Jan 24, 2026
A rat with a severed sciatic nerve. Ten days of cortagen injections. The result? Nerve fiber regeneration increased by 27 percent. Conduction velocity improved by 40 percent. These are not hypothetical projections. These are published findings from controlled research.
Cortagen represents a fascinating class of compounds that most Western researchers have never encountered. It is a tetrapeptide bioregulator, just four amino acids long, designed to influence gene expression in brain tissue at the most fundamental level. Where traditional nootropics modulate neurotransmitters or growth factors, cortagen works deeper. It enters cell nuclei and changes how neurons produce their own regulatory proteins.
This guide covers everything researchers need to understand about cortagen peptide. What it is. How it differs from other brain peptides. The specific research findings on nerve regeneration, cognitive effects, and gene expression. The protocols that have shown efficacy. And the important limitations every serious researcher should understand before working with this compound.
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources for researchers exploring bioregulator peptides, including detailed protocols and guidance on combining cortagen with other compounds for optimized outcomes.
What is cortagen peptide
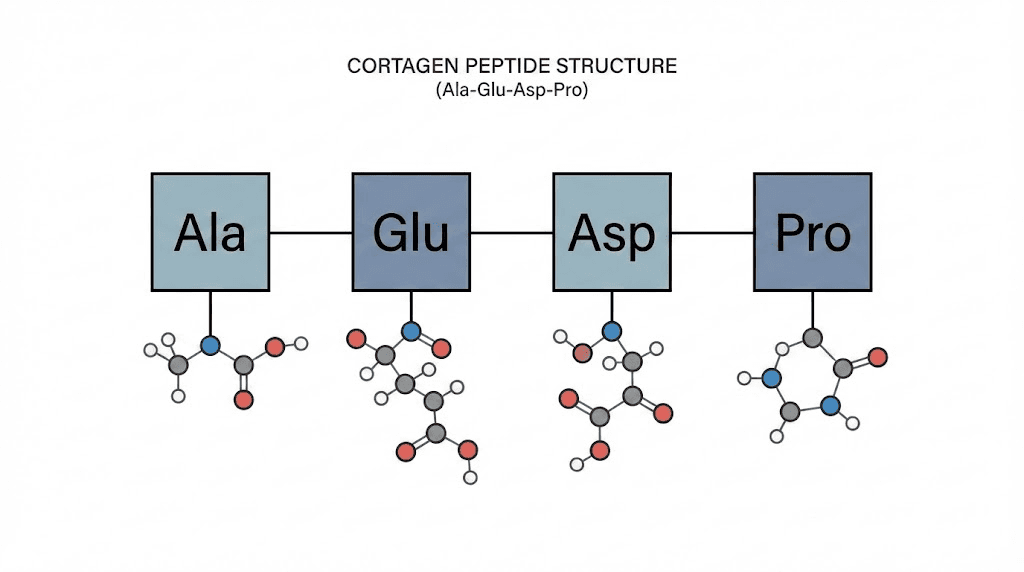
Cortagen is a synthetic tetrapeptide with the amino acid sequence Ala-Glu-Asp-Pro. It was developed by Russian scientist Vladimir Khavinson as part of decades of research into bioregulator peptides and their effects on organ function and aging.
The peptide was synthesized based on amino acid analysis of cortexin, a polypeptide preparation derived from the cerebral cortex that possesses neurotrophic activity. Cortagen represents a simplified, targeted version of the active components found in that natural brain extract.
Unlike longer peptides that must bind to cell surface receptors to produce effects, cortagen is small enough to penetrate cell membranes directly. It can enter the nucleus and interact with DNA to influence gene expression. This makes cortagen fundamentally different from compounds like Semax or Selank that work through neurotransmitter modulation.
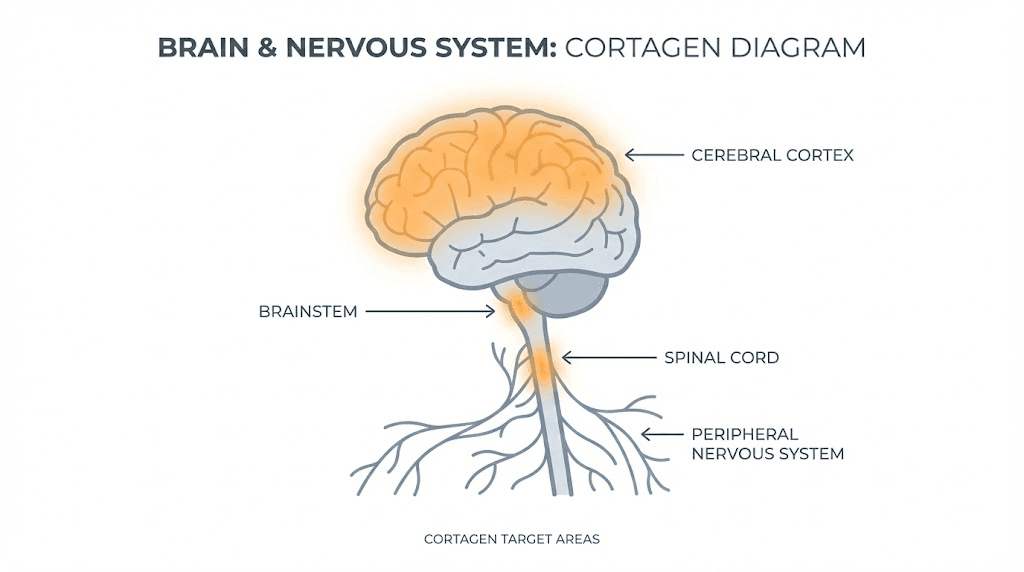
Cortagen belongs to the Khavinson peptide family, a collection of short bioregulatory peptides that have been studied for over four decades in Russian research institutions. Each Khavinson peptide targets specific organ systems. Epithalon targets the pineal gland. Cardiogen targets cardiac tissue. Pinealon targets brain tissue broadly. Cortagen specifically targets the cerebral cortex and nervous system.
How cortagen works at the molecular level
Understanding cortagen requires understanding how bioregulator peptides differ from traditional peptides. The mechanism is fundamentally different from what most researchers expect.
Penetrating cellular barriers
Most peptides cannot easily cross cell membranes. Larger peptides like IGF-1 or insulin must bind to receptors on cell surfaces to exert their effects. The signal is then transmitted inside the cell through secondary messenger systems.
Cortagen bypasses this limitation entirely.
Its compact four-amino-acid structure allows it to pass through both the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane. This grants cortagen direct access to the DNA within the cell nucleus. Once inside, cortagen can interact with specific DNA sequences to influence which genes are activated or suppressed.
This direct nuclear access makes bioregulators uniquely powerful. Rather than sending signals from outside the cell, they work at the source of protein production itself.
Gene expression modulation
Research has examined exactly how cortagen affects gene expression. In one landmark study, researchers used microarray technology to analyze 15,247 transcripts in mouse heart tissue following a five-day course of cortagen injections.
The results were striking. Out of more than 15,000 genes studied, cortagen significantly affected 110 known genes across various functional categories. Some genes became much more active while others became less active. The maximum upregulation was 5.42-fold while downregulation reached 2.86-fold.
This study also compared cortagen with other peptides including Vilon, Epithalon, and the hormone melatonin. The comparison revealed both common and specific effects, with each compound producing its own distinct pattern of gene expression changes.
Cortagen was found to increase the activity of ribosome genes and to unpack chromatin fibrils in a way that released genes that had been repressed as a result of age-specific condensation. This decondensation of DNA is seen with other bioregulatory peptides, with each peptide having tissue-specific effects.
Epigenetic mechanisms
The term epigenetic refers to changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations to the DNA sequence itself. Instead, epigenetic modifications determine which genes are accessible for transcription and which remain silenced.
Cortagen appears to function as an epigenetic switch. It can activate genes that have become silenced with age or suppress genes that contribute to dysfunction. This mechanism explains why its effects can persist long after the peptide itself has been metabolized and cleared from the body.
The peptide induces unrolling deheterochromatinization, which is the decondensation of total heterochromatin. It activates synthetic processes of ribosomal genes and releases repressed genes that had been silenced because of the condensation of euchromatic regions. This is a fundamental reprogramming of cellular function at its source.
Tissue-specific recognition
Each organ in the body has characteristic peptide sequences involved in local regulatory functions. Bioregulators are designed to match these sequences, which is why they show organ-specific effects.
Cortagen was derived from cerebral cortex tissue and contains sequences recognized by neural cells. When cortagen enters the body, it is recognized by brain and nervous system tissue because it matches peptide sequences that these cells use for internal communication. This recognition causes the peptide to concentrate its effects in neural tissue rather than being distributed randomly throughout the body.
This specificity represents a significant advantage over many traditional therapeutic approaches. Rather than affecting all tissues equally, cortagen concentrates its effects precisely where its matching sequences are found.
Cortagen research on nerve regeneration
Perhaps the most compelling research on cortagen involves its effects on peripheral nerve regeneration. For researchers interested in healing peptides, this data provides valuable context for understanding cortagen mechanisms.
The sciatic nerve study
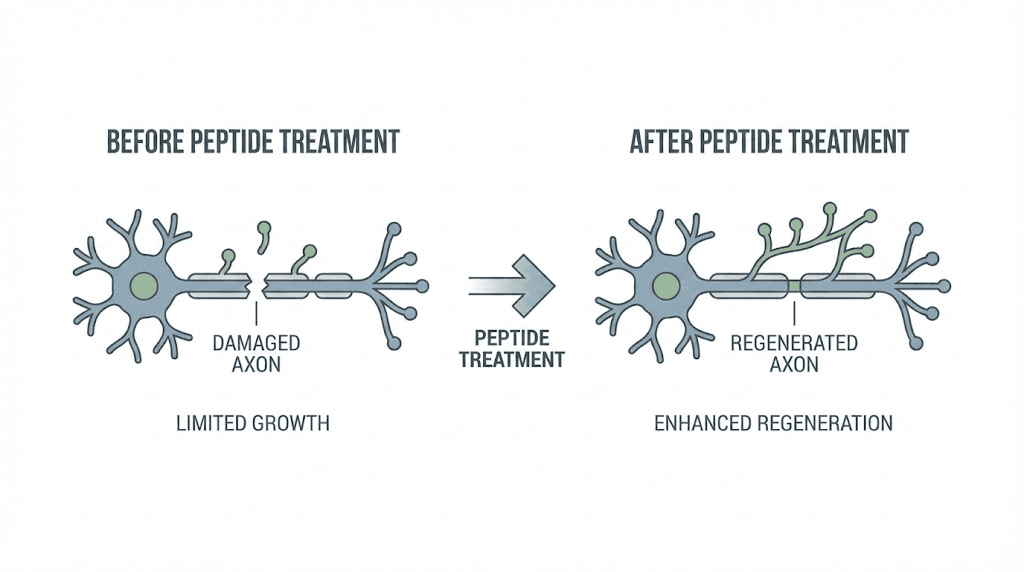
A landmark study published in the Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine examined cortagen effects on sciatic nerve regeneration in rats. Sixteen male Wistar rats weighing 200 to 250 grams underwent surgical transection of the sciatic nerve, followed by suturing of the nerve ends with an epineural suture.
Following surgery, animals received intramuscular injections of cortagen at 10 micrograms per kilogram daily for 10 days. Control animals received saline injections according to the same schedule. The study was performed five months after the nerve injury, which is sufficient time for the majority of regenerating fibers to reach target tissues and complete myelination.
The results demonstrated significant improvements in nerve recovery. Growth rate in regenerating nerve fibers increased by 27 percent. Conduction velocity improved by 40 percent, primarily in sensory and motor thick myelinated A-fibers.
The research team concluded that cortagen elicits potent neurotrophic activity and promotes both functional and structural recovery of damaged afferent nerves. Researchers also noted that cortagen administration resulted in a decrease in neuroma formation at the suture site, suggesting improved quality of nerve healing.
Implications for injury recovery
These findings have significant implications for understanding how cortagen might support nerve health. While BPC-157 and TB-500 are commonly discussed for injury healing, they work through different mechanisms than cortagen.
BPC-157 promotes healing through growth factor modulation and angiogenesis. TB-500 works through actin binding and cell migration. Cortagen appears to work by influencing gene expression in nerve cells, potentially reprogramming them to produce more regenerative proteins.
For researchers exploring peptides for pain or nerve-related conditions, cortagen offers a complementary mechanism to these better-known healing peptides. Some protocols combine multiple approaches to address both direct tissue repair and cellular programming.
Cortagen effects on brain function and cognition
Beyond peripheral nerve effects, cortagen has been studied for its impact on central nervous system function. For researchers interested in cognitive peptides, this research provides important context.
Locomotor activity and anxiety studies
A study published in The Open Neuropsychopharmacology Journal examined the psychoactive effects of cortagen in mice using elevated plus maze and locomotor activity habituation paradigms. Mice were injected with cortagen at doses of 0.01, 0.03, or 0.10 mg/kg and tested for both acute and sub-chronic responses.
The results revealed an interesting dose-dependent pattern. The 0.03 mg/kg dose of cortagen enhanced locomotion both upon acute and after sub-chronic treatment while having minimal effects on anxiety-related behavior.
The researchers concluded that cortagen leads to motor stimulation with no side effects on emotional-affective profiles at optimal doses. They noted that such behavioral stimulation may find beneficial employment in the treatment of affective or depressive symptoms.
This finding is particularly relevant because it suggests cortagen can provide cognitive or behavioral benefits without the anxiogenic effects sometimes seen with other stimulating compounds. The study noted that peptides are active in very low dosages with no side effects and deserve deeper investigation for their promising role in therapy.
Comparison with cortexin
The study compared cortagen with cortexin, the polypeptide complex from which cortagen was derived. Cortexin showed anxiolytic-like effects when given acutely, with anxiogenic-like arousal emerging following repeated treatment.
Cortagen, by contrast, provided motor stimulation without these emotional-affective fluctuations. This suggests that by isolating the specific tetrapeptide sequence, researchers achieved a more targeted effect with fewer confounding variables.
Both agents stimulate neural growth in vitro, presumably in association with neurotrophic factors. However, their behavioral profiles differ, with cortagen showing a cleaner stimulatory effect.
Neuroprotective mechanisms
Cortagen exerts its central nervous system effects primarily through neuroprotective and neuromodulatory mechanisms. It interacts with neuronal cells to promote repair and regeneration, particularly in the context of neurological damage.
The peptide enhances synaptic plasticity by modulating neurotransmitter activity, including the regulation of glutamate and GABA, which supports balanced neuronal signaling. This is fundamentally different from how compounds like Semax work, which primarily modulate BDNF and melanocortin pathways.
Cortagen also demonstrates influence on neuronal metabolism and antioxidant defenses within the central nervous system. Research suggests it can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and directly influence protein synthesis within neurons and glial cells.
For researchers exploring nootropic peptides or memory enhancement, cortagen offers an epigenetic approach rather than direct neurotransmitter modulation. The effects may be more subtle initially but potentially more durable because they address cellular programming rather than acute signaling.
Cortagen and the cardiovascular system
While cortagen is primarily considered a brain peptide, research has revealed interesting effects on cardiac tissue as well. This discovery came from the gene expression studies examining cortagen effects across different organ systems.
Gene expression in heart tissue
The microarray study that examined 15,247 transcripts specifically looked at mouse heart tissue. The finding that cortagen affected 110 genes in cardiac tissue was somewhat unexpected given its origins as a brain-derived peptide.
This cross-system activity is not unique to cortagen. Many bioregulators show effects beyond their primary target organs. Chonluten, for example, is a respiratory bioregulator that also shows effects on gastrointestinal function.
The cardiac effects of cortagen may be relevant for researchers exploring comprehensive wellness protocols. While Cardiogen remains the primary bioregulator for cardiac tissue, understanding cortagen secondary effects helps inform combination strategies.
Immune system connections
Studies have shown that cortagen stimulates interleukin-2 expression and helps regulate immune function, primarily by reducing autoimmune responses. This positions cortagen as having secondary benefits for immune support beyond its primary neural effects.
The immune-neural connection is well established in modern research. The brain and immune system communicate extensively, and compounds that affect one system often influence the other. Cortagen appears to modulate this neuro-immune axis in beneficial ways.
Anti-aging and oxidative stress effects
Cortagen is considered a geroprotective and anti-aging peptide within the bioregulator research framework. Its effects on aging operate through several distinct mechanisms.
DNA restoration effects
Cortagen helps restore DNA to a more youthful state by reducing senescence and increasing the expression of certain genes often silenced by age. This is the fundamental mechanism through which bioregulators produce their anti-aging effects.
As cells age, regions of DNA become increasingly condensed and inaccessible. Genes that were active in youth become silenced. This condensation contributes to declining cellular function and the accumulation of damage associated with aging.
Cortagen appears to reverse some of this age-related gene silencing by inducing chromatin decondensation. It literally opens up regions of DNA that had become compacted, allowing cells to once again produce proteins they had stopped making.
This mechanism aligns with how other bioregulators like Epithalon work on telomerase expression and cellular aging. For researchers interested in anti-aging peptides, cortagen offers complementary mechanisms that specifically target neural tissue.
Antioxidant enhancement
Cortagen also appears to affect aging by boosting the body natural anti-oxidative mechanisms. Research in rats shows that cortagen decreases levels of lipid peroxidation products, reducing the number of proteins affected by pathological oxidation processes.
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to cellular aging and dysfunction. By enhancing antioxidant defenses, cortagen may help protect neural tissue from the cumulative damage that leads to cognitive decline and neurodegeneration.
This antioxidant effect complements other approaches researchers use for brain health. Compounds that directly scavenge free radicals work differently than cortagen, which appears to enhance the cells own antioxidant production. Combining multiple approaches could provide more comprehensive protection.
Ischemic brain injury research
Cortagen has been investigated as a potential treatment approach following ischemic brain injury. Research shows that cortagen stabilizes the inflammatory response in the central nervous system, helping to promote a balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory pathways.
Animal studies have shown that cortagen reduces the long-term consequences of ischemic injury in the brain. This protective effect likely relates to its ability to modulate gene expression in neural tissue under stress conditions.
The anti-inflammatory effects are particularly relevant given the role of inflammation in neurodegeneration and age-related cognitive decline. Many researchers are exploring ways to modulate neuroinflammation as part of comprehensive brain health strategies.
Cortagen vs pinealon: comparing brain bioregulators
Researchers often ask how cortagen compares to Pinealon, another popular brain bioregulator. While both target the central nervous system, they have distinct characteristics that inform their different applications.
Structural differences
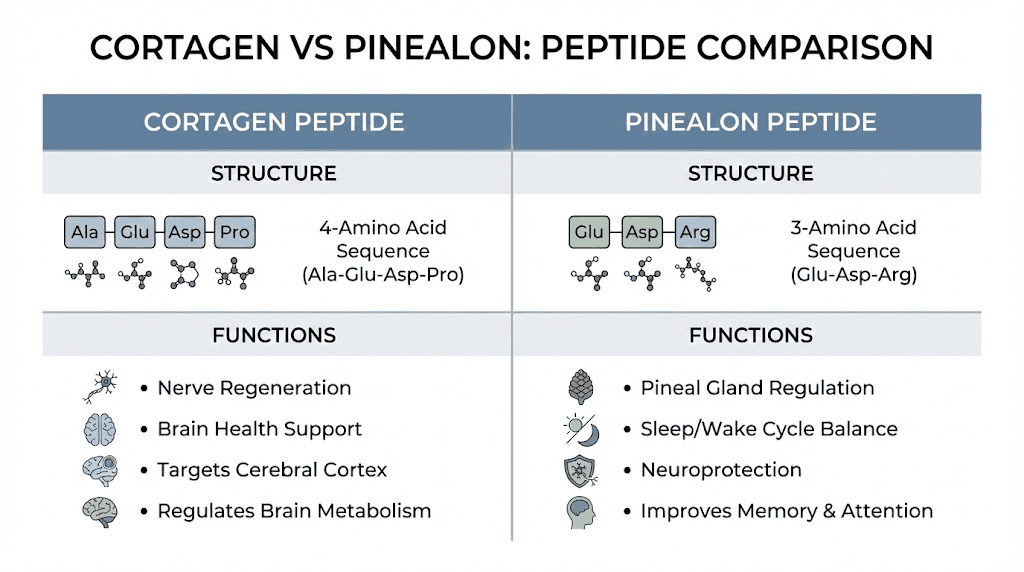
Cortagen is a tetrapeptide with the sequence Ala-Glu-Asp-Pro. Pinealon is a tripeptide with the sequence Glu-Asp-Arg. This structural difference influences how each peptide interacts with DNA and which genes it affects.
Pinealon was originally discovered in extracts of brain tissue, especially the cerebral cortex and pineal gland, by Russian researchers. While both peptides come from brain tissue, they represent different active sequences with different regulatory functions.
Primary mechanisms
Cortagen seems to have a regenerative effect. Research has focused on its ability to promote nerve fiber regeneration and functional recovery after neural injury. The sciatic nerve study demonstrated this regenerative capacity clearly.
Pinealon seems to have a protective effect on the brain. Research has emphasized its neuroprotective properties and its influence on mitochondrial enzyme activity. Pinealon focuses on maintaining neuronal health and preventing damage rather than actively promoting regeneration.
This distinction is somewhat simplified. Both peptides likely have both protective and regenerative properties. However, the research emphasis differs, suggesting each may be more suited to different applications.
Application considerations
For researchers dealing with active neural injury or seeking to promote nerve regeneration, the research suggests cortagen may be particularly relevant. The documented 40 percent improvement in nerve conduction velocity is notable.
For researchers focused on neuroprotection, cognitive maintenance, and brain aging, Pinealon research is more directly applicable. Its effects on antioxidant defenses and mitochondrial function support long-term neural health.
Many protocols combine both peptides to address brain health from multiple angles. Since bioregulators work through gene expression rather than receptor activation, combining different bioregulators may produce complementary effects without the receptor competition issues seen with some peptide combinations.
Cortagen and adrenal function
Some research has explored connections between cortagen and adrenal gland function, though this remains less well-documented than its neural effects.
HPA axis modulation
Cortagen has been described as working by modulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, thereby aiding in the body natural response to stress and supporting overall immune system health. This mechanism would position cortagen as potentially relevant for stress management and adrenal support.
The HPA axis is the primary hormonal pathway through which the body responds to stress. Chronic stress can dysregulate this axis, leading to various health issues including cognitive problems, fatigue, and immune dysfunction.
If cortagen does modulate HPA axis function, this could explain some of its observed effects on immune function and stress resilience. However, this mechanism is less well-documented than its direct neural effects, and researchers should approach these claims with appropriate caution.
Cortisol regulation
Some sources suggest cortagen helps regulate stress responses by balancing cortisol levels. By modulating adrenal gland activity, it may aid in controlling the body reaction to stress and reducing the harmful effects of chronic stress on the immune system and overall health.
This potential cortisol-regulating effect would make cortagen relevant for researchers exploring stress resilience and adrenal optimization. However, direct studies specifically examining cortisol levels following cortagen administration are limited in the accessible research literature.
The peptide may also help regulate the production of essential hormones such as cortisol and aldosterone, contributing to improved hormonal balance. By potentially optimizing cortisol levels, these peptides might improve the body ability to cope with stress.
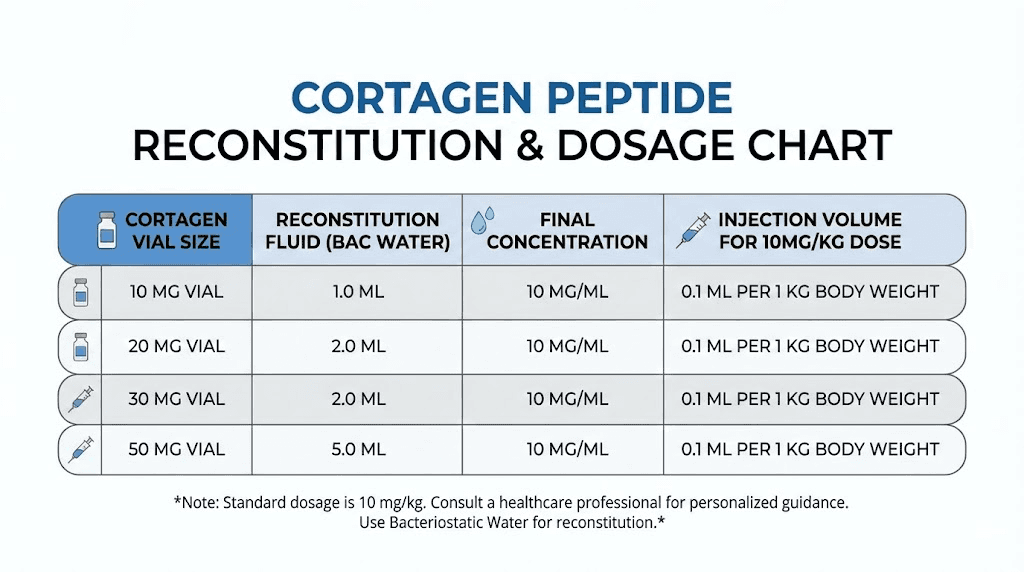
Cortagen dosage protocols and administration
Understanding proper peptide dosing is essential for researchers working with cortagen. The compound has specific characteristics that influence optimal administration approaches.
Dosage ranges in research
Dosage recommendations vary across sources, reflecting different research contexts and objectives. The scientific literature provides several reference points.
The sciatic nerve regeneration study used 10 micrograms per kilogram of body weight, administered intramuscularly daily for 10 days after nerve injury. This produced significant regenerative effects.
The locomotor and anxiety study in mice found optimal behavioral effects at 0.03 mg/kg. Higher and lower doses showed different effect profiles, suggesting a dose-response curve with an optimal range.
For human applications, various sources suggest ranges from 0.1 to 5 milligrams per day depending on the specific condition being addressed. Some protocols recommend 200-400 mcg per day for male subjects, with adjustments based on study objectives.
The research suggests that cortagen dose effect follows a bell curve, whereby too low a dose produces no effect and too high a dose produces undesirable effects. Finding the optimal dose range appears important for achieving desired outcomes.
Administration methods
Subcutaneous injection is the most common route for cortagen administration. This method delivers the peptide directly into circulation for maximum effect. The peptide injection guide provides detailed information on proper injection technique.
Intranasal formulations are also available for cortagen. This route may be more convenient but comes with the trade-off of potentially lower bioavailability compared to injection.
Oral capsule formulations exist as well. These are convenient but may be affected by digestive processes. Understanding injectable versus oral peptides helps inform route selection.
For injectable forms, proper peptide reconstitution is essential. The peptide reconstitution calculator can help determine appropriate mixing volumes. Using bacteriostatic water maintains sterility for multi-dose vials.
Injection protocol
Morning administration is generally preferred for cortagen. Rotation of injection sites helps prevent issues at any single location.
Clean the vial stopper and skin with alcohol and allow to dry. Pinch a skinfold and insert the needle at 45 to 90 degrees into subcutaneous tissue. Do not aspirate for subcutaneous injections. Inject slowly and steadily. Rotate sites systematically through abdomen, thighs, and upper arms to avoid lipohypertrophy.
The peptide calculator can help determine exact dosing volumes based on concentration and desired dose.
Treatment duration and cycling
Treatment cycles for cortagen typically last between 10 to 30 days depending on research objectives and individual response. This cycling approach reflects how bioregulators work through gene expression changes that persist after administration stops.
Unlike some peptides that require continuous use to maintain effects, bioregulators produce changes at the epigenetic level that can last for extended periods. The cells continue producing proteins according to modified gene expression patterns even after the peptide is cleared from the system.
Some protocols call for periodic administration, such as one or two treatment cycles per year. The long-term mortality studies with other bioregulators that showed the most dramatic results used annual administration over multiple years.
For researchers exploring peptide cycling strategies, bioregulators represent a distinct approach from compounds that require continuous use.
Cortagen storage and handling
Proper peptide storage is essential for maintaining cortagen integrity and ensuring consistent results.
Lyophilized storage
Lyophilized cortagen should be stored at -20 degrees Celsius for long-term preservation. Storage at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius is acceptable for short-term periods of weeks to months.
The lyophilized powder form is stable for extended periods when stored properly. Understanding how long peptides last at room temperature helps inform handling decisions during shipping and use.
Reconstituted storage
Once reconstituted, cortagen should be refrigerated at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius. Use within four weeks and avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Understanding how long reconstituted peptides last in the fridge helps researchers plan their usage schedules appropriately. The peptide refrigeration guide provides additional storage details.
Handling considerations
Peptides are sensitive to heat, light, and contamination. Handle with clean technique to maintain sterility. Avoid shaking reconstituted solutions vigorously, as this can damage peptide structures.
The peptide vial research guide provides additional information on proper handling procedures.
Cortagen safety profile and considerations
Understanding peptide safety is crucial for any researcher. Cortagen has demonstrated a favorable safety profile across multiple studies.
Research safety data
Across multiple studies, cortagen consistently shows minimal to no side effects with short-term or long-term use. This peptide bioregulator is derived from natural brain proteins and mimics the body own repair signals. It does not interfere with brain chemistry like many synthetic drugs do, meaning there is no withdrawal and no tolerance buildup.
The locomotor and anxiety study in mice found that acute and sub-chronic administration enhances motor activity without causing anxiety or emotional-affective disturbances, particularly at the optimal dose of approximately 0.03 mg/kg. No behavioral side effects were observed under either acute or repeated dosing regimens at this level.
Animal research indicates cortagen is generally well tolerated in preclinical models, with no significant adverse effects reported in published animal studies.
Potential side effects
Occasional mild injection-site reactions such as redness or itching may occur with subcutaneous administration. These typically resolve quickly without intervention.
The bell-curve dose response suggests that exceeding optimal dosing ranges may produce different effects. Researchers should start at lower doses and adjust based on response.
Contraindications and cautions
While human clinical data remain limited, appropriate caution is warranted for certain populations.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid cortagen due to insufficient safety data in these populations. Children should not use cortagen without specialist supervision, as effects on developing systems have not been adequately studied.
Individuals with known peptide hypersensitivity should exercise caution and may need to start with lower doses to assess tolerance.
Researchers with active neurological conditions should consult with knowledgeable practitioners before using cortagen or any bioregulator peptide.
Quality and sourcing
Cortagen quality varies significantly between suppliers. Sourcing from reputable peptide vendors who provide third-party testing verification is essential.
Peptide testing labs can verify purity and confirm that products contain what they claim. Given the gene-expression-level effects of bioregulators, ensuring product quality is particularly important.
Combining cortagen with other peptides
Many researchers use cortagen alongside other peptides as part of comprehensive protocols. Understanding potential interactions and synergies helps optimize these combinations.
With other bioregulators
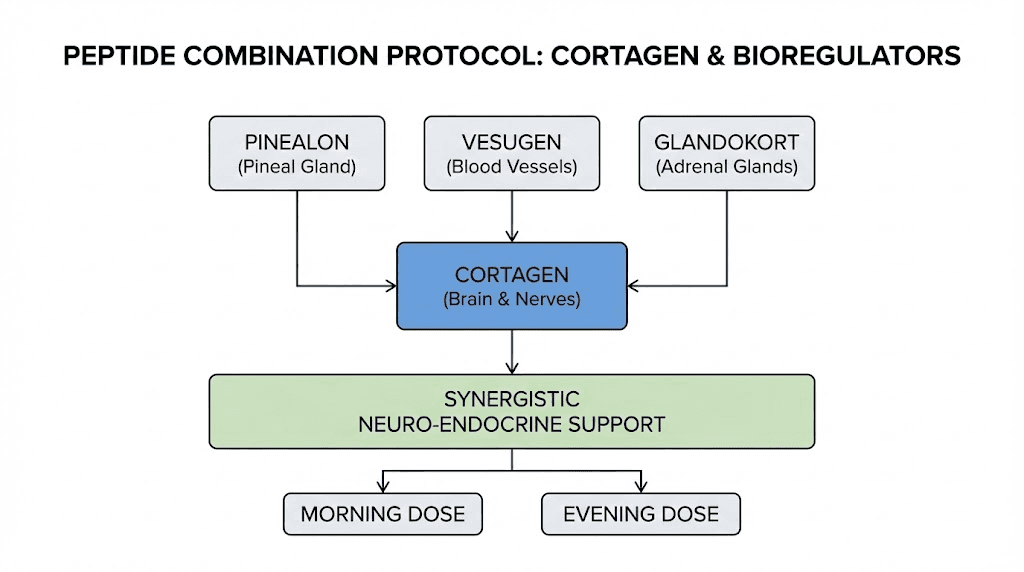
Cortagen can be combined with other bioregulator peptides that target different organ systems. Logical combinations include pairing cortagen with Vesugen for combined neural and vascular support, or with Epithalon for comprehensive anti-aging effects.
Combining cortagen with Pinealon addresses brain health from two angles. Cortagen provides regenerative support while Pinealon provides protective support. Since both work through gene expression rather than receptor activation, they are unlikely to compete with each other.
The peptide stacking guide provides additional information on combining multiple peptides effectively. The peptide stack calculator can help plan multi-peptide protocols.
With healing peptides
For nerve injury recovery, combining cortagen with traditional healing peptides may provide complementary benefits. BPC-157 and TB-500 stacks promote direct tissue repair while cortagen works on cellular programming.
BPC-157 promotes healing through growth factor modulation and has documented effects on various tissue types. TB-500 works through actin binding and cell migration. Neither directly addresses gene expression the way cortagen does.
Combining these different mechanisms could theoretically provide more comprehensive recovery support than any single compound alone. However, specific interaction studies between cortagen and these healing peptides are limited.
With nootropic peptides
Cortagen works differently than traditional nootropic peptides like Semax or Selank. Those peptides work through neurotransmitter modulation and growth factor expression. Cortagen works at the epigenetic level.
This mechanistic difference suggests the compounds could potentially complement each other. Semax provides acute cognitive enhancement through BDNF modulation while cortagen provides longer-term support through gene expression changes.
However, specific research on these combinations is limited. Conservative researchers may prefer to assess each compound individually before combining.
With growth hormone secretagogues
Growth hormone secretagogues like Ipamorelin and CJC-1295 work through hormonal pathways rather than gene expression. They stimulate growth hormone release from the pituitary gland.
Cortagen may influence how cells respond to growth hormone rather than how much growth hormone is released. This represents a different level of intervention that could complement secretagogue effects.
Understanding Ipamorelin versus CJC-1295 helps researchers choose appropriate secretagogues for combination protocols.
Practical considerations for cortagen research
Researchers interested in working with cortagen face several practical considerations beyond the scientific questions.
Availability and sourcing
Cortagen is available from various peptide suppliers, though availability varies by region. It is one of the more commonly stocked bioregulators alongside Epithalon and Pinealon.
Quality varies significantly between suppliers. The peptide vendor guide provides information on evaluating supplier quality. Always request certificates of analysis and verify through third-party testing when possible.
The peptide cost calculator can help researchers budget for their protocols. Bioregulator prices tend to be higher than traditional peptides of similar mass, reflecting specialized manufacturing requirements.
Documentation and tracking
Given the long-term nature of bioregulator effects, documentation becomes particularly important. Researchers should establish baseline measurements before beginning protocols and track relevant parameters over time.
For cognitive protocols, useful measurements include memory tests, processing speed assessments, and subjective cognitive function ratings. For nerve-related protocols, relevant functional tests help document effects.
The persistence of bioregulator effects means that research timelines must extend beyond the treatment period. Effects may continue developing for weeks or months after a treatment cycle ends.
Legal and regulatory status
Cortagen is not FDA-approved as a drug. No robust clinical or peer-reviewed human trials have been reported in the accessible Western literature. The compound is available for research purposes in most jurisdictions.
Understanding peptide legality in your specific jurisdiction is important before beginning any research. Regulations vary by location and are subject to change.
Working with knowledgeable practitioners
The specialized nature of bioregulator peptides means that not all healthcare providers are familiar with them. Working with practitioners who understand peptides and how to use them properly can help optimize outcomes and manage any concerns that arise.
SeekPeptides members access connections to knowledgeable practitioners and a community of experienced researchers who can provide practical insights beyond what published research covers.
Cortagen in the context of brain optimization
Cortagen represents one approach among many for supporting brain health and cognitive function. Understanding how it fits into the broader landscape helps researchers make informed decisions.
Comparing approaches
Traditional nootropics work primarily through neurotransmitter modulation. Racetams affect acetylcholine signaling. Modafinil affects dopamine pathways. These produce relatively acute effects that require ongoing use to maintain.
Growth factor approaches use compounds like Semax to enhance BDNF and other neurotrophic factors. These support neural health and plasticity but still work through signaling pathways rather than gene expression.
Bioregulators like cortagen work at a more fundamental level. By influencing gene expression directly, they may produce more durable changes in cellular function. However, the effects may also be more subtle and develop over longer timeframes.
When cortagen may be appropriate
Based on the research, cortagen may be particularly relevant for certain situations.
Neural injury recovery is the best-documented application, with the sciatic nerve study showing significant regenerative effects. Researchers dealing with peripheral nerve issues may find cortagen research particularly relevant.
Long-term brain health and anti-aging protocols may benefit from cortagen inclusion alongside other approaches. The epigenetic mechanism addresses cellular aging at its source rather than just treating symptoms.
Stress resilience and HPA axis optimization is a less well-documented but potentially relevant application based on the research suggesting adrenal function effects.
When other approaches may be preferable
For acute cognitive enhancement, traditional nootropics or peptides like Semax may be more appropriate. Cortagen effects develop over time rather than providing immediate cognitive boost.
For well-characterized conditions with established treatments, proven approaches should be considered first. Cortagen research, while promising, remains limited compared to better-studied compounds.
For individuals seeking simple, single-compound approaches, the complexity of bioregulator protocols may not be ideal. Cortagen works best as part of comprehensive strategies rather than as a standalone solution.
Frequently asked questions
What is cortagen peptide used for?
Cortagen is a tetrapeptide bioregulator studied primarily for its effects on the central nervous system and peripheral nerve regeneration. Research has examined its potential for supporting nerve repair after injury, cognitive function, neuroprotection, and anti-aging effects. It works by entering cell nuclei and influencing gene expression in neural tissue.
How does cortagen differ from other brain peptides?
Cortagen is a bioregulator peptide that works at the epigenetic level by influencing gene expression. This differs from nootropic peptides like Semax that work through neurotransmitter modulation, or growth factors that work through receptor activation. Cortagen effects may be more durable because they address cellular programming rather than acute signaling.
What is the typical cortagen dosage?
Research has used various dosages depending on the application. The sciatic nerve study used 10 micrograms per kilogram. Behavioral studies found optimal effects at 0.03 mg/kg. Human protocols typically range from 200-400 mcg per day. The peptide calculator can help determine appropriate dosing volumes.
How long does a cortagen cycle last?
Treatment cycles typically last 10 to 30 days depending on research objectives. Because cortagen works through gene expression changes that persist after administration, continuous use is not required. Some protocols use one or two cycles per year for maintenance.
Can cortagen be combined with other peptides?
Yes, cortagen can be combined with other bioregulators or traditional peptides. Common combinations include pairing with Pinealon for comprehensive brain support or with healing peptides like BPC-157 for injury recovery. The peptide stacking guide provides more information.
What are cortagen side effects?
Research shows minimal side effects. Occasional mild injection-site reactions may occur. The compound is derived from natural brain proteins and does not interfere with brain chemistry like synthetic drugs. No withdrawal or tolerance buildup has been reported.
How should cortagen be stored?
Lyophilized cortagen should be stored at -20 degrees Celsius for long-term or 2-8 degrees Celsius for shorter periods. Reconstituted cortagen should be refrigerated and used within four weeks. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. The peptide storage guide provides detailed information.
Is cortagen the same as cortexin?
No. Cortexin is a polypeptide complex extracted from animal brain cortex. Cortagen is a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from analyzing the active components in cortexin. Cortagen represents a simplified, targeted version with a specific four-amino-acid sequence.
How long until cortagen effects are noticeable?
Unlike acute-acting compounds, cortagen effects develop over time as gene expression changes accumulate. Some effects may be noticeable within the treatment period, but full benefits may develop over weeks or months. Understanding how long peptides take to work helps set appropriate expectations.
External resources
For researchers seeking to understand the full potential of bioregulator peptides, cortagen represents a fascinating compound that addresses neural function at the most fundamental level. Its ability to influence gene expression and produce lasting effects through periodic treatment opens possibilities that continuous-administration peptides cannot match.
SeekPeptides members access detailed protocols for cortagen and other bioregulators, along with guidance on combining these compounds with other peptide approaches for comprehensive optimization strategies. The community includes researchers with extensive experience using bioregulators who can provide practical insights beyond what published research covers.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your neurons stay protected, your nerve fibers stay regenerating, and your gene expression stay optimized.



