Feb 2, 2026
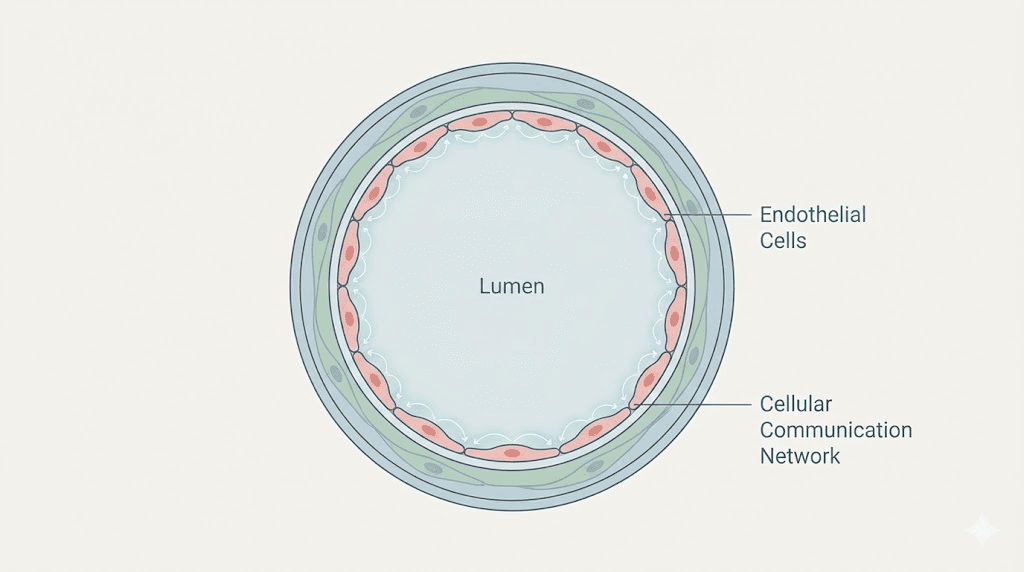
The walls of your blood vessels change with every passing decade. At the cellular level, endothelial cells that line your arteries gradually lose their ability to produce nitric oxide. Oxidative stress accumulates. The smooth muscle cells surrounding these vessels stiffen. Connexin proteins that allow cells to communicate begin to degrade. This is not inevitable aging but rather a cascade of epigenetic changes that make cardiovascular disease the leading cause of death worldwide. Ventfort peptide targets these changes at their source.
It works not by blocking symptoms or forcing temporary improvements but by restoring the genetic expression patterns that keep vascular tissue young. This is bioregulation. When you understand how Ventfort interacts with the promoter regions of genes encoding antioxidant systems and endothelial function proteins, you begin to see why clinical studies show cholesterol dropping from 8.6 to 6.0 mmol/L and why capillary wall strength improves in patients with senile purpura.
The mechanism is precise, the evidence is documented, and the safety profile spans three decades across fifteen million patients.
Understanding Ventfort requires understanding what happens when vascular tissue loses regulatory control. Bioregulator peptides represent a class of compounds fundamentally different from synthetic peptides designed to stimulate hormone release or mimic signaling molecules. These are tissue-specific peptide complexes extracted from healthy young animal organs that restore gene expression patterns in corresponding human tissues. The science began in Russia under Professor Vladimir Khavinson, whose research into geroprotection led to the development of both Cytomaxes like Ventfort and their synthetic counterparts called Cytogens.
What makes this approach compelling is not marketing but mechanism. When vascular endothelial cells receive the right peptide signals, they remember how to function optimally. SeekPeptides has compiled this comprehensive guide to help researchers understand every aspect of Ventfort, from molecular mechanisms to practical dosing protocols.
What is Ventfort peptide
Ventfort is a Cytomax bioregulator containing peptide complex A-3 isolated from the vascular tissue of young calves under twelve months of age. Specifically, the source is aortic tissue. The molecular weight of these peptides reaches up to 10,000 Daltons, placing them in the category of short-chain peptide complexes that can interact with DNA regulatory regions. This is not a single peptide but a complex of naturally occurring vascular peptides that work synergistically to restore endothelial and smooth muscle cell function. The extraction process preserves the native structure and sequence of these peptides, which is why Khavinson peptides maintain their regulatory effects even at extremely low doses.
The classification as a Cytomax distinguishes Ventfort from Vesugen, its Cytogen counterpart. Vesugen contains the synthetic tripeptide KED (Lys-Glu-Asp), which mimics one of the active sequences found in the natural complex. Both target vascular tissue, but their pharmacokinetics differ significantly. Cytomaxes like Ventfort produce effects that last six to twelve months after a single course, while Cytogens require more frequent administration with effects lasting one and a half to two months. The trade-off is accumulation speed. Cytogens reach therapeutic levels twenty to thirty percent faster than Cytomaxes. This matters when choosing between immediate intervention and long-term regulation.
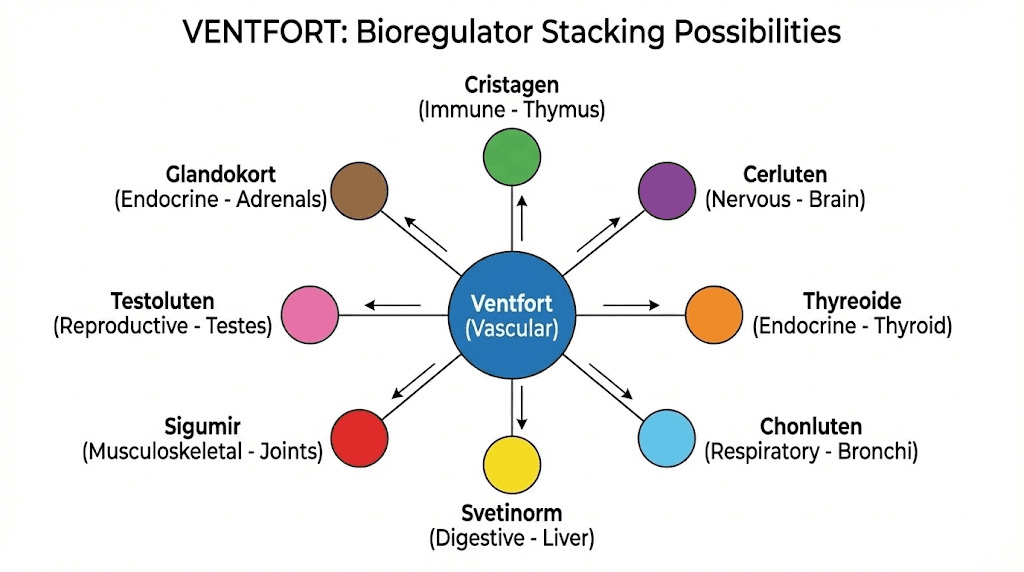
Ventfort belongs to the Khavinson first-class stack, which consists of six fundamental bioregulators targeting the systems most critical for longevity. These six are Ventfort for vascular tissue, Thymalin for immune function, Epitalon for pineal gland and telomerase activation, Cerluten for brain and central nervous system support, Sigumir for joints and bones, and Svetinorm for liver function. The logic behind this stack is straightforward. If you regulate the vascular system, immune system, pineal gland, brain, joints, and liver, you address the primary drivers of biological aging. Ventfort handles the cardiovascular component, which is particularly important given that atherosclerosis and vascular dysfunction underlie much of age-related disease.
The active ingredient in Ventfort is the A-3 peptide complex. This designation refers to the specific fraction isolated from aortic tissue that demonstrates vascular regulatory activity. Research has identified several key peptides within the complex, including sequences that bind to promoter regions of genes encoding antioxidant enzymes and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. What you need to know is that this complex has been studied in clinical settings, not just cell cultures.
The Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology conducted controlled trials that measured objective markers like cholesterol levels, VLDL concentrations, and capillary wall strength using standardized Hesse testing.
When you compare Ventfort to other peptides commonly used for cardiovascular support, the differences become clear. BPC-157 promotes angiogenesis and endothelial repair through growth factor signaling. TB-500 upregulates actin and facilitates cell migration during tissue healing. These are valuable mechanisms, but they operate at the level of emergency repair rather than regulatory restoration. Ventfort does not force new blood vessel formation or accelerate healing timelines. Instead, it resets the epigenetic markers that determine how vascular cells express their genetic programs. This is why the effects persist long after the peptide clears from circulation.
The form factor matters for practical use. Ventfort is typically available in capsule form with each capsule containing 10 milligrams of the peptide complex. This oral delivery method works because these are short-chain peptides with molecular weights low enough to survive gastric acid and cross intestinal barriers. Peptide capsules offer convenience compared to injectable formulations, though absorption rates and bioavailability differ from subcutaneous or intramuscular administration. The clinical studies used oral Ventfort exclusively, so the demonstrated effects reflect this route of administration. For those comparing delivery methods, the injectable versus oral peptides comparison provides additional context.
How Ventfort works at the molecular level
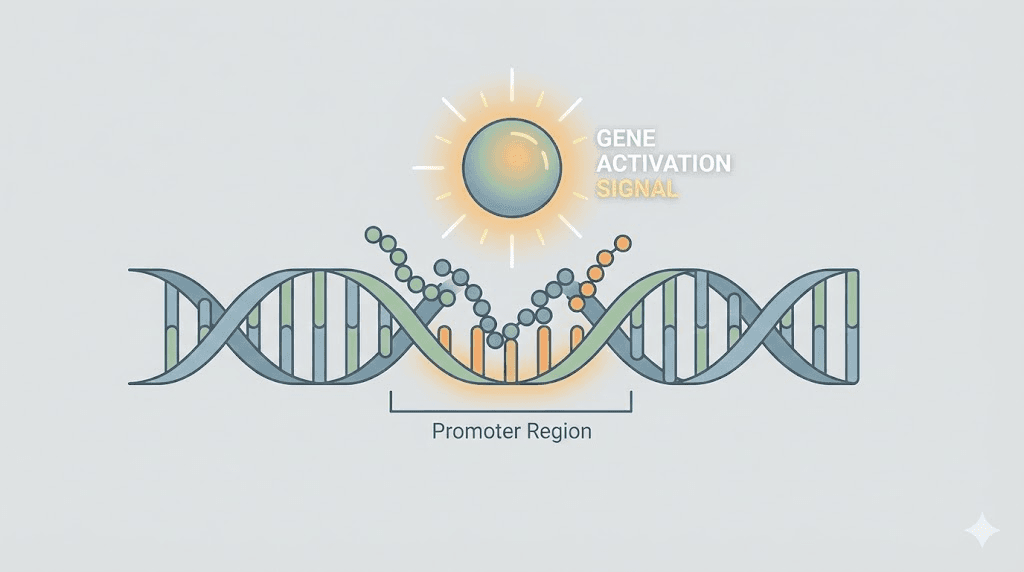
The mechanism begins when Ventfort peptides enter circulation and reach vascular tissue. These peptides exhibit tropism for endothelial and smooth muscle cells, meaning they preferentially accumulate in vessel walls rather than dispersing randomly throughout the body. Once at the target tissue, the peptides interact with cell surface receptors and transport mechanisms that facilitate internalization. The critical action occurs in the cytoplasm and at the nuclear membrane, where these peptide complexes influence gene transcription through epigenetic modification.
Research on Vesugen, the synthetic KED tripeptide that replicates part of the natural Ventfort complex, reveals how this works. The KED sequence binds to the minor groove of DNA in the promoter region of the MKI67 gene, which encodes the Ki-67 proliferation marker. This binding does not alter the DNA sequence itself but changes how accessible that gene is to transcription factors. The result is upregulation of Ki-67, which indicates increased cellular proliferation capacity. In the context of vascular tissue, this means endothelial cells regain their ability to replicate and repair damaged areas of the vessel lining. Understanding how peptides work at this level of gene regulation differs fundamentally from receptor-based signaling.
Endothelin-1 represents another key regulatory target. This is a potent vasoconstrictor produced by endothelial cells that increases with age and oxidative stress. Elevated endothelin-1 contributes to hypertension, atherosclerosis, and endothelial dysfunction. Studies show that the KED peptide normalizes endothelin-1 expression, bringing levels back toward youthful ranges without suppressing production entirely. This is regulation rather than inhibition. The system maintains its ability to produce endothelin-1 when needed for vasoconstriction but does not overproduce it chronically.
Connexin proteins deserve attention because they control gap junction communication between vascular cells. These gap junctions allow ions and small molecules to pass directly between adjacent cells, coordinating contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle and enabling endothelial cells to respond to signals as a unified layer. With aging, connexin expression decreases and existing connexin proteins become disorganized. Research demonstrates that vascular bioregulator peptides restore connexin expression patterns, effectively rebuilding the cellular communication network that maintains vascular tone and responsiveness.
SIRT1 expression provides another window into the mechanism. Sirtuins are NAD-dependent deacetylases that regulate cellular metabolism, stress resistance, and longevity pathways. SIRT1 specifically affects endothelial function by deacetylating and activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme responsible for producing the nitric oxide that causes vasodilation. Studies show that vascular bioregulator peptides increase SIRT1 expression in endothelial cells. This creates a cascade effect where increased SIRT1 leads to more active eNOS, which produces more nitric oxide, which improves vascular function and reduces oxidative stress. The system reinforces itself once properly regulated. Researchers exploring NAD peptides and sirtuin pathways will recognize the overlap between vascular bioregulation and broader longevity mechanisms.
The antioxidant system responds to Ventfort through gene regulation as well. Oxidative stress in blood vessels comes primarily from superoxide produced by dysfunctional mitochondria and NADPH oxidase enzymes. The body has multiple antioxidant defense systems including superoxide dismutase, catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and others that neutralize reactive oxygen species. With aging, the genes encoding these antioxidant enzymes become less active due to epigenetic modifications like DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. Ventfort addresses this by modifying the epigenetic landscape at these gene loci, making them more accessible to transcription factors and restoring normal expression levels. The result is increased antioxidant capacity without supplementing exogenous antioxidants. This contrasts with the approach of taking SS-31, which targets mitochondrial oxidative stress directly rather than through gene expression changes.
Neurological effects emerge from vascular bioregulation as well. The KED peptide has been studied in models of Alzheimer disease, where it increases the number of functional mushroom spines by twenty to twenty-seven percent in both in vitro and in vivo neurological models. Dendritic spines are the structures where neurons receive synaptic input, and mushroom spines represent mature, stable connections. The fact that a vascular bioregulator affects neuronal morphology makes sense when you consider that the blood-brain barrier consists of specialized endothelial cells and that cerebral blood flow determines neuronal health. By improving the function of cerebral blood vessels, vascular bioregulators indirectly support neuronal function. Research also shows that KED decreases apoptosis in both endothelial and neuronal cells in Alzheimer models, suggesting a protective effect against the vascular dysfunction that contributes to neurodegeneration. For those studying peptides for brain function, the vascular component of cognitive health is often overlooked.
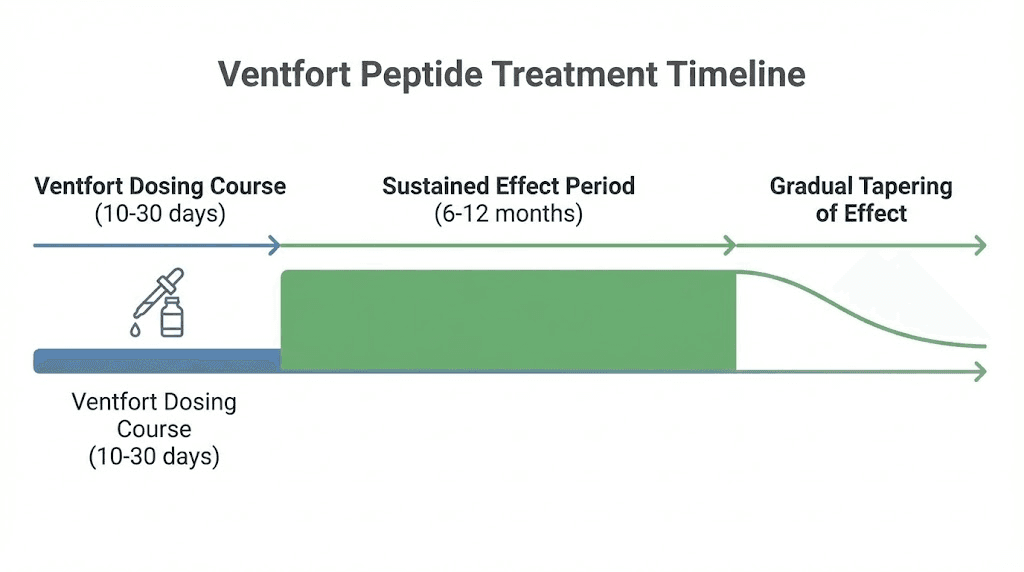
The pharmacokinetics of Ventfort differ from most peptides due to its oral administration and tissue-specific accumulation. After ingestion, the peptide complex survives gastric acid and is absorbed in the small intestine. Bioavailability is lower than injectable routes, but sufficient peptide reaches circulation to exert effects. The peptides then preferentially accumulate in vascular tissue over days to weeks, building up in vessel walls where they exert prolonged regulatory effects. This is not a fast-acting emergency intervention but a gradual restoration of function. The clinical protocols reflect this with courses lasting ten to thirty days rather than single injections or short courses typical of other peptide dosing approaches.
Understanding this mechanism helps explain why Ventfort works for conditions as diverse as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and senile purpura.
All three involve endothelial dysfunction and vascular wall deterioration. By restoring the gene expression patterns that maintain healthy vascular tissue, Ventfort addresses the underlying cause rather than managing symptoms. This is why effects persist for months after treatment ends. The epigenetic modifications remain stable until environmental factors or continued aging gradually shift them back toward dysfunctional states. This is also why periodic maintenance courses every six to twelve months make sense from a mechanistic perspective.
The clinical evidence behind Ventfort
The primary clinical study for Ventfort was conducted at the Saint Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology between November 2003 and February 2004. This was a controlled trial involving forty-nine patients with atherosclerotic disease aged fifty-two to eighty-four years. Twenty-seven patients received Ventfort treatment alongside standard therapy while twenty-two served as controls receiving only standard care without bioregulator supplementation. The study population included thirty-five patients with arterial atherosclerosis and fourteen with senile purpura.
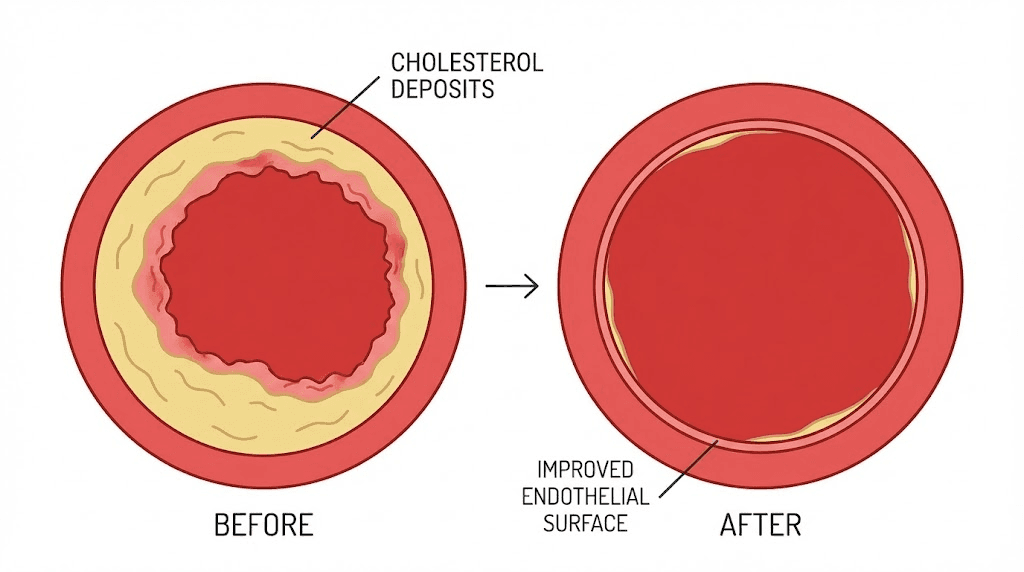
Cholesterol results provide the most striking data point. Before treatment, the Ventfort group had mean general cholesterol levels of 8.6 plus or minus 0.4 millimoles per liter. After the course of Ventfort, cholesterol dropped to 6.0 plus or minus 0.7 millimoles per liter. The P value was less than 0.05, indicating statistical significance. This represents a reduction of approximately thirty percent. The control group receiving only standard treatment saw cholesterol drop from 8.6 to 7.2, a more modest decline. The difference between standard treatment alone and standard treatment plus Ventfort was clinically meaningful.
VLDL cholesterol changed as well. Very low-density lipoprotein carries triglycerides and contributes to atherosclerotic plaque formation when oxidized. The Ventfort group showed VLDL levels decreasing from 1.32 plus or minus 0.05 to 0.91 plus or minus 0.07 millimoles per liter. This thirty-one percent reduction suggests improved hepatic lipid metabolism and better clearance of triglyceride-rich particles from circulation. The control group showed VLDL decreasing from 1.32 to 1.13, again a lesser improvement compared to the Ventfort-supplemented group.
Capillary wall strength was assessed using the Hesse test in patients with senile purpura, a condition characterized by spontaneous bruising from fragile capillaries common in elderly populations. Patients receiving Ventfort showed increased capillary wall resistance and decreased frequency of hemorrhagic episodes. This indicates structural strengthening of small vessel walls, likely through increased collagen synthesis, improved endothelial tight junction integrity, and restoration of basement membrane composition. The result demonstrates that Ventfort affects vessels of all sizes, from the aorta to capillaries. For researchers interested in peptides for anti-aging, the capillary strengthening data is particularly relevant since microvascular deterioration drives many visible signs of aging.
Safety data across the study showed no adverse effects. Not a single patient in the treatment group reported side effects, adverse reactions, or problems related to Ventfort administration. This aligns with the broader safety profile of bioregulator peptides, which have been used in over fifteen million patients across three decades without reported serious side effects. The study was well-tolerated across all age groups, from fifty-two to eighty-four years old.
The clinical dosing protocols used in the study provide guidance for practical application. For atherosclerosis patients, the protocol was one to three capsules taken two to three times daily, ten to fifteen minutes before meals, for ten to twenty days.
For senile purpura patients, the same dosing range was used for ten to thirty days. These higher-intensity protocols make sense for active disease requiring intervention. Each capsule contained 10 milligrams of the active peptide complex, meaning daily doses ranged from 20 to 90 milligrams depending on the protocol selected.
A separate study examined the efficacy of peptide bioregulators in treating chronic arterial insufficiency of the lower limbs in elderly patients. This PubMed-indexed study (PMID 25051774) assessed vascular peptide bioregulators in patients with peripheral artery disease, demonstrating benefits for blood flow to extremities. The results supported the broader application of vascular bioregulators beyond coronary and cerebral vasculature to include peripheral circulation.
Research on the synthetic counterpart Vesugen provides additional mechanistic validation. The study on epigenetic aspects of peptidergic regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation during aging (PMID 25051766) demonstrated that the KED peptide stimulates Ki-67 proliferation marker expression in endothelial cells through molecular interaction with the MKI67 gene promoter. This connects the molecular mechanism to the clinical observations. The cells that line blood vessels regain their ability to divide and repair damage because their proliferation genes are reactivated. The peptide research database continues to grow as more studies characterize these mechanisms.
Long-term observational data from Russia and Eastern Europe, where bioregulator peptides have been integrated into geriatric and preventive medicine for decades, suggests that regular use of vascular bioregulators correlates with reduced cardiovascular events, better blood pressure control, and maintained cognitive function in aging populations. These are not randomized controlled trials, but the consistency of outcomes across large populations over extended periods provides supporting evidence. The broader Khavinson research program, which included a 266-person clinical trial showing up to four-fold mortality reduction with bioregulator treatment, provides context for the cardiovascular benefits observed with Ventfort specifically.
The limitation of current clinical evidence is the geographic concentration of research in Russia and former Soviet states. Western medical institutions have not conducted independent validation studies, which creates understandable skepticism about the magnitude and consistency of effects. However, the mechanistic research on Vesugen has been published in international peer-reviewed journals with rigorous methodology. The gene expression changes, protein upregulation, and cellular function improvements are well-documented. As peptide regulation evolves and international interest grows, additional validation studies will likely emerge.
Ventfort vs Vesugen: Cytomax vs Cytogen
The relationship between Ventfort and Vesugen mirrors the broader distinction between Cytomaxes and Cytogens in the Khavinson peptide system. Ventfort is the natural peptide complex extracted from calf aortic tissue. Vesugen is the synthetic tripeptide KED (Lys-Glu-Asp) that replicates the primary active sequence found in that natural complex. Both target vascular tissue, both produce measurable improvements in endothelial function and lipid profiles, but their pharmacokinetics and optimal use cases differ considerably.
Cytomax peptides like Ventfort are approximately thirty-three percent more potent than their Cytogen counterparts. This means a given course of Ventfort produces stronger regulatory effects and those effects last approximately twice as long. A course of Ventfort creates regulatory changes that persist for six to twelve months, while Vesugen effects typically last one and a half to two months. The practical implication is significant. Ventfort requires less frequent administration for maintenance. Two courses per year of Ventfort may provide continuous vascular benefit, while Vesugen might require four to six courses to maintain similar effects throughout the year.
Speed favors Vesugen. Cytogens accumulate in target tissues twenty to thirty percent faster than Cytomaxes. This faster onset makes Cytogens preferable when you need relatively quick results or when starting a bioregulator protocol for the first time. Some practitioners recommend beginning with a Cytogen to establish regulatory improvements within four to six weeks, then transitioning to the corresponding Cytomax for long-term maintenance. In the case of vascular bioregulation, this would mean starting with Vesugen for one month, then switching to Ventfort for subsequent courses.
Molecular complexity differs significantly between the two. Ventfort contains dozens of peptide sequences in its natural complex, each potentially targeting different aspects of vascular gene regulation. Vesugen contains only the KED tripeptide, which binds to specific promoter regions and modulates specific genes. The natural complex may produce more comprehensive regulation because it affects multiple genetic pathways simultaneously. The synthetic peptide offers precise, targeted action at specific gene loci. Neither approach is inherently superior. They represent different philosophies of intervention, and experienced researchers often use both at different points in their protocols. Understanding the peptide formula behind each helps clarify these distinctions.
Cost and availability influence practical choices. Vesugen is easier to synthesize since it is a simple tripeptide, which typically makes it less expensive and more widely available. Ventfort requires extraction from animal tissue and standardization of the peptide complex, which increases manufacturing complexity. Regulatory status varies by country. In Russia and some Eastern European countries, both are available as registered pharmaceuticals. In Western countries, both are typically sold as research compounds. The cost of peptides varies significantly based on source, purity, and manufacturing standards. Understanding peptide legality in your jurisdiction is essential before purchasing either compound.
Research publication volume favors Vesugen because synthetic peptides are easier to study with consistent dosing and characterization. The KED sequence has been characterized in detail with published data on its DNA binding properties and documented effects on specific gene expression patterns. The natural Ventfort complex is harder to fully characterize because it contains multiple sequences. This does not mean Ventfort is less effective, but it does mean the scientific literature provides more mechanistic detail about Vesugen than about the natural complex.
Stacking protocols sometimes use both Cytomax and Cytogen forms of the same bioregulator. The logic is to start with Vesugen for faster onset, then introduce Ventfort around week four to extend the duration of effects. This creates overlapping regulatory waves where the Cytogen initiates improvements and the Cytomax maintains them. Whether this offers advantages over using one form consistently remains unclear from available data, but practitioners report positive results from the combination approach, particularly for patients with significant vascular dysfunction.
For preventive use in younger individuals without overt cardiovascular disease, Vesugen may suffice due to lower cost and easier availability. For therapeutic use in older patients with established atherosclerosis or vascular dysfunction, Ventfort is preferable for its greater potency and longer duration. For protocols targeting multiple organ systems with peptide stacks, mixing Cytomaxes and Cytogens can balance cost and effectiveness across the full range of compounds.
Complete Ventfort dosing protocols
Standard maintenance dosing for Ventfort is one to two capsules once or twice daily for ten days. This represents the minimal effective course for healthy individuals seeking preventive vascular support. Each capsule contains 10 milligrams of peptide complex A-3, so the total peptide dose per course ranges from 100 to 400 milligrams depending on whether you use one capsule once daily or two capsules twice daily. This course is repeated every six months as maintenance. The logic is that regulatory effects from a single course persist for six to twelve months, so repeating courses biannually maintains continuous benefit.
Therapeutic protocols for established cardiovascular disease increase both dose and duration. The clinical atherosclerosis study used one to three capsules two to three times daily for ten to twenty days. This higher intensity makes sense when trying to reverse existing pathology rather than prevent it. The maximum protocol would be three capsules three times daily for twenty days, totaling 1800 milligrams of peptide complex over the course. This is repeated biannually or quarterly depending on disease severity and response. The peptide dosage chart provides quick reference for standard bioregulator courses.
Timing of administration should be ten to fifteen minutes before meals based on clinical study protocols. This empty-stomach timing may improve absorption by avoiding competition with dietary proteins for intestinal transport mechanisms. Some practitioners find that splitting doses between morning and evening produces more stable tissue levels than taking all capsules at once. The key is consistency. Taking Ventfort at the same times each day maintains stable concentrations and optimizes regulatory effects.
Peptide cycle planning for Ventfort differs from typical peptide cycling with growth factors or synthetic hormones. Bioregulators require breaks because the regulatory effects persist long after the peptide clears. Continuous use would be unnecessary and wasteful since the epigenetic changes remain stable for months. The standard approach is ten to thirty days on, then five to eleven months off, repeated indefinitely. There is no tolerance development, receptor downregulation, or diminishing returns with this pattern.
Age-related dosing adjustments follow a logical progression. Individuals in their thirties and forties using Ventfort preventively might use lower doses (one capsule twice daily) for shorter courses (ten days) repeated annually. Individuals in their fifties and sixties might use moderate doses (two capsules twice daily) for twenty days, repeated biannually. Those in their seventies and beyond with multiple vascular risk factors might use the full therapeutic protocol (two to three capsules two to three times daily) for thirty days, repeated every three to six months. The general principle is that greater dysfunction requires more intensive intervention, while minimal dysfunction requires only light maintenance.
Sublingual administration offers an alternative to capsules. Ventfort is available in lingual preparations where five to six drops (approximately 0.25 to 0.35 milliliters) are placed under the tongue for ten to fifteen minutes before eating, three to four times daily for thirty days.
The sublingual route bypasses the digestive system entirely, providing more direct absorption through the oral mucosa. This may improve bioavailability compared to swallowed capsules, though the convenience trade-off is more frequent daily dosing. After a thirty-day sublingual course, a sixty-day break follows before repeating.
Combining Ventfort with other bioregulators requires consideration of overlapping cycles. If you are using the Khavinson first-class stack, you might run all six bioregulators simultaneously for convenience, taking the recommended dose of each compound during the same ten to twenty day period. Alternatively, stagger them throughout the year with different bioregulators in different months. Simultaneous use creates a comprehensive regulatory wave across all major systems but increases daily capsule count. Staggered use extends regulatory coverage throughout the year but requires more organization. The peptide stack calculator at SeekPeptides can help plan multi-compound protocols.
Monitoring response helps optimize dosing. If you have access to lipid panels, checking cholesterol and VLDL before and after a Ventfort course provides objective feedback. Blood pressure tracking offers another marker of vascular function. Subjective improvements in energy, mental clarity, and exercise capacity may reflect improved blood flow and oxygen delivery. The peptides before and after timeline for bioregulators looks different from traditional compounds, with changes emerging gradually over weeks to months rather than appearing immediately.
Storage and handling follow standard peptide storage principles. Ventfort capsules should be kept in a cool, dry place away from light. Refrigeration is not necessary but may extend shelf life. The peptides are relatively stable in capsule form compared to reconstituted injectables. Understanding how long peptides last at room temperature and in powder form helps maintain potency through the full duration of any course.
Discontinuation does not cause rebound effects. When you stop Ventfort, the regulatory improvements gradually fade over six to twelve months as epigenetic modifications slowly revert. There is no sudden crash or withdrawal syndrome. This makes Ventfort suitable for intermittent use based on need and circumstances. You can run a course, take a year off, then resume without problems. This contrasts with some pharmaceutical interventions where stopping causes immediate return of symptoms or even rebound worsening.
Ventfort in the Khavinson first-class stack
The Khavinson first-class stack represents the core bioregulator protocol for comprehensive longevity support. Six compounds form this foundation, each targeting a critical system. Ventfort handles the vascular system. Vladonix regulates the immune system through thymic restoration. Endoluten modulates the pineal gland and neuroendocrine regulation. Cerluten supports brain and central nervous system function. Sigumir addresses joints and bones. Svetinorm maintains liver health. Together, these six address the primary drivers of biological aging.
The rationale comes from decades of gerontological research identifying which systems deteriorate first and contribute most to age-related disease. Vascular dysfunction drives cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, and multi-organ failure through reduced blood flow. Immune dysregulation causes increased infection susceptibility, cancer risk, and chronic inflammation. Pineal gland decline disrupts circadian rhythms, melatonin production, and cellular repair cycles. Brain deterioration causes cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disease. Joint and bone deterioration limits mobility and quality of life. Liver dysfunction impairs detoxification and metabolic regulation. Address these six systems and you address the majority of aging pathology.
Ventfort occupies a central position in the stack because vascular health determines the function of all other organs. Your thymus cannot function optimally if it receives inadequate blood flow. Your brain cannot maintain cognitive function if cerebral blood flow is compromised. Your liver cannot process toxins efficiently if hepatic perfusion is reduced. Your joints cannot heal if their blood supply is diminished. By restoring vascular regulation, Ventfort creates the foundation that allows other bioregulators to work more effectively.
Running the full first-class stack simultaneously creates synergistic effects. When vascular function improves through Ventfort while immune function improves through Vladonix, the enhanced blood flow delivers more immune cells to sites of infection or inflammation. When brain function improves through Cerluten while vascular function improves through Ventfort, the improved cerebral blood flow enhances the neurological benefits. These interactions mean the total benefit exceeds the sum of individual bioregulator effects. This is why the first-class stack is recommended as a unit rather than using bioregulators in isolation.
The typical approach is to run all six bioregulators for one to two months, twice per year, as Khavinson himself recommended. For Ventfort, this means two capsules daily during the course period. For the other bioregulators, standard dosing protocols apply. The combined daily capsule count during a stacking course may reach ten to twelve capsules, which is manageable though requires organization. Planning tools like the peptide cost calculator help estimate the financial investment for comprehensive stacking protocols.
Women adjust the first-class stack by ensuring it addresses female-specific systems. While the six core bioregulators remain the same for both sexes, women going through menopause or perimenopause might add Zhenoluten (ovarian bioregulator) to support hormonal transition. Men might add Testagen for testicular support alongside testosterone-supporting protocols. Ventfort remains constant in both approaches because vascular health is equally critical regardless of sex.
Adding bioregulators beyond the first-class six creates second-tier protocols for specific needs. If you have cardiac concerns, adding Cardiogen creates comprehensive cardiovascular coverage alongside Ventfort. If you have respiratory issues, Bronchogen addresses pulmonary tissue. If you have bladder problems, Chitomur targets urinary system regulation. The first-class stack provides the foundation while additional bioregulators address specific organ systems requiring extra support.
Stacking Ventfort with other bioregulators
Beyond the first-class stack, Ventfort combines effectively with organ-specific bioregulators for targeted interventions. Cardiogen represents the natural companion to Ventfort because it targets cardiac muscle specifically while Ventfort targets blood vessels. Together they provide comprehensive cardiovascular regulation covering both the pump and the plumbing. Running Cardiogen and Ventfort simultaneously for twenty to thirty days creates coordinated restoration of both contractile function and vascular delivery capacity.
Brain health stacks pair Ventfort with neurological bioregulators because cerebral blood flow determines cognitive function. Pinealon supports cortical neurons and neuroprotection. Cortagen regulates cerebral cortex function.
Ventfort improves cerebrovascular health. This three-way combination addresses vascular delivery, neuronal function, and overall cortical regulation. People experiencing age-related cognitive decline, memory problems, or brain fog may benefit from this stack. The vascular component is critical because even healthy neurons cannot function without adequate oxygen and glucose delivery through properly functioning blood vessels. For those exploring nootropic peptides, the vascular foundation is often the missing piece.
Immune system stacks combine Ventfort with Crystagen (synthetic immune Cytogen) or Vladonix (natural thymus Cytomax). The immune system depends on blood flow to transport immune cells to infection sites, deliver antibodies to tissues, and clear inflammatory debris. When vascular function is compromised, immune responses become sluggish and less effective. Ventfort ensures the delivery system works while thymic bioregulators ensure the immune cells themselves are properly produced and regulated. For anyone studying peptides for immune function, this combined approach addresses both the immune cells and the infrastructure they depend on.
Metabolic optimization stacks combine Ventfort with Pancragen for pancreatic support and Livagen or Svetinorm for hepatic function.
The pancreas regulates insulin and glucagon secretion. The liver processes nutrients and maintains glucose homeostasis. The vasculature delivers nutrients to tissues and removes metabolic waste. When all three systems function optimally, metabolic syndrome risk decreases, energy levels stabilize, and body composition improves. Researchers interested in peptides for energy should consider the metabolic triad of pancreas, liver, and vasculature.
Joint and connective tissue stacks pair Ventfort with Cartalax for cartilage regulation. Joint health requires both structural integrity of cartilage and adequate blood flow to synovial tissue and subchondral bone. Ventfort provides the vascular component while Cartalax addresses structural repair at the gene expression level. Those already using BPC-157 or TB-500 for acute joint pain can layer bioregulators beneath these compounds for long-term gene expression restoration that surface-receptor peptides cannot provide. The wolverine stack concept takes on new dimensions when bioregulators are integrated into healing protocols.
Sexual health stacks use Ventfort to support the vascular component of sexual function. For men, combining Ventfort with Testagen addresses both penile blood flow and hormonal support. Erectile dysfunction requires healthy endothelium in penile arteries for adequate blood flow during arousal. Ventfort restores this vascular capacity while Testagen optimizes testosterone production. For women, Ventfort combined with ovarian bioregulators supports pelvic blood flow and hormonal balance, which affect libido, arousal, and reproductive health.
Athletic performance stacks sometimes include Ventfort for improved oxygen delivery and waste removal during exercise. While Ventfort is not primarily a performance peptide, the vascular improvements it provides enhance exercise capacity and recovery. Combining Ventfort with the BPC-157 and TB-500 stack creates a protocol addressing tissue repair, angiogenesis, and vascular regulation. For athletes interested in muscle growth and injury recovery, the vascular foundation supports every other compound in the stack.
Skin health protocols combine Ventfort with dermal-focused peptides because skin aging involves both structural changes and underlying microvascular deterioration. GHK-Cu stimulates collagen synthesis and wound healing topically, while Ventfort improves the microvascular bed that nourishes dermal tissue from within. This inside-out approach produces better results for skin tightening and skin health than either approach alone because healthy dermis requires both structural proteins and adequate blood supply.
The key principle for stacking is matching bioregulators to your specific weaknesses rather than trying to use everything simultaneously. Identify your two or three priority systems based on symptoms, lab work, and health history. Choose bioregulators targeting those systems. Run them together for twenty to thirty days. Assess response. Adjust subsequent courses based on results. How many peptides you can take at once depends on monitoring capability and complexity tolerance, but two to five compounds is typically manageable without losing track of what produces which effects.
Ventfort for specific conditions
Atherosclerosis represents the primary indication for Ventfort based on clinical study data. The lipid improvements, plaque stabilization, and endothelial function restoration make it appropriate for anyone with documented atherosclerotic disease. The therapeutic protocol of two to three capsules two to three times daily for twenty to thirty days addresses active disease. Maintenance after improvement requires biannual courses to prevent recurrence. Combining Ventfort with standard medical management is appropriate, as the clinical study specifically used Ventfort alongside standard therapy with superior outcomes compared to standard therapy alone.
Hypertension with vascular origin responds to Ventfort through improved endothelial function and vascular compliance. High blood pressure has multiple causes, but endothelial dysfunction and arterial stiffness are common contributors in aging populations. By restoring nitric oxide production, reducing oxidative stress, and improving vascular smooth muscle function, Ventfort can lower blood pressure through regulatory mechanisms rather than forced vasodilation. This makes it complementary to antihypertensive drugs. Monitoring blood pressure during Ventfort courses helps assess response and determine whether medication adjustments are warranted.
Cognitive decline related to vascular insufficiency benefits from Ventfort as part of a comprehensive protocol. Vascular dementia and vascular contributions to Alzheimer disease involve chronic cerebral hypoperfusion, blood-brain barrier dysfunction, and microvessel damage. Ventfort addresses these mechanisms by restoring cerebrovascular endothelial function. Combined with neuronal bioregulators like Pinealon and Cortagen, plus Semax for acute neuroprotection, this creates multi-modal support for brain health. The KED peptide research showing decreased neuronal apoptosis and increased dendritic spine density in Alzheimer models directly supports this application.
Peripheral artery disease causes claudication and reduced exercise tolerance due to inadequate blood flow to leg muscles. Ventfort may improve symptoms by enhancing endothelial function in affected vessels and promoting collateral vessel health. The PubMed-indexed study on peptide bioregulators for lower limb chronic arterial insufficiency demonstrated benefits in elderly patients with this condition. While severe PAD requires medical management, mild to moderate disease may respond favorably to bioregulator therapy as part of comprehensive care.
Diabetic vascular complications including retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy all involve endothelial dysfunction and microvascular damage from chronic hyperglycemia. Ventfort addresses the vascular component while metabolic management controls glucose levels. For those already exploring peptides for hormone balance and metabolic optimization, adding vascular bioregulation creates a more comprehensive approach to diabetic complication prevention.
Senile purpura, the condition characterized by easy bruising and skin hemorrhages in elderly individuals, responded directly to Ventfort in clinical studies. Capillary wall strength increased and hemorrhage frequency decreased after treatment. This condition reflects microvascular fragility that affects not just visible bruising but organ perfusion throughout the body. Improving capillary integrity through Ventfort may benefit organ function broadly, even in cases where the primary presentation is skin bruising.
Erectile dysfunction with vascular etiology may improve with Ventfort as part of a comprehensive approach. Many cases of ED in older men involve endothelial dysfunction in penile arteries. Ventfort restores the vascular component while addressing systemic endothelial health. Combined with peptides for men targeting hormonal and reproductive function, this creates comprehensive support for sexual health.
Chronic venous disease, including varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency, involves endothelial dysfunction and vascular wall weakness in the venous system. While Ventfort primarily targets arterial tissue based on its aortic extraction source, the regulatory effects on endothelial gene expression may benefit venous health as well. Combining Ventfort with compression therapy and other measures creates comprehensive management for venous conditions.
Prevention in healthy individuals with cardiovascular risk factors represents perhaps the most logical use of Ventfort. Family history of cardiovascular disease, multiple risk factors like elevated lipids or hypertension, early markers of vascular aging on imaging, or simply advancing age all warrant consideration of preventive vascular bioregulation. The maintenance protocol of ten days every six months provides ongoing regulatory support to prevent or delay disease development. This is genuine preventive medicine, intervening at the regulatory level before pathology becomes clinically apparent.
Safety profile and what to watch for
The safety data for Ventfort and bioregulator peptides generally is remarkably clean. Over fifteen million patients have used these compounds across three decades in Russia and Eastern Europe without reported serious adverse effects. The clinical trial in atherosclerosis patients showed no adverse effects in the treatment group. This level of safety is unusual for compounds producing measurable physiological effects, but it makes sense given the mechanism. Bioregulators restore normal function rather than forcing abnormal states, which inherently carries less risk. Peptide safety is a critical consideration for any compound, and the bioregulator track record is among the best in the entire peptide field.
Contraindications are minimal. Pregnancy and breastfeeding represent theoretical concerns due to lack of safety data in these populations. Active cancer is sometimes listed as a relative contraindication because peptides that promote cellular proliferation might theoretically enhance tumor growth, though bioregulators target differentiated cells rather than undifferentiated cancer stem cells. Individual hypersensitivity to any component is a standard contraindication. Beyond these, there are no established contraindications for Ventfort in adult populations.
Drug interactions appear minimal based on decades of clinical experience. Ventfort does not affect cytochrome P450 enzymes or compete for protein binding sites, which eliminates most common interaction mechanisms. It has been used alongside statins, blood pressure medications, anticoagulants, and other cardiovascular drugs without known interactions. However, as vascular function improves, medication requirements may decrease. Blood pressure might drop enough to require reduction of antihypertensive doses. Lipids might improve enough to consider statin dose adjustment. This requires monitoring and medical supervision.
Allergic reactions are theoretically possible since Ventfort is derived from bovine tissue. People with severe beef allergies might react, though the processing removes most allergenic proteins. No documented cases of anaphylaxis or serious allergic reactions appear in available literature. The common mistakes beginners make with peptides include not checking for known allergies before starting a new compound.
Quality control represents a practical safety concern. Ventfort must be sourced from reputable manufacturers using pharmaceutical-grade extraction and purification. Peptide testing labs can verify purity and peptide content. Choosing established brands with track records in Eastern European pharmaceutical markets provides some assurance of quality. The peptide vial research mindset applies equally to capsule products, where batch consistency and manufacturing standards matter.
Long-term use safety is supported by decades of clinical experience in geriatric populations using bioregulators continuously for years. Annual or biannual courses repeated indefinitely have not produced cumulative toxicity, organ damage, or tolerance development. The intermittent nature of dosing with long breaks between courses likely contributes to this safety profile by allowing complete clearance and preventing chronic tissue accumulation.
Signs to watch for during use include changes in blood pressure, which could indicate medication adjustment needs. If energy levels dramatically improve, this reflects strong vascular response and confirms the protocol is working.
If no changes are observed after two or three courses, the protocol may need intensification or the specific presentation may not be responsive to vascular bioregulation. Most people notice subtle improvements rather than dramatic acute effects.
How long peptides take to work varies by mechanism, and bioregulators produce the most gradual onset of any peptide class.
How Ventfort compares to traditional peptides
The distinction between bioregulator peptides like Ventfort and traditional synthetic peptides is fundamental. Traditional peptides are designed compounds that bind to specific receptors or mimic growth factors to stimulate acute physiological responses. BPC-157 promotes angiogenesis and wound healing through growth factor signaling. TB-500 upregulates actin to facilitate cell migration during repair. Ipamorelin stimulates growth hormone release through ghrelin receptor activation. These produce measurable effects within days to weeks and require continuous or frequent dosing.
Bioregulators like Ventfort operate through epigenetic modification of gene expression rather than acute signaling. They do not bind to cell surface receptors or activate second messenger cascades. Instead, they enter cells and influence which genes are transcribed by modifying chromatin accessibility. The effects develop gradually over weeks as new proteins are synthesized based on altered gene expression, and they persist for months after the peptide clears because epigenetic modifications are relatively stable. This makes them fundamentally different from every other peptide class.
Duration of effect represents the key practical difference. When you stop BPC-157, effects fade within days. When you stop TB-500, tissue repair slows within weeks. When you stop Ventfort, regulatory improvements persist for six to twelve months. This makes bioregulators more convenient and potentially more cost-effective for long-term management. The cost of peptide therapy depends heavily on compound selection and dosing frequency, and bioregulators often prove more economical for sustained protocols.
Specificity differs as well. Traditional peptides often have effects across multiple tissue types. BPC-157 affects gut, tendon, muscle, and vascular tissue because it acts through pathways present in all these locations. Ventfort exhibits tissue tropism, preferentially accumulating in vascular tissue and affecting primarily vascular gene expression. This targeted action produces system-specific benefits without broadly affecting unrelated tissues. The research versus pharmaceutical peptide comparison takes on new dimensions when bioregulators enter the picture.
Safety profiles diverge based on mechanism. Traditional peptides that force acute responses can potentially overstimulate pathways. Growth factors can theoretically promote tumor growth if cancer is present. Hormone-mimicking peptides can disrupt endocrine feedback loops. Bioregulators that restore normal gene expression patterns have intrinsically lower risk because they push toward physiological norms rather than supraphysiological states. This explains the exceptionally clean safety record.
Stacking traditional peptides with bioregulators often produces complementary benefits. Using TB-500 and BPC-157 for acute tissue repair while using Ventfort for long-term vascular regulation addresses both immediate healing needs and underlying system optimization. The traditional peptides handle emergency repair while the bioregulator prevents future problems through improved tissue quality. This layered approach represents the most comprehensive strategy currently available in peptide research.
Research accessibility differs between the two classes. Traditional synthetic peptides have extensive Western research literature. Bioregulator research is concentrated in Russian and Eastern European literature. This creates perception that traditional peptides are better validated, though the clinical safety record of bioregulators is actually superior. The world of peptides continues expanding as Western researchers begin exploring bioregulator mechanisms that were first characterized decades ago in Eastern Europe.
For those comparing delivery methods, traditional peptides typically require reconstitution with bacteriostatic water and subcutaneous injection. Bioregulators work as oral capsules or sublingual preparations. This convenience factor significantly impacts adherence, especially for long-term protocols. Understanding the peptide injection pen and proper mixing procedures matters for injectable peptides, while bioregulator capsules require no preparation.
Tolerance development separates the two classes. Many traditional peptides lose effectiveness over time as receptors downregulate from repeated stimulation. This is why cycling different peptides is important for growth hormone secretagogues and similar compounds. Bioregulators do not face this problem because they work through gene expression modulation rather than receptor activation. There is no receptor to desensitize. This means bioregulators can be used on the same schedule indefinitely without diminishing returns.
Frequently asked questions
How long does it take to see results from Ventfort?
Measurable changes in lipid profiles typically appear within four to eight weeks based on clinical study data. Cholesterol and VLDL reductions become apparent on blood work by this timeframe. Subjective improvements in energy, exercise capacity, and cognitive function may occur earlier as vascular perfusion improves. Structural changes like improved capillary wall strength take longer, showing improvement by eight to twelve weeks. Maximum regulatory effects continue developing for three to six months as epigenetic modifications stabilize and new cellular proteins fully replace old dysfunctional ones.
Can I use Ventfort if I am already taking blood pressure medication?
Yes. Ventfort can be used alongside antihypertensive medications without known interactions. However, as vascular function improves, your blood pressure may decrease, potentially requiring adjustment of medication doses to avoid excessive lowering. Monitor blood pressure regularly during Ventfort courses. If readings consistently drop below target ranges, consult your prescribing physician about reducing medication doses. The goal is to optimize vascular function while maintaining blood pressure in healthy ranges.
Should I use Ventfort or Vesugen for cardiovascular support?
The choice depends on your priorities. Ventfort is more potent and produces longer-lasting effects (six to twelve months), making it ideal for maintenance. Vesugen accumulates faster and typically costs less, making it suitable for initial treatment when faster results are desired. A hybrid approach uses Vesugen for the first course, then switches to Ventfort for subsequent courses. For prevention in younger healthy individuals, Vesugen may suffice. For therapeutic use in patients with established disease, Ventfort offers greater potency and duration.
Can Ventfort reverse existing atherosclerotic plaque?
Ventfort improves endothelial function, reduces oxidative stress, and favorably affects lipid profiles, all of which can stabilize plaque and potentially promote gradual regression. Clinical data shows significant cholesterol reduction (thirty percent decrease) and improved vascular markers. However, dramatic plaque regression requires comprehensive intervention including aggressive lipid management, blood pressure control, lifestyle modification, and often pharmaceutical therapy. Ventfort should be viewed as part of comprehensive atherosclerosis management, not monotherapy.
How does Ventfort compare to taking antioxidant supplements for vascular health?
Ventfort increases endogenous antioxidant enzyme expression through gene regulation, while supplemental antioxidants provide exogenous compounds to neutralize free radicals. Upregulating your own antioxidant enzyme production is generally more effective because the enzymes are precisely localized where needed, regenerate continuously, and do not carry the pro-oxidant risks that high-dose supplements sometimes exhibit. Ventfort produces sustained increases in superoxide dismutase, catalase, and other defenses that persist for months after a course. This represents a more physiological and sustained approach to vascular antioxidant protection.
Can I use Ventfort for cognitive enhancement without cardiovascular disease?
Yes. Vascular health is critical for cognitive function even without overt cardiovascular disease. Cerebral blood flow determines oxygen and glucose delivery to neurons, and endothelial dysfunction in brain microvasculature contributes to age-related cognitive decline before dementia develops. Using Ventfort as part of a cognitive stack with BDNF peptides and neuronal bioregulators addresses the vascular foundation of brain health. The research showing KED increases dendritic spine density and reduces neuronal apoptosis directly supports this use.
What is the best way to stack Ventfort with other compounds?
The optimal stack depends on goals. For comprehensive longevity, the Khavinson first-class stack (Ventfort plus five other core bioregulators) provides broad regulatory support. For cardiovascular focus, Ventfort plus Cardiogen targets both vessels and heart. For cognitive enhancement, Ventfort plus Pinealon plus Cortagen addresses vascular and neuronal components. For athletic performance, Ventfort plus BPC-157 plus TB-500 supports vascular function alongside tissue repair. Run complementary bioregulators simultaneously during the same course period. Traditional peptides can be used continuously around bioregulator courses.
Do I need to cycle Ventfort or can I use it continuously?
Ventfort requires cycling with breaks between courses. The standard protocol is ten to thirty days on, then five to eleven months off, repeated indefinitely. Continuous use is unnecessary because the epigenetic regulatory effects persist long after the peptide clears. Using Ventfort continuously would waste product without providing additional benefit. The cycling pattern differs fundamentally from traditional peptides that require continuous use for sustained effects. There is no tolerance development, so each subsequent course remains equally effective.
External resources
For researchers serious about implementing vascular bioregulator protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based guides on individual bioregulators like Epitalon, Thymalin, Vesugen, and Cartalax, along with stacking guides, dosing calculators, and a growing community of experienced researchers navigating the world of peptide bioregulation. Membership includes detailed protocol builders, cardiovascular biomarker interpretation guides, and personalized support for building multi-compound bioregulator stacks tailored to your specific health goals.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your blood vessels stay supple, your endothelium stay healthy, and your circulation stay strong.



