Dec 26, 2025

Same sources claim Cardiogen rejuvenates heart cells and improves cardiac function, but at the same time mention blood pressure benefits and improved circulation. Y
ou've seen it called a "bioregulator" but don't fully understand what that means or how it differs from other peptides.
You just need clear information about what Cardiogen does, who benefits, and whether clinical evidence supports the claims.
Look: Cardiogen is a short peptide bioregulator originally developed in Russia for cardiovascular health.
It works by regulating gene expression in heart cells, potentially improving cardiac function, reducing oxidative stress, supporting healthy blood pressure, and promoting cardiovascular longevity.
While most widely used in Russia and Eastern Europe with decades of clinical observation, Western clinical trials are limited but growing.
This guide breaks down exactly what Cardiogen is, how it works for cardiovascular health, specific benefits for heart function and circulation, clinical evidence and research, dosing protocols, who should consider it, and how it compares to other cardiovascular peptides and interventions.
Let's start with understanding what Cardiogen actually is.
What is Cardiogen peptide
Bioregulator peptides explained
What bioregulators are:
Short peptides (typically 2-4 amino acids)
Tissue-specific (each targets specific organ or tissue type)
Work by regulating gene expression in target cells
Developed by Russian scientist Professor Vladimir Khavinson
How they differ from other peptides:
Most peptides signal receptors on cell surface
Bioregulators enter cell nucleus and interact with DNA
Influence gene transcription and protein synthesis
Organ-specific: Cardiogen for heart, Epitalon for pineal gland, Thymalin for thymus, etc.
Theory behind bioregulators:
Aging cells lose ability to properly regulate gene expression
Bioregulator peptides restore youthful gene expression patterns
Tissue regenerates and functions better
Organ function improves, aging slows
Learn more about anti-aging peptides in our best peptides for anti-aging guide and Epithalon guide (another bioregulator).
Cardiogen composition and mechanism
Cardiogen structure:
Dipeptide or tripeptide (exact sequence varies by formulation)
Derived from bovine heart tissue extracts
Synthesized versions now available
Mechanism of action:
Enters cardiomyocytes (heart muscle cells)
Travels to cell nucleus
Interacts with specific DNA sequences
Upregulates genes involved in cardiac function
Increases protein synthesis for cellular repair
Reduces expression of aging-related genes
Target tissues:
Cardiac muscle (myocardium)
Vascular endothelium (blood vessel lining)
Cardiac fibroblasts (support cells)
Development and clinical history
Origins:
Developed at St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology
Part of Khavinson Peptides® line
Used clinically in Russia since 1990s
Approved as pharmaceutical in Russia and some Eastern European countries
Clinical use:
Prescribed for cardiovascular diseases in Russia
Post-myocardial infarction (heart attack) recovery
Chronic heart failure support
Hypertension management
Preventive cardiology and longevity
Western adoption:
Growing interest in anti-aging and longevity communities
Available as supplement in some countries
Limited Western clinical trials (most research in Russian)
See our peptide research and studies guide for more on peptide clinical evidence.
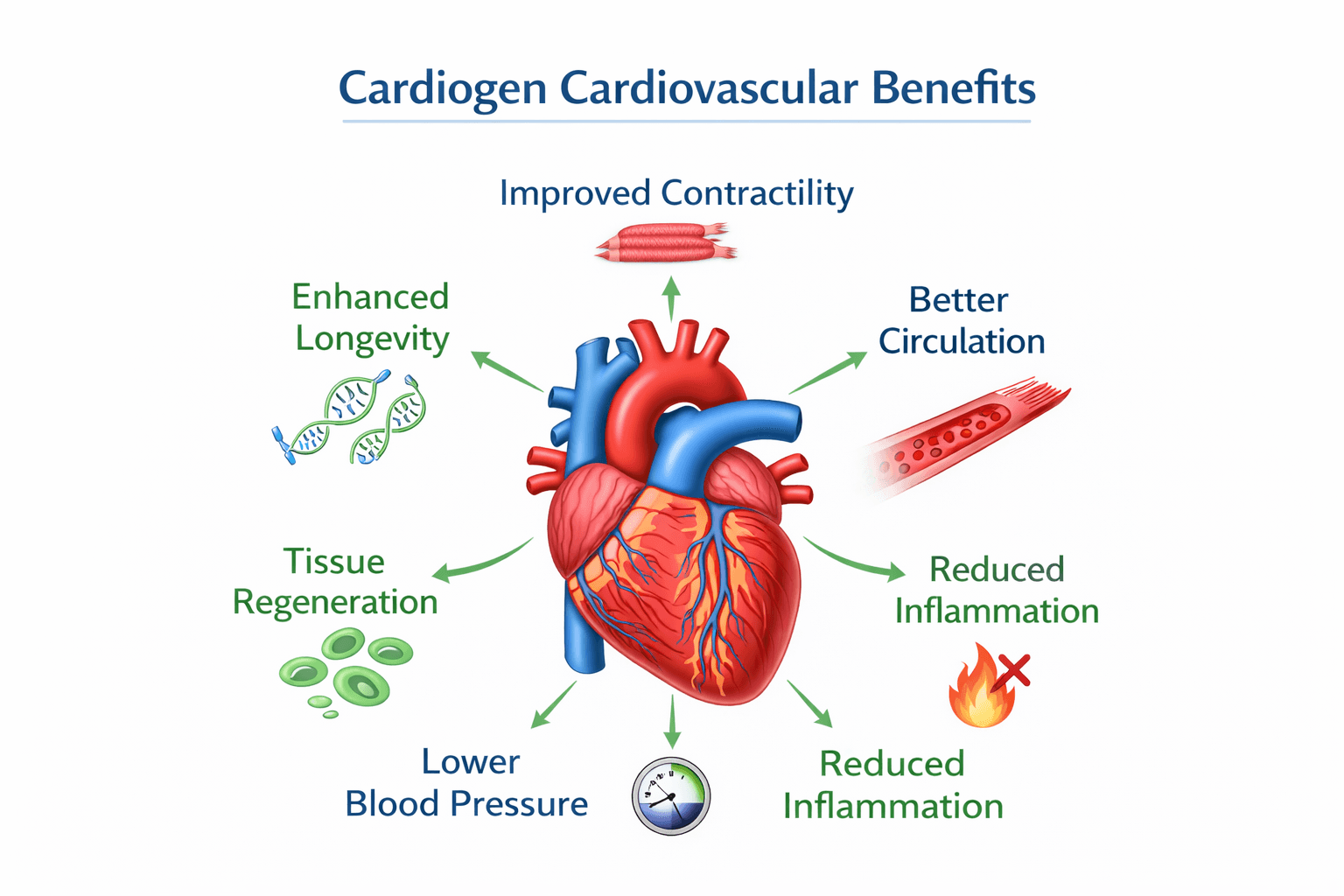
Cardiogen peptide benefits for cardiovascular health
Cardiogen targets multiple aspects of heart and vascular function.
Improved cardiac contractility and heart function
What research shows:
Enhanced myocardial contractility (heart pumps more effectively)
Improved ejection fraction in heart failure patients
Better cardiac output
Mechanism:
Increases synthesis of contractile proteins
Optimizes calcium handling in cardiac cells
Improves mitochondrial function in heart muscle
Who benefits:
Heart failure patients (reduced ejection fraction)
Post-heart attack recovery
Age-related cardiac function decline
Athletes seeking cardiovascular optimization
Clinical observations:
Improved exercise tolerance
Reduced shortness of breath
Better quality of life in heart failure patients
For muscle and performance enhancement, also see best peptides for muscle growth and peptides for athletic performance.
Blood pressure regulation
Effects on blood pressure:
Modest reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
Improved vascular compliance (blood vessels more flexible)
Better endothelial function
Mechanism:
Enhances nitric oxide production in endothelium
Reduces vascular inflammation
Improves arterial elasticity
Clinical data:
Studies show 5-15 mmHg reduction in systolic BP
3-10 mmHg reduction in diastolic BP
More pronounced in those with mild-moderate hypertension
Important note: Cardiogen is not a replacement for blood pressure medication. It's complementary support. Always work with physician for hypertension management.
Reduced cardiovascular inflammation
Anti-inflammatory effects:
Decreases inflammatory markers (CRP, IL-6)
Reduces oxidative stress in cardiac tissue
Protects against inflammatory damage
Why this matters:
Chronic inflammation drives atherosclerosis
Inflammation contributes to heart failure progression
Oxidative stress damages cardiac cells
Mechanism:
Upregulates antioxidant enzymes
Reduces NF-κB inflammatory pathway activation
Enhances cellular stress resistance
Learn about other anti-inflammatory peptides in our KPV peptide guide and KPV dosage guide.
Improved circulation and vascular health
Vascular benefits:
Enhanced microcirculation
Better capillary function
Improved tissue oxygenation
Effects on blood vessels:
Reduces arterial stiffness
Improves endothelial function
May slow atherosclerosis progression
Practical benefits:
Better peripheral circulation
Improved energy levels
Enhanced recovery from cardiovascular stress
Cardioprotection and heart tissue regeneration
Protective effects:
Reduces damage from ischemia (reduced blood flow)
Protects against reperfusion injury
Supports cardiac cell survival during stress
Regenerative potential:
May stimulate cardiac stem cell activity
Enhances protein synthesis for tissue repair
Improves healing after cardiac injury
Post-heart attack benefits:
Smaller infarct size (less permanent damage)
Better recovery of function
Reduced risk of heart failure development
For tissue healing and recovery, also see BPC-157 guide, TB-500 guide, and best peptides for injury recovery.
Longevity and anti-aging benefits
Cardiovascular aging effects:
Slows age-related cardiac decline
Preserves cardiac function in older adults
May extend healthspan through cardiovascular optimization
Mechanism:
Restores youthful gene expression patterns
Enhances cellular stress resistance
Supports mitochondrial function
Longevity perspective:
Cardiovascular disease is leading cause of death
Maintaining cardiac health extends lifespan
Cardiogen may be preventive intervention for healthy aging
See our complete anti-aging peptides guide for comprehensive longevity protocols.
Metabolic benefits
Glucose and lipid metabolism:
May improve insulin sensitivity
Potential beneficial effects on cholesterol
Supports healthy metabolic function
Why cardiovascular metabolic health matters:
Metabolic syndrome increases heart disease risk
Insulin resistance damages blood vessels
Lipid imbalances drive atherosclerosis
For metabolic health and weight management, see peptides for weight loss guide and best peptide stack for weight loss.
Clinical evidence and research on Cardiogen
Understanding the science behind Cardiogen benefits.
Russian clinical studies
Most Cardiogen research comes from Russia:
Dozens of studies over 30+ years
Published in Russian medical journals
Limited translation to English
Key findings from Russian research:
Improved outcomes in heart failure patients
Reduced mortality after myocardial infarction
Better quality of life in cardiovascular disease
Enhanced exercise tolerance
Limitations:
Smaller sample sizes than Western trials
Different research standards than US/Europe
Limited independent replication
Mechanisms studies
Laboratory research shows:
Gene expression changes in cardiac cells
Increased protein synthesis
Enhanced mitochondrial function
Reduced oxidative stress markers
Animal studies:
Extended lifespan in aged animals
Improved cardiac function in disease models
Reduced infarct size after induced heart attack
Better recovery from cardiovascular stress
Western research (limited but growing)
Emerging Western interest:
Few published Western clinical trials
Growing research into bioregulator peptides
Increased adoption in longevity medicine
Need for more research:
Large-scale randomized controlled trials needed
Independent verification of Russian findings
Mechanism studies in Western labs
Learn about peptide research standards in our peptide research and studies guide.
Cardiogen dosing and protocols
How to use Cardiogen for cardiovascular benefits.
Standard dosing
Typical Cardiogen protocol:
Dose: 10-20mg per cycle
Administration: Oral or sublingual tablets (most common), injectable (less common)
Frequency: Daily for 10-20 days
Cycles: Every 3-6 months
Oral/sublingual dosing:
10mg daily for 10 days (100mg total per cycle)
OR 20mg daily for 10 days (200mg total)
Take on empty stomach or under tongue
Best in morning
Injectable dosing (if available):
5-10mg injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously
Daily for 5-10 days
Less common than oral formulations
Preventive vs therapeutic protocols
Preventive use (healthy individuals):
10mg daily for 10 days
Repeat every 6 months
Goal: Maintain cardiovascular health, slow aging
Therapeutic use (cardiovascular disease):
20mg daily for 20 days
Repeat every 3 months
Higher frequency for active disease management
Work with physician
Cycling and timing
Why cycling:
Bioregulators work best in cycles
Continuous use may reduce effectiveness
Body needs integration period between cycles
Optimal timing:
Spring and fall cycles (traditional Russian protocol)
OR quarterly cycles (every 3 months)
Align with seasonal changes for some practitioners
Duration of effects:
Benefits accumulate over multiple cycles
Single cycle provides 3-6 months of benefit
Long-term use shows progressive improvement
Use our peptide cycle planning guide for complete cycle protocols and our peptide dosing guide for general dosing principles.
Combining with other cardiovascular interventions
Cardiogen works well with:
Prescription heart medications (under physician guidance)
CoQ10 supplementation
Omega-3 fatty acids
Other bioregulator peptides
Stacking with other bioregulators:
Thymalin (immune support)
Epitalon (longevity, pineal gland)
Vladonix (thymus support)
Rotate or combine depending on goals
Learn peptide stacking in our peptide stacks guide.
Who should consider Cardiogen peptide
Cardiogen has specific use cases and contraindications.
Ideal candidates for Cardiogen
People who may benefit:
Family history of cardiovascular disease
Mild-moderate heart failure
Post-heart attack recovery (with physician approval)
Hypertension (as complementary support)
Age-related cardiac decline
Preventive cardiology and longevity optimization
Athletes seeking cardiovascular performance
Age considerations:
Most studied in 40+ age group
Younger adults may use for prevention
Older adults (60+) often see most dramatic benefits
Who should avoid or use caution
Contraindications:
Acute cardiac emergency (requires immediate medical care)
Severe heart failure without physician oversight
Recent major cardiac surgery (timing matters)
Pregnancy and breastfeeding (no safety data)
Use with caution if:
Taking multiple cardiac medications
Significant kidney or liver disease
Active infections
Always work with physician if:
You have diagnosed cardiovascular disease
You take prescription heart medications
You're considering Cardiogen for therapeutic (not just preventive) use
Cardiogen for healthy aging and prevention
Preventive cardiology perspective:
Cardiovascular health determines longevity
Early intervention may prevent disease
Bioregulators fit into preventive paradigm
Who uses preventively:
Longevity enthusiasts
People with family history of heart disease
Individuals optimizing healthspan
Anti-aging medicine practitioners
See our getting started with peptides guide for beginning peptide protocols.
Cardiogen vs other cardiovascular peptides
How Cardiogen compares to alternatives.
Cardiogen vs Epithalon
Epithalon:
Pineal gland bioregulator
Primary benefit: Telomere lengthening and longevity
Secondary cardiovascular benefits through overall anti-aging
Cardiogen:
Heart-specific bioregulator
Primary benefit: Cardiovascular function and health
Broader longevity through cardiovascular optimization
Which to choose:
Epithalon for general longevity and anti-aging
Cardiogen for targeted cardiovascular health
Many use both in rotation
See our Epithalon guide for comparison.
Cardiogen vs Thymosin Alpha-1
Thymosin Alpha-1:
Immune system support
Cardiovascular benefits indirect through reduced inflammation
Well-studied in Western medicine
Cardiogen:
Direct cardiovascular tissue targeting
Heart function and structure benefits
More cardiovascular-specific
Combination potential:
Both support cardiovascular health from different angles
Thymosin Alpha-1 reduces immune-driven inflammation
Cardiogen directly improves cardiac function
Cardiogen vs BPC-157
BPC-157:
Healing peptide for injuries and gut health
Cardiovascular benefits: Improves circulation, protects blood vessels
Angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation)
Cardiogen:
Specific to heart tissue and cardiac cells
Bioregulator mechanism (gene expression)
More targeted for cardiac function
When to use which:
BPC-157 for vascular health and circulation
Cardiogen for heart muscle function
Can combine for comprehensive cardiovascular support
See our BPC-157 complete guide and BPC-157 dosage calculator.
Cardiogen vs TB-500
TB-500:
Tissue repair and regeneration
Cardiovascular benefits through angiogenesis
Reduces inflammation
Cardiogen:
Heart-specific bioregulator
Improves cardiac function directly
Works through gene regulation
Combination approach:
TB-500 for tissue repair after cardiac event
Cardiogen for long-term cardiac function
Complementary mechanisms
See our TB-500 guide and TB-500 dosage calculator.
Cardiogen benefits comparison table
Benefit | Cardiogen | Epithalon | BPC-157 | TB-500 | Thymosin Alpha-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Heart function improvement | Excellent | Moderate | Good | Moderate | Poor |
Blood pressure regulation | Good | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
Vascular health | Good | Moderate | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate |
Anti-inflammatory | Good | Moderate | Excellent | Excellent | Excellent |
Longevity benefits | Good (via cardio) | Excellent | Moderate | Moderate | Good (via immune) |
Tissue regeneration | Moderate | Poor | Excellent | Excellent | Poor |
Clinical evidence | Moderate (mostly Russian) | Moderate | Good | Good | Excellent |
Mechanism | Gene regulation | Gene regulation | Healing/protection | Tissue repair | Immune modulation |
Safety, side effects and contraindications
Cardiogen has excellent safety profile with minimal side effects.
Common side effects (rare)
Reported side effects are minimal:
Mild headache (uncommon)
Slight fatigue initially
Digestive changes (rare with oral form)
Why side effects are rare:
Bioregulators are endogenous (body recognizes them)
Low dose compared to pharmacological peptides
Tissue-specific action limits systemic effects
Serious side effects (extremely rare)
No serious adverse events widely reported:
Decades of use in Russia with good safety record
No documented cases of major complications
Theoretical concerns:
Allergic reaction (possible with any substance)
Unknown long-term effects in Western populations
Drug interactions
Potential interactions:
Blood pressure medications (may enhance effect)
Blood thinners (theoretical interaction, not documented)
Other cardiac medications
Recommendation:
Inform physician about Cardiogen use
Monitor blood pressure if on antihypertensives
Don't replace prescribed medications with Cardiogen
Contraindications
Avoid if:
Pregnant or breastfeeding
Acute cardiovascular emergency
Allergic to bovine-derived products (if using extract)
Use caution if:
Severe cardiovascular disease (physician oversight required)
Recent cardiac surgery or procedure
Significant comorbidities
Learn about peptide safety in our peptide safety and risks guide.
Sourcing and quality considerations
Finding legitimate Cardiogen requires care.
Where to find Cardiogen
Sources:
Russian/European pharmaceutical suppliers
Anti-aging and longevity clinics
Online peptide research suppliers
Some compounding pharmacies
Availability varies by country:
Russia/Eastern Europe: Pharmaceutical product
Western Europe: Supplement or research chemical
United States: Research chemical or supplement
Other regions: Limited availability
Quality markers
Look for:
Clear source information (bovine extract vs synthetic)
Third-party testing if available
Established supplier with bioregulator expertise
Proper storage and handling
Red flags:
Extremely low prices (suggests questionable quality)
No information about source or synthesis
Suppliers with poor reputation
No storage/handling instructions
Forms available
Oral/sublingual tablets:
Most common form
Easy to use
No reconstitution needed
Convenient for cycling protocols
Injectable (less common):
Lyophilized powder requiring reconstitution
More similar to other peptides
May have better bioavailability
Requires proper storage
Nasal spray (rare):
Some bioregulators available in nasal form
Cardiogen less commonly found this way
For storage and handling, see our peptide storage guide and how to reconstitute peptides if using injectable form.
Final thoughts
Cardiogen peptide offers targeted cardiovascular benefits through a unique bioregulator mechanism. By regulating gene expression in cardiac tissue, it improves heart function, supports healthy blood pressure, reduces inflammation, enhances circulation, and promotes cardiovascular longevity.
The evidence is strongest from decades of Russian clinical use, showing benefits for heart failure, post-heart attack recovery, hypertension, and age-related cardiac decline. Western clinical trials are limited but growing as bioregulator peptides gain attention in longevity medicine.
Typical protocols involve 10-20mg daily for 10-20 days, cycled every 3-6 months. Oral/sublingual forms are most common and convenient. Safety profile is excellent with minimal side effects reported over 30+ years of use.
Cardiogen works well as standalone cardiovascular support or combined with other bioregulators like Epithalon for comprehensive anti-aging. It can complement (not replace) standard cardiovascular care under physician guidance.
For those focused on cardiovascular health and longevity, Cardiogen represents an interesting option backed by Russian clinical experience, though Western adopters should understand the limitations in English-language research.
Your cardiovascular health determines your longevity. Cardiogen may be a valuable tool in comprehensive heart health optimization.
Helpful resources for cardiovascular peptides
Peptide calculator - Calculate doses for all peptides
Peptide cycle planning guide - Plan Cardiogen cycles
Peptide dosing guide - General dosing principles
Peptide cost calculator - Budget longevity protocols
Related guides worth reading
Best peptides for anti-aging: complete protocols - Comprehensive anti-aging
Epithalon peptide benefits: longevity guide - Compare to Cardiogen
BPC-157 complete guide: healing and circulation - Vascular benefits
TB-500 guide: tissue regeneration - Cardiovascular repair