Jan 21, 2026

Some people apply copper peptide cream and see firmer, smoother skin within weeks. Others use the same ingredient for months and notice nothing. The difference rarely comes down to genetics or luck. It comes down to choosing the right cream, using it correctly, and understanding what realistic results actually look like.
Copper peptides have earned their reputation as one of the most research-backed anti-aging ingredients available today. The science behind GHK-Cu is impressive, with studies showing increased collagen production, accelerated wound healing, and visible improvements in skin density and firmness. But here's the thing most skincare guides won't tell you: the formulation matters as much as the ingredient itself.
A cream delivers copper peptides differently than a serum. The concentration changes everything. The supporting ingredients can enhance or undermine the active. And the way you integrate a copper peptide cream into your skincare routine determines whether you get the results you're hoping for or end up disappointed.
This guide covers everything you need to know about creams with copper peptides. We'll explore how these compounds work at the cellular level, what makes cream formulations unique compared to other delivery methods, which concentrations actually produce results, what ingredients to look for alongside GHK-Cu, and how to avoid the common mistakes that lead to side effects or underwhelming outcomes.
Whether you're considering your first copper peptide product or troubleshooting why your current cream isn't delivering, you'll find specific, actionable guidance here.
What makes copper peptide creams different from serums
Understanding the distinction between creams and serums isn't just marketing terminology. These two formulation types deliver active ingredients to your skin in fundamentally different ways, and choosing the wrong format for your skin type or goals can significantly impact your results.
Serums are water-based, lightweight, and highly concentrated. They absorb quickly and penetrate deeper into the skin layers. Most copper peptide serums contain higher percentages of GHK-Cu precisely because the delivery vehicle allows for faster, more efficient absorption.
Creams work differently.
They're emulsion-based, combining water and oil phases to create a thicker, more nourishing texture. This formulation style offers several distinct advantages for copper peptide delivery. The occlusive properties of creams help seal the active ingredients against the skin, extending contact time and potentially improving penetration through the lipid barrier. Creams also provide additional moisturizing benefits that serums simply cannot match.
For people with mature or dry skin, this matters enormously. The skin's natural barrier function weakens with age, leading to increased transepidermal water loss and reduced ability to retain moisture. A well-formulated copper peptide cream addresses both the active ingredient delivery and the fundamental hydration needs that mature skin requires.
However, cream formulations typically contain lower concentrations of copper peptides than serums. This isn't necessarily a disadvantage. The extended contact time and improved barrier support can compensate for lower active percentages. Some research suggests that consistent, moderate exposure to copper peptides may produce better long-term results than sporadic high-dose applications.
When to choose a cream over a serum
Cream formulations work best for specific situations and skin types. If your skin tends toward dryness, a cream provides the hydrating base that serums lack. If you're looking to simplify your routine, a cream can replace both your peptide treatment and moisturizer in a single step.
Consider a copper peptide cream if you have dry to very dry skin that needs substantial moisturizing support alongside active treatment. The emollient base in creams helps restore and maintain the skin barrier while delivering GHK-Cu.
Are you over 40 and noticing significant loss of firmness or skin density? Mature skin benefits from the richer formulation and sustained delivery that creams provide.
Want to minimize the number of products in your routine without sacrificing results? Layering multiple products increases the risk of ingredient conflicts, and creams offer a more streamlined approach.
Experience sensitivity to highly concentrated actives? The buffered delivery of cream formulations tends to be gentler on reactive skin.
Prefer nighttime application when the skin's natural repair processes are most active? The occlusive properties of creams work especially well during sleep, when there's no makeup, sunscreen, or environmental exposure to interfere.
When a serum might be the better choice
Serums aren't inferior to creams. They're different tools for different situations.
If you have oily or acne-prone skin, heavy cream formulations may clog pores and worsen breakouts. A lightweight serum allows you to get the benefits of copper peptides without the comedogenic risk of rich creams.
If you're already using multiple products in your routine and need the copper peptides to layer smoothly under other treatments, a serum's thin consistency makes this easier. Serums absorb quickly and don't leave the residue that can interfere with subsequent product application.
If you want maximum potency and are willing to add a separate moisturizer afterward, a higher-concentration serum followed by a basic moisturizer might deliver more noticeable results than a moderate-concentration cream alone.
Understanding GHK-Cu concentrations in creams
Not all copper peptide creams are created equal. The concentration of GHK-Cu varies dramatically between products, and understanding what these percentages mean helps you make informed choices about which cream will actually deliver results for your skin concerns.
Dr. Loren Pickart, who isolated GHK-Cu from human plasma albumin in 1973, spent decades studying optimal concentrations for topical application. His research, along with subsequent clinical studies, provides useful benchmarks for evaluating cream formulations.
Clinical trials have demonstrated visible cosmetic effects with creams containing anywhere from 0.03% to 3.0% GHK-Cu. That's a hundredfold difference in concentration, yet both ends of the spectrum produced measurable improvements in skin appearance. This suggests that copper peptides are effective across a broad range of concentrations, though higher percentages tend to produce faster, more dramatic results.
Concentration guidelines by skin concern
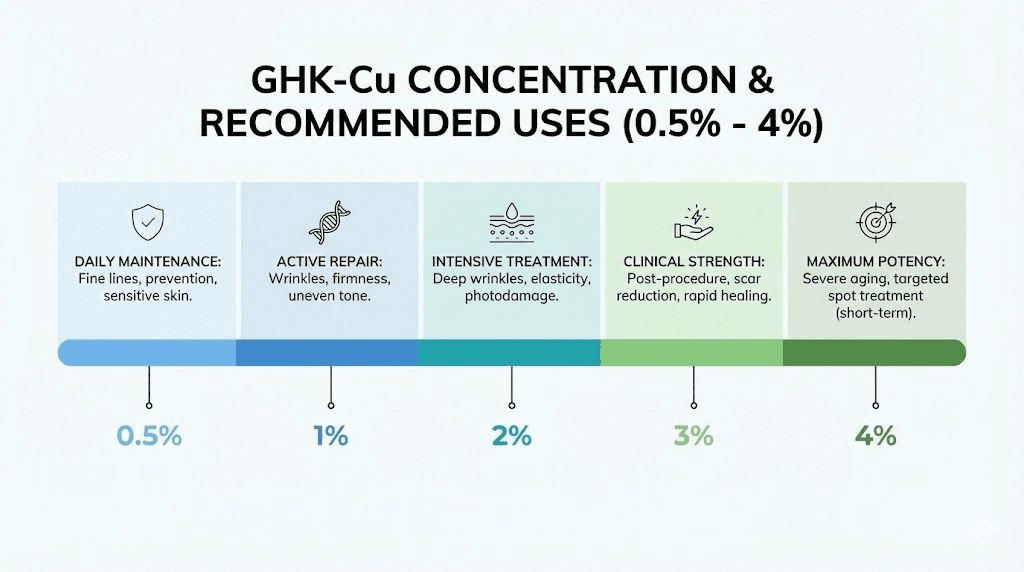
For general anti-aging maintenance and preventive care, creams in the 0.5% to 1% GHK-Cu range offer a good balance of efficacy and tolerability. These concentrations are gentle enough for daily use while still providing meaningful support for collagen production and skin barrier function.
For more significant concerns like loss of firmness, deeper wrinkles, or post-procedure healing, higher concentrations between 2% and 4% may produce better results. A 4% concentration is generally considered the sweet spot for face and neck applications, offering robust activity while remaining gentle enough for most skin types.
For the delicate eye area, lower concentrations around 2% are recommended. The skin around the eyes is thinner and more sensitive, and the reduced concentration minimizes the risk of irritation while still targeting dark circles and fine lines.
Pharmaceutical-grade compounded creams, available through specialized pharmacies, sometimes contain GHK-Cu at 0.5% with precise standardization. These products cost more but offer consistent, verified potency that mass-market products cannot always guarantee.
Why concentration isn't everything
Here's something the marketing materials don't emphasize: concentration alone doesn't determine effectiveness. The stability of the formulation, the quality of the raw GHK-Cu, the pH of the product, and the supporting ingredients all influence how much active ingredient actually reaches your skin cells and produces biological effects.
A 3% GHK-Cu cream with poor formulation stability might deliver less actual benefit than a well-formulated 1% product. The copper-peptide bond is relatively fragile, and improper formulation or storage can degrade the active before it ever touches your skin.
This is why buying from reputable brands with transparent sourcing and proper stability testing matters more than simply chasing the highest percentage you can find.
Key ingredients to look for alongside copper peptides
The best copper peptide creams don't rely on GHK-Cu alone. Strategic ingredient combinations can enhance the peptide's effectiveness, improve delivery, and provide complementary benefits that create better overall results than any single ingredient could achieve.
Understanding which ingredients work well with copper peptides, and which to avoid, helps you evaluate products and build an effective skincare routine.
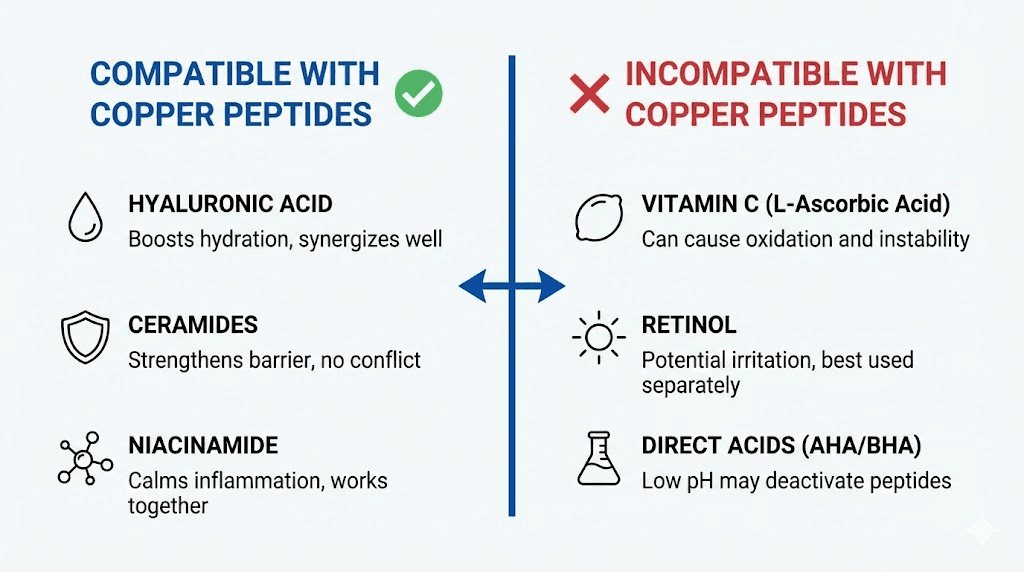
Hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is perhaps the ideal companion for copper peptides. This humectant can hold up to 1,000 times its weight in water, providing intense hydration that supports the skin's natural healing processes. When GHK-Cu stimulates collagen production and tissue regeneration, hyaluronic acid ensures the skin has the moisture it needs for these processes to occur optimally.
Look for creams containing multiple molecular weights of hyaluronic acid. Lower molecular weight versions penetrate deeper into the skin, while higher molecular weights form a hydrating film on the surface. This combination provides both immediate plumping effects and sustained deep hydration.
Complementary peptides
Many effective copper peptide creams include additional peptides that work through different mechanisms. Palmitoyl tripeptide and palmitoyl pentapeptide, for example, are signal peptides that encourage collagen synthesis through pathways distinct from GHK-Cu's actions.
The Snap-8 peptide relaxes facial muscles that contribute to expression lines.
Syn-Ake mimics the effects of snake venom peptides to smooth wrinkles. When these peptides are combined with GHK-Cu, the multi-pathway approach can produce more comprehensive anti-aging results.
Ceramides and fatty acids
Ceramides are lipids that naturally occur in the skin's barrier layer. As we age, ceramide levels decline, contributing to dryness, sensitivity, and increased transepidermal water loss. Copper peptide creams formulated with ceramides provide both the active treatment and the structural support the skin barrier needs to function properly.
Essential fatty acids like linoleic acid and oleic acid also support barrier function and can improve the overall health of the skin alongside GHK-Cu's regenerative effects.
Antioxidants with caution
Antioxidants can complement copper peptides by protecting the skin from environmental damage while GHK-Cu works on repair and regeneration. However, this combination requires careful formulation.
Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, but it's also highly acidic. The low pH can destabilize the copper-peptide bond, potentially reducing the effectiveness of both ingredients. If a cream contains both vitamin C and copper peptides, the formulation needs to be carefully balanced to prevent degradation.
Vitamin E, green tea extracts, and other antioxidants with less acidic profiles can work more harmoniously with copper peptides in the same formulation.
Soothing and anti-inflammatory agents
Ingredients like niacinamide, centella asiatica (cica), and aloe vera can help manage any initial irritation during the adjustment period when you first introduce copper peptides to your routine. They also provide their own skin benefits, from pore refinement to redness reduction.
Copper peptides already have anti-inflammatory properties, so these complementary ingredients enhance rather than duplicate the calming effects.
Ingredients to avoid in copper peptide creams
What's not in a cream matters as much as what's included. Certain ingredients can deactivate copper peptides, cause irritation when combined, or simply indicate poor formulation practices.
Direct acids
Alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) like glycolic acid and lactic acid, as well as beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) like salicylic acid, should not be in the same cream as copper peptides. The acidic pH required for these exfoliants to work effectively destabilizes the GHK-Cu complex.
This doesn't mean you can't use both in your routine, just not in the same product or at the same time. Applying acids in the morning and copper peptides at night allows you to get benefits from both without the conflict.
Retinoids in the same product
Retinol and retinoids are potent anti-aging ingredients in their own right, but combining them with copper peptides in a single product increases the risk of irritation. Both are active ingredients that stimulate cell turnover and collagen production through different mechanisms.
The good news is that copper peptides are often recommended as a gentler alternative to retinol for people who experience too much dryness or sensitivity with retinoids. If you want to use both, alternate nights rather than combining them in a single cream.
Heavy fragrances and essential oils
Fragrance is a common cause of skin sensitization, and when you're using an active ingredient like copper peptides, adding potential irritants to the mix is counterproductive. The best copper peptide creams are either fragrance-free or use only minimal, non-sensitizing scenting.
Essential oils, despite their natural origins, can be irritating or photosensitizing. Citrus oils are particularly problematic. If a copper peptide cream contains essential oils, check whether they're present in functional concentrations or just trace amounts for scent.
Zinc oxide at the same time
Dr. Pickart's research suggests that zinc oxide, commonly found in physical sunscreens, may interfere with copper ions' actions on the skin. The zinc can compete with copper for binding sites, potentially reducing the effectiveness of GHK-Cu.
The solution is simple: apply copper peptide cream in the evening and zinc oxide sunscreen in the morning. This timing allows you to benefit from both without the interference.
How to use copper peptide cream in your routine
The application method and timing of your copper peptide cream significantly impact results. Proper usage maximizes the active ingredient's effectiveness while minimizing the risk of irritation or ingredient conflicts.
Application order
Where copper peptide cream fits in your routine depends on your other products. The general principle is to apply products from thinnest to thickest consistency, allowing each layer to absorb before adding the next.
If your copper peptide product is a true cream with substantial thickness, it typically goes near the end of your routine. After cleansing and any water-based treatments like toner or essence, apply any serums you're using, then follow with the copper peptide cream. If you have a very rich cream or sleeping mask, that would go last.
If your copper peptide cream is lighter in consistency, more like a lotion, it can go earlier in the routine with a heavier moisturizer layered over top.
Morning versus evening application
Copper peptides can be used in either your morning or evening routine, but nighttime application often produces better results. During sleep, the skin shifts into repair mode, with increased cell turnover and regenerative activity. GHK-Cu's collagen-stimulating and healing properties align well with these natural nighttime processes.
Evening application also avoids potential conflicts with sunscreen ingredients and provides extended contact time without interference from makeup or environmental exposure throughout the day.
If you prefer morning application, the antioxidant properties of copper peptides can help protect skin from daytime environmental damage.
Just remember to apply sunscreen as your final step, and consider using a separate zinc-oxide free formula if you want to maximize the copper peptide activity.
How much to apply
More isn't better with active skincare ingredients.
A pea-sized amount of cream for the face is typically sufficient. Using too much can overwhelm the skin, leading to irritation, product pilling, or simply wasted product.
For the neck and décolletage, which also show signs of aging and benefit from copper peptide treatment, use an additional pea-sized amount and apply with gentle upward strokes.
Introduction protocol for beginners
If you're new to copper peptides, jumping straight to daily use isn't recommended. Your skin needs time to adjust to any new active ingredient, and gradual introduction reduces the risk of purging or irritation.
Week one: Apply the cream every third day, monitoring for any adverse reactions.
Week two: If your skin tolerates the initial frequency well, increase to every other day.
Week three and beyond: Move to daily application if your skin has adjusted without significant irritation, redness, or breakouts.
This graduated approach gives your skin's barrier time to adapt while still building toward the consistent use that produces visible results.
Expected results timeline
One of the biggest mistakes people make with copper peptide creams is expecting overnight transformation. GHK-Cu works by supporting the skin's natural regenerative processes, which take time. Understanding realistic timelines helps you stay consistent long enough to see actual results.
Weeks 1-2: Initial adjustment
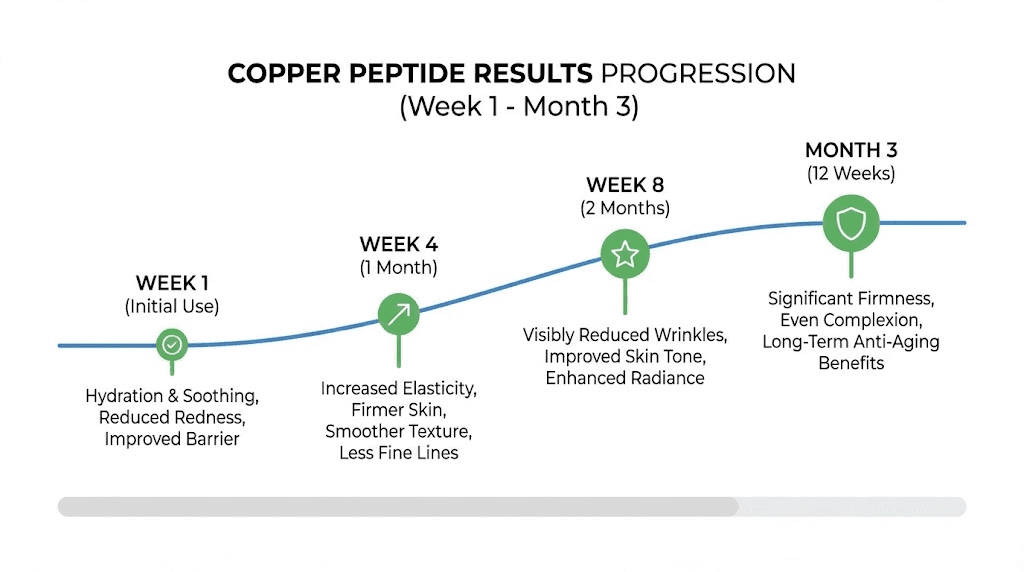
During the first two weeks, the most noticeable changes are often related to hydration and skin texture. The cream's moisturizing base provides immediate smoothing effects, and the copper peptides begin their work beneath the surface.
Some people experience mild purging during this period. If copper peptides accelerate cell turnover for your skin, congestion that was forming beneath the surface may come to a head more quickly. This is temporary and different from a true adverse reaction.
What you might notice: Improved hydration, smoother texture, possible temporary breakouts if you're prone to congestion.
Weeks 2-4: Early improvements
By the end of the first month, the skin barrier should be noticeably stronger. Redness and sensitivity often decrease as the copper peptides' anti-inflammatory effects take hold. The skin may appear calmer, more even-toned, and better able to retain moisture.
Fine lines, especially those caused by dehydration rather than deep structural changes, may begin to soften.
What you might notice: Reduced redness, calmer skin, early softening of fine lines, better moisture retention.
Weeks 6-8: Visible anti-aging effects
This is when the collagen-boosting effects become more apparent. GHK-Cu stimulates the production of collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans, the structural proteins that give skin its firmness and bounce. It takes several weeks for these new proteins to accumulate to levels that produce visible changes.
Texture improvements become more significant. Pore appearance may refine as the surrounding skin gains firmness and density.
What you might notice: Firmer feel, reduced fine lines, improved texture, more even skin tone.
Months 2-3: Significant transformation
Clinical studies on GHK-Cu typically measure outcomes at the 8-12 week mark because this is when the most dramatic before-and-after differences emerge. By this point, consistent users often report visibly improved skin density, reduced sagging, and noticeable wrinkle reduction.
A study of 71 women with mild to advanced photoaging found that 12 weeks of GHK-Cu cream application improved skin laxity, clarity, and appearance while reducing fine lines and the depth of wrinkles.
What you might notice: Improved skin density and thickness, reduced sagging, visible wrinkle reduction, overall rejuvenated appearance.
Beyond 3 months: Maintenance and continued improvement
Copper peptide benefits compound with continued use. While the most dramatic improvements often occur in the first three months, skin continues to benefit from ongoing GHK-Cu application. The key is consistency, using the cream regularly to maintain the collagen-stimulating and regenerative effects.
For researchers serious about optimizing their skincare protocols, SeekPeptides offers comprehensive resources on peptide-based skincare strategies and evidence-based guidance for long-term use.
Copper peptide cream for different skin types
While copper peptides are generally well-tolerated across skin types, optimizing your cream choice and usage approach based on your specific skin characteristics produces better results with fewer problems.
Dry skin
Copper peptide creams are particularly well-suited for dry skin. The emollient base provides the substantial hydration that dry skin needs, while GHK-Cu supports barrier function and helps the skin better retain moisture over time.
Look for formulations that include ceramides, fatty acids, and hyaluronic acid alongside the copper peptides. These ingredients work synergistically to address both the active treatment and the fundamental hydration needs.
People with dry skin can often use richer cream formulations without problems and may benefit from applying a thin layer of facial oil over the copper peptide cream to further seal in moisture.
Oily skin
Oily skin requires more careful product selection. Heavy cream formulations can clog pores and worsen acne, even though copper peptides themselves have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit breakout-prone skin.
Look for lightweight, non-comedogenic copper peptide creams or lotion-consistency products. Gel-cream hybrids can provide the peptide benefits without the heaviness. Alternatively, consider using a copper peptide serum followed by a lightweight moisturizer rather than a rich cream.
The good news is that copper peptides can actually help with acne scarring and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation common in oily skin types, making them a valuable addition to the routine when chosen appropriately.
Sensitive skin
Sensitive skin often reacts to potent active ingredients, but copper peptides are generally one of the gentler options available.
GHK-Cu's natural anti-inflammatory properties mean it tends to calm rather than irritate reactive skin.
Still, proceed with caution. Start with a lower concentration (0.5-1% GHK-Cu), introduce gradually, and choose formulations free of common sensitizers like fragrance, essential oils, and dyes. Barrier-supporting ingredients like niacinamide and centella asiatica can help buffer any initial adjustment period.
People with conditions like rosacea or eczema may actually benefit from copper peptides, as the anti-inflammatory and barrier-supporting effects can help manage symptoms. However, consult with a dermatologist before adding any new active to a reactive skin routine.
Combination skin
Combination skin with oily T-zone and dry cheeks can be tricky. A medium-weight copper peptide cream applied primarily to the drier areas, with a thinner layer on the oily zone, often works well. Alternatively, use a lighter serum on oily areas and the cream only where extra hydration is needed.
Pay attention to how different areas of your face respond and adjust application accordingly.
Mature skin
Mature skin, typically over 40, is perhaps the ideal candidate for copper peptide cream. Age-related decline in collagen, elastin, and skin thickness means there's more room for improvement, and the repair-stimulating effects of GHK-Cu directly address these concerns.
Mature skin also tends toward dryness as oil production decreases with age, making the rich moisturizing base of cream formulations especially appropriate. Higher concentrations (2-4% GHK-Cu) are generally well-tolerated in mature skin and may be necessary to produce meaningful improvements in significant laxity or deep wrinkles.
SeekPeptides provides tailored guidance for perimenopause and menopause skin concerns, including how copper peptides fit into a comprehensive anti-aging strategy.
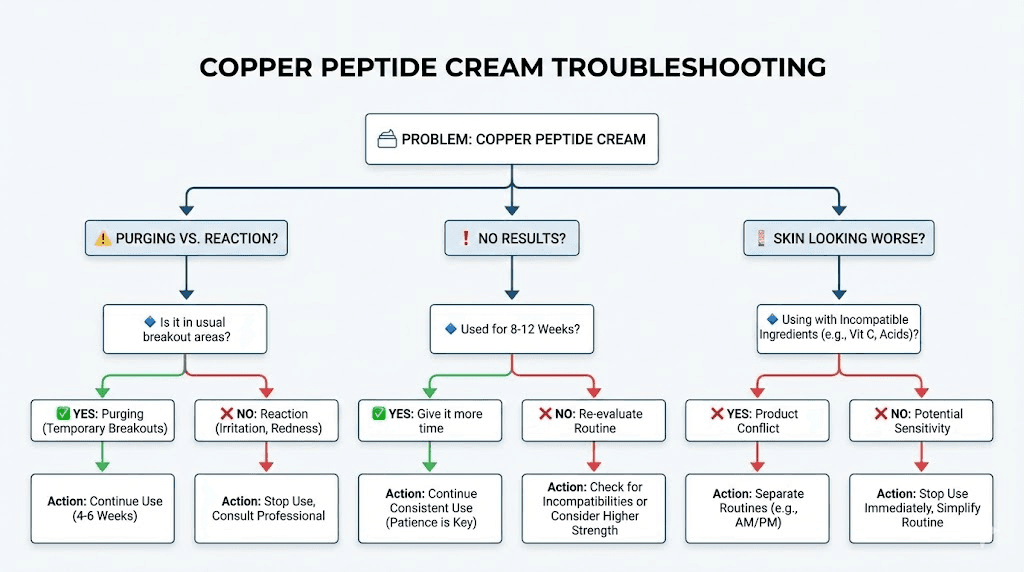
Troubleshooting common problems
Even with careful product selection and proper usage, issues can arise. Knowing how to identify and address common problems helps you get back on track rather than abandoning an otherwise beneficial ingredient.
Purging versus allergic reaction
This distinction is crucial. Purging is a temporary increase in breakouts that occurs when ingredients accelerating cell turnover bring existing congestion to the surface faster. It's uncomfortable but ultimately a sign that the product is working, and it resolves within 4-6 weeks as the congestion clears.
Allergic reactions are different. They involve symptoms like persistent redness, burning, stinging, hives, or swelling that occur immediately upon application and worsen with continued use. True copper sensitivity is rare, but it does exist.
How to tell the difference: Purging appears in areas where you typically break out, develops gradually over days to weeks, and resolves within one skin cycle (about 4-6 weeks). The breakouts clear relatively quickly and don't cause additional symptoms like itching or burning.
Reactions appear anywhere on the face, occur quickly after application, persist or worsen with continued use, and are accompanied by symptoms like stinging, itching, or unusual redness.
If you're experiencing a reaction rather than purging, stop using the product immediately and focus on barrier repair until symptoms resolve.
No visible results after 8+ weeks
If you've been using your copper peptide cream consistently for two months or more without any noticeable improvement, several factors might be involved.
The concentration may be too low for your skin concerns. Creams with minimal GHK-Cu (under 0.5%) may not deliver enough active ingredient to produce visible changes, especially for significant aging concerns.
The product may have degraded. GHK-Cu is relatively unstable, and improper storage or old product can significantly reduce effectiveness. Check the expiration date, ensure you're storing properly, and consider whether the product might have been compromised.
Ingredient conflicts in your routine may be neutralizing the copper peptides. Review your other products for acids, retinoids, or vitamin C that might be applied too close in time to the copper peptide cream.
Your expectations may need adjustment. Copper peptide creams support and enhance natural skin function; they don't produce dramatic overnight changes. The improvements can be subtle enough that you don't notice them unless you compare photos from before you started.
Skin looks worse after starting
Sometimes called "copper peptide uglies," this phenomenon involves the skin appearing older or more damaged rather than improved after starting copper peptide use. It's rare but real, and there are several possible explanations.
You may be using too much too fast. High concentrations applied daily from day one can overwhelm the skin, causing irritation that manifests as increased fine lines, dryness, or dullness. Scale back frequency and amount.
You may have an incompatible routine. Copper peptides combined with other potent actives can stress the skin barrier, leading to a degraded appearance. Simplify your routine and eliminate potential conflicts.
You may be one of the small percentage of people whose skin simply doesn't respond well to copper peptides. Despite the ingredient's generally excellent tolerance profile, individual variation exists. If problems persist after troubleshooting, discontinue use.
Blue residue on skin
Copper peptides have a naturally blue color due to the copper content, and some formulations can leave a slight blue tint on the skin. This is usually temporary and fades after the product absorbs, but it can be more noticeable with higher concentrations or certain formulation types.
If the blue tint bothers you, try applying a thinner layer, waiting longer for absorption before adding other products, or switching to evening-only use when the temporary color is less of a concern.
How to evaluate copper peptide cream quality
The skincare market offers countless copper peptide creams at dramatically different price points. Understanding what separates quality products from ineffective ones helps you invest wisely.
Transparency about concentration
Quality brands clearly state the GHK-Cu concentration in their products. Vague language like "contains copper peptides" without specifying percentage is a red flag.
If a company won't tell you how much active ingredient is in the formula, you have no way to evaluate whether the product can actually deliver results.
Be wary of products that bury copper peptides low on the ingredient list. Ingredients are listed in order of concentration, so a copper peptide cream with GHK-Cu as the 15th ingredient contains very little of the active.
Appropriate packaging
Copper peptides are sensitive to light and air exposure. Products packaged in clear jars that you open repeatedly expose the contents to degradation-promoting conditions. Better options include opaque containers that protect from light, airless pump systems that minimize air exposure with each use, tubes that can be squeezed from the bottom reducing air contact, and individual-dose packaging that keeps unused product sealed.
A beautifully designed clear glass jar might look luxurious, but it's a poor choice for protecting a sensitive active ingredient.
Formulation stability evidence
Some companies provide stability testing data showing that their product maintains potency over time. While this information isn't always publicly available, brands that invest in proper stability testing are more likely to deliver consistent, effective products.
Customer service should be able to answer questions about shelf life, storage recommendations, and formulation stability.
Clean formulation practices
The absence of problematic ingredients is as important as the presence of beneficial ones. Look for products free from parabens (controversial preservatives), synthetic fragrances (common sensitizers), phthalates (endocrine-disrupting compounds), and artificial dyes (which serve no functional purpose and can irritate).
Third-party testing
Some copper peptide products undergo third-party testing for purity and potency. Certificates of analysis from independent labs verify that the product contains what the label claims. While not all quality products have third-party testing, its presence is a strong positive indicator.
Copper peptide cream versus other anti-aging treatments
How does copper peptide cream compare to other anti-aging options? Understanding the relative strengths and limitations helps you decide where copper peptides fit in your overall skincare strategy.
Copper peptide cream versus retinol
Retinol is often considered the gold standard for anti-aging, and for good reason. It has decades of research supporting its effectiveness for wrinkles, texture, and skin tone.
However, retinol comes with significant drawbacks. Many people can't tolerate it due to dryness, peeling, redness, and sensitivity. Sun sensitivity increases with retinol use. And the adaptation period can be uncomfortable.
Copper peptides offer similar benefits, stimulating collagen and improving skin regeneration, with dramatically better tolerability. For people who can't use retinol, copper peptides provide a gentler alternative that still delivers meaningful anti-aging results.
For those who tolerate retinol well, the two ingredients can be used together, just not at the same time. Alternating nights allows you to benefit from both.
Copper peptide cream versus vitamin C serum
Vitamin C is primarily an antioxidant that protects against environmental damage and brightens the skin. Copper peptides focus more on repair and regeneration. These different mechanisms make them potentially complementary rather than directly competing.
The challenge is that vitamin C's acidity can destabilize copper peptides. Using vitamin C in the morning and copper peptides at night avoids this conflict while giving you the benefits of both.
Copper peptide cream versus Botox
Botox and copper peptide cream work through completely different mechanisms. Botox temporarily paralyzes muscles to reduce expression lines. Copper peptides stimulate skin's own repair processes to improve overall skin quality.
They're not really competitors. Botox addresses dynamic wrinkles (those caused by muscle movement), while copper peptides address skin texture, firmness, and static wrinkles.
Many people use both: Botox for specific expression lines and copper peptide cream for overall skin health.
Copper peptide cream versus professional treatments
Professional treatments like laser resurfacing, chemical peels, and microneedling produce more dramatic results than any topical product, including copper peptide cream. However, they also require downtime, carry more risks, and cost significantly more.
Copper peptide creams are most appropriate for maintenance between professional treatments, people who prefer non-invasive approaches, those with mild to moderate concerns that don't warrant professional intervention, and post-procedure healing support, as GHK-Cu has been shown to improve recovery from laser treatments and other procedures.
For people serious about optimizing their approach to skin health, SeekPeptides members access comprehensive comparisons and personalized guidance for combining topical and professional treatments effectively.
Storage and shelf life considerations
Proper storage extends the effective life of your copper peptide cream and ensures you're getting the full benefit of the active ingredient.
Temperature requirements
Most copper peptide creams should be stored at room temperature away from heat sources. However, refrigeration can extend shelf life and may improve stability for some formulations.
Check the specific storage instructions for your product. Some formulations are designed for refrigeration, while others may separate or thicken excessively when cold.
Light exposure
Light degrades many cosmetic actives, including copper peptides.
Store your cream in a dark location, and if the product comes in a clear container, consider wrapping it in foil or keeping it in a drawer.
Shelf life
Unopened copper peptide creams typically last 1-2 years from manufacture date. Once opened, most products should be used within 6-12 months, though this varies by formulation and preservative system.
Signs of degradation include color changes (particularly browning of the normally blue-tinted product), unusual odor, separation of the cream phases, or texture changes. If your product shows these signs, it's time to replace it regardless of the expiration date.
Duration of use for a container depends on application amount and frequency. A 50ml cream used twice daily typically lasts 2-3 months.
Combining copper peptide cream with other skincare products
Building an effective skincare routine around copper peptide cream requires understanding how it interacts with other products. The goal is synergy rather than conflict.
Compatible products to layer
Hyaluronic acid serums can be applied before copper peptide cream to boost hydration. The humectant properties help the skin absorb subsequent products while providing complementary benefits.
Niacinamide products work well alongside copper peptides, offering pore-refining and barrier-supporting benefits without ingredient conflicts.
Gentle cleansers that don't strip the skin barrier set the stage for effective copper peptide absorption. Avoid harsh sulfate cleansers that compromise barrier function.
Non-zinc sunscreens in the morning allow you to protect from UV damage without the potential copper-zinc interaction concern.
Products requiring separation
AHAs, BHAs, and other chemical exfoliants should be used at a different time than copper peptides. Morning acids with evening copper peptides, or alternating days, prevents pH conflicts.
Retinoids are best used on alternate nights from copper peptides. Both are powerful actives that can over-stress the skin when combined.
Vitamin C serums work best in the morning, with copper peptides reserved for evening use. This timing allows both ingredients to work optimally without the stability issues that arise from direct combination.
Sample routine for dry skin
Morning: Gentle cleanser, hyaluronic acid serum, vitamin C serum, moisturizer, sunscreen.
Evening: Gentle cleanser, hydrating toner, copper peptide cream, facial oil (optional).
Sample routine for oily skin
Morning: Gentle cleanser, niacinamide serum, lightweight moisturizer, sunscreen.
Evening: Gentle cleanser, BHA toner (2-3 nights per week), lightweight copper peptide cream or lotion.
Sample routine for mature skin
Morning: Gentle cleanser, antioxidant serum, moisturizer, sunscreen.
Evening: Gentle cleanser, hyaluronic acid serum, copper peptide cream (higher concentration), eye cream with peptides.
Frequently asked questions
Can I use copper peptide cream every day?
Yes, once your skin has adjusted to the ingredient. Start with every third day for the first week, increase to every other day, and progress to daily use if your skin tolerates it well. Many people use copper peptides daily without issues, though twice daily isn't necessary and can increase irritation risk.
What concentration of GHK-Cu should I look for?
For general anti-aging maintenance, 0.5-1% GHK-Cu is appropriate. For more significant concerns like loss of firmness or deeper wrinkles, 2-4% concentrations may be more effective. See our concentration guide for detailed recommendations by skin concern.
Can I use copper peptide cream around my eyes?
Yes, copper peptides can benefit the delicate eye area. Look for products specifically formulated for the eyes, which typically contain lower concentrations (around 2%) and are tested for safety near the eyes. Some people use their regular copper peptide cream around the eyes without issues, but be cautious with higher-concentration products.
Will copper peptide cream make me purge?
Some people experience temporary purging when starting copper peptides due to accelerated cell turnover. This typically resolves within 4-6 weeks. If breakouts persist beyond 6 weeks or are accompanied by irritation symptoms, it may be a reaction rather than purging.
Can I use copper peptide cream if I have rosacea?
Copper peptides' anti-inflammatory properties can actually benefit rosacea-prone skin. However, introduce the product gradually and choose formulations without fragrances, essential oils, or other potential irritants. Consult with a dermatologist before adding new actives to a rosacea management routine.
How long until I see results from copper peptide cream?
Initial improvements in hydration and texture may appear within 2-4 weeks. Visible anti-aging effects like firmer skin and reduced fine lines typically emerge at 6-8 weeks, with the most significant results appearing after 2-3 months of consistent use. See our before and after guide for detailed timeline information.
What happens if I stop using copper peptide cream?
If you discontinue use, the skin won't immediately revert to its previous state, but the ongoing collagen-stimulating and regenerative benefits will stop. Over time, natural aging processes will continue. There's no rebound effect or worsening from stopping copper peptides.
Can I use copper peptide cream during pregnancy?
There's limited research on topical GHK-Cu use during pregnancy. While copper is a naturally occurring element in the body and topical products have minimal systemic absorption, consult with your healthcare provider before using any active skincare ingredients during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
External resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your copper peptides stay potent, your skin barrier stay intact, and your results stay consistent. Join us.