Jan 3, 2026

Chonluten (also spelled Honluten or Khonluten) represents a Russian bioregulator peptide specifically targeting respiratory system optimization through short peptide sequences extracted from lung and bronchial tissues. Unlike Western synthetic peptides like BPC-157 or semaglutide that target specific receptors, Russian bioregulators propose organ-specific cellular communication supporting function optimization, repair processes, and age-related decline reversal.
The bioregulator approach developed through Soviet-era research proposes that short peptide sequences (typically 2-4 amino acids) extracted from healthy young animal organs can communicate with corresponding human tissues, promoting cellular optimization. Chonluten specifically targets lung tissue, bronchial mucosa, and respiratory epithelium for applications including COPD support, asthma management, post-viral respiratory recovery, smoking-related damage, and general respiratory optimization.
Russian bioregulator studies rarely meet Western randomized controlled trial standards, creating evaluation challenges for users accustomed to conventional pharmaceutical research.
This guide examines Chonluten through available evidence, realistic benefits assessment, dosing protocols, safety considerations, and honest comparison to Western alternatives helping determine whether this bioregulator represents legitimate respiratory support or insufficiently-validated experimental intervention.
Russian bioregulator background
What makes bioregulators different
Core bioregulator theory:
Short peptides (2-4 amino acids typically)
Extracted from healthy young animal organs
Provide organ-specific regulatory signals
Support cellular function optimization
Target corresponding human tissues
Development history:
Soviet-era research 1970s-1990s
Professor Vladimir Khavinson led development
St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology
Military and longevity applications initially
Continued in modern Russia
Mechanism proposed:
Peptides communicate with cell DNA
Influence gene expression patterns
Support protein synthesis optimization
Restore age-related cellular decline
Organ-specific targeting claimed
Different from Western peptides:
Western: Synthetic compounds, receptor-specific
Bioregulators: Natural extracts, cellular communication
Western: Single mechanism understood
Bioregulators: Multi-level regulation proposed
Evidence standards: Western RCTs vs Russian observational
Learn about what peptides are and how they work.
Chonluten-specific characteristics
Organ targeting:
Source tissue: Lung/bronchial (young animals)
Target human tissue: Respiratory system
Specific effects: Lung, bronchi, respiratory epithelium
Application: Respiratory health optimization
Related bioregulators: Each targets different organs
Other bioregulators for comparison:
Epitalon: Pineal gland, longevity
Cartalax: Cartilage, joint health
Vesugen: Vascular system
Ovagen: Liver, digestive system
Chonluten: Respiratory system
Each designed for specific organ optimization
Theoretical advantages:
Natural tissue-derived (not synthetic)
Organ-specific targeting
Multiple regulatory pathways
Cellular-level optimization
Age-related decline reversal claimed
Respiratory applications and uses
What Chonluten targets.
Primary respiratory conditions
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD):
Adjunct therapy for COPD management
May support lung tissue function
Could slow progression (claimed)
Not replacement for medical treatment
Russian research shows benefit
COPD protocol approach:
Continue all prescribed medications
Add Chonluten as supportive therapy
Monitor lung function parameters
Medical supervision recommended
Realistic expectations required
Asthma management:
Bronchial hyperreactivity support
Mucosal inflammation modulation
Respiratory epithelium optimization
Adjunct to conventional asthma treatment
Preliminary evidence exists
Asthma application:
Not rescue inhaler replacement
Long-term optimization focus
May reduce attack frequency (anecdotal)
Continues controller medications
Supportive role only
Post-viral respiratory recovery:
Post-COVID lung complications
Viral pneumonia recovery support
Respiratory infection aftermath
Tissue repair promotion claimed
Growing interest in this application
Post-viral protocol:
After acute infection resolves
Support recovery phase
Tissue regeneration focus
2-3 month timeline typical
Medical clearance recommended
Additional respiratory applications
Smoking-related lung damage:
Chronic smoker tissue damage
Emphysema supportive therapy
Bronchial irritation reduction
Tissue regeneration support claimed
Preventive application possible
Smoking damage approach:
Ideally combined with smoking cessation
Damage mitigation if can't quit
Long-term tissue support
Realistic expectations critical
Not miracle cure for smoking
Age-related respiratory decline:
Natural lung capacity decrease with aging
Epithelial tissue aging processes
Reduced respiratory efficiency
Preventive optimization approach
Longevity application focus
Aging prevention protocol:
Starting 40-50+ years old
2-3 cycles annually maintenance
Preventive rather than therapeutic
Long-term health optimization
Benefits difficult to measure
Exercise performance optimization:
Enhanced oxygen delivery claimed
Improved respiratory efficiency
Better endurance performance
Athletic application interest
Limited evidence for this use
See peptide safety and risks for general safety information.
Available research and evidence
What studies actually show.
Russian research summary
Published Russian studies:
Multiple Russian-language papers available
Primarily from Khavinson institute
Small sample sizes (20-100 participants typical)
Observational studies predominantly
Positive results claimed consistently
Study design characteristics:
Not randomized controlled trials mostly
Before-after comparisons common
No placebo control often
Subjective measurements included
Objective parameters sometimes
Claimed benefits from Russian research:
Improved lung function test parameters
Reduced respiratory symptoms reported
Enhanced exercise tolerance measured
Better quality of life scores
Tissue regeneration markers improved
Specific findings examples:
FEV1 improvement 10-15% (claimed)
Reduced dyspnea scores
Fewer exacerbations reported
Better 6-minute walk test
Improved quality of life questionnaires
Study quality concerns:
Publication bias likely (positive results published)
Small sample sizes limit generalizability
Lack of independent replication
Translation accuracy questions
Conflict of interest (institute produces product)
Western evidence gap
Western research status:
Very limited English-language studies
Mostly case reports if anything
No major randomized controlled trials
Mechanism not validated Western science
Skepticism warranted from Western perspective
Why Western validation lacking:
Patent/profit incentive minimal (natural extract)
Language barrier limits access
Different research paradigm
Western focus on synthetic compounds
Bioregulator theory not mainstream
The evidence quality problem:
Russian research positive but limited quality
Western validation essentially absent
Mechanism unclear by Western standards
User testimonials mixed and unreliable
Evidence quality: Low by Western RCT standards
What would constitute good evidence:
Large randomized controlled trials
Placebo-controlled double-blind design
Independent replication by Western labs
Mechanistic studies explaining pathway
Publication in high-impact journals
None of this exists for Chonluten
Anecdotal user reports
What users self-report:
Some breathing improvement noted
Reduced respiratory symptoms claimed
Better exercise tolerance reported (some)
Effects described as subtle not dramatic
Highly variable individual responses
Positive anecdotal reports:
"Breathing easier after 2-month cycle"
"Fewer asthma attacks noticed"
"Post-COVID recovery seemed faster"
"Less shortness of breath climbing stairs"
Subjective improvements primarily
Neutral/negative reports:
"Didn't notice any difference honestly"
"Hard to tell if working or placebo"
"Expected more based on claims"
"Too subtle to confirm effect"
No effect reported by some
Anecdotal evidence problems:
Placebo effect very powerful respiratory
Subjective assessment unreliable
Natural improvement over time
Confirmation bias (want it to work)
Cannot draw conclusions from anecdotes
User feedback reality:
Mixed reports typical
Some enthusiastic testimonials
Many report nothing noticeable
Few report negative effects
Variable responses suggest placebo role
See peptide research and studies for evidence evaluation guidance.
Dosing protocols and administration
How Chonluten is used.
Standard Russian dosing protocol
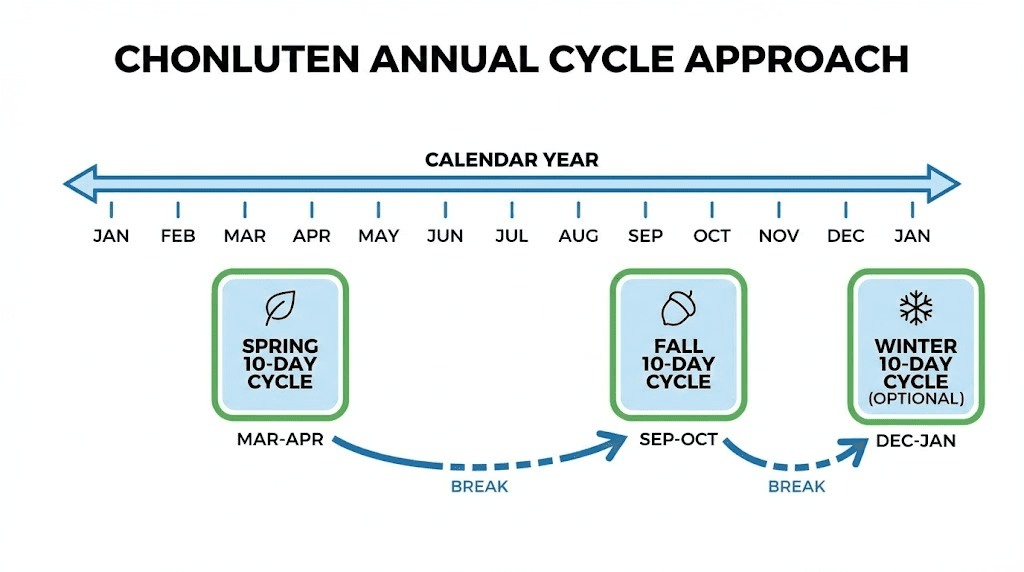
Typical cycle structure:
10-20 capsules per cycle (10mg each usually)
10-20 days continuous dosing
2-3 cycles per year recommended
Break periods between cycles
Maintenance approach long-term
Common dosing schedule:
Days 1-10: One 10mg capsule daily
Break: 2-6 months off
Repeat cycle 2-3 times annually
Spring and fall timing popular
Flexible scheduling acceptable
Dosing rationale:
Bioregulatory signals provided cyclically
Body continues optimization during break
Don't need continuous dosing
Cost-effective approach
Russian protocol tradition
Administration routes
Oral capsules (most common):
Convenient administration
Take on empty stomach preferred
Morning dosing typical
Bioavailability lower than injection
Most user-friendly option
Sublingual administration:
Under tongue absorption
Better bioavailability than swallowing
Hold 1-2 minutes before swallowing
Slightly less convenient
Some users prefer this method
Subcutaneous injection:
Highest bioavailability claimed
Requires reconstitution skills
Similar to other peptide injections
More complex than oral
Used by experienced peptide users
Route comparison:
Oral: Easiest, lowest bioavailability
Sublingual: Moderate both dimensions
Injection: Hardest, highest bioavailability
Most choose oral for convenience
Cycle frequency and timing
Annual cycle recommendations:
2-3 cycles per year standard
Spring cycle: March-April
Fall cycle: September-October
Optional winter cycle: December-January
Flexible based on needs
Timing rationale:
Seasonal respiratory challenges
Preventive before cold/flu season
After illness recovery support
Personal health optimization schedule
No strict timing required
Long-term approach:
Maintenance strategy years-long
Not acute treatment approach
Preventive health optimization
Cumulative benefits proposed
Patience required for assessment
Use peptide calculator for protocol planning.
Realistic benefits expectations
What you might actually experience.
Likely outcomes for different conditions
COPD patients:
Subtle lung function improvement possible
May reduce exacerbation frequency (unproven)
Could improve exercise tolerance slightly
Symptom reduction variable
Not replacement for medical management
Realistic expectation: Modest supportive benefit if any
Asthma management:
May reduce attack frequency (anecdotal)
Bronchial hyperreactivity modulation claimed
Continue all controller medications
Rescue inhaler still needed
Realistic expectation: Possible reduction in symptoms
Post-viral recovery:
Tissue repair support theoretical
Recovery timeline may shorten (unproven)
Symptom improvement possible
Most recover naturally anyway
Hard to attribute improvement
Realistic expectation: Uncertain added benefit
Smoking damage:
Cannot reverse established damage
May slow progression (unproven)
Best combined with cessation
Tissue support theoretical
Realistic expectation: Minimal proven benefit
Age-related decline:
Preventive benefits unverifiable
May slow lung aging (claimed)
Effects too subtle to measure
Long-term commitment required
Realistic expectation: Unknown, possibly placebo
Who might benefit most
Best candidates:
Mild to moderate respiratory issues
Seeking complementary approaches
Under medical supervision
Realistic expectations maintained
Patient for subtle effects
Already tried conventional options
Characteristics of potential responders:
Open to alternative approaches
Comfortable with uncertain evidence
Can afford experimental therapy
Not severely ill (medical care priority)
Health optimization mindset
Long-term perspective
Who probably won't benefit:
Severe respiratory disease (needs proven treatments)
Expecting dramatic rapid improvement
Unwilling to maintain medical care
Very skeptical mindset (placebo less likely)
Acute respiratory distress (emergency care needed)
Short-term quick-fix mentality
Timeframe for potential results
Typical progression reported:
Weeks 1-2: Usually nothing noticeable
Weeks 3-4: Some may notice subtle changes
Months 2-3: Maximum effects if working
Months 3-6: Maintenance of benefits
Long-term: Cumulative effects proposed
Important timeline notes:
Effects develop slowly if at all
Most improvement subjective
Difficult to separate from natural variation
Placebo effect powerful early on
Patience absolutely required
Expect subtle gradual changes only
Measurement challenges:
Lung function tests: Objective but variable
Symptom scales: Subjective and biased
Exercise tolerance: Many confounding factors
Quality of life: Hard to attribute
Proving effect very difficult
Safety profile and side effects
What to watch for.
General safety assessment
Overall safety profile:
Bioregulators generally well-tolerated
Low toxicity in Russian studies
Minimal side effects reported typically
Long-term safety data limited
No major safety signals identified
Appears relatively safe overall
Why considered safe:
Natural tissue-derived peptides
Short amino acid sequences
Low doses used
Decades of Russian use
No serious adverse events reported widely
Similar safety to other bioregulators
Safety limitations:
Long-term Western studies absent
Manufacturing quality variable
Purity concerns possible
Allergic reactions theoretically possible
Individual responses vary
Safety assumed not proven
Reported side effects
Common side effects (rare even these):
Mild digestive upset (if oral)
Nausea occasionally
Injection site reactions (if injecting)
Usually resolve quickly
Most users report zero side effects
Side effect profile: Very minimal
Uncommon reactions:
Allergic responses (very rare)
Skin reactions possible
Headache mentioned occasionally
Hard to confirm causation
May be unrelated to peptide
Serious reactions extremely rare
What to monitor:
Any unusual respiratory symptoms
Allergic reaction signs
Worsening of existing conditions
New symptoms developing
General wellbeing changes
Report concerns to doctor
Contraindications and precautions
Who should avoid:
Pregnancy and breastfeeding (no safety data)
Active respiratory infections (wait until resolved)
Severe uncontrolled disease (medical focus first)
Known allergies to animal proteins
Children (no pediatric data)
Consult doctor if unsure
Medical supervision recommended:
Existing respiratory disease
Taking multiple medications
Chronic health conditions
Monitoring lung function
Adjusting conventional treatments
Never replace medical care
Drug interactions:
Unknown interaction potential
Inform doctor about all supplements
Monitor closely if on medications
Bioregulators poorly studied for interactions
Conservative approach warranted
Medical supervision important
See comprehensive peptide safety and risks guide.
Comparing to alternative approaches
Chonluten vs other options.
Vs Western respiratory peptides
Limited Western peptide options:
Few peptides specifically target lungs
BPC-157: General healing, may help respiratory
TB-500: Tissue repair, systemic effects
No direct Western equivalent to Chonluten
Different mechanism approaches entirely
Chonluten theoretical advantages:
Specific respiratory system targeting
Organ-specific bioregulation approach
Russian research backing (limited)
Oral administration convenient
Designed specifically for lungs
Western peptide advantages:
Much better research quality
Mechanisms better understood
More validation overall
Greater medical acceptance
Higher confidence in effects
Comparison verdict:
Western peptides: Better evidence, not lung-specific
Chonluten: Lung-specific, weaker evidence
Could potentially use both
Different mechanisms theoretically
Choose based on risk tolerance
Vs conventional respiratory treatments
Chonluten role in treatment hierarchy:
Always secondary to medical treatment
Adjunct/complementary only
Experimental supportive therapy
Not proven or approved
Patient must understand limitations
Conventional treatments comparison:
Inhalers: Proven immediate relief, first-line
Steroids: Strong evidence, serious conditions
Bronchodilators: Well-established, effective
Oxygen therapy: Life-saving when needed
Chonluten: Experimental, unproven, adjunct only
When conventional treatment insufficient:
Tried all standard options
Still have symptoms
Seeking complementary approach
Under medical supervision
Realistic about limitations
Then consider Chonluten
Critical message:
Never replace proven treatments
Always continue medical care
Inform doctor about supplements
Monitor carefully with physician
Emergency care when needed
Medical treatment always priority
Vs other natural respiratory supports
Natural alternatives comparison:
NAC (N-acetylcysteine): Better evidence, mucolytic
Quercetin: Some research, anti-inflammatory
Vitamin D: Respiratory health association
Omega-3s: Anti-inflammatory properties
Chonluten: Specific but unproven
Chonluten advantages vs naturals:
Targeted organ-specific action (theory)
More specialized than general supplements
Bioregulatory approach unique
May work differently than antioxidants
Natural supplement advantages:
Better Western research typically
Cheaper usually
More accessible
Less controversial
Established safety profiles
Combination approach:
Could use Chonluten with naturals
Different mechanisms potentially
Medical supervision still important
Cost considerations matter
Many options to explore
Sourcing and quality considerations
Finding reliable Chonluten.
Vendor options
Russian pharmaceutical sources:
Original Russian manufacturers
Khavinson institute products
Higher confidence in authenticity
Import challenges for some countries
Language barrier possible
Western supplement vendors:
Some carry Russian bioregulators
Quality verification challenging
Third-party testing rare
Authenticity concerns possible
Convenience for Western buyers
Quality verification challenges:
No standardized testing protocols
COAs rarely provided
Purity difficult to verify
Authenticity hard to confirm
Buyer must trust vendor
Cost considerations
Typical pricing:
10-capsule pack: $30-60 typically
Full 20-day cycle: $60-120
Annual cost (2-3 cycles): $120-360
More expensive than basic supplements
Less than many pharmaceuticals
Cost-benefit analysis:
Uncertain benefits vs measurable cost
Experimental therapy investment
Compare to proven alternatives
Personal budget considerations
Risk-benefit-cost trade-off
How you can use SeekPeptides
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive peptide guidance including Russian bioregulators. Learn about Epitalon peptide benefits, Cartalax peptide, BPC-157, TB-500 benefits.
Access guides - what are peptides, how peptides work, getting started with peptides, peptide safety and risks, peptide research and studies.
Use calculators - peptide calculator, cost calculator.
Final thoughts
Chonluten represents Russian bioregulator approach to respiratory system optimization through short peptide sequences theoretically providing organ-specific cellular regulatory signals supporting lung tissue function, bronchial health, and respiratory epithelium optimization. Russian research claims respiratory benefits including improved lung function parameters, reduced symptoms, and tissue regeneration support, though Western validation remains essentially absent with evidence quality insufficient for confident therapeutic recommendations by conventional medical standards.
Your decision requires personal risk-benefit assessment balancing relatively safe profile with minimal reported side effects against highly uncertain efficacy due to limited high-quality research meeting Western randomized controlled trial standards.
Appropriate for experimental-minded individuals exploring respiratory optimization adjuncts under medical supervision while maintaining all conventional treatments for any serious respiratory conditions, understanding Chonluten represents unproven complementary approach rather than evidence-based primary therapy.
The bioregulator category broadly - including Epitalon, Cartalax, and Chonluten - occupies interesting position within peptide therapy landscape: decades of Russian research and use suggesting safety and possible benefits, yet lacking Western validation creating evidence gap requiring users comfortable with uncertainty and experimental approaches to navigate through informed personal decision-making rather than relying on established medical consensus.
Related bioregulator and peptide resources
Epitalon peptide benefits - Longevity bioregulator
Cartalax peptide - Joint bioregulator
BPC-157 complete guide - Western healing peptide
TB-500 benefits - Recovery peptide
What are peptides - Basics