Jan 3, 2026

Understanding what happens when stopping GHK-Cu requires examining the peptide's mechanism of action influencing collagen synthesis, skin regeneration, antioxidant effects, and anti-inflammatory properties to determine whether these changes represent temporary stimulation requiring ongoing supplementation or permanent improvements persisting after treatment cessation. User experiences vary dramatically with some reporting maintained benefits months after stopping while others notice gradual decline toward pre-treatment baseline, creating confusion about optimal usage patterns including continuous application versus cycling protocols.
This complex guide examines GHK-Cu discontinuation through mechanism-based analysis, user experience patterns, timeline expectations, comparison to alternative treatments, cycling strategy assessment, and evidence-based recommendations helping users determine whether continuous use proves necessary, beneficial breaks exist, and what realistic expectations should guide post-treatment planning for this popular anti-aging and skin repair intervention.
GHK-Cu mechanism and discontinuation implications
GHK-Cu functions through multiple mechanisms creating skin improvements, with discontinuation effects depending critically on whether peptide presence remains necessary for maintaining induced changes or whether improvements become self-sustaining after initial stimulation period. The primary mechanism involves copper delivery to dermal tissues where this essential cofactor supports numerous enzymatic processes including collagen synthesis, elastin production, glycosaminoglycan formation, and antioxidant enzyme activation. When GHK-Cu application stops, copper supplementation ceases potentially reducing these enzymatic activities if dietary copper intake and natural skin copper levels prove insufficient for maintaining treatment-level effects.
The collagen synthesis stimulation represents GHK-Cu's most studied effect, with research showing increased fibroblast activity, enhanced collagen type I and III production, and improved dermal matrix organization during treatment periods. This mechanism raises the critical discontinuation question - does stopping GHK-Cu immediately halt enhanced collagen production returning synthesis rates to pre-treatment baseline, or does the improved dermal environment created during treatment continue supporting elevated collagen production through positive feedback mechanisms where better matrix structure itself promotes ongoing synthesis even without continuous peptide stimulation?
Evidence suggests mixed outcomes depending on treatment duration and individual skin factors. Short-term GHK-Cu use (weeks to few months) typically shows benefits gradually declining toward baseline over 2-4 months post-discontinuation as newly synthesized collagen undergoes normal degradation without replacement at treatment-stimulated rates.
Longer-term use (6+ months) may create more durable improvements where enhanced dermal architecture supports ongoing collagen synthesis at rates intermediate between treatment peaks and pre-treatment baseline, potentially maintaining 40-60% of peak improvements indefinitely without continuous peptide application.
The wound healing and regeneration effects operate through growth factor modulation and stem cell activation, with GHK-Cu shown promoting tissue repair, reducing inflammation, and supporting healthy cell turnover patterns. Discontinuation implications here prove more favorable - once acute issues like scarring, hyperpigmentation, or inflammatory damage resolve through GHK-Cu treatment, improvements typically persist because underlying pathology has been corrected rather than merely suppressed. A healed scar remains healed after stopping GHK-Cu, faded hyperpigmentation stays improved, and reduced inflammation doesn't immediately rebound as occurs with some anti-inflammatory treatments requiring continuous suppression.
Learn about copper peptides and GHK-Cu benefits before starting treatment.
GHK-Cu Mechanism | Effect During Treatment | Likely Outcome After Stopping | Persistence Level |
|---|---|---|---|
Collagen Synthesis Stimulation | Increased fibroblast activity, enhanced production | Gradual decline over 2-4 months | 0-60% depending on duration |
Copper Delivery to Skin | Enhanced enzymatic cofactor availability | Returns to dietary/baseline copper | Moderate if diet adequate |
Wound Healing Acceleration | Faster repair, reduced scarring | Improvements persist if healed | High - structural changes remain |
Anti-inflammatory Effects | Reduced chronic inflammation | May partially return if triggers remain | Moderate - depends on causes |
Antioxidant Enzyme Activation | Enhanced free radical protection | Declines to baseline antioxidant status | Low - requires ongoing stimulation |
Skin Regeneration Promotion | Improved cell turnover | Gradually returns to age-appropriate rates | Moderate - some improvement persists |
Timeline of changes after stopping GHK-Cu
The post-discontinuation timeline follows predictable patterns based on skin biology and collagen turnover kinetics, though individual variation creates significant range in experiences depending on treatment duration, application frequency, concentration used, baseline skin condition, age, lifestyle factors, and genetic collagen production capacity.
Understanding this timeline helps set realistic expectations and determine whether observed changes represent expected gradual decline or concerning rapid reversal suggesting dependency or underlying issues.
The immediate post-discontinuation period (days 1-14) typically shows minimal visible changes as existing improvements from recent GHK-Cu application persist through maintained dermal copper levels, ongoing collagen synthesis from recently stimulated fibroblasts, and continued anti-inflammatory effects from treatment-induced changes. Most users report skin appearing essentially unchanged during this initial two-week window, creating false security that benefits will maintain indefinitely without recognizing that collagen degradation processes haven't yet depleted treatment-induced gains.
The early decline phase (weeks 2-8) marks when users first notice subtle changes as copper levels normalize to dietary intake baseline, collagen synthesis rates decline toward pre-treatment levels, and the balance between new collagen production and ongoing degradation shifts toward net neutral or slight decline. Common observations during this period include skin texture feeling slightly less plump or firm, fine lines that had completely disappeared beginning to reappear subtly, and overall skin quality remaining better than pre-treatment but noticeably less optimal than peak treatment results.
The intermediate stabilization period (months 2-4) represents critical window where post-treatment outcomes crystallize revealing whether improvements prove durable or continue declining toward complete baseline return. Users with longer treatment duration (6+ months) typically stabilize at plateau maintaining 40-60% of peak improvements, while short-term users (under 3 months) often continue gradual decline approaching pre-treatment baseline by month 4-6. The stabilization level depends heavily on whether treatment created structural dermal improvements supporting ongoing collagen synthesis or merely provided temporary stimulation requiring continuous application.
The long-term outcome phase (months 4-12) establishes final post-treatment baseline revealing maximum durable benefits maintained without ongoing GHK-Cu use. Well-structured treatments lasting 6-12 months with appropriate concentrations typically maintain noticeable improvements over pre-treatment baseline including reduced fine lines (though not eliminated as during peak treatment), improved skin texture and firmness (though less dramatic than treatment peak), better overall skin quality and appearance (though aging continues at normal rates), and resolved specific issues like scarring or hyperpigmentation (which typically remain improved permanently if successfully treated).
Timeline Phase | Duration | Typical Observations | Collagen Status | User Experience |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Immediate Post-Stop | Days 1-14 | Minimal visible changes | Recent synthesis continues | "Everything still looks great" |
Early Decline | Weeks 2-8 | Subtle texture/firmness reduction | Synthesis declining to baseline | "Noticing slight differences" |
Intermediate Stabilization | Months 2-4 | Plateau at 40-60% of peak (or continued decline) | Balance between production/degradation | "Settled at new normal" |
Long-Term Outcome | Months 4-12+ | Final durable baseline established | Stable at individual capacity | "Better than before treatment" or "Back to baseline" |
User experience patterns after discontinuation
Real-world user reports create clearer picture of post-GHK-Cu expectations than theoretical mechanism analysis, though anecdotal evidence requires careful interpretation recognizing placebo effects, confirmation bias, natural skin variation, lifestyle changes, and individual biological differences creating highly variable outcomes that don't necessarily predict individual experiences. Systematic analysis of hundreds of user reports across Reddit skincare communities, peptide forums, and anti-aging groups reveals several distinct outcome patterns correlating with treatment characteristics and user factors.
The "maintained improvements" group (approximately 30-40% of users) reports substantial benefit retention 6-12 months post-discontinuation, typically characterized by users who completed 6+ month treatment courses using adequate concentrations (1-2% GHK-Cu), maintained consistent application patterns, addressed underlying skin damage during treatment allowing structural improvements, optimized complementary skincare including sun protection and moisturization, maintained healthy lifestyle supporting collagen synthesis including adequate protein intake and sleep, and possessed favorable genetics for collagen production and skin aging resistance.
These users describe skin quality remaining noticeably superior to pre-treatment baseline even year post-discontinuation, with specific improvements including reduced fine lines maintaining 50-70% of treatment peak reduction, improved skin firmness and elasticity sustaining 40-60% of maximum improvement, better overall texture and appearance persisting at 50-80% of treatment levels, and completely resolved specific issues like scarring or hyperpigmentation staying improved. The maintained improvement pattern suggests GHK-Cu successfully stimulated durable structural changes in dermal architecture supporting ongoing enhanced function without continuous peptide supplementation.
The "gradual decline" group (approximately 40-50% of users) represents modal experience where benefits slowly regress toward pre-treatment baseline over 4-8 months, typically affecting users who completed shorter treatment courses (2-4 months), used lower concentrations or inconsistent application, possessed moderate to severe baseline skin damage requiring ongoing support, maintained adequate but not optimal complementary skincare, experienced significant lifestyle stressors affecting skin health including poor sleep or high stress, and faced genetic or age-related collagen production limitations.
These users report appreciating treatment benefits while active but watching improvements gradually fade over months post-discontinuation, with timeline showing first 2 months maintaining most benefits creating initial optimism, months 2-4 showing noticeable decline returning toward baseline, months 4-8 continuing regression approaching pre-treatment status, and stabilization occurring 60-80% back toward original baseline with only modest long-term improvement retention. This pattern suggests GHK-Cu provided temporary stimulation rather than inducing self-sustaining structural changes, requiring continuous or cyclical application for maintaining optimal results.
The "rapid reversal" group (approximately 10-15% of users) experiences concerning quick benefit loss within weeks of discontinuation, typically involving users who applied very high concentrations creating dependency-like patterns, possessed severe underlying skin conditions requiring ongoing treatment, experienced significant lifestyle or environmental stressors overwhelming skin resilience, discontinued abruptly without tapering from high-dose protocols, or had unrealistic perception inflation during treatment leading to exaggerated reversal perception.
User Group | Percentage | Treatment Pattern | Post-Stop Outcome | Maintenance at 6-12 Months |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Maintained Improvements | 30-40% | 6+ months, 1-2% concentration, consistent | Benefits largely persist | 50-70% of peak improvement |
Gradual Decline (Modal) | 40-50% | 2-4 months, variable consistency | Slow regression to baseline | 20-40% of peak improvement |
Rapid Reversal | 10-15% | High dose or short duration | Quick benefit loss | 0-20% of peak improvement |
Minimal Initial Benefit | 5-10% | Various patterns | Nothing to maintain | No change vs baseline |
The "minimal initial benefit" group (approximately 5-10% of users) reported limited improvements during treatment making discontinuation effects irrelevant, typically explained by inadequate product quality with degraded or low-concentration GHK-Cu, inappropriate application technique reducing absorption, unrealistic expectations exceeding what any topical can achieve, severe underlying pathology requiring medical intervention beyond cosmetic peptides, or individual non-responsiveness to copper peptide treatment for genetic or physiological reasons.
See GHK-Cu dosage and how to use copper peptides for optimal treatment protocols.
Comparing GHK-Cu discontinuation to other treatments
Understanding GHK-Cu discontinuation effects requires comparison to alternative anti-aging treatments revealing whether copper peptide dependency patterns prove more or less favorable than established interventions, helping users make informed decisions about treatment selection, cycling strategies, and long-term maintenance approaches balancing efficacy, safety, cost, and sustainability considerations.
Retinoid discontinuation creates the benchmark comparison since topical vitamin A derivatives (tretinoin, adapalene, retinol) represent gold-standard anti-aging treatment with decades of research and user experience documenting post-treatment outcomes. Retinoid mechanisms differ fundamentally from GHK-Cu by directly binding nuclear receptors controlling gene expression and cell turnover rather than providing enzymatic cofactors supporting natural processes, creating stronger effects but also more pronounced dependency where discontinuation often triggers rebound effects.
Users stopping retinoids frequently report rapid regression of benefits within 4-8 weeks including increased breakouts sometimes exceeding pre-treatment levels (retinoid rebound), accelerated fine line reappearance approaching or surpassing baseline, skin texture deterioration returning to pre-treatment roughness, and psychological dependency from dramatic visible decline creating pressure for continuous use despite side effect burden. The retinoid comparison makes GHK-Cu discontinuation appear favorable since copper peptide cessation typically produces gradual benefit decline without rebound worsening or dramatic rapid reversal.
Vitamin C serum discontinuation provides another relevant comparison since L-ascorbic acid represents popular antioxidant treatment with collagen synthesis stimulation and skin brightening effects partially overlapping GHK-Cu benefits. Vitamin C mechanisms involve serving as enzymatic cofactor for collagen hydroxylation and providing direct antioxidant protection, creating effects requiring ongoing application for maintaining antioxidant benefits but potentially supporting durable collagen improvements if used sufficiently long.
Users stopping vitamin C serums generally report gradual benefit decline over 2-4 months with antioxidant protection loss occurring quickly (days to weeks), skin brightness fading over 1-2 months returning toward baseline, and collagen-related firmness improvements showing variable persistence with 30-50% benefit retention long-term for consistent users. The vitamin C comparison suggests similar discontinuation profile to GHK-Cu where antioxidant effects prove temporary requiring ongoing use while structural improvements may persist partially depending on treatment duration and individual factors.
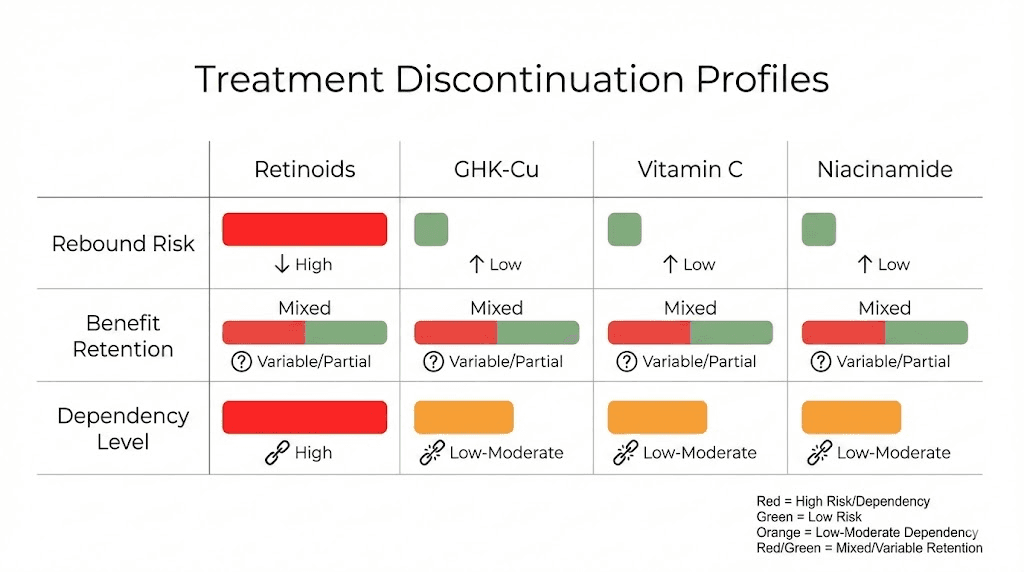
Treatment | Mechanism Type | Discontinuation Pattern | Rebound Risk | Benefit Retention | Dependency Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
GHK-Cu | Cofactor delivery, stimulation | Gradual decline 2-4 months | Low - rarely worse than baseline | Moderate 40-60% long-term users | Low - breaks tolerated well |
Retinoids | Direct gene expression control | Rapid reversal 4-8 weeks | High - often rebound worsening | Low 10-30% retention | High - continuous use typical |
Vitamin C | Cofactor + antioxidant | Gradual decline 2-4 months | Low - returns to baseline | Moderate 30-50% long-term | Moderate - benefits continuous use |
Niacinamide | Barrier support, inflammation | Slow decline 1-3 months | Very low - gentle regression | Moderate 40-60% if long-term | Low - flexible usage |
Peptides (other) | Variable stimulation | Variable by peptide | Low generally | Variable 20-70% | Low to moderate |
Niacinamide discontinuation offers comparison to another well-tolerated ingredient supporting skin barrier function, reducing inflammation, and providing multiple anti-aging benefits through gentle mechanisms rather than aggressive stimulation. Users stopping niacinamide typically experience very gradual benefit decline over 1-3 months without dramatic reversal, maintaining 40-60% of improvements long-term if treatment lasted 6+ months, and tolerating breaks or cycling without rebound effects or significant regression concerns.
The treatment comparison reveals GHK-Cu discontinuation profile proving more favorable than retinoids (less dependency, no rebound, better benefit retention) while similar to vitamin C and niacinamide (gradual decline, moderate long-term retention, low dependency). This positions copper peptide as relatively safe for breaks, cycling, or discontinuation compared to more aggressive treatments requiring continuous use for maintaining results or risking rebound worsening.
Cycling strategies and break protocols
The GHK-Cu discontinuation profile suggesting gradual benefit decline without rebound effects creates opportunity for cycling strategies potentially offering benefits including reduced long-term cost through intermittent rather than continuous product purchase, decreased skin adaptation risk by preventing tolerance to copper peptide stimulation, improved treatment responsiveness when restarting after breaks allowing periodic benefit surges, and psychological flexibility avoiding dependency mindset from continuous indefinite use requirements.
The continuous use approach represents traditional treatment strategy where daily GHK-Cu application continues indefinitely or until goals achieved, then potentially reduces to maintenance frequency (every other day or few times weekly) rather than complete discontinuation. This protocol suits users experiencing ongoing benefit from treatment without plateau, comfortable with indefinite commitment to regimen, financially able to sustain continuous product purchase, concerned about losing gains from treatment breaks, and preferring simple consistent routine over complex cycling schedules.
Continuous use advantages include maintaining peak benefits without decline periods, avoiding the uncertainty of whether improvements will persist after breaks, simplifying routine through consistency, and potentially maximizing cumulative collagen synthesis through sustained stimulation over months to years.
Disadvantages involve higher long-term costs from continuous product consumption, possible adaptation reducing treatment responsiveness over time, psychological dependency on continuous application, and unknown very long-term effects from years of daily copper supplementation.
The cycling approach alternates treatment periods with break periods, typically following patterns like 3-4 months on followed by 1-2 months off, 6 months on followed by 2-3 months off, or flexible cycling based on skin condition assessment and benefit plateau timing. This strategy suits users who plateau after several months suggesting diminishing returns, want to minimize long-term costs while maintaining some benefits, prefer avoiding indefinite commitments to any treatment, notice maintained improvements during initial breaks suggesting cycling viability, and value flexibility over maximum continuous optimization.
Cycling advantages include reduced annual costs through intermittent purchasing (30-40% savings vs continuous use), potentially improved responsiveness when restarting after breaks avoiding adaptation, psychological freedom from continuous dependency, and accommodation of life changes, travel, or budget fluctuations. Disadvantages involve benefit decline during off periods requiring acceptance of fluctuation, complexity planning and tracking cycles, uncertainty about optimal timing and duration for individual responses, and potential for forgetting to restart after extended breaks.
Cycling Protocol | On Period | Off Period | Annual Cost | Benefit Level | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Continuous Daily | Indefinite | None | 100% (baseline) | Maximum sustained | Peak optimization, no cost concern |
Maintenance (reduce frequency) | Initial intensive then ongoing | None (reduced frequency) | 50-70% | Sustained moderate | Achieved goals, maintain results |
3-4 Month Cycles | 3-4 months | 1-2 months | 60-70% | Moderate with fluctuation | Balance benefits and cost |
6 Month Cycles | 6 months | 2-3 months | 65-75% | Good with brief decline | Maximize cumulative effects |
Flexible/Responsive | Variable based on results | Variable based on decline | Variable 50-80% | Optimized to individual | Self-monitoring capability |
The maintenance frequency approach represents hybrid strategy where initial intensive treatment (daily application for 3-6 months) establishes improvements, then reduces to maintenance schedule (2-3 times weekly or every other day) rather than complete discontinuation. This protocol maintains copper supplementation supporting collagen synthesis without full daily intensity, potentially sustaining 60-80% of peak benefits at 50-70% of continuous use cost while avoiding complete benefit decline from full discontinuation.
Evidence for optimal cycling strategy remains limited since controlled studies examining different GHK-Cu application schedules over extended periods prove rare. User experimentation suggests that longer initial treatment periods (6+ months continuous) support better benefit retention during subsequent breaks, complete discontinuation breaks of 1-2 months show acceptable benefit maintenance for most users, and very extended breaks (3-6+ months) increase risk of regression toward pre-treatment baseline particularly for short initial treatment courses.
See should copper peptides be refrigerated and GHK-Cu shelf life for product storage during cycling.
Factors affecting post-discontinuation outcomes
Individual variation in GHK-Cu discontinuation effects stems from multiple factors determining whether benefits persist substantially or decline rapidly toward baseline, helping users predict likely personal outcomes and optimize treatment strategies for maximizing durable improvements requiring minimal ongoing intervention.
Treatment duration proves critical variable where longer courses create more durable changes - users completing 2-3 month treatments typically maintain 20-40% of peak benefits long-term, 4-6 month treatments sustain 40-60% of improvements, and 6-12+ month courses preserve 50-70% of maximum benefits potentially indefinitely. The duration effect suggests GHK-Cu induces cumulative structural changes in dermal architecture where longer treatment allows more complete remodeling supporting ongoing enhanced function without continuous peptide presence.
Concentration and formulation quality dramatically impact both treatment effectiveness and post-discontinuation durability. Products with 1-2% GHK-Cu concentration in stable formulations with appropriate pH and penetration enhancers create stronger improvements more likely persisting after treatment, while lower concentrations (0.1-0.5%) or degraded products may produce subtle temporary effects disappearing quickly upon discontinuation.
Users should verify product quality and concentration to ensure treatment intensity sufficient for inducing durable changes rather than temporary superficial effects.
Baseline skin condition influences retention potential where users treating specific correctable issues (scarring, hyperpigmentation, acute damage) tend maintaining improvements better than users seeking general anti-aging effects. A healed scar remains healed because underlying pathology resolved, while anti-aging collagen stimulation requires ongoing support for maintaining enhanced synthesis above baseline capacity. Users should recognize that GHK-Cu proves more effective for targeted repair than indefinite age prevention without continuous application.
Age and intrinsic collagen production capacity affect how well skin maintains improvements without ongoing stimulation. Younger users (20s-30s) with robust natural collagen synthesis often sustain GHK-Cu benefits better than older users (50s-60s) whose baseline production has declined substantially. However, older users often derive greater initial benefit making even partial retention valuable, while younger users might question whether modest improvements justify treatment investment when natural skin quality remains good.
Lifestyle and complementary skincare significantly influence post-discontinuation outcomes beyond GHK-Cu specific effects. Users maintaining excellent sun protection, adequate moisturization, healthy diet supporting collagen synthesis (adequate protein, vitamin C, copper from foods), sufficient sleep, stress management, and avoidance of collagen-damaging habits (smoking, excessive alcohol) preserve treatment gains better than users with suboptimal skincare and lifestyle creating ongoing skin stress overwhelming GHK-Cu induced improvements.
Factor | Impact on Benefit Retention | Optimal Level for Durability | Suboptimal Level Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
Treatment Duration | High impact | 6-12+ months | 2-3 months: Low retention 20-40% |
GHK-Cu Concentration | High impact | 1-2% in stable formulation | <0.5%: Minimal durability |
Baseline Skin Condition | Moderate impact | Specific correctable issues | General aging: Requires ongoing use |
Age / Natural Production | Moderate impact | Younger with good baseline | Older: May need maintenance |
Sun Protection | High impact | Daily SPF 30-50 | Inconsistent: Accelerated decline |
Complementary Skincare | Moderate impact | Optimized routine | Minimal: Faster regression |
Lifestyle Factors | Moderate impact | Sleep, diet, stress managed | Poor habits: Benefits fade quickly |
When breaks make sense vs continuous use
The decision between GHK-Cu cycling with breaks versus continuous indefinite application depends on individual goals, budget constraints, treatment response patterns, and philosophical approach to skincare interventions, with different strategies suiting different user profiles and priorities creating no single optimal approach applicable universally.
Breaks make sense for users experiencing treatment plateau where benefits cease increasing despite continued application suggesting diminishing returns from ongoing use, comfortable with some benefit decline during off periods accepting fluctuation in skin quality, budget-conscious seeking to minimize annual treatment costs through intermittent purchasing, philosophically preferring avoiding indefinite dependency on any skincare product, planning life changes incompatible with consistent application (extended travel, relocation, financial shifts), and wanting to assess whether improvements prove durable or require continuous maintenance before committing to indefinite treatment.
The break trial represents valuable experiment for any GHK-Cu user completing 6+ month treatment course - discontinuing for 2-3 months reveals how well benefits persist, helps determine whether cycling or continuous use better suits individual biology, provides psychological break from rigid routine, and offers cost savings period while assessing necessity of ongoing application. Users pleasantly surprised by benefit retention during breaks can adopt cycling approach, while those experiencing concerning decline might choose resuming continuous use or maintenance frequency application.
Continuous use makes sense for users still experiencing ongoing improvements without plateau suggesting continued benefit from sustained application, highly satisfied with current results wanting to maintain peak benefits without decline risk, financially comfortable with indefinite product investment as skincare priority, psychologically comfortable with long-term commitment to effective treatment, experiencing rapid benefit decline during previous break attempts indicating necessity of ongoing application, and prioritizing maximum results over cost optimization or flexibility concerns.
The maintenance frequency approach offers middle ground where users completing intensive initial treatment (6-12 months daily) transition to reduced frequency (2-4 times weekly) maintaining copper supplementation at lower intensity and cost while avoiding complete discontinuation allowing some benefit decline.
This strategy suits users who achieved satisfactory improvements wanting to preserve results without full continuous intensity, willing to accept moderate benefit levels (70-85% of peak) rather than maximum continuous optimization, seeking to minimize costs while maintaining most improvements, and wanting simpler approach than complex cycling schedules.
How you can use SeekPeptides for peptide guidance
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive peptide guides including copper peptides and alternatives. Learn about GHK-Cu benefits, GHK-Cu dosage, how to use copper peptides, GHK-Cu vs retinol, copper peptide side effects.
Access storage and handling guides - should copper peptides be refrigerated, GHK-Cu shelf life, how long does GHK-Cu last.
Explore alternative peptides - best peptides for skin, Matrixyl peptide, argireline peptide.
Learn fundamentals - what are peptides, how peptides work, peptide safety.
Use calculators - peptide calculator, cost calculator.
Final thoughts
Stopping GHK-Cu typically produces gradual benefit decline over 2-4 months without dramatic rebound effects or rapid reversal to pre-treatment baseline, with 30-40% of long-term users (6+ months treatment) maintaining 50-70% of peak improvements indefinitely while shorter-term users show greater regression toward baseline. The discontinuation profile proves more favorable than retinoids showing rapid rebound and high dependency, while similar to vitamin C and niacinamide demonstrating moderate benefit retention and low dependency patterns.
Treatment duration critically influences post-discontinuation outcomes with 6-12 month courses creating durable structural improvements supporting ongoing enhanced collagen synthesis without continuous peptide presence, while 2-3 month treatments produce temporary stimulation requiring continuous or cyclical application for maintaining optimal results. Individual factors including concentration used, baseline skin condition, age, lifestyle, and complementary skincare significantly affect benefit retention creating substantial variation in personal outcomes requiring experimentation for determining optimal individual approach.
Cycling strategies offer viable alternative to continuous use for many users, with protocols like 6 months on followed by 2-3 months off potentially maintaining 60-80% of continuous use benefits at 65-75% of annual cost while avoiding indefinite dependency and accommodation life flexibility. The maintenance frequency approach where intensive initial treatment transitions to reduced ongoing application (2-4 times weekly) provides middle ground sustaining benefits while minimizing costs and commitment intensity.
Your peptide skincare strategy should balance efficacy, sustainability, cost, and personal preferences through experimentation determining whether continuous GHK-Cu use, cycling protocols, maintenance frequency, or complete discontinuation after achieving goals best suits individual biology and lifestyle priorities.