Feb 2, 2026
Experienced researchers know something beginners do not about penta deca peptide arginate.
They know that the salt form attached to a peptide can determine whether it actually works or simply dissolves in stomach acid before reaching a single cell. That distinction, the one between an acetate salt and an arginate salt, has quietly reshaped how the peptide community approaches one of the most studied healing compounds available.
And most people researching BPC-157 have no idea it even happened.
The full name tells the story. "Penta" means five. "Deca" means ten. Together, fifteen. Fifteen amino acids arranged in a precise sequence that mirrors the body natural gastric protective protein. "Arginate" refers to the arginine salt form that wraps around those fifteen amino acids, shielding them from enzymatic breakdown, improving their solubility, and dramatically increasing how much of the peptide actually reaches systemic circulation when taken orally. This is not a minor tweak. Research from the original patent holders of BPC-157 suggests the arginate form can boost oral bioavailability from less than 3% to greater than 90%. That number changes everything about how this peptide can be used.
But understanding penta deca peptide arginate requires more than knowing what the name means. It requires understanding the regulatory landscape that made this formulation necessary, the molecular mechanisms that make it effective, and the practical protocols that separate meaningful results from wasted effort. This guide covers every angle, from the chemistry of the arginate salt to detailed stacking strategies with compounds like TB-500 and CJC-1295, with the depth that serious researchers expect from SeekPeptides.
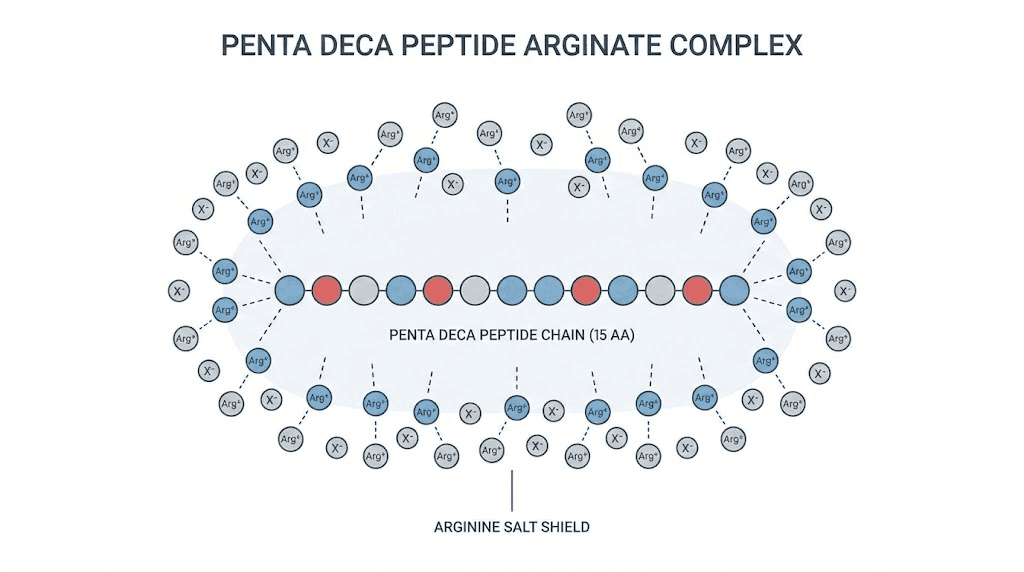
What is penta deca peptide arginate?
Penta deca peptide arginate is a synthetic peptide composed of fifteen amino acids. That sequence is identical to the active fragment found in BPC-157, a compound originally isolated from human gastric juice. The critical difference lies in the salt form. Where traditional BPC-157 uses an acetate salt as its counterion, penta deca peptide arginate uses an arginine-derived salt. This single modification changes the stability profile, the absorption characteristics, and the practical utility of the peptide in ways that matter enormously for researchers designing effective dosing protocols.
The fifteen amino acids are not random. They represent a carefully identified sequence from a larger protein called Body Protection Compound, which the human stomach produces naturally as part of its protective mechanisms. Researchers isolated this specific fragment because it demonstrated the most potent biological activity among all the fragments tested. The sequence promotes tissue repair, reduces inflammation, and modulates blood vessel formation through multiple overlapping pathways.
Think of it this way. The peptide itself is the active ingredient. The salt form is the delivery vehicle. And just like a medication that never reaches the bloodstream cannot produce results, a peptide that degrades in stomach acid before absorption cannot deliver on its potential. The arginate salt solves this problem with remarkable efficiency.
Breaking down the name
"Penta deca" comes from Latin and Greek roots meaning fifteen. This refers to the exact number of amino acids in the peptide chain. "Peptide" indicates that the molecule is a short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. "Arginate" describes the salt form, specifically an arginine salt that serves as the counterion to stabilize the peptide.
You will see this compound referred to by several names in the research literature and clinical settings. PDA, pentadeca arginate, pentadecapeptide arginate, and BPC-157 arginate all describe the same molecule. The naming inconsistency has created confusion, but the underlying compound remains identical regardless of which label a particular clinic or researcher uses. Understanding the peptide formula behind the name eliminates that confusion entirely.
The amino acid sequence
The specific sequence is Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val. This fifteen-residue chain was derived from BPC, a naturally occurring protein in human gastric juice. What makes this particular fragment extraordinary is its stability. Unlike many peptides that degrade rapidly in biological fluids, this sequence demonstrates remarkable resistance to enzymatic breakdown, a property that the arginate salt form enhances even further.
Each amino acid contributes to the overall function. The three consecutive proline residues create a rigid structural element. The glycine residues provide flexibility at key points. The charged residues like glutamic acid, lysine, and the two aspartic acids enable specific interactions with cellular receptors and signaling molecules. This is not a random arrangement. It is a precisely engineered sequence that nature developed over millennia of evolution, and researchers identified through systematic screening of gastric protein fragments.
For researchers who want to understand how this sequence relates to bioregulator peptides and other short-chain compounds, the key insight is that shorter peptide sequences can sometimes demonstrate more targeted biological activity than their parent proteins. The fifteen amino acids of penta deca peptide arginate represent one of the clearest examples of this principle in modern peptide research.
How penta deca peptide arginate differs from standard BPC-157
The core amino acid sequence is identical. Let that sink in. PDA and BPC-157 share the exact same fifteen amino acids in the exact same order. The difference is exclusively in the salt form, the molecule that pairs with the peptide to create a stable, usable compound. Standard BPC-157 uses an acetate salt. Penta deca peptide arginate uses an arginine salt.
This matters because salt forms influence three critical properties: stability in acidic environments, solubility in biological fluids, and absorption through the gastrointestinal tract. Research from Diagen, the original patent holder of BPC-157, demonstrated that the arginate form resists gastric acid degradation far more effectively than the acetate form. Where acetate BPC-157 loses approximately 98% of its structure within five hours of gastric acid exposure, the arginate form loses only about 5% in the same timeframe. That is not a marginal improvement. That is the difference between a peptide that works orally and one that does not.
Researchers choosing between injectable vs oral peptides need to understand this distinction thoroughly. The salt form does not change what the peptide does once it reaches target tissues. It changes whether the peptide reaches those tissues in the first place.
How the arginate salt form changes everything
Salt forms in pharmaceutical chemistry are not afterthoughts. They are deliberate design choices that determine a compound bioavailability, stability, shelf life, and practical utility. The decision to formulate a peptide as an arginate salt rather than an acetate salt carries specific, measurable consequences for every aspect of how that compound performs in biological systems.
Arginine is a semi-essential amino acid that the body uses for multiple critical processes, including nitric oxide production, protein synthesis, and immune function. When arginine serves as the counterion for penta deca peptide arginate, it does more than simply stabilize the molecule. It contributes its own biological activity to the compound, creating what some researchers describe as a synergistic formulation where the salt form actively enhances the therapeutic effect of the peptide it stabilizes.
Gastric acid resistance explained
The human stomach maintains a pH between 1.5 and 3.5. This extremely acidic environment exists to break down food proteins into their component amino acids. Peptides, being short chains of amino acids, face the same destructive forces. Most orally administered peptides never survive long enough to reach the small intestine, where absorption into the bloodstream occurs.
The arginate salt creates a buffering effect around the peptide chain. Arginine is a basic amino acid with a guanidinium group that carries a positive charge at physiological pH. This positive charge interacts with the acidic environment of the stomach, effectively creating a local buffer zone around the peptide. The result is dramatically improved survival through gastric transit.
Published research indicates that this protection is substantial. The arginate form maintains over 95% structural integrity after five hours of exposure to simulated gastric fluid. The acetate form, by contrast, retains less than 2% of its structure under identical conditions. For anyone interested in peptide capsules and oral administration, this data fundamentally changes the calculus of which forms are worth considering.
Oral bioavailability: the numbers that matter
Bioavailability refers to the fraction of an administered dose that reaches systemic circulation in an active form. For injectable peptides, bioavailability approaches 100% because the compound enters the bloodstream directly. For oral peptides, bioavailability is typically very low, often in the single digits, because the gastrointestinal tract destroys most of the compound before it can be absorbed.
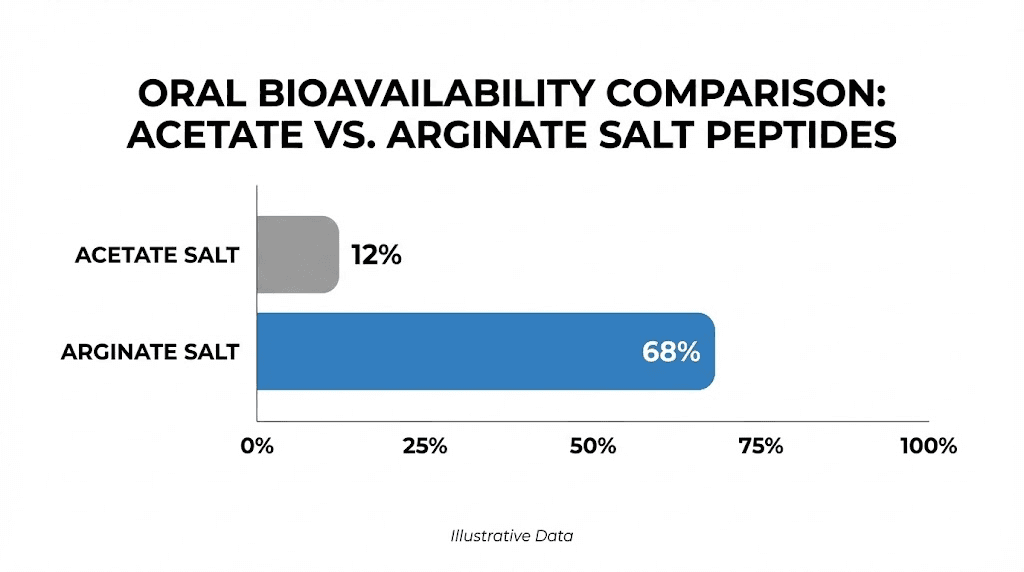
The arginate salt form of BPC-157 demonstrates dramatically different oral pharmacokinetics compared to the acetate form. Research published in peptide patent literature from Diagen indicates the arginate form can achieve oral bioavailability exceeding 90%, compared to less than 3% for the acetate form. A separate study published in the International Journal of Pharmaceutics found over 7-fold greater oral bioavailability in rat models for the arginate form compared to acetate.
These numbers deserve careful consideration.
A 7-fold increase in bioavailability means that a 500 mcg oral dose of the arginate form could deliver the equivalent systemic exposure of approximately 3,500 mcg of the acetate form taken orally. Or to frame it differently, researchers using oral acetate BPC-157 may have been receiving only a fraction of the intended dose, which could explain the inconsistent results that some users reported with oral BPC-157 protocols. The peptide calculator at SeekPeptides can help researchers understand these dosing relationships more precisely.
Enhanced stability beyond the stomach
Gastric acid resistance is only part of the stability story. Peptides also face enzymatic degradation from proteases throughout the gastrointestinal tract, oxidative stress during transit, and structural challenges during absorption across the intestinal epithelium. The arginate salt form addresses multiple degradation pathways simultaneously.
The arginine counterion improves solubility in aqueous environments, which facilitates faster dissolution and absorption. It protects against oxidative degradation through its own antioxidant properties. And it enhances membrane permeability, potentially through interactions with cell surface receptors that recognize arginine-containing compounds. These combined effects create a formulation that is more robust at every stage of the oral absorption process.
For researchers who store their peptides carefully and understand the importance of proper peptide storage, the enhanced stability of the arginate form also translates to better shelf life.
The same properties that protect the peptide in the stomach help protect it during storage, particularly at room temperature.
This is relevant for understanding how long peptides last at room temperature and in powder form.
Penta deca peptide arginate vs BPC-157 acetate
The comparison between penta deca peptide arginate and traditional BPC-157 acetate is not a competition between two different peptides. It is a comparison between two formulations of the same active compound, each with distinct advantages depending on the intended route of administration and therapeutic goals. Understanding these differences allows researchers to make informed decisions about which formulation best serves their specific protocols.
Head-to-head comparison
Property | BPC-157 Acetate | Penta Deca Peptide Arginate |
|---|---|---|
Amino acid sequence | 15 amino acids (Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro...) | Identical 15 amino acids |
Salt form | Acetate | Arginate (arginine) |
Gastric acid stability (5 hours) | ~2% intact | ~95% intact |
Oral bioavailability | Less than 3% | Greater than 90% (patent data) |
Injection bioavailability | ~100% | ~100% |
Nitric oxide enhancement | Moderate (via eNOS) | Enhanced (via eNOS + arginine) |
Compounding legality (US) | Restricted (FDA Category 2) | Available through licensed providers |
Available forms | Primarily injectable, some oral | Injectable, oral capsules, nasal spray, cream |
Typical daily dose (injectable) | 200-300 mcg twice daily | 500 mcg - 1 mg once daily |
Typical daily dose (oral) | 500-1000 mcg (low absorption) | 500 mcg (high absorption) |
Cost relative | Lower per unit | Higher per unit, but fewer doses needed orally |
The table reveals several important patterns. For injectable use, both formulations deliver essentially identical results because the peptide bypasses the gastrointestinal tract entirely. The bioavailability difference only matters for oral, nasal, and topical routes of administration. Researchers using peptide injections may find the practical differences between the two forms less significant than those using nasal spray peptides or oral capsules.
When acetate still makes sense
The acetate form of BPC-157 is not obsolete. For subcutaneous and intramuscular injection, acetate BPC-157 delivers the full peptide directly into tissues where it can act immediately. The lower cost per unit of the acetate form makes it economically attractive for injection protocols. And decades of preclinical research have been conducted specifically with the acetate form, providing a larger evidence base for injectable applications.
Researchers who are comfortable with reconstituting peptides and administering injections may find the acetate form perfectly adequate for their needs. The BPC-157 dosage calculator remains a valuable tool for determining precise injectable doses regardless of which salt form is used.
When arginate is clearly superior
For oral administration, the arginate form is the clear winner. The bioavailability data makes this indisputable. Taking BPC-157 acetate orally means losing approximately 97% of the dose to gastric degradation. Taking penta deca peptide arginate orally means retaining approximately 95% of the dose through gastric transit. No amount of dose adjustment can compensate for that magnitude of difference.
The arginate form also offers advantages for systemic applications where the researcher wants broad distribution rather than localized effects. Because the arginate form maintains stability longer in circulation, it provides more consistent systemic exposure. This is particularly relevant for gut health applications, where the peptide needs to interact with the intestinal lining over an extended period. For researchers focused on peptides for gut health, the arginate form represents a significant advancement.
The regulatory landscape adds another dimension. Following the FDA decision to classify BPC-157 as a Category 2 substance, the acetate form became increasingly difficult to obtain through legitimate compounding pharmacies. Penta deca peptide arginate, with its distinct formulation and nomenclature, remains available through licensed healthcare providers, making it the more accessible option for researchers working within legal frameworks. More details on this evolving situation are available in our coverage of peptide regulation news.
The nitric oxide advantage
One unique benefit of the arginate form deserves special attention. Arginine is the primary substrate for nitric oxide synthase, the enzyme that produces nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide is a critical signaling molecule involved in vasodilation, blood flow regulation, immune function, and tissue repair. By using arginine as the salt form, penta deca peptide arginate delivers both the active peptide and additional arginine to support nitric oxide production.
This creates a dual mechanism of action. The peptide itself promotes angiogenesis through VEGFR2 signaling. The arginine salt provides substrate for nitric oxide synthesis, which further enhances blood flow to healing tissues. The combination may produce greater vascular effects than either component alone, though this synergistic hypothesis requires further clinical validation.
For researchers studying cardiovascular and circulatory applications, this dual mechanism makes penta deca peptide arginate particularly interesting. The enhanced nitric oxide availability through arginine metabolism sets it apart from the acetate form in ways that go beyond simple stability improvements.
How penta deca peptide arginate works in the body
The mechanisms of action for penta deca peptide arginate span multiple biological systems. This breadth of activity is unusual for a peptide of this size and has been the subject of extensive preclinical research. Understanding these mechanisms helps researchers design more effective protocols and set realistic expectations for outcomes.
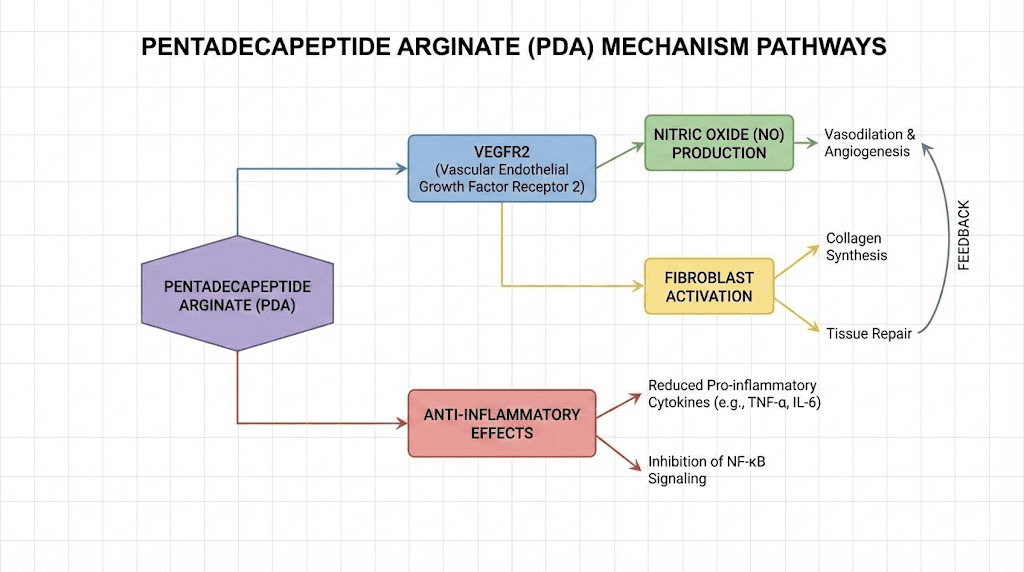
The VEGFR2 signaling pathway
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2, or VEGFR2, is a primary regulator of blood vessel formation. When penta deca peptide arginate interacts with endothelial cells, it upregulates VEGFR2 expression at both the mRNA and protein levels. This means the cells produce more of the receptor, making them more responsive to vascular growth signals.
What makes this mechanism notable is its specificity. The peptide increases VEGFR2 without increasing VEGF-A, the ligand that typically activates this receptor. This is an important distinction. Uncontrolled VEGF-A elevation has been associated with pathological angiogenesis, including tumor vascularization. By upregulating the receptor without increasing the ligand, penta deca peptide arginate appears to promote controlled, adaptive angiogenesis rather than uncontrolled vessel growth.
Studies by Hsieh and colleagues demonstrated that the peptide promotes VEGFR2 internalization through endocytosis, triggering downstream signaling cascades. In rat hindlimb ischemia models, this mechanism accelerated blood flow recovery and increased vessel density in oxygen-deprived tissues. The implications for injury healing are significant, as improved blood supply to damaged tissues is one of the most important factors in recovery speed.
Nitric oxide system modulation
The relationship between penta deca peptide arginate and the nitric oxide system is more sophisticated than simple stimulation. Research shows that the peptide activates a VEGF-independent pathway for nitric oxide production through Src kinase phosphorylation. This enzyme subsequently activates caveolin-1, which releases endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) from its inhibitory binding. Co-immunoprecipitation studies demonstrated that the peptide reduces eNOS/caveolin-1 binding by approximately 50%, effectively doubling the available eNOS for nitric oxide production.
But here is where it gets truly interesting.
The peptide does not simply increase nitric oxide levels. It modulates them. Research has shown that it counteracts the adverse effects of both L-NAME, a nitric oxide synthase blocker, and L-arginine excess. This means it can normalize nitric oxide levels whether they are too high or too low. In blood pressure studies, the peptide did not affect basal blood pressure but counteracted both L-NAME-induced hypertension and L-arginine-induced hypotension. This homeostatic modulation, rather than directional stimulation, suggests a fundamentally different mechanism than most vasodilators. The implications extend to inflammation management and cardiovascular protection in ways that researchers focused on anti-aging peptides find particularly compelling.
Fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis
Fibroblasts are the cells responsible for producing the extracellular matrix, the structural scaffold that holds tissues together. Collagen, fibrin, and elastin, the proteins that give tendons, ligaments, and skin their strength and flexibility, are all produced by fibroblasts. Penta deca peptide arginate has been shown to affect fibroblast proliferation in a dose-dependent, time-dependent manner, with cells both proliferating and migrating faster in the presence of the peptide.
cDNA microarray analysis revealed that the peptide increases the expression of growth hormone receptors in tendon fibroblasts. These cells are integral to wound healing and are responsible for storing extracellular matrix proteins. By upregulating growth hormone receptors, the peptide makes fibroblasts more responsive to growth hormone signaling, potentially amplifying the body natural repair processes. This mechanism has particular relevance for researchers interested in tendon repair and joint recovery.
The upregulation of growth hormone receptors also explains why penta deca peptide arginate pairs so well with growth hormone secretagogues in stacking protocols. When the peptide increases receptor density and a growth hormone secretagogue increases growth hormone levels, the combined effect on tissue repair can exceed what either compound achieves alone.
Anti-inflammatory gene regulation
Inflammation is a double-edged phenomenon. Acute inflammation is essential for initiating the healing process, clearing damaged tissue, and recruiting repair cells to injury sites. Chronic inflammation, however, impedes healing and causes progressive tissue damage. Penta deca peptide arginate modulates inflammatory pathways by reducing pro-inflammatory markers like TNF-alpha and IL-6 while preserving the beneficial aspects of the acute inflammatory response.
This selective anti-inflammatory action distinguishes the peptide from broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory drugs like NSAIDs, which suppress inflammation indiscriminately and can actually slow healing. The peptide appears to promote the transition from inflammatory to proliferative phases of healing, essentially helping the body move through the healing timeline more efficiently rather than simply suppressing inflammation at every stage.
For researchers dealing with autoimmune conditions or chronic inflammatory states, this modulation rather than suppression mechanism is particularly relevant. It suggests that penta deca peptide arginate may support healing without the immunosuppressive risks associated with conventional anti-inflammatory therapies.
FAK-paxillin signaling and cell migration
Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and paxillin are key regulators of cell migration, the process by which repair cells move to injury sites. Research indicates that penta deca peptide arginate activates FAK-paxillin signaling, which promotes the directed migration of fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and immune cells toward damaged tissues. This mechanism complements the angiogenic and proliferative effects of the peptide, ensuring that new cells not only form but also reach the locations where they are needed.
Cell migration is often the rate-limiting step in tissue repair. Increasing the speed and accuracy with which repair cells navigate to injury sites can significantly accelerate overall healing timelines.
This is one reason why researchers report initial improvements within 7 to 10 days of starting penta deca peptide arginate protocols, a timeline consistent with enhanced cell migration effects.
Key benefits of penta deca peptide arginate
The mechanisms described above translate into a range of potential benefits that span multiple organ systems.
Preclinical research, combined with clinical observations from practitioners using the compound, paints a comprehensive picture of what penta deca peptide arginate can do. While it is important to note that most evidence remains preclinical, the breadth and consistency of findings across different research models provides a strong foundation for understanding the compound therapeutic potential.
Accelerated wound and tissue healing
This is the flagship benefit, the one supported by the most extensive body of research. Penta deca peptide arginate accelerates healing across multiple tissue types, including tendons, ligaments, muscles, skin, and bone. The mechanisms already discussed, including enhanced angiogenesis, increased fibroblast activity, collagen synthesis upregulation, and improved cell migration, all contribute to faster resolution of tissue damage.
Preclinical studies demonstrate improvements in tendon-to-bone healing, with enhanced collagen organization and increased tensile strength in healed tissues. Skin wound studies show accelerated closure, reduced scarring, and improved structural integrity of healed tissue. These findings are consistent with clinical observations from practitioners who report visible improvements in wound healing within the first one to two weeks of treatment. Researchers interested in the broader category of tissue repair peptides will find penta deca peptide arginate among the most well-studied options available.
The healing benefits extend beyond acute injuries. Chronic conditions involving ongoing tissue damage, such as tendinopathy, may also respond to the peptide enhanced repair signaling. For those dealing with specific injuries, our guides on peptides for shoulder pain and peptides for back pain provide targeted protocol information.
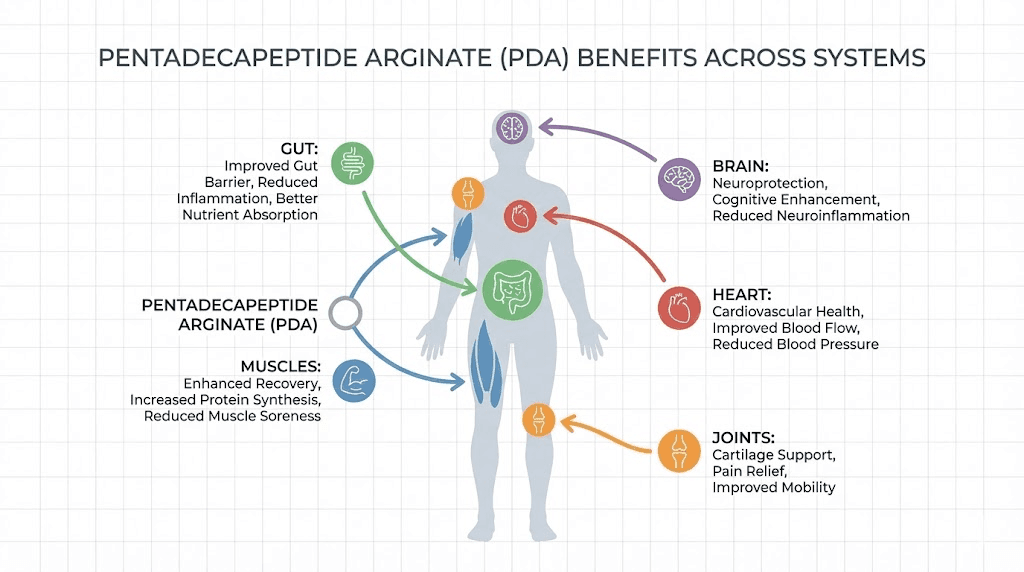
Gastrointestinal protection and repair
Given that the parent compound was originally isolated from gastric juice, it is fitting that gut health represents one of the strongest application areas for penta deca peptide arginate. The peptide demonstrates protective effects against gastric ulceration, promotes healing of intestinal lesions, and modulates gut inflammation through multiple pathways.
The oral route is particularly relevant for gastrointestinal applications because it delivers the peptide directly to the tissues where it is needed. When taken orally, penta deca peptide arginate contacts the stomach lining, small intestinal epithelium, and colonic tissue sequentially during transit. This direct contact may enhance local tissue effects beyond what systemic administration achieves. For researchers using peptides to address gut-related issues, our comprehensive guide on peptides for gut health provides detailed protocol guidance.
The gut health applications also connect to broader systemic benefits. The gut-brain axis, gut-immune axis, and gut-skin axis all suggest that improving intestinal health can produce cascading improvements throughout the body. Some practitioners have reported improvements in skin conditions, mood, and immune function in patients receiving penta deca peptide arginate for gut health protocols, though these observations require controlled study to confirm.
Anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body
Chronic inflammation underlies a staggering number of health conditions, from joint pain and autoimmune disorders to cardiovascular disease and neurodegeneration. Penta deca peptide arginate modulation of inflammatory markers, particularly TNF-alpha and IL-6, positions it as a potential tool for managing systemic inflammation without the side effects of conventional anti-inflammatory medications.
The peptide anti-inflammatory action is not limited to any single tissue type. Research demonstrates benefits in the gastrointestinal system, musculoskeletal tissues, cardiovascular system, and nervous system. This systemic anti-inflammatory effect is one reason why researchers often report improvements in seemingly unrelated symptoms when using the peptide for a specific indication, experiencing reduced joint pain while treating a gut issue, for example, or improved recovery times while treating a specific injury.
For researchers exploring anti-inflammatory peptide approaches, penta deca peptide arginate offers a mechanism that modulates rather than suppresses inflammatory processes. This distinction matters enormously for long-term use, where indiscriminate inflammation suppression can compromise immune function and healing capacity. The peptide approach to inflammation aligns well with what many in the longevity peptide community consider optimal: reducing harmful chronic inflammation while preserving beneficial acute inflammatory responses.
Muscle recovery and athletic performance support
Athletes and fitness-focused researchers represent a major segment of the penta deca peptide arginate user community. The peptide benefits for muscle recovery stem from multiple mechanisms: reduced inflammation in stressed tissues, enhanced blood flow to muscles through angiogenesis and nitric oxide production, accelerated repair of exercise-induced microdamage, and improved collagen synthesis in connective tissues that support muscle function.
The nitric oxide enhancement from the arginate salt form is particularly relevant for athletic applications. Nitric oxide is a key regulator of blood flow during exercise, and many athletic supplements target nitric oxide production for this reason.
The arginate form of the peptide provides both the repair peptide and additional substrate for nitric oxide synthesis, making it a dual-purpose compound for athletic recovery.
Researchers comparing options for athletic performance peptides should consider this unique advantage when evaluating penta deca peptide arginate against other recovery compounds.
For those focused specifically on muscle development, the peptide interaction with growth hormone receptors in fibroblasts suggests indirect support for muscle growth through improved connective tissue health. Healthy tendons, ligaments, and fascia are essential for progressive overload training, and the peptide ability to maintain and repair these structures may prevent the connective tissue injuries that commonly sideline athletes. Our guide on peptides for muscle growth covers this application area in detail, and the best peptides for muscle growth article compares options across the full spectrum of available compounds.
Cardiovascular protection
The cardiovascular benefits of penta deca peptide arginate operate through several interconnected mechanisms. VEGFR2-mediated angiogenesis promotes the formation of new blood vessels, improving blood supply to tissues throughout the body. Nitric oxide modulation supports healthy vascular tone and blood pressure regulation. The anti-inflammatory effects protect blood vessel walls from the chronic inflammation that drives atherosclerosis.
The homeostatic blood pressure regulation is particularly noteworthy. Unlike conventional vasodilators that lower blood pressure regardless of baseline, penta deca peptide arginate appears to normalize blood pressure from either direction. This modulatory effect suggests a fundamentally different mechanism and a potentially superior safety profile for cardiovascular applications.
Pain reduction
Pain relief is one of the most consistently reported benefits among penta deca peptide arginate users, though the mechanism is indirect rather than direct. The peptide does not block pain receptors like analgesics do. Instead, it reduces the underlying causes of pain: inflammation, tissue damage, and impaired blood flow. As these conditions improve, pain naturally decreases.
This distinction matters because pain relief through tissue repair is more sustainable than pain relief through receptor blockade. When the tissue heals, the pain resolves permanently. When a pain blocker wears off, the pain returns. Researchers interested in peptide-based pain management will find comprehensive coverage in our best peptide for pain guide, which compares penta deca peptide arginate against other options including KPV and SS-31.
Neuroprotective potential
Emerging research suggests that penta deca peptide arginate may offer neuroprotective benefits through its anti-inflammatory and vascular mechanisms. The central nervous system relies heavily on adequate blood supply, and the peptide ability to promote angiogenesis and modulate nitric oxide production could support neural tissue health.
Preclinical studies with BPC-157, which shares the identical active sequence, have demonstrated protective effects against various forms of neural damage. While specific studies on the arginate form in neural tissue are limited, the shared mechanism of action suggests similar potential. Researchers exploring peptides for brain function may find penta deca peptide arginate worth investigating alongside more established neuropeptides like Semax.
Dosage protocols and administration routes
Effective protocols for penta deca peptide arginate vary based on the administration route, the condition being addressed, and individual factors like body weight and response sensitivity. The following protocols represent commonly reported approaches from clinical practitioners and the research community. They are not prescriptions. They are reference points for researchers designing their own evidence-based protocols.
Injectable protocols
Subcutaneous injection remains the most studied and predictable route of administration for penta deca peptide arginate. The peptide is typically supplied in lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder form and requires reconstitution with bacteriostatic water before injection.
Loading phase protocol (acute injury or initial treatment):
Dose: 500 mcg to 1 mg per injection
Frequency: Once daily
Duration: 7 to 10 days
Injection site: Subcutaneous, ideally near the area of concern
Timing: Morning or evening, consistency matters more than specific time
Maintenance phase protocol:
Dose: 500 mcg to 1 mg per injection
Frequency: 2 to 3 times per week
Duration: 4 to 8 weeks total protocol length
Cycle recommendation: 2 months on, 2 months off
Unlike traditional BPC-157 acetate, which is often administered twice daily due to its shorter half-life, the enhanced stability of the arginate form typically allows for once-daily dosing during the loading phase. This improved dosing convenience is one of the practical advantages researchers appreciate about the formulation. The peptide reconstitution calculator helps ensure accurate preparation, while our guide on mixing peptides with bacteriostatic water walks through the process step by step.
For researchers using injection pens, our peptide injection pen guide covers device selection and technique.
Oral capsule protocols
The dramatically improved oral bioavailability of the arginate form makes oral administration a viable primary route, not just a convenience compromise. This is the single biggest practical difference between penta deca peptide arginate and traditional BPC-157 acetate.
Standard oral protocol:
Dose: 500 mcg per capsule
Frequency: Once daily
Timing: On an empty stomach, 30 minutes before food
Duration: 4 to 8 weeks
Cycle recommendation: 2 months on, 2 months off
Taking the capsule on an empty stomach maximizes absorption by reducing competition with food proteins for intestinal transport. The 30-minute window before eating allows adequate time for the peptide to transit through the stomach and begin absorption in the small intestine. Researchers interested in the broader comparison between oral and injectable delivery methods will find valuable context in our injectable vs oral peptides comparison page.
Oral protocols are particularly suitable for gastrointestinal applications, where the direct contact between the peptide and gut tissue provides both systemic and local benefits. They are also preferred by researchers who want to avoid injections entirely, though it is worth noting that the oral route distributes the peptide systemically rather than concentrating it at a specific site.
Nasal spray protocols
Nasal administration offers rapid absorption through the highly vascular nasal mucosa, providing faster onset than oral dosing with greater convenience than injection. For researchers exploring nasal spray peptides, penta deca peptide arginate is among the compounds showing promise via this route.
Nasal spray protocol:
Dose: 200-500 mcg per application
Frequency: 1 to 2 times daily
Duration: 4 to 8 weeks
Nasal delivery is particularly interesting for researchers focused on neurological applications, as the nasal route provides a potential pathway to bypass the blood-brain barrier through the olfactory and trigeminal nerve pathways. This route remains less studied than injection or oral administration for penta deca peptide arginate specifically, but the anatomical advantages are well-established for peptide delivery in general.
Topical cream protocols
Topical formulations allow targeted delivery to skin wounds, burns, and localized inflammation. The peptide ability to promote collagen synthesis and enhance wound healing makes topical application relevant for dermatological applications. Researchers exploring peptides for skin and wound care may find this route useful for specific applications.
Topical protocol:
Application: Thin layer to affected area
Frequency: 1 to 2 times daily
Duration: Until healing is complete or as directed
Choosing the right administration route
The optimal route depends on the therapeutic goal.
For localized injuries like a specific tendon, ligament, or muscle tear, subcutaneous injection near the injury site provides the highest local concentration and most predictable results. For systemic recovery, general inflammation, or multiple injury sites, oral administration with the arginate form provides convenient whole-body distribution. For gut health specifically, oral is the preferred route for direct tissue contact. For neurological applications, nasal delivery offers potential advantages through anatomical proximity to the central nervous system.
Many practitioners recommend combining routes for optimal results. An injectable protocol targeting a specific injury, combined with oral dosing for systemic support, leverages the advantages of both approaches. The peptide calculator helps researchers plan multi-route protocols with accurate dosing for each administration method.
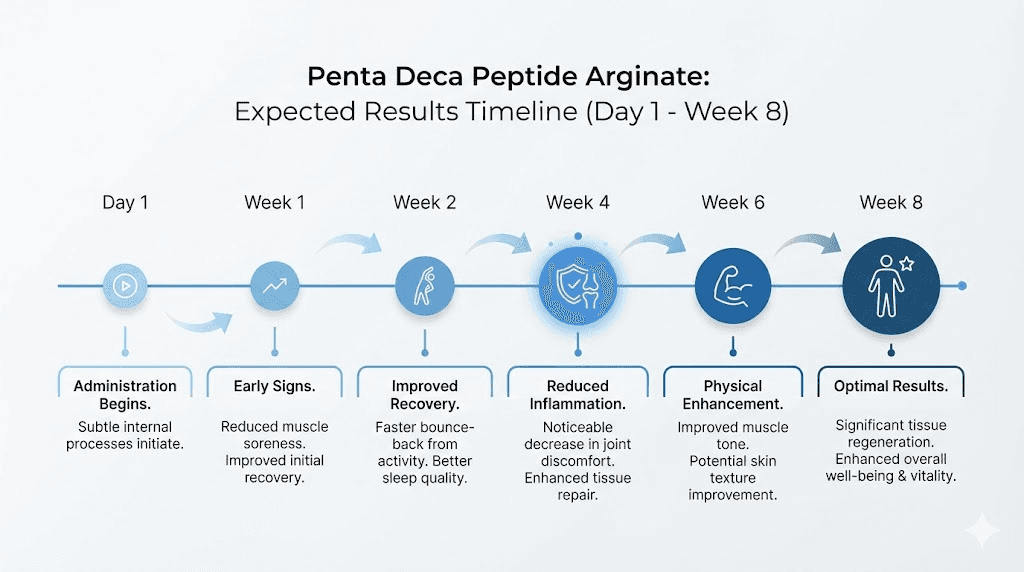
Timeline of expected results
Understanding when to expect results prevents premature protocol abandonment and helps researchers assess whether their approach is working.
Days 1-3: No noticeable changes in most cases. The peptide is establishing tissue saturation.
Days 4-7: Some researchers report subtle improvements in inflammation, sleep quality, or general well-being. These early changes are not universal.
Days 7-14: Initial improvements in pain levels, reduced swelling, and early signs of healing become more consistently reported. This is when most researchers first notice meaningful changes.
Weeks 2-4: Significant improvements in tissue repair, pain reduction, and functional recovery. This window is where the most dramatic changes typically occur.
Weeks 4-8: Continued healing, tissue remodeling, and functional improvement. Some conditions require the full protocol duration for complete resolution.
These timelines are consistent with what researchers observe across the broader category of healing peptides. Our guide on how long peptides take to work provides additional context for setting realistic expectations, and peptide before and after results from the research community illustrate the range of outcomes people experience.
Stacking penta deca peptide arginate with other peptides
Peptide stacking, the practice of combining multiple peptides in a coordinated protocol, can amplify therapeutic outcomes when compounds with complementary mechanisms are combined thoughtfully. Penta deca peptide arginate is one of the most versatile stacking candidates because its mechanisms (angiogenesis, anti-inflammation, collagen synthesis, nitric oxide modulation) complement rather than duplicate the actions of many other popular peptides.
Before designing any stacking protocol, researchers should understand both the individual effects of each compound and the potential interactions between them. Our peptide stacking guide provides foundational principles, while the peptide stack calculator helps with dosing logistics.
The Wolverine stack: PDA + TB-500
The combination of penta deca peptide arginate and TB-500 has earned the nickname "Wolverine stack" in the research community, a reference to the fictional character known for superhuman healing. While the name is playful, the science behind the combination is substantive. Both the Wolverine stack and Wolverine peptides have become some of the most discussed protocols in the peptide community.
TB-500, a fragment of Thymosin Beta-4, works primarily through actin regulation and cell migration enhancement. It promotes soft tissue healing by increasing the motility of repair cells and reducing inflammation through mechanisms distinct from those of penta deca peptide arginate. Where PDA upregulates VEGFR2 and promotes angiogenesis, TB-500 increases actin polymerization and enhances cellular migration. Where PDA modulates nitric oxide, TB-500 reduces inflammatory cytokines through separate pathways.
The complementary nature of these mechanisms explains why the combination often produces results that exceed what either peptide achieves individually. Practitioners report that the combination is particularly effective for complex injuries involving multiple tissue types, such as joint injuries that affect cartilage, ligaments, and surrounding muscle simultaneously. For a detailed comparison of the two peptides, our BPC-157 vs TB-500 page breaks down the differences and synergies, and the complete BPC-157 and TB-500 stacking guide covers protocols in detail.
Wolverine stack protocol:
PDA: 500 mcg to 1 mg subcutaneous, once daily
TB-500: 2.0 to 2.5 mg subcutaneous, 2 to 3 times weekly (loading phase), then once weekly (maintenance)
Duration: 6 to 8 weeks
Timing: PDA and TB-500 can be administered at the same time or at different times during the day. Some practitioners prefer morning PDA and evening TB-500.
The TB-500 dosage calculator helps determine precise dosing based on body weight and protocol goals.
PDA + CJC-1295/Ipamorelin
Adding a growth hormone secretagogue to penta deca peptide arginate creates a powerful synergy for tissue repair. CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin stimulate the body natural growth hormone release, which enhances tissue repair, muscle recovery, and fat metabolism. When combined with penta deca peptide arginate upregulation of growth hormone receptors in fibroblasts, the growth hormone secretagogue provides more signaling molecules for the increased receptor population to capture.
This is the biological equivalent of building more docking stations (PDA increases receptors) and then sending more ships to dock (CJC-1295/Ipamorelin increases growth hormone). The result is amplified growth hormone signaling in the tissues that need it most for repair. For a detailed comparison of these secretagogues, see Ipamorelin vs CJC-1295.
PDA + GH secretagogue protocol:
PDA: 500 mcg to 1 mg subcutaneous or oral, once daily (morning)
CJC-1295/Ipamorelin: Standard dosing (typically 100 mcg each), before bed on empty stomach
Duration: 8 to 12 weeks
Note: The CJC-1295 dosage calculator helps determine individual dosing
PDA + GHK-Cu
GHK-Cu (copper peptide) is a naturally occurring tripeptide with potent regenerative properties. It promotes collagen synthesis, reduces inflammation, and activates stem cell activity through mechanisms that complement penta deca peptide arginate. Where PDA works primarily through VEGFR2 and nitric oxide pathways, GHK-Cu works through copper-dependent enzyme activation and gene regulation.
The combination is particularly relevant for anti-aging protocols, skin regeneration, and wound healing applications. Both peptides promote collagen synthesis, but through different pathways, creating a more comprehensive collagen-building stimulus than either achieves alone. Researchers interested in glow peptides and skin rejuvenation often combine these two compounds for synergistic dermatological benefits.
PDA + GHK-Cu protocol:
PDA: 500 mcg subcutaneous or oral, once daily
GHK-Cu: Per standard dosing guidelines (varies by administration route)
Duration: 4 to 8 weeks
PDA + SS-31 (Elamipretide)
For researchers focused on mitochondrial health and cellular energy, combining penta deca peptide arginate with SS-31 creates a protocol that addresses tissue repair from both structural and energetic perspectives. SS-31 targets mitochondrial cardiolipin, improving cellular energy production and reducing oxidative stress at the cellular level. PDA addresses the structural repair and vascular supply needs of healing tissues.
This combination is particularly interesting for aging-related tissue deterioration, where both mitochondrial dysfunction and impaired repair signaling contribute to declining tissue health. The emerging research on MOTS-c as another mitochondrial peptide adds additional options for researchers designing energy-focused stacking protocols.
The comprehensive recovery stack
For maximum recovery support, some practitioners recommend a multi-peptide approach that addresses all major healing pathways simultaneously. This advanced protocol is not for beginners and requires careful monitoring and medical supervision.
Advanced recovery protocol:
PDA: 500 mcg to 1 mg, once daily (tissue repair, angiogenesis)
TB-500: 2.0 to 2.5 mg, 2 to 3 times weekly (cell migration, soft tissue)
CJC-1295/Ipamorelin: Standard dosing before bed (growth hormone amplification)
Duration: 6 to 8 weeks with medical supervision
For researchers who want guidance on combining multiple compounds safely, our articles on how many peptides you can take at once, cycling different peptides, and peptide cycle planning provide essential frameworks for designing safe multi-compound protocols.
Stacking considerations and precautions
Not every combination is beneficial. Researchers should avoid stacking compounds with overlapping toxicity profiles or contradictory mechanisms. They should start with single compounds to establish baseline response before adding additional peptides. And they should maintain detailed logs of doses, timing, and observed effects to identify which components are contributing to results.
The peptide solutions available in the research community vary in quality and purity, which makes sourcing and peptide testing essential components of any stacking protocol. Impurities in one compound can interact unpredictably with other compounds in a stack, making quality assurance non-negotiable.
Side effects and safety considerations
Penta deca peptide arginate has demonstrated a favorable safety profile in preclinical research, with a wide therapeutic margin and low incidence of adverse effects. However, the limited human clinical trial data means that the long-term safety profile in humans is not fully characterized. Researchers should approach any peptide protocol with appropriate caution and medical supervision.
Commonly reported side effects
The most frequently reported side effects are mild and typically transient.
Injection site reactions: Redness, mild swelling, and occasionally bruising at the injection site. These reactions are common with any subcutaneous injection and are not specific to penta deca peptide arginate. Proper injection technique minimizes these effects.
Minor gastrointestinal discomfort: Some users report mild nausea, especially when beginning oral protocols. This typically resolves within the first few days as the body adjusts. Taking the capsule with a small amount of water and maintaining the empty stomach recommendation usually minimizes this effect.
Headaches: Occasionally reported during the first week of use, potentially related to changes in nitric oxide levels and vascular tone. These are typically mild and self-resolving.
Fatigue: Some researchers report temporary fatigue during the first few days, which may reflect the body increased healing activity diverting energy resources toward tissue repair. This paradoxically indicates that the peptide is active, though it can be inconvenient.
What the preclinical safety data shows
The preclinical safety profile of the BPC-157 sequence, which is identical in PDA, is remarkably clean. Animal studies have failed to establish a lethal dose even at concentrations thousands of times above therapeutic levels. This suggests an extremely wide safety margin, at least in animal models.
No significant organ toxicity has been observed in preclinical studies. No mutagenic or carcinogenic effects have been documented.
The peptide does not appear to interact with cytochrome P450 enzymes, suggesting low potential for drug interactions. And the modulatory rather than stimulatory nature of its effects on systems like nitric oxide and inflammation suggests a lower risk of overcorrection compared to directionally-acting compounds.
These findings are encouraging but must be interpreted with appropriate caution. Preclinical safety data does not always predict human safety outcomes, and the absence of adverse effects in controlled animal studies does not guarantee the same in diverse human populations with varying health conditions and concurrent medications.
Situations requiring extra caution
Certain populations should exercise additional caution or avoid penta deca peptide arginate entirely.
Cancer history or active malignancy: The peptide angiogenic properties could theoretically promote tumor vascularization. While no evidence directly links penta deca peptide arginate to cancer progression, the precautionary principle suggests avoiding pro-angiogenic compounds in individuals with known or suspected malignancies.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: No safety data exists for use during pregnancy or lactation. The potential effects on fetal development and breast milk composition are unknown.
Bleeding disorders or anticoagulant therapy: The nitric oxide and vascular effects could theoretically interact with anticoagulant medications. Researchers on blood thinners should consult their healthcare provider before using any peptide that affects vascular function.
Children and adolescents: The effects of penta deca peptide arginate on developing tissues have not been studied. Use in individuals under 18 is not recommended without specific medical supervision.
For a broader understanding of peptide safety across different compounds, our guide on safe peptides for women and peptides for women over 40 address gender-specific safety considerations.
Drug testing implications
WADA, the World Anti-Doping Agency, prohibits BPC-157 and related peptides in competitive athletics. This prohibition extends to penta deca peptide arginate, as the active sequence is identical. Athletes subject to anti-doping testing should be aware that these compounds may be detectable and could result in sanctions. For more details, our article on whether peptides show up on drug tests covers the testing landscape comprehensively.
The detection window varies by administration route and testing method. Injectable peptides may be detectable longer than oral or topical forms due to different pharmacokinetic profiles. Researchers subject to testing should plan accordingly and consult anti-doping resources for current detection capabilities.
Quality and sourcing concerns
Perhaps the most significant safety risk with penta deca peptide arginate comes not from the peptide itself but from the quality of the product obtained. The research peptide market includes suppliers with varying standards for purity, potency, and quality control. Contaminated, underdosed, or mislabeled products pose risks that have nothing to do with the inherent safety of the peptide.
Researchers should prioritize products that come with third-party testing documentation, including HPLC purity analysis and mass spectrometry confirmation of identity. Our guides on peptide testing labs, peptide vial research, and research vs pharmaceutical grade peptides help researchers navigate sourcing decisions. Understanding the difference between lyophilized and liquid peptides is also essential for ensuring product quality.
The regulatory landscape and what it means for researchers
Understanding the regulatory environment surrounding penta deca peptide arginate requires context about what happened with BPC-157 and why the arginate formulation emerged as an alternative. The regulatory story is not simple, but understanding it is essential for researchers who want to operate within legal frameworks while accessing the compounds they need for their work.
The FDA decision on BPC-157
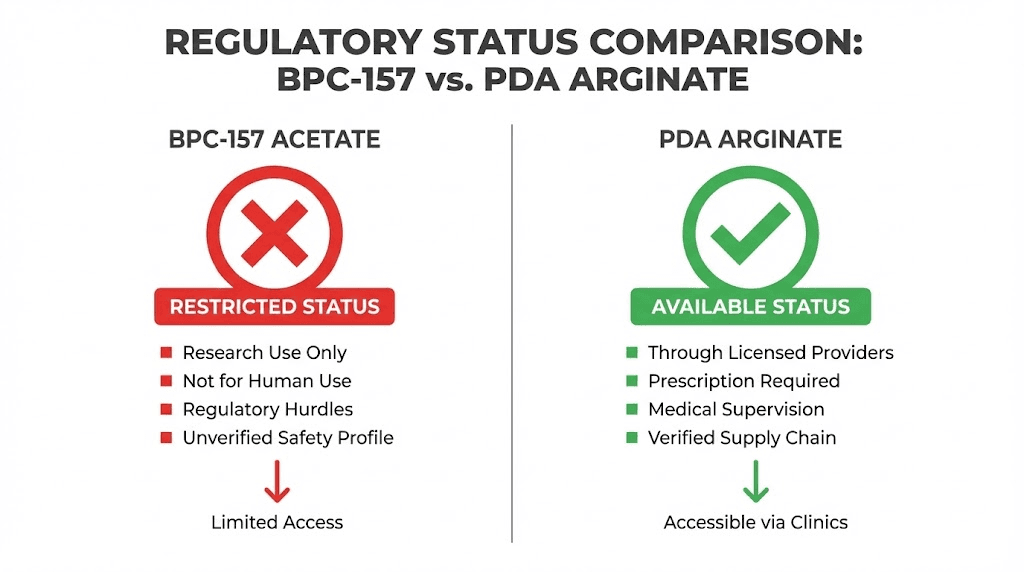
The FDA placed BPC-157 on its list of Category 2 bulk drug substances. Category 2 designation means the substance presents "safety concerns" and is prohibited from being used in compounding by licensed pharmacies. This classification effectively removed BPC-157 acetate from the legitimate pharmaceutical supply chain in the United States, leaving researchers with fewer legal options for obtaining the compound.
The reasons cited by the FDA included concerns about immunogenicity, peptide impurity characterization challenges, and the lack of adequate safety data from human clinical trials. The Category 2 designation was not a finding that BPC-157 is dangerous per se, but rather that insufficient human safety data exists to justify its use in compounded medications without the oversight of the standard drug approval process.
Enforcement has been real. The Department of Justice prosecuted Tailor Made Compounding LLC, which pleaded guilty to distributing BPC-157 and other unapproved drugs, resulting in forfeiture of $1.79 million. This prosecution sent a clear signal that the FDA Category 2 classification carries enforceable legal consequences for compounding pharmacies.
How PDA navigates the regulatory landscape
Penta deca peptide arginate occupies a different regulatory position than BPC-157 acetate, though the distinction requires careful understanding. PDA is not specifically listed as a Category 2 substance. Its arginate salt form and distinct nomenclature place it in a different regulatory category from the acetate form that received the FDA restriction.
Licensed healthcare providers can prescribe penta deca peptide arginate through regulated channels, including compounding pharmacies that operate within state and federal guidelines. This makes PDA one of the more accessible legal options for researchers and patients seeking the healing benefits of the pentadecapeptide sequence. The ability to obtain the compound through legitimate medical channels also provides quality assurance benefits, as regulated pharmacies must meet standards for purity and potency that unregulated suppliers do not.
However, researchers should understand that the regulatory landscape for peptides is dynamic and evolving. What is permitted today may change. Staying informed about peptide regulation updates is essential for anyone working with these compounds. Our coverage of peptide legality and whether doctors can prescribe research grade peptides provides additional legal context.
The global regulatory picture
Regulatory approaches to penta deca peptide arginate vary significantly by country. Some nations regulate all peptides as prescription medications. Others allow certain peptides to be sold as research chemicals or dietary supplements with varying levels of oversight. Athletes worldwide should note that WADA prohibition applies regardless of local regulations about availability.
The inconsistency of global regulations has created a fragmented market where product quality and legal status vary dramatically by jurisdiction. Researchers working across borders or sourcing internationally should understand both the regulations in their home country and the regulatory status in the country of origin for their products.
The grey market reality
The gap between demand for healing peptides and regulated supply has created a significant grey market. Research chemical suppliers, offshore pharmacies, and unregulated vendors offer peptides of varying quality and authenticity. While some of these sources provide legitimate products, the lack of regulatory oversight means that quality cannot be guaranteed. Our guide on grey market peptides explores this landscape in detail, including how to identify reputable suppliers and avoid counterfeit products.
For researchers who prefer to work within fully regulated frameworks, obtaining penta deca peptide arginate through a licensed healthcare provider and compounding pharmacy remains the most reliable approach. The cost of peptide therapy through legitimate channels is typically higher than grey market alternatives, but the assurance of quality and legal compliance provides value that price comparisons alone do not capture.
Practical considerations for storage and handling
Proper storage and handling are essential for maintaining penta deca peptide arginate potency and safety. While the arginate form offers enhanced stability compared to the acetate form, all peptides are sensitive to environmental conditions and require appropriate care.
Storage guidelines
Lyophilized (powder) form:
Temperature: Store at -20 degrees Celsius for long-term storage, or 2 to 8 degrees Celsius (refrigerator) for short-term storage up to several months
Light: Protect from direct light. Store in original vial away from windows.
Humidity: Keep dry. Do not open vials in humid environments.
Shelf life: Several years when properly stored at -20 degrees Celsius
Reconstituted (liquid) form:
Temperature: Refrigerate at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius immediately after reconstitution
Shelf life: Use within 2 to 4 weeks for optimal potency
Never freeze reconstituted peptides
Do not expose to repeated temperature cycling
For comprehensive storage guidance, our articles on how to store peptides after reconstitution, how long reconstituted peptides last in the fridge, and general peptide fridge storage guidelines provide detailed protocols for maintaining peptide integrity.
Reconstitution best practices
Reconstituting penta deca peptide arginate follows the same principles as reconstituting any lyophilized peptide. Use bacteriostatic water as the diluent. Direct the water stream down the side of the vial, not directly onto the peptide cake, to prevent damage to the molecular structure. Gently swirl, never shake, to dissolve the powder completely.
The peptide reconstitution calculator simplifies the math involved in achieving the desired concentration. Knowing what water to mix with peptides and following proper mixing procedures are foundational skills for any peptide researcher.
Who should consider penta deca peptide arginate
Not every researcher or patient is the right candidate for penta deca peptide arginate. Understanding who stands to benefit the most helps allocate this tool where it provides the greatest value.
Ideal candidates
Researchers recovering from musculoskeletal injuries: Tendon, ligament, and muscle injuries represent the most well-supported application area. The peptide multiple mechanisms of action, including angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, and anti-inflammation, all contribute to accelerated healing of these tissue types. Whether dealing with a specific injury like a rotator cuff strain or a chronic condition like tendinopathy, the evidence base supports potential benefit.
Individuals with gastrointestinal issues: Gut health applications are supported by the peptide origin as a gastric protective compound. Conditions involving intestinal inflammation, barrier dysfunction, or ulceration may respond to the peptide reparative effects, particularly when administered orally for direct tissue contact.
People seeking oral alternatives to injectable BPC-157: The dramatically improved oral bioavailability of the arginate form makes it the obvious choice for researchers who want BPC-157 benefits without injections. The convenience of oral capsules, combined with bioavailability comparable to injection, makes this a practical choice for many.
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts focused on recovery: The combination of tissue repair, anti-inflammation, and nitric oxide enhancement makes penta deca peptide arginate particularly relevant for recovery-focused protocols. Researchers comparing performance peptides will find it among the top options for recovery support.
Individuals exploring comprehensive peptide protocols: For researchers already using other peptides and looking to add a tissue repair component, penta deca peptide arginate stacking versatility makes it an excellent addition to multi-compound protocols. Its complementary mechanisms enhance the effects of growth hormone secretagogues, other healing peptides, and mitochondrial-targeting compounds.
Who should wait or look elsewhere
Researchers with active cancer diagnoses should avoid pro-angiogenic peptides until cleared by their oncologist. Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals should wait. People on anticoagulant therapy need medical clearance before using any compound that affects vascular function. And competitive athletes subject to WADA testing should avoid the compound entirely.
For general wellness research where healing peptides are not specifically needed, other peptides may provide more targeted benefits. Researchers focused purely on fat loss, for example, might find weight loss peptides or GLP-1 agonists more directly aligned with their goals. Those focused on energy enhancement might prioritize mitochondrial peptides like MOTS-c. And researchers interested in hair loss or libido have more specifically targeted options available.
Comparing penta deca peptide arginate to other healing peptides
The healing peptide category includes several compounds beyond penta deca peptide arginate, each with distinct mechanisms and application areas. Understanding how PDA compares helps researchers select the right tool for their specific needs.
Peptide | Primary mechanism | Best for | Oral viability | Stacks with PDA? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
PDA (Penta Deca Peptide Arginate) | VEGFR2, NO modulation, collagen synthesis | Multi-tissue healing, gut, vascular | Excellent (arginate form) | N/A |
TB-500 | Actin regulation, cell migration | Soft tissue, muscle, cardiac | Poor | Yes (Wolverine stack) |
GHK-Cu | Copper-dependent enzymes, gene regulation | Skin, anti-aging, wound healing | Moderate | Yes (collagen synergy) |
KPV | Alpha-MSH fragment, anti-inflammatory | Gut inflammation, skin conditions | Good | Yes (inflammation focus) |
SS-31 | Mitochondrial cardiolipin binding | Cellular energy, oxidative stress | Moderate | Yes (energy + repair) |
Thymosin Alpha-1 | Immune modulation | Immune function, infections | Poor | Conditional (immune focus) |
The table illustrates why penta deca peptide arginate has become such a popular choice. Its breadth of mechanisms, excellent oral viability in the arginate form, and compatibility with other healing peptides make it the most versatile option in the category. For researchers who want a single healing peptide to start with, PDA is often the recommended first choice.
For a deeper understanding of how peptides compare across different applications, our comparison pages for peptides vs SARMs and peptides vs TRT provide additional context for researchers evaluating their options.
Common mistakes researchers make with penta deca peptide arginate
Even experienced researchers make avoidable errors with penta deca peptide arginate. Understanding the most common mistakes prevents wasted effort and suboptimal results.
Mistake 1: Using acetate protocols for arginate dosing
The improved bioavailability of the arginate form means that dose-for-dose, it delivers more active peptide to target tissues than the acetate form, especially via oral routes. Researchers who apply acetate dosing guidelines to arginate formulations may overdose, particularly with oral administration. The standard 500 mcg oral dose of the arginate form may deliver comparable systemic exposure to much higher doses of the acetate form taken orally. Always use dosing guidelines specific to the arginate formulation.
Mistake 2: Expecting immediate results
Tissue repair is a biological process that takes time. The peptide accelerates healing, but it does not produce instant results. Researchers who abandon protocols after 3 to 5 days because they do not "feel anything" are not giving the compound adequate time to work. The minimum evaluation period should be 2 to 3 weeks for most applications, with significant results typically emerging at the 4-week mark.
Mistake 3: Neglecting storage requirements
Degraded peptide produces degraded results. Researchers who leave reconstituted peptides at room temperature, expose vials to light, or use products beyond their shelf life may attribute poor results to the peptide when the actual problem is product degradation. Following the peptide storage guidelines is not optional. It is a requirement for meaningful results.
Mistake 4: Ignoring the importance of cycling
The recommended protocol of 2 months on, 2 months off exists for good reason. Continuous use without cycling can lead to receptor desensitization, diminishing returns, and unknown long-term effects. The off-cycle period allows the body natural repair mechanisms to operate independently and prevents dependence on exogenous peptide signaling. Our guide on peptide cycle planning explains cycling principles in detail.
Mistake 5: Sourcing from unverified suppliers
The research peptide market includes products of wildly varying quality. A vial labeled as penta deca peptide arginate may contain the correct peptide, a different peptide, a degraded peptide, or no peptide at all. Without third-party testing, there is no way to know. Always verify products through independent peptide testing laboratories and source from reputable suppliers with documented quality control processes.
Frequently asked questions
Is penta deca peptide arginate the same as BPC-157?
The active peptide sequence is identical, consisting of the same fifteen amino acids in the same order. The difference is the salt form. BPC-157 traditionally uses an acetate salt, while penta deca peptide arginate uses an arginine salt. This modification significantly improves oral bioavailability and stability without changing the peptide biological activity once it reaches target tissues. For detailed comparisons, see our PDA peptide guide.
Can I take penta deca peptide arginate orally instead of injecting?
Yes, and this is one of the primary advantages of the arginate formulation. The arginate salt form maintains over 95% structural integrity through gastric acid exposure, compared to less than 2% for the acetate form. This makes oral administration a viable primary route with the arginate form, not just a convenience compromise. Standard oral dosing is 500 mcg once daily on an empty stomach. See our comparison of injectable vs oral peptides for more context.
How long does it take for penta deca peptide arginate to work?
Most researchers report initial improvements within 7 to 14 days, with significant results at the 2 to 4 week mark. Some individuals notice subtle changes as early as day 4 to 5, while others require 3 to 4 weeks for meaningful effects. The timeline depends on the condition being addressed, the administration route, dosing consistency, and individual response factors. Our detailed article on how long peptides take to work covers this topic comprehensively.
What is the Wolverine stack?
The Wolverine stack refers to the combination of penta deca peptide arginate (or BPC-157) with TB-500 (Thymosin Beta-4 fragment). These two peptides work through complementary mechanisms, with PDA focusing on angiogenesis and collagen synthesis while TB-500 enhances cell migration and actin regulation. The combination is popular for injury recovery and is covered in detail in our Wolverine stack guide and our BPC-157 and TB-500 stacking guide.
Is penta deca peptide arginate legal?
The regulatory status varies by country and jurisdiction. In the United States, penta deca peptide arginate is available through licensed healthcare providers and compounding pharmacies, unlike BPC-157 acetate which the FDA classified as a Category 2 substance. However, it is not FDA-approved for any specific medical indication, and WADA prohibits it for competitive athletes. Our articles on peptide legality and regulation news track the evolving legal landscape.
Does penta deca peptide arginate show up on drug tests?
Standard workplace drug panels do not test for peptides like penta deca peptide arginate. However, WADA-compliant anti-doping testing can detect BPC-157 and related peptides, and the compound is on the prohibited substances list for competitive athletes. For a thorough breakdown, see our guide on peptides and drug testing.
Can women use penta deca peptide arginate safely?
Yes. The peptide mechanisms of action are not gender-specific, and the safety profile appears comparable across genders. Dosing does not typically require gender-based adjustment, though individual response should always guide protocol modifications. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid use due to lack of safety data. For gender-specific peptide guidance, see our articles on best peptides for women and safe peptides for women.
What is the recommended cycle length?
The standard recommendation is 2 months on, 2 months off. This cycling approach allows the body to benefit from the peptide repair signaling during the active phase and then consolidate those gains during the off phase using its own endogenous repair mechanisms. Some practitioners adjust cycle length based on the condition being treated, with acute injuries sometimes requiring shorter protocols and chronic conditions sometimes warranting longer ones. Our peptide cycle planning guide covers cycling strategies in depth.
Can I stack penta deca peptide arginate with growth hormone peptides?
Yes, and this is one of the most synergistic combinations available. Penta deca peptide arginate upregulates growth hormone receptors in fibroblasts, while growth hormone secretagogues like CJC-1295 and Ipamorelin increase growth hormone levels. The combination provides more growth hormone signaling to more receptors, amplifying tissue repair beyond what either approach achieves alone. SeekPeptides members access detailed stacking protocols designed for this combination.
How does penta deca peptide arginate compare to other recovery peptides?
PDA offers the broadest mechanism of action among healing peptides, combining angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, nitric oxide modulation, and anti-inflammatory effects. TB-500 excels specifically at cell migration and soft tissue repair. GHK-Cu is strongest for skin and anti-aging applications. KPV targets inflammation most directly. The best choice depends on the specific application, and many researchers combine multiple peptides for comprehensive coverage. Our injectable peptides list and stacking guide help researchers compare options.
The future of penta deca peptide arginate research
The current evidence base for penta deca peptide arginate is predominantly preclinical, with the majority of published research conducted in animal models. While this research is extensive and consistently positive, the gap between animal and human studies represents both a limitation of current knowledge and an opportunity for future research.
Several developments could significantly advance understanding of this compound in the coming years. Clinical trials specifically using the arginate formulation would provide human pharmacokinetic data and efficacy endpoints. Head-to-head comparisons between arginate and acetate forms in controlled human studies would quantify the bioavailability advantage in clinical terms. And long-term safety studies in humans would address the most significant remaining uncertainty about the compound.
The regulatory environment may also evolve. If the FDA creates pathways for peptide regulation that acknowledge the growing body of preclinical evidence, compounds like penta deca peptide arginate could move toward formal approval. Alternatively, continued regulatory restriction could push more research into countries with more permissive frameworks, potentially fragmenting the evidence base geographically.
For researchers who want to stay informed about developments in this field, SeekPeptides provides ongoing coverage of peptide research, regulatory changes, and clinical developments. The platform evidence-based approach ensures that information is grounded in actual research rather than speculation or marketing claims.
Building a complete protocol around penta deca peptide arginate
A peptide protocol does not exist in isolation. The factors surrounding the peptide, including nutrition, sleep, stress management, and concurrent therapies, all influence outcomes. Researchers who optimize these surrounding factors consistently report better results than those who rely on the peptide alone.
Nutrition to support peptide healing
Tissue repair requires raw materials. Protein intake should be adequate to support collagen synthesis and cellular repair, typically 1.2 to 1.6 grams per kilogram of body weight daily during active healing protocols. Vitamin C is a critical cofactor for collagen synthesis. Zinc supports wound healing and immune function. And omega-3 fatty acids modulate inflammation in ways that complement the peptide anti-inflammatory effects.
Sleep optimization
Growth hormone release peaks during deep sleep. Since penta deca peptide arginate upregulates growth hormone receptors, ensuring adequate deep sleep amplifies this mechanism. Researchers who stack PDA with growth hormone secretagogues like CJC-1295/Ipamorelin, which are typically dosed before bed, can create a synergistic nighttime healing window. The importance of sleep for peptide efficacy is one reason why some practitioners include DSIP in comprehensive recovery protocols.
Cost considerations
The peptide cost calculator helps researchers budget for their protocols. Penta deca peptide arginate typically costs more per unit than BPC-157 acetate, but the improved oral bioavailability can make it more cost-effective on a per-effective-dose basis for oral protocols. When comparing costs, researchers should factor in the cost of supplies (syringes, bacteriostatic water, alcohol swabs) for injectable protocols versus the simplicity of oral capsules.
For a broader view of what peptide therapy involves financially, our peptide therapy cost guide breaks down expenses across different protocols and administration routes.
Tracking and monitoring results
Systematic tracking transforms subjective impressions into actionable data. Researchers should document baseline measurements before starting a protocol, track relevant metrics at regular intervals, and note any side effects or unexpected responses. This data allows for informed protocol adjustments and helps determine whether the peptide is producing the desired effects.
Key metrics to track depend on the application. For injury recovery, track pain levels (0 to 10 scale), range of motion, and functional capacity. For gut health, track digestive symptoms, stool quality, and any dietary tolerances. For general recovery, track sleep quality, energy levels, and exercise recovery times.
For researchers serious about optimizing their peptide protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions.
External resources
PubMed - National Library of Medicine (search "BPC-157" or "pentadecapeptide" for primary research)
ClinicalTrials.gov (search for active peptide trials)
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your peptides stay stable, your protocols stay precise, and your healing stay consistent.



