Dec 30, 2025

Danish pharmaceutical research produced tesofensine while searching for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's treatments in the early 2000s. Clinical trials failed to show neurological benefits, but researchers noticed something unexpected - participants were losing significant weight without trying. This accidental discovery redirected tesofensine development entirely toward obesity treatment, where it demonstrated 10-12% body weight reduction in 24-week trials - rivaling results from semaglutide and tirzepatide but through a completely different mechanism.
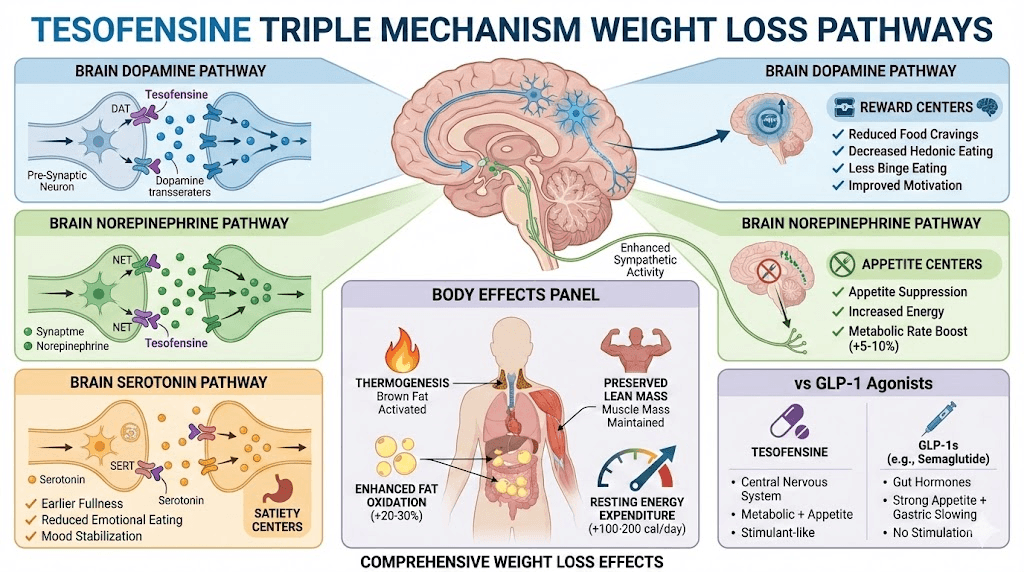
Tesofensine isn't technically a peptide - it's a small molecule drug that acts as a triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor affecting dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin simultaneously.
This distinguishes it from GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide that work through gut hormones and appetite suppression. Tesofensine targets brain neurochemistry directly, increasing metabolic rate and reducing appetite through central nervous system effects.
The weight loss results proved impressive - 24-week trials showed average 10.6% weight loss at 1mg daily dose compared to 2% placebo, with some participants losing 15-20%. This puts tesofensine in the same effectiveness range as modern weight loss peptides, but unlike semaglutide's gradual appetite suppression, tesofensine works through metabolic acceleration and dopamine-mediated satiety changes.
However, tesofensine faces significant challenges - cardiovascular side effects (increased heart rate and blood pressure) raised safety concerns, FDA has not approved it despite promising efficacy data, development stalled after Phase 3 trials, currently available only through research chemical suppliers with questionable legality, and the stimulant-like mechanism creates dependency and tolerance risks not seen with GLP-1 agonists.
This guide examines what tesofensine is and its triple reuptake mechanism, clinical trial results and weight loss efficacy data, complete dosing protocols from research, side effects and cardiovascular safety concerns, comparing tesofensine to semaglutide, tirzepatide, and other weight loss interventions, legal status and availability issues, and whether tesofensine belongs in weight loss peptide stacks.
Understanding tesofensine's unique mechanism and risk profile helps determine if this powerful but controversial weight loss compound merits consideration despite its FDA rejection and safety concerns.
What is tesofensine and how does it work
The science behind the triple reuptake inhibitor.
Tesofensine structure and classification
Chemical identity:
Small molecule drug (not a peptide)
Chemical name: (1R,2S)-2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)cyclopropyl]methylamine
Molecular weight: 216.11 g/mol
Synthetic compound (not naturally occurring)
Originally code-named NS2330
Why called "tesofensine":
Generic pharmaceutical name
Developed by NeuroSearch (Danish company)
Initially for neurological conditions
Repurposed for obesity after accidental discovery
Now primarily researched for weight loss
Drug classification:
Triple monoamine reuptake inhibitor (TRI)
Affects: Dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin
Similar mechanism to ADHD medications
CNS stimulant properties
Schedule classification: Unscheduled but controlled
Not a peptide - why included here:
Often grouped with weight loss peptides
Compared to semaglutide and tirzepatide
Sold by peptide vendors
Used in weight loss stacks
Similar goals as weight loss peptides
Learn about what peptides are and how they work at SeekPeptides.
Triple reuptake inhibitor mechanism
What reuptake inhibition means:
Neurotransmitters normally reabsorbed after release
Reuptake inhibitors block this reabsorption
Results in higher neurotransmitter levels
Longer signaling duration
Enhanced effects on target neurons
Three neurotransmitters affected:
1. Dopamine reuptake inhibition:
Increases dopamine in reward pathways
Reduces food cravings and hedonic eating
Enhances motivation and energy
Similar to stimulant medications
Creates euphoric feelings (can lead to dependency)
2. Norepinephrine reuptake inhibition:
Increases metabolic rate (thermogenesis)
Enhances fat oxidation
Suppresses appetite centrally
Increases energy expenditure
Also increases heart rate and blood pressure (side effects)
3. Serotonin reuptake inhibition:
Enhances satiety signals
Reduces appetite
Improves mood (reduces emotional eating)
Stabilizes cravings
Similar to SSRIs but different profile
Potency ratios:
Neurotransmitter | Reuptake Inhibition Potency | Primary Weight Loss Effect |
|---|---|---|
Dopamine | Moderate (IC50: 6.5 nM) | Reduces hedonic eating, increases motivation |
Norepinephrine | Strong (IC50: 1.7 nM) | Increases metabolic rate, appetite suppression |
Serotonin | Strong (IC50: 11 nM) | Enhances satiety, reduces cravings |
Why triple inhibition powerful:
Attacks weight loss from multiple angles
Metabolic + appetite + behavioral changes
Synergistic effects stronger than single pathway
But also multiplies side effect risks
Different from GLP-1 single mechanism
Compare to semaglutide mechanism and other weight loss approaches.
Metabolic rate increase and thermogenesis
How tesofensine boosts metabolism:
Norepinephrine stimulates beta-adrenergic receptors
Activates thermogenesis in brown and white fat
Increases basal metabolic rate 5-10%
Enhanced fat oxidation (preferential fat burning)
Similar to ephedrine effects but stronger
Energy expenditure studies:
Clinical trials showed increased resting energy expenditure
24-hour metabolic rate elevated 5-10%
Translates to ~100-200 extra calories burned daily
Combined with appetite suppression = larger deficit
Thermogenesis mechanism:
Metabolic Effect | Mechanism | Calorie Impact |
|---|---|---|
Basal metabolic rate | Norepinephrine-mediated increase | +50-100 cal/day |
Non-exercise activity | Increased fidgeting, movement | +30-50 cal/day |
Fat oxidation | Enhanced lipolysis | +20-50 cal/day |
Thermogenesis | Brown fat activation | +20-40 cal/day |
Total increase | Combined effects | +120-240 cal/day |
Why metabolism boost matters:
Creates deficit even without appetite changes
Counteracts metabolic adaptation
Preserves lean mass better
Enhanced fat loss vs muscle loss
Different advantage vs GLP-1 agonists
Cardiovascular cost:
Increased metabolism = increased heart rate
Blood pressure elevation
Cardiac workload increased
Major safety concern
Why FDA rejected despite efficacy
See best peptides for energy and fat loss peptides.
Appetite suppression through dopamine modulation
Central appetite control:
Tesofensine acts on hypothalamus
Affects arcuate nucleus (appetite center)
Different pathway from GLP-1 receptors
Direct neurotransmitter modulation
Rapid onset (hours not days)
Dopamine's role in eating:
Mediates food reward (hedonic eating)
High-dopamine = reduced food seeking
Decreases obsessive food thoughts
Reduces binge eating tendencies
Similar to ADHD medication effects
Subjective appetite changes reported:
Reduced hunger (moderate, not as strong as semaglutide)
Less food preoccupation
Earlier satiety (smaller portions satisfying)
Reduced cravings especially for high-calorie foods
More mental focus on non-food activities
Appetite suppression comparison:
Weight Loss Agent | Primary Appetite Mechanism | Strength | Onset |
|---|---|---|---|
Tesofensine | Dopamine/norepinephrine CNS | Moderate-strong | Hours |
GLP-1 receptor, gastric slowing | Very strong | Days-weeks | |
GIP/GLP-1 dual, gastric slowing | Very strong | Days-weeks | |
Amylin receptor, gastric slowing | Very strong | Days-weeks |
Why dopamine approach different:
Addresses psychological/behavioral eating
Reduces food as reward behavior
Helps with emotional eating
Less GI side effects than GLP-1s
But creates stimulant-like dependency risk
Clinical trial results and efficacy
Evidence from human studies.
Phase 2 and Phase 3 trial data
Major clinical trials:
Phase 2 (24-week trial, 2008):
203 obese participants
Three dose groups: 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 1.0mg daily
Placebo-controlled, randomized
Primary outcome: Weight loss percentage
Phase 2 results:
Group | Average Weight Loss | % Lost >5% | % Lost >10% | Completion Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Placebo | 2.0% | 31% | 13% | 79% |
0.25mg | 4.5% | 57% | 24% | 72% |
0.5mg | 9.2% | 76% | 48% | 68% |
1.0mg | 10.6% | 81% | 62% | 61% |
Key findings:
Dose-dependent weight loss
1mg dose: Average 23 lbs lost (starting weight ~220 lbs)
Best responders: 15-20% weight loss
Comparable to semaglutide 2.4mg
But higher dropout due to side effects
Phase 3 trials (planned but never completed):
Intended for FDA approval
Halted due to cardiovascular concerns
Increased heart rate 5-10 bpm average
Blood pressure elevation 2-5 mmHg
Risk-benefit ratio questioned
Development suspended 2010
Long-term data (limited):
1-year extension studies showed sustained loss
Weight plateau at 6-9 months
Some regain if discontinued
No controlled trials beyond 1 year
Safety concerns prevented longer studies
Compare to semaglutide trials and tirzepatide results.
Weight loss effectiveness
Average weight loss expectations:
0.5mg daily: 8-10% over 24 weeks
1.0mg daily: 10-12% over 24 weeks
Starting weight ~220 lbs: Lose 22-26 lbs
Better than most weight loss medications
Similar to GLP-1 agonists
Individual variation:
Response Category | % of Users | Weight Loss Range | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
Poor responders | 15-20% | <5% | Non-adherent, side effects, metabolic resistance |
Average responders | 50-60% | 8-12% | Most users, good tolerance |
Excellent responders | 20-25% | 15-20% | High adherence, good tolerance, lifestyle synergy |
Non-responders | 5-10% | <3% | Unknown reasons, possible genetic factors |
Timeline for weight loss:
Week 1-2: 2-4 lbs (water weight + appetite suppression)
Week 3-4: 1-2 lbs/week (fat loss beginning)
Month 2-3: 1-1.5 lbs/week (steady loss)
Month 4-6: 0.5-1 lb/week (slowing, approaching plateau)
Month 6-9: 0-0.5 lb/week (maintenance/plateau)
Total: 20-30 lbs typical over 6 months
Body composition changes:
Primarily fat loss (75-80% of loss)
Some muscle loss (20-25%) - unavoidable in deficit
Better muscle preservation than pure caloric restriction
Waist circumference reduction significant
Visceral fat preferentially lost
See peptides before and after results and how long peptides take to work.
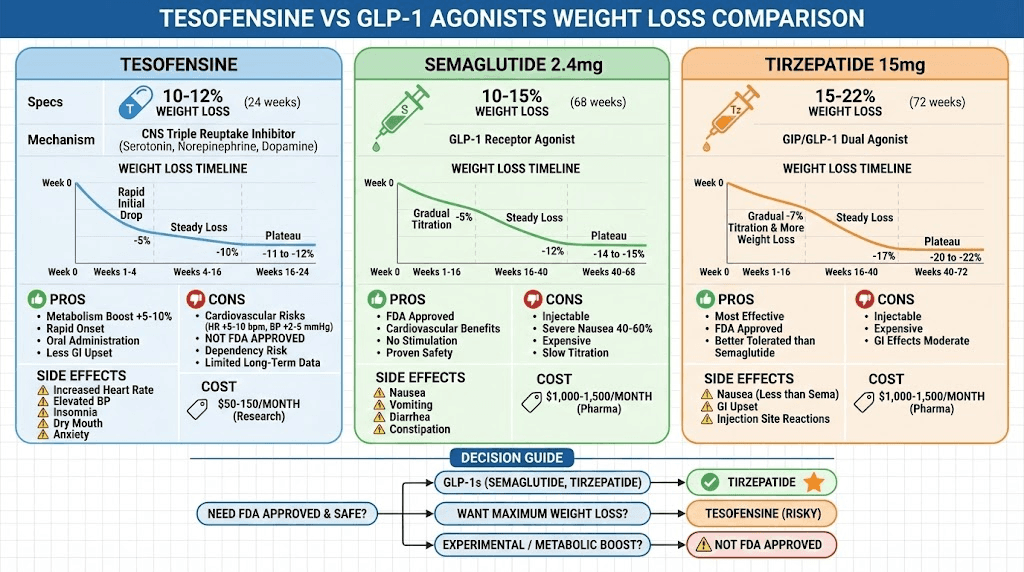
Comparison to semaglutide and tirzepatide
Head-to-head effectiveness:
Medication | Average Weight Loss (24 weeks) | Mechanism | Side Effect Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
Tesofensine 1mg | 10-12% | CNS stimulant, triple reuptake | Cardiovascular, stimulant effects |
10-15% | GLP-1 receptor agonist | GI upset, nausea common | |
15-22% | GIP/GLP-1 dual agonist | GI upset, better tolerated | |
15-25% | GLP-1 + amylin | GI upset, strong appetite suppression |
Tesofensine advantages:
Boosts metabolism (GLP-1s don't)
Rapid onset (hours vs days)
Less GI side effects (no nausea)
Oral administration (vs injection for GLP-1s)
Cheaper (research chemical pricing)
Tesofensine disadvantages:
Cardiovascular risks (heart rate, BP)
Stimulant-like effects (dependency potential)
Not FDA approved (legal concerns)
Limited long-term safety data
Higher dropout rates in trials
Why GLP-1s preferred clinically:
FDA approved (safe, legal)
Cardiovascular benefits (tesofensine has risks)
Better long-term safety profile
No dependency/tolerance issues
More comprehensive clinical data
When tesofensine might be considered:
GLP-1 intolerance (severe nausea)
Desire for metabolic boost
Research/experimental use only
Combined with other interventions
Under medical supervision
Learn about semaglutide vs tirzepatide and best weight loss stacks.
Tesofensine dosing protocols
Evidence-based and practical approaches.
Clinical trial dosing
Standard dosing from trials:
Starting dose: 0.25mg daily
Low dose: 0.25-0.5mg daily (safer, moderate efficacy)
Standard dose: 0.5mg daily (optimal risk-benefit)
High dose: 1.0mg daily (maximum efficacy, higher risks)
Route: Oral capsule
Titration schedule (recommended):
Week | Dose | Purpose | Expected Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
1-2 | 0.25mg daily | Assess tolerance | Mild appetite suppression, slight energy boost |
3-4 | 0.5mg daily | Standard therapeutic | Noticeable appetite reduction, weight loss begins |
5-24 | 0.5mg daily | Maintenance | Steady 1-2 lbs/week loss |
Optional 5+ | 1.0mg daily | Maximum effect | Stronger effects, higher side effect risk |
Timing:
Morning dosing: Most common (prevents insomnia)
With or without food (doesn't matter)
Same time daily for consistency
Avoid evening dosing (stimulant effects disrupt sleep)
Duration:
Clinical trials: 24 weeks standard
Some continued 1+ year
No defined maximum duration
Tolerance may develop over time
Use our peptide cost calculator and dosing guide at SeekPeptides.
Oral administration and bioavailability
Why oral dosing works:
Small molecule (not peptide)
Survives stomach acid
Good oral bioavailability ~30-40%
Absorbed in small intestine
Unlike injectable peptides required for most
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption: 2-4 hours to peak plasma levels
Half-life: 8-10 hours (once daily dosing)
Metabolism: Liver (CYP450 enzymes)
Excretion: Primarily urine
Duration of action: 12-16 hours
Advantages of oral:
Convenient (no injections)
Easy adherence
Portable, discreet
Major advantage vs semaglutide
Capsule vs solution:
Usually sold as capsules
Can open and mix (powder)
Solution rare but possible
Sublingual not studied (no advantage)
Side effect management during treatment
Common side effects (>10% incidence):
Side Effect | Frequency | Severity | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
Increased heart rate | 60-70% | Moderate | Monitor, reduce dose, medical eval if >100 bpm resting |
Elevated blood pressure | 40-50% | Moderate-high | Monitor weekly, reduce dose, discontinue if hypertensive |
Insomnia | 30-40% | Mild-moderate | Morning dosing, sleep hygiene, consider melatonin |
Dry mouth | 30-40% | Mild | Hydration, sugar-free gum, saliva substitutes |
Anxiety/jitteriness | 20-30% | Mild-moderate | Reduce dose, anxiolytic support, caffeine reduction |
Nausea | 15-20% | Mild | Less common than GLP-1s, ginger, small meals |
Headache | 15-20% | Mild | Hydration, typical analgesics |
Cardiovascular monitoring critical:
Baseline blood pressure and heart rate
Weekly monitoring first month
Biweekly thereafter
Discontinue if HR >100 resting or BP >140/90
Major reason for medical supervision
Tolerance and dependency concerns:
Amphetamine-like mechanism raises concerns
Tolerance to weight loss may develop (months)
Psychological dependency possible
Rebound weight gain after stopping
When to discontinue:
Resting heart rate consistently >100 bpm
Blood pressure >140/90 despite management
Severe anxiety or panic attacks
Insomnia affecting function
Any cardiac symptoms (chest pain, palpitations)
Psychological issues (dependency behaviors)
See peptide safety and risks and common mistakes.
Combining with other weight loss agents
Tesofensine + GLP-1 agonists (theoretical):
Different mechanisms = potential synergy
Tesofensine: Metabolic + CNS appetite
GLP-1s: Strong appetite + gastric slowing
Could enhance weight loss to 20-25%+
BUT: No clinical data, significant risks
Not recommended without supervision
Potential combination benefits:
Address multiple pathways
Overcome plateaus
Better than either alone (theoretically)
Metabolic boost + strong appetite suppression
Maximum fat loss
Combination risks:
Compounded cardiovascular strain
Unknown drug interactions
Excessive weight loss risks
Cost ($1,500-2,000/month)
Safer alternatives to tesofensine combinations:
Tirzepatide alone (15-22% loss, FDA approved)
CagriSema (sema + cagrilintide, 15-25%)
GLP-1 + lifestyle (safer, proven)
Learn about peptide stacking strategies at SeekPeptides.
Legal status and availability
Understanding access and regulatory issues.
FDA rejection and regulatory status
Development timeline:
2000s: Developed for Parkinson's/Alzheimer's
2008: Phase 2 obesity trials (successful)
2010: Phase 3 trials initiated
2010: Development halted due to safety concerns
2012: FDA rejected obesity indication
Present: No approved indication anywhere
Why FDA rejected:
Cardiovascular safety concerns primary reason
Increased heart rate and blood pressure
Risk-benefit ratio unfavorable
Safer alternatives available (GLP-1 agonists)
Development company abandoned pursuit
No current path to approval
Regulatory status by country:
Country/Region | Status | Legal to Possess? | Legal to Sell? |
|---|---|---|---|
United States | Not approved | Gray area | No (not for human use) |
European Union | Not approved | Varies by country | No |
Canada | Not approved | Unclear | No |
Australia | Not approved | Illegal | Illegal |
Most countries | Not approved | Gray area/illegal | No |
Current legal classification:
Not a controlled substance (not scheduled)
Not approved for any human use
Sold as "research chemical" only
"Not for human consumption" labels
Legal gray area (enforcement rare)
See are peptides legal guide at SeekPeptides.
Research chemical market availability
Where tesofensine is sold:
Research chemical websites
Some peptide vendors
Underground bodybuilding suppliers
International sources (China, India)
Gray market online pharmacies
Typical product offerings:
Capsules: 0.25mg, 0.5mg, 1.0mg
Powder (raw): 1g, 5g, 10g
Solutions (rare)
Usually sold in monthly supplies
"Research use only" disclaimer
Pricing:
0.5mg capsules: $2-5 per capsule
Monthly supply (30 × 0.5mg): $60-150
Cheaper than pharmaceutical GLP-1s ($1,000+)
More expensive than generic weight loss meds
Price varies widely by vendor
Quality and purity concerns:
No FDA oversight (research chemicals)
Testing varies by vendor
Some provide COA (certificate of analysis)
Purity ranges 95-99% (claimed)
Contamination possible
Dosing accuracy uncertain
Vendor reputation critical:
Established peptide vendors safer
Third-party testing important
User reviews helpful
Avoid unknown sources
Higher price often indicates quality
Legal risks and considerations
Possession risks:
Technically legal in most places (not scheduled)
"Research use only" provides legal cover
Personal use rarely prosecuted
No case law establishing precedent
Gray area = uncertain legal standing
Import/customs risks:
International orders may be seized
Customs may confiscate as unapproved drug
Usually no legal consequences (just loss)
Domestic sources lower risk
Small quantities for personal use typically okay
Selling/distribution risks:
Illegal to sell for human consumption
FDA enforcement on sellers, not buyers
"Research chemical" label required
Cannot market for weight loss
Vendors face legal risks
Medical/insurance implications:
No insurance coverage (not approved)
Can't get prescription legally
Discussing with doctor may cause concerns
Medical records implications
Self-medicating risks acknowledged
Ethical considerations:
Using unapproved drug without oversight
Risks to self (informed consent?)
Supporting gray market industry
Alternative FDA-approved options available
Safety vs access debate
Learn about peptide legality and finding therapy clinics.
How you can use SeekPeptides for weight loss optimization
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive weight loss peptide guidance focusing on safe, effective, FDA-approved options. Compare semaglutide and tirzepatide to experimental compounds, understand stacking strategies, and access clinical research.
Use our calculators - semaglutide dosage calculator, peptide cost calculator, stack calculator - for weight loss planning.
Learn about safe approaches - best peptides for weight loss, semaglutide vs tirzepatide, CagriSema dosing, cagrilintide weight loss.
Find peptide therapy clinics for supervised treatment, understand peptide safety, and access best peptide vendors for quality sourcing.
Final thoughts
Tesofensine represents a powerful weight loss compound with proven 10-12% average weight loss through triple monoamine reuptake inhibition targeting dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. The unique metabolic boost (5-10% increase) combined with central appetite suppression creates effectiveness rivaling semaglutide and tirzepatide but through completely different mechanisms.
However, cardiovascular side effects (increased heart rate and blood pressure) led to FDA rejection despite promising efficacy data. This relegates tesofensine to research chemical status - available through gray market vendors but without regulatory approval, quality assurance, or medical oversight. The stimulant-like mechanism creates dependency risks absent from GLP-1 agonists.
The standard 0.5mg daily dose provides optimal risk-benefit ratio according to clinical trials, though 1.0mg shows stronger effects with proportionally higher risks.
Oral administration offers convenience advantages over injectable peptides, but cardiovascular monitoring remains essential throughout treatment.
FDA-approved alternatives like semaglutide (10-15% loss), tirzepatide (15-22% loss), and CagriSema (15-25% loss) offer comparable or superior results with proven long-term safety profiles, cardiovascular benefits rather than risks, and legal medical oversight. These make tesofensine an unnecessary gamble for most seeking weight loss optimization.
Your weight loss strategy should prioritize safety and legality - tesofensine's cardiovascular risks and regulatory rejection make FDA-approved GLP-1 agonists the clear first choice despite higher costs and injection requirements.
Helpful resources for weight loss
Best peptides for weight loss - Comprehensive guide
Semaglutide vs tirzepatide - FDA-approved comparison
Semaglutide dosage calculator - Dosing tool
Best peptide stack for weight loss - Stacking guide
In case I don’t see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Take care of yourself.