Jan 16, 2026

The mirror doesn't lie. Every morning you see them. The tiny craters where cystic acne once raged. The textured terrain across your cheeks from years of breakouts. The reminder that even after the acne finally cleared, it left its mark.
You've tried the acids. The retinoids. The expensive treatments that promised results but delivered frustration. And now you're wondering whether copper peptides might finally be different.
Here's what the research actually shows.
Copper peptides work through mechanisms that directly address scar tissue formation. They stimulate collagen production, yes, but more importantly, they influence how that collagen organizes. Random, disorganized collagen creates visible scars. Properly structured collagen creates smooth, healthy skin. Copper peptides help tip the balance toward organization.
Clinical studies on acne scars specifically show promising results. Improvement in superficial and moderately deep scars. Reduction in post-acne pigmentation. Better outcomes when combined with treatments like microneedling. This isn't theoretical, it's documented in peer-reviewed research with before-and-after assessments using standardized scoring systems.
This guide covers everything you need to know about using copper peptides for acne scars. We'll examine the different scar types and which respond best, the research findings that matter, practical protocols you can implement, and realistic timelines for seeing results. SeekPeptides members consistently report that understanding these specifics transforms their scar treatment outcomes.
Understanding Acne Scars and Why They Form
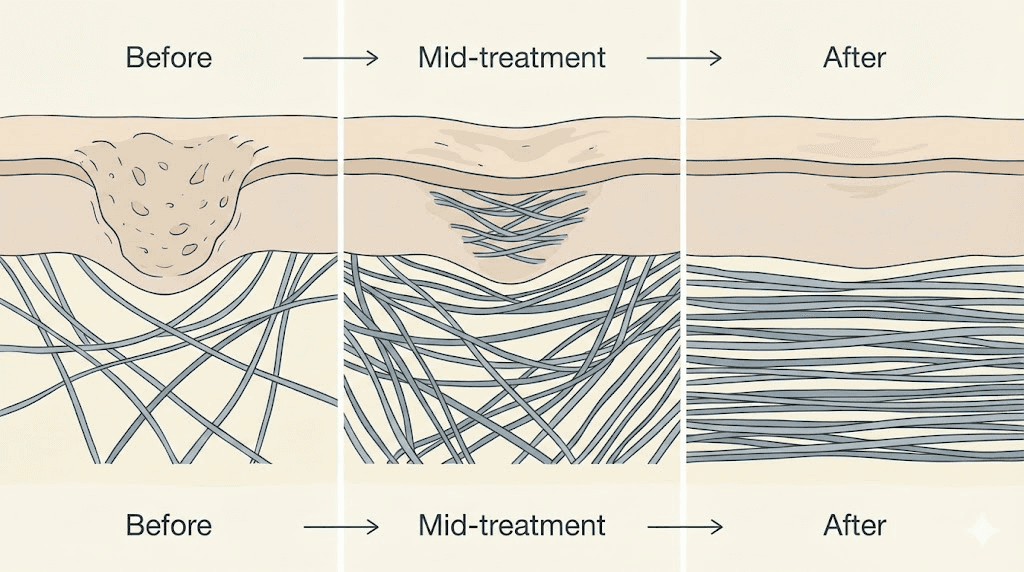
Before treating any condition, you need to understand what you're treating. Acne scars aren't simply surface marks. They represent structural changes in the skin that occurred during the healing process after inflammatory acne.
The Biology of Scar Formation
When acne causes inflammation deep in the skin, your body responds with a wound-healing cascade. Immune cells arrive at the site. Growth factors signal fibroblasts to produce collagen. New blood vessels form to supply nutrients. Eventually, the wound closes.
The problem is how that collagen gets deposited.
In normal wound healing, collagen fibers organize in a basket-weave pattern that matches surrounding tissue. The repair blends seamlessly with healthy skin. But when inflammation is severe or prolonged, the healing process rushes.
Collagen gets laid down chaotically instead of organized properly. The result is scar tissue that looks and feels different from normal skin.
Some acne causes the opposite problem. Instead of producing disorganized collagen, the body fails to produce enough collagen at all. The tissue never fully rebuilds. What remains is a depression, a permanent indent where skin structure was lost and never replaced.
Understanding how peptides influence these processes explains why they help with scarring.
The Different Types of Acne Scars
Not all acne scars are the same. Dermatologists classify them into distinct categories, each with different characteristics and treatment responses.
Atrophic scars are depressions in the skin, the most common type from inflammatory acne. They form when the wound-healing response doesn't produce enough new tissue to fill the damaged area. Atrophic scars divide into three subtypes.
Ice pick scars comprise 60 to 70 percent of atrophic scars. They're narrow, deep, V-shaped pits that extend vertically into the dermis or even the subcutaneous tissue. Think of them as tiny, sharp punctures. They're called ice pick scars because they look like wounds from an ice pick, narrow at the surface but extending deep. These are the most challenging scars to treat because of their depth and narrow shape.
Boxcar scars comprise 20 to 30 percent of atrophic scars. They're wider than ice pick scars, typically 1.5 to 4 millimeters, with round or oval shapes and sharply defined vertical edges. Picture a box pressed into the skin. The walls are steep, the floor is flat, and the edges are clearly demarcated. Boxcar scars most commonly form on the lower cheeks and jaw where skin is relatively thick.
Rolling scars have sloping edges that create a wavy, undulating appearance across the skin surface. They're caused by fibrous bands that tether the skin surface to deeper structures, pulling down in multiple spots. Rolling scars become more pronounced as skin ages and loses elasticity, making the wave-like texture more visible.
Hypertrophic scars are the opposite of atrophic scars, raised rather than depressed. They form when the wound-healing response produces too much collagen. The excess tissue stays within the boundaries of the original wound. Keloid scars are similar but grow beyond the original wound boundaries, sometimes significantly larger than the initial acne lesion.
The peptide results guide shows how different scar types respond to treatment.
Why Scar Age Matters
Clinical research reveals an important finding: scar age affects treatment response. Scars less than five years old respond better to copper peptide treatment than older scars. This makes sense biologically, younger scars have more active remodeling potential, more cellular activity, more opportunity for intervention to redirect the healing process.
Scars that have been present for six to ten years still improve with treatment, but the process takes longer and results may be more modest. The tissue has become more stable, more resistant to change. You're working against established structures rather than redirecting active processes.
This doesn't mean older scars are hopeless. It means expectations should be calibrated accordingly, and treatment duration may need to extend beyond what younger scars require.
How Copper Peptides Work on Scar Tissue
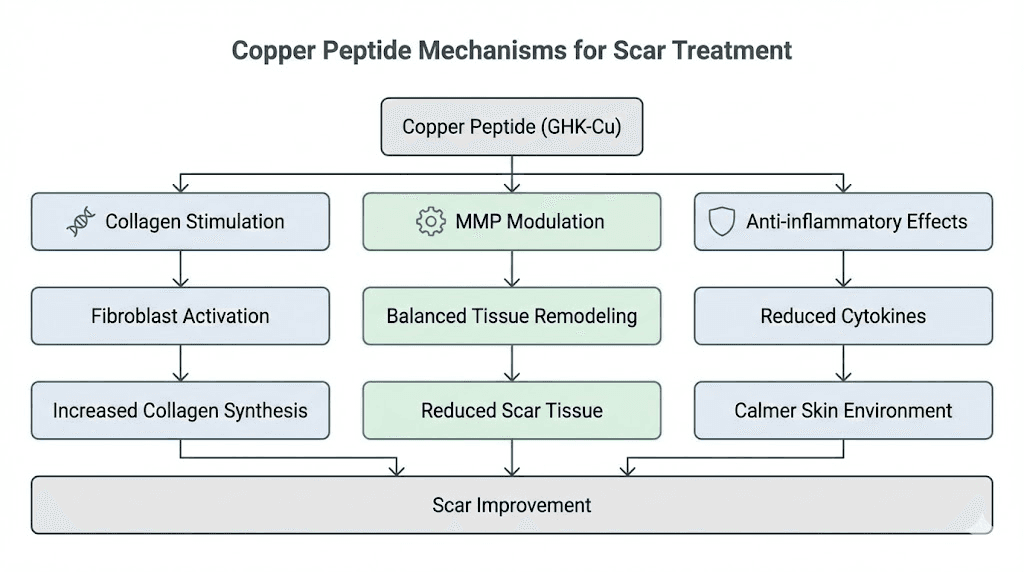
Copper peptides offer several mechanisms relevant to scar treatment. Understanding these mechanisms helps explain why they work and how to optimize their effects.
Collagen Production and Organization
GHK-Cu stimulates fibroblasts to produce collagen, but quantity isn't the only factor. The peptide also influences collagen quality and organization. Research shows that GHK-Cu promotes the production of Type I collagen for structural support and Type III collagen for tissue flexibility and repair.
More importantly, copper peptides appear to promote organized collagen deposition rather than the random arrangement typical of scar tissue. Studies report reduced scar formation with improved aesthetic outcomes when copper peptides are part of the wound-healing process. The collagen that forms creates smoother, more natural-appearing tissue.
Laboratory studies demonstrate that human dermal fibroblasts treated with GHK-Cu at various concentrations showed enhanced collagen and elastin synthesis. Some research suggests collagen production increases by up to 70% in copper peptide-treated samples.
The copper peptide concentration guide helps optimize these effects.
Matrix Metalloproteinase Modulation
Copper peptides do something counterintuitive. They stimulate both collagen production and collagen breakdown. This dual action is actually crucial for scar treatment.
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are enzymes that break down extracellular matrix components including collagen. In scar tissue, you don't just need new collagen, you need the old, disorganized collagen removed and replaced. GHK-Cu modulates both MMP activity and their inhibitors, essentially overseeing a tissue remodeling process rather than just adding more material.
Think of renovation rather than just construction.
To transform a damaged room, you can't just pile new materials on top of the mess. You need to clear damaged elements while building new ones. Copper peptides support both demolition and construction phases of tissue remodeling.
Growth Factor Signaling
GHK-Cu influences multiple growth factors involved in wound healing and tissue repair. It affects transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) signaling, which plays a central role in scar formation.
The balance of TGF-β isoforms determines whether healing produces scars or regenerates normal tissue.
Research highlights copper peptides as promising agents for scar-minimizing and potentially scarless wound healing due to their ability to modulate growth factor signaling. They help shift the balance from scarring toward more normal tissue regeneration.
This growth factor modulation helps explain why copper peptides might be useful not just for treating existing scars but also for preventing new scars from forming during active acne healing.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation drives scar formation. The more severe and prolonged the inflammation during acne, the worse the resulting scars. Copper peptides possess anti-inflammatory properties that may help on multiple fronts.
For existing scars, reducing background inflammation creates a better environment for tissue remodeling. For active breakouts, calming inflammation may reduce the severity of scars that form from current lesions. The anti-inflammatory action works through inhibition of NFkB, a master regulator of inflammatory response.
The KPV peptide offers additional anti-inflammatory support that some researchers combine with copper peptides.
What Clinical Research Shows
Theory matters, but clinical evidence matters more. Let's examine what controlled studies actually demonstrate about copper peptides and acne scars.
The Dermaroller Comparison Study
One of the most significant studies directly examined copper peptides for acne scars. Researchers compared dermaroller treatment alone versus dermaroller combined with copper peptide compound. Patients with facial acne scars were divided into two groups and followed for 16 weeks, with assessments every three weeks using the Goodman and Baron scoring system, a standardized method for evaluating acne scar severity.
The findings were nuanced and instructive.
Both groups showed significant improvement in superficial and moderately deep scars. Both groups showed improved skin texture and reduction in post-acne pigmentation. The copper peptide group showed faster initial improvements in the early weeks. However, from week six onward, the differences between groups narrowed, with both treatments producing similar long-term results.
The study concluded that copper peptides may drive faster initial improvement, but microneedling alone achieves comparable outcomes over extended treatment periods. This suggests copper peptides accelerate the healing process rather than fundamentally changing the outcome.
Results by Scar Type
The research showed different response patterns for different scar types. Boxcar scars showed the best results when copper peptides were added to dermaroller treatment. This makes sense given boxcar scars' relatively accessible structure, wide enough for treatment penetration but with clear boundaries for remodeling.
Ice pick scars, the most challenging type, showed improvement but remained difficult to fully resolve.
Their narrow, deep structure limits how much any topical or microneedling approach can accomplish. Many dermatologists recommend punch excision or grafting for severe ice pick scars, with copper peptides potentially playing a supporting role in healing.
Rolling scars responded well to treatment, likely because their tethered fibrous bands benefit from the tissue remodeling copper peptides promote. Breaking up the bands that pull skin downward, combined with new collagen formation, addresses the fundamental problem causing rolling scars' appearance.
Age-Related Response Patterns
The research revealed interesting age-related findings. Patients under 25 in the copper peptide group showed faster decline in scar severity scores compared to dermaroller alone. This suggests copper peptides may accelerate improvement particularly in younger individuals whose tissue has higher regenerative potential.
Patients over 25 showed improvement in both groups, but the copper peptide group maintained slightly better results. The difference was less dramatic than in younger patients but still present. These findings indicate that copper peptides benefit all ages but may produce faster results in younger patients.
Skin Type Considerations
For patients with Fitzpatrick skin type 5, those with darker skin tones, the copper peptide group showed greater improvement compared to dermaroller alone. This finding is significant because darker skin types face higher risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from many acne scar treatments.
However, the research also noted a complication. Hyperpigmentation was observed more commonly in the copper peptide group than in dermaroller alone in some assessments. This hyperpigmentation typically diminished in follow-ups after the study period, but it represents a temporary concern requiring management.
The copper peptide results guide provides additional visual documentation of treatment outcomes.
Scar Age Impact
For scars less than five years old, dermaroller with copper peptide showed greater improvement compared to dermaroller alone. The difference was statistically significant and clinically meaningful. For scars lasting six to ten years, both groups improved, but the copper peptide group maintained a more pronounced decline in scar severity.
This finding has practical implications. If your scars are relatively recent, adding copper peptides to treatment may provide meaningful acceleration. If your scars are older, copper peptides still help but the advantage over other treatments becomes less dramatic.
Copper Peptides Versus Other Scar Treatments
How do copper peptides compare to other approaches for acne scars? Understanding the landscape helps you make informed decisions about incorporating copper peptides into a treatment plan.
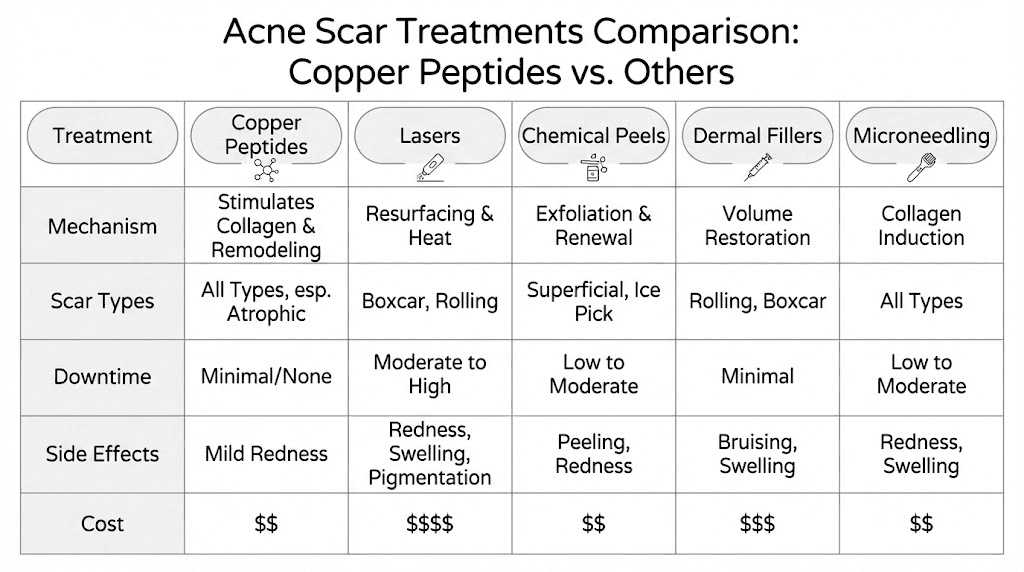
Versus Retinoids
Retinoids, including retinol and prescription tretinoin, stimulate cell turnover and collagen production. They're proven effective for improving skin texture and reducing fine lines. For acne scars, retinoids can help by promoting overall skin renewal and collagen synthesis.
Copper peptides work through different mechanisms. They modulate tissue remodeling rather than simply accelerating turnover. They promote organized collagen formation rather than just increased collagen quantity. They support wound healing specifically rather than general skin renewal.
The approaches can be complementary. Some researchers use both, applying copper peptides and retinol on different nights or at different times of day. The retinoid provides ongoing skin renewal stimulus while copper peptides address tissue organization and healing support.
Versus Chemical Peels
Chemical peels remove damaged surface skin, prompting regeneration of new tissue. Superficial peels address minor textural issues. Medium and deep peels can improve more significant scarring by removing damaged layers and triggering collagen production during healing.
Copper peptides work from a different angle. Rather than removing tissue to prompt regeneration, they support the remodeling of existing tissue. Research suggests that combining approaches may provide synergistic benefits, with chemical peels removing damaged surface tissue and copper peptides optimizing the healing that follows.
Scientific evidence indicates copper peptides can heal scars on their own, but combining them with procedures like chemical peels and laser resurfacing produces superior results than either approach alone.
Versus Laser Treatments
Laser treatments, particularly fractional lasers, create controlled micro-injuries that trigger collagen production and tissue remodeling. They're among the most effective treatments for moderate to severe acne scars. Multiple sessions produce cumulative improvement, with studies showing 25 to 75 percent improvement after three to four treatment sessions.
Copper peptides can support laser treatment outcomes. Applied during the healing period after laser procedures, they may accelerate recovery and optimize the collagen formation that gives laser treatments their results. Some clinics specifically incorporate copper peptide serums into their laser aftercare protocols.
The peptide timeline guide helps set realistic expectations for treatment duration.
Versus Injectable Fillers
Dermal fillers like hyaluronic acid can immediately improve the appearance of depressed scars by physically filling the depression. Results are visible immediately but temporary, requiring repeat treatments every six months to two years.
Copper peptides offer a different value proposition. They take longer to produce visible results but work by actually changing the tissue structure rather than temporarily filling space. For patients seeking lasting improvement rather than quick fixes, copper peptides address the underlying problem.
Some treatment protocols use fillers for immediate improvement while beginning copper peptide treatment for longer-term structural change. As the peptides gradually improve tissue quality, the need for filler maintenance may decrease.
Versus Microneedling Alone
The clinical research directly compared this question. Microneedling alone produces significant improvement in acne scars. Adding copper peptides accelerates early results but may not dramatically change long-term outcomes.
The decision to add copper peptides to microneedling depends on your priorities. If you want the fastest possible improvement and don't mind the additional product cost, adding copper peptides makes sense. If cost is a concern and you're willing to wait longer for results, microneedling alone remains effective.
One consideration: the potential for temporary hyperpigmentation with copper peptides during microneedling treatment. For some skin types, this complication may outweigh the benefit of faster initial improvement.
Practical Protocols for Using Copper Peptides
Research findings are only useful if you can translate them into practical action. Here are specific protocols for using copper peptides to address acne scars.
Topical-Only Protocol
The simplest approach uses topical copper peptide products applied to scarred areas as part of a daily skincare routine. This method is accessible to anyone without requiring professional treatments or procedures.
Morning routine: Cleanse gently, apply copper peptide serum to scarred areas, allow absorption for two to three minutes, follow with hydrating serum if desired, apply moisturizer, finish with SPF 30 or higher sunscreen.
Evening routine: Double cleanse to remove sunscreen and daily accumulation, apply copper peptide serum to scarred areas, allow absorption, apply barrier-supporting moisturizer or night cream.
Concentration matters. Products containing 1% to 4% GHK-Cu provide effective concentrations for scar treatment. Lower concentrations may be insufficient; much higher concentrations don't necessarily improve results and may increase irritation risk.
Consistency matters more than intensity. Daily application over months produces better results than occasional use of stronger products. The tissue remodeling process is gradual and responds to sustained stimulus rather than occasional intervention.
The best copper peptide serum guide helps identify quality products.
Microneedling Combination Protocol
Combining copper peptides with microneedling leverages the research showing accelerated early results. This protocol requires either professional microneedling treatments or careful at-home microneedling with appropriate devices.
Pre-treatment preparation: For one to two weeks before microneedling, use topical copper peptide serum daily to prepare the skin. This establishes peptide presence in the tissue before creating the channels that will enhance absorption.
Treatment day: After microneedling, apply copper peptide serum directly to the treated areas. The micro-channels created by needling dramatically increase penetration. The peptide reaches deeper tissue layers where scar remodeling occurs.
Post-treatment care: Continue daily copper peptide application for at least two weeks following each session. Avoid vitamin C products immediately after treatment since copper can oxidize vitamin C. Wait one to two weeks before reintroducing vitamin C if it's part of your routine.
Treatment frequency: Professional microneedling sessions are typically spaced three to four weeks apart. At-home microneedling with shorter needles can be performed weekly or every two weeks. Significant improvement typically requires three to six sessions for moderate scars, potentially eight to ten sessions for severe scarring.
The copper peptide skincare routine guide provides detailed product layering instructions.
Injectable Protocol for Systemic Support
Some researchers use injectable GHK-Cu to provide systemic copper peptide support while also applying topical products to scarred areas. This approach delivers copper peptides both from within and from outside.
The injectable protocol provides peptide exposure to all tissues, potentially supporting skin health and healing capacity throughout the body. The topical application delivers concentrated peptide directly to scarred areas where it's needed most.
Typical injectable protocols use 1 to 2mg GHK-Cu daily via subcutaneous injection. The reconstitution guide ensures proper preparation. The reconstitution calculator helps with dosing accuracy.
Note that as of 2023, injectable forms of GHK-Cu face regulatory restrictions for commercial compounding. Researchers should verify current legal status in their jurisdiction.
Post-Procedure Healing Protocol
If you're undergoing professional scar treatments like laser resurfacing, chemical peels, or clinical microneedling, copper peptides can optimize the healing phase. This protocol focuses on the recovery period rather than standalone treatment.
Beginning immediately after procedures when advised by your provider, apply copper peptide serum to treated areas twice daily. Continue for four to eight weeks through the primary healing and remodeling phase. The peptide supports organized collagen formation during the critical window when tissue is actively regenerating.
This approach doesn't replace the primary treatment but enhances its results by optimizing the healing it triggers. Patients often report reduced downtime, faster recovery, and improved outcomes when copper peptides are part of post-procedure care.
Timeline and Realistic Expectations
Patience is essential when treating acne scars. No product or procedure produces instant results for structural skin damage. Understanding realistic timelines prevents frustration and premature abandonment of effective treatment.
Week by Week Progression
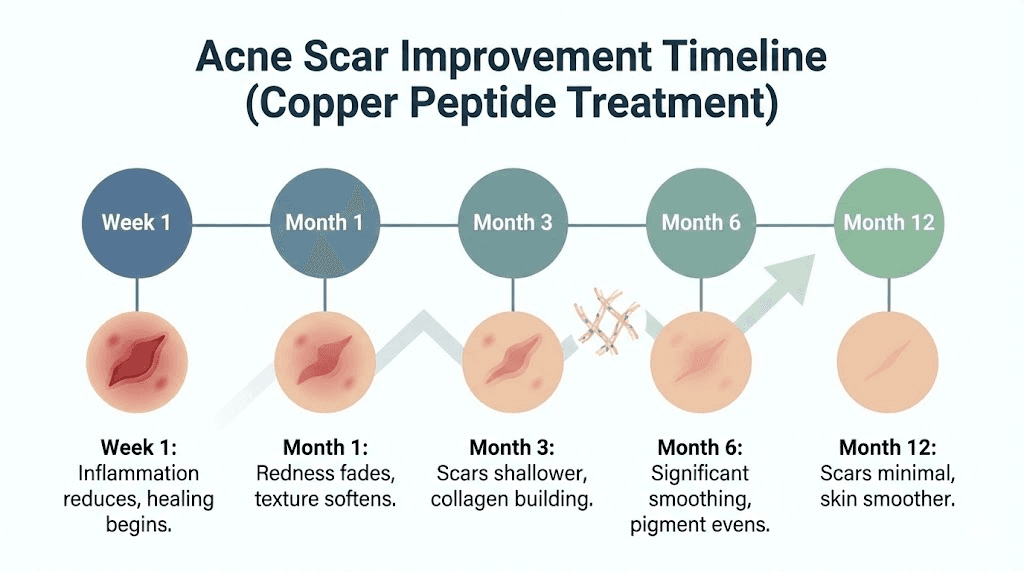
Weeks 1 through 2: Minimal visible change in scars. You may notice improved skin hydration and texture in non-scarred areas. The copper peptide is beginning to influence cellular activity, but tissue remodeling hasn't produced visible results yet.
Weeks 3 through 4: Subtle improvement may become detectable in shallow scars. Skin quality continues improving. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from recent breakouts may begin fading. Deep scars show no significant change yet.
Weeks 5 through 8: More noticeable improvement in superficial scars. Some softening of boxcar and rolling scar edges. Overall skin texture shows improvement. This is typically when comparison photos start revealing visible differences.
Weeks 9 through 12: Significant improvement becomes apparent for responsive scars. Rolling scars show reduced waviness. Boxcar scars appear less sharply defined. Ice pick scars may show modest softening but remain challenging. Post-acne pigmentation continues fading.
Months 4 through 6: Continued gradual improvement. Scars that responded early continue improving. Scars that showed minimal initial response may finally begin showing change. The tissue remodeling process is well established and producing cumulative results.
Months 7 through 12: Approach to optimal results for the given protocol. Improvement rate slows as scars reach their maximum response potential. Some scars may plateau while others continue gradually improving.
What Different Scar Types Can Expect
Shallow boxcar scars: These respond best to copper peptide treatment. Expect 40 to 60 percent improvement with consistent topical use over six to twelve months. Combined with microneedling, improvement may reach 60 to 70 percent.
Deep boxcar scars: Moderate improvement is realistic. Expect 25 to 40 percent improvement with optimal protocols. Scars will soften and become less prominent but likely won't fully resolve without additional interventions like subcision or fillers.
Rolling scars: Good response potential because copper peptides address the fibrous tethering that causes rolling appearance. Expect 40 to 55 percent improvement with consistent treatment. Combining with subcision that releases tethered bands can significantly enhance results.
Ice pick scars: Limited improvement from topical or microneedling approaches due to their narrow, deep structure. Expect 15 to 30 percent improvement, mostly in softening the scar edges rather than filling the depth. Severe ice pick scars typically require punch excision for significant improvement.
Hypertrophic scars: Variable response. Some hypertrophic scars soften and flatten with copper peptide treatment. Others may require additional interventions like silicone sheets, steroid injections, or laser treatment.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: Generally excellent response. Dark marks from healed acne typically fade significantly within two to four months of consistent copper peptide use. This is one area where copper peptides perform particularly well.
Factors Affecting Your Results
Several variables influence how well you'll respond to copper peptide treatment for acne scars.
Scar age: Newer scars respond faster and more completely than older, established scars. Scars under five years old show the best results. Treating scars early, before they fully mature, produces optimal outcomes.
Scar severity: Mild to moderate scars improve more than severe scars. This doesn't mean severe scars can't improve, but expectations should be calibrated accordingly.
Consistency of treatment: Daily application over months produces better results than sporadic use. Missing days or weeks undermines the sustained stimulus that tissue remodeling requires.
Protocol intensity: Combining topical copper peptides with microneedling or professional procedures produces faster, more significant results than topical alone. However, these combinations also require more time, cost, and potential for side effects.
Skin type: Some research suggests darker skin types may respond particularly well to copper peptide treatment, though they also face higher hyperpigmentation risk during microneedling combinations.
Overall skin health: Well-hydrated, healthy skin responds better to any treatment. Supporting your copper peptide protocol with good basic skincare optimizes results.
Managing Potential Side Effects
Copper peptides are generally well-tolerated, but side effects can occur, especially with combination treatments like microneedling. Knowing what to watch for and how to respond ensures successful treatment.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation Risk
The most significant concern, particularly with microneedling combination protocols, is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). Ironically, you might be treating scars while creating temporary discoloration.
Research findings are mixed. Some studies found less hyperpigmentation in copper peptide groups compared to microneedling alone. Others found more hyperpigmentation with copper peptides. The difference likely relates to specific protocols, skin types, and individual responses.
Risk factors for PIH include darker skin tones (Fitzpatrick types 4 through 6), history of PIH from other treatments or injuries, sun exposure during or after treatment, and aggressive microneedling depths.
Mitigation strategies include strict sun protection during treatment, using moderate rather than aggressive microneedling depths, incorporating niacinamide which helps prevent PIH, considering patch testing before full-face treatment, and being prepared to pause treatment if significant PIH develops.
If PIH occurs, it typically resolves within weeks to months after treatment stops. The troubleshooting guide provides additional management strategies.
Irritation and Sensitivity
Some users experience mild irritation from copper peptide products, especially at higher concentrations or when combined with other active ingredients. Signs include redness beyond normal temporary flushing, stinging or burning sensation, dryness or flaking, and increased sensitivity to other products.
If irritation occurs, reduce application frequency from twice daily to once daily or every other day.
Ensure you're not combining copper peptides with irritating ingredients like acids or high-concentration vitamin C. Consider reducing copper peptide concentration. Support skin barrier with ceramide-rich moisturizers.
The copper peptide problem-solving guide addresses more significant reactions.
The Copper Uglies Phenomenon
Some experienced copper peptide users report a phenomenon called "copper uglies," a period where skin appears to worsen before improving. This can include temporary increase in fine lines, dull or sallow appearance, and increased texture before improvement.
The proposed mechanism involves the matrix metalloproteinase activity that breaks down old collagen faster than new collagen replaces it. During this transition, skin may temporarily look worse.
If you experience this pattern, consider whether it might be normal adjustment that will resolve with continued use, a sign that concentration is too high and should be reduced, or indication that copper peptides aren't suitable for your skin.
Give the process four to eight weeks before concluding that copper peptides cause more harm than benefit. Many users report that pushing through the initial worsening phase leads to eventual improvement.
Ingredient Interactions
Copper peptides interact with certain skincare ingredients in ways that can cause problems.
Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid): The acidic environment destabilizes the copper-peptide bond, potentially releasing free copper ions while deactivating both ingredients. Don't apply simultaneously. Use vitamin C and copper peptides at different times of day or on different days.
Strong acids (AHA, BHA): These can increase penetration and irritation when combined with copper peptides. Use acids at different times or reduce frequency of one or both.
Retinoids: Both ingredients accelerate tissue turnover. Combining may overwhelm skin's adaptive capacity. See the copper peptides and retinol guide for safe combination protocols.
Optimizing Results: Supporting Strategies
Copper peptides work best as part of a comprehensive approach. These supporting strategies enhance their scar-healing effects.
Nutritional Support
Tissue repair requires building blocks. Ensuring adequate nutrition supports the collagen synthesis and tissue remodeling that copper peptides stimulate.
Protein: Collagen is built from amino acids derived from dietary protein. Inadequate protein intake limits what your body can construct regardless of how strongly copper peptides signal production. Aim for 0.8 to 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight daily.
Vitamin C: Essential cofactor for collagen synthesis. While you shouldn't apply vitamin C simultaneously with copper peptides, internal vitamin C status matters. Consider 500 to 1000mg oral vitamin C daily.
Zinc: Supports wound healing and balances copper in the body. Copper and zinc compete for absorption, so increasing copper exposure through GHK-Cu warrants attention to zinc status. A ratio of 8:1 to 15:1 zinc to copper generally maintains balance.
Collagen peptides: Oral collagen supplementation provides building blocks specifically for collagen synthesis. Some studies show improved skin elasticity and hydration with consistent collagen peptide supplementation.
Lifestyle Factors
Sleep: Tissue repair accelerates during sleep when growth hormone peaks. Poor sleep undermines any tissue regeneration protocol. Prioritize seven to nine hours nightly.
Sun protection: UV exposure damages collagen and can worsen scarring while also increasing hyperpigmentation risk. Rigorous sun protection during copper peptide treatment is essential, not optional.
Stress management: Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which impairs wound healing and tissue repair. Managing stress supports the regenerative processes copper peptides promote.
Avoid smoking: Smoking severely impairs wound healing and collagen production. If you smoke, scar treatment outcomes will be compromised regardless of what products you use.
Complementary Treatments
Several treatments can be combined with copper peptides for enhanced results.
Subcision: For rolling scars with fibrous tethering, subcision releases the bands pulling skin downward. Combined with copper peptide treatment, the released tissue can heal with better collagen organization rather than reforming the same tethered pattern.
Microneedling: Already discussed, but worth emphasizing. The research specifically supports microneedling plus copper peptides for faster initial improvement in acne scars.
LED light therapy: Red light at 630 to 660nm supports collagen synthesis through mechanisms distinct from copper peptides. Combining the approaches may provide additive benefits.
Other peptides: BPC-157 and TB-500 offer healing support through different pathways. Some researchers combine multiple peptides for comprehensive tissue repair support. The peptide stacking guide covers combination approaches.
Protocol by Scar Severity
Different scar severity levels warrant different treatment intensity. These protocols match approach to need.
Mild Scarring Protocol
For scattered shallow scars, minor textural irregularities, or post-inflammatory marks without true tissue loss, a simple topical approach often suffices.
Apply copper peptide serum 1% to 2% concentration twice daily, morning and evening. Focus on affected areas but can apply to full face for overall skin quality improvement. Combine with gentle, hydrating skincare. Avoid harsh actives during initial three months.
Expected timeline: Visible improvement in two to three months. Optimal results in six to nine months. Many mild scars may resolve nearly completely.
Moderate Scarring Protocol
For multiple boxcar or rolling scars of moderate depth, more intensive intervention produces better results.
Use topical copper peptide serum 2% to 4% concentration twice daily. Add monthly professional microneedling or weekly at-home microneedling with 0.5mm needles. Apply copper peptide serum immediately after microneedling and continue daily application between sessions.
Continue for minimum six months, ideally twelve months. Consider adding injectable GHK-Cu for systemic support if topical plus microneedling provides insufficient improvement after three months.
Expected timeline: Early improvement visible in six to eight weeks. Significant improvement by four to six months. Maximum results by twelve months.
Severe Scarring Protocol
For extensive deep scarring, ice pick scars, or scars unresponsive to moderate approaches, comprehensive treatment is warranted.
Begin with professional consultation for possible procedural interventions. Laser treatments, subcision, and TCA CROSS for ice pick scars may be appropriate. Use copper peptides as adjunctive therapy supporting procedural treatments rather than standalone solution.
Apply topical copper peptide serum during healing from procedures. Consider injectable GHK-Cu for systemic support. Continue topical application between and after procedural treatments.
Expected timeline: Variable based on procedures performed. Copper peptides support healing from primary treatments rather than providing primary improvement. Realistic expectation is optimizing procedural outcomes, not replacing procedures.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long do copper peptides take to improve acne scars?
Visible improvement typically begins around weeks five to eight with consistent daily use. Significant improvement develops over three to six months. Optimal results require six to twelve months of continued treatment. The process is gradual because tissue remodeling takes time. Scars that took months or years to form require months to remodel. The peptide timeline guide provides detailed expectations.
Do copper peptides work for ice pick scars?
Ice pick scars show limited improvement from copper peptides alone due to their narrow, deep structure. Topical products can't effectively reach tissue at the base of these scars. Expect modest softening of scar edges rather than filling of the depth. Severe ice pick scars typically require punch excision, TCA CROSS, or similar procedural interventions for significant improvement. Copper peptides can support healing after these procedures.
Can copper peptides cause hyperpigmentation?
Research shows mixed findings. Some studies found less hyperpigmentation with copper peptides; others found more, particularly when combined with microneedling.
Risk is higher for darker skin types. If hyperpigmentation occurs, it typically resolves within weeks to months after treatment stops. Strict sun protection and possibly niacinamide addition help mitigate risk. The results guide includes pigmentation considerations.
Should I use copper peptides before or after microneedling?
Apply copper peptides immediately after microneedling while channels are still open for enhanced penetration. The micro-channels created by needling allow the peptide to reach deeper tissue where scar remodeling occurs. Continue daily application between microneedling sessions. Some protocols also use copper peptides for one to two weeks before microneedling to prepare tissue.
Can I use copper peptides with retinol for acne scars?
Yes, but not simultaneously. Both ingredients accelerate tissue turnover, and combining directly may overwhelm skin. Use copper peptides in the morning and retinol in the evening, or alternate nights. The combination guide provides detailed protocols for using both safely.
How do copper peptides compare to vitamin C for acne scars?
They work differently and can be complementary. Vitamin C primarily brightens and provides antioxidant protection. Copper peptides specifically address tissue remodeling and organized collagen formation. For acne scars with both textural issues and discoloration, using both at different times of day may provide comprehensive improvement.
What concentration of copper peptides works best for scars?
Products containing 1% to 4% GHK-Cu provide effective concentrations for scar treatment based on available research. Higher concentrations don't necessarily improve results and may increase irritation risk. The concentration guide helps select appropriate products.
Can copper peptides prevent new acne scars from forming?
Theoretically, yes. Copper peptides' anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties may reduce scar formation during active acne healing. Applying copper peptides during active breakouts may result in better healing outcomes and less scarring. However, this preventive use hasn't been specifically studied in clinical trials the way treatment of existing scars has been.
External Resources
For additional scientific background on copper peptides and acne scar treatment:
Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery: Dermaroller vs Dermaroller with Copper Peptide Study
PMC: GHK Peptide as a Natural Modulator of Multiple Cellular Pathways in Skin Regeneration
PMC: Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide
PMC: Acne Scarring, Pathogenesis, Evaluation, and Treatment Options
For researchers serious about treating acne scars effectively, SeekPeptides provides the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based protocols, detailed treatment guides, and a community of thousands who've successfully addressed their scarring concerns.