Jan 15, 2026

Everything you've read about copper peptide concentration is probably backwards. Higher isn't better. More isn't faster. And the "stronger is superior" mentality that dominates skincare marketing leads millions of users to sabotage their own results every single day. The research tells a completely different story, one where nanomolar concentrations outperform percentage-based thinking and where the sweet spot sits far lower than most product labels suggest.
The confusion runs deep. Walk into any skincare store and you'll find copper peptide products ranging from 0.1% to 7% or higher, each claiming superior efficacy. Some brands market high concentrations as premium formulations worthy of premium prices. Others quietly deliver better results at fractions of those percentages. Understanding why requires diving into the science of how GHK-Cu actually works at the cellular level.
This guide cuts through the marketing noise.
You'll learn exactly which concentrations produce results for different skin types, why more can actually mean less when it comes to copper peptides, and how to build a concentration strategy that maximizes benefits while minimizing risks.
SeekPeptides has compiled the research, analyzed the formulations, and distilled the science into actionable guidance you can use today.
Understanding copper peptide concentrations
Copper peptide concentration refers to the percentage of active GHK-Cu compound in a skincare formulation. A 1% copper peptide serum contains 1 gram of GHK-Cu per 100 grams of product. Simple math. But the biological reality is far more nuanced than these percentages suggest.
GHK-Cu, the tripeptide glycyl-L-histidyl-L-lysine bound to copper, demonstrates activity at concentrations that would seem impossibly small to anyone familiar with standard peptide dosing. Research shows cellular responses at picomolar to nanomolar ranges, meaning effective concentrations can be measured in billionths of a gram. This creates an interesting paradox: the concentrations listed on product labels far exceed what cells actually need to respond.
The disconnect between product concentrations and biological effective doses matters for practical reasons. Copper peptide problems often stem from concentration misunderstandings. Users assume higher percentages guarantee better results, purchase the strongest formulas available, and then wonder why their skin reacts poorly or improvements plateau.
The nanomolar reality
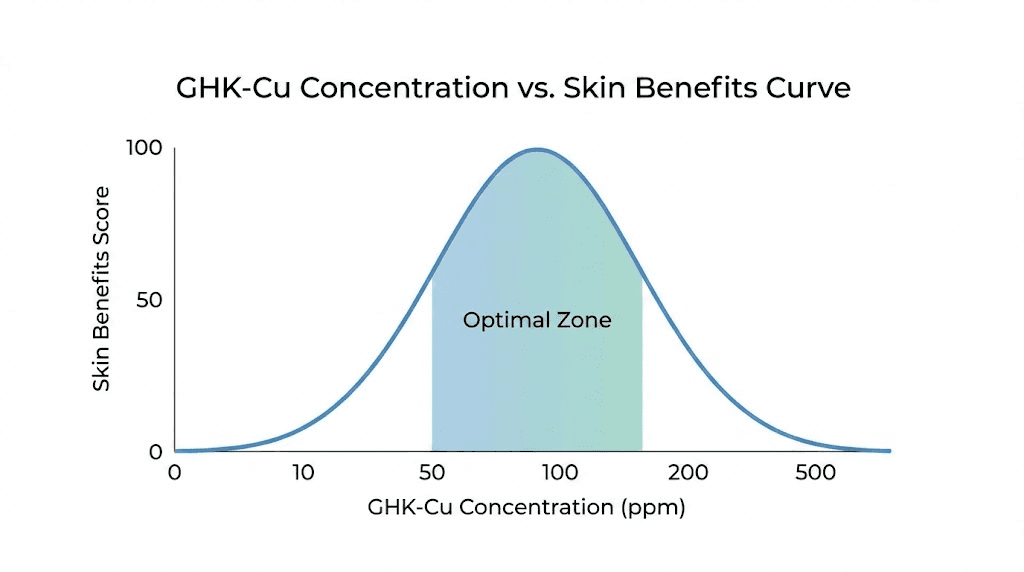
Research from the University of California demonstrated that GHK-Cu at concentrations of 0.01, 1, and 100 nanomolar all increased collagen and elastin production in human dermal fibroblasts. That's nanomolar, not millimolar. Not percentage points. Nanomolar. The effective concentration sits at levels so small they challenge conventional thinking about dose-response relationships in skincare.
This isn't unique to GHK-Cu. Many peptides demonstrate similar potency patterns. The tripeptide structure allows receptor binding at minimal concentrations because the interaction is highly specific. Unlike broad-spectrum ingredients that require flooding the system to produce effects, peptides work through precise cellular communication that needs only small amounts of the signaling molecule.
One nanomolar equals 0.0000001% concentration. Yet products commonly contain 1% or higher, delivering concentrations millions of times greater than the minimum effective dose. This excess doesn't necessarily translate to proportionally better results. Understanding why requires examining what happens when copper peptide levels climb too high.
The MMP paradox
Matrix metalloproteinases, or MMPs, are enzymes that break down collagen and other structural proteins in the skin. They're essential for healthy tissue remodeling, allowing removal of damaged proteins so new ones can take their place. GHK-Cu influences MMP activity, but the direction of that influence depends on concentration.
At low concentrations, GHK-Cu promotes healthy collagen synthesis while maintaining normal MMP levels. The balance favors building over breaking down. Skin gets the benefits of increased anti-aging protein production without excessive degradation of existing structures.
Higher concentrations shift this balance. Research published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry found that GHK-Cu "significantly increased gene expression of MMP-1 and MMP-2 at the lowest concentration" tested, but this relationship becomes more complex at higher levels. Push concentration too far and you risk tipping the balance toward excessive breakdown, potentially fragmenting the collagen you're trying to build.
This doesn't mean high-concentration products are dangerous or ineffective. It means the relationship between concentration and results isn't linear. Doubling concentration doesn't double results. In some cases, it might actually reduce them.
Concentration ranges explained
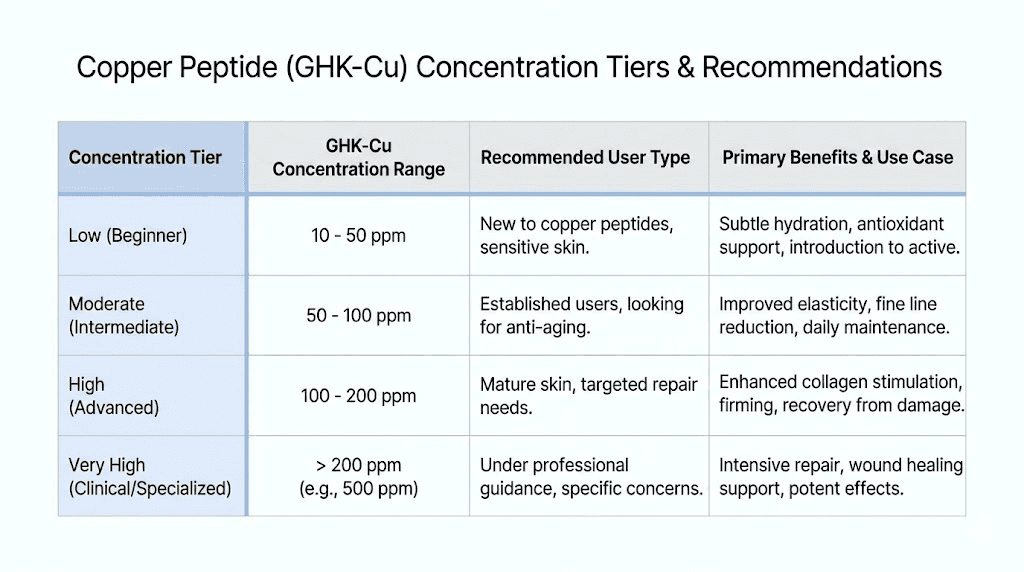
Commercial copper peptide products span a wide concentration range, from 0.1% starter formulas to 7% or higher professional-strength preparations. Each range serves different purposes and skin types. Understanding these tiers helps you select appropriate starting points and progression strategies.
Low concentration: 0.1% to 0.5%
Entry-level copper peptide products typically contain 0.1% to 0.5% GHK-Cu. These concentrations work well for several user categories: those new to copper peptides, people with sensitive skin, and anyone seeking maintenance rather than intensive treatment.
At 0.5%, you're still delivering concentrations far exceeding the nanomolar levels shown effective in research. This isn't a weakness. It accounts for variables like penetration efficiency, stability degradation, and individual absorption differences. Not all applied product reaches target cells, so formulations include buffer above the minimum effective dose.
Low-concentration products allow skin to adapt gradually. Peptide signaling increases cellular activity, and jumping straight to high concentrations can overwhelm cells that aren't accustomed to that level of stimulation. Starting low builds tolerance and establishes baseline response patterns.
The Ordinary's Buffet serum represents this category well. It combines multiple peptides including copper peptides at concentrations designed for daily use without irritation risk. Users report steady improvements over months rather than dramatic short-term changes, which often indicates sustainable rather than inflammatory response.
Moderate concentration: 0.5% to 2%
The moderate range captures the majority of effective copper peptide products. Research frequently cites 0.5% as an effective sweet spot, balancing meaningful results against low irritation risk. Many reputable peptide suppliers formulate their flagship products in this range.
A 1% copper peptide serum delivers reliable results for most skin types. The Ordinary offers a dedicated 1% copper peptide serum that has become a benchmark product in the category. Users across age ranges and skin conditions report visible improvements in wrinkle appearance, skin texture, and overall radiance.
Two percent pushes toward the upper limit of what most dermatologists recommend for unsupervised home use. At this concentration, results typically accelerate compared to lower percentages, but so does the potential for irritation. Users with established tolerance who haven't achieved desired results at 1% may benefit from stepping up to 2%.
Eye-area formulations commonly use 2% concentrations. The delicate periorbital skin responds well to copper peptides for dark circles and fine lines, but requires careful formulation to avoid irritation. Two percent provides meaningful activity without overwhelming the sensitive tissue around the eyes.
High concentration: 2% to 4%
High-concentration copper peptide products target users who have built tolerance through lower percentages and want intensified results. Products in the 2% to 4% range often carry descriptions like "intensive," "advanced," or "professional strength."
Four percent represents a common ceiling for face and neck applications in daily-use products. Copper peptide skincare routines at this level typically involve application once or twice daily, with careful attention to supporting skin barrier function.
At these concentrations, the importance of complementary skincare increases. Copper peptides at 4% stimulate significant cellular activity. Supporting this activity with appropriate storage practices, compatible ingredients, and adequate hydration helps skin respond optimally rather than reactively.
Users stepping into this range should establish tolerance gradually. Even experienced copper peptide users benefit from introducing 4% products slowly, perhaps every other day initially, then building to daily use as skin demonstrates consistent positive response without signs of irritation or sensitivity.
Very high concentration: 4% to 7%+
The upper tier of copper peptide concentrations includes products like Skin Biology's 7% GHK-Cu Accelerant, designed for users seeking maximum intensity. These formulations push concentration toward practical limits for topical application.
Seven percent and above enters territory where the MMP balance concerns become more relevant. Users of very high concentration products need to monitor closely for signs of excessive breakdown activity: persistent redness, thinning appearance, or failure to see continued improvement despite consistent use.
Very high concentration products often work best as targeted treatments rather than all-over applications. Using 7% GHK-Cu on specific areas of concern, like deep wrinkles or stubborn scarring, while maintaining moderate concentrations elsewhere can deliver intensive results without systemic overexposure.
Cycling very high concentration products provides another approach. Rather than daily use indefinitely, some protocols involve intensive periods at 7% followed by maintenance phases at lower concentrations. This pulsing strategy may help maintain the collagen synthesis benefits while periodically reducing MMP stimulation.
Finding your optimal concentration
The best copper peptide concentration for your skin depends on multiple factors: current skin condition, sensitivity level, experience with active ingredients, specific goals, and how your skin responds to initial trials. No single percentage works optimally for everyone, which explains why products span such wide concentration ranges.
For beginners
If you've never used copper peptides, start at 0.5% or below. This applies regardless of your experience with other peptide products. GHK-Cu works through different mechanisms than most peptides and produces distinct effects on skin tissue.
Begin with alternate-day application. Watch for signs of irritation: redness, itching, burning, increased sensitivity, or unusual breakouts. If two weeks pass without issues, move to daily application. If another two weeks go smoothly, consider whether results warrant increasing concentration or maintaining the current level.
Many beginners see meaningful results at starter concentrations. The temptation to escalate quickly should be resisted. Common peptide mistakes include rushing to high concentrations before lower levels have time to demonstrate their full effects.
SeekPeptides recommends new users commit to at least eight weeks at a starting concentration before considering increases. Copper peptide results build progressively, and judging efficacy too early leads to unnecessary concentration escalation.
For sensitive skin
Sensitive skin requires extra caution with copper peptides. The cellular stimulation that produces benefits can also trigger inflammatory responses in reactive skin types. Starting concentrations should be minimal, around 0.1% to 0.25%, with extended observation periods.
Patch testing matters more for sensitive skin users. Apply your chosen product to a small area behind the ear or on the inner arm for 48 hours before facial application. Monitor for any reaction, however minor. Copper peptides in any concentration can potentially trigger sensitivity in predisposed individuals.
Product formulation matters as much as concentration for sensitive skin. Some copper peptide products contain additional actives that compound sensitivity risk. Look for simple formulations that minimize potential irritants. Avoid products combining copper peptides with retinol, vitamin C, or exfoliating acids if you have sensitive skin.
Progress slowly. A sensitive skin user might take six months to work from 0.1% to 1%, and that timeline is perfectly appropriate. Better slow progress than fast regression from an irritation setback that requires weeks of healing before resuming copper peptide use.
For normal skin
Users with normal, non-reactive skin have more flexibility in concentration selection. Starting at 0.5% to 1% provides a reasonable baseline that delivers meaningful effects while maintaining safety margins.
Normal skin typically tolerates daily application from the start, though alternate-day introduction remains a sensible precaution. Two weeks of monitoring should reveal whether your skin accepts the product without issues.
From a 1% baseline, normal skin users can consider progression based on results. If improvements plateau after three to four months, stepping up to 2% may reinvigorate progress. If results continue developing at 1%, maintaining that concentration makes sense until improvements naturally level off.
The best copper peptide serums for normal skin often fall in the 1% to 2% range, balancing efficacy with broad usability. This range works well for long-term maintenance programs once initial improvement goals are achieved.
For aging concerns
Skin showing visible signs of aging, including fine lines, wrinkles, loss of firmness, and uneven texture, may benefit from moderate to high copper peptide concentrations. The increased cellular activity helps address accumulated damage and supports regeneration processes that slow with age.
Users over 40 often start successfully at 1% to 2% if their skin tolerates active ingredients well. The regenerative benefits of copper peptides align with aging skin's needs for enhanced collagen support and tissue repair signaling.
Advanced aging concerns might warrant higher concentrations after tolerance establishment. Users in their 50s and beyond who have successfully used 2% products for several months can consider carefully monitored trials of 3% to 4% formulations for intensified results.
Combining copper peptide use with proper dosing protocols for other anti-aging ingredients requires attention to ingredient interactions. Copper peptides work well alongside hyaluronic acid, niacinamide, and gentle peptides, but can conflict with certain actives.
For specific concerns
Different skin concerns may respond better to different concentration strategies. Skin tightening goals might benefit from moderate concentrations (1% to 2%) used consistently over extended periods, allowing gradual collagen remodeling.
Scar improvement often responds to higher concentrations applied specifically to scarred areas. The tissue remodeling effects of copper peptides can help reorganize scar collagen into more normal patterns. Concentrations of 3% to 4% applied directly to scars, with lower concentrations on surrounding skin, provides targeted intensity.
Hair applications follow different concentration guidelines. Scalp skin tolerates different levels than facial skin, and the target tissues (hair follicles) respond to different signaling intensities. Most hair-focused copper peptide protocols use 1% to 3%, with concentrations above 3% increasing risk of scalp irritation and redness.
Wound healing applications, supporting recovery from procedures or injuries, may use higher concentrations under professional guidance. The injury healing context differs from cosmetic use, and concentration decisions should involve qualified practitioners.
Body area concentration guidelines
Different body areas have different skin characteristics and tolerance levels.
The same concentration that works perfectly on your cheeks might irritate your eye area or underwhelm on your neck. Understanding regional concentration guidelines helps optimize results across all treatment areas.
Face and neck
Facial skin serves as the primary application area for most copper peptide users. Concentration guidelines for faces span the full range, from 0.5% for sensitive users to 4% for advanced users seeking intensive treatment.
The cheeks, forehead, and chin typically tolerate concentrations well. These areas have relatively thick skin with good barrier function. Most users can apply their chosen concentration to these areas without special precautions beyond the general guidelines already discussed.
The nose and area around the nostrils sometimes shows increased sensitivity. Some users tolerate lower concentrations here than on other facial areas. If you notice irritation patterns concentrated around the nose, consider using a lighter formula on this area.
Neck skin differs from facial skin in several ways. It's thinner, has fewer oil glands, and often shows aging signs earlier than the face. Despite these differences, the neck typically tolerates similar concentrations to the face. Many users successfully treat face and neck with the same product at the same concentration.
The décolletage (chest area) responds well to copper peptides but may need lower concentrations than the face. Start with half your facial concentration on the chest and adjust based on response. This area is prone to sun damage and may have compromised barrier function requiring gentler treatment.
Eye area
The periorbital region requires special consideration. Skin around the eyes is significantly thinner than other facial areas, has minimal oil glands, and sits close to the sensitive eyeball. Irritation here causes more discomfort than elsewhere and can affect vision temporarily.
Eye-area copper peptide products typically use 2% or lower concentrations. Some users successfully apply their regular facial product (1% to 2%) around the eyes, while others need dedicated eye formulations at reduced strength.
Application technique matters as much as concentration for eye area treatment. Apply with gentle patting motions rather than rubbing. Keep product away from the lash line where it could migrate into the eye. Allow product to absorb fully before applying other products or makeup.
Signs of eye area intolerance include puffiness, redness, itching, or excessive watering. If these occur, reduce concentration or frequency immediately. The eye area recovers relatively quickly from irritation if caught early, but persistent problems require complete cessation of copper peptide use in that region.
Scalp and hair
Scalp application for hair loss prevention or hair growth support involves different considerations than facial use. Hair follicles respond to copper peptide signaling, but the scalp environment differs from facial skin.
Recommended scalp concentrations range from 1% to 3%. Above 3%, many users experience scalp redness, irritation, or discomfort. The scalp's many nerve endings make it sensitive to irritating substances, and high copper peptide concentrations can trigger inflammation responses.
Application method affects effective concentration delivery to follicles. Serums penetrate better than creams. Applying to clean, slightly damp scalp improves absorption. Massaging product in for several minutes helps distribute it to follicle-dense areas.
Scalp applications often use different product formulations than facial products. Hair-focused copper peptide products may include additional ingredients supporting hair health that wouldn't be appropriate for facial use. Using products formulated for their intended application area improves results.
Body skin
Body skin outside the face, neck, and scalp can benefit from copper peptides but requires different concentration considerations. Body skin is generally thicker and less sensitive than facial skin, potentially tolerating higher concentrations.
However, the larger surface area makes high-concentration body treatment expensive and impractical. Most body applications use moderate concentrations (1% to 2%) applied to specific areas rather than whole-body treatment.
Areas with thin skin, like the inner arms, inner thighs, and abdomen, should receive concentrations similar to facial products. Areas with thicker skin, like the backs of hands, elbows, and knees, can potentially tolerate higher concentrations.
Post-procedure body treatment, like after laser treatments or certain surgeries, may involve copper peptides at concentrations determined by the treating practitioner. These applications fall outside general consumer guidelines and should follow professional recommendations.
Concentration and product formulation
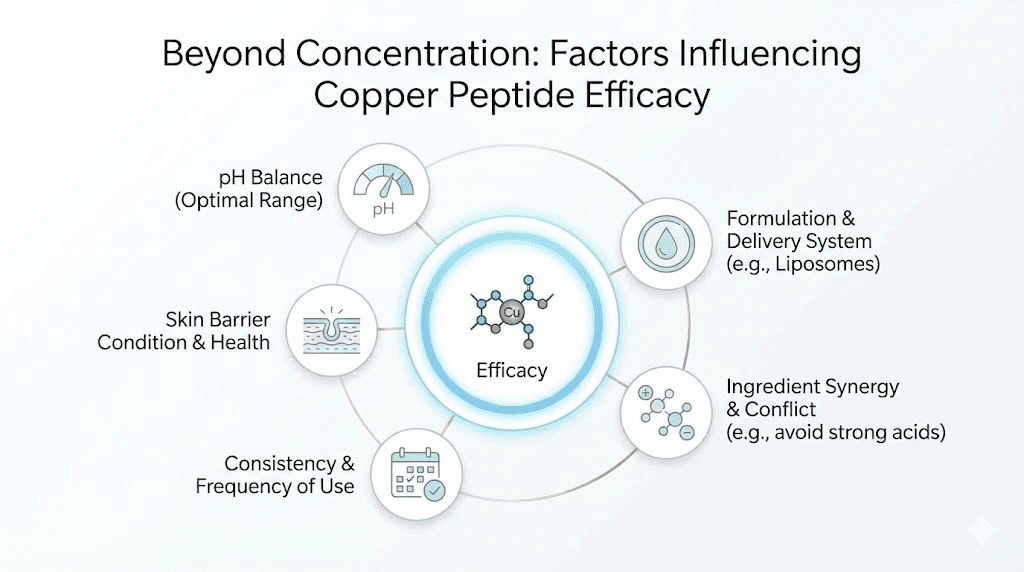
The GHK-Cu percentage listed on a product represents only part of the efficacy equation. Formulation factors significantly impact how effectively that concentration delivers results. Two products with identical percentages can produce vastly different outcomes based on their overall composition.
Delivery systems
How copper peptides reach their target cells matters as much as how much is present. Advanced delivery systems can make lower concentrations more effective than higher concentrations in basic formulations.
Liposomal encapsulation surrounds copper peptide molecules with phospholipid spheres that enhance penetration through skin barriers. A 0.5% liposomal copper peptide formula may deliver more active compound to dermal layers than a 2% formula using standard water-based delivery.
Nanoparticle delivery uses microscopic particles to carry copper peptides deeper into skin than they would penetrate alone. These systems require sophisticated manufacturing but can dramatically improve bioavailability.
Basic formulations without advanced delivery rely on higher concentrations to compensate for less efficient penetration. This approach works but is less elegant than optimized delivery systems. It's also why some budget products require higher concentrations to match results from premium formulations at lower percentages.
Understanding your product's delivery system helps contextualize its concentration. A 1% serum with liposomal delivery might outperform a 3% serum without it. Product specifications and manufacturer information sometimes indicate delivery technology, though not always.
Supporting ingredients
Copper peptide formulations typically include additional ingredients that can enhance or interfere with GHK-Cu activity. Ideal supporting ingredients complement copper peptide function without creating conflicts.
Hyaluronic acid pairs excellently with copper peptides. It provides hydration that supports the cellular activity stimulated by GHK-Cu. The combination addresses multiple anti-aging mechanisms simultaneously.
Niacinamide (vitamin B3) works well alongside copper peptides for most users. Both ingredients support skin barrier function through different mechanisms, creating complementary benefits. Some users with very sensitive skin may need to introduce these ingredients separately to identify any reactivity.
Hyaluronic acid peptide combinations represent formulation approaches that leverage multiple peptide types for comprehensive effects. These products often maintain moderate copper peptide concentrations (0.5% to 1%) to allow room for other active peptides.
Problematic ingredient combinations include high-concentration vitamin C, which can destabilize copper peptides and reduce efficacy. Strong acids (glycolic, salicylic, lactic at high percentages) may irritate when combined with copper peptides and should be used at different times of day. Retinoids intensify skin sensitivity and can make copper peptide tolerance unpredictable.
pH and stability
GHK-Cu maintains stability within specific pH ranges. Products formulated outside these ranges may contain degraded copper peptides delivering less activity than their concentration suggests.
Optimal pH for copper peptide stability falls between 5.0 and 6.0. Products significantly outside this range, whether more acidic or more basic, risk accelerated degradation. Some manufacturers add stabilizing systems to extend acceptable pH ranges, but basic formulation principles favor the natural stability window.
Stability over time also affects effective concentration. A fresh 2% copper peptide serum delivers 2% active compound. That same serum after improper storage or past its expiration date might deliver significantly less. Proper storage maintains concentration integrity.
Signs of degraded copper peptides include color changes (darkening or unusual discoloration), changes in smell, or texture alterations. If your product shows these signs, its effective concentration has likely decreased regardless of what the label states.
Building a concentration progression strategy
Rather than jumping to your target concentration immediately, strategic progression improves outcomes and safety. A well-planned concentration journey allows skin to adapt, reveals individual response patterns, and identifies optimal levels without trial-and-error waste.
Phase 1: Introduction (weeks 1 to 4)
Start below your expected long-term concentration. If you're targeting 2% for regular use, begin at 0.5% to 1%. This introduction phase establishes baseline tolerance and reveals any underlying sensitivity to copper peptides specifically.
Apply every other day for the first two weeks. Watch for any reaction: redness lasting more than 30 minutes, itching, burning, breakouts in treated areas, or increased skin sensitivity to other products or environmental factors.
If no issues appear after two weeks, transition to daily application. Continue monitoring through week four. Some reactions take time to develop, and daily application may trigger responses that alternate-day use didn't reveal.
Document your starting skin condition at the beginning of this phase. Photos in consistent lighting help track changes objectively. Note specific concerns you're addressing: fine lines, texture issues, firmness, or other targets.
Phase 2: Establishment (weeks 5 to 12)
Maintain your introduction concentration through the establishment phase. This extended period allows initial improvements to manifest and provides data on how your skin responds to consistent copper peptide exposure.
Most users begin seeing improvements during this phase. Changes are typically subtle initially, becoming more apparent over weeks. Patience matters. Copper peptide results compound over time, and eight weeks of consistent use often produces results invisible at four weeks.
If irritation appears during this phase, reduce application frequency rather than abandoning the product entirely. Some users settle into every-other-day patterns long-term without needing to progress to daily use. Results may develop more slowly but will still occur.
At the end of establishment phase, evaluate your results against your documented starting condition. Decide whether your current concentration delivers satisfactory progress or whether increasing concentration might accelerate results.
Phase 3: Optimization (ongoing)
Optimization involves gradual concentration adjustments based on established tolerance and observed results. Users satisfied with establishment phase results may remain at their introduction concentration indefinitely. Others may benefit from careful increases.
Increase concentration by small increments. Moving from 0.5% to 1%, or from 1% to 2%, represents appropriate steps. Larger jumps risk triggering intolerance that wouldn't occur with gradual progression.
After each concentration increase, allow four to six weeks for your skin to adjust before assessing results. Shorter assessment periods don't provide reliable data on whether the higher concentration truly improves outcomes.
Optimization also involves finding your ceiling, the concentration above which results plateau or decline. This ceiling varies individually. Some users optimize at 1%, others at 3% or higher. Discovering your personal optimum through methodical testing beats guessing based on product marketing or others' experiences.
Phase 4: Maintenance (long-term)
Once you've identified your optimal concentration, maintenance phase focuses on consistent use with periodic reassessment. Skin changes over time, and what works optimally now may need adjustment months or years later.
Reassess your concentration annually or when significant skin changes occur (seasonal shifts, hormonal changes, medication changes, or other factors affecting skin condition). Your optimal concentration might shift in either direction.
Some long-term users cycle concentrations strategically. Periods at higher concentration for intensive improvement alternate with lower-concentration maintenance phases. This approach may help avoid long-term tolerance issues while maintaining results.
Track results throughout maintenance phase. Photos at consistent intervals, perhaps monthly or quarterly, document long-term outcomes.
This documentation proves valuable if you need to adjust strategy or convince yourself that consistent use continues producing benefits.
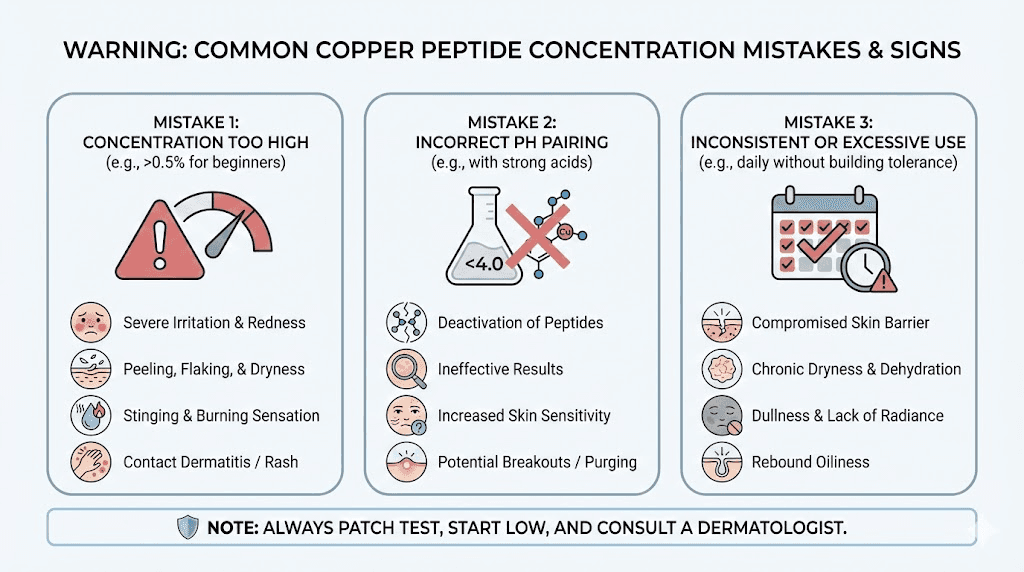
Concentration mistakes to avoid
Understanding common concentration errors helps you avoid setbacks that derail copper peptide results. These mistakes affect users at all experience levels, from beginners to long-term enthusiasts.
Starting too high
The most common concentration mistake involves beginning with advanced formulations before establishing tolerance to basic ones. Marketing promotes high-concentration products as superior, and users naturally want the "best" option. But best for experienced users isn't best for beginners.
Starting at 3% or higher virtually guarantees some level of irritation for most users. Even those who eventually tolerate high concentrations well typically experience problems when starting there. The irritation requires stopping use, waiting for recovery, and restarting at appropriate levels, wasting both time and product.
Worse, negative initial experiences can bias perception of copper peptides generally. Users who irritated their skin with aggressive first attempts sometimes conclude that copper peptides don't work for them, when actually they just didn't work at that concentration without tolerance building.
Progressing too fast
Related to starting too high, progressing too quickly through concentration levels doesn't allow skin adequate time to adapt. Users who tolerate 0.5% for two weeks and immediately jump to 2% often encounter problems.
Skin adaptation to copper peptides involves cellular-level adjustments that take weeks to complete. The absence of visible irritation doesn't mean adaptation is finished. Internal processes continue developing tolerance even when external signs look normal.
Rapid progression also prevents accurate assessment of what concentration actually delivers results. If you move from 0.5% to 1% to 2% in quick succession, you can't know which concentration was responsible for any observed improvements. Methodical progression provides clearer cause-and-effect understanding.
Stacking multiple copper peptide products
Using copper peptide serum plus copper peptide moisturizer plus copper peptide eye cream dramatically increases total concentration beyond what any single product delivers.
This stacking often causes problems even when each individual product would be well-tolerated alone.
If you want comprehensive copper peptide coverage across multiple product types, choose lower concentrations for each. A 0.5% serum combined with a 0.5% eye cream delivers appropriate total exposure. A 2% serum plus 2% cream plus 2% eye cream potentially triples your intended concentration.
Some users prefer copper peptide treatment from a single product, using non-copper-peptide formulations for other skincare steps.
This approach simplifies concentration management and makes troubleshooting easier if problems occur.
Ignoring ingredient interactions
Combining copper peptides with certain ingredients at inappropriate times can cause irritation that seems like concentration intolerance. Understanding peptide and retinol interactions and similar concerns prevents unnecessary concentration reduction when the real problem is timing.
Vitamin C and copper peptides shouldn't be applied simultaneously. Use them at different times of day, morning and evening being the typical separation. Applied together, they can destabilize each other and cause irritation that neither would cause alone.
Strong exfoliating acids (glycolic, salicylic, lactic) increase skin sensitivity. Using these and copper peptides together, especially at higher concentrations of either, compounds irritation risk. Alternating nights for acids and copper peptides often works better than same-night application.
Retinoids present complex interaction considerations. Some users successfully combine them, others don't. If you use retinoids, introduce copper peptides even more gradually than standard guidelines suggest, and consider using them on alternate nights rather than together.
Judging results too quickly
Copper peptide concentration changes require adequate time to demonstrate effects. Users who expect dramatic results in one or two weeks from concentration increases will be disappointed, and may unnecessarily escalate further based on inaccurate assessment.
Minimum assessment periods of four weeks, preferably eight, provide realistic timeframes for evaluating concentration changes. Collagen synthesis, the primary benefit most users seek, takes weeks to manifest visibly. Faster-appearing changes often reflect superficial effects rather than the deep structural improvements copper peptides provide.
Patience distinguishes successful copper peptide users from frustrated ones. The users who report best long-term results typically maintained consistent protocols over months, resisting the urge to constantly adjust based on short-term perception.
Signs you need concentration adjustment
Your skin communicates whether its current copper peptide concentration is appropriate, too low, or too high. Learning to read these signals enables responsive concentration management.
Signs concentration may be too low
Plateau without improvement despite consistent use over three or more months suggests your concentration might not be stimulating sufficient cellular activity. Skin has adapted to current levels and requires higher signaling intensity to continue progressing.
Complete absence of results after proper establishment phase may indicate concentrations too low to penetrate effectively to target cells. This particularly affects users with thicker skin or compromised barrier function that reduces penetration efficiency.
Easy tolerance from the first application, with no adjustment period needed, might indicate starting concentrations below your skin's capability. While gentle introduction is wise, some skin types can handle moderate concentrations from the start and don't benefit from extended time at minimal levels.
Signs concentration may be too high
Persistent irritation that doesn't resolve after two weeks of consistent use signals concentration exceeding your skin's tolerance. Occasional minor irritation during adaptation is normal, but ongoing redness, sensitivity, or discomfort indicates problems.
Barrier compromise symptoms, including increased sensitivity to other products, unusual dryness, or flakiness, suggest copper peptide concentration is overwhelming skin's repair capacity. The cellular stimulation exceeds what skin can support.
Paradoxical worsening, where skin looks worse despite using a product intended to improve it, may indicate concentration-related MMP imbalance. Too much breakdown activity relative to synthesis can degrade skin quality rather than enhance it.
Breakouts in treated areas can signal over-stimulation. While copper peptides aren't typically comedogenic, the increased cellular turnover at high concentrations can sometimes trigger acne in susceptible individuals. Peptide-related acne concerns often resolve with concentration reduction.
Signs concentration is optimal
Gradual, steady improvement over time indicates your concentration is working effectively. Changes should be positive and progressive, even if slow. The absence of dramatic day-to-day shifts doesn't indicate problems; it indicates sustainable improvement.
Skin that tolerates daily application without irritation but shows clear benefits compared to baseline has found its appropriate concentration. This balance of efficacy and tolerance represents the optimization goal.
Maintenance of results without needing constant escalation suggests you've found a sustainable concentration. Users at their optimal level report steady results without feeling pressure to continually increase intensity.
Concentration and SeekPeptides protocols
Understanding concentration helps you implement comprehensive copper peptide protocols that integrate with other peptide stacks and skincare approaches. SeekPeptides provides personalized guidance for building effective protocols tailored to individual needs.
Integration with other peptides
Copper peptides work well alongside certain other peptides in comprehensive skincare protocols. Snap-8 and similar expression-line peptides complement GHK-Cu's collagen-building effects by addressing different aging mechanisms.
Syn-Ake peptide combinations with copper peptides provide muscle-relaxation benefits alongside tissue regeneration. These stacks often use moderate copper peptide concentrations (1% to 2%) to allow room for other actives without overwhelming skin.
Multi-peptide products like The Ordinary's Buffet include copper peptides at lower concentrations alongside multiple other peptides. These formulations trade maximum individual-peptide intensity for breadth of peptide benefits. They work well for users seeking comprehensive peptide exposure without managing multiple single-peptide products.
When combining copper peptides with other peptide products, total peptide load matters. Skin has limited capacity to respond to signaling molecules. Excessive combined peptide exposure can overwhelm cellular systems, reducing overall efficacy. Moderate concentrations of multiple peptides often outperform maximum concentrations of any single one.
Integration with injectable protocols
Some users combine topical copper peptide products with injectable GHK-Cu protocols. Systemic and topical administration work through different pathways, potentially complementing each other.
Topical copper peptides primarily affect the epidermis and upper dermis, where penetration allows direct delivery. Injectable protocols deliver copper peptides systemically, affecting all tissues including those unreachable by topical application.
Users combining both approaches typically maintain moderate topical concentrations (1% to 2%) rather than maximum intensity. The systemic contribution from injection reduces the need for aggressive topical concentration.
Coordination with peptide therapy clinics helps users implementing combined protocols ensure appropriate total exposure and avoid potential complications from excessive copper peptide intake through multiple routes.
Long-term protocol design
Sustainable copper peptide protocols balance intensity with skin health maintenance. Long-term users report best results from consistent moderate concentrations rather than aggressive intensity.
Cycling strategies, alternating between higher and lower concentrations periodically, may help maintain sensitivity and prevent tolerance plateau. Some long-term users cycle three months at maintenance concentration followed by one month at elevated concentration for periodic intensive phases.
Protocol adjustment over years should account for changing skin needs. Aging skin may benefit from gradually increasing concentration over time, while skin that has achieved improvement goals may reduce to maintenance levels. Flexibility and responsiveness characterize successful long-term protocols.
SeekPeptides members access detailed protocol templates and personalized guidance for designing sustainable copper peptide approaches. The platform's resources help users avoid common mistakes and optimize results throughout their copper peptide journey.
Frequently asked questions
What concentration should I start with?
Most users should start at 0.5% or below regardless of experience with other skincare actives. This baseline concentration establishes tolerance while still delivering meaningful peptide activity. Begin with alternate-day application and progress to daily use after two weeks without irritation.
Can higher concentration cause skin damage?
Excessive copper peptide concentration can potentially shift the collagen synthesis-breakdown balance unfavorably. Research shows GHK-Cu influences MMP enzymes that degrade collagen. At appropriate concentrations, this supports healthy remodeling. At excessive concentrations, breakdown may exceed synthesis. Copper peptide problems typically resolve with concentration reduction.
Why doesn't higher percentage mean better results?
GHK-Cu demonstrates activity at nanomolar concentrations, levels millions of times lower than typical product percentages. Cells respond to specific signaling intensities, and exceeding optimal ranges doesn't produce proportionally better responses. The relationship between concentration and results follows a curve that plateaus rather than climbing indefinitely.
How long before I can increase concentration?
Allow minimum eight weeks at any concentration before considering increases. This provides adequate time for initial results to manifest and reveals whether current concentration meets your needs. Rushing to higher concentrations before lower ones have demonstrated their effects leads to unnecessary escalation.
Should I use different concentrations on different areas?
Yes, different facial areas and body regions often benefit from different concentrations. Eye area typically uses 2% or below. Face and neck can use higher concentrations based on tolerance. Scalp applications should stay at 3% or below to avoid irritation. Dosing guidelines vary by application area and individual factors.
Do expensive high-concentration products work better than affordable lower-concentration options?
Not necessarily. Formulation factors beyond concentration significantly impact efficacy. A well-formulated 1% product with optimized delivery systems can outperform a basic 3% formula. Price often reflects packaging, marketing, and brand positioning rather than concentration or efficacy. Evaluate products based on formulation quality, not concentration or price alone.
Can I mix different concentration products?
Mixing products adds their concentrations together, which can unexpectedly exceed intended levels. A 1% serum mixed with 1% moisturizer delivers 2% total concentration. If you want to use multiple copper peptide products, choose lower concentrations for each or use only one copper peptide product in your routine.
How do I know if my concentration is working?
Document your starting condition with photos in consistent lighting. Compare at 8-week intervals. Meaningful changes include smoothed fine lines, improved texture, enhanced firmness, and more even skin tone. Changes are typically gradual and compound over time. Quick dramatic changes more likely indicate inflammatory response than genuine improvement.
External resources
Regenerative and Protective Actions of the GHK-Cu Peptide (National Institutes of Health)
GHK Peptide as a Natural Modulator of Multiple Cellular Pathways (National Institutes of Health)
Human Skin Penetration of Copper Tripeptide (National Institutes of Health)
Copper Peptide GHK-Cu Overview (Wikipedia)
For researchers serious about optimizing copper peptide protocols, SeekPeptides offers comprehensive resources, evidence-based guides, and a community of experienced users who have navigated these exact concentration questions.
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night.