Dec 31, 2025

Peptide timing strategies recognize that biological processes follow circadian rhythms, inflammatory responses peak at specific times, and gut healing mechanisms operate differently during fed versus fasted states.
KPV (lysine-proline-valine tripeptide) demonstrates anti-inflammatory and gut healing properties through alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) pathway activation, but whether morning or night dosing optimizes these benefits depends on individual goals, administration route, and underlying condition being treated.
The timing question matters because inflammatory cytokines follow diurnal patterns - IL-6 and TNF-α typically peak in early morning (6-8 AM), suggesting morning dosing might intercept inflammation at its highest point. However, gut repair processes accelerate during sleep when digestive activity decreases and cellular regeneration predominates, potentially favoring evening administration for conditions like inflammatory bowel disease or leaky gut.
KPV's anti-inflammatory mechanism through NF-κB pathway inhibition and mast cell stabilization works regardless of timing, but practical considerations influence optimal scheduling - oral/sublingual KPV requires empty stomach for absorption (morning before eating or night before bed most practical), subcutaneous injection timing flexibility allows either morning or evening based on routine and side effect patterns, and transdermal application can occur anytime but consistency matters more than specific hour.
For inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and Crohn's/colitis, evening dosing shows theoretical advantages as nocturnal gut rest periods enhance mucosal healing when inflammation suppression coincides with reduced digestive burden. For skin inflammation and systemic inflammatory conditions, morning dosing may better intercept early-day cytokine peaks while maintaining convenient routine adherence.
This guide examines KPV's mechanism and timing relevance, morning versus evening dosing pros and cons for different conditions, circadian rhythm effects on inflammation and healing, optimal timing by administration route (oral, subcutaneous, transdermal), condition-specific timing strategies (IBD, skin inflammation, systemic conditions), split-dosing protocols for maximum coverage, and determining personal optimal timing through systematic experimentation.
Understanding KPV timing optimization ensures anti-inflammatory benefits align with your body's natural rhythms and condition-specific needs.
Understanding KPV mechanism and timing relevance
Why timing might matter for this peptide.
KPV's anti-inflammatory mechanism
KPV (Lys-Pro-Val) overview:
Tripeptide fragment of α-MSH (alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone)
Potent anti-inflammatory properties
Especially effective for gut inflammation
NF-κB pathway inhibition
Mast cell stabilization
Primary mechanisms:
NF-κB inhibition: Blocks key inflammatory transcription factor
Cytokine suppression: Reduces IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β production
Mast cell stabilization: Prevents histamine/inflammatory mediator release
Gut barrier protection: Enhances tight junction integrity
Antimicrobial: Direct effects on certain bacteria
How mechanism relates to timing:
Anti-inflammatory works 24/7 once in system
But: Inflammation follows daily patterns
Cytokines peak certain times (morning typically)
Gut healing processes vary by time (enhanced during sleep)
Dosing timing may optimize interception
Half-life considerations:
KPV half-life: ~4-6 hours (relatively short)
Means effects don't last full 24 hours from single dose
Multiple daily doses or strategic timing needed
Unlike long-acting peptides (e.g., semaglutide weekly)
Timing window matters more for short half-life
Does timing affect mechanism?
Core mechanism (NF-κB inhibition) = time-independent
But: Target inflammation timing = time-dependent
Morning dose catches AM cytokine peaks
Evening dose supports nocturnal gut healing
Both valid depending on goals
Learn about KPV peptide benefits and how peptides work at SeekPeptides.
Circadian inflammation patterns
Inflammatory cytokine diurnal rhythms:
IL-6: Peaks 6-8 AM (early morning highest)
TNF-α: Peaks 6-8 AM (follows similar pattern)
IL-1β: Peaks morning to midday
Cortisol: Peaks 8 AM (anti-inflammatory counter-response)
CRP: Peaks around 6 AM
Why inflammation peaks morning:
Circadian clock genes regulate immune function
Cortisol awakening response (CAR) triggers
Evolutionary advantage (ready for daytime threats)
Sympathetic nervous system activation
Pro-inflammatory state to prepare for activity
Evening/night inflammation patterns:
Inflammatory markers lowest 8 PM - midnight
Parasympathetic dominance (rest/digest)
Repair and regeneration processes activate
Reduced cytokine production
Anti-inflammatory environment
Implications for KPV timing:
Time of Day | Inflammation Level | KPV Timing Strategy |
|---|---|---|
Morning (6-10 AM) | Peak cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) | Dose here to intercept morning surge |
Midday (10 AM - 4 PM) | Moderate inflammation | Maintenance dosing if split protocol |
Evening (4-8 PM) | Declining inflammation | Prepare for nocturnal healing |
Night (8 PM - 6 AM) | Lowest inflammation | Support gut repair, healing processes |
Individual variation:
Some people more inflammatory at night (rare)
Shift workers have altered circadian rhythms
Chronic stress disrupts normal patterns
Autoimmune conditions may not follow typical rhythms
Track personal patterns for optimization
Gut healing and sleep cycles
Nocturnal gut healing processes:
Reduced digestive burden: No food intake during sleep
Enhanced repair: Cellular regeneration peaks during sleep
Tight junction restoration: Gut barrier repair occurs
Stem cell activation: Intestinal stem cells proliferate
Immune modulation: Regulatory T-cells active
Why evening KPV might support gut healing:
KPV present during peak healing window (sleep)
Anti-inflammatory during nocturnal repair
Supports tight junction integrity overnight
Reduces inflammation while gut rests
Synergizes with natural healing processes
Fasted state benefits:
KPV absorption better on empty stomach
Morning before eating = fasted
Night before bed = fasted (3+ hours post-dinner)
Both times optimal for absorption
Avoid dosing with or right after meals
Gut motility considerations:
Digestive motility slows during sleep
May increase mucosal contact time (good for oral KPV)
Longer exposure to intestinal lining
Enhanced local effects possible
Theoretical advantage for IBD treatment
Research evidence (limited):
No specific studies on KPV timing
Extrapolated from general gut healing principles
Clinical observations suggest evening dosing effective
Morning dosing also works (anti-inflammatory)
Individual experimentation recommended
See peptides for gut health guide.
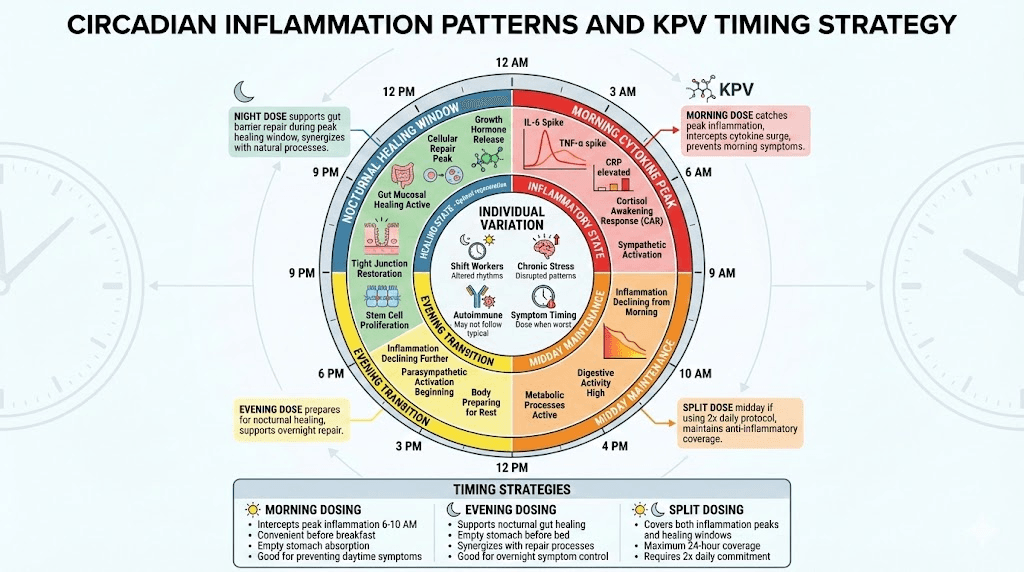
Morning vs evening dosing comparison
Pros and cons of each approach.
Morning dosing advantages
When morning dosing makes sense:
IBD symptoms worse in AM
Morning inflammatory flares
Daytime symptom control priority
Convenient routine (before breakfast)
Active lifestyle during day
Morning dosing benefits:
Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
Intercepts cytokine peak | IL-6/TNF-α highest 6-8 AM, dose catches surge |
Prevents daytime symptoms | Anti-inflammatory active during waking hours |
Convenient timing | Before breakfast, empty stomach natural |
Routine adherence | Part of morning ritual, easy to remember |
Active day coverage | Symptoms controlled when most active |
Optimal morning protocol:
Wake up
Wait 10-15 minutes (fully awake)
Dose KPV (oral/sublingual on empty stomach)
Wait 30-45 minutes before eating
Peak effects during morning cytokine surge
Morning dosing considerations:
Need to wait before breakfast (inconvenient for some)
May miss nocturnal healing window
Short half-life means effects wane by evening
Symptoms may return late day/night
Consider split dosing if evening symptoms present
Who benefits most from morning dosing:
Morning diarrhea/urgency (IBD)
Morning stiffness (systemic inflammation)
Daytime skin flares
Work/school during day (need symptom control)
Morning routine adherent personalities
Subcutaneous morning injection:
Can dose immediately upon waking
No meal timing concerns
Convenient if using other peptides AM
Same anti-inflammatory benefits
Evening dosing advantages
When evening dosing makes sense:
Nocturnal gut symptoms
Night-time inflammation
Gut healing priority (IBD, leaky gut)
Morning rush prevents AM dosing
Prefer bedtime routine
Evening dosing benefits:
Benefit | Explanation |
|---|---|
Supports nocturnal healing | KPV active during peak gut repair (sleep) |
Empty stomach convenient | 3+ hours post-dinner, before bed natural |
Overnight symptom control | Prevents night symptoms, morning urgency |
Synergizes with sleep healing | Anti-inflammatory during regeneration peak |
Convenient for busy mornings | No need to wait before breakfast |
Optimal evening protocol:
Dinner by 6-7 PM
Wait 3+ hours (empty stomach)
Dose KPV 9-10 PM (oral/sublingual)
Go to sleep within 1-2 hours
Peak effects during sleep healing window
Evening dosing considerations:
Need dinner timing discipline (3+ hour gap)
May miss morning cytokine peak
Requires consistent bedtime
Hard to remember (no morning routine)
But: Potentially better for gut healing
Who benefits most from evening dosing:
Night-time gut symptoms
Morning urgency/diarrhea (dose night before)
IBD focused on healing not just symptom control
Rushed mornings (no time for 30-45 min wait)
Evening routine adherent personalities
Subcutaneous evening injection:
Can dose anytime evening
No meal timing concerns
Before bed common
Supports overnight healing
Split dosing protocol (twice daily)
Split dosing rationale:
KPV half-life ~4-6 hours
Single daily dose = gaps in coverage
Twice daily = more consistent levels
Covers both AM peak and nocturnal healing
Maximum benefit approach
Typical split protocol:
Morning dose: 250-500mcg (upon waking, before breakfast)
Evening dose: 250-500mcg (before bed, empty stomach)
Total daily: 500-1000mcg split
12-hour intervals ideal
Maintains anti-inflammatory coverage 24/7
Split dosing advantages:
Advantage | Impact |
|---|---|
Catches AM cytokine peak | Morning dose intercepts inflammation surge |
Supports nocturnal healing | Evening dose active during sleep repair |
More consistent levels | Reduces peaks/troughs from single dose |
Better symptom control | 24-hour coverage vs 12-hour gaps |
Flexible total dose | Can increase by splitting, not just single dose |
Split dosing disadvantages:
Twice daily commitment (adherence harder)
Two empty stomach windows required
More expensive (higher total dose)
More injections if subcutaneous
Complexity vs simplicity
When split dosing worth it:
Severe IBD (need maximum control)
Single daily dose insufficient
Both AM and PM symptoms
Failed single-dose protocols
Willing to commit to twice-daily routine
When single dose sufficient:
Mild-moderate symptoms
Adherence concerns (prefer simplicity)
Budget-conscious (uses more peptide)
Single peak symptom time (dose then)
Responding well to once-daily
See peptide dosing guide for strategies.
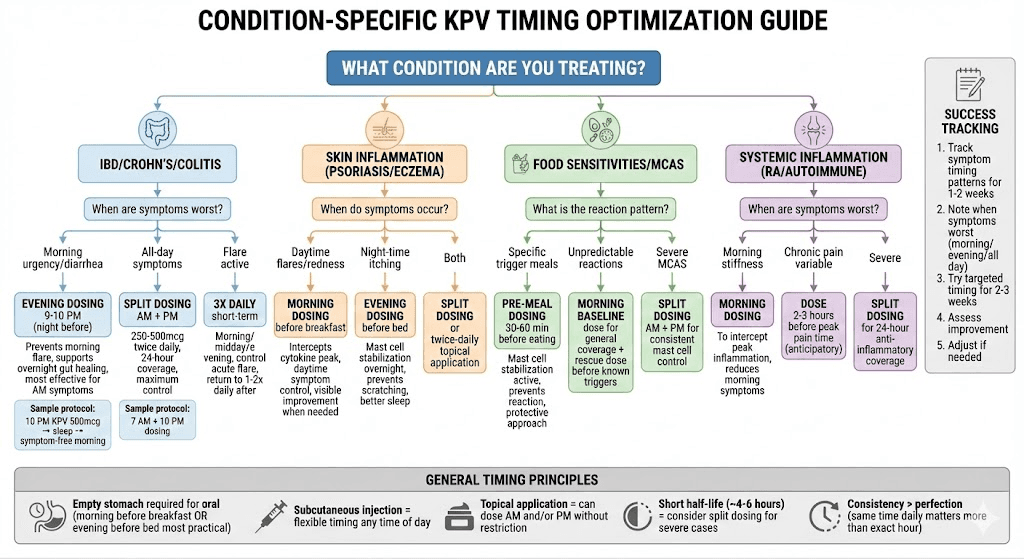
Condition-specific timing strategies
Optimal timing based on what you're treating.
IBD and inflammatory bowel conditions
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis timing:
Most IBD patients report morning urgency/diarrhea
Morning symptoms = cytokine-driven inflammation
Nocturnal gut healing critical for remission
Consider timing based on symptom pattern
Morning urgency/diarrhea (most common):
Best approach: Evening dosing night before
Dose 9-10 PM → effects peak overnight → prevents AM flare
Supports nocturnal healing simultaneously
Reduces morning urgency/diarrhea
Many report this most effective
All-day IBD symptoms:
Best approach: Split dosing (AM + PM)
Morning dose: 250-500mcg before breakfast
Evening dose: 250-500mcg before bed
Provides 24-hour coverage
Maximum anti-inflammatory effect
Flare management timing:
Acute flare: Consider 3x daily dosing temporarily
Morning, midday, evening dosing
Short-term (1-2 weeks) to control flare
Then back to 1-2x daily maintenance
Higher doses during acute phases
Maintenance remission timing:
Once daily sufficient for many in remission
Evening dosing supports healing
Prevents morning breakthrough symptoms
Less aggressive than split dosing
Cost-effective maintenance
KPV + other IBD peptides:
Peptide Combo | Timing Strategy |
|---|---|
KPV + BPC-157 | KPV AM or PM, BPC-157 2x daily |
KPV + Thymosin Beta-4 | Both can dose simultaneously |
KPV + Larazotide | Coordinate with meal timing |
Learn about peptides for gut health stacking.
Skin inflammation and systemic conditions
Skin inflammation timing (psoriasis, eczema, dermatitis):
Inflammatory skin conditions follow circadian patterns
Itching often worse at night (histamine release)
But inflammation peaks morning (cytokines)
Timing depends on symptom dominance
Morning dosing for skin:
Best for: Daytime flares, morning redness
Catches cytokine peak (6-8 AM)
Prevents daytime inflammation
Visible symptom control when matters (social/work)
Many skin conditions worse with sun exposure (daytime)
Evening dosing for skin:
Best for: Night-time itching, healing focus
Supports nocturnal skin repair
Prevents nighttime scratching
Better sleep (less itching)
Mast cell stabilization during sleep
Systemic inflammatory conditions:
Rheumatoid arthritis: Morning stiffness common (dose AM)
General inflammation: Morning cytokine peak (dose AM)
Autoimmune: May need split dosing (twice daily)
Chronic pain: Time to peak pain period
Topical vs systemic KPV timing:
Topical KPV: Can apply morning and/or evening
No timing restrictions for topical
Often twice daily (AM after shower, PM before bed)
Systemic oral/injectable: Timing matters more
Food sensitivities and reactions
Managing food sensitivities with KPV:
Food reactions = mast cell activation + inflammation
KPV stabilizes mast cells
Timing relative to meals important
Pre-meal dosing strategy:
30-60 minutes before trigger foods
Oral KPV absorbed, active before eating
Prevents mast cell degranulation from food
Reduces inflammatory response
Protective rather than reactive
Post-meal dosing (less ideal):
After reaction already started
Still provides benefit but delayed
Better than nothing
Consider pre-dosing next time
Multiple meals timing:
If eating trigger foods all day: Dose AM before meals
If specific meal problematic: Dose 30-60 min before that meal
If reactions unpredictable: Morning dose (general coverage)
KPV for MCAS (Mast Cell Activation Syndrome):
Split dosing often needed (AM + PM)
Provides more consistent mast cell stabilization
Prevents breakthrough reactions
May dose before known trigger events
Part of comprehensive MCAS protocol
How you can use SeekPeptides for KPV optimization
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive KPV peptide guidance beyond timing. Learn about KPV benefits for gut and inflammation, peptides for gut health comprehensive guide, and IBD treatment protocols.
Use our calculators - peptide calculator, dosing calculator, cost calculator - for KPV protocol planning.
Access guides - peptide dosing guide, peptide stacks guide, cycle planning, how peptides work.
Find best peptide vendors for quality KPV sourcing and peptide therapy clinics for supervised treatment.
Final thoughts
KPV peptide timing optimization depends primarily on symptom patterns and treatment goals - morning dosing intercepts peak inflammatory cytokine surges (IL-6, TNF-α highest 6-8 AM) making it ideal for preventing daytime symptoms, while evening dosing supports nocturnal gut healing processes that accelerate during sleep when digestive burden decreases and cellular regeneration predominates.
For inflammatory bowel disease with morning urgency or diarrhea, evening dosing 9-10 PM proves most effective as KPV's anti-inflammatory effects peak overnight preventing morning flares while simultaneously supporting mucosal healing during the body's natural repair window. For systemic inflammatory conditions or skin inflammation with daytime flares, morning dosing before breakfast catches the circadian cytokine peak providing symptom control when most needed.
Split dosing protocols (250-500mcg twice daily, morning and evening) provide maximum 24-hour anti-inflammatory coverage for severe conditions, accounting for KPV's relatively short 4-6 hour half-life, but require twice-daily commitment and increased peptide consumption. Single daily dosing suffices for mild-moderate conditions with clear symptom timing patterns.
Your KPV timing strategy should align with symptom patterns - evening dosing for morning IBD symptoms and healing focus, morning dosing for daytime inflammatory control, split dosing for severe all-day symptoms, and consistent timing (same hour daily) matters more than perfect hour selection for maintaining therapeutic effects.
Helpful resources for KPV
KPV peptide benefits - Complete KPV guide
Peptides for gut health - Gut healing comprehensive
Peptide dosing guide - Dosing principles