Jan 8, 2026

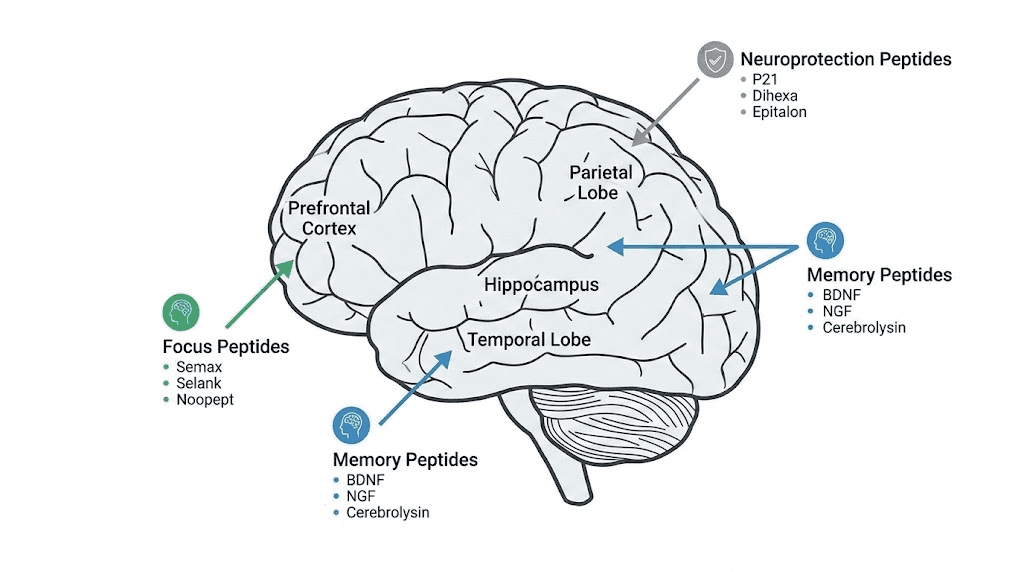
Nootropic peptides demonstrate remarkable capacity for enhancing cognitive function through mechanisms that pharmaceutical nootropics cannot replicate, including direct neurotrophic factor modulation, synaptic plasticity enhancement, and neuroprotective effects that address both immediate cognitive performance and long-term brain health.
Unlike stimulant-based cognitive enhancers that borrow energy from tomorrow to pay for today's focus, peptide nootropics like Semax, Selank, Dihexa, and P21 work by optimizing the brain's underlying neurochemistry and structural integrity, producing sustainable improvements in memory formation, information processing, mental clarity, and cognitive resilience under stress. The research literature documents benefits ranging from enhanced working memory and accelerated learning to protection against age-related cognitive decline and recovery from neurological injury, with several compounds holding regulatory approval for cognitive indications in countries where peptide therapeutics receive more progressive treatment.
This guide covers the complete landscape of cognitive-enhancing peptides including mechanism breakdowns, evidence quality assessments, dosing protocols for different cognitive goals, stacking strategies for synergistic effects, and practical implementation guidance. SeekPeptides provides personalized nootropic peptide protocols tailored to individual cognitive optimization goals.
Understanding nootropic peptides
Nootropic peptides enhance cognitive function through fundamentally different mechanisms than traditional nootropics. Where racetams modulate acetylcholine receptors and stimulants increase catecholamine release, peptide nootropics directly influence neurotrophic factors, neuroplasticity pathways, and neuroprotective mechanisms that determine the brain's structural and functional capacity.
The term nootropic, coined by Romanian psychologist Corneliu Giurgea, originally described compounds that enhance learning and memory while being virtually non-toxic and lacking the pharmacological effects of typical psychotropic drugs. Peptide nootropics often meet these criteria more completely than synthetic nootropics, working with the brain's existing systems rather than forcing unnatural neurochemical states.
Several key mechanisms distinguish peptide nootropics from other cognitive enhancers.
Neurotrophic factor modulation: Peptides like Semax and Dihexa directly influence brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), nerve growth factor (NGF), and other proteins essential for neuron survival, growth, and synaptic plasticity. These factors determine the brain's capacity for learning and memory at the most fundamental level.
Synaptic plasticity enhancement: Rather than temporarily boosting neurotransmitter levels, nootropic peptides enhance the brain's ability to form and strengthen synaptic connections. This produces more durable cognitive improvements that persist beyond the period of active administration.
Neuroprotection: Many nootropic peptides protect neurons against oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, and other damaging processes that accumulate with age. This protective effect supports cognitive maintenance over time rather than just acute enhancement.
Anxiolytic synergy: Several nootropic peptides, particularly Selank, combine cognitive enhancement with anxiety reduction. Since anxiety impairs cognitive function, this dual action produces greater net cognitive improvement than pure nootropics in anxious individuals.
Understanding these mechanisms helps match peptides to specific cognitive goals. Someone seeking pure memory enhancement needs different peptides than someone whose cognitive function suffers from chronic stress and anxiety. Getting started with peptides provides foundational context for newcomers to peptide research.
Semax: the premier cognitive peptide
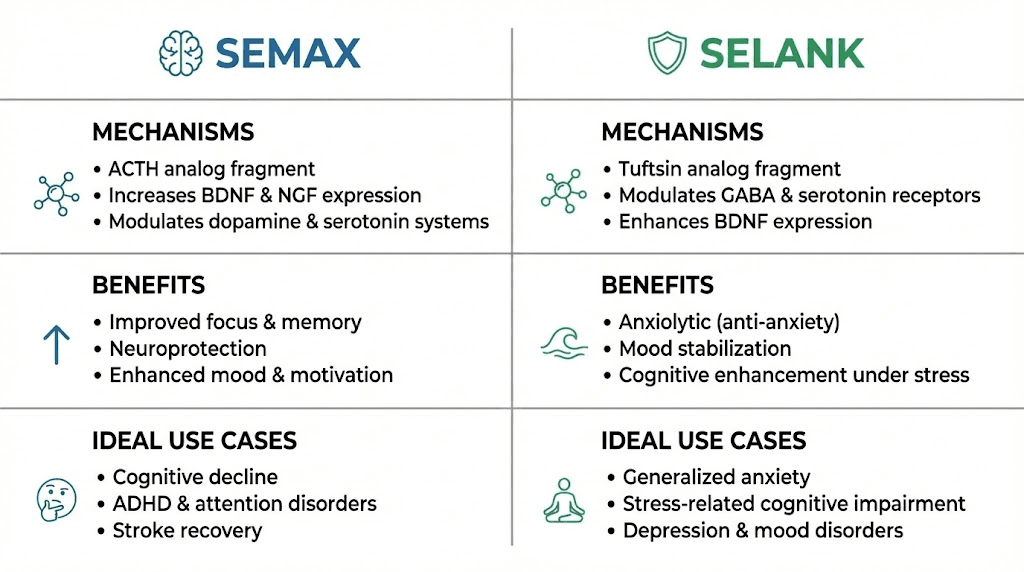
Semax stands as the most extensively researched and widely used nootropic peptide, with decades of clinical application in Russia where it holds regulatory approval for cognitive and neurological indications. Derived from adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) fragment 4-10 with added stabilizing amino acids, Semax demonstrates remarkable cognitive-enhancing properties without the hormonal effects of its parent molecule.
Mechanism of action
Semax works primarily through modulation of neurotrophic factors that determine neuronal health and plasticity. The peptide significantly increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression, particularly in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, regions critical for memory formation and executive function. BDNF elevation supports synaptogenesis, the formation of new synaptic connections that underlies learning and memory.
Beyond BDNF, Semax influences multiple neurotransmitter systems. Dopaminergic activity increases in ways that enhance motivation, focus, and reward processing without the dysregulation associated with stimulant drugs. Serotonergic modulation contributes to mood stability and cognitive flexibility. These neurotransmitter effects complement the neurotrophic mechanisms for comprehensive cognitive enhancement.
Gene expression studies reveal Semax activates transcription of numerous genes involved in neuroplasticity, immune function, and vascular regulation in the brain. This broad genomic influence suggests mechanisms beyond simple receptor activation, potentially explaining the peptide's diverse cognitive and neuroprotective effects.
The peptide also demonstrates significant neuroprotective properties. Research shows Semax protects neurons against oxidative stress, reduces inflammation in neural tissue, and improves cerebral blood flow. These protective effects support both acute cognitive enhancement and long-term brain health maintenance.
Clinical evidence
Russian clinical research provides substantial evidence for Semax's cognitive effects across various populations and conditions.
Healthy cognitive enhancement: Studies in healthy individuals demonstrate improved attention, memory, and information processing following Semax administration. Effects appear within days of starting treatment and accumulate with continued use. Working memory, the cognitive system responsible for temporarily holding information for manipulation, shows particularly consistent improvement.
Stroke recovery: Semax holds approval in Russia for treating ischemic stroke, where it accelerates cognitive and motor recovery. The peptide's neuroprotective effects limit damage during the acute phase while neurotrophic factor modulation supports subsequent recovery and rehabilitation.
Cognitive decline: Research in patients with mild cognitive impairment and early dementia shows Semax slows progression and improves function in some cases. While not curative, the peptide appears to support remaining cognitive capacity and potentially delay advancement to more severe stages.
ADHD and attention: Limited research suggests Semax may benefit attention deficit conditions, though evidence remains preliminary. The dopaminergic modulation and focus enhancement observed in healthy individuals theoretically applies to attention disorders.
Semax dosing protocols
Standard cognitive enhancement:
200-600mcg intranasally, one to three times daily. Most users begin with 200mcg twice daily and adjust based on response. Effects typically appear within 30-60 minutes of administration and persist for 4-6 hours.
Intensive cognitive demands:
600-900mcg daily, divided into two to three doses, during periods requiring peak cognitive performance. This higher dosing suits exam preparation, complex projects, or demanding cognitive work.
Neuroprotection and maintenance:
200-400mcg daily for ongoing cognitive support and brain health maintenance. Lower doses suffice for protective effects without necessarily maximizing acute cognitive enhancement.
Cycling:
Most protocols recommend 2-4 week cycles followed by 1-2 week breaks. Some researchers run Semax continuously at lower doses without apparent tolerance development, though cycling remains the conservative approach.
The Semax peptide dosage guide provides comprehensive dosing information. Intranasal administration offers the most practical delivery method, with the nasal spray peptides guide covering proper technique.
Selank: cognitive enhancement meets anxiolysis
Selank represents a unique nootropic that combines cognitive enhancement with potent anxiolytic effects, making it particularly valuable when anxiety impairs mental performance. Developed from the immunomodulatory peptide tuftsin, Selank demonstrates that anxiety reduction and cognitive enhancement can synergize rather than trade off against each other.
Dual mechanism profile
Selank's cognitive effects stem from multiple mechanisms operating simultaneously. Like Semax, Selank modulates BDNF expression, supporting neuroplasticity and synaptic strengthening. The peptide also influences enkephalin metabolism, affecting endogenous opioid systems in ways that reduce anxiety without sedation or cognitive impairment.
The anxiolytic mechanism involves GABA system modulation, enhancing inhibitory neurotransmission that counteracts excessive anxiety-driven neural activity. Unlike benzodiazepines that cause sedation and cognitive blunting, Selank's GABAergic effects appear more selective, reducing anxiety while preserving and even enhancing cognitive function.
Serotonergic effects contribute to both mood stability and cognitive flexibility. By modulating serotonin systems, Selank supports the mental adaptability necessary for complex problem-solving and creative thinking.
The stress-cognition connection makes Selank particularly valuable. Chronic stress and anxiety demonstrably impair working memory, attention, and executive function through elevated cortisol and altered prefrontal cortex activity. By addressing anxiety directly, Selank removes a major impediment to optimal cognitive function in stressed individuals.
Research evidence
Russian clinical research, where Selank holds approval for anxiety disorders, provides the primary evidence base.
Anxiety with cognitive impairment: Studies show Selank improves both anxiety symptoms and cognitive performance in anxious patients. Memory, attention, and information processing all improve alongside anxiety reduction, suggesting the effects are not simply removing anxiety-induced impairment but actively enhancing underlying cognitive capacity.
Generalized anxiety disorder: Clinical trials demonstrate Selank's efficacy for generalized anxiety comparable to benzodiazepines but without sedation, dependence potential, or cognitive impairment. This makes Selank suitable for situations requiring both anxiety control and mental sharpness.
Healthy individuals under stress: Research in healthy subjects facing stressful cognitive demands shows Selank improves performance compared to placebo. The peptide helps maintain cognitive function under pressure that would otherwise impair performance.
Immune modulation: Selank also demonstrates immunomodulatory effects inherited from its parent peptide tuftsin. While not primarily a cognitive mechanism, immune function influences brain health and cognitive performance, particularly during illness or chronic inflammation.
The peptides for anxiety complete guide covers Selank's anxiolytic mechanisms in greater detail, and the Selank peptide injection dosage guide provides administration specifics.
Selank dosing protocols
Cognitive enhancement with anxiolysis:
200-400mcg per nostril, two to three times daily. Intranasal delivery provides rapid onset suitable for situational use before stressful cognitive demands.
Subcutaneous injection:
250-500mcg daily or every other day for more consistent systemic levels. Some users prefer injection for reliable dosing compared to nasal spray variability.
Acute stress situations:
400-600mcg intranasally 30-60 minutes before anticipated stressful events. This provides acute anxiolysis and cognitive support for presentations, exams, or high-pressure situations.
Cycling:
2-4 week cycles followed by equal break periods prevent potential receptor adaptations. Continuous low-dose use appears tolerated by some users but lacks long-term data.
Dihexa: the potent neurogenic peptide
Dihexa represents one of the most potent cognitive-enhancing compounds ever studied, demonstrating effects at picomolar concentrations that dwarf the potency of traditional nootropics by orders of magnitude. Originally developed for Alzheimer's disease research, Dihexa's remarkable neurogenic properties have attracted significant interest from the cognitive enhancement community despite limited human data.
Mechanism of action
Dihexa works primarily through hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and its receptor c-Met, a signaling system involved in neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and neuroprotection. By potentiating HGF/c-Met signaling, Dihexa dramatically enhances the brain's capacity to form new synaptic connections and potentially new neurons.
The HGF system plays crucial roles in brain development and repair that diminish with age. Dihexa essentially reactivates developmental neuroplasticity mechanisms, potentially explaining its remarkable effects on learning and memory in animal models.
Synaptogenic effects appear particularly pronounced. Research shows Dihexa increases dendritic spine density, the physical structures where synaptic connections form. More spines mean more potential connections, directly expanding the brain's information processing and storage capacity.
The peptide's extraordinary potency, active at concentrations seven orders of magnitude lower than BDNF itself, suggests highly specific receptor interactions rather than broad pharmacological effects. This specificity theoretically supports a favorable safety profile, though human data remains limited.
Research evidence
Animal research provides striking evidence for Dihexa's cognitive effects, though human studies remain scarce.
Animal cognition studies: Rats treated with Dihexa show dramatically improved performance on spatial memory tasks, with some studies suggesting effects comparable to reversing years of age-related cognitive decline. The peptide enhances both acquisition (learning new information) and retention (remembering learned information).
Synaptic density: Microscopy studies confirm increased dendritic spine density in Dihexa-treated animals, providing structural evidence for the observed cognitive improvements. More connections correlate with better memory and learning capacity.
Alzheimer's models: Research in Alzheimer's disease animal models shows Dihexa can reverse cognitive deficits even after significant disease progression. This recovery of lost function distinguishes Dihexa from compounds that merely slow decline.
Human evidence: Limited anecdotal reports from human users describe significant cognitive enhancement, particularly in memory formation and recall. However, controlled human trials have not been published, making evidence quality substantially lower than for Semax or Selank.
Dihexa considerations
Dosing:
Typical research doses range from 0.5-2mg daily, administered orally or subcutaneously. The peptide's extreme potency means even small doses produce significant effects. Most users start at the lower end and assess response before increasing.
Duration:
Short cycles of 2-4 weeks with extended breaks represent the conservative approach given limited safety data. The potentially permanent synaptic changes Dihexa induces warrant caution about extended use.
Cautions:
Limited human safety data means Dihexa carries more uncertainty than well-studied peptides. Theoretical concerns about excessive neuroplasticity or uncontrolled growth factor signaling remain unresolved. Users should approach Dihexa more cautiously than compounds with established safety profiles.
The peptide's potent effects on growth factor signaling theoretically raise concerns about interactions with cancer biology, though no direct evidence supports this concern. Individuals with cancer history may wish to avoid HGF-modulating compounds out of caution.
P21: targeted neurogenesis
P21, also known as Cerebrolysin-derived peptide, represents a small peptide fragment designed to replicate the neurotrophic effects of the complex Cerebrolysin mixture in a defined, single-peptide format. P21 specifically targets mechanisms of neurogenesis and neuroplasticity with a cleaner pharmacological profile than the multi-peptide Cerebrolysin.
Mechanism of action
P21 enhances BDNF signaling and promotes neurogenesis in the hippocampus, the brain region most critical for memory formation. The peptide increases the production of new neurons in the dentate gyrus, a phenomenon once thought impossible in adult brains but now recognized as ongoing throughout life at varying rates.
The peptide also inhibits glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3β), an enzyme implicated in various neurodegenerative processes. GSK-3β inhibition supports neuronal survival and may contribute to P21's antidepressant-like effects observed in animal models.
Synaptogenic effects complement neurogenic activity. P21 promotes the formation and strengthening of synaptic connections, enhancing the brain's capacity for learning and memory through structural changes rather than temporary neurochemical modulation.
Research evidence
Animal cognition: Rodent studies demonstrate P21 enhances performance on memory tasks, particularly those involving hippocampal function. Spatial memory and contextual memory both improve following P21 administration.
Neurogenesis quantification: Histological studies confirm increased neurogenesis in P21-treated animals, validating the proposed mechanism. More new neurons correlate with better memory performance in these studies.
Depression models: P21 shows antidepressant-like effects in animal models of depression, potentially through neurogenesis enhancement and GSK-3β inhibition. Depression involves hippocampal volume reduction that neurogenesis-promoting compounds may help address.
Human evidence: Like Dihexa, human evidence remains limited to anecdotal reports. Users describe improvements in memory, mood, and overall cognitive function, but controlled trials are lacking.
P21 dosing
Standard protocol:
1-2mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously daily for 2-4 weeks. Some protocols use every-other-day dosing to reduce injection frequency while maintaining effects.
Cycling:
4-week cycles followed by 4-8 week breaks allow assessment of lasting effects and prevent potential receptor adaptations. The neurogenic changes P21 induces may persist beyond the treatment period.
Cerebrolysin: the complex mixture
Cerebrolysin consists of low-molecular-weight peptides and amino acids derived from porcine brain tissue, representing a complex mixture rather than a single defined peptide. Despite this complexity, Cerebrolysin has accumulated substantial clinical evidence for cognitive and neurological applications, particularly in stroke recovery and dementia treatment.
Mechanism and evidence
Cerebrolysin's effects arise from multiple peptide components acting on various neurotrophic pathways. The mixture includes peptide fragments that mimic or enhance BDNF, NGF, and other growth factors, producing broad neurotrophic support.
Stroke recovery: Multiple clinical trials demonstrate Cerebrolysin accelerates cognitive and motor recovery following stroke. The peptide mixture appears particularly effective when administered early after stroke onset, limiting damage and supporting subsequent recovery.
Alzheimer's disease: Clinical evidence suggests modest benefits for Alzheimer's patients, with some trials showing slowed cognitive decline and improved function. Effects appear more pronounced in earlier disease stages.
Traumatic brain injury: Research supports Cerebrolysin use in TBI recovery, where neurotrophic support aids healing and functional restoration.
Healthy cognition: Limited research in healthy individuals suggests cognitive enhancement, though less evidence exists for this application than for neurological conditions.
Administration
Cerebrolysin requires intramuscular or intravenous injection, typically 5-30ml depending on indication. Treatment protocols often involve daily injections for 10-20 days, repeated as needed. The complexity and injection requirements make Cerebrolysin less practical than intranasal peptides for casual cognitive enhancement.
Pinealon: the pineal peptide
Pinealon represents a tripeptide (Glu-Asp-Arg) derived from pineal gland research, demonstrating effects on circadian rhythm regulation, neuroprotection, and cognitive function. As part of the Khavinson peptide family developed in Russia, Pinealon offers a short-peptide approach to brain optimization focusing on the pineal gland's regulatory functions.
Mechanism and effects
Pinealon influences gene expression related to circadian rhythm and melatonin synthesis, potentially optimizing sleep-wake cycles that profoundly impact cognitive function. Quality sleep represents one of the most powerful cognitive enhancers, and compounds that improve sleep architecture indirectly enhance daytime cognition.
Neuroprotective effects appear through antioxidant activity and gene expression modulation in neural tissues. The peptide may protect against age-related oxidative damage that contributes to cognitive decline.
Direct cognitive effects include improved memory and information processing in some studies, though evidence remains less robust than for Semax or Selank. The cognitive benefits may arise partly from improved sleep rather than direct nootropic mechanisms.
Pinealon applications
Sleep optimization:
100-200mcg daily, particularly in the evening, may support circadian rhythm regulation and sleep quality. Better sleep translates to improved next-day cognitive function.
Neuroprotection:
100-200mcg daily for ongoing brain health support, particularly in older individuals or those with oxidative stress concerns.
Cognitive enhancement:
Higher doses up to 400mcg daily may provide more direct cognitive effects, though individual response varies.
The Pinealon peptide benefits article covers this peptide in greater detail.
BPC-157: the gut-brain connection
While primarily known for tissue healing, BPC-157 demonstrates significant effects on the brain through the gut-brain axis and direct neuroprotective mechanisms. This body protection compound offers cognitive benefits as part of its broader systemic effects.
Cognitive mechanisms
The gut-brain axis connects intestinal health directly to brain function through neural, hormonal, and immune pathways. BPC-157's profound gut-healing effects support this connection, potentially improving cognitive function through enhanced gut health and reduced systemic inflammation.
Direct neuroprotective effects include protection against various neurotoxic insults and support for dopaminergic systems. Research shows BPC-157 protects against dopamine system damage from various sources, potentially supporting the dopaminergic activity essential for motivation, focus, and reward processing.
Serotonin system modulation also occurs with BPC-157, affecting mood regulation and cognitive flexibility. The peptide's effects on both dopamine and serotonin systems suggest broad neuromodulatory activity beyond simple tissue healing.
BPC-157 for cognitive support
Gut-brain optimization:
Standard BPC-157 dosing of 250-500mcg twice daily supports both gut health and the gut-brain connection. Oral administration may particularly benefit gut-focused effects.
Neuroprotection:
The same dosing protocol provides neuroprotective effects, particularly valuable when cognitive function may be threatened by stress, toxins, or other damaging factors.
Combination with nootropic peptides:
BPC-157 combines well with primary nootropic peptides, providing complementary neuroprotection and gut-brain support. The peptide stack calculator helps plan multi-peptide protocols.
The BPC-157 vs TB-500 comparison covers healing peptide selection, while the peptides for gut health page details intestinal applications.
Comparison: nootropic peptide selection guide
Different cognitive goals benefit from different peptide selections. This comparison helps match peptides to specific needs.
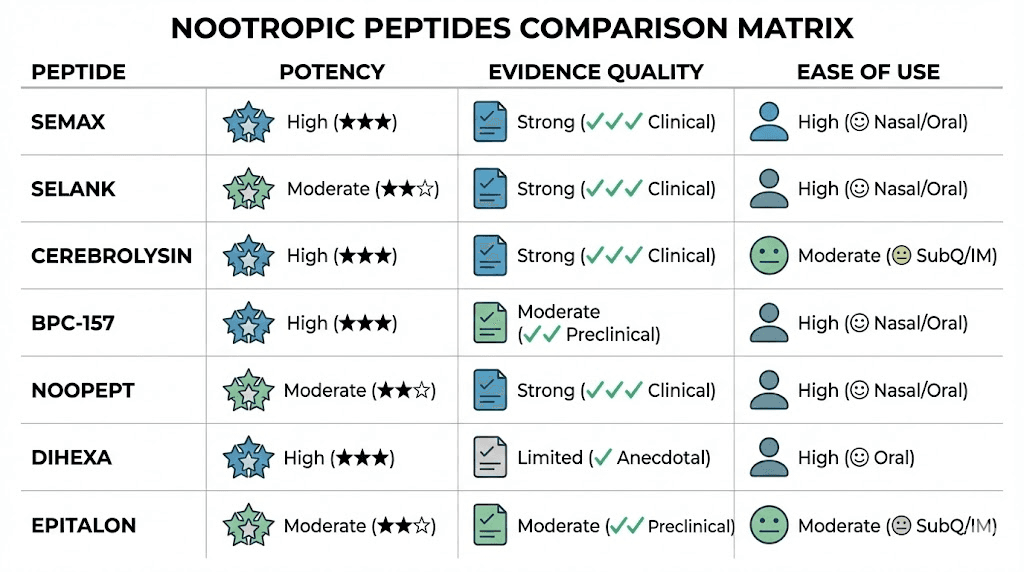
Peptide | Primary Effect | Best For | Evidence Quality | Administration | Potency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Semax | BDNF enhancement, focus | General cognitive enhancement | Strong clinical | Intranasal | Moderate |
Selank | Anxiolysis + cognition | Stress-impaired cognition | Strong clinical | Intranasal/SC | Moderate |
Dihexa | HGF/synaptogenesis | Memory enhancement | Strong preclinical | Oral/SC | Extreme |
P21 | Neurogenesis | Memory, mood | Moderate preclinical | SC/IM | High |
Cerebrolysin | Multi-neurotrophic | Neurological recovery | Strong clinical | IM/IV | Moderate |
Pinealon | Circadian/neuroprotection | Sleep-cognition link | Moderate clinical | Oral/SC | Low |
BPC-157 | Gut-brain, neuroprotection | Systemic support | Strong preclinical | Oral/SC | Moderate |
Evidence quality ratings consider both research quantity and accessibility. "Clinical" indicates human trials, "preclinical" indicates primarily animal research.
Nootropic peptide protocols by goal
Specific cognitive goals benefit from tailored peptide combinations and dosing strategies.
Protocol 1: general cognitive enhancement
Goal: Improve overall cognitive function in healthy individuals
Primary peptide: Semax 300-600mcg intranasally twice daily
Supporting peptide: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily for neuroprotection and gut-brain support
Duration: 4-week cycles with 2-week breaks
Expected outcomes:
Week 1: Improved focus and mental clarity
Week 2-3: Enhanced memory and learning speed
Week 4: Peak cognitive enhancement, assess for cycling
Cost estimate: $100-200/month
Protocol 2: stress and anxiety-impaired cognition
Goal: Restore cognitive function impaired by chronic stress or anxiety
Primary peptide: Selank 400mcg intranasally two to three times daily
Supporting peptide: Semax 200mcg twice daily for additional cognitive boost
Gut-brain support: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily
Duration: 4-week cycles with 2-week breaks
Expected outcomes:
Week 1: Reduced anxiety, improved mental calm
Week 2-3: Cognitive function restoration as anxiety diminishes
Week 4: Optimal anxiety-cognition balance achieved
Cost estimate: $150-250/month
Protocol 3: memory enhancement focus
Goal: Maximize memory formation and recall
Primary peptide: Dihexa 1mg daily (oral or SC)
Supporting peptide: Semax 400mcg intranasally twice daily
Duration: 2-3 week cycles with 4-week breaks (conservative approach for Dihexa)
Expected outcomes:
Week 1: Subtle improvements in information retention
Week 2-3: Significant enhancement of memory formation and recall
Post-cycle: Some benefits may persist due to synaptic changes
Cautions: Limited human safety data for Dihexa warrants conservative approach
Cost estimate: $150-300/month
Protocol 4: neuroprotection and longevity
Goal: Protect cognitive function over time, slow age-related decline
Primary peptide: Semax 200-400mcg daily
Sleep support: Pinealon 200mcg daily in evening
Gut-brain: BPC-157 250mcg twice daily
Optional: Epithalon cycles for telomere support
Duration: Ongoing with periodic cycling of individual components
Expected outcomes:
Month 1-3: Cognitive maintenance, improved sleep quality
Month 3-6: Sustained cognitive function, reduced age-related concerns
Long-term: Preserved cognitive capacity compared to unprotected aging
Cost estimate: $150-300/month
The peptides for anti-aging page covers comprehensive longevity protocols.
Protocol 5: neurological recovery support
Goal: Support recovery from TBI, stroke, or other neurological injury
Primary peptide: Cerebrolysin 10-20ml IM daily for 10-20 days (requires medical supervision)
Alternatively: Semax 600-900mcg daily if Cerebrolysin unavailable
Supporting peptide: BPC-157 500mcg twice daily for tissue healing
Duration: Acute phase treatment, may repeat cycles as recovery progresses
Considerations: Neurological injury recovery should involve medical supervision. Peptides support but don't replace appropriate medical care.
Cost estimate: Variable depending on Cerebrolysin access
Stacking nootropic peptides
Combining nootropic peptides can produce synergistic effects exceeding individual compound benefits. Strategic stacking addresses multiple cognitive mechanisms simultaneously.
Synergistic combinations
Semax + Selank: The classic nootropic peptide stack combines pure cognitive enhancement with anxiolytic support. This combination suits individuals who experience both focus issues and anxiety, addressing both simultaneously. The peptides work through complementary mechanisms without competition.
Semax + BPC-157: Combines direct cognitive enhancement with neuroprotection and gut-brain support. BPC-157's systemic benefits complement Semax's targeted nootropic effects for comprehensive brain optimization.
Dihexa + Semax: Stacks the potent synaptogenic effects of Dihexa with Semax's BDNF modulation for maximum neuroplasticity enhancement. This powerful combination suits those seeking dramatic memory improvement but requires caution given Dihexa's limited human safety data.
Selank + Pinealon: Combines daytime anxiolysis and cognition with nighttime sleep optimization. Better sleep enhances next-day cognitive function while Selank handles stress-induced cognitive impairment.
Stacking principles
Start with one peptide to establish baseline response before adding others. This allows identification of individual effects and any adverse reactions. Add new peptides one at a time, waiting at least one week between additions.
Consider mechanism overlap when stacking. Peptides affecting similar pathways may produce diminishing returns rather than synergy. Peptides affecting different mechanisms typically combine more effectively.
Track effects systematically when running stacks. Subjective cognitive assessment, reaction time tests, memory exercises, and mood tracking help quantify stack effectiveness. The peptide stacking guide covers general stacking principles.
Safety considerations
Nootropic peptides generally demonstrate favorable safety profiles, but informed use requires understanding potential risks and appropriate precautions.
General safety principles
Start low: Begin with minimum effective doses and increase gradually based on response. Individual sensitivity varies significantly, and starting low identifies optimal personal dosing.
Cycle appropriately: Most nootropic peptides benefit from cycling to prevent receptor adaptations and allow system normalization. Typical patterns involve 2-4 week active periods followed by 1-4 week breaks.
Monitor response: Track both positive effects and any adverse reactions. Discontinue if concerning effects appear and resume at lower doses if appropriate.
Quality sourcing: Peptide quality significantly affects both effectiveness and safety. Source from reputable vendors with third-party testing. The best peptide vendors guide evaluates sources, and learning to read peptide testing results supports quality verification.
Compound-specific considerations
Semax: Generally well-tolerated with minimal reported side effects. Some users report transient irritability at high doses. Theoretical concerns about cortisol modulation remain largely unsubstantiated in practice.
Selank: Excellent safety profile with regulatory approval backing. Sedation is uncommon despite GABAergic activity. May potentiate other GABAergic compounds.
Dihexa: Limited human safety data warrants particular caution. Theoretical concerns about growth factor modulation include potential interactions with cancer biology, though unsubstantiated. Conservative dosing and cycling recommended.
P21: Limited safety data similar to Dihexa. Conservative approach advised pending more human research.
Cerebrolysin: Extensive clinical use provides substantial safety data. Injection site reactions represent the most common adverse effect. Requires appropriate injection technique.
Contraindications
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Insufficient safety data for any nootropic peptides during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Avoid unless specifically cleared by healthcare providers.
Seizure disorders: Compounds affecting neuroplasticity and excitability theoretically warrant caution in seizure-prone individuals. Consult neurologists before use.
Cancer history: Growth factor-modulating peptides like Dihexa may warrant avoidance in those with cancer history, though evidence for concern remains theoretical.
The peptide safety and risks guide covers general peptide safety principles.
Practical implementation
Successful nootropic peptide use requires attention to administration, storage, and assessment practices.
Administration methods
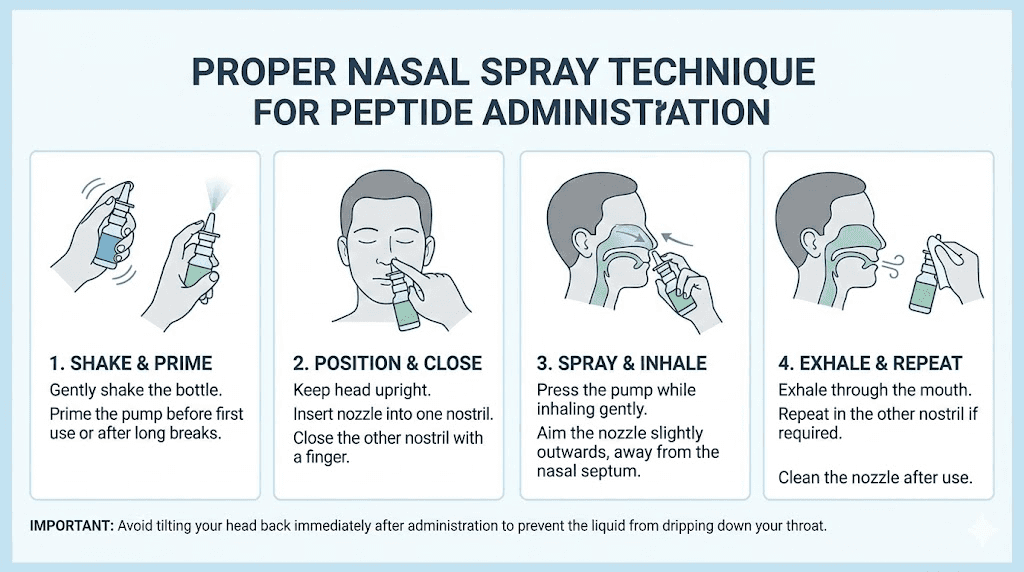
Intranasal: Semax, Selank, and some other peptides work effectively via nasal spray. This method provides rapid absorption and convenient dosing. The nasal spray peptides guide covers proper technique.
Subcutaneous injection: Provides reliable dosing and consistent absorption. Required for some peptides and preferred by some users for others. The peptide injections guide covers proper technique.
Oral: Some peptides like Dihexa demonstrate oral bioavailability. Convenience favors oral dosing when effective for the compound in question.
Storage and reconstitution
Proper storage maintains peptide potency and safety. Most peptides require refrigeration before reconstitution and after. The peptide storage guide covers proper handling.
Reconstitution with bacteriostatic water prepares lyophilized peptides for injection. The peptide reconstitution calculator determines proper dilution, and the bacteriostatic water guide covers appropriate diluents. The reconstituted peptide storage guide addresses post-reconstitution handling.
Tracking cognitive effects
Subjective assessment provides useful but limited information. Consider supplementing with:
Reaction time testing through various apps and websites
Memory exercises like n-back training with performance tracking
Mood and energy journals capturing daily patterns
Work output metrics when applicable
Objective measures help distinguish genuine cognitive enhancement from placebo effects or wishful thinking.
Lifestyle factors for cognitive optimization
Peptides work within the context of overall brain health practices. Optimizing lifestyle factors enhances nootropic peptide results.
Sleep optimization
Sleep represents the brain's maintenance period when memories consolidate, toxins clear, and neural systems restore. No nootropic can compensate for chronic sleep deprivation. Prioritize 7-9 hours of quality sleep to maximize peptide benefits.
Pinealon and Selank may improve sleep quality as part of their effects, but external sleep hygiene remains essential. Consistent schedules, dark sleeping environments, and screen limitation before bed support the sleep quality that underlies cognitive performance.
Exercise for brain health
Physical exercise increases BDNF more reliably than almost any other intervention. Combining exercise with nootropic peptides that also enhance BDNF creates synergistic neuroplasticity support.
Both cardiovascular exercise and resistance training benefit brain health through different mechanisms. The peptides for athletic performance page covers exercise-peptide optimization.
Nutrition and supplementation
The brain requires adequate omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, antioxidants, and various minerals for optimal function. Nutritional deficiencies impair cognition regardless of peptide use.
Consider foundational supplements like fish oil, B-complex, and magnesium alongside nootropic peptides. These address common deficiencies that limit cognitive capacity.
Stress management
Chronic stress impairs cognitive function through elevated cortisol and altered prefrontal cortex activity. While Selank addresses stress directly, external stress management practices complement any nootropic protocol.
Meditation, social connection, nature exposure, and adequate rest all reduce stress load and support cognitive function.
Frequently asked questions
How quickly do nootropic peptides work?
Most users notice effects within days to weeks. Semax and Selank often show effects within the first week. More structurally-focused peptides like Dihexa may take 2-4 weeks for full effects as synaptic changes develop. Neuroprotective benefits accumulate over months of use.
Are nootropic peptides addictive?
Nootropic peptides do not produce the dopamine surges associated with addictive substances. They lack the dependence potential of stimulants or benzodiazepines. Users can discontinue without withdrawal symptoms, though cognitive benefits may diminish after stopping.
Can I combine nootropic peptides with other nootropics?
Many users combine peptides with racetams, modafinil, or other nootropics. Consider mechanism overlap and start combinations cautiously. Some combinations may synergize while others offer diminishing returns or potential interactions.
Are nootropic peptides legal?
Legality varies by jurisdiction and compound. Most nootropic peptides are legal to possess for research purposes in many countries but may not be approved for human consumption. The peptide legality guide covers regulatory considerations.
How do nootropic peptides compare to prescription medications like Adderall?
Peptides work through fundamentally different mechanisms than stimulant medications. Stimulants produce acute, powerful focus enhancement through catecholamine release but carry dependence risk and side effects. Peptides offer more sustainable, moderate enhancement through neuroplasticity support without stimulant side effects.
Can nootropic peptides help with ADHD?
Limited research exists specifically for ADHD applications. The focus and attention enhancement observed with Semax theoretically applies, but clinical evidence for this indication remains minimal. ADHD treatment should involve healthcare providers.
How SeekPeptides supports cognitive optimization
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for navigating nootropic peptide research with confidence and clarity.
Personalized protocol guidance helps match cognitive goals with appropriate peptide selections. The complex landscape of nootropic peptides benefits from structured approaches tailored to individual situations and objectives.
Educational resources including dosage guides, mechanism explanations, and research summaries build understanding necessary for informed decisions about cognitive enhancement.
Dosing tools including the peptide calculator, reconstitution calculator, and cost calculator support practical implementation of nootropic protocols.
SeekPeptides remains committed to evidence-based guidance for cognitive optimization through peptide research.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your cognition stay sharp, your focus stay clear, and your memory stay strong. Join SeekPeptides, now.