Feb 3, 2026
Some researchers watch belly fat shrink in weeks. Others wait months with zero visible change. The difference is not genetics. It is not willpower. It is not even the number of hours spent in the gym. The difference comes down to which peptide they chose, how they dosed it, and whether their protocol actually matched the biology of abdominal fat.
Belly fat is not just a cosmetic frustration. It is a metabolic engine that drives inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular risk. And it does not respond to the same strategies that strip fat from arms, legs, or chest. Visceral adipose tissue, the deep fat wrapped around organs in the abdominal cavity, has its own receptor profile, its own hormonal sensitivity, and its own stubborn resistance to standard calorie deficits. That is why so many people hit a wall. They lose weight everywhere except the midsection.
Peptides change that equation. Specific compounds like tesamorelin, AOD-9604, CJC-1295 paired with ipamorelin, MOTS-c, and GLP-1 receptor agonists target the biological mechanisms that make belly fat so persistent. Some stimulate growth hormone to trigger lipolysis directly. Others activate AMPK to convert white fat into metabolically active brown fat. A few shut down appetite through incretin pathways that bypass willpower entirely. The science behind each approach is different, and the results vary dramatically based on which one you choose. This guide covers every peptide with meaningful evidence for abdominal fat reduction, complete with dosages, timelines, stacking protocols, and the mistakes that sabotage results. Whether you are exploring peptides for fat loss for the first time or refining an advanced protocol, this is the reference you will come back to.
Why belly fat is different from other body fat
Not all fat is created equal. That statement sounds like a cliche until you understand the biology. The fat on your thighs, arms, and under your chin is subcutaneous fat. It sits between the skin and muscle. It is relatively benign from a metabolic standpoint, and the body releases it fairly easily during a calorie deficit.
Belly fat is a different animal entirely.
The abdominal region contains two distinct types of adipose tissue. Subcutaneous belly fat sits just under the skin, and you can pinch it. Visceral adipose tissue, often called VAT, wraps around the liver, intestines, kidneys, and other organs deep inside the abdominal cavity. You cannot pinch it. You cannot see it directly. But it is the fat that matters most for health, and it is the fat that resists standard fat loss strategies with remarkable stubbornness. Understanding this distinction is the foundation of every effective visceral fat loss approach.
Visceral fat behaves more like an endocrine organ than a passive energy storage depot. It secretes inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. It pumps out free fatty acids directly into the portal vein, flooding the liver and driving insulin resistance. It produces hormones that dysregulate appetite, increase cortisol sensitivity, and impair growth hormone secretion. The more visceral fat you carry, the worse these feedback loops become, creating a cycle where the fat itself makes more fat loss harder to achieve.
This matters for anyone exploring peptides for weight loss because the hormonal environment around visceral fat is fundamentally different from subcutaneous fat. Visceral adipocytes have a higher density of cortisol receptors and beta-3 adrenergic receptors. They respond more aggressively to stress hormones. They are more resistant to insulin signaling. And they have a different relationship with growth hormone than fat cells elsewhere in the body. Standard calorie restriction and cardio often strip subcutaneous fat first, leaving the dangerous visceral compartment largely intact. That is why someone can lose 20 pounds and still have a protruding midsection.
The health risks are not trivial. Elevated visceral fat is directly linked to type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and even certain cancers. A waist circumference above 40 inches for men or 35 inches for women is considered a significant risk marker, independent of total body weight. You can have a normal BMI and still carry dangerous levels of visceral fat, a condition sometimes called TOFI (thin outside, fat inside). Tracking your body composition with tools like the peptide calculator alongside waist measurements gives a more complete picture than the scale alone.
Several hormonal factors make belly fat particularly stubborn. Low growth hormone output, common in adults over 30, reduces the body ability to mobilize visceral fat stores. Elevated cortisol, driven by chronic stress, directly promotes visceral fat deposition. Declining testosterone in men and estrogen shifts in women during perimenopause and menopause redirect fat storage toward the abdominal compartment. Insulin resistance, which both causes and is caused by visceral fat, creates a metabolic trap where the body preferentially stores energy as belly fat while struggling to release it. These hormonal factors explain why peptides for hormone balance play such a critical role in abdominal fat reduction.
This is precisely where peptides enter the picture. Different peptides target different nodes in this web of dysfunction. Growth hormone secretagogues like CJC-1295 and ipamorelin directly address the GH deficit that allows visceral fat to accumulate. Tesamorelin, a GHRH analog, has been shown in clinical trials to selectively reduce visceral fat while preserving subcutaneous tissue. GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide reduce caloric intake through appetite suppression while improving insulin sensitivity. And metabolic peptides like MOTS-c activate the AMPK pathway, essentially mimicking exercise at the cellular level and converting metabolically inactive white fat into energy-burning brown fat. Each mechanism attacks a different piece of the belly fat puzzle.
How peptides target abdominal fat
Peptides do not burn fat the way stimulants do. There is no thermogenic jolt, no racing heartbeat, no jittery energy spike. Instead, peptides work through the same signaling pathways the body already uses to regulate fat metabolism. They restore, amplify, or redirect those signals. The result is fat loss that targets specific biological mechanisms rather than brute-force calorie burning.
Five major pathways explain how peptides reduce belly fat.
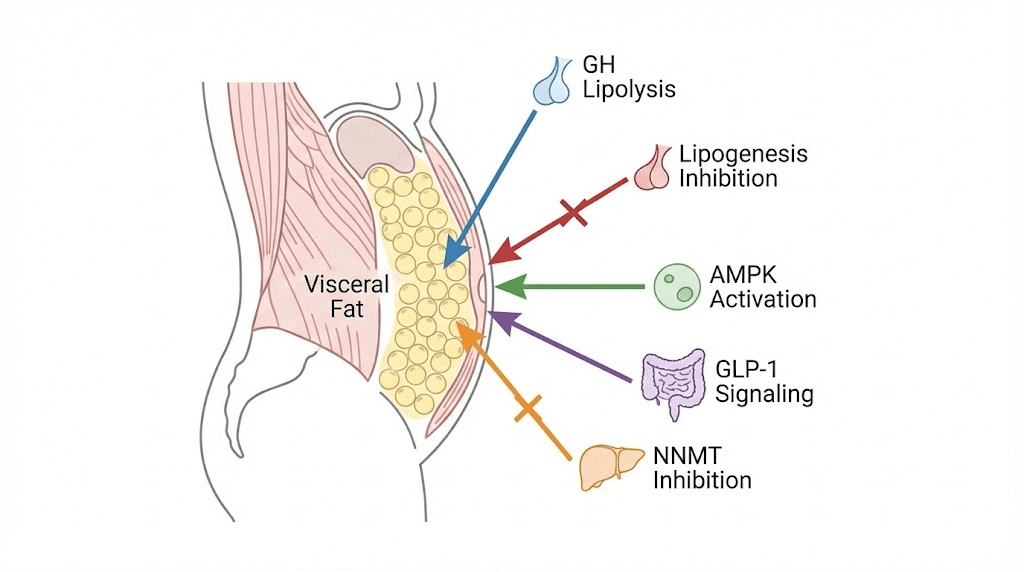
Growth hormone-mediated lipolysis
Growth hormone is the body primary fat-mobilizing hormone. When GH levels rise, it triggers hormone-sensitive lipase, the enzyme that breaks stored triglycerides inside fat cells into free fatty acids and glycerol. Those free fatty acids then enter circulation and get oxidized for energy. Visceral fat cells are particularly responsive to GH-mediated lipolysis because they have a higher density of GH receptors than subcutaneous fat cells. This is why growth hormone secretagogues and GHRH analogs tend to reduce belly fat preferentially.
Peptides like CJC-1295 and ipamorelin stimulate the pituitary gland to release more GH naturally. The body produces GH in pulses, with the largest pulse occurring during deep sleep. These peptides amplify those pulses without introducing exogenous hormone, which makes them fundamentally different from synthetic HGH. The ipamorelin vs CJC-1295 comparison reveals why they work even better together, as they stimulate GH release through complementary receptor pathways. Using the CJC-1295 dosage calculator ensures precise dosing for optimal GH output.
Lipogenesis inhibition
Fat loss is not just about burning existing fat. It is equally about preventing new fat from being created. Lipogenesis is the metabolic process where the body converts excess calories into stored fat. Several peptides inhibit this process at the enzymatic level. AOD-9604, a fragment of human growth hormone, stimulates lipolysis while simultaneously inhibiting lipogenesis. It does both. That dual action means the body breaks down existing belly fat while making it harder to deposit new fat in the abdominal compartment. Understanding this mechanism helps explain why the AOD-9604 complete guide emphasizes the dual-pathway advantage.
AMPK activation and fat browning
This is where the science gets genuinely exciting. AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is the master metabolic switch inside cells. When AMPK activates, it shifts the cell from energy storage mode to energy burning mode. It increases fatty acid oxidation, enhances glucose uptake, and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis. Essentially, it mimics what happens during exercise at the cellular level.
MOTS-c, a mitochondrial-derived peptide, is one of the most potent AMPK activators identified. But its effects go beyond simple enzyme activation. Research published in the Journal of Physiology demonstrated that MOTS-c promotes the conversion of white adipose tissue into beige or brown fat through the ERK signaling pathway. White fat stores energy. Brown fat burns it. By converting white belly fat into metabolically active brown fat, MOTS-c creates an internal furnace that burns calories even at rest. The MOTS-c benefits guide covers the full range of metabolic effects, and the MOTS-c dosage chart provides weight-based protocols.
GLP-1 signaling and appetite regulation
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonists represent the most dramatic weight loss results of any peptide class. Semaglutide, tirzepatide, and the newer triple-agonist retatrutide work primarily by mimicking the incretin hormone GLP-1, which signals satiety to the brain. The result is a profound reduction in appetite that makes caloric deficits effortless rather than agonizing.
But the mechanism goes deeper than appetite suppression. GLP-1 agonists slow gastric emptying, which keeps you feeling full longer. They improve insulin sensitivity, which helps redirect nutrients away from fat storage. And emerging research suggests they may have direct effects on adipose tissue metabolism independent of calorie reduction. The semaglutide dosage guide walks through the titration schedule that clinics use, while the semaglutide dosage calculator helps determine starting points based on body weight. For those comparing options, the semaglutide vs tirzepatide comparison breaks down the differences in mechanism and efficacy.
NNMT inhibition and metabolic reprogramming
Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) is an enzyme that becomes overexpressed in adipose tissue during obesity. It essentially slows down fat metabolism. 5-Amino-1MQ, a small molecule NNMT inhibitor, blocks this enzyme and restores normal metabolic function in fat cells. In mouse studies, NNMT inhibition reduced white adipose tissue mass by approximately 35% without any change in food intake. The compound also reduced adipocyte size by 30% and volume by 40%, while cutting lipogenesis by 50-70%. The full mechanism and research are covered in the 5-Amino-1MQ complete guide.
The best peptides for belly fat (ranked by evidence)
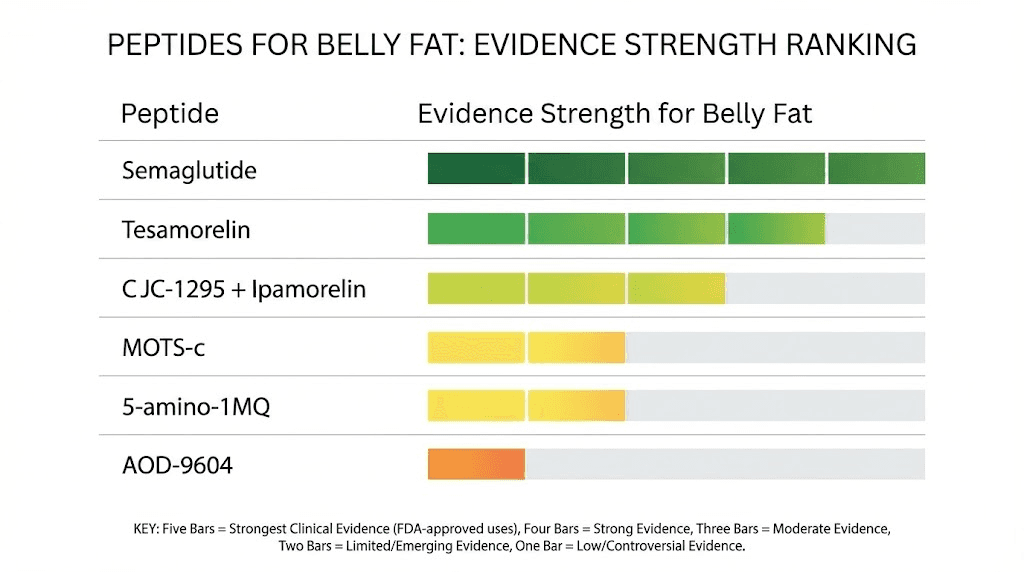
Not every peptide claiming fat loss benefits has the science to back it up. Some have randomized controlled trials. Others have promising animal data. A few rely mostly on anecdotal reports. Ranking peptides by the strength of their evidence helps you make informed decisions rather than chasing marketing claims. Here is every peptide with meaningful data for belly fat reduction, ordered from strongest evidence to most preliminary. For a broader view of all options, the best peptides for weight loss guide covers the full landscape.
Tesamorelin: the strongest clinical evidence for visceral fat
Tesamorelin is the only peptide with FDA approval for reducing abdominal fat. That alone sets it apart from everything else on this list. Approved specifically for HIV-associated lipodystrophy, tesamorelin is a synthetic analog of growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) that stimulates the pituitary to produce and release GH in a physiologic, pulsatile pattern.
The clinical data is substantial. In the LIPO-010 trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, tesamorelin reduced visceral adipose tissue by 19.6% over 26 weeks compared to placebo. That is not total body weight. That is specifically visceral fat, the dangerous deep abdominal fat that drives metabolic disease. Across two pivotal Phase 3 trials, 69% of patients receiving tesamorelin achieved at least an 8% reduction in visceral fat, compared to only 33% in the placebo group.
The selectivity is remarkable. Tesamorelin reduced visceral fat without significantly affecting subcutaneous fat. It targeted exactly where the health risk concentrates. Additional research by Stanley and colleagues showed that tesamorelin reduced hepatic (liver) fat by approximately 37% in individuals with fatty liver disease, making it one of the few compounds that addresses both visceral adiposity and its downstream consequence of liver fat accumulation.
The standard protocol is 2mg administered subcutaneously once daily, typically in the abdominal area. Most clinical improvements appear within 12-26 weeks. Tesamorelin also preserves and may increase lean muscle tissue, making it valuable for body recomposition rather than just weight loss. However, tesamorelin requires a prescription in the United States and is significantly more expensive than research-grade peptides. It is also important to understand peptide safety and risks before starting any GHRH analog protocol. The best peptide for visceral fat loss article provides detailed comparisons with other options in this category.
Semaglutide and GLP-1 receptor agonists
If tesamorelin has the best evidence for visceral fat specifically, semaglutide and its cousins have the most dramatic total fat loss results of any peptide class. Semaglutide (marketed as Wegovy for weight management and Ozempic for diabetes) produced an average 15.8% body weight reduction over 68 weeks in the STEP trials. Tirzepatide, a dual GLP-1/GIP agonist marketed as Zepbound and Mounjaro, pushed that even further with up to 22.5% weight reduction. And retatrutide, a triple agonist targeting GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors simultaneously, achieved up to 24% weight loss in early trials.
These are staggering numbers. And while the studies measured total body weight rather than visceral fat specifically, imaging substudies have shown that GLP-1 agonists reduce both visceral and subcutaneous fat compartments. The appetite suppression is profound, often described by users as a complete silencing of food noise. You simply stop thinking about food constantly.
Semaglutide follows a titration schedule starting at 0.25mg weekly and gradually increasing to 2.4mg weekly over 16-20 weeks.
The tirzepatide dosing guide walks through a similar escalation pattern. Retatrutide is still in clinical trials but the retatrutide dosing guide covers available protocol data. For those evaluating whether GLP-1 agonists are the right choice versus other approaches, the Ozempic alternatives guide and what peptides help with weight loss article provide thorough comparisons.
The downsides are real. Nausea, especially during dose escalation, affects a significant percentage of users. Muscle loss is a concern without adequate protein intake and resistance training. Cost remains high for brand-name formulations. And there are emerging questions about gallbladder issues and pancreatitis risk with long-term use. Still, for pure fat loss magnitude, nothing in the peptide world currently matches the GLP-1 agonist class.
AOD-9604: the growth hormone fragment
AOD-9604 takes a different approach. Rather than stimulating the body to produce more growth hormone, it uses a specific fragment of GH, amino acids 177-191, that retains the fat-metabolizing properties without the growth-promoting effects. This is a crucial distinction. Full GH therapy raises IGF-1 levels, which carries potential concerns about cell proliferation. AOD-9604 does not significantly affect IGF-1, making it a cleaner option for those focused purely on fat metabolism.
The mechanism is dual-action. AOD-9604 stimulates lipolysis (fat breakdown) while simultaneously inhibiting lipogenesis (new fat creation). In a 12-week clinical trial, participants receiving 1mg per day of AOD-9604 lost an average of 2.6kg compared to 0.8kg in the placebo group. While those numbers are modest compared to GLP-1 agonists, the advantage of AOD-9604 is its targeted mechanism and favorable safety profile.
The AOD-9604 dosage guide recommends 300-500mcg daily administered subcutaneously, typically on an empty stomach in the morning. Timeline expectations are important here. Metabolic changes begin within 2-4 weeks. Visible fat reduction typically appears at 4-8 weeks. Significant results require 8-12 weeks of consistent use. A standard cycle runs 12 weeks on followed by 4 weeks off. Side effects are generally mild and covered in the AOD-9604 side effects article. Many researchers stack AOD-9604 with other peptides for enhanced results, a strategy explored in the best peptide stack for weight loss guide. The HGH fragment 176-191 calculator helps determine precise dosing based on vial concentration.
CJC-1295 and ipamorelin: the body recomposition duo
This combination is arguably the most popular peptide stack in the fat loss space, and for good reason. CJC-1295, a GHRH analog, extends the duration of growth hormone release. Ipamorelin, a selective growth hormone secretagogue, amplifies the pulsatile GH signal. Together, they create sustained elevation of growth hormone that mimics the natural patterns the body produces during youth.
The fat loss mechanism works through GH-mediated lipolysis. Higher growth hormone levels activate hormone-sensitive lipase, which breaks down stored triglycerides in fat cells. Visceral fat cells, with their dense GH receptor population, respond particularly well. But what makes this combination special is the body recomposition effect. Users do not just lose fat. They simultaneously gain or preserve lean muscle tissue, which increases basal metabolic rate and creates a positive feedback loop for further fat loss.
Standard dosing runs 200-300mcg of each peptide, administered subcutaneously before bed on an empty stomach. The timing matters. GH release peaks during deep sleep, and eating within two hours of injection blunts the response significantly. Many protocols follow a 5-days-on, 2-days-off schedule to prevent receptor desensitization. Cycles typically run 12-16 weeks. The sermorelin-ipamorelin blend guide covers an alternative formulation, while the peptide stacks guide explores how to combine these with other compounds.
The results timeline follows a predictable pattern. Weeks 1-2 bring improved sleep quality and recovery. Weeks 3-4 show appetite normalization and early metabolic changes. Weeks 5-8 produce visible changes in body composition, particularly around the midsection. By weeks 12-16, the full body recomposition effect is apparent. Most users report losing 10-20 pounds of fat while gaining 3-8 pounds of muscle over a 4-6 month period. The scale may not show dramatic numbers, but the mirror tells a completely different story. To understand the full benefits of each component, read the ipamorelin benefits breakdown and the CJC-1295 complete guide. Side effects are minimal but worth understanding through the ipamorelin side effects article.
MOTS-c: the mitochondrial fat burner
MOTS-c stands alone in this list because of its mechanism. While every other peptide here works through hormonal signaling, MOTS-c is encoded by the mitochondrial genome and works at the cellular energy level. It is a 16-amino acid peptide that activates AMPK, the master metabolic regulator, by inhibiting the folate cycle and accumulating AICAR, a potent endogenous AMPK activator.
The fat loss data from animal studies is compelling. Mice treated with MOTS-c showed dramatic resistance to diet-induced obesity even without changes in caloric intake. Let that sink in. Same food. Same calories. Less fat accumulation. The mechanism involves enhanced fatty acid oxidation, improved insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle, and, perhaps most impressively, the browning of white adipose tissue through the ERK signaling pathway. White fat stores energy passively. Brown fat actively generates heat by burning calories. Converting one to the other is like turning a storage closet into a furnace.
Research on MOTS-c in ovariectomized mice (a model for postmenopausal metabolic dysfunction) showed reduced fat accumulation in white adipose tissue, increased brown fat activation, and improved insulin sensitivity after just 5 weeks of treatment. This makes MOTS-c particularly relevant for peptides for menopause and peptides for women over 40 who experience midsection weight gain during hormonal transitions.
Exercise studies in healthy young men showed that skeletal muscle MOTS-c levels increase nearly 12-fold after acute exercise, suggesting this peptide mediates some of the metabolic benefits of physical activity. Supplemental MOTS-c may therefore act as a partial exercise mimetic. Current protocols suggest 5mg administered every 3 days subcutaneously. The MOTS-c side effects profile is relatively mild, though the peptide faces bioavailability and stability challenges that limit its clinical development. Learn more about dosing in the MOTS-c dosage chart.
5-Amino-1MQ: the NNMT inhibitor
Technically, 5-Amino-1MQ is not a peptide. It is a small molecule. But it appears in nearly every conversation about peptides for belly fat because of its unique mechanism and because it is sold alongside peptides by most research suppliers.
NNMT (nicotinamide N-methyltransferase) is an enzyme that becomes overexpressed in adipose tissue during obesity. When NNMT is overactive, it depletes NAD+ stores and slows metabolic rate in fat cells. 5-Amino-1MQ inhibits NNMT, restoring normal NAD+ levels and reactivating fat cell metabolism.
The mouse data is striking. In diet-induced obese mice treated with 5-Amino-1MQ for just 11 days, researchers observed a 35% decrease in white adipose tissue mass, a 30% decrease in adipocyte cell size, a 40% decrease in adipocyte volume, 50-70% reduction in lipogenesis, 30% lower total cholesterol, and no change in food intake. The compound also attenuated hepatic steatosis (fatty liver) and improved liver enzyme markers. Combined with a low-fat diet, 5-Amino-1MQ treatment rapidly normalized body weight and adiposity to levels matching age-matched lean animals, an outcome that diet alone could not achieve in the same timeframe. The full breakdown of evidence and protocols is in the 5-Amino-1MQ complete guide.
The critical caveat: there are no published human clinical trials for 5-Amino-1MQ. All data comes from in vitro cell studies and mouse models. While the mechanism is well-characterized and the animal results are impressive, human dosing protocols are based on extrapolation rather than controlled clinical evidence. Current community protocols typically use 50-100mg taken orally once daily, but these are not clinically validated.
The compound is administered orally, which distinguishes it from most injectable peptides. It is considered experimental and should be approached with appropriate caution.
Other peptides worth mentioning
Several additional compounds appear in discussions about belly fat reduction. Tesofensine, a triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor, showed significant weight loss in Phase 2 trials through appetite suppression and increased metabolic rate.
Lipo-C, a lipotropic injection containing methionine, inositol, choline, and often combined with L-carnitine, supports fat metabolism through nutrient cofactors rather than peptide signaling. The lipotropic peptides guide covers these approaches in detail. Cagrilintide, a long-acting amylin analog, is being studied in combination with semaglutide (the CagriSema combination) with results suggesting up to 25% weight loss potential. And Pep19, a novel oral peptide that acts as an inverse agonist of the cannabinoid type 1 receptor, showed a 17% visceral fat reduction at the 5mg dose in a 60-day pilot trial, with every subject in the treatment group losing visceral fat.
The lemon bottle fat dissolving guide covers yet another approach to localized fat reduction.
Peptide stacks for maximum belly fat loss
Individual peptides produce results. Stacking them strategically produces significantly better results. The logic is straightforward: belly fat is maintained by multiple biological mechanisms simultaneously, so targeting multiple mechanisms at once creates synergistic effects that exceed what any single compound achieves alone. The peptide stacks guide covers stacking principles in depth, and the peptide stack calculator helps determine doses when combining compounds.
Here are four evidence-informed stacking protocols for different situations.
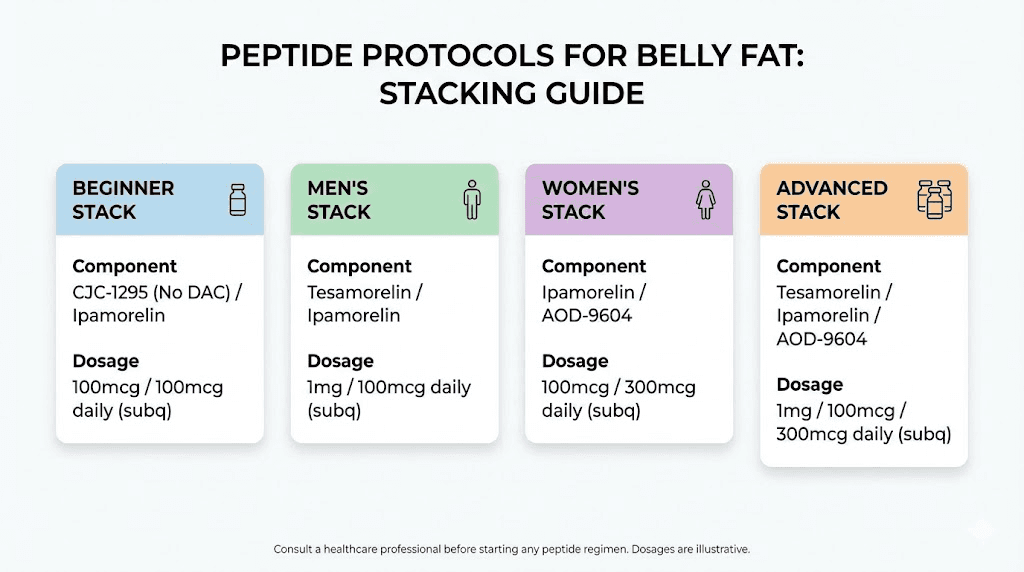
Stack 1: the beginner belly fat protocol
Goal: Moderate belly fat reduction with minimal complexity and low side effect risk.
Components:
CJC-1295 (no DAC): 200mcg subcutaneous before bed
Ipamorelin: 200mcg subcutaneous before bed
Schedule: 5 days on, 2 days off. 12-week cycle followed by 4 weeks off.
Why this works for beginners: This is the gentlest entry point into peptide-assisted fat loss. The combination amplifies natural growth hormone pulses during sleep, which preferentially mobilizes visceral fat through GH-mediated lipolysis. Side effects are minimal. The injection is once daily. And the GH increase supports better sleep, faster recovery, and improved mood alongside the fat loss. Beginners should read getting started with peptides and common peptide mistakes beginners make before starting any protocol. Learning how to reconstitute peptides properly is essential, and the peptide reconstitution calculator ensures accurate preparation.
Expected results: 5-10% body fat reduction over 12 weeks with proper nutrition and training. Improved sleep quality within the first two weeks. Visible midsection changes by weeks 6-8.
Stack 2: the aggressive visceral fat protocol (men)
Goal: Maximum visceral fat reduction with body recomposition.
Components:
Tesamorelin: 2mg subcutaneous daily (morning)
AOD-9604: 300mcg subcutaneous daily (fasted, morning, separate injection)
CJC-1295 (no DAC) + Ipamorelin: 200mcg each subcutaneous before bed
Schedule: Tesamorelin and AOD-9604 daily. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin 5 days on, 2 off. 16-week cycle.
Why this is aggressive: You are attacking visceral fat from three angles. Tesamorelin provides the strongest evidence-based GHRH stimulation for VAT reduction. AOD-9604 adds direct lipolysis stimulation and lipogenesis inhibition through the GH fragment pathway. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin at night provides a second wave of GH elevation during sleep for overnight fat mobilization and muscle preservation. The fat burning peptides for men guide covers male-specific considerations, and the peptides for men complete guide provides broader context. Use the peptide cost calculator to budget a multi-compound protocol like this.
Expected results: 15-25% visceral fat reduction over 16 weeks. Significant body recomposition with muscle preservation or gain. Visible abdominal changes by weeks 4-6. This is a premium protocol in both cost and complexity.
Stack 3: the women-focused belly fat protocol
Goal: Address hormonal belly fat accumulation common during perimenopause and menopause.
Components:
MOTS-c: 5mg subcutaneous every 3 days
CJC-1295 (no DAC): 150mcg subcutaneous before bed
Ipamorelin: 150mcg subcutaneous before bed
Schedule: MOTS-c every third day. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin nightly, 5 days on, 2 off. 12-week cycle.
Why this suits women: Hormonal shifts during perimenopause and menopause redirect fat storage toward the abdominal compartment through declining estrogen, increasing cortisol sensitivity, and reduced growth hormone output. MOTS-c directly addresses the AMPK-mediated metabolic slowdown that accompanies these hormonal changes, while promoting the browning of white adipose tissue. The GH secretagogue component restores growth hormone pulses that decline with age. Lower doses of CJC-1295/Ipamorelin reflect the fact that women generally need less GH stimulation than men. The safest peptides for women guide covers female-specific safety considerations, and best peptides for women explores all options. The best peptide for perimenopause article addresses hormonal context specifically.
Expected results: Reduced midsection bloating within 2-3 weeks. Measurable visceral fat reduction by weeks 6-8. Improved insulin sensitivity and energy levels throughout. Better sleep quality. Many women report the waist measurement changes are more dramatic than the scale changes.
Stack 4: the advanced recomposition protocol
Goal: Aggressive fat loss with maximum muscle preservation for experienced users.
Components:
CJC-1295 (no DAC) + Ipamorelin: 300mcg each subcutaneous before bed
AOD-9604: 500mcg subcutaneous morning (fasted)
5-Amino-1MQ: 50mg oral once daily
Schedule: Daily for AOD-9604 and 5-Amino-1MQ. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin 5 days on, 2 off. 12-week cycle.
Why this is for advanced users only: This stack combines injectable and oral compounds across three different fat loss mechanisms. GH secretagogues drive lipolysis. AOD-9604 inhibits lipogenesis while promoting fat breakdown. And 5-Amino-1MQ addresses NNMT overexpression to reactivate fat cell metabolism. The complexity requires careful monitoring and solid experience with peptide handling, reconstitution, and injection technique. Review the peptide injections guide and how to mix peptides with bac water before attempting a multi-compound protocol. The peptide cycle planning guide helps structure timing and transitions. Use the how to calculate peptide dosages resource for precision.
Expected results: Dramatic body recomposition over 12 weeks. Significant visible change in abdominal fat. Enhanced metabolic rate.
Preservation of lean mass even in a moderate calorie deficit.
Week-by-week timeline: what to expect
Patience kills more peptide protocols than bad dosing does. People start a new compound on Monday and step on the scale on Friday expecting transformation. When nothing has changed, they double the dose, switch compounds, or quit entirely. Understanding the realistic timeline prevents all three mistakes. Timelines vary by compound, but the general pattern holds remarkably consistent across most peptide categories for belly fat. The how long do peptides take to work article covers timelines across all peptide types.
Week 1: internal changes only
Do not expect visible changes. The body is responding at the cellular level. GH secretagogues begin amplifying growth hormone pulses, but the downstream effects on fat metabolism take time to accumulate. Most users notice improved sleep quality and possibly more vivid dreams within the first few days of CJC-1295/Ipamorelin. Some report slight water retention as GH levels adjust. GLP-1 agonists at starting doses may produce mild nausea as the body acclimates. MOTS-c users may notice subtle improvements in energy levels during exercise. The scale will not move meaningfully, and that is normal.
Weeks 2-3: metabolic shifts begin
This is when the metabolic machinery starts turning. GH-mediated lipolysis increases free fatty acid availability. Appetite begins to normalize for GH secretagogue users. GLP-1 agonist users experience significant appetite reduction as doses titrate up. You may notice clothes fitting slightly differently, though the mirror will not show dramatic changes yet. Recovery from workouts improves noticeably. Sleep deepens. Energy stabilizes.
Weeks 4-6: the first visible changes
Now the fat loss becomes measurable. Waist measurements typically decrease by 0.5-1.5 inches during this window, depending on the protocol and starting point. The midsection begins to feel less bloated, less puffy. Body composition scans show shifts even when the scale moves slowly. Tesamorelin users may see more dramatic visceral fat reduction at this stage because the compound acts directly on VAT. GLP-1 agonist users often report the most significant scale changes during this period as the appetite suppression reaches full effect. This is an excellent time to track peptides before and after results with progress photos and waist measurements.
Weeks 6-8: momentum builds
The visible changes accelerate. Friends and family start noticing. The midsection appears flatter, tighter. The combination of GH-driven lipolysis and improved body composition creates a feedback loop where lean muscle becomes more visible as fat recedes. This is where the body recomposition effect of CJC-1295/Ipamorelin becomes most apparent. Users who have been consistent with nutrition and resistance training see dramatic changes during this window. Motivation peaks because the protocol is clearly working.
Weeks 8-12: significant results
This is the payoff window. Visceral fat measurements show meaningful reduction. Waist circumference may be down 2-4 inches from baseline. Body fat percentage drops are often 3-6% for users following a comprehensive protocol with proper nutrition.
The AOD-9604 12-week cycle reaches its completion, and the cumulative effect of daily lipogenesis inhibition becomes fully apparent. Metabolic markers including fasting insulin, triglycerides, and liver enzymes often improve in parallel with the fat loss. Users who started with significant belly fat report the biggest relative changes during this phase.
Weeks 12-16+: optimization and maintenance
Beyond the 12-week mark, the rate of change typically slows as the body reaches a new equilibrium. This is natural and expected. Tesamorelin clinical trials showed continued improvement out to 26 weeks, suggesting that longer protocols produce greater cumulative benefit. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin users often take a 4-week break after 12-16 weeks to prevent receptor desensitization before starting another cycle. The cycling different peptides guide and how many peptides can you take at once article help with planning transitions. GLP-1 agonist users may continue at maintenance doses long-term under medical supervision. The key insight is that the belly fat lost during a well-run peptide cycle tends to stay off if the underlying metabolic improvements are maintained through continued nutrition and exercise habits.
Diet and training strategies that amplify peptide fat loss
Peptides are not a replacement for nutrition and exercise. They are an amplifier. A peptide protocol layered on top of poor eating habits and a sedentary lifestyle will produce mediocre results at best. But peptides combined with strategic nutrition and training produce results that neither approach achieves alone. The synergy is multiplicative, not additive.
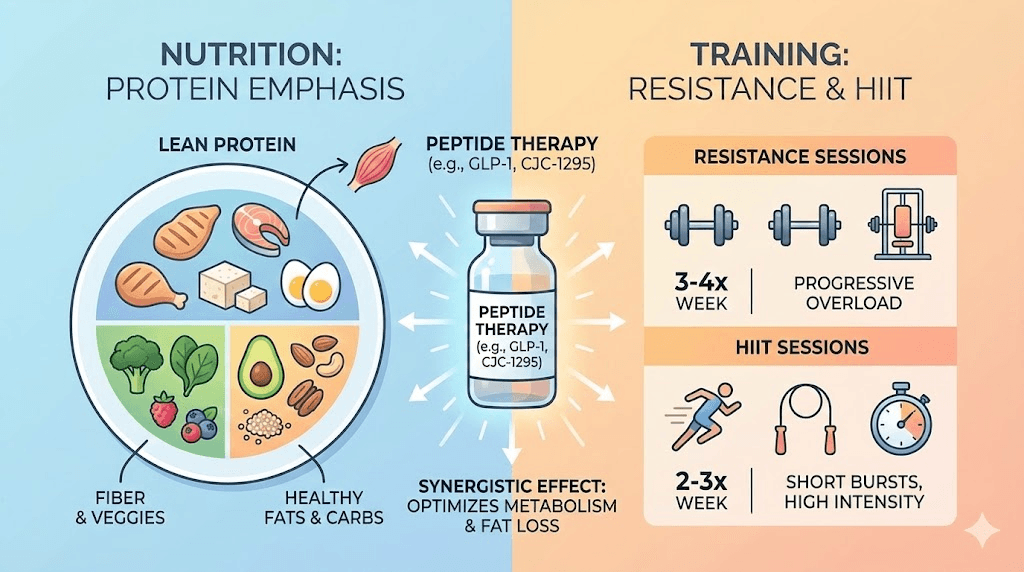
Nutrition strategies for peptide-assisted belly fat loss
Protein comes first. A minimum of 1 gram per pound of lean body mass ensures that the growth hormone increase from peptides has the raw materials to preserve and build muscle while fat is mobilized. Higher protein intake also supports satiety, thermic effect of food, and metabolic rate. When running a GH secretagogue protocol, the anabolic environment is primed. Feeding it adequate protein ensures the body favors fat loss over muscle catabolism. The peptide dosage chart helps pair compound doses with nutritional targets.
Calorie deficit matters, but the size depends on the protocol. With GLP-1 agonists, the appetite suppression often creates a naturally large deficit without conscious effort. Monitor protein intake carefully in this situation because undereating protein while on semaglutide or tirzepatide is the primary driver of the muscle loss concern. With GH secretagogues, a moderate deficit of 300-500 calories below maintenance works well. The GH elevation protects lean mass, allowing fat loss without the metabolic slowdown that accompanies aggressive restriction.
Meal timing interacts directly with peptide effectiveness. For CJC-1295/Ipamorelin administered before bed, stop eating at least 2-3 hours before injection. Elevated blood sugar and insulin blunt the GH response. For AOD-9604 taken in the morning, administer fasted and wait 30-45 minutes before eating. GLP-1 agonists reduce the urgency of meal timing because they manage blood sugar and appetite pharmacologically, but front-loading protein at each meal remains optimal.
Carbohydrate cycling complements GH-based protocols. Lower carbohydrate intake on rest days keeps insulin lower, allowing more sustained fat mobilization. Higher carbohydrate intake around training sessions fuels performance and supports muscle glycogen without undermining fat loss. This is not about going keto. It is about matching carbohydrate intake to activity level and insulin sensitivity.
Training strategies that maximize peptide-driven fat loss
Resistance training is not optional. It is the single most important training modality for peptide-assisted belly fat loss. The growth hormone elevation from secretagogues amplifies the muscle-building response to resistance training. More muscle means higher basal metabolic rate. Higher metabolic rate means more passive fat burning throughout the day. Prioritize compound movements: squats, deadlifts, presses, rows, and pulls. Three to four sessions per week with progressive overload. The peptide strength protocol article provides specific training frameworks designed to complement peptide use.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) synergizes powerfully with MOTS-c and GH secretagogues. HIIT naturally elevates MOTS-c levels and triggers AMPK activation, the same pathway that exogenous MOTS-c targets. Combining supplemental MOTS-c with HIIT creates a double activation of the fat-browning pathway. Two to three HIIT sessions per week, lasting 15-25 minutes each, provide the metabolic stimulus without overtaxing recovery capacity. Peptides for athletic performance covers how different compounds support various training modalities.
Walking matters more than most people realize. Daily walking of 8,000-12,000 steps provides a substantial increase in non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT) without stressing the recovery system. For individuals on GLP-1 agonists who may feel less energetic during dose escalation periods, walking is the easiest and most sustainable activity. For those on GH secretagogues, morning fasted walks take advantage of the overnight GH-mediated fatty acid mobilization. The free fatty acids released during sleep are available for oxidation during that morning walk.
Common mistakes that sabotage belly fat peptide results
Most peptide protocol failures are not caused by the peptide itself. They are caused by user errors in preparation, dosing, timing, or expectations. Avoiding these seven mistakes will save you months of frustration and hundreds of dollars in wasted product. The common peptide mistakes beginners make article covers additional pitfalls beyond fat-loss-specific errors.
Mistake 1: eating too close to GH secretagogue injections
This is the most common mistake and the most damaging. Insulin is the direct antagonist of growth hormone secretion. When you eat, blood sugar rises, insulin rises, and the GH response to CJC-1295/Ipamorelin is severely blunted. Eating a meal within two hours before injection can reduce the GH spike by 60-80%. That is not a minor reduction. That is the difference between the protocol working and the protocol failing. Fast for at least two hours, preferably three, before evening injections. Administer AOD-9604 fasted in the morning and wait at least 30 minutes before eating.
Mistake 2: expecting GLP-1 results from GH secretagogues
GLP-1 agonists produce 15-25% total body weight loss. GH secretagogues produce body recomposition. These are fundamentally different outcomes. Someone who expects to lose 40 pounds on CJC-1295/Ipamorelin will be disappointed because that is not what the compound does. It reduces fat while adding muscle, which means the scale may barely move while the body transforms dramatically. Set expectations based on body composition measurements, progress photos, and waist circumference rather than scale weight.
Mistake 3: improper storage and reconstitution
Peptides are fragile molecules. Heat, light, agitation, and contamination destroy them. A vial of CJC-1295 left on a bathroom counter for a week has significantly reduced potency. Reconstituting with tap water instead of bacteriostatic water introduces contaminants. Shaking a vial instead of gently swirling it can denature the peptide. These seem like minor details until you realize you are injecting degraded or inactive product and wondering why nothing is happening. The how to reconstitute peptides guide, bacteriostatic water for peptides article, and peptide storage guide cover these topics thoroughly. Understanding how long peptides last in the fridge and how long peptides last in powder form prevents potency loss from time-based degradation. The how to store peptides after reconstitution article covers the critical post-mixing window.
Mistake 4: running too short a cycle
Four weeks is not enough. Six weeks is barely enough. Most peptide protocols require 8-12 weeks minimum to produce meaningful belly fat results. Visceral fat is metabolically active and the body defends it aggressively. Breaking through that defense takes sustained hormonal pressure over weeks and months. Tesamorelin trials ran 26 weeks for a reason. Quitting at week 4 because the scale has not moved is like planting a seed and digging it up after three days to check for roots.
Mistake 5: neglecting protein intake
Growth hormone is a powerful anabolic signal. But anabolism requires raw materials. If you flood the system with GH while eating 60 grams of protein per day, the body cannot build the muscle that drives long-term metabolic improvement. And without adequate protein to support muscle synthesis, more of the GH-mobilized energy may be wasted. Aim for 1 gram per pound of lean body mass. This is especially critical for GLP-1 agonist users, where reduced appetite makes it easy to undereat protein dramatically.
Mistake 6: inconsistent dosing schedules
Peptides work through sustained biological signaling. Skipping doses, changing injection times randomly, or taking weeklong breaks in the middle of a cycle disrupts the hormonal patterns these compounds are trying to establish.
The 5-on-2-off schedule for GH secretagogues exists for a specific reason: maintaining receptor sensitivity. Deviating from it by doing 3 on, 4 off, or dosing at random times each day significantly reduces effectiveness. Set an alarm.
Be consistent. The peptide dosing guide provides scheduling frameworks for every major compound.
Mistake 7: buying from unverified sources
The peptide market is unregulated. Third-party testing has shown that some products contain less peptide than labeled, wrong peptides entirely, or harmful contaminants. If you are injecting a product that is underdosed or contains impurities, your results will suffer and your health may be at risk. Source from vendors who provide certificates of analysis with HPLC purity testing and mass spectrometry verification. The best peptide vendors guide evaluates suppliers by testing standards, and the peptide testing labs guide explains how to verify product quality independently.
Safety considerations and side effects
Honest discussion of risks separates useful information from marketing copy. Every peptide in this guide carries potential side effects, and understanding them in advance allows informed decision-making and proper monitoring. The comprehensive peptide safety and risks article covers the full landscape, while individual compound articles address specific concerns.
Growth hormone secretagogues (CJC-1295, ipamorelin, tesamorelin)
Side effects from GH secretagogues tend to be mild and transient. Water retention, particularly in the first two weeks, is the most common. Some users experience tingling or numbness in the hands and feet (carpal tunnel-like symptoms) from fluid shifts. Increased hunger is possible, which runs counter to fat loss goals if not managed through meal planning. Joint stiffness can occur at higher doses. Rare but possible: headaches, dizziness, and injection site reactions.
The more serious concern with sustained GH elevation is the theoretical risk of promoting growth of existing abnormal cells. While the evidence for this with secretagogues is much weaker than with exogenous GH, it is worth noting for individuals with a personal or family history of certain conditions. The ipamorelin side effects article covers the GH secretagogue risk profile in detail.
GLP-1 receptor agonists (semaglutide, tirzepatide, retatrutide)
Gastrointestinal side effects dominate this class. Nausea is the most common, affecting 20-44% of semaglutide users in clinical trials. It typically peaks during dose escalation and improves at stable doses. Vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation are also common. Less common but more serious: pancreatitis (rare but documented), gallbladder issues including gallstones, and potential thyroid concerns based on animal data. Muscle loss is a significant practical concern, with studies showing that 30-40% of weight lost on GLP-1 agonists can be lean mass if protein intake and resistance training are neglected. The semaglutide dosage guide covers the titration approach that minimizes GI side effects.
AOD-9604
AOD-9604 has one of the most favorable safety profiles in this group. Because it does not raise IGF-1 levels, many of the concerns associated with GH therapy do not apply. The most commonly reported side effects are mild injection site reactions, occasional headache, and transient nausea. Serious adverse events in clinical trials were rare and generally not attributed to the compound. The AOD-9604 side effects article provides the complete risk assessment.
MOTS-c
MOTS-c side effect data in humans is limited due to the early stage of clinical research. The peptide is naturally produced by the body, which suggests a favorable safety profile, but exogenous administration at supraphysiological doses may carry unknown risks. Injection site reactions are the most commonly reported issue. The compound faces bioavailability challenges, and some users report that effects vary significantly between batches, possibly due to stability issues. The MOTS-c side effects article covers what is currently known.
5-Amino-1MQ
Without human clinical trials, the side effect profile of 5-Amino-1MQ is based on animal data and anecdotal reports. Mouse studies showed no observable adverse effects at the doses used. Human users have reported occasional headaches, mild GI discomfort, and transient fatigue. However, the lack of controlled human safety data means unknown risks remain. This compound should be considered experimental.
General safety practices
Regardless of which peptide you choose, several safety practices apply universally. Use sterile injection technique for all subcutaneous injections. The peptide injections guide and what is a peptide injection article cover proper technique. Store reconstituted peptides in the refrigerator and track their shelf life after reconstitution.
Use bacteriostatic water for reconstitution, never sterile water for injection or saline. Monitor for allergic reactions, especially during the first few administrations.
Track basic health markers including fasting blood glucose, insulin, and liver enzymes if running extended protocols. And understand the legal landscape through the are peptides legal guide before purchasing any compound.
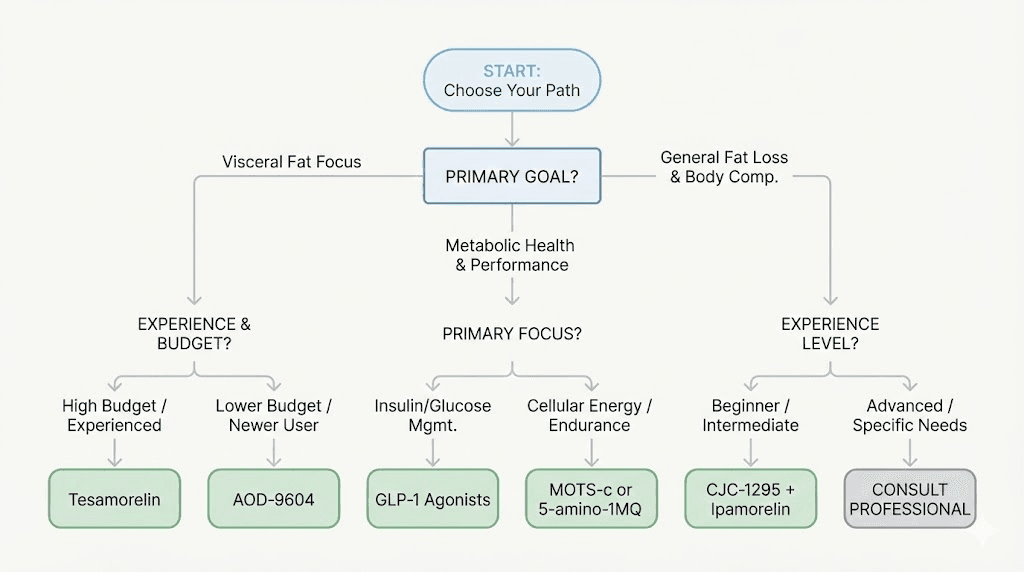
How to choose the right peptide for your belly fat goals
With six or more viable options, choosing the right peptide feels overwhelming. The decision tree below simplifies the process by matching your specific situation to the compound most likely to produce results. Three factors matter most: your primary goal, your experience level, and your budget.
Choose based on primary goal
If your primary goal is visceral fat reduction specifically, tesamorelin has the strongest evidence. The LIPO-010 trial demonstrated selective visceral fat reduction without significant subcutaneous fat loss. No other peptide has this level of clinical validation for the abdominal compartment specifically.
If your goal is maximum total weight loss and you have significant weight to lose (30+ pounds), GLP-1 agonists deliver the largest magnitude of change. Semaglutide, tirzepatide, and retatrutide produce 15-24% body weight reduction in clinical settings. The best peptide for fat loss article helps compare total fat loss options.
If your goal is body recomposition, meaning you want to lose belly fat while gaining or preserving muscle, CJC-1295/Ipamorelin is the strongest choice. The GH elevation supports both lipolysis and muscle protein synthesis simultaneously. The peptides for weight loss and muscle gain article explores this dual-outcome approach in depth.
If your goal is metabolic improvement, addressing insulin resistance, improving mitochondrial function, and enhancing exercise capacity alongside fat loss, MOTS-c offers a unique mechanism that no other peptide replicates.
Choose based on experience level
If you have never used peptides before, CJC-1295/Ipamorelin is the gentlest starting point. Mild side effect profile, simple dosing schedule, well-understood mechanism. Read getting started with peptides and learn how to reconstitute peptides before beginning. The peptide injection pen guide covers the easiest injection method for newcomers.
If you have moderate experience with peptides and want to escalate, adding AOD-9604 to a GH secretagogue base creates a two-pronged attack on belly fat. The best fat burning peptide article compares options at this level.
If you are experienced and want maximum results, multi-compound stacks combining GH secretagogues with AOD-9604, MOTS-c, or 5-Amino-1MQ offer the most comprehensive approach. But complexity increases the importance of proper preparation, storage, and monitoring. The how much bacteriostatic water to add guide and the reconstitution calculator become essential tools at this level.
Choose based on budget
Budget reality matters. Tesamorelin is the most expensive option, often costing several hundred dollars per month through clinical channels. GLP-1 agonists are also premium-priced, though compounded versions exist at lower cost. CJC-1295/Ipamorelin from research suppliers is among the most affordable options. AOD-9604 falls in the moderate range. 5-Amino-1MQ is relatively affordable because it is taken orally, eliminating the need for bacteriostatic water and syringes. The peptide therapy cost guide and how much do peptides cost article provide detailed pricing breakdowns across all compounds. Use the peptide cost calculator to estimate monthly costs for any protocol.
Choose based on administration preference
Not everyone is comfortable with injections. If needles are a barrier, 5-Amino-1MQ offers oral administration. GLP-1 agonists use a pre-filled pen that many people find less intimidating than drawing from vials. The injectable vs oral peptides comparison explores the tradeoffs between delivery methods. Some peptides are also available in nasal spray form or as peptide capsules, though bioavailability typically decreases with non-injectable routes.
Frequently asked questions
What is the fastest peptide for belly fat loss?
GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide produce the fastest visible results because they create immediate appetite suppression and large caloric deficits from the first week. However, for visceral fat specifically, tesamorelin shows the most dramatic reduction in the deep abdominal compartment. Speed also depends on starting point. Someone with 50 pounds to lose will see faster scale changes than someone with 15 pounds to lose. For body recomposition where fat loss and muscle gain happen simultaneously, the best peptide stack combines GH secretagogues with a fat-targeting compound.
Can women use the same belly fat peptides as men?
Yes, with dosage adjustments. Women generally require lower doses of GH secretagogues because they produce more GH naturally per pulse than men. The peptides themselves do not discriminate by sex, but the hormonal context differs significantly. MOTS-c may be particularly valuable for women experiencing perimenopause or menopause-related belly fat accumulation due to its effects on AMPK and estrogen-related metabolic pathways. The peptides for weight loss for women guide covers female-specific protocols and considerations.
Do peptides for belly fat require a prescription?
It depends on the specific peptide and your jurisdiction. Tesamorelin requires a prescription in the United States. Semaglutide and tirzepatide require prescriptions. Many other peptides including CJC-1295, ipamorelin, AOD-9604, and MOTS-c are available as research chemicals without prescription, though they are not FDA-approved for human use in a clinical context. The are peptides legal guide covers the regulatory landscape in detail, and peptide therapy online explains the telemedicine pathway for prescription compounds.
How long should I cycle peptides for belly fat?
Minimum effective cycles run 8-12 weeks for most compounds. Tesamorelin clinical trials ran 26 weeks. GH secretagogues typically cycle 12-16 weeks on followed by 4 weeks off to maintain receptor sensitivity. GLP-1 agonists are often used continuously under medical supervision. AOD-9604 follows a 12-weeks-on, 4-weeks-off pattern. The peptide cycle planning guide provides detailed cycling frameworks for every compound, and cycling different peptides covers how to transition between compounds across multiple cycles.
Can I stack a GLP-1 agonist with other belly fat peptides?
Some practitioners combine GLP-1 agonists with GH secretagogues to address both appetite reduction and growth hormone optimization simultaneously. The theoretical advantage is that the GLP-1 agonist manages caloric intake while the GH secretagogue preserves lean mass and enhances lipolysis. However, multi-compound protocols involving prescription medications should be supervised by a healthcare provider. The peptides to take with Ozempic article discusses combination strategies specifically for GLP-1 users.
Will the belly fat come back after stopping peptides?
It depends on what you do after stopping. If you return to the habits that created the belly fat in the first place, yes, it will return. Peptides create a metabolic window where fat loss is easier, but they do not permanently alter the body set point by themselves. Maintaining results requires continued attention to nutrition, exercise, and possibly periodic peptide cycles. GLP-1 agonists have the highest regain rate after discontinuation because the appetite suppression effect disappears, leading many people to regain 60-70% of lost weight within a year. GH secretagogues may produce more durable results because the muscle gained during the protocol continues to burn calories after the cycle ends.
What blood tests should I get before starting peptide therapy for belly fat?
Baseline bloodwork should include a comprehensive metabolic panel, fasting insulin, fasting glucose, HbA1c, lipid panel, liver enzymes (AST and ALT), IGF-1 levels, thyroid panel, and for men, testosterone levels. These markers serve two purposes: they establish your baseline metabolic health and they provide reference points for monitoring changes during the protocol. Repeat testing at weeks 6-8 and at the end of the cycle. The peptide research and studies page covers the evidence base that informs monitoring recommendations.
Are peptides for belly fat safe to use with diabetes medications?
GLP-1 agonists are themselves diabetes medications, so combining them with other glucose-lowering drugs requires careful medical supervision to avoid hypoglycemia. GH secretagogues can temporarily affect blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, which may require diabetes medication adjustments. AOD-9604 does not significantly impact blood glucose in studies. Any individual taking diabetes medication should work with their healthcare provider before starting peptide therapy. The how peptides work article provides the biological context for understanding these interactions.
External resources
For researchers serious about optimizing their peptide protocols for belly fat loss, SeekPeptides provides the most comprehensive resource available. Members access evidence-based guides, detailed protocol databases, dosing calculators, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions. Whether you are choosing your first peptide or refining an advanced stack, SeekPeptides offers the tools and expertise to maximize your results safely and effectively.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your belly fat stay shrinking, your protocols stay precise, and your results stay lasting.
Join SeekPeptides.



