Jan 22, 2026
Ninety-three percent of people who attempt to lose weight through caloric restriction alone fail to maintain their results. The metabolism adapts. Hunger hormones surge. Fat cells cling to their reserves with evolutionary desperation.
What if you could change the conversation entirely?
Lipotropic peptides represent a fundamentally different approach to fat loss. Instead of fighting your biology through willpower and deprivation, these compounds work with your metabolic machinery to unlock stored fat, optimize liver function, and shift your body toward preferential fat burning.
The term lipotropic literally means fat-loving or fat-attracting. These are molecules that enhance the breakdown, transport, and utilization of fat throughout your body. Some operate at the liver level, helping process dietary fats more efficiently. Others work directly on fat cells, activating receptors that trigger lipolysis, the breakdown of stored triglycerides into usable fuel.
This guide covers every major category of lipotropic peptide, from the MIC injections used in weight loss clinics to the cutting-edge mitochondrial peptide MOTS-c. You will learn precisely how each compound works, which combinations produce the strongest results, and what the research actually shows about safety and efficacy. Whether you are hitting a plateau on your current weight loss program or looking for every possible advantage in body recomposition, understanding lipotropic peptides gives you tools most people do not even know exist. SeekPeptides provides the comprehensive protocols and guidance needed to navigate these options safely and effectively.
What makes a peptide lipotropic
The classification lipotropic encompasses any compound that enhances the metabolism of fat. This includes molecules that support liver detoxification, enhance fatty acid transport, activate fat-burning receptors, or improve mitochondrial function. The mechanisms vary dramatically between different lipotropic agents, but they share a common goal.
They help your body use stored fat as fuel.
Traditional lipotropic compounds include amino acids like methionine, nutrients like choline and inositol, and B vitamins that serve as cofactors in metabolic pathways. More recent additions to the category include synthetic peptides designed specifically to enhance lipolysis or optimize growth hormone signaling for preferential fat burning.
How fat metabolism actually works
Understanding lipotropic peptides requires understanding the basic mechanics of fat storage and mobilization. Fat tissue, or adipose tissue, functions as an energy reserve. When you consume more calories than you burn, excess energy gets converted to triglycerides and stored in adipocytes.
Releasing that stored energy involves a cascade of signals.
Hormones like norepinephrine and growth hormone bind to receptors on fat cell membranes. This activates enzymes, particularly hormone-sensitive lipase, that break triglycerides into glycerol and free fatty acids. Those fatty acids then travel through the bloodstream to tissues that need energy, primarily muscle and liver.
Here is where things get interesting. The fatty acids cannot simply diffuse into cells and burn spontaneously. They require transport proteins to cross cell membranes. They need carnitine to shuttle them across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Once inside mitochondria, they undergo beta-oxidation, a process that requires multiple B vitamins and cofactors.
A breakdown at any point in this chain means fat stays stored instead of burned.
Lipotropic peptides target multiple points in this cascade. Some enhance the initial signals that trigger lipolysis. Others improve the transport mechanisms that move fatty acids to where they can be oxidized. Still others optimize mitochondrial function to burn more fat once it arrives. The most effective approaches combine compounds that work at different levels for synergistic effects.
For a deeper exploration of how peptides support fat loss, our dedicated guide covers the mechanisms in greater detail.
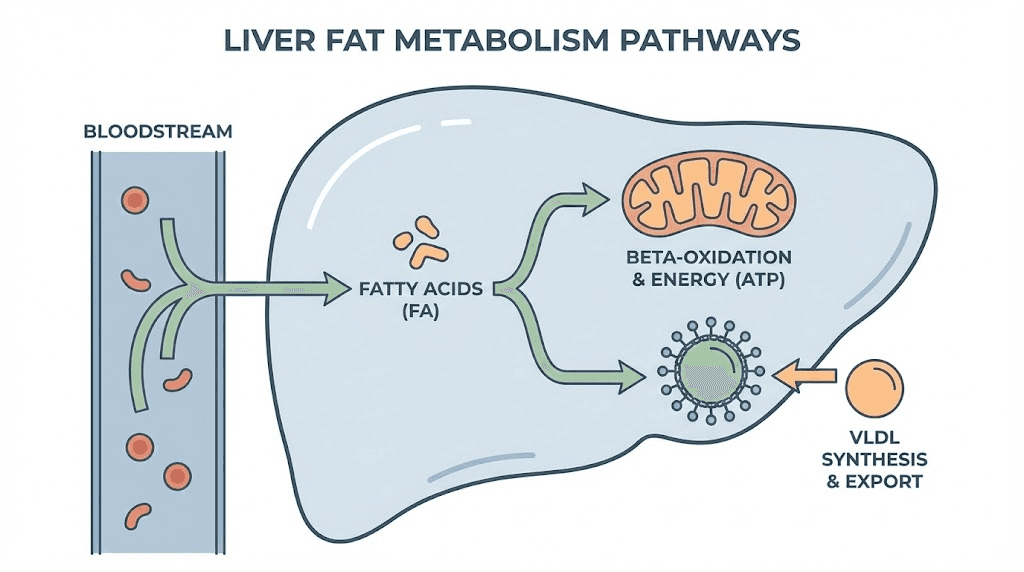
The liver connection
Your liver plays a central role in fat metabolism that most people underestimate. Every fatty acid released from adipose tissue passes through the liver for processing. The liver decides whether to burn those fats for energy, package them into lipoproteins for transport to other tissues, or re-esterify them for storage.
When liver function is compromised, fat accumulates.
This is why the original lipotropic compounds, methionine, inositol, and choline, target hepatic function specifically. They support the biochemical pathways the liver uses to process and export fat. Without adequate amounts of these nutrients, triglycerides build up in liver cells, creating a metabolic bottleneck that slows everything downstream.
The connection between liver health and body composition explains why people with fatty liver disease struggle so much with weight loss. Their central processing unit for fat metabolism is overwhelmed. Addressing liver function often produces dramatic improvements in fat loss that diet and exercise alone could not achieve.
Our comprehensive guide to peptides for gut health explores how digestive and hepatic function influence body composition.
MIC lipotropic injections
MIC stands for methionine, inositol, and choline, the three core compounds found in most lipotropic injection formulations. These injectable nutrient blends have been used in weight loss clinics for decades, though they have gained renewed attention as adjuncts to modern GLP-1 medications.
The components explained
Methionine is an essential amino acid your body cannot produce. It serves as a methyl donor, providing the chemical groups needed to synthesize phosphatidylcholine and assemble very-low-density lipoproteins. These lipoproteins transport triglycerides out of the liver, preventing accumulation that impairs metabolic function.
Beyond liver support, methionine helps preserve lean muscle tissue during caloric restriction. Since muscle mass directly influences metabolic rate, maintaining muscle while losing fat leads to better long-term outcomes.
Inositol is sometimes classified as a B vitamin, though technically it is a carbocyclic sugar your body can synthesize in small amounts. Its primary benefit for weight loss comes through improved insulin sensitivity. When cells respond better to insulin signals, your body stores less fat and accesses stored fat more readily.
Research shows particular benefit for women with polycystic ovary syndrome, where inositol supplementation improved metabolic markers and supported weight loss. Studies demonstrate reductions in triglycerides, cholesterol, and blood pressure alongside improved body composition.
Choline is essential for cell membrane synthesis, bile production, and lipid transport. It enhances the emulsification of dietary fats for absorption and maintains liver cell membrane integrity under oxidative stress. Clinical studies show adequate choline intake lowers liver enzymes and improves hepatic insulin sensitivity.
Without sufficient choline, fat accumulates in liver cells instead of being exported and burned. Choline deficiency is remarkably common, particularly among people restricting calories.
Why injections beat oral supplements
You can find MIC components in oral supplement form. So why do clinics use injections?
Bioavailability.
When you swallow methionine, inositol, or choline, they must survive stomach acid, cross the intestinal lining, pass through the portal circulation to the liver, and reach systemic circulation. Each step involves losses. Some nutrients compete for absorption. Others get metabolized before reaching target tissues.
Injectable delivery bypasses the entire digestive system. The full dose enters your bloodstream directly, reaching tissues at significantly higher concentrations than oral administration could achieve. For carnitine specifically, only a small fraction of oral doses gets absorbed. Injectable carnitine delivers the equivalent of roughly 2000mg oral dosing.
This difference matters when you are trying to support metabolic pathways that may already be struggling due to dietary restriction or underlying dysfunction.
What to expect from MIC injections
MIC injections are not magic fat-burning shots. They create more favorable conditions for fat loss when combined with appropriate diet and exercise.
Most users notice energy improvements within the first week. This makes biological sense. If your metabolic enzymes have been operating without adequate cofactors, or if carnitine insufficiency has been limiting fatty acid oxidation, correcting these deficiencies should produce noticeable results.
Fat loss typically becomes measurable after two to four weeks of consistent use. Clinical experience suggests losses of two to four pounds per week when MIC injections are combined with caloric restriction and physical activity. The injections appear particularly helpful for breaking through plateaus where previous weight loss has stalled.
Typical protocols involve one to two milliliter injections given once or twice weekly, either intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Duration typically runs twelve to sixteen weeks initially before reassessing.
For detailed information on MIC formulations, our Lipo-C peptide guide covers specific ingredients and protocols.
Enhanced MIC formulations
Basic MIC injections often get enhanced with additional compounds. Common additions include B12 for energy production, additional B vitamins as metabolic cofactors, and L-carnitine for improved fatty acid transport.
L-Carnitine deserves special attention. This amino acid derivative shuttles long-chain fatty acids across the inner mitochondrial membrane where they can be oxidized for energy. Without adequate carnitine, fatty acids cannot enter mitochondria efficiently, regardless of how much lipolysis you have triggered.
Meta-analyses of carnitine supplementation in overweight adults show increased maximal oxygen consumption and modest weight loss. The effects become more pronounced when combined with exercise that demands fatty acid oxidation.
Some formulations include lipotropic enhancers like chromium for insulin sensitivity or vitamin C for antioxidant support. Always verify the complete ingredient list for your specific formulation.
For understanding how these injections work with exercise, our guide to peptides for athletic performance provides relevant context.
AOD-9604 and HGH fragment 176-191
These represent the cutting edge of lipotropic peptide development. Both derive from human growth hormone but have been modified to retain only the fat-burning properties while eliminating unwanted effects on blood sugar and IGF-1 levels.
The science behind HGH fragments
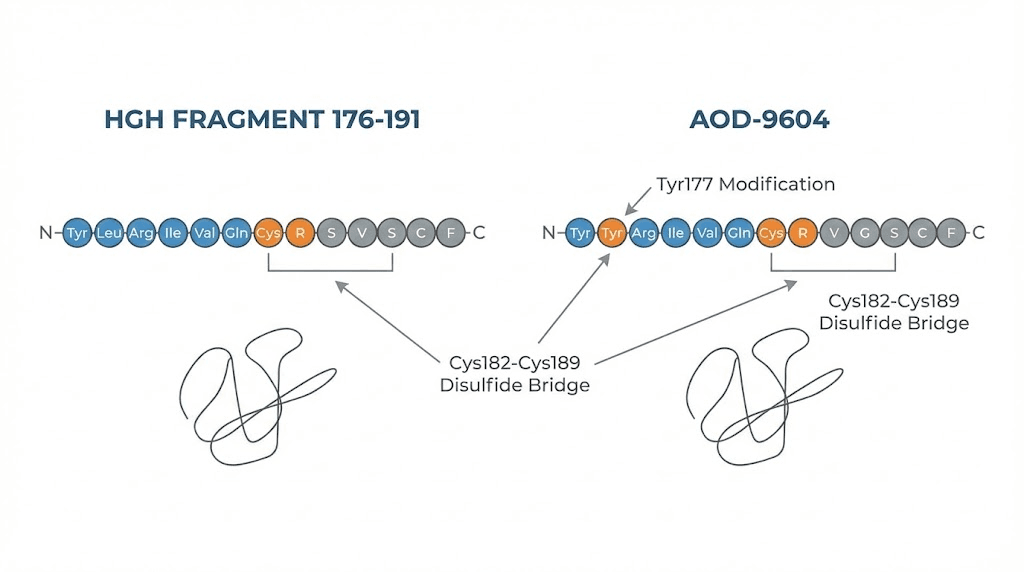
Human growth hormone is a 191-amino-acid protein with multiple effects throughout the body. It promotes muscle growth, enhances bone density, affects blood sugar regulation, and stimulates lipolysis. Researchers discovered that different regions of the molecule are responsible for different effects.
Fragment 176-191 contains only the tail end of the growth hormone molecule, amino acids 176 through 191. This is the region responsible for fat-burning activity. By isolating this fragment, researchers created a compound that stimulates lipolysis without the broader metabolic effects of full growth hormone.
AOD-9604 takes this concept further. It contains amino acids 177-191 with a modified N-terminus that improves stability and potency. The name literally stands for Anti-Obesity Drug, reflecting its intended purpose during development.
How they burn fat
These fragments work primarily through the beta-3 adrenergic receptor pathway. When activated, beta-3 receptors on fat cells signal for the breakdown of stored triglycerides into fatty acids that can be used for energy.
Research in mice shows that AOD-9604 upregulates beta-3 adrenergic receptor expression in adipose tissue. In obese mice, where these receptors are often suppressed, treatment restored receptor levels comparable to lean mice. This effectively sensitizes fat cells to lipolytic signals.
Both fragments also appear to inhibit lipogenesis, the formation of new fat from dietary carbohydrates and fats. This dual action, enhancing breakdown while reducing formation, creates net fat loss even without dramatic changes in caloric intake.
Importantly, neither fragment significantly affects blood sugar or insulin-like growth factor levels. This distinguishes them from full growth hormone therapy, which can cause insulin resistance and other metabolic disruption.
For comprehensive coverage of these compounds, see our AOD-9604 complete guide.
Clinical evidence and limitations
AOD-9604 completed six human clinical trials involving over 900 participants. Early studies showed promising reductions in body fat mass. However, the largest Phase IIb trial failed to achieve statistical significance, and development was terminated.
This does not necessarily mean the compound does not work. It may mean the dosing, duration, or patient selection in the trials was suboptimal. It may mean the effects are real but modest, requiring combination with other interventions for clinical significance.
What we know from research is that these fragments can stimulate lipolysis in laboratory settings and animal models. Human evidence is mixed but suggestive of benefit, particularly when combined with diet and exercise.
One fascinating finding from fragment 176-191 research is that the compound appears self-regulating. In mouse studies, obese animals lost weight while normal-weight animals simply maintained their body weight. This suggests some degree of homeostatic control that prevents excessive fat loss.
Neither fragment carries regulatory approval from any major health authority. Their use remains in the research and clinical practice realm rather than approved pharmaceutical treatment.
For understanding peptide regulation, our peptide regulation news article provides current context.
Dosing protocols
Typical research protocols for AOD-9604 use 250 to 500 micrograms administered subcutaneously once daily, often split into two doses. Some protocols increase to 1000 micrograms daily for enhanced effects, though evidence for dose-response relationships in humans remains limited.
Timing recommendations often suggest morning dosing, particularly before fasted cardio, to maximize fatty acid availability during exercise. Some researchers prefer evening dosing to align with natural growth hormone release patterns during sleep.
Fragment 176-191 protocols typically use similar dosing ranges, often 250 to 500 micrograms twice daily. The lack of standardized protocols reflects the research status of these compounds.
For safe administration, review our peptide reconstitution guide and injection techniques.
MOTS-c mitochondrial peptide
MOTS-c represents a completely different approach to lipotropic peptides. Rather than targeting fat cells directly or supporting liver function, it works at the deepest level of cellular metabolism: the mitochondria.
A peptide from mitochondrial DNA
Most peptides are encoded by nuclear DNA, synthesized in the cytoplasm, and sent where they are needed. MOTS-c is different. It is encoded directly by mitochondrial DNA, making it one of a small class of mitochondrial-derived peptides.
This origin grants unique properties. The mitochondrial genome is ancient, inherited maternally, and highly conserved across species. MOTS-c appears to function as a retrograde signal from mitochondria to the rest of the cell and body, communicating information about cellular energy status.
The peptide consists of 16 amino acids encoded by the 12S rRNA region of mitochondrial DNA. Its primary target is skeletal muscle, where it exerts profound effects on energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
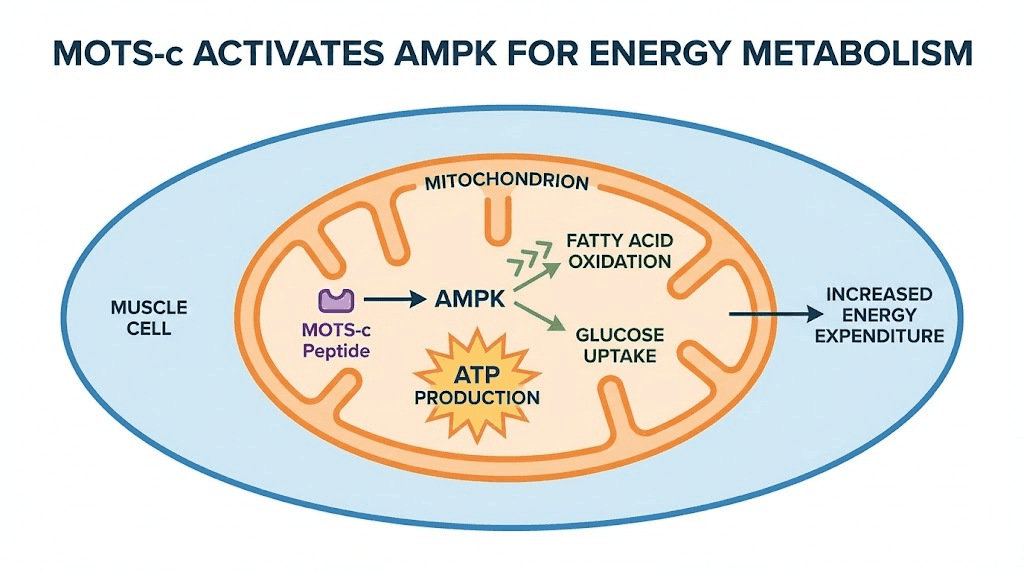
The AMPK connection
MOTS-c activates AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase, often called the master metabolic regulator. AMPK responds to cellular energy status. When energy is low (high AMP to ATP ratio), AMPK activates pathways that generate energy while inhibiting those that consume it.
Activation of AMPK promotes glucose uptake into cells, enhanced fatty acid oxidation, inhibition of fatty acid synthesis, increased mitochondrial biogenesis, and improved insulin sensitivity.
The MOTS-c to AMPK pathway works through inhibition of the folate cycle and de novo purine biosynthesis. This creates the metabolic stress signal that activates AMPK, but in a controlled, physiological way rather than the potentially harmful stress of energy starvation.
For understanding how MOTS-c compares to other metabolic peptides, our MOTS-c benefits guide provides detailed analysis.
Fat burning and metabolic flexibility
MOTS-c shifts cellular metabolism toward fatty acid oxidation rather than fat storage. Studies in mice show reduced diet-induced obesity even without changes in caloric intake. The peptide appears to increase white fat browning, essentially converting storage fat into metabolically active tissue that burns calories.
Particularly interesting is the effect on metabolic flexibility, your body's ability to switch between burning carbohydrates and fats depending on availability and demand. Poor metabolic flexibility characterizes insulin resistance and obesity. MOTS-c improves this flexibility, allowing cells to respond appropriately to fed and fasted states.
MOTS-c also reduces mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species, decreasing the chronic low-grade inflammation associated with obesity and metabolic dysfunction. This anti-inflammatory effect may contribute significantly to improved body composition outcomes.
The exercise connection
Perhaps the most fascinating aspect of MOTS-c is its relationship with exercise. The peptide is significantly expressed in response to physical activity and stress. It translocates to the nucleus where it regulates genes involved in stress adaptation.
In humans, exercise induces MOTS-c expression in skeletal muscle and circulation. This suggests that some of the metabolic benefits of exercise are mediated through this peptide. MOTS-c may be an exercise mimetic, providing some benefits of physical activity even in the absence of actual exercise.
Studies in mice show that late-life MOTS-c treatment increased physical capacity and healthspan. The peptide prevented age-dependent physical decline and muscle loss that typically accompanies aging.
MOTS-c levels naturally decline with age. Young people have approximately 11 to 21 percent higher circulating levels than middle-aged and older individuals. This decline may contribute to the metabolic dysfunction and muscle loss of aging.
For protocols on MOTS-c administration, see our MOTS-c dosage chart.
Tesamorelin for visceral fat
Tesamorelin stands apart from other lipotropic peptides because it carries actual FDA approval. Specifically, it is approved for reducing excess abdominal fat in HIV-infected patients with lipodystrophy. This regulatory status comes with extensive clinical trial data that most peptides lack.
How tesamorelin works
Tesamorelin is a synthetic analog of growth hormone-releasing hormone, GHRH. It stimulates the pituitary gland to release growth hormone, which then acts throughout the body to enhance lipolysis and fat oxidation.
But tesamorelin works differently than exogenous growth hormone.
When you inject growth hormone directly, you bypass the natural feedback systems that regulate its release. This can overwhelm normal hormonal signaling and cause problems with blood sugar and IGF-1 levels.
Tesamorelin works through your natural pituitary response. It enhances growth hormone release while allowing feedback systems to function normally. The result is a more physiological hormonal pattern that preferentially targets visceral fat without the metabolic disruption of direct growth hormone therapy.
The peptide features enhanced stability through N-terminal modification with a trans-3-hexenoic acid group. This provides greater resistance to enzymatic degradation than natural GHRH.
Clinical trial evidence
The evidence base for tesamorelin is stronger than for most peptides. Phase III clinical trials involving 806 HIV-infected patients demonstrated visceral adipose tissue reductions of 11.7 to 19.6 percent compared to placebo.
In the combined trials, 69 percent of subjects receiving tesamorelin achieved at least 8 percent reduction in visceral fat, compared to only 33 percent of placebo recipients. A landmark trial showed visceral fat reduction of 34 cubic centimeters with tesamorelin versus an 8 cubic centimeter increase with placebo.
What makes these findings particularly compelling is the selectivity. Subcutaneous fat, the fat just under the skin, remained relatively unchanged. Tesamorelin acts where it matters most: the deep, metabolically active visceral fat surrounding vital organs.
Beyond fat reduction, studies show improvements in lipid profiles, liver enzymes, and markers of metabolic health. In subjects with elevated liver enzymes at baseline, those who responded to tesamorelin experienced significant reductions in ALT and AST.
For complete tesamorelin protocols, see our tesamorelin complete guide.
Limitations and considerations
Important to note: tesamorelin is not indicated for general weight loss. It has weight-neutral effects overall, meaning the visceral fat reduction does not necessarily translate to scale weight changes. Fat is being reduced but the weight-neutral effect suggests simultaneous changes in muscle or other tissue.
Applications beyond the FDA-approved indication require careful consideration.
The approval is specific to HIV-associated lipodystrophy.
Use for general obesity or body composition goals represents off-label application that should involve appropriate medical supervision.
Cost can also be prohibitive. As an FDA-approved medication, tesamorelin carries pharmaceutical pricing that significantly exceeds research peptides. Insurance coverage may be available for the approved indication but rarely for cosmetic use.
Growth hormone secretagogues
Beyond tesamorelin, a category of peptides called growth hormone secretagogues, or GHS, enhance natural growth hormone release. These include GHRP-2, GHRP-6, ipamorelin, and combinations with growth hormone-releasing hormone analogs like CJC-1295.
How secretagogues enhance fat loss
Growth hormone is one of the primary lipolytic hormones. It activates hormone-sensitive lipase, triggers fatty acid release from adipose tissue, and promotes fat oxidation in peripheral tissues. Enhancing growth hormone release through secretagogues creates a more favorable hormonal environment for fat loss.
These peptides work through the ghrelin receptor, GHS-R1a. By mimicking ghrelin signaling, they trigger pulsatile growth hormone release from the pituitary. Different secretagogues have varying selectivity and side effect profiles.
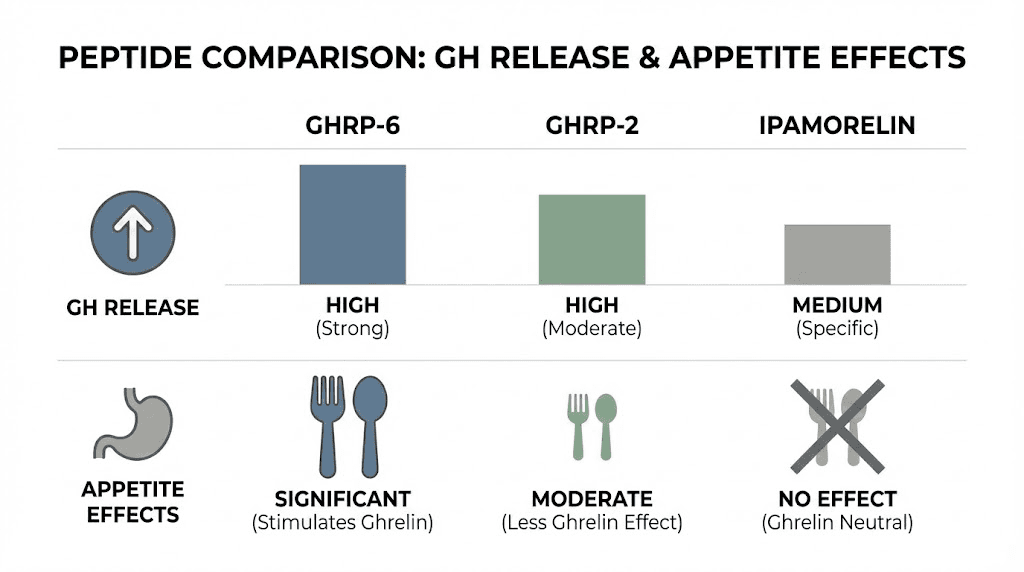
GHRP-6 provides strong growth hormone stimulation but also significantly increases appetite, which can be counterproductive for weight loss. The appetite stimulation relates to its ghrelin-mimetic activity, since ghrelin normally signals hunger.
GHRP-2 offers cleaner growth hormone release with less impact on appetite and prolactin levels. This makes it better suited for body recomposition and cutting phases where appetite control matters.
Ipamorelin shows the highest receptor selectivity with minimal off-target effects. It does not induce the ravenous appetite associated with GHRP-6 and has minimal effects on cortisol or prolactin. For pure fat loss goals, ipamorelin often represents the best secretagogue choice.
For detailed comparison, see our ipamorelin vs CJC-1295 guide.
Combining GHRH and GHRP
Stacking a growth hormone releasing hormone analog with a secretagogue produces synergistic effects. CJC-1295 enhances GHRH signaling while secretagogues activate the ghrelin pathway. Together, they increase both the frequency and amplitude of growth hormone pulses.
The most common combination pairs CJC-1295 with ipamorelin. This stack provides robust growth hormone elevation without appetite stimulation, making it suitable for fat loss phases. Typical protocols use 100 to 200 micrograms of each compound administered together once or twice daily.
Some protocols add a GHRP to CJC-1295 with DAC, a modified version that remains active in circulation for days rather than minutes. This allows less frequent dosing while maintaining elevated growth hormone levels.
For understanding how to stack these peptides safely, our peptide stacking guide covers the principles.
The fat loss mechanism
Enhanced growth hormone does not directly burn fat. It creates metabolic conditions favoring fat utilization. The elevated growth hormone promotes lipolysis, releasing fatty acids from storage. It also enhances insulin sensitivity in muscle while promoting relative insulin resistance in adipose tissue, directing nutrients toward muscle rather than fat storage.
The effects compound over time. As body composition improves, metabolic rate increases due to greater muscle mass. This creates a positive feedback loop where fat loss becomes progressively easier.
Results typically take longer to manifest than with direct-acting peptides like AOD-9604. Secretagogue protocols often run for months rather than weeks. The effects are more subtle day-to-day but accumulate to meaningful body composition changes.
For understanding growth hormone peptides more broadly, our best peptides for muscle growth guide covers the anabolic applications.
GLP-1 medications and lipotropic peptides
The explosion of GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide has transformed weight loss medicine. Understanding how these medications relate to lipotropic peptides helps create optimal protocols.
Different mechanisms complement each other
GLP-1 medications work primarily through appetite suppression and delayed gastric emptying. They make you less hungry and feel fuller longer. The dramatic weight loss results, often 15 to 25 percent of body weight, come largely from sustained caloric reduction.
Lipotropic peptides work through entirely different mechanisms. They enhance fat metabolism rather than reducing caloric intake. They support liver function, improve fatty acid transport, and optimize the cellular machinery that burns fat.
These mechanisms are complementary rather than redundant.
Combining GLP-1 medications with lipotropic support may enhance fat loss beyond what either achieves alone. While the GLP-1 creates caloric deficit, lipotropic peptides ensure that deficit translates to maximum fat burning with minimal muscle loss.
For detailed comparison of these approaches, see our semaglutide vs tirzepatide comparison.
Practical combination protocols
Many weight loss clinics now offer lipotropic injections alongside GLP-1 medications. MIC or Lipo-C injections provide metabolic support that may address some common issues with GLP-1 therapy:
Fatigue during aggressive weight loss often improves with B vitamin and carnitine supplementation. The energy boost from lipotropic injections can offset the low-energy feeling some people experience on GLP-1 medications.
Muscle preservation becomes critical during rapid weight loss. The methionine in lipotropic formulations supports protein synthesis and nitrogen balance. Adding muscle-sparing peptides like BPC-157 may further protect lean mass.
Liver support matters as fat mobilization increases. Rapid weight loss can temporarily stress the liver as it processes increased fatty acid traffic. The MIC combination specifically supports hepatic function during this transition.
When combining treatments, space injections on different days to simplify tracking any reactions. Most protocols use GLP-1 medication on one day and lipotropic injection on a separate day, often three to four days apart.
For GLP-1 dosing information, our tirzepatide dosing guide and semaglutide calculator provide specific protocols.
Cost and access considerations
GLP-1 medications carry high costs, often $400 to $1500 monthly without insurance. Lipotropic peptides are generally more affordable, typically $100 to $300 monthly depending on formulation and frequency.
For those who cannot access or afford GLP-1 medications, comprehensive lipotropic protocols can still produce meaningful fat loss. The results may be less dramatic than GLP-1 therapy but represent meaningful improvement over diet and exercise alone.
Some researchers explore combinations like lipotropic peptides with growth hormone secretagogues as alternatives to GLP-1 medications. These protocols require more complex administration but may achieve substantial body composition improvements at lower cost.
For budget planning, our peptide cost calculator helps estimate total protocol expenses.
Choosing the right lipotropic approach
With multiple categories of lipotropic peptides available, selecting the right approach requires matching your goals, health status, and practical considerations to the available options.
For general metabolic support
If you are primarily looking for enhanced energy, improved fat metabolism during dieting, and general metabolic support, MIC or Lipo-C injections offer an excellent starting point. They are well-tolerated, affordable, and provide broad metabolic benefits.
Start with once-weekly injections and assess response. If energy improves and fat loss accelerates, continue the protocol. If effects are minimal after four weeks, consider adding or switching to more targeted compounds.
This approach works particularly well for people hitting plateaus on calorie-restricted diets. The metabolic support can restart stalled weight loss without requiring further caloric reduction.
For stubborn body fat
If you carry fat that refuses to respond to diet and exercise, particularly in the abdominal region, consider AOD-9604 or HGH Fragment 176-191. These peptides specifically target adipose tissue for enhanced lipolysis.
Combine them with fasted morning cardio for maximum effect. The fatty acids released through enhanced lipolysis need somewhere to go. Exercise provides the demand that burns them rather than allowing re-deposition.
Expect more gradual results than dramatic transformation. These peptides work best as part of comprehensive programs rather than standalone interventions.
For visceral fat specifically
Tesamorelin offers the strongest evidence for visceral fat reduction.
If you carry significant abdominal fat, particularly if it appears hard and protuberant rather than soft and pinchable, visceral fat may be the primary issue.
Access to tesamorelin requires prescription and carries higher costs. For those with appropriate indications and resources, it represents the most proven option for visceral fat reduction.
For metabolic dysfunction
If poor insulin sensitivity, low energy, or metabolic inflexibility characterize your situation, MOTS-c addresses these root causes. It works at the mitochondrial level to improve how your cells process fuel.
MOTS-c pairs well with exercise, potentially amplifying the metabolic benefits of physical activity. For those who struggle to see results from workouts, this peptide may help unlock the response you are seeking.
For comprehensive body recomposition
If goals extend beyond fat loss to include muscle preservation or growth, growth hormone secretagogue protocols offer the most complete approach. Enhanced growth hormone supports both lipolysis and anabolic processes.
These protocols require more complex administration and longer time frames. Plan for months of consistent use to see meaningful results. The investment of time and resources pays off in sustainable body composition improvements.
For personalized protocol development, SeekPeptides offers comprehensive guidance based on individual goals and circumstances.
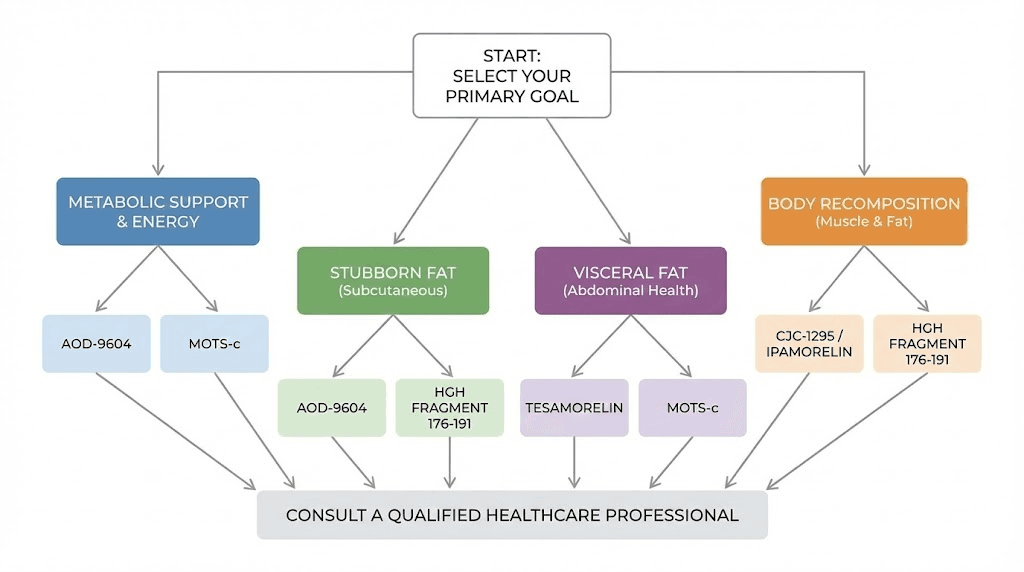
Stacking lipotropic peptides
Combining multiple lipotropic compounds can produce synergistic effects. The key is selecting peptides that work through complementary mechanisms rather than redundant pathways.
Effective combinations
MIC plus AOD-9604: This combination addresses both liver function and direct lipolysis. The MIC components ensure efficient fat processing while AOD-9604 enhances fat cell breakdown. Administer on the same day or alternate days.
MOTS-c plus growth hormone secretagogues: MOTS-c optimizes mitochondrial function while secretagogues enhance the hormonal signal for fat mobilization. This creates a state where fatty acids are both released and efficiently burned. Space dosing appropriately to allow each compound to work.
Lipotropic injections plus ipamorelin/CJC-1295: The metabolic support from lipotropic nutrients combines with enhanced growth hormone for comprehensive body recomposition. This stack supports fat loss while preserving lean mass.
AOD-9604 plus carnitine: Enhanced lipolysis paired with improved fatty acid transport. Carnitine ensures the fatty acids released by AOD-9604 can enter mitochondria for oxidation. This prevents released fat from simply being re-deposited.
Combinations to approach carefully
Multiple compounds targeting the same pathway may produce diminishing returns. Using both GHRP-6 and GHRP-2, for example, provides less additional benefit than adding a GHRH analog that works through a different mechanism.
High-dose growth hormone enhancement from multiple sources can create metabolic stress. If combining secretagogues with tesamorelin, reduce individual doses and monitor for signs of excessive growth hormone activity.
Some pre-mixed formulations combine lipotropic nutrients with GLP-1 agonists. If you are already taking semaglutide or tirzepatide separately, verify your lipotropic formulation does not contain additional GLP-1 compounds to avoid overdosing.
For detailed stacking protocols, our peptide stack calculator helps plan combinations.
Timing considerations
Most lipotropic peptides work best when administered on an empty stomach. This is particularly true for compounds that affect growth hormone release, since food intake blunts the GH response.
Morning dosing before fasted exercise maximizes fat burning for most protocols. The enhanced lipolysis and fatty acid transport support fat oxidation during activity.
Some researchers prefer evening dosing for growth hormone secretagogues to align with natural nocturnal GH release patterns. This may enhance sleep quality and recovery while maintaining lipolytic effects.
Split dosing, administering half the daily dose in the morning and half before bed, can maintain more consistent effects throughout the day. This approach works well for compounds with short half-lives.
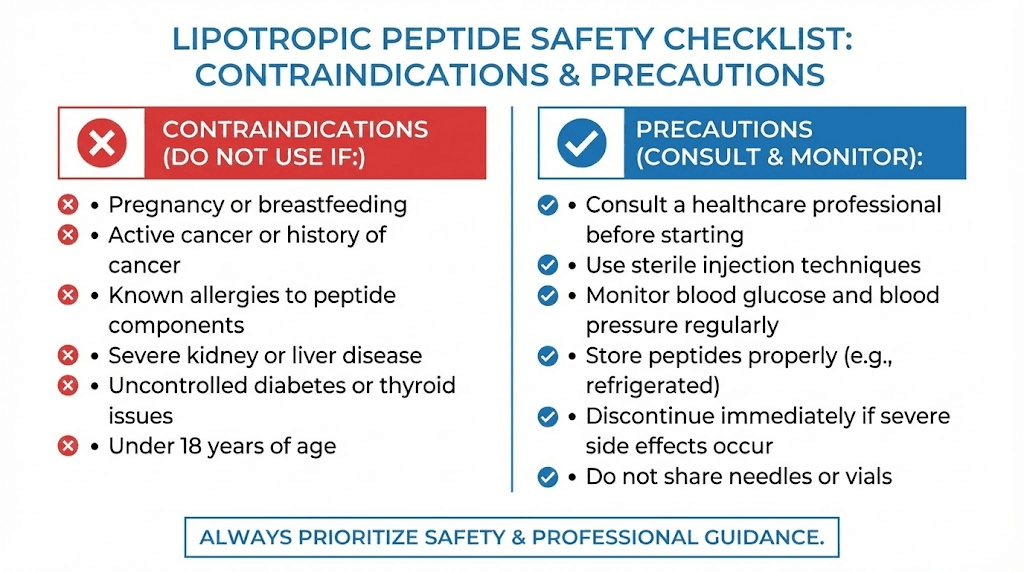
Safety and side effects
Lipotropic peptides generally carry favorable safety profiles, though individual responses vary. Understanding potential issues helps you use these compounds responsibly.
Common side effects
Injection site reactions: Mild redness, soreness, or bruising at injection sites is the most common complaint across all injectable peptides. Proper technique and site rotation minimize these issues.
Gastrointestinal effects: Some people experience nausea, loose stools, or digestive discomfort, particularly with MIC injections. These effects typically resolve within 24 to 48 hours.
Energy changes: Initial fatigue followed by improved energy is common during the first week. The adjustment period reflects metabolic changes as your body adapts to enhanced fat oxidation.
Fishy body odor: Excessive trimethylamine production from choline and carnitine metabolism can cause temporary odor. Reducing dose and increasing hydration usually resolves this.
Peptide-specific concerns
Growth hormone secretagogues can cause water retention, joint discomfort, and carpal tunnel-like symptoms at higher doses. These effects relate to elevated growth hormone and typically resolve with dose reduction.
GHRP-6 increases appetite significantly, which can undermine fat loss goals. If using this peptide, plan for appetite management strategies or consider ipamorelin as an alternative.
AOD-9604 and HGH fragments occasionally cause headaches or injection site reactions. Serious adverse effects are rare in available evidence.
Tesamorelin carries the most comprehensive safety data due to its FDA approval. Common side effects include injection site reactions, joint pain, and peripheral edema. It should not be used during pregnancy or in people with active malignancy.
For comprehensive safety information, our peptide safety and risks guide covers all major considerations.
Contraindications
Avoid lipotropic peptides if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, as safety data is insufficient. Active cancer is a contraindication for anything that enhances growth hormone, given potential effects on tumor growth.
Severe liver or kidney disease requires medical supervision before using these compounds. While lipotropic nutrients generally support liver function, severely compromised organs may not respond appropriately.
Always disclose all medications and supplements to your healthcare provider. While most lipotropic peptides have minimal drug interactions, individual situations may create unexpected concerns.
Storage and handling
Proper storage ensures your peptides remain effective throughout the treatment course. Different formulations have different requirements.
MIC and lipotropic injections
Most MIC formulations store at controlled room temperature, 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit. Keep vials in original packaging to protect from light, which can degrade B vitamins.
After first puncture, most formulations remain stable for 28 days when stored properly. Always verify the beyond-use date on your specific product.
Do not freeze. Do not expose to excessive heat. Discard if you notice cloudiness, particulates, or color changes.
Peptide lyophilized powders
Peptides like AOD-9604, MOTS-c, and secretagogues typically ship as lyophilized, or freeze-dried, powders. These require reconstitution before use.
Unreconstituted peptides store best in the freezer for long-term stability or refrigerated for near-term use. Once reconstituted with bacteriostatic water, store refrigerated and use within the specified timeframe, typically two to four weeks.
Never freeze reconstituted peptides. The water expands and can damage the peptide structure.
For detailed storage protocols, our peptide storage guide covers all requirements.
Reconstitution basics
Add bacteriostatic water slowly to the vial, allowing it to run down the inside wall. Never inject water directly onto the peptide powder, as the force can damage the molecules.
Swirl gently to dissolve. Do not shake vigorously. Once fully dissolved, the solution should be clear.
Record the concentration based on the amount of water added. This allows accurate dosing with insulin syringes.
Our peptide reconstitution calculator simplifies the math for accurate dosing.
Expected results and realistic timelines
Setting appropriate expectations helps you stay motivated and recognize progress when it happens.
First two weeks
Energy changes are typically the first noticeable effect. Improved morning alertness, reduced caffeine dependence, and better workout performance often appear within days of starting lipotropic protocols.
Scale weight may fluctuate due to water shifts rather than fat loss. Do not read too much into early weight changes.
Some people notice reduced cravings, particularly for fatty and sugary foods. This may relate to improved metabolic signaling or simply better energy reducing the drive for quick fuel.
Weeks two through four
Measurable fat loss should become apparent with consistent diet and exercise. Most people lose two to four pounds per week during this phase when protocols are followed correctly.
Body composition changes may exceed scale weight changes if you are preserving or building muscle. Measurements and how clothes fit often tell a better story than the scale.
Workout performance and recovery typically improve, supporting more effective training.
Weeks four through twelve
This is where accumulated benefits become dramatic. Expect ten to twenty-five or more pounds of fat loss with diligent adherence to diet, exercise, and supplementation.
Metabolic rate stabilizes at a higher level as body composition improves. The positive feedback loop of more muscle supporting greater caloric expenditure kicks in.
Plateaus may occur and are normal. Adjusting protocols, caloric intake, or exercise can restart progress.
What lipotropic peptides cannot do
No peptide causes fat loss without caloric deficit or metabolic demand. These compounds enhance your body's fat-burning capacity. They do not override physics.
Lipotropic peptides cannot compensate for poor lifestyle choices. Consistent diet and exercise remain the foundation. The peptides amplify your efforts. They do not replace them.
Results vary between individuals based on starting point, adherence, and individual response. Some people are high responders who see dramatic changes. Others experience more modest benefits.
For tracking progress effectively, consider the assessment tools and protocols available through SeekPeptides membership.
Frequently asked questions
What is the most effective lipotropic peptide for fat loss?
Effectiveness depends on individual circumstances.
For general metabolic support with proven safety, MIC injections offer reliable benefits.
For targeted fat burning, AOD-9604 provides direct lipolytic activity.
For visceral fat specifically, tesamorelin has the strongest clinical evidence.
For metabolic optimization, MOTS-c addresses fundamental mitochondrial function.
Can I take lipotropic peptides without dieting?
Lipotropic peptides enhance fat metabolism but do not override caloric balance. You will see some benefit from improved metabolic efficiency, but meaningful fat loss requires caloric deficit through diet, exercise, or both. These compounds work best as part of comprehensive programs rather than standalone interventions.
How long should I use lipotropic peptides?
Initial treatment courses typically run twelve to sixteen weeks. Many people continue with maintenance protocols indefinitely to sustain results. Growth hormone secretagogue protocols often run for months to achieve meaningful body composition changes. Reassess periodically with your healthcare provider.
Are lipotropic peptides safe for long-term use?
MIC injections contain nutrients your body uses naturally and can be used long-term with appropriate medical supervision. Research peptides have less long-term safety data. Tesamorelin has been studied for extended use in approved populations. Individual response and health status should guide duration decisions.
Can I combine lipotropic peptides with my prescription medications?
Most lipotropic compounds have minimal drug interactions. However, always disclose all peptides and supplements to your healthcare provider. Some medications may require monitoring or dose adjustments when combined with metabolic enhancers.
Do lipotropic peptides require a prescription?
MIC injections and compounded lipotropic formulations are typically available through wellness clinics without prescription. Tesamorelin requires prescription. Research peptides occupy a gray area and are sold for research purposes. Local regulations vary.
Will I regain weight after stopping lipotropic peptides?
Maintaining weight loss requires continuing the habits that produced it. If you return to previous eating and activity patterns, weight will return. Lipotropic peptides support fat metabolism but do not permanently change it. Many people use maintenance protocols long-term while others transition off successfully by maintaining lifestyle changes.
How do I know if lipotropic peptides are working?
Track multiple markers beyond scale weight. Measurements, particularly waist circumference, often show changes before weight does. Energy levels, workout performance, and how clothes fit all indicate progress. Blood work can show improvements in lipid profiles and liver enzymes.
External resources
PubMed - Research database for peptide studies
FDA - Regulatory information on approved treatments
National Institutes of Health - Health information resources
PubMed Central - Full-text research articles
ClinicalTrials.gov - Ongoing research studies
For researchers serious about optimizing their fat loss protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Join us.



