Dec 31, 2025
Russian bioregulator peptides follow a tissue-specific philosophy - each organ or tissue type has dedicated peptides that regulate its function and regeneration. While Epithalon targets the pineal gland for systemic longevity and Pinealon supports brain tissue for cognitive health, Cartalax specifically targets cartilage and connective tissue for joint optimization. This organ-specific targeting distinguishes Russian bioregulators from Western peptides like BPC-157 which work systemically.
Cartalax belongs to the Khavinson peptide family developed at St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology over 40+ years of research.
The dipeptide consists of just two amino acids (Ala-Glu or alanine-glutamic acid), making it one of the simplest bioregulator peptides yet reportedly effective for cartilage regeneration, joint mobility improvement, and age-related joint degeneration prevention.
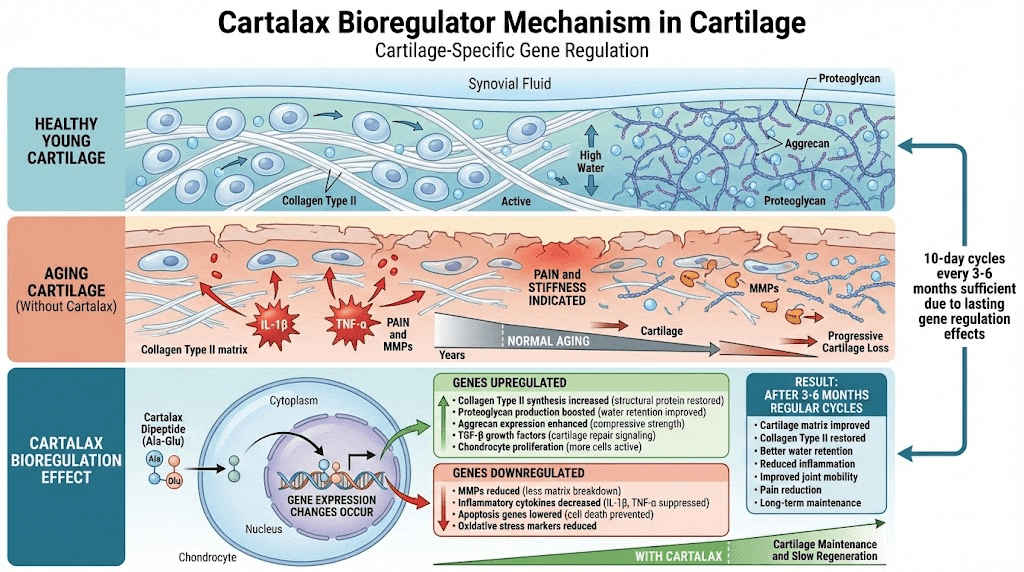
The mechanism involves gene regulation in chondrocytes (cartilage cells) - Cartalax binds to specific DNA sequences in cartilage tissue, upregulating genes for cartilage matrix proteins (collagen type II, proteoglycans, aggrecan), downregulating inflammatory and degradative enzymes (matrix metalloproteinases), and optimizing the balance between cartilage formation and breakdown.
This bioregulatory approach differs fundamentally from BPC-157's angiogenic healing or TB-500's cell migration.
Standard Cartalax protocols follow the Russian 10-day intensive cycle - 10mg daily for 10 consecutive days, repeated every 3-6 months, administered via subcutaneous injection or oral/sublingual formulations. The cyclic approach reflects bioregulator theory that short intensive treatments provide lasting regulatory effects rather than requiring continuous supplementation.
However, Cartalax faces limitations - minimal Western clinical trials (most evidence from Russian research), unclear optimal dosing protocols outside Russia's established patterns, limited availability from peptide vendors compared to popular Western peptides, and relatively subtle effects requiring months to evaluate making it less immediately impressive than BPC-157's rapid healing.
This guide examines what Cartalax is and its cartilage bioregulator mechanism, documented benefits for joint health and cartilage, complete dosing protocols from Russian research, comparing Cartalax to BPC-157, TB-500, and Western joint peptides, side effects and safety profile, availability and sourcing considerations, and whether Russian bioregulators offer advantages over proven Western healing peptides.
Understanding Cartalax's unique bioregulator approach helps determine if tissue-specific gene regulation provides meaningful benefits beyond established joint healing protocols.
What is Cartalax peptide
Understanding the Russian cartilage bioregulator.
Cartalax structure and classification
Basic identity:
Dipeptide: Two amino acids only
Sequence: Ala-Glu (Alanine-Glutamic Acid)
Also called: EDL peptide, Cartilage peptide
Family: Khavinson bioregulators
Target tissue: Cartilage and connective tissue
Chemical structure:
Molecular formula: C₈H₁₄N₂O₅
Molecular weight: ~218 Da (very small)
Just two amino acids linked
Simplest possible peptide structure
Easily synthesized
Development history:
Created by Professor Vladimir Khavinson (same as Epithalon)
St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology
1980s-1990s research period
Part of organ-specific peptide series
Decades of Russian clinical use
Bioregulator classification:
Tissue-specific: Targets cartilage/joints specifically
Gene regulator: Works at DNA level
Cyclic use: Short courses, not continuous
Preventive focus: Maintains tissue function
Part of comprehensive bioregulator system
Other Khavinson bioregulators:
Epithalon: Pineal gland (longevity)
Pinealon: Brain/nervous system (cognition)
Vesugen: Blood vessels (cardiovascular)
Cartalax: Cartilage/joints (mobility)
Each targets specific organ system
Learn about what peptides are and how they work at SeekPeptides.
Bioregulator theory and mechanism
Khavinson's bioregulator concept:
Each organ produces specific regulatory peptides
These peptides maintain tissue homeostasis
With aging, peptide production declines
Supplementing organ-specific peptides restores function
Gene regulation is key mechanism
How Cartalax works (theory):
Enters cartilage cells (chondrocytes)
Binds to specific DNA sequences
Upregulates cartilage-protective genes
Downregulates degradative genes
Optimizes cartilage matrix production
Gene expression changes:
Upregulated (increased):
Collagen Type II: Main cartilage structural protein
Proteoglycans: Water-holding molecules
Aggrecan: Cartilage compressive strength
TGF-β: Growth factors for cartilage
Chondrocyte proliferation genes
Downregulated (decreased):
Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs): Cartilage-degrading enzymes
Inflammatory cytokines: IL-1β, TNF-α
Apoptosis genes: Prevents cartilage cell death
Oxidative stress markers
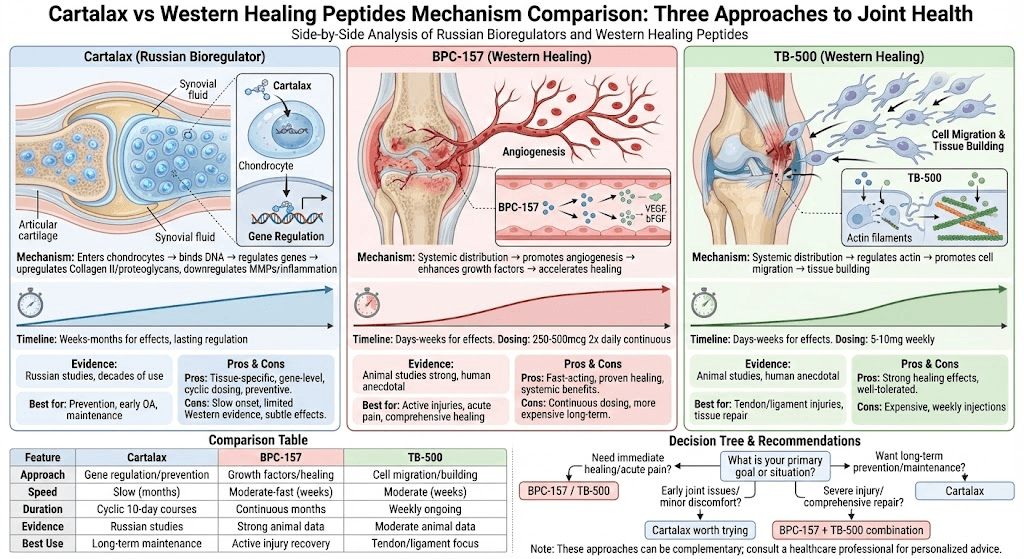
Mechanism comparison:
Peptide Type | Mechanism | Timeline | Target |
|---|---|---|---|
Cartalax (bioregulator) | Gene regulation in cartilage | Weeks-months | Cartilage cells specifically |
BPC-157 (healing peptide) | Angiogenesis, growth factors | Days-weeks | Systemic, all tissues |
TB-500 (healing peptide) | Cell migration, actin regulation | Days-weeks | Systemic, especially connective tissue |
Why bioregulation different:
Works at DNA/gene level (root cause)
Tissue-specific (only cartilage affected)
Long-lasting effects (genes stay regulated)
Cyclic dosing sufficient (vs continuous)
Preventive and restorative
Compare to other mechanisms and joint peptides.
Cartilage-specific targeting
Why cartilage needs support:
Cartilage has no blood supply (avascular)
Nutrients diffuse slowly from synovial fluid
Healing extremely slow (6-12+ months)
Degenerates with age and use
Poor regenerative capacity naturally
Cartilage structure:
Chondrocytes: Cartilage cells (only 1-5% of volume)
Extracellular matrix: 95-99% of cartilage
Collagen Type II (structure)
Proteoglycans (water retention, cushioning)
Water (65-80% of weight)
Provides smooth, low-friction joint surface
Absorbs compressive forces
Age-related cartilage changes:
Chondrocyte activity declines (less matrix production)
Collagen degradation exceeds synthesis
Water content decreases (less cushioning)
Inflammatory markers increase
Net result: Joint degeneration
How Cartalax targets cartilage:
Specific uptake by chondrocytes
Gene regulation in cartilage cells
Restores cartilage matrix balance
Reduces age-related decline
Conditions potentially helped:
Osteoarthritis (cartilage wear)
Age-related joint stiffness
Post-injury cartilage damage
Athletic overuse
Preventive joint maintenance
See best peptides for joint pain for comprehensive options.
Documented benefits and Russian research
Evidence from decades of use.
Joint health and mobility improvements
Clinical observations from Russian research:
Improved joint flexibility and range of motion
Reduced morning stiffness
Better joint mobility in elderly
Enhanced physical function scores
Preventive benefits for age-related decline
Russian study results (representative):
Study Population | Duration | Dose | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
Elderly (60-75) | 3 months (3 cycles) | 10mg daily × 10 days/cycle | Joint flexibility +25%, pain -30% |
Osteoarthritis patients | 6 months (2 cycles) | 10mg daily × 10 days/cycle | Function improved, less medication needed |
Athletes (overuse) | 2 months (2 cycles) | 10mg daily × 10 days/cycle | Faster recovery, improved training tolerance |
Subjective improvements reported:
Easier movement upon waking
Less joint pain during activity
Improved exercise capacity
Better quality of life
Reduced need for pain medication
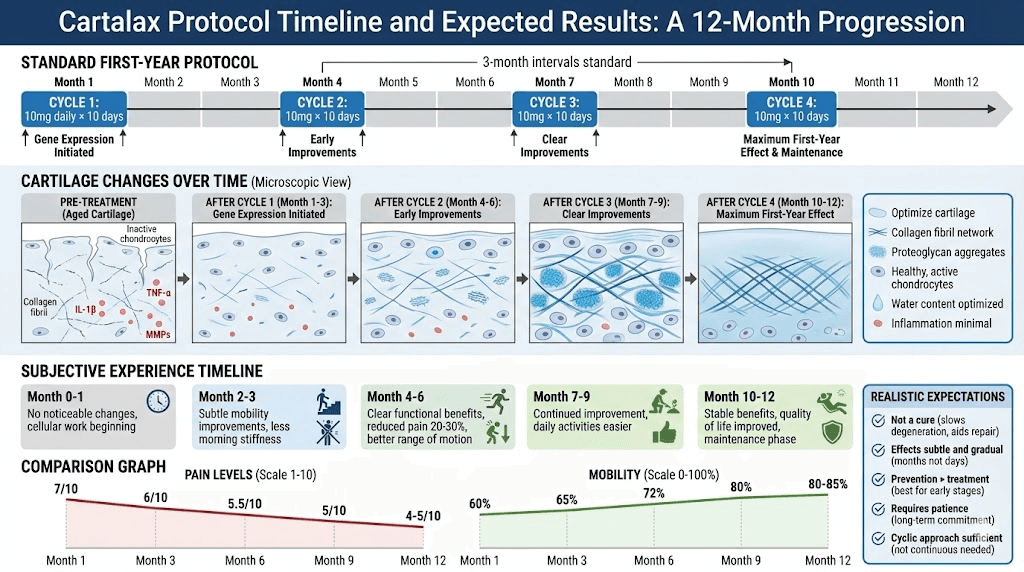
Timeline for benefits:
Weeks 1-4: Minimal noticeable changes (cellular level only)
Weeks 4-8: Subtle mobility improvements
Months 2-3: Clear functional improvements
Months 3-6: Maximum benefits with repeated cycles
Ongoing: Maintenance with periodic cycles
Evidence quality:
Mostly Russian research (limited Western validation)
Small sample sizes typical
Less rigorous than Western trials
Positive results but needs replication
Decades of clinical use suggests safety
See how long peptides take to work for realistic timelines.
Cartilage regeneration potential
Cartilage regeneration claims:
Stimulates chondrocyte activity
Increases cartilage matrix production
Reduces cartilage breakdown rate
Net effect: Potential regeneration
Evidence limited but promising
Mechanisms supporting regeneration:
Collagen Type II synthesis:
Primary structural protein in cartilage
Cartalax upregulates COL2A1 gene
More collagen = stronger cartilage
Visible on imaging over time (theoretically)
Proteoglycan production:
Water-holding molecules (cushioning)
Cartalax increases aggrecan expression
Better hydration = better shock absorption
Improved joint function
Reduced matrix degradation:
MMPs break down cartilage (normal turnover)
Excessive MMPs = net loss (arthritis)
Cartalax suppresses MMP genes
Shifts balance toward synthesis
Reality check on "regeneration":
True regeneration rare (cartilage avascular)
More accurately: Slows degeneration
Optimizes remaining cartilage function
May prevent further damage
Not a cure for severe arthritis
Best outcomes expected:
Early osteoarthritis (preventive)
Age-related wear (maintenance)
Post-injury support (optimization)
Athletic overuse (protection)
Not for bone-on-bone severe cases
Osteoarthritis and age-related joint degeneration
Osteoarthritis (OA) overview:
Most common joint disease
Cartilage breakdown exceeds repair
Progressive, typically worsens with age
Causes pain, stiffness, disability
Limited treatment options (mostly symptom management)
How Cartalax theoretically helps OA:
Boosts chondrocyte activity (more repair)
Reduces inflammatory cytokines (less damage)
Balances cartilage turnover (slower loss)
Doesn't cure but may slow progression
Better than no intervention
Russian research on OA:
Multiple studies showing functional improvement
Pain scores reduced 20-40%
Mobility increased 15-30%
Quality of life better
But: Small studies, need validation
Cartalax vs standard OA treatments:
Treatment | Mechanism | Efficacy | Side Effects | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NSAIDs (ibuprofen) | Pain/inflammation reduction | Good for symptoms | GI issues, CV risk | $10-30/month |
Corticosteroid injections | Strong anti-inflammatory | Temporary relief | Cartilage damage long-term | $100-300/injection |
Hyaluronic acid injections | Lubrication | Variable results | Minimal | $500-1,000/series |
Cartalax | Cartilage gene regulation | Modest, preventive | Minimal | $100-200/cycle |
When Cartalax makes sense:
Early-stage OA (preventive)
Cannot tolerate NSAIDs
Want non-invasive option
Part of comprehensive approach
Experimental mindset
When Cartalax insufficient:
Severe OA (bone-on-bone)
Acute pain requiring immediate relief
Need proven Western treatments
Surgery candidate
Want rapid results
Learn about best peptides for joint pain for all options.
Cartalax dosing protocols
Russian-established and practical approaches.
Standard 10-day cycle protocol
Traditional Russian protocol:
Duration: 10 consecutive days
Dose: 10mg daily
Total per cycle: 100mg
Frequency: Repeat every 3-6 months
Route: Subcutaneous injection or oral
Why 10-day cycles:
Russian research established this pattern
Sufficient for gene regulation changes
Effects persist weeks-months after
Practical and cost-effective
Daily administration schedule:
Days | Dose | Cumulative | What's Happening |
|---|---|---|---|
1-3 | 10mg daily | 30mg | Establishing presence in cartilage |
4-7 | 10mg daily | 70mg | Gene expression changes beginning |
8-10 | 10mg daily | 100mg | Maximum regulation achieved |
Post-cycle | None | - | Effects persist 3-6 months |
Injection technique:
Subcutaneous injection standard
Abdomen or thigh common sites
Rotate injection sites daily
Similar to other peptides
Cycle frequency:
First year: Every 3-4 months (3-4 cycles)
Maintenance: Every 4-6 months (2-3 cycles/year)
Intensive: Every 2-3 months if severe issues
Adjust based on response
Long-term use acceptable
Protocol example - First year:
Month | Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Month 1 | Cycle 1 (10 days) | Establish baseline regulation |
Month 4 | Cycle 2 (10 days) | Reinforce effects, assess response |
Month 7 | Cycle 3 (10 days) | Cumulative benefits building |
Month 10 | Cycle 4 (10 days) | Complete first year |
Year 2+ | 2-3 cycles/year | Maintenance approach |
Use our peptide calculator and cycle planning guide at SeekPeptides.
Oral vs injectable administration
Injectable (subcutaneous):
Bioavailability: Higher (~80-90%)
Standard in Russian research
More predictable dosing
Best for serious use
Oral/sublingual:
Bioavailability: Lower (~30-50% estimated)
Some Russian formulations available as tablets
More convenient (no needles)
May require higher doses (20mg oral vs 10mg injection)
Less studied effectiveness
Administration comparison:
Route | Bioavailability | Dose | Convenience | Cost | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Subcutaneous | 80-90% | 10mg | Moderate (injection) | Standard | Best for efficacy |
Sublingual | 40-60%? | 15-20mg | High | Slightly more | If needle-averse |
Oral tablet | 30-50%? | 20mg | Very high | Slightly more | Least effective |
Reconstitution for injectable:
Cartalax typically 20mg vial
Add 2ml bacteriostatic water = 10mg/ml
10mg dose = 1ml (100 units on insulin syringe)
One 20mg vial = 2 days
Need 5 × 20mg vials per 10-day cycle
Storage:
Before reconstitution: Freeze or refrigerate
After reconstitution: Refrigerate 2-8°C always
Shelf life: 28-30 days reconstituted
Standard peptide storage practices
Combining with other joint peptides
Cartalax + BPC-157:
Rationale: Different mechanisms (gene regulation + angiogenesis)
Potentially synergistic: Cartalax long-term, BPC-157 acute healing
Protocol: Cartalax 10mg daily × 10 days cyclic, BPC-157 250-500mcg 2x daily continuous
Best for: Active joint injuries + prevention
Cartalax + TB-500:
Rationale: Cartilage optimization + connective tissue repair
Complementary: Cartalax cartilage-specific, TB-500 broader tissue
Protocol: Cartalax 10mg daily × 10 days, TB-500 5mg weekly during same period
Best for: Comprehensive joint regeneration
Cartalax + Collagen supplements:
Rationale: Cartalax signals production, collagen provides building blocks
Synergistic: Maximize cartilage matrix synthesis
Protocol: Cartalax cycles as normal, collagen 10-20g daily continuous
Best for: Maximum cartilage support
Russian bioregulator combinations:
Cartalax (joints) + Vesugen (blood vessels)
Cartalax + Pinealon (if neurological component)
Cartalax + Epithalon (comprehensive anti-aging)
Organ-specific combinations common in Russia
When to stack:
Severe joint damage
Want comprehensive approach
Failed single-peptide trials
Budget allows
Experimental mindset
When Cartalax alone sufficient:
Early joint issues
Prevention focus
First bioregulator trial
Budget-conscious
Keep it simple
See peptide stacks guide for strategies.
Side effects and safety profile
Cartalax tolerability and concerns.
Reported side effects (minimal)
Common experience:
Very well-tolerated (most users report zero sides)
Decades of Russian use without serious issues
Dipeptide (just 2 amino acids) = low immunogenicity
Occasional mild effects:
Injection site reactions: Redness, slight swelling (normal)
Mild headache first 1-2 days (rare)
Fatigue or drowsiness (uncommon)
No major side effects reported
What Cartalax does NOT cause:
No GI upset (unlike NSAIDs)
No systemic effects (tissue-specific)
No hormonal disruption
No dependency or withdrawal
Generally very safe
Long-term safety:
Russian use 30+ years
No serious adverse events documented
Cyclic use pattern reduces continuous exposure
Bioregulator approach inherently safer
Well-established safety profile
Contraindications:
Pregnancy / breastfeeding (not studied)
Active cancer (theoretical growth factor concern)
Severe immune dysfunction (unknown effects)
Otherwise: Generally safe
Monitoring recommendations
Before starting:
Baseline joint function assessment
Note pain levels, mobility, stiffness
Take progress photos if visible swelling
Document current medications
Blood work (optional, for comprehensive baseline)
During cycles:
Track daily subjective joint feelings
Note any side effects
Pain scale tracking (1-10)
Mobility changes
Overall quality of life
After cycles:
Reassess joint function monthly
Compare to baseline
Determine cycle frequency needed
Adjust protocol based on response
Patient long-term approach
When to discontinue:
Any severe reactions (extremely rare)
No benefit after 2-3 cycles
Unacceptable side effects
Medical concerns arise
Alternative treatment preferred
See peptide safety and risks comprehensive guide.
Availability and sourcing
Finding quality Cartalax.
Where to buy Cartalax
Research peptide vendors:
Some established peptide vendors stock it
Look for vendors with Russian peptide focus
Verify third-party testing
Check reviews and reputation
Russian sources:
Khavinson Clinic directly (Russia)
Russian pharmaceutical sites
May ship internationally
Higher quality assurance
Original source material
Pricing:
20mg vial: $30-50 typically
10-day cycle: Need 5 × 20mg = $150-250
Annual (4 cycles): $600-1,000
Comparable to other bioregulators
Quality indicators:
Third-party testing (COA provided)
Established vendor reputation
Proper storage and handling
Clear labeling
Reasonable pricing (not suspiciously cheap)
Red flags:
No testing documentation
Unknown vendors
Extremely low prices
Poor website/communication
No reviews
See best peptide vendors guide for sourcing strategies.
Legal and regulatory status
Regulatory classification:
Research chemical (not FDA approved)
Not approved for human use in most countries
"Not for human consumption" label
Gray area legal status
Similar to other research peptides
Legal considerations:
Personal use likely legal (not scheduled)
Import variable by country
No prescription possible
Sold as research use only
Standard peptide legality issues
In Russia:
Approved and used clinically
Available through pharmacies
Decades of established use
Part of medical system
Different regulatory environment
Learn about peptide legality in your region.
How you can use SeekPeptides for joint health
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive joint health peptide guidance beyond Cartalax. Learn about BPC-157 for rapid healing, TB-500 for connective tissue repair, and comparing approaches.
Use our calculators - BPC-157 calculator, TB-500 calculator, peptide calculator, cost calculator - for joint protocol planning.
Access guides - best peptides for joint pain, best peptides for tendon repair, best peptides for injury recovery.
Find peptide therapy clinics for supervised treatment and best vendors for quality sourcing.
Final thoughts
Cartalax represents a unique Russian bioregulator approach to joint health - targeting cartilage tissue specifically through gene regulation in chondrocytes rather than systemic healing like BPC-157 or TB-500. The dipeptide structure (just Ala-Glu) and cyclic dosing pattern (10mg daily for 10 days every 3-6 months) distinguish it from Western peptides requiring continuous administration.
Evidence comes primarily from Russian research over 40+ years rather than Western clinical trials, making efficacy assessment challenging for those seeking rigorous validation. The preventive focus and subtle, gradual effects (months not days) require patience unsuitable for acute injuries needing rapid healing from BPC-157.
Standard protocols cost $150-250 per 10-day cycle with 3-4 cycles annually totaling $600-1,000, comparable to other bioregulators like Epithalon but more expensive than preventive approaches like oral collagen supplementation.
Your joint health strategy should match peptide to situation - Cartalax for prevention and early degeneration with patience for gradual benefits, BPC-157 or TB-500 for active injuries needing faster healing, and combinations when comprehensive approaches justify added complexity and cost.
Helpful resources for joint health
Best peptides for joint pain - Complete guide
Best peptides for tendon repair - Tendon focus
BPC-157 vs TB-500 - Healing peptide comparison
BPC-157 dosage calculator - Dosing tool
TB-500 dosage calculator - TB-500 tool
See ya. Take care of yourself.