Jan 26, 2026
You have heard about HK Peptides. Maybe a forum post caught your eye. Maybe someone mentioned them in a thread about Chinese peptide sources. Or maybe you found their name while researching grey market peptide vendors and wondered if they were legitimate.
Here is the problem. The peptide vendor landscape is complicated. New suppliers appear constantly. Some deliver quality products. Others disappear after a few months, taking customer money with them. And distinguishing between the two before you place an order requires research that most people do not have time to conduct.
HK Peptides operates in this murky middle ground. They have been around since approximately 2020. They have accumulated hundreds of independent lab tests. Some products score exceptionally well. Others fail spectacularly. And the community feedback ranges from enthusiastic praise to serious warnings about verification issues.
This guide dissects everything researchers need to know about HK Peptides. We examine their company background, product catalog, independent test results from Finnrick Analytics, community experiences from forums, shipping logistics, tariff implications, and the critical steps for verifying any purchase. Whether you are considering HK Peptides or simply trying to understand the Chinese peptide vendor ecosystem, the information here will help you make an informed decision.
SeekPeptides has compiled this research to help researchers navigate vendor selection with real data rather than marketing claims. Because choosing the wrong vendor does not just waste money. It can compromise your entire research protocol.
Who is HK Peptides
The name HK Peptides actually refers to multiple entities, which creates immediate confusion for researchers trying to verify their source. Understanding which company you are dealing with matters significantly for quality expectations and customer service experiences.
HK Peptides Worldwide
Founded in Hong Kong in 2020, HK Peptides Worldwide positions itself as a global distributor of research grade peptides. They claim to source from Hong Kong biotech facilities and distribute to over 80 countries. Their website emphasizes ISO certified laboratory synthesis and 99% purity standards verified by HPLC testing.
This entity focuses primarily on the Western research market. They offer English language customer service, accept multiple payment methods including cryptocurrency and PayPal, and ship internationally with tracking. Their product range includes popular research compounds like BPC-157, TB-500, GHK-Cu, and various weight loss peptides including semaglutide and tirzepatide.
HK Peptide (Henan Kuisu Technology)
The second major entity is HK Peptide, operated by Henan Kuisu Technology Co., Ltd based in mainland China. This company has been mentioned extensively in forum discussions, particularly on GLP-1 Forum where users discuss purchasing peptides for weight management research.
Their website at hkpeptide.com emphasizes direct manufacturing capability rather than distribution. They claim purity levels above 99%, offer various payment methods including bank transfer, Bitcoin, USDT, and PayPal, and provide product test reports on request. Forum discussions frequently reference sales representatives named Bella, Sue, Nicole, and Ailsa.
HENGKUN Peptides
A third entity, HENGKUN Peptides at hk-peptide.com, describes itself as one of the most reputable peptide sources in China. They supply laboratories, universities, and research facilities with peptides manufactured under what they call strict quality controls. Every product allegedly undergoes testing for purity before shipping.
This entity serves a more institutional market. Their emphasis on supplying research facilities suggests higher volume sales with potentially different quality control standards than consumer facing operations.
The key takeaway? When someone mentions HK Peptides, clarify which entity they mean. The quality, service, and reliability can vary significantly between these related but distinct operations. Most community discussions reference HK Peptide (Henan Kuisu Technology) when discussing forum experiences and Finnrick test results.
Product catalog and offerings
HK Peptides offers a comprehensive catalog of research compounds. Understanding their product range helps researchers identify whether they carry the specific peptides needed for their protocols.
GLP-1 receptor agonists
The weight loss peptide category represents their most discussed product line. They offer semaglutide and tirzepatide in various dosage sizes, along with newer compounds like retatrutide and cagrilintide. These compounds have driven significant forum discussion due to their popularity for metabolic research.
According to their March pricing list shared on GLP-1 Forum, they offer tirzepatide in various vial sizes and retatrutide at multiple milligram options. Pricing tends to be competitive with other Chinese vendors, though exact figures fluctuate with market conditions and currency exchange rates.
Growth hormone secretagogues
Their catalog includes CJC-1295 both with and without DAC, ipamorelin, sermorelin, tesamorelin, and hexarelin. These compounds remain popular among researchers studying growth hormone modulation and its effects on various biological systems.
The sermorelin ipamorelin blend has gained particular attention for researchers interested in combination protocols. HK Peptides offers both individual compounds and some pre-made blends, though independent testing of blends remains less common than single compound verification.
Healing and recovery peptides
BPC-157 and TB-500 form the backbone of their healing peptide category. These compounds are among the most requested for tissue repair research and injury recovery studies. However, Finnrick testing has revealed concerning quality variations in their BPC-157 specifically.
They also carry wolverine stack components and various peptide stack combinations that researchers use for comprehensive healing protocols. Understanding the independent test results for each component matters significantly when planning multi-compound research.
Skin and cosmetic peptides
GHK-Cu appears prominently in their catalog, marketed toward researchers studying copper peptide effects on skin biology. They offer various vial sizes suitable for different research durations. However, independent testing has shown significant quality inconsistency in this product line.
Snap-8 and other cosmetic peptides round out this category for researchers focused on topical skin peptide applications.
Tanning and sexual function peptides
Melanotan II and PT-141 represent their offerings in the melanocortin receptor category. These compounds remain popular for researchers studying melanogenesis and sexual function pathways. Finnrick testing indicates better quality control for these products compared to some others in their catalog.
Research supplies
Beyond peptides themselves, HK Peptides offers bacteriostatic water for reconstitution. They also carry some related research supplies, though their primary focus remains on the peptide compounds themselves.
Independent testing and quality ratings
Marketing claims mean nothing without verification. The peptide research community has developed robust independent testing infrastructure specifically because vendor claims frequently do not match reality. For HK Peptides, Finnrick Analytics provides the most comprehensive third party verification available.
Finnrick Analytics overview
Finnrick Analytics operates as an independent laboratory testing service that analyzes peptide samples from various vendors. They do not sell peptides. They test them. Their methodology involves HPLC and mass spectrometry analysis to verify both purity and identity of submitted samples.
For HK Peptides specifically, Finnrick has conducted 225 sample tests across 11 different products as of January 2026. This represents one of the larger test sample sizes among Chinese vendors, providing statistically meaningful quality insights.
Product by product ratings
The results reveal significant quality variation across different products. Understanding these ratings helps researchers identify which HK Peptides products meet acceptable standards and which ones present quality concerns.
Semaglutide receives an A rating (Great). Based on 7 tests, scores average 7.1 with a minimum of 6.2 and maximum of 8.0. This indicates relatively consistent quality for their semaglutide product, making it one of their more reliable offerings for researchers studying GLP-1 agonist effects.
Melanotan II receives a B rating (Good). With 6 tests averaging 6.9, this product shows acceptable consistency. Researchers studying melanocortin pathways can have reasonable confidence in this compound.
PT-141 receives a tentative B rating (Good). Only 4 tests exist, but they average 7.8 with a range from 5.6 to a perfect 10.0. The tentative rating reflects the smaller sample size rather than quality concerns. This aligns with positive community feedback on this product.
Cagrilintide receives a tentative C rating (Okay). Five tests average 5.5 with scores ranging from 5.0 to 6.0. This narrow range suggests consistent but mediocre quality, requiring researchers to factor in potential potency variations when designing protocols.
Ipamorelin receives a C rating (Okay). Eight tests average 7.8 but include a concerning low score of 4.8. The wide range from 4.8 to 10.0 indicates batch to batch variability that researchers should consider.
Retatrutide receives a D rating (Poor). This product has the largest test sample with 71 tests averaging 7.3. However, some batches scored as low as 3.9. The D rating reflects concerning quality inconsistency for a compound many researchers specifically seek for metabolic research.
BPC-157 receives an E rating (Bad). Twelve tests average 6.8 but include scores as low as 2.4. This represents a serious concern for researchers interested in BPC-157 protocols. The inconsistency means some batches may contain minimal active compound.
GHK-Cu receives an E rating (Bad). Nineteen tests average 6.3 with scores ranging from 2.0 to 10.0. This extreme variability makes GHK-Cu research protocols unreliable when sourcing from HK Peptides.
Tesamorelin receives an E rating (Bad). Sixteen tests average 6.5 but include a devastating low score of 1.0. Some batches are essentially inactive. Researchers studying growth hormone pathways should consider alternative sources.
Tirzepatide receives an E rating (Bad). Despite 72 tests, scores range from 0.0 to 10.0 with an average of 7.2. The fact that some batches received a 0.0 score, indicating no active compound, represents a major concern for researchers working with this popular metabolic research compound.
CJC-1295 has insufficient data for rating. Only one test exists, scoring 7.5. Researchers interested in CJC-1295 protocols should request additional verification before ordering.
What the ratings mean
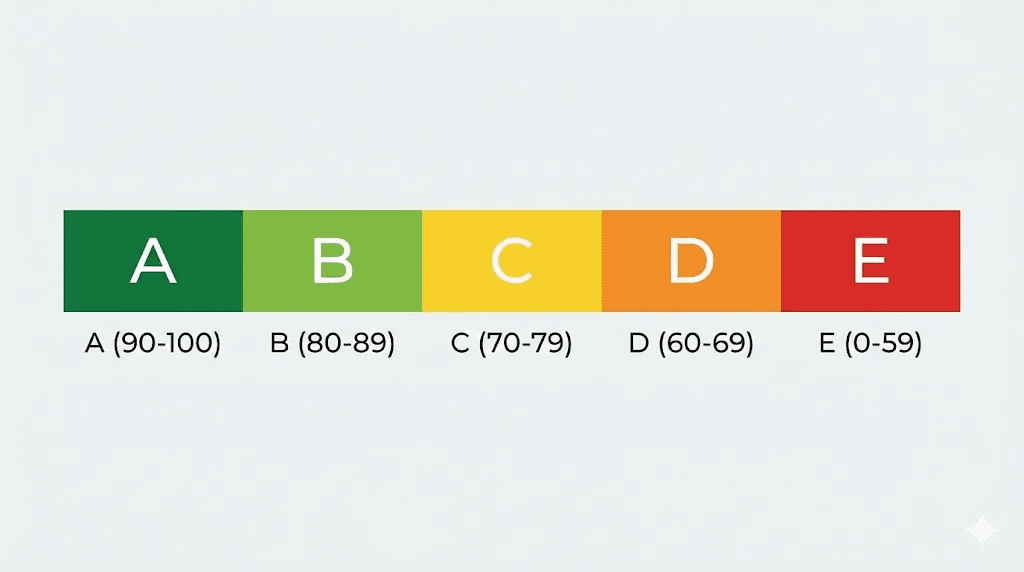
Finnrick uses a letter grading system from A (Great) to E (Bad) based on average scores and score consistency. A products average above 7.0 with no scores below 5.0. E products either average below 4.0 or have some scores below 3.0.
For researchers, this means HK Peptides shows clear product quality stratification. Their semaglutide and Melanotan II appear reliable. Their healing peptides like BPC-157 and GHK-Cu present significant quality risks. And their popular tirzepatide shows unacceptable batch variation despite reasonable averages.
The practical implication? If ordering from HK Peptides, consider independent testing of your specific batch before beginning any research protocol. The overall vendor averages obscure significant batch to batch variability.
How to verify HK Peptides purchases
Given the quality variation documented in independent testing, verification becomes essential rather than optional. Researchers can take several steps to confirm they have received legitimate, properly dosed product before beginning any protocol.
Understanding certificates of analysis
A Certificate of Analysis (COA) documents the testing performed on a specific batch of product. Legitimate COAs include HPLC purity data showing what percentage of the sample consists of the target peptide, mass spectrometry data confirming the molecular weight matches the expected compound, and batch numbers that correspond to your specific vials.
HK Peptides provides COAs on request. However, forum discussions have raised concerns about COA authenticity. One user reported receiving a Janoshik COA that appeared to belong to a different vendor, suggesting potential document recycling or fraud. This makes independent verification even more critical.
Janoshik verification process
Janoshik Analytical is considered the gold standard for independent peptide testing. They operate a verification system that allows you to confirm whether a COA actually originated from their laboratory.
To verify a Janoshik COA, locate the Task number at the top of the document. Visit janoshik.com/verify and enter this task number. The system will confirm whether that specific test exists in their database. You can also scan the QR code on legitimate Janoshik COAs for instant verification.
If a COA cannot be verified through this process, it may be fabricated or recycled from a different batch. Do not proceed with research until verification succeeds.
Independent testing of your batch
The most reliable verification involves testing your actual received product rather than relying on vendor provided documentation. This adds cost but eliminates uncertainty about what you actually possess.
Services like Janoshik and Finnrick accept sample submissions from researchers. The process typically involves sending a small portion of your reconstituted or lyophilized peptide for analysis. Results confirm purity, identity, and actual content weight.
For high value research or protocols where dosing accuracy matters significantly, this investment protects both your research validity and potential safety. A batch that scores 2.0 on Finnrick testing contains approximately 20% of the expected peptide content, meaning your dosing calculations would be off by a factor of five.
Red flags to watch for
Several warning signs suggest potential quality or authenticity issues. COAs claiming exactly 100.00% purity rarely represent real test results, as analytical variation always produces slight variations. Missing chromatograms or mass spectra suggest incomplete or fabricated documentation. Blurred batch numbers or laboratory details may indicate document manipulation.
Additionally, legitimate vendors provide batch specific COAs, not generic company wide documents. If the same COA appears for multiple different products or batch numbers, question its authenticity.
Community verification resources
The GLP-1 Forum and Peptide Source Forum contain extensive discussion threads about HK Peptides experiences. Searching for specific batch numbers or product experiences can reveal whether others have tested the same product. This crowdsourced verification provides additional data points beyond individual testing.
Peptide testing laboratories and peptide research forums serve as valuable resources for researchers navigating the verification process.
Community experiences and reviews
Beyond laboratory testing, community feedback provides qualitative insights into ordering experience, customer service, shipping reliability, and product consistency over time. Forum discussions reveal patterns that pure test data cannot capture.
Positive experiences
Multiple forum users report satisfactory transactions with HK Peptides. Common positive feedback includes fast shipping times, with some users receiving orders within a week of payment. Customer service receives praise for responsiveness, particularly when communicating through verified sales representatives.
One user specifically noted good experience with HK, good service, fast delivery and good quality, summarizing the positive feedback pattern. Another mentioned that their representative was helpful and product arrived in 10 days.
The availability of PayPal as a payment option receives frequent mention as a positive differentiator. Many Chinese peptide vendors require cryptocurrency or wire transfers, making PayPal availability notable for researchers preferring traditional payment methods.
Negative experiences and warnings
Concerns center on several areas. The COA authenticity issue mentioned earlier, where COAs from other vendors allegedly appeared as HK Peptide documentation, represents a significant trust concern. This suggests potential systematic documentation issues rather than isolated incidents.
Scam impersonation remains a persistent problem. Multiple warnings exist about individuals claiming to represent HK Peptides on TikTok who are actually scammers. The legitimate company has distanced itself from these accounts, advising customers to only order through verified representatives like Bella or Sue.
Tariff and customs issues have increased since early 2025 regulatory changes. Some users report being asked to pay additional tariffs, typically around 30 dollars, before receiving their shipments. This adds unexpected cost to orders and represents the new normal for Hong Kong to US shipping.
Sales representative confusion
Forum discussions reveal multiple sales representatives using different names, including Bella, Sue, Nicole, and Ailsa. One representative confirmed that Ailsa is me, Bella is me too, indicating the same person operates under multiple aliases. This practice confuses customers trying to verify they are communicating with legitimate company representatives.
The recommendation from experienced users is clear. Contact only through official channels, not social media platforms. Verify you are speaking with a known representative before sending payment. And be skeptical of anyone reaching out proactively, as this pattern typically indicates scammers rather than legitimate outreach.
Long term reliability concerns
An experienced forum member offered a broader warning about Chinese peptide vendors generally. It is common for a company to pop up, sell high quality products for six months to a year for little to no profit, then start making their profits later by selling junk. The safest bet is to stick with companies that have been around well over a year and have been consistent with quality.
HK Peptides has operated since 2020, giving them a track record of approximately five years. However, the Finnrick data showing some products with zero active content suggests quality may not remain consistent across all products or time periods.
Shipping and logistics
Understanding shipping logistics helps researchers plan timelines and budget for potential additional costs. Recent regulatory changes have significantly impacted peptide imports from China and Hong Kong to the United States.
Standard shipping times
HK Peptides offers express and standard shipping options. Express shipping typically delivers within 7 to 10 days for US destinations. Standard shipping can take 3 to 4 weeks, with some variability based on customs processing and final destination.
Users report relatively consistent shipping times when no customs issues occur. One user noted receiving their order within 7 days, though this likely represents express shipping. Another received product the day after paying an additional tariff, suggesting customs holds can extend timelines unpredictably.
Regulatory changes affecting imports
Significant changes in early 2025 dramatically impacted Chinese peptide imports. The de minimis exemption, which previously allowed shipments under 800 dollars to enter without formal customs processing, was eliminated for China and Hong Kong sourced goods as of May 2025.
This means all peptide shipments now require full customs declaration and duty assessment. Tariffs reaching 55% or higher apply to many peptide compounds classified as hormone derivatives. The practical result is increased cost and longer processing times for all Chinese peptide imports.
Additionally, Hong Kong Post suspended surface and air mail services for goods to the US as of May 2025, accepting only document mail. This forces vendors to use private courier services, which typically cost more but may process faster through customs.
Customs documentation requirements
Successful customs clearance requires proper documentation. Shipments should include clear labeling identifying the material as research use only and not for human consumption. Certificates of Analysis should accompany the shipment. Commercial invoices must accurately describe contents and value.
Peptide shipments are often delayed at customs due to missing or incomplete documentation. Researchers should ensure their vendor provides complete paperwork and should retain copies of all documentation for potential customs queries.
The FDA regulates peptide APIs even when imported for research purposes. Importers may need to provide additional documentation stating research use only status. Noncompliance can result in delays, penalties, or seizure of materials.
Cost considerations
Beyond product cost and base shipping fees, researchers should budget for potential tariffs. The 55% tariff rate on peptide compounds from China can significantly increase total costs. For example, a 100 dollar product order could incur 55 dollars in tariffs plus shipping fees and potential brokerage charges.
Some users report being asked to pay tariffs separately upon delivery, typically in the 30 dollar range for smaller orders. This represents an additional cost not always clearly communicated at the time of purchase.
Currency fluctuations between US dollars and Chinese yuan also affect pricing over time. Vendors may adjust prices periodically to account for exchange rate changes.
Cold chain considerations
Peptides require proper handling to maintain stability. Lyophilized peptides tolerate shipping at ambient temperature reasonably well for short periods. However, extended transit times or exposure to extreme temperatures can degrade product quality.
Proper peptide storage immediately upon receipt helps preserve potency. Room temperature stability varies by compound, with some tolerating brief exposure better than others. Refrigerator storage extends shelf life for most peptides once received.
Researchers ordering during summer months or to hot climates should consider expedited shipping to minimize temperature exposure during transit.
Payment methods and pricing
HK Peptides offers multiple payment options, differentiating them from vendors requiring only cryptocurrency. Understanding available methods helps researchers choose their preferred transaction approach.
Available payment methods
Bank transfer represents the traditional payment method for international peptide purchases. HK Peptides accepts wire transfers to their Chinese bank accounts. However, some vendors in this space have experienced frozen bank accounts due to Chinese regulatory action, which can disrupt this payment method periodically.
Cryptocurrency options include Bitcoin, USDT, and USDC. These provide pseudonymous transactions and avoid traditional banking system scrutiny. Transaction fees and exchange rate volatility represent considerations for cryptocurrency payments.
PayPal availability distinguishes HK Peptides from many competitors. PayPal offers buyer protection and familiar payment processing for researchers uncomfortable with cryptocurrency or international wire transfers. However, PayPal may limit or suspend accounts involved in peptide transactions if they detect such activity.
Some users report additional payment options including Apple Pay for certain transactions. Availability may vary based on order size and specific products.
Pricing structure
HK Peptides prices competitively with other Chinese vendors. Exact pricing fluctuates based on exchange rates, market conditions, and specific products. The GLP-1 Forum threads occasionally contain updated price lists shared by the vendor or customers.
Bulk pricing typically offers significant discounts. Researchers planning extended protocols may benefit from larger single orders rather than multiple smaller purchases, both for per unit cost and to minimize multiple shipping and tariff events.
Researchers should compare total cost including product, shipping, and anticipated tariffs rather than just product price when evaluating vendor options. A cheaper product price can become more expensive overall after adding 55% tariffs and higher shipping costs.
Payment security considerations
Wire transfers and cryptocurrency provide minimal recourse if products never arrive or arrive defective. PayPal offers dispute resolution but may side with buyers who claim product quality issues.
The community recommends starting with smaller test orders to verify vendor reliability before committing significant funds. This approach limits financial exposure while establishing trust through successful transactions.
Comparing HK Peptides to alternatives
Researchers evaluating HK Peptides should understand how they compare to other vendor options. The peptide sourcing landscape includes US domestic companies, other Chinese vendors, and various international sources.
Other Chinese vendors
QSC (Qingdao Sigma Chemical) represents the most discussed Chinese peptide vendor in research communities. They maintain both Chinese shipping and a US domestic warehouse for faster delivery. However, QSC has experienced customer service issues and frozen bank accounts that have disrupted operations periodically.
Finnrick Analytics rates QSC alongside HK Peptides, allowing direct quality comparison. Researchers should check current ratings as vendor quality can shift over time based on manufacturing changes or sourcing adjustments.
Other Chinese vendors like Asymchem focus on different market segments. Asymchem operates as a contract manufacturing organization serving pharmaceutical companies, making them less accessible to individual researchers but potentially higher quality for institutional purchasers.
US domestic vendors
Domestic US vendors eliminate international shipping and customs concerns but typically charge significantly higher prices. The trade off involves convenience and reduced regulatory complexity versus higher per unit costs.
Vendors like Amino Asylum, Core Peptides, and others maintain US based operations. Some source raw materials from China but perform final processing domestically. This hybrid approach provides faster shipping while potentially maintaining competitive pricing.
Quality verification remains important regardless of vendor location. US companies can still have quality issues, and the research use only label applies equally to domestic and international sources. Independent testing benefits researchers purchasing from any source.
Vendor rating comparisons
Finnrick Analytics maintains ratings for over 160 peptide vendors, enabling direct comparison based on independent test results. Their vendor ratings page shows overall safety ratings alongside product specific scores.
When comparing HK Peptides to alternatives, researchers should examine ratings for their specific compounds of interest rather than overall vendor scores. A vendor with excellent semaglutide but poor BPC-157 serves different researchers differently.
Selecting peptide vendors requires balancing multiple factors including quality consistency, price, shipping logistics, customer service, and payment options. No single vendor excels across all dimensions, making individual research needs the primary decision driver.
Safety and legal considerations
Peptide research involves navigating complex regulatory environments. Researchers must understand both the legal status of their activities and the safety implications of working with compounds from various sources.
Research use only classification
HK Peptides, like virtually all grey market vendors, labels products as research use only and not for human consumption. This labeling attempts to create legal distance from FDA regulation, which applies primarily to products intended for human therapeutic use.
The research use label represents what legal experts call a thin legal fiction. Products arrive in formats ready for injection. Vendors sometimes provide dosing guidance despite disclaiming therapeutic intent. The practical reality differs from the legal positioning.
This ambiguity creates risk for researchers. Importation of research chemicals generally remains legal, but authorities can challenge this classification if evidence suggests human use intent. The regulatory environment continues evolving, with increased scrutiny following widespread adoption of grey market GLP-1 agonists.
FDA perspective
The FDA has issued warnings about research peptides sold online. Products labeled as semaglutide, retatrutide, cagrilintide, tirzepatide, and similar compounds are considered unapproved new drugs when marketed with any suggestion of therapeutic use.
For compounds like retatrutide that remain investigational, the FDA states that these unregulated research chemical powders are for laboratory research purposes only. The only legitimate access to some compounds comes through clinical trials.
FDA approved alternatives exist for some compounds. Wegovy (semaglutide) and Zepbound (tirzepatide) provide clinically proven options under medical supervision. Researchers should understand the distinction between approved medications and research compounds.
Quality and safety risks
Peptides from unauthorized sources carry documented risks. Contamination with bacteria, heavy metals, or other substances can occur without pharmaceutical grade manufacturing controls. Under dosing or complete absence of active compound wastes research resources and produces invalid results.
Immune reactions represent a serious concern. The FDA has documented hospitalizations following peptide injections, including incidents at anti-aging festivals involving swollen tongues, breathing difficulties, and increased heart rate.
The lack of systematic safety monitoring creates what pharmacovigilance experts call an evidence vacuum. Individual anecdotes proliferate while serious adverse events remain undetected or unreported. This asymmetry can make grey market peptides appear safer than they actually are.
Supply chain transparency
Even vendors claiming US manufacturing often source raw active ingredients from China. The claim that peptides are made in the US may mean only that final dosing and lyophilization occur domestically, while synthesis happened overseas without oversight.
This supply chain opacity affects all market segments. Compounding pharmacies, research chemical suppliers, and grey market vendors all rely heavily on Chinese peptide synthesis. The difference lies in quality control standards, testing protocols, and regulatory oversight rather than manufacturing geography.
Researchers should approach all vendor claims with appropriate skepticism. Independent testing remains the only reliable method for confirming product quality regardless of vendor marketing.
Best practices for ordering from HK Peptides
Researchers who decide to order from HK Peptides can follow specific practices to maximize likelihood of positive outcomes. These recommendations synthesize community experience and quality data.
Product selection strategy
Focus on products with demonstrated quality. Based on Finnrick data, semaglutide (A rating) and Melanotan II (B rating) show the best quality consistency. PT-141 also appears promising though has fewer test data points.
Avoid products with E ratings unless planning independent testing. Their BPC-157, GHK-Cu, tesamorelin, and tirzepatide show unacceptable batch variation. The risk of receiving inactive or significantly under dosed product is too high for reliable research.
For products with C or D ratings like ipamorelin or retatrutide, budget for independent testing of each batch before incorporating into research protocols.
Order verification process
Request batch specific COAs before ordering if possible. Verify any Janoshik COAs through their official verification system. Be suspicious of any COA that cannot be independently verified.
Start with small test orders to evaluate vendor reliability. A single vial order that arrives properly packaged with verifiable documentation provides confidence for larger subsequent orders.
Submit samples from received products to independent testing before beginning research. The cost of testing pales compared to invalidated research results from unknown quality compounds.
Communication best practices
Contact only through official verified channels. The official HK Peptide website or verified forum contacts provide the safest communication path. Avoid anyone reaching out through TikTok or other social media, as scam impersonation is documented.
Document all communications. Keep records of order confirmations, payment receipts, tracking numbers, and any quality claims. This documentation proves valuable if disputes arise.
Be patient with response times. Chinese vendors operate across significant time zone differences from Western researchers. Allow 24 to 48 hours for responses before following up.
Shipping and receiving
Budget for potential tariffs. Plan for 55% or higher duty on declared value plus shipping. This additional cost should factor into total project budgets.
Track shipments actively. Know when packages clear customs and anticipate delivery. Having someone available to receive packages prevents products sitting in hot delivery vehicles or mailboxes.
Store products properly immediately upon receipt. Transfer to refrigerated storage for lyophilized peptides. Reconstituted peptides require even more careful temperature management.
Inspect packaging for damage or tampering. Vials should be intact with proper seals. Report any concerns to the vendor immediately with photographic documentation.
Calculating doses with verified peptides
Once researchers verify their HK Peptides products through independent testing, proper dosing calculations ensure accurate protocol implementation. Understanding peptide dosage calculations matters for reproducible research.
Reconstitution fundamentals
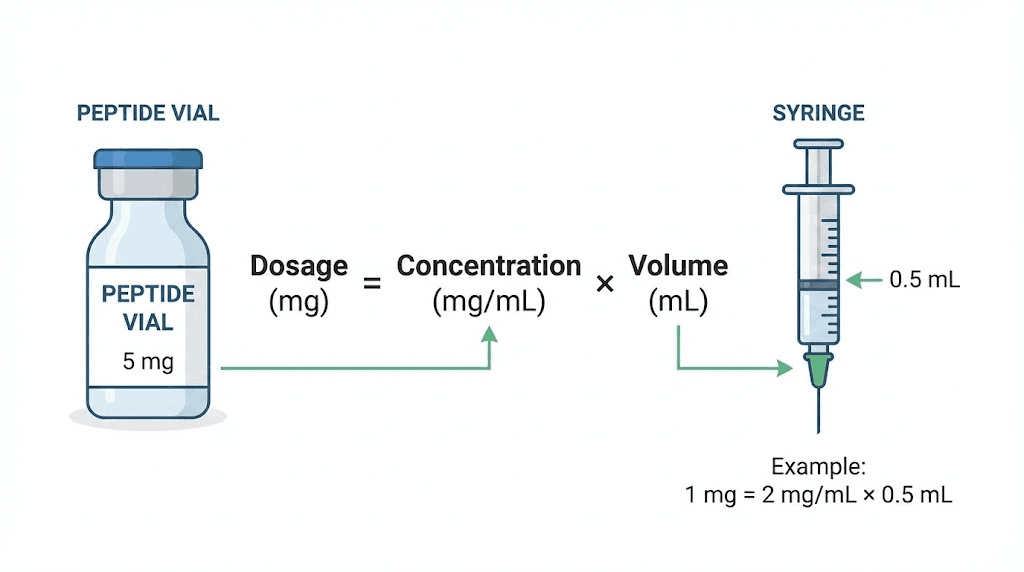
Most HK Peptides products arrive as lyophilized powder requiring reconstitution before use. The amount of bacteriostatic water added determines final concentration.
For a 10mg vial reconstituted with 2mL of bacteriostatic water, the resulting concentration equals 5mg per mL, or 5000mcg per mL. This simple math forms the basis for all subsequent dose calculations.
The peptide reconstitution calculator helps researchers determine appropriate water volumes for their target concentrations.
Adjusting for actual purity
Here is where independent testing becomes critical. If a vial labeled as 10mg actually contains only 7mg based on testing, all dosing calculations must adjust accordingly.
A batch scoring 70% on purity testing means the actual peptide content is 70% of labeled amount. That 10mg vial contains approximately 7mg of active peptide. Researchers must either adjust water volume or injection amounts to achieve intended doses.
This adjustment becomes impossible without knowing actual content. Researchers using products with unknown or assumed purity introduce significant dosing uncertainty into their protocols.
Compound specific considerations
Different peptides have different typical research dosing ranges. BPC-157 dosing typically uses 250 to 500mcg amounts. GHK-Cu dosing varies based on application method. MOTS-c dosing follows different protocols entirely.
The peptide calculator helps researchers determine injection volumes based on reconstitution and target dose. BPC-157 specific calculators, semaglutide calculators, and TB-500 calculators provide compound specific guidance.
Researchers should consult relevant scientific literature for dosing protocols used in published studies. Peptide research literature provides the foundation for evidence based protocol design.
Frequently asked questions
Is HK Peptides a legitimate company?
HK Peptides operates as a real business that has fulfilled orders for multiple years. Finnrick Analytics has tested 225 samples from their products. However, legitimate does not mean high quality, as their test results show significant variation from excellent to very poor depending on the specific product. Forum users confirm receiving real products, though quality consistency remains a documented concern.
How long does HK Peptides shipping take to the USA?
Express shipping typically delivers within 7 to 10 days. Standard shipping takes 3 to 4 weeks on average. Customs processing can add additional time, and tariff payment requirements may cause delays if researchers are not prepared to pay duties upon delivery.
What payment methods does HK Peptides accept?
HK Peptides accepts bank transfers, Bitcoin, USDT, USDC, and PayPal. The PayPal option distinguishes them from many Chinese vendors that only accept cryptocurrency or wire transfers. Payment method availability may vary based on order size or specific products.
Which HK Peptides products have the best quality ratings?
According to Finnrick Analytics testing, semaglutide receives an A rating (Great) and Melanotan II receives a B rating (Good). PT-141 shows promising B rated results though with fewer test samples. Products like BPC-157, GHK-Cu, and tirzepatide receive E ratings (Bad) due to significant batch variation including some batches with zero active content.
How can I verify an HK Peptides COA is real?
For Janoshik COAs, visit janoshik.com/verify and enter the Task number from the document. Legitimate COAs will appear in their database. You can also scan QR codes on authentic Janoshik certificates. If a COA cannot be verified through these methods, consider it potentially fabricated and do not rely on it for quality assurance.
Are HK Peptides safe to use?
This guide covers peptide safety considerations generally. HK Peptides products are labeled for research use only and not for human consumption. The quality variation documented in independent testing means some batches may contain contaminants or incorrect dosing. Researchers should conduct independent testing and understand that grey market peptides lack the safety oversight of pharmaceutical products.
What is the difference between HK Peptides and HK Peptide?
Multiple entities use similar names including HK Peptides Worldwide (founded in Hong Kong 2020), HK Peptide operated by Henan Kuisu Technology (mainland China), and HENGKUN Peptides. Most forum discussions reference HK Peptide (Henan Kuisu Technology) when discussing quality and experiences. Researchers should clarify which entity they are dealing with before ordering.
Does HK Peptides offer refunds for quality issues?
HK Peptide claims to bear costs and reissue products if quality problems are confirmed through testing. However, this requires proving quality issues through independent testing, which adds cost and time. Community experiences with refund claims vary. Starting with small test orders reduces financial risk from potential quality issues.
External resources
For researchers serious about optimizing their peptide protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions. Understanding how peptides work, proper dosing protocols, and common mistakes to avoid helps researchers achieve better outcomes regardless of their chosen vendor.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your verification processes stay thorough, your peptides stay potent, and your research stay productive.



