Dec 29, 2025

Probably you've seen impressive weight loss data from clinical trials showing 15-25% body weight loss with the combination, but you don't understand the mechanisms, proper dosing protocols, how to source these peptides, whether you can combine them yourself, or if the combination is safe.
You just need clear guidance on cagrilintide and semaglutide used together.
Cagrilintide is an amylin analog that complements semaglutide's GLP-1 mechanism by slowing gastric emptying, reducing appetite through different brain pathways, and enhancing satiety. The CagriSema combination produces 15-25% body weight loss (superior to semaglutide's 10-15% alone) by targeting multiple weight regulation pathways simultaneously. Dosing typically combines semaglutide 2.4mg weekly with cagrilintide 2.4mg weekly, though research protocols vary. This dual-peptide approach represents the next evolution in medical weight loss.
This guide breaks down exactly what cagrilintide is and how it differs from GLP-1s, why combining cagrilintide and semaglutide produces synergistic weight loss, complete dosing protocols for the combination, clinical trial results and real-world outcomes, side effects and management strategies, comparing CagriSema to other weight loss combinations, sourcing considerations, and protocols for maximum safe weight loss.
Let's start with understanding what cagrilintide is and why it's paired with semaglutide.
What is cagrilintide and how does it differ from semaglutide
Cagrilintide: Long-acting amylin analog
What cagrilintide is:
Synthetic analog of amylin (human hormone)
Long-acting formulation (weekly dosing)
Developed by Novo Nordisk
Currently in Phase 3 clinical trials
Not yet FDA approved (as of 2024)
Paired with semaglutide as "CagriSema"
How amylin works naturally:
Co-secreted with insulin from pancreatic beta cells
Released after meals
Slows gastric emptying (food stays in stomach longer)
Reduces glucagon secretion
Signals satiety to brain
Regulates postprandial glucose
Cagrilintide's mechanisms:
Mimics natural amylin but lasts much longer
Dramatically slows gastric emptying
Increases satiety and fullness
Reduces food intake
Lowers postprandial glucose
Works on amylin receptors (different from GLP-1)
Primary benefits:
Powerful appetite suppression
Extended feeling of fullness
Reduced meal frequency
Lower caloric intake
Glucose regulation
Complements GLP-1 action
Learn about peptides, how peptides work, and what are peptides used for in our foundational guides.
Semaglutide: GLP-1 receptor agonist
What semaglutide is:
GLP-1 (glucagon-like peptide-1) receptor agonist
FDA approved for weight loss (Wegovy)
Also approved for diabetes (Ozempic)
Weekly injection
Well-established safety profile
Most popular weight loss peptide
How GLP-1 works:
Mimics natural GLP-1 hormone
Increases insulin secretion (glucose-dependent)
Suppresses glucagon
Slows gastric emptying (moderate)
Reduces appetite via brain centers
Increases satiety
Semaglutide's benefits:
10-15% average body weight loss
Improved glucose control
Cardiovascular benefits
Reduced food cravings
Better metabolic health
Established track record
See our peptides for weight loss, best peptides for weight loss, semaglutide dosage calculator, semaglutide vs tirzepatide, and best peptide stack for weight loss.
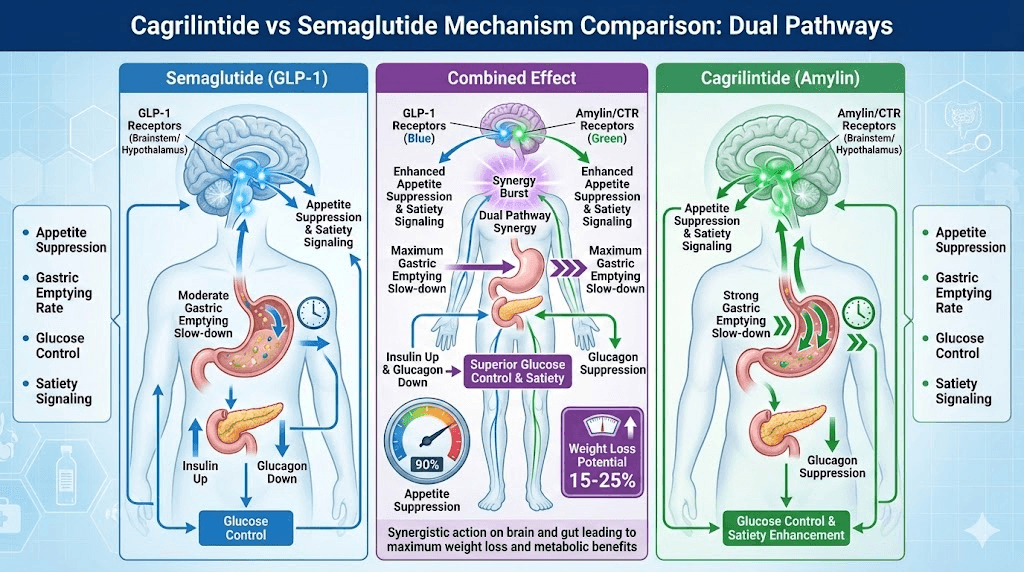
Key differences between cagrilintide and semaglutide
Mechanism:
Cagrilintide: Amylin receptor agonist
Semaglutide: GLP-1 receptor agonist
Different pathways, complementary effects
Gastric emptying:
Cagrilintide: Very strong effect (dramatic slowing)
Semaglutide: Moderate effect
Combined: Maximum slowing
Appetite suppression:
Cagrilintide: Works via amylin/calcitonin receptors
Semaglutide: Works via GLP-1 receptors in brain
Combined: Dual-pathway suppression
Side effects:
Cagrilintide: More nausea/GI effects (stronger gastric slowing)
Semaglutide: Moderate GI effects
Combined: Higher side effect risk but manageable
Approval status:
Cagrilintide: Investigational (not approved)
Semaglutide: FDA approved
CagriSema combination: Phase 3 trials
Weight loss monotherapy:
Cagrilintide alone: 10-12% body weight loss
Semaglutide alone: 10-15% body weight loss
Combined: 15-25% body weight loss
Why combining cagrilintide and semaglutide works synergistically
The combination targets weight loss through multiple pathways.
Complementary mechanisms of action
Dual appetite suppression:
Semaglutide: GLP-1 receptors in arcuate nucleus (brain)
Cagrilintide: Amylin/CTR receptors in area postrema (brain)
Two different brain pathways → stronger appetite reduction
More comprehensive hunger control
Enhanced gastric emptying delay:
Semaglutide: Moderate gastric emptying slowdown
Cagrilintide: Very strong gastric emptying slowdown
Combined: Maximum slowdown without complete stasis
Extended fullness after meals
Multiple satiety signals:
Semaglutide: Increases satiety hormones
Cagrilintide: Direct satiety signaling via amylin
Combined: Multiple satiety pathways activated
Earlier meal termination
Glucose regulation:
Semaglutide: Glucose-dependent insulin secretion
Cagrilintide: Glucagon suppression + slowed gastric emptying
Combined: Superior glucose control
Beneficial for diabetes + obesity
Clinical trial results: CagriSema superiority
STEP trials (semaglutide alone):
Average weight loss: 10-15% body weight
At 2.4mg weekly dose
68 weeks duration
Well-established efficacy
Cagrilintide monotherapy trials:
Average weight loss: 10-12% body weight
At 2.4mg weekly dose
Similar timeline
Comparable to semaglutide
CagriSema combination trials (Phase 2/3):
Average weight loss: 15-25% body weight
Significantly superior to either alone
Some participants lost 25%+ (exceptional responders)
68 weeks duration
Synergistic effect confirmed
Key findings:
50-60% more weight loss than semaglutide alone
More patients achieving >20% weight loss
Better glycemic control
Maintained lean mass better
Side effects manageable with proper titration
Real-world implications:
CagriSema could help patients lose 40-60 lbs (starting 240 lbs)
Semaglutide alone: 24-36 lbs (same starting weight)
Game-changing for significant obesity
May reduce need for bariatric surgery
See our peptides for fat loss and ozempic alternatives.
Why dual-pathway targeting is more effective
Single pathway limitations:
GLP-1 alone eventually plateaus
Body compensates over time
Weight loss slows after 6-12 months
Some people don't respond optimally
Dual pathway advantages:
Harder for body to compensate
Multiple redundant systems targeted
Sustained weight loss longer
Better for non-responders to single therapy
Mechanistic synergy:
Amylin + GLP-1 naturally work together
Both released after meals normally
Physiologic combination
Not forcing unnatural state
Clinical implications:
Patients who plateau on semaglutide benefit from adding cagrilintide
Initial combination produces maximum results
May prevent or delay weight regain
Better long-term outcomes
Cagrilintide and semaglutide dosing protocols
Proper dosing ensures maximum efficacy with manageable side effects.
Standard CagriSema dosing from clinical trials
Phase 3 trial protocol:
Semaglutide: Titrate to 2.4mg weekly
Cagrilintide: Titrate to 2.4mg weekly
Both given as separate weekly injections
Slow titration over 16-20 weeks
Semaglutide titration schedule:
Week 1-4: 0.25mg weekly
Week 5-8: 0.5mg weekly
Week 9-12: 1.0mg weekly
Week 13-16: 1.7mg weekly
Week 17+: 2.4mg weekly (maintenance)
Cagrilintide titration schedule (when combined):
Week 1-4: 0.6mg weekly
Week 5-8: 1.2mg weekly
Week 9-12: 1.8mg weekly
Week 13+: 2.4mg weekly (maintenance)
Why slow titration matters:
GI side effects worse if escalated quickly
Especially with combination
Body needs time to adapt
Better long-term adherence
Alternative dosing strategies
Conservative approach (better tolerated):
Semaglutide: Max 1.7-2.0mg weekly
Cagrilintide: Max 1.8-2.0mg weekly
Slower titration (20-24 weeks)
For GI-sensitive individuals
Aggressive approach (maximum weight loss):
Semaglutide: 2.4mg weekly
Cagrilintide: 2.4-3.0mg weekly (some trials test higher)
Standard titration timeline
For excellent tolerators seeking maximum results
Higher side effect risk
Sequential addition approach:
Start semaglutide alone, titrate to 2.4mg (16 weeks)
Stabilize for 4-8 weeks
Add cagrilintide, starting at 0.6mg
Titrate cagrilintide to 2.4mg (12 weeks)
Total timeline: 32-36 weeks to full dose
May reduce side effects
Maintenance dosing:
Once target weight achieved
May reduce to: Semaglutide 1.7mg + Cagrilintide 1.8mg
Maintain weight loss
Better long-term tolerability
More affordable
Use our peptide calculator, peptide cost calculator, peptide dosing guide, and peptide dosage chart.
Injection protocols and timing
Separate injections:
Semaglutide: Subcutaneous, abdomen or thigh
Cagrilintide: Subcutaneous, different site
Same day, different locations
Both weekly
Timing considerations:
Most take both same day (simplicity)
Can split: Semaglutide Monday, Cagrilintide Thursday
No evidence one timing superior
Choose based on preference
Injection technique:
Standard subcutaneous injection
29-31 gauge needles
Rotate injection sites
No special requirements
See our peptide injections guide, how to calculate peptide dosages, and how to reconstitute peptides if using research peptides.
When to adjust doses
Increase dose if:
Minimal side effects at current dose
Weight loss plateaued (after 4+ weeks on dose)
Following standard titration schedule
Good tolerability
Hold or reduce dose if:
Severe nausea/vomiting
Unable to eat adequate protein
Significant GI distress
Dehydration concerns
Too rapid weight loss (>3 lbs/week consistently)
Discontinue if:
Intolerable side effects despite dose reduction
Severe adverse events
Pregnancy
Medical contraindication develops
Expected weight loss results and timeline
Understanding realistic outcomes helps set expectations.
Weight loss by timeframe
Month 1-2 (initial titration):
5-10 lbs lost
Lower doses, body adapting
Some appetite suppression
Establishing habits
Month 3-4 (dose escalation):
10-20 lbs total lost
Significant appetite reduction
Noticeable changes
Plateau possible, keep titrating
Month 5-8 (approaching maintenance dose):
20-35 lbs total lost
Near or at full dose
Maximum appetite suppression
Consistent weekly loss (1-3 lbs)
Month 9-12 (maintenance dose):
30-50 lbs total lost
Full dose combination
Continued steady loss
Body composition improving
Month 12-18 (long-term):
40-60+ lbs total lost (or 15-25% body weight)
Exceptional responders: 60-80 lbs
Weight stabilizing
Focus shifts to maintenance
Individual variation:
Starting weight matters (higher = more absolute loss)
Metabolism, activity level, diet affect results
Some lose faster, some slower
Consistency most important
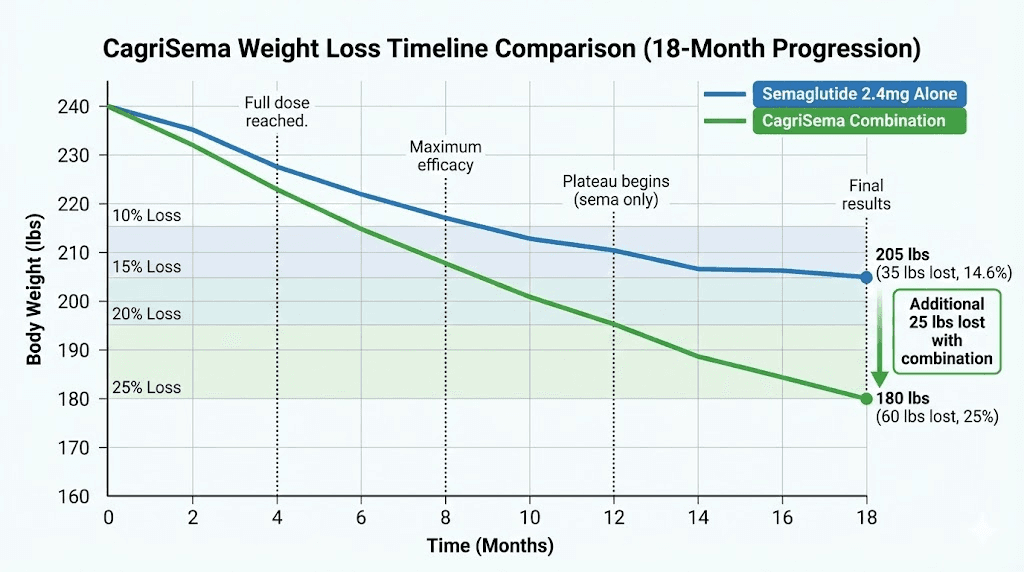
Comparison to semaglutide monotherapy
Semaglutide 2.4mg alone (typical):
6 months: 20-30 lbs
12 months: 30-40 lbs
18 months: 35-45 lbs
Average: 10-15% body weight
CagriSema combination (typical):
6 months: 25-40 lbs
12 months: 40-60 lbs
18 months: 50-70+ lbs
Average: 15-25% body weight
Additional benefit:
50-75% more weight loss with combination
Example: 240 lb person
Semaglutide alone: Lose 24-36 lbs → 204-216 lbs
CagriSema combo: Lose 36-60 lbs → 180-204 lbs
Clinically significant difference
See our peptides before and after results and how long do peptides take to work.
Who responds best to CagriSema
Ideal candidates:
Significant obesity (BMI 30-40+)
Previously plateaued on GLP-1s alone
Need maximum weight loss
Good GI tolerability
Metabolic syndrome or diabetes
Commitment to long-term use
Excellent responders:
Higher baseline weight (more to lose)
Good adherence to protocol
Combine with diet/exercise
Younger patients (better metabolism)
No significant medication interactions
May respond less optimally:
Very low starting weight (BMI <30)
Extremely slow metabolism
Significant muscle loss during weight loss
Multiple metabolic medications
Advanced age with comorbidities
Side effects and management strategies
The combination increases side effect risk but they're manageable.
Common side effects (ranked by frequency)
Very common (>30%):
Nausea (most common)
Decreased appetite (intended effect)
Constipation
Fatigue (especially first months)
Common (10-30%):
Vomiting (if nausea not managed)
Diarrhea (alternating with constipation)
Abdominal pain/discomfort
Headache
Dizziness
Less common (<10%):
Reflux/GERD
Bloating and gas
Injection site reactions
Gallstones (with rapid weight loss)
Hypoglycemia (if diabetic on other meds)
Rare but serious (<1%):
Pancreatitis
Severe gastroparesis
Severe dehydration
Thyroid tumors (animal studies, human risk unclear)
Managing nausea (biggest complaint)
Why nausea worse with combination:
Both drugs slow gastric emptying
Synergistic effect → very slow stomach
Food sits longer → nausea
Cagrilintide has stronger effect
Nausea management strategies:
Dietary modifications:
Smaller, more frequent meals (5-6 per day)
Avoid fatty, greasy, spicy foods
Cold foods better tolerated than hot
Bland foods initially (crackers, rice, bananas)
Don't lie down after eating (2+ hours upright)
Eating habits:
Eat slowly (20-30 minutes per meal)
Chew thoroughly
Stop at first sign of fullness
Don't force food
Liquid calories easier initially
Supplementation:
Ginger (tea, capsules, chews) before meals
Vitamin B6 (25-50mg daily)
Anti-nausea medication if severe:
Zofran/ondansetron (prescription)
Promethazine (prescription)
Dramamine (over-counter, less effective)
Timing strategies:
Inject at night (sleep through peak nausea)
Take meds with food, not empty stomach
Avoid nausea triggers (strong smells, etc.)
Dose management:
Slower titration if nausea severe
Stay at current dose 1-2 extra weeks
Reduce dose temporarily if needed
Don't rush escalation
Preventing and managing constipation
Why constipation occurs:
Slow gastric emptying → slow transit throughout
Less food intake → less stool
Dehydration risk
Very common with combination
Prevention strategies:
Increase water intake (8-10 glasses daily)
High fiber foods (vegetables, fruits, whole grains)
Fiber supplements (psyllium, methylcellulose)
Prune juice or prunes
Magnesium citrate supplement (300-500mg)
Regular physical activity
Stool softeners (docusate) daily
Osmotic laxatives if needed (MiraLAX)
Maintaining adequate nutrition
Protein priority:
Minimum 60-80g protein daily
Prevent muscle loss during weight loss
Protein shakes if can't eat solids
Spread throughout day
Hydration critical:
64-80 oz water minimum
Electrolyte drinks if needed
Monitor for dehydration (dark urine, dizziness)
IV fluids if severe dehydration
Vitamin supplementation:
Multivitamin daily
Vitamin B12 (GLP-1s can reduce absorption)
Vitamin D
Iron if deficient
Calcium
See our peptide safety and risks and common peptide mistakes beginners make.
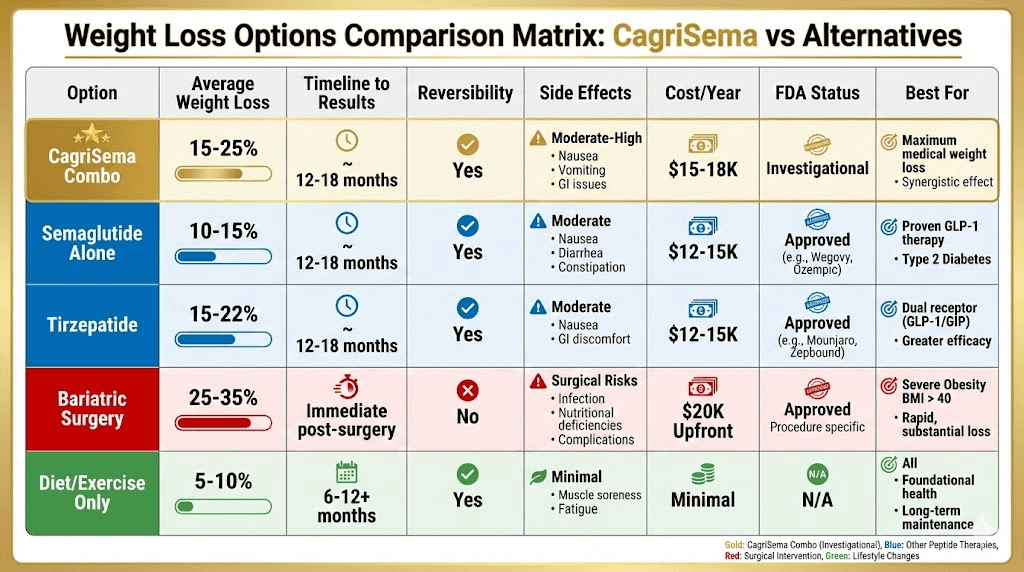
Comparing CagriSema to other weight loss options
How the combination stacks up against alternatives.
CagriSema vs tirzepatide (Mounjaro/Zepbound)
Tirzepatide mechanism:
Dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist
Single molecule, two pathways
15-22% average weight loss
FDA approved for weight loss
CagriSema mechanism:
Amylin + GLP-1
Two separate molecules
15-25% average weight loss
Not yet FDA approved
Comparison:
Similar weight loss potential
Both superior to single-agent GLP-1s
Tirzepatide: One injection, approved
CagriSema: Two injections, investigational
Side effect profiles similar
Cost likely similar when CagriSema approved
Which to choose:
Currently: Tirzepatide (approved, available)
Future: May depend on individual response and cost
Both excellent options
See our semaglutide vs tirzepatide and tirzepatide dosing guide.
CagriSema vs semaglutide + other peptides
Semaglutide + CJC-1295/Ipamorelin:
Semaglutide: Weight loss
GH peptides: Preserve muscle, improve body composition
Not as much additional weight loss
Better muscle preservation
Different mechanism than cagrilintide
Semaglutide + BPC-157:
Semaglutide: Weight loss
BPC-157: Gut healing, inflammation
Complementary for health
Not weight loss synergy
Good combination for overall wellness
Verdict: Cagrilintide specifically designed to synergize with semaglutide for weight loss. Other combinations serve different purposes.
See our peptide stacks guide, CJC-1295 dosage calculator, Ipamorelin benefits, BPC-157 guide, BPC-157 dosage calculator, and peptides for muscle growth.
CagriSema vs bariatric surgery
Bariatric surgery:
25-35% weight loss typical
Permanent anatomical change
Surgical risks
High upfront cost ($15,000-25,000)
Insurance may cover
CagriSema:
15-25% weight loss
Reversible (stop medication)
No surgical risk
Ongoing cost ($1,000-1,500/month estimated)
Insurance coverage unclear
When CagriSema may be preferred:
Want to avoid surgery
Good with injections/medication
BMI 30-40 (not severe enough for surgery)
Can afford ongoing cost
When surgery may be better:
BMI >40 with comorbidities
Insurance covers surgery
Want permanent solution
Don't want ongoing injections
Sourcing cagrilintide and semaglutide
Obtaining these peptides requires understanding current availability.
Current availability status
Semaglutide:
FDA approved as Wegovy (weight loss) and Ozempic (diabetes)
Prescription required
Widely available through pharmacies
Also available as research chemical
Well-established sourcing
Cagrilintide:
NOT FDA approved (as of 2024)
In Phase 3 clinical trials
Not commercially available via prescription
Only available as research chemical
Limited vendors carry it
CagriSema (combined product):
Novo Nordisk's brand name
In Phase 3 trials
Not yet approved
Anticipated FDA review 2025-2026
Will require prescription when approved
Research chemical sourcing
For semaglutide:
Many established research chemical vendors
Quality varies significantly
Third-party testing essential
Typical cost: $150-300 per 5mg vial
Lasts 2-4 weeks at 2.4mg dose
For cagrilintide:
Very limited vendors currently
Newer peptide, less available
Quality even more variable
Higher cost due to scarcity: $200-400 per 2.4mg vial
Many vendors don't carry it yet
Quality verification:
Certificate of Analysis (COA) required
Purity should be ≥95%
Recent testing (within 6 months)
Batch number matching
Established vendor reputation
Red flags:
No testing documentation
Suspiciously cheap prices
New, unknown vendors
Poor communication
Inconsistent product quality reports
See our best peptide vendors, are peptides legal, and research vs pharmaceutical peptides.
Cost considerations
Pharmaceutical semaglutide (Wegovy):
$1,300-1,500/month without insurance
Insurance may cover (varies)
Patient assistance programs available
Research semaglutide:
$150-300/month
No insurance
No patient assistance
User assumes risk
Research cagrilintide:
$200-400/month
Not prescription available yet
Higher cost due to limited availability
Total CagriSema combination cost (research chemicals):
$350-700/month
Both peptides at full dose
Significant investment
Compare to bariatric surgery ($15,000-25,000 upfront)
Budget planning:
Year 1 (titration + maintenance): $4,200-8,400
Ongoing maintenance: $350-700/month
Consider reducing to maintenance doses
May need 12-24+ months total
Use our peptide cost calculator to budget protocols.
Storage and handling
Both peptides require refrigeration:
Before reconstitution: 2-8°C (refrigerator) or -20°C (freezer)
After reconstitution: 2-8°C (refrigerator)
Use within 28-30 days after reconstitution
Protect from light
Do not freeze liquid peptide
Traveling with peptides:
Cooler with ice packs
Refrigerate ASAP at destination
Pre-filled pens easier for travel
Check local laws if international
See our peptide storage guide, how long reconstituted peptides last in fridge, bacteriostatic water for peptides, and lyophilized vs liquid peptides.
Complete protocols for different goals
Tailored approaches for various objectives.
Protocol 1: Maximum weight loss (aggressive)
Goal: Lose 50-80+ lbs in 12-18 months
Approach:
Semaglutide: Titrate to 2.4mg weekly over 16 weeks
Cagrilintide: Titrate to 2.4mg weekly over 12 weeks (starting week 5)
Both at maximum approved doses
Maintain for 12-18 months
Supporting strategies:
High-protein diet (1g per lb goal weight)
Resistance training 3-4x weekly
10,000+ steps daily
Sleep 7-9 hours
Stress management
Expected results:
Month 6: 30-45 lbs lost
Month 12: 50-70 lbs lost
Month 18: 60-85 lbs lost
Percentage: 20-25% body weight
Cost: $6,000-12,000 total
Protocol 2: Conservative approach (better tolerated)
Goal: Steady weight loss with minimal side effects
Approach:
Semaglutide: Titrate to 1.7mg weekly over 20 weeks
Cagrilintide: Titrate to 1.8mg weekly over 16 weeks
Slower escalation
Lower maintenance doses
Benefits:
Reduced GI side effects
Better tolerability
Easier to sustain
More affordable
Expected results:
Month 12: 35-50 lbs lost
Percentage: 15-20% body weight
Better adherence long-term
Cost: $5,000-8,400/year
Protocol 3: Adding cagrilintide to existing semaglutide
Goal: Break through plateau on semaglutide
Approach:
Already on semaglutide 2.4mg (or lower)
Add cagrilintide starting at 0.6mg weekly
Titrate cagrilintide to 2.4mg over 12 weeks
Continue both
Timeline:
Plateau broken within 4-8 weeks of adding cagrilintide
Additional 10-20 lbs lost over 6-12 months
Renewed progress
Who this helps:
Plateaued on semaglutide alone
Lost initial weight but stuck
Want to avoid stopping semaglutide
Protocol 4: Maintenance after goal weight
Goal: Maintain weight loss long-term
Approach:
Reduce to maintenance doses:
Semaglutide: 1.0-1.7mg weekly
Cagrilintide: 1.2-1.8mg weekly
Monitor weight weekly
Adjust up if regaining
Benefits:
Lower cost
Fewer side effects
Sustainable long-term
Prevents regain
Duration: Indefinite (may need lifelong)
See our peptide cycle planning guide and can you cycle different peptides.
How you can use SeekPeptides for CagriSema protocols
SeekPeptides provides personalized guidance for combining cagrilintide and semaglutide safely and effectively. Get customized protocols based on your starting weight, weight loss goals, GI tolerance, and whether you're already on semaglutide or starting fresh.
AI advisor helps you determine optimal titration schedules, manage side effects proactively, decide between aggressive vs conservative approaches, and plan maintenance strategies after reaching goal weight.
Access research on the CagriSema combination, clinical trial data, and real-world protocols from early adopters.
Learn proper dosing, injection technique, storage, and reconstitution through our guides - peptide injections guide, how to reconstitute peptides, peptide storage guide, water to mix with peptides.
Use our calculators - peptide calculator, semaglutide dosage calculator, peptide cost calculator, peptide stack calculator - for precise combination protocols.
Access our best peptide vendors for quality sourcing once cagrilintide becomes more widely available.
Final thoughts
Cagrilintide and semaglutide represent the next evolution in medical weight loss through dual-pathway appetite suppression and metabolic optimization. The combination produces 15-25% body weight loss - significantly superior to semaglutide's 10-15% alone - by targeting both GLP-1 and amylin receptors simultaneously.
Proper dosing requires slow titration to maximum tolerated doses, typically semaglutide 2.4mg weekly plus cagrilintide 2.4mg weekly, though conservative approaches using lower maintenance doses work well for many. Side effects, particularly nausea, are more pronounced than single-agent therapy but manageable with proper strategies.
Currently, cagrilintide remains investigational and available only as a research chemical while awaiting FDA approval expected 2025-2026. Semaglutide is widely available both as prescription (Wegovy) and research chemical.
The combination offers hope for patients who've plateaued on GLP-1s alone or need maximum weight loss.
Quality sourcing with third-party testing remains critical, especially for cagrilintide given limited vendor availability. Budget $350-700 monthly for the combination using research chemicals, with 12-18 months needed for maximum results.
Your path to significant weight loss with CagriSema requires commitment to proper titration, managing side effects proactively, maintaining adequate protein and hydration, supporting with diet and exercise, and understanding this is a long-term approach requiring sustained use.
Helpful resources for cagrilintide and semaglutide
Peptide calculator - Calculate doses
Semaglutide dosage calculator - Semaglutide dosing
Peptide cost calculator - Budget combination
Peptide stack calculator - Plan protocols
Peptide reconstitution calculator - Mix correctly
See you soon, join SeekPeptides