Jan 3, 2026

Ovagen represents the Russian bioregulator peptide category targeting hepatic (liver) and gastrointestinal system optimization through short peptide sequences extracted from liver and digestive tissues. The bioregulator approach proposes organ-specific cellular communication supporting function optimization, detoxification capacity, and age-related decline reversal through naturally-derived peptide signals rather than synthetic receptor-specific compounds dominating Western peptide therapy.
The liver-specific targeting makes Ovagen relevant for individuals experiencing hepatic stress from medications, alcohol consumption, metabolic syndrome, fatty liver concerns, age-related liver function decline, or general digestive system optimization.
Western medicine offers limited peptide options for liver support - BPC-157 shows some hepatoprotective effects but wasn't designed specifically for liver tissue, while Ovagen represents purpose-built hepatic bioregulation according to Russian peptide theory.
Evidence challenges persist with Russian bioregulators - Soviet/Russian research rarely meets Western randomized controlled trial standards, independent replication proves limited, mechanisms remain incompletely elucidated, and English-language validation stays minimal.
This guide examines Ovagen through available evidence, realistic assessment, dosing protocols, safety considerations, and comparison to alternatives helping determine whether this bioregulator represents legitimate hepatic support or insufficiently-validated experimental intervention.
Russian bioregulator category overview
Understanding Ovagen's classification.
Bioregulator peptide theory
Core concepts:
Short peptides (2-4 amino acids typically)
Extracted from healthy young animal organs
Organ-specific tissue communication
Cellular function optimization support
Gene expression influence proposed
Historical development:
Soviet-era research 1970s-1990s
Professor Vladimir Khavinson led work
St. Petersburg Institute of Bioregulation and Gerontology
Military and longevity applications initially
Continued research in modern Russia
Mechanism proposed:
Peptides enter cells and reach nucleus
Interact with DNA regulatory regions
Influence protein synthesis patterns
Support cellular repair processes
Restore age-related function decline
Different from Western peptides:
Western: Synthetic, receptor-targeting (like semaglutide)
Bioregulators: Natural extract, cellular communication
Western: Single pathway, well-understood
Bioregulators: Multi-level regulation, theory-based
Evidence: Western RCTs vs Russian observational
Learn about what peptides are and how peptides work.
Ovagen-specific characteristics
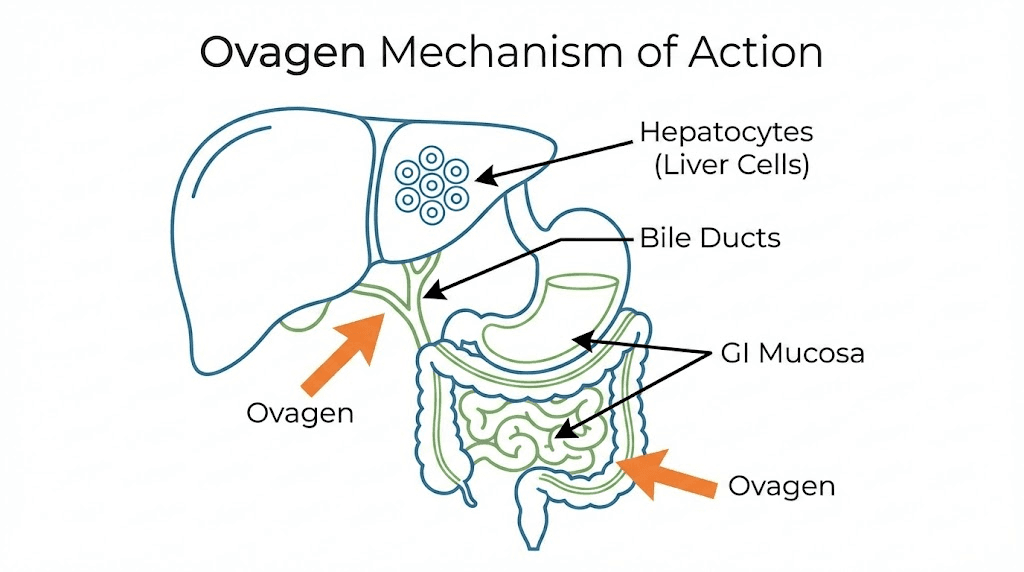
Hepatic targeting:
Source tissue: Liver (young healthy animals)
Target human tissue: Liver, digestive system
Specific focus: Hepatocytes, GI mucosa
Application: Liver health, digestion optimization
Mechanism: Bioregulatory cellular communication
Other bioregulators for reference:
Epitalon: Pineal gland, longevity, telomeres
Cartalax: Cartilage, joint health
Chonluten: Respiratory system, lungs
Vesugen: Vascular system, blood vessels
Ovagen: Liver, digestive system
Each targets specific organ system
Why liver targeting matters:
Liver central to detoxification
Metabolic functions critical
Age-related decline significant
Few Western peptide alternatives
High interest in liver support
Liver and digestive applications
What Ovagen targets.
Primary liver conditions
Fatty liver disease (NAFLD/NASH):
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease support
Metabolic syndrome liver component
Adjunct to lifestyle interventions
May support hepatocyte function
Russian research shows promise
Fatty liver approach:
Continue dietary modifications
Maintain exercise program
Add Ovagen as supportive therapy
Monitor liver enzymes
Medical supervision essential
Alcohol-related liver stress:
Chronic alcohol consumption effects
Hepatic tissue damage from drinking
Support during reduction/cessation
Not excuse to continue drinking
Harm reduction approach
Alcohol protocol considerations:
Ideally combined with reduced consumption
Liver support during recovery
Not protection for continued abuse
Medical oversight recommended
Realistic expectations critical
Medication-induced hepatotoxicity:
Pharmaceutical liver stress support
Multiple medication burden
Age-related medication accumulation
Preventive hepatoprotection
Adjunct to necessary medications
Medication support approach:
Continue required medications
Medical supervision essential
Monitor liver function tests
Ovagen as supportive addition
Never replace medical management
Additional liver applications
Age-related liver decline:
Natural hepatic function decrease
Reduced detoxification capacity
Metabolic efficiency decline
Preventive optimization focus
Longevity application interest
Aging liver protocol:
Starting 40-50+ years typically
2-3 cycles annually maintenance
Long-term preventive approach
Benefits difficult to measure
Health optimization mindset
Post-hepatitis recovery:
After acute hepatitis resolution
Viral hepatitis B or C support
Tissue regeneration assistance
Under medical care always
Long-term liver health focus
Metabolic syndrome support:
Insulin resistance liver component
Lipid metabolism optimization
Central obesity liver effects
Comprehensive metabolic approach
Part of broader intervention
Digestive system applications
General GI function optimization:
Mucosal tissue support
Digestive enzyme function
Gut-liver axis optimization
Overall digestive health
Preventive maintenance
Inflammatory bowel conditions:
Supportive therapy only
Continue medical treatment
Mucosal healing support claimed
Limited evidence for this use
Medical supervision required
Gut-liver axis support:
Intestinal permeability concerns
Liver-gut communication
Microbiome-liver interactions
Systemic optimization approach
Emerging interest area
See peptide safety and risks for general safety information.
Available research and evidence quality
What studies actually show.
Russian research summary
Published Russian studies:
Multiple Russian-language papers
Primarily Khavinson institute research
Small sample sizes (20-100 participants)
Observational designs predominantly
Positive results claimed consistently
Study design characteristics:
Before-after comparisons common
No randomized controlled trials mostly
Placebo control often absent
Subjective and objective measures mixed
Short-term follow-up typical
Claimed benefits from Russian research:
Improved liver enzyme markers (ALT, AST)
Enhanced detoxification capacity
Reduced hepatic inflammation markers
Better digestive function reported
Tissue regeneration indicators improved
Specific findings examples:
ALT/AST reduction 15-25% reported
Improved ultrasound liver appearance
Reduced fatty infiltration claimed
Better quality of life scores
Fewer digestive complaints
Study quality concerns:
Publication bias (positive results published)
Small sample sizes limit power
Lack of independent replication
Conflict of interest (institute produces product)
Translation accuracy questions
Overall: Low quality by Western standards
Western evidence gap
Western research status:
Essentially no English-language studies
No randomized controlled trials
Mechanism not validated Western science
Independent verification absent
Skepticism warranted from Western view
Why Western validation lacking:
Natural extract (limited patent potential)
Language barrier limits access
Different research paradigm (bioregulation)
Western focus on synthetic compounds
Regulatory challenges importing products
The evidence problem:
Russian studies positive but limited quality
Western validation completely absent
Mechanism unclear by Western standards
User testimonials unreliable evidence
Cannot make confident efficacy claims
What good evidence requires:
Large randomized controlled trials
Double-blind placebo-controlled design
Independent replication multiple sites
Mechanistic studies explaining pathway
High-impact journal publication
None of this exists for Ovagen
Anecdotal user reports
What users self-report:
Some improved digestion noted
Better alcohol tolerance claimed
Reduced fatigue reported (some)
Lab improvements mentioned (anecdotal)
Highly variable individual responses
Positive anecdotal feedback:
"Digestion improved after 1 month"
"Liver enzymes decreased per bloodwork"
"Less bloating and better energy"
"Alcohol hangovers less severe"
"Feel cleaner and lighter overall"
Neutral/negative reports:
"Didn't notice any difference"
"Hard to tell if working"
"Too subtle to confirm"
"Labs unchanged after cycle"
"Not worth the cost personally"
Anecdotal evidence problems:
Placebo effect very powerful
Natural improvement over time
Lifestyle changes confound (diet, exercise)
Confirmation bias (want it to work)
Selective reporting (positive more shared)
Cannot draw conclusions from testimonials
User feedback reality:
Mixed reports typical
Some enthusiastic testimonials exist
Many report subtle or no effects
Few report negative experiences
Variable responses suggest placebo component
See peptide research and studies for evidence evaluation.
Dosing protocols and administration
How Ovagen is used.
Standard Russian dosing protocol
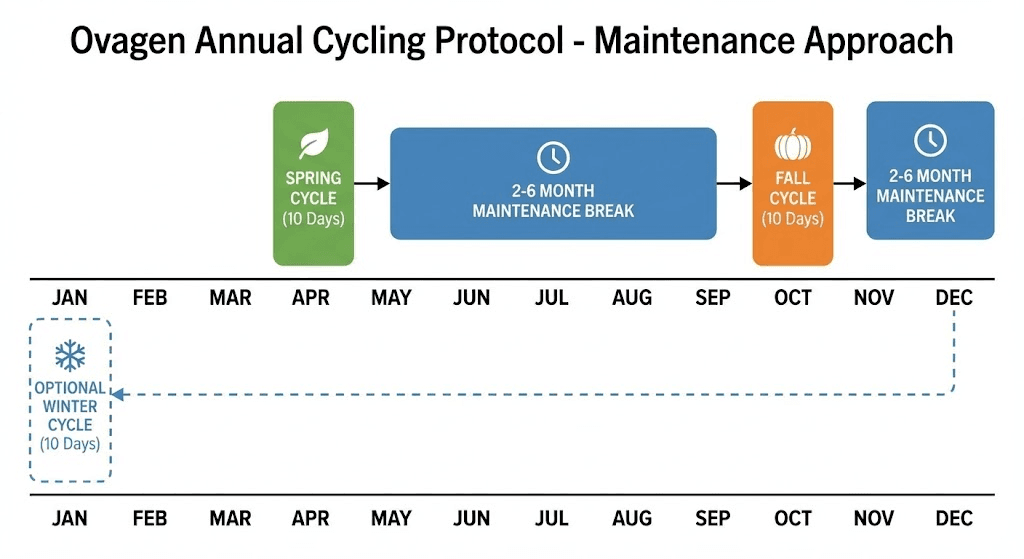
Typical cycle structure:
10-20 capsules per cycle (10mg each)
10-20 days continuous dosing
2-3 cycles annually recommended
Break periods between cycles
Maintenance approach long-term
Common dosing schedule:
Days 1-10: One 10mg capsule daily
Break: 2-6 months off
Repeat: 2-3 times per year
Timing: Spring, fall cycles common
Flexibility: Schedule adaptable to needs
Dosing rationale (Russian theory):
Bioregulatory signals provided cyclically
Body continues optimization during break
Continuous dosing unnecessary
Cost-effective cycling approach
Follows Russian bioregulator tradition
Administration methods
Oral capsules (most common):
Convenient self-administration
Take on empty stomach preferred
Morning 20-30 minutes before breakfast
Swallow with water
Most user-friendly method
Oral administration tips:
Consistent timing daily
Empty stomach for absorption
Avoid food 30 minutes after
Stay hydrated throughout day
Most practical long-term
Sublingual administration:
Under tongue 1-2 minutes
Better absorption than swallowing
Open capsule, place under tongue
Slightly less convenient
Some users prefer this
Subcutaneous injection:
Highest bioavailability theoretically
Requires reconstitution (if powder)
Similar to other peptide injections
More complex preparation
Used by experienced peptide users only
Route comparison:
Oral: Easiest, adequate bioavailability
Sublingual: Moderate convenience, better absorption
Injection: Hardest, highest bioavailability
Most choose: Oral for simplicity
Cycle frequency and timing
Annual cycle recommendations:
2-3 cycles per year: Standard approach
Spring cycle: March-April typical
Fall cycle: September-October typical
Optional third: Winter December-January
Flexibility: Adjust based on needs
Timing considerations:
After periods of liver stress (holidays, travel)
Before anticipated challenges (events, celebrations)
Seasonal health optimization
Personal health calendar
No strict rules required
Long-term maintenance strategy:
Years-long commitment for prevention
Not acute treatment approach
Cumulative benefits proposed
Patience required for assessment
Lifestyle foundation essential
Special considerations:
Combine with liver-healthy diet
Reduce alcohol if applicable
Maintain exercise routine
Monitor liver function periodically
Medical supervision recommended
Use peptide calculator for protocol planning and cost calculator for budgeting.
Realistic benefits expectations
What you might actually experience.
Likely outcomes by condition
Fatty liver disease:
Modest enzyme improvement possible
May slow progression (unproven)
Lifestyle changes still primary
Adjunct benefit uncertain
Realistic: Possible supportive benefit
Alcohol-related stress:
May ease recovery if reducing consumption
Not protection for continued abuse
Tissue support theoretical
Best with cessation/reduction
Realistic: Uncertain benefit, don't rely on it
Medication-induced stress:
Possible hepatoprotective support
Continue monitoring liver function
Don't assume protection
Medical supervision essential
Realistic: Unknown added protection
Age-related decline:
Preventive benefits unverifiable
Effects too subtle to measure
Long-term commitment required
No clear endpoints
Realistic: Unknown, possibly placebo
Digestive symptoms:
Some improvement possible
Many factors influence digestion
Hard to attribute to Ovagen
Dietary changes more impactful
Realistic: Subtle if any
Who might benefit most
Best candidate characteristics:
Mild liver issues (not severe disease)
Under medical supervision
Realistic expectations maintained
Already optimizing lifestyle
Patient for subtle effects
Comfortable with uncertainty
Good candidate profiles:
Health optimization focus
Preventive medicine mindset
Can afford experimental therapy
Open to alternative approaches
Long-term perspective
Complement to conventional care
Who probably won't benefit:
Severe liver disease (needs proven treatments)
Expecting dramatic rapid results
Unwilling to change lifestyle
Very skeptical mindset (placebo less likely)
Acute liver failure (emergency care needed)
Looking for quick fix
Timeframe for potential results
Typical progression if working:
Weeks 1-2: Usually nothing noticeable
Weeks 3-4: May notice subtle digestion changes
Months 2-3: Lab improvements possible
Months 3-6: Maximum effects if responding
Long-term: Maintenance of benefits unclear
Important timeline notes:
Effects develop slowly if at all
Most changes subtle and subjective
Labs provide objective measure (sometimes)
Natural variation confounds assessment
Patience absolutely essential
Expect gradual subtle changes only
Measurement approaches:
Liver function tests (ALT, AST, GGT)
Imaging (ultrasound for fatty liver)
Symptom scales (subjective)
Energy levels (very subjective)
Objective measures preferred when possible
Safety profile and side effects
What to watch for.
General safety assessment
Overall safety profile:
Bioregulators generally well-tolerated
Low toxicity in Russian studies
Minimal side effects typically
Long-term safety data limited
No major safety concerns identified
Appears relatively safe overall
Safety rationale:
Natural tissue-derived peptides
Short amino acid sequences (2-4)
Low doses administered
Decades of Russian use reported
No serious adverse events widespread
Similar profile to other bioregulators
Safety data limitations:
Long-term Western studies absent
Manufacturing quality variable
Purity testing inconsistent
Individual responses vary
Allergic reactions possible
Safety assumed more than proven
Reported side effects
Common side effects (even these rare):
Mild digestive upset occasionally
Nausea (uncommon)
Loose stools (rare)
Injection site reactions (if injecting)
Most users: Zero side effects
Side effect profile: Very minimal
Uncommon reactions:
Allergic responses (very rare)
Skin reactions possible
Headache mentioned occasionally
Fatigue initially (paradoxical)
Hard to confirm causation
Serious reactions extremely rare
What to monitor:
Digestive symptoms changes
Allergic reaction signs
Worsening liver function (get labs)
New unusual symptoms
General wellbeing
Report concerns to doctor immediately
Contraindications and precautions
Who should avoid Ovagen:
Pregnancy and breastfeeding (no safety data)
Acute liver failure (medical emergency)
Severe hepatic disease (medical focus first)
Known allergies to animal proteins
Children (no pediatric data)
Consult doctor if any doubt
Medical supervision recommended:
Existing liver disease
Taking hepatotoxic medications
Multiple chronic conditions
Monitoring liver function
Adjusting treatments
Never replace medical care
Drug interaction concerns:
Unknown interaction potential
Inform doctor about all supplements
Monitor closely with medications
Bioregulators poorly studied for interactions
Conservative approach safest
Full disclosure to medical team
Special populations:
Elderly: Start cautiously, monitor closely
Compromised liver: Medical supervision essential
Multiple medications: Extra caution warranted
Chronic disease: Comprehensive care coordination
Individualize approach always
See comprehensive peptide safety and risks guide.
Comparing to alternative approaches
Ovagen vs other liver support options.
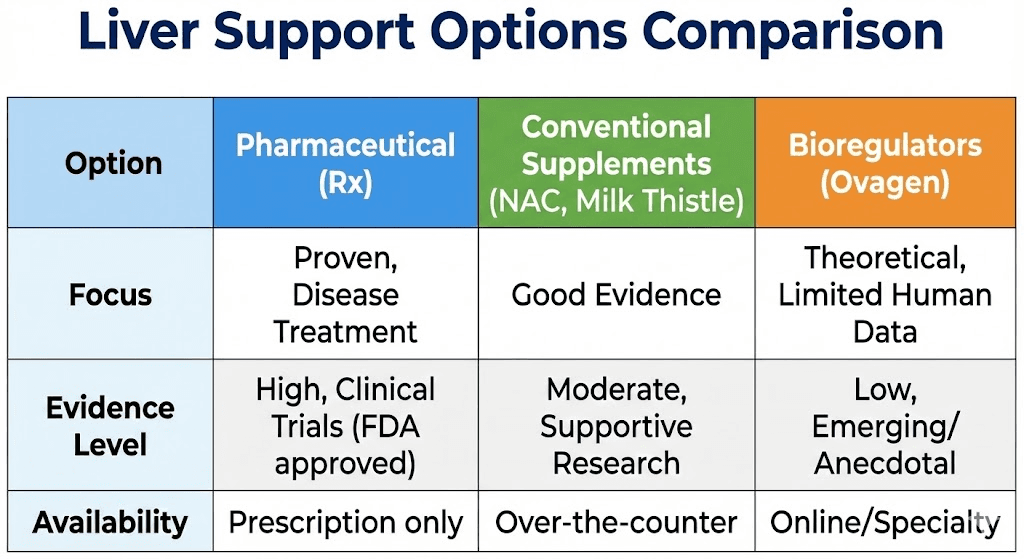
Vs Western hepatoprotective peptides
Limited Western peptide options:
Few peptides specifically target liver
BPC-157: General healing, some hepatoprotection
TB-500: Tissue repair, systemic
No direct Western liver-specific equivalent
Different mechanisms entirely
Ovagen theoretical advantages:
Specific liver/GI targeting
Organ-specific bioregulation approach
Decades of Russian use
Oral administration convenient
Designed for hepatic tissue
Western peptide advantages:
Much better research quality
Mechanisms better understood
More medical acceptance
Higher confidence in effects
Proven safety profiles
Comparison conclusion:
Western: Better evidence, not liver-specific
Ovagen: Liver-specific, weaker evidence
Could potentially combine both
Different proposed mechanisms
Choose based on evidence vs theory preference
Vs conventional liver supplements
Natural supplement comparison:
NAC (N-acetylcysteine):
Strong evidence for liver protection
Antioxidant mechanism well-studied
Used medically (acetaminophen overdose)
Cheaper than Ovagen typically
Better evidence overall
Milk thistle (silymarin):
Some research supporting benefit
Traditional use extensive
Hepatoprotective effects shown
Variable product quality
More established than Ovagen
TUDCA (tauroursodeoxycholic acid):
Bile acid with hepatoprotection
Good research supporting use
Expensive but effective
Medical-grade options exist
Strong evidence base
SAMe (S-adenosylmethionine):
Liver health support shown
Methylation support
Mood benefits additionally
More expensive than basics
Decent evidence base
Ovagen positioning:
More theoretical than evidence-based
Unique bioregulator mechanism proposed
Less studied than conventional supplements
More expensive than some alternatives
Experimental vs established
Vs medical hepatoprotective treatments
Pharmaceutical liver treatments:
Prescription medications when needed
Evidence-based proven efficacy
Medical supervision required
Disease-specific targeting
Gold standard when applicable
When pharmaceuticals needed:
Diagnosed liver disease
Significant hepatic impairment
Viral hepatitis treatment
Advanced fibrosis/cirrhosis
Medical treatment priority always
Ovagen role in hierarchy:
Preventive/optimization focus
Adjunct to medical care only
Not replacement for treatment
Experimental supportive approach
Secondary to proven therapies
Combination approaches
Using Ovagen with other interventions.
Lifestyle foundation (essential)
Diet optimization:
Liver-healthy Mediterranean diet
Reduced processed foods
Limited alcohol consumption
Adequate protein intake
Antioxidant-rich foods
Foundation for any liver support
Exercise benefits:
Improves fatty liver
Enhances detoxification
Supports metabolic health
Reduces inflammation
Essential component always
Stress management:
Reduces systemic inflammation
Improves liver function
Supports overall health
Sleep optimization critical
Foundational intervention
Combining with supplements
Ovagen + NAC combination:
Different mechanisms potentially
NAC: Antioxidant pathway
Ovagen: Bioregulation pathway (theory)
May be complementary
Monitor response
Ovagen + Milk Thistle:
Traditional plus novel approach
Milk thistle: Established use
Ovagen: Experimental addition
Combining reasonable
Cost considerations matter
Multiple supplement cautions:
More isn't always better
Monitor liver function
Watch for interactions
Expensive combining many
Focus on essentials first
Medical integration
Communicating with doctor:
Disclose all supplements
Share bioregulator use
Monitor labs regularly
Adjust based on results
Full transparency essential
Working with medical team:
Ovagen as adjunct only
Continue prescribed treatments
Regular monitoring crucial
Evidence-based care priority
Supplement secondary role
Sourcing and quality considerations
Finding reliable Ovagen.
Vendor options
Russian pharmaceutical sources:
Original manufacturers (Khavinson institute)
Highest authenticity confidence
Import challenges possible
Language barrier for some
Quality control established
Western supplement distributors:
Some carry Russian bioregulators
Convenience for Western buyers
Quality verification challenging
Third-party testing rare
Authenticity concerns possible
Quality verification challenges:
No standardized testing
COAs rarely provided
Purity hard to verify independently
Authenticity difficult to confirm
Trust vendor reputation primarily
Cost considerations
Typical pricing:
10-capsule pack: $30-60
20-day cycle: $60-120
Annual cost (2-3 cycles): $120-360
More than basic supplements
Less than pharmaceuticals
Cost-benefit analysis:
Uncertain benefits vs definite cost
Experimental investment
Compare to proven alternatives
Personal budget matters
Risk-benefit-cost trade-off decision
Value assessment:
Conventional supplements cheaper often
Proven options may offer better value
Unique mechanism theoretical appeal
Personal experimentation tolerance
Decide based on priorities
How you can use SeekPeptides
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive peptide guidance including Russian bioregulators and Western alternatives. Learn about Epitalon peptide benefits, Cartalax peptide, Chonluten peptide, BPC-157 complete guide, TB-500 benefits.
Access fundamental guides - what are peptides, how peptides work, getting started with peptides, peptide safety and risks, peptide research and studies.
Use planning tools - peptide calculator, cost calculator, reconstitution calculator.
Your decision requires personal risk-benefit assessment balancing relatively safe profile with minimal reported side effects against highly uncertain efficacy due to limited high-quality research. Appropriate for experimental-minded individuals exploring liver optimization adjuncts under medical supervision while maintaining evidence-based interventions including lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise, alcohol reduction), conventional supplements with stronger evidence (NAC, milk thistle, TUDCA), and pharmaceutical treatments when medically indicated for diagnosed liver conditions.
The bioregulator peptide category - including Epitalon, Cartalax, Chonluten, and Ovagen - occupies unique position within broader peptide therapy landscape combining decades of Russian research suggesting safety and theoretical benefits with Western evidence gap requiring users comfortable with uncertainty to navigate through informed personal decision-making rather than established medical consensus, weighing interesting theoretical mechanisms against limited validation meeting contemporary pharmaceutical research standards.
Related bioregulator and liver support resources
Epitalon peptide benefits - Longevity bioregulator
Cartalax peptide - Joint bioregulator
Chonluten peptide - Respiratory bioregulator
BPC-157 complete guide - Healing peptide (some liver benefits)
TB-500 benefits - Tissue repair peptide