways: Other compounds that modulate TGF-beta family signaling could create unpredictable interactions with ACE-031. The TGF-beta system is interconnected, and blocking multiple nodes simultaneously could produce effects that neither compound would cause alone.
The practical reality
Given the quality concerns with black market ACE-031 products, the discontinued clinical program, the high cost, and the documented vascular risks, most experienced peptide researchers opt for better-characterized compounds. A well-designed peptide stack using established compounds with known safety profiles typically offers a more favorable risk-to-benefit ratio than experimental myostatin inhibition.
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive protocol guidance, evidence-based stacking recommendations, and community insight from experienced researchers who have navigated these decisions. Members access detailed comparison tools and protocol databases that make informed compound selection straightforward.
Who should care about ACE-031 research
Not every peptide researcher needs to understand ACE-031 in detail. But certain audiences benefit significantly from this knowledge.
Muscle wasting researchers
Anyone studying sarcopenia, cachexia, or muscular dystrophy treatment approaches needs to understand the ACE-031 story. It represents both the promise and the peril of myostatin inhibition as a therapeutic strategy. The clinical data, especially the postmenopausal women trial, provides the strongest evidence available that acute myostatin inhibition can produce rapid, measurable muscle gains in humans.
Body composition researchers
The simultaneous muscle-building, bone-strengthening, and fat-reducing effects of ACE-031 make it a landmark compound for body composition research. Understanding these multi-tissue effects helps researchers evaluate which pathways might achieve similar results with better safety profiles.
The dual-action peptide concept that ACE-031 exemplifies continues to drive research in metabolic health.
Peptide safety researchers
The ACE-031 safety story is a case study in why broad-spectrum compounds carry unpredictable risks. Anyone evaluating peptide safety should understand the BMP9/BMP10 mechanism and how structural similarity between target and off-target proteins can create unexpected adverse effects. These lessons generalize to other compound classes.
Anti-doping researchers
The development of detection methods for myostatin inhibitory peptides, including ACE-031, represents an active area of anti-doping science. Detection methods achieving 3-9 ng/mL sensitivity have been developed, demonstrating that this compound class is detectable in biological samples despite being unavailable as approved pharmaceuticals.
Frequently asked questions
Is ACE-031 still available for research?
ACE-031 is sold by various research chemical vendors, but a major quality study (Reichel, 2025) found that none of 14 tested black market products contained the actual ACVR2B-Fc fusion protein used in clinical trials. The products contained full-length activin receptor 2B instead, which is a different compound. Researchers should approach any "ACE-031" product with significant skepticism about its identity and purity. Third-party testing is essential but may not be able to distinguish ACE-031 from related proteins without sophisticated analytical methods.
What dose of ACE-031 showed the best results in trials?
The 3 mg/kg single subcutaneous dose produced the most significant effects in the Phase 1 trial: 3.3% lean mass increase and 5.1% thigh muscle volume increase within 29 days. Lower doses showed dose-proportional but less impressive effects. The peptide calculator can help determine weight-based amounts, though ACE-031 dosing in mg/kg differs from most peptides dosed in micrograms.
Can ACE-031 be combined with other peptides?
No clinical data exists for ACE-031 combinations with any other compound. The documented vascular side effects (from BMP9/BMP10 disruption) mean that stacking ACE-031 with other compounds carries unknown additional risks. Most researchers focused on muscle growth achieve better risk-adjusted results using established peptide stacking protocols with well-characterized safety profiles.
How does ACE-031 compare to SARMs for muscle building?
ACE-031 and SARMs work through completely different mechanisms. SARMs activate androgen receptors selectively, while ACE-031 removes myostatin-mediated growth inhibition. The muscle growth data for ACE-031 (5.1% thigh volume from a single dose) exceeds what most SARMs achieve over full cycles, but ACE-031 carries unique vascular risks that SARMs do not. SARMs have their own concerns including liver stress and hormonal suppression.
Is ACE-031 the same as ACVR2B?
Not exactly. ACE-031 is a specific fusion protein that combines the extracellular domain of ACVR2B (the activin receptor type IIB) with the Fc region of human IgG1. "ACVR2B" refers to the full-length natural receptor. The Fc fusion design gives ACE-031 an extended half-life and allows it to circulate freely as a soluble decoy receptor. Black market products often contain full-length ACVR2B rather than the engineered ACE-031 fusion protein.
Why was ACE-031 development stopped if it worked so well?
The muscle-building efficacy was never in doubt. ACE-031 clearly works for increasing lean body mass. Development stopped because the compound also trapped BMP9 and BMP10, proteins essential for maintaining healthy blood vessels. This caused nosebleeds, gum bleeding, and visible dilated blood vessels in trial participants. While these effects were not considered dangerous in themselves, regulators and the sponsoring companies could not proceed without understanding and resolving the vascular mechanism. Ultimately, the structural limitation (ACE-031 cannot bind myostatin without also binding BMPs) meant the problem was inherent to the compound design.
Are there better myostatin inhibitors available now?
Bimagrumab, which blocks ActRIIB receptors directly rather than trapping ligands, has shown muscle-building and fat-reducing effects without ACE-031 vascular issues. However, bimagrumab is not commercially available as a peptide and is only studied in clinical trial settings. No currently available research peptide matches ACE-031 clinical data for myostatin pathway muscle building. The field continues to work toward compounds that combine ACE-031 potency with acceptable safety.
Does ACE-031 affect testosterone or other hormones?
In the Phase 1 trial with postmenopausal women, ACE-031 caused a significant drop in FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) levels. The mechanism and full implications of this hormonal effect were not fully characterized before clinical development stopped. Myostatin and related TGF-beta family members interact with reproductive hormones, so hormonal effects are plausible. This is another area where the incomplete clinical program leaves important questions unanswered. Researchers concerned about hormonal effects should review the published trial data (Attie et al., 2013) and consult with testosterone-related peptide information for comparison.
External resources
For researchers serious about understanding the full landscape of muscle-building peptides, SeekPeptides provides comprehensive protocol databases, evidence-based stacking guides, and a community of experienced researchers who have evaluated these compounds firsthand. From beginner guides to advanced protocol optimization, the platform covers every stage of the research journey.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your myostatin stay inhibited, your lean mass stay growing, and your research stay evidence-based.



