Jan 17, 2026

The answer depends on three separate factors that most guides confuse or conflate. First, there's supply duration, how many days of injections you'll get before the vial runs empty. Second, there's stability duration, how long the reconstituted solution remains potent and safe to use. Third, there's protocol duration, how long you should run a GHK-Cu cycle before taking a break. These three timelines intersect in ways that determine whether you'll need one vial or several for your research protocol.
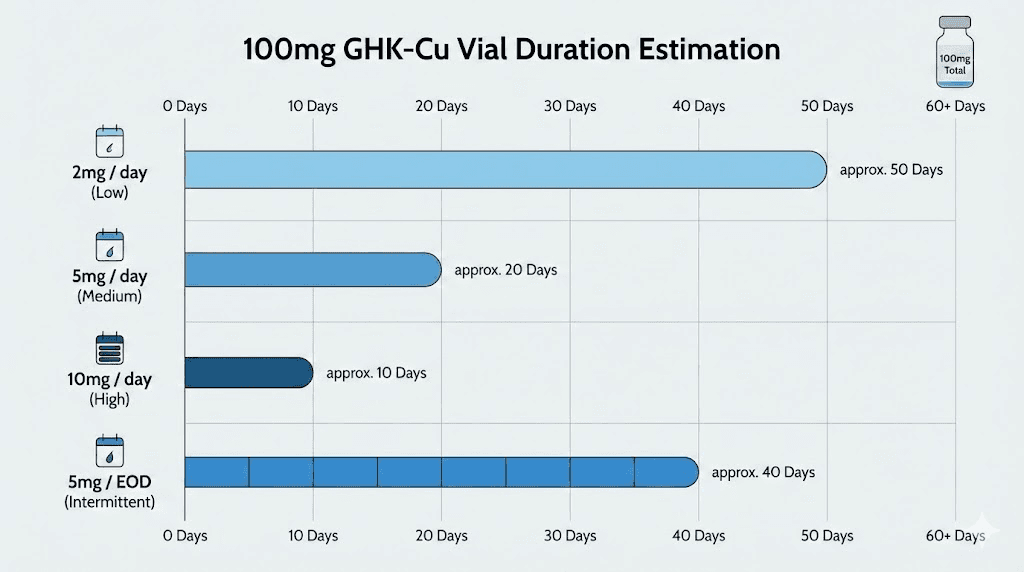
At standard dosing of 1-2mg daily, a 100mg vial provides roughly 50-100 days of supply. But here's where things get complicated. Reconstituted GHK-Cu only remains stable for 21-30 days refrigerated due to copper oxidation concerns. This creates a planning problem most researchers don't anticipate until they're staring at leftover solution approaching its expiration.
Understanding how to calculate peptide dosages correctly becomes essential for avoiding waste.
This guide breaks down exactly how long your 100mg GHK-Cu will last from every angle. We'll cover the math for different dosing schedules, optimal reconstitution strategies to prevent waste, storage requirements for maximum stability, and how to align your supply with recommended cycle protocols. SeekPeptides members access personalized dosing calculations and protocol planning, but understanding these fundamentals helps any researcher maximize their investment in this powerful regenerative peptide.
The math: supply duration at different doses
Let's start with the straightforward calculation. How many doses does 100mg of GHK-Cu provide?
The math is simple division: total peptide amount divided by dose per administration equals number of doses. But the practical application requires understanding typical dosing ranges and their implications. The complete GHK-Cu dosage guide covers the rationale behind different dose selections.
Conservative dosing (1mg daily)
At 1mg per day, 100mg provides exactly 100 doses. That's over three months of daily administration. This represents the lower end of effective dosing for most applications.
The conservative approach suits several situations. First-time users establishing tolerance often start here. Those prioritizing longevity and general anti-aging benefits over aggressive tissue repair may find this sufficient. Budget-conscious researchers seeking to extend their supply while still achieving meaningful results also favor this range.
At this dose, your 100mg vial theoretically lasts 100 days. But remember, reconstituted stability limits actual usability to roughly 30 days per batch. You'll need to reconstitute in portions rather than all at once. We'll cover optimal reconstitution strategies shortly.
Standard dosing (2mg daily)
Most clinical protocols and research applications use 2mg as the standard daily dose. At this level, 100mg provides 50 doses, enough for about 7 weeks of daily administration.
The 2mg dose balances effectiveness with efficiency. Research suggests this amount provides robust regenerative signaling for skin health, wound healing, and hair growth support without excessive copper exposure. The GHK-Cu injection dosage guide explains why this has become the standard reference point.
Many protocols don't use daily administration.
Three-times-weekly dosing (Monday, Wednesday, Friday) remains popular, especially for subcutaneous injection. At 2mg three times weekly, your 100mg vial provides approximately 16-17 weeks of supply, well over the typical 8-12 week cycle length.
Higher dosing (3-5mg daily)
Some protocols call for higher doses, particularly for acute wound healing, significant tissue repair, or when combining injectable with topical applications. At 3mg daily, 100mg provides roughly 33 days. At 5mg daily, you're looking at 20 days of supply.
Higher doses accelerate results but increase cost per cycle and potentially raise concerns about copper accumulation. The dosage chart shows how different amounts correspond to various research goals.
These aggressive protocols typically run shorter durations. A 4-week intensive cycle at higher doses may produce comparable or superior results to longer moderate-dose protocols, depending on your specific application.
Supply duration reference table
Here's a quick reference for 100mg vial duration at common dosing schedules:
Daily Dose | Frequency | Weekly Total | Days of Supply | Weeks of Supply |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1mg | Daily | 7mg | 100 days | ~14 weeks |
1mg | 5x/week | 5mg | 100 days | ~20 weeks |
2mg | Daily | 14mg | 50 days | ~7 weeks |
2mg | 5x/week | 10mg | 50 days | ~10 weeks |
2mg | 3x/week | 6mg | 50 days | ~16 weeks |
3mg | Daily | 21mg | 33 days | ~5 weeks |
5mg | Daily | 35mg | 20 days | ~3 weeks |
The peptide calculator handles these calculations automatically when you input your specific parameters.
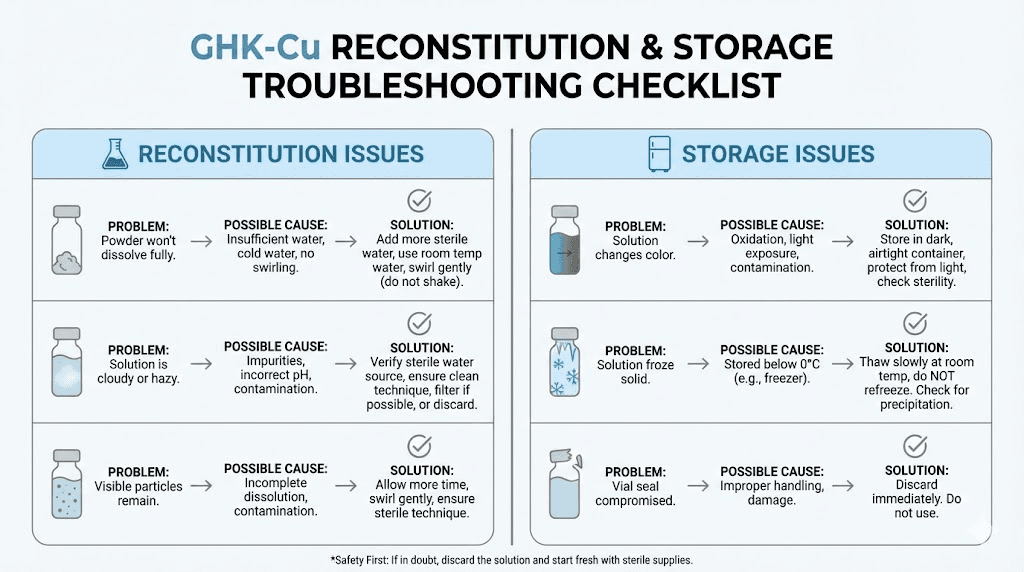
Reconstituted stability: the 30-day limit
Here's where supply duration meets practical limitation. Your 100mg vial may contain enough peptide for 100 days, but once reconstituted, the solution only remains stable for approximately 21-30 days.
This isn't arbitrary. It reflects the biochemistry of copper peptides in solution.
Why GHK-Cu has shorter stability
Most peptides remain stable in reconstituted form for 4-6 weeks refrigerated. GHK-Cu has a shorter window due to its copper component. The copper ion that gives GHK-Cu its regenerative properties also creates oxidation vulnerabilities that other peptides don't face.
Copper in solution tends to oxidize, and this oxidation can damage the peptide structure over time. The 21-28 day recommendation accounts for this additional degradation pathway. The complete shelf life guide explains the science behind these timelines.
Temperature proves critical. Every 10°C increase in temperature doubles the degradation rate. Room temperature storage (25°C) degrades peptides 4-8 times faster than proper refrigeration (2-8°C). Leaving your reconstituted vial on the counter even briefly accelerates deterioration.
The peptide storage guide covers optimal conditions for all peptide types.
Signs of degradation
Freshly reconstituted GHK-Cu should appear clear with a distinctive blue tint from the copper. This color is normal and expected. Any deviation suggests problems.
Watch for cloudiness, which indicates bacterial contamination or protein aggregation. Particles floating in solution suggest degradation. Color change, either loss of the blue tint or darkening, indicates copper oxidation affecting the peptide. Unusual odor can signal bacterial growth.
If your solution shows any of these signs, discard it regardless of how recently you reconstituted. Using degraded peptide wastes your research and potentially introduces contaminants.
The GHK-Cu viability guide provides additional assessment criteria.
Strategic reconstitution for 100mg vials
The stability limit creates a planning challenge. If you're dosing 1mg daily, you can only use about 30mg before the solution expires. The remaining 70mg stays as powder until you're ready for your next batch.
This actually works in your favor with proper planning. Here's the strategy:
Option 1: Partial reconstitution
Only reconstitute what you'll use within 30 days. At 2mg daily, that's about 60mg. Keep the remaining 40mg as powder (stored frozen) for your next batch. This requires carefully measuring powder, which is impractical for most researchers since the peptide comes in sealed vials.
Option 2: Full reconstitution with portion freezing
Reconstitute the entire 100mg vial, then immediately divide into multiple sterile vials. Freeze portions you won't use within 30 days. When you need more, thaw a frozen portion and refrigerate for use.
This approach has drawbacks. Freezing reconstituted GHK-Cu isn't ideal because ice crystal formation can damage peptide structure. Some potency loss occurs. But losing 10-15% to freeze damage may be preferable to losing 70% to expiration at room temperature or refrigeration beyond 30 days.
Option 3: Higher dose, shorter cycle
Increase your dose to use the full vial within the stability window. At 3.3mg daily, you'd use 100mg in exactly 30 days. This intensifies your protocol but eliminates waste.
The reconstitution guide walks through the practical steps for each approach.
Reconstitution math for 100mg
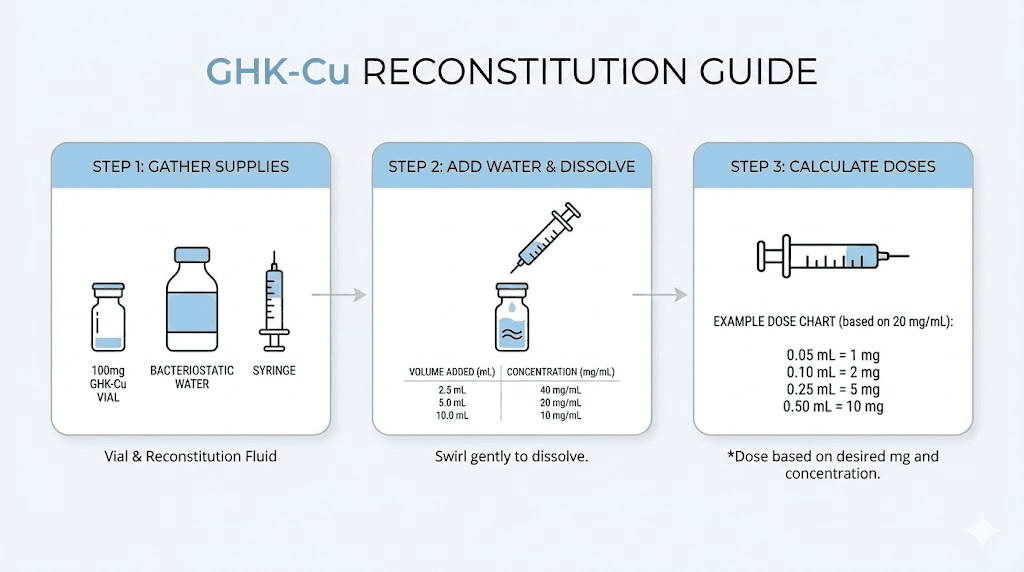
Standard reconstitution adds 3mL of bacteriostatic water to 100mg, creating a concentration of approximately 33.3mg/mL.
At this concentration:
1mg dose = 0.03mL (3 units on U-100 insulin syringe)
2mg dose = 0.06mL (6 units)
3mg dose = 0.09mL (9 units)
5mg dose = 0.15mL (15 units)
You can adjust concentration by adding more or less water. Adding 2mL creates 50mg/mL for smaller injection volumes. Adding 5mL creates 20mg/mL for easier measurement of smaller doses. The reconstitution calculator determines exact volumes for any desired concentration.
Reconstitution technique matters. Add water slowly along the vial wall, not directly onto the powder. Avoid creating foam or bubbles. Gently swirl, never shake, until fully dissolved. The solution should appear uniformly blue-tinted and completely clear. Understanding proper reconstitution technique prevents damage to the peptide during preparation.
Protocol duration: cycle length considerations
Beyond supply and stability, there's protocol duration to consider. How long should you actually run a GHK-Cu cycle?
This question determines how many 100mg vials you'll need for a complete protocol, and whether your single vial will suffice.
Standard cycle lengths
Recommended GHK-Cu cycle lengths typically range from 4 to 16 weeks, with 8-12 weeks being most common. The variation reflects different research goals and individual responses.
Shorter cycles (4-6 weeks) suit acute applications like wound healing support or intensive skin rejuvenation. The peptide works quickly for surface-level improvements, and shorter bursts maintain effectiveness without prolonged exposure.
Standard cycles (8-12 weeks) allow deeper tissue effects to manifest. Hair growth support, systemic anti-aging benefits, and comprehensive regenerative effects require this duration to reach full potential. Most clinical observations and research protocols use this timeframe. The cycle planning guide discusses how to structure protocols for different goals.
Extended cycles (12-16 weeks) may benefit those seeking maximum regenerative effects, particularly for hair restoration or significant tissue repair. However, longer isn't always better. Extended continuous use can reduce receptor sensitivity and potentially cause copper accumulation concerns.
Why cycling matters
Cycling, alternating periods of use with periods off, maintains the peptide's effectiveness and reduces potential risks.
Receptor sensitivity decreases with continuous stimulation. Your cells respond to GHK-Cu through specific receptors. Constant exposure can downregulate these receptors, requiring higher doses for the same effect. Breaks allow receptor populations to recover and resensitize.
Copper accumulation presents another concern with extended use. While the copper amounts in standard GHK-Cu doses are small, prolonged daily exposure without breaks allows gradual accumulation. Cycling provides periods where your body can normalize copper levels through normal metabolism and excretion.
The effects of stopping GHK-Cu guide discusses what happens during off-periods and how results change with discontinuation.
Common cycling protocols
30 days on, 14 days off: This aggressive approach maximizes time on the peptide while providing brief recovery periods. Popular for intensive protocols targeting specific issues like acute healing or rapid skin improvement.
8 weeks on, 4 weeks off: The most common cycling pattern balances sustained exposure with adequate recovery. Two cycles per year provides substantial regenerative support.
12 weeks on, 8-12 weeks off: Extended cycles with equivalent rest periods. This approach suits those seeking deeper, longer-term benefits while maintaining safety margins.
Seasonal cycling: Some researchers run one 12-16 week cycle annually, typically in winter when sun exposure is reduced. This conservative approach treats GHK-Cu as a periodic regenerative boost rather than ongoing maintenance.
Matching vial supply to cycle length
Here's how 100mg aligns with common protocols at standard 2mg dosing:
2mg daily, 5x/week (10mg/week):
100mg = 10 weeks of supply
Matches well with 8-12 week cycles
One vial covers most standard protocols
2mg daily, 7x/week (14mg/week):
100mg = ~7 weeks of supply
May need 1.5-2 vials for 12-week cycle
One vial covers shorter 4-6 week cycles with extra
2mg three times weekly (6mg/week):
100mg = ~16 weeks of supply
One vial covers even extended cycles
May have leftover for maintenance or second cycle
The 50mg vial guide provides comparison for smaller vial sizes if 100mg exceeds your needs.
Storage requirements for maximum longevity
How you store your GHK-Cu directly impacts how long it remains effective. Proper storage can extend usability. Poor storage can destroy your peptide before you even use it.
Lyophilized (powder) storage
Before reconstitution, GHK-Cu powder is remarkably stable when stored correctly. The freeze-dried form eliminates water, which is the primary catalyst for degradation reactions.
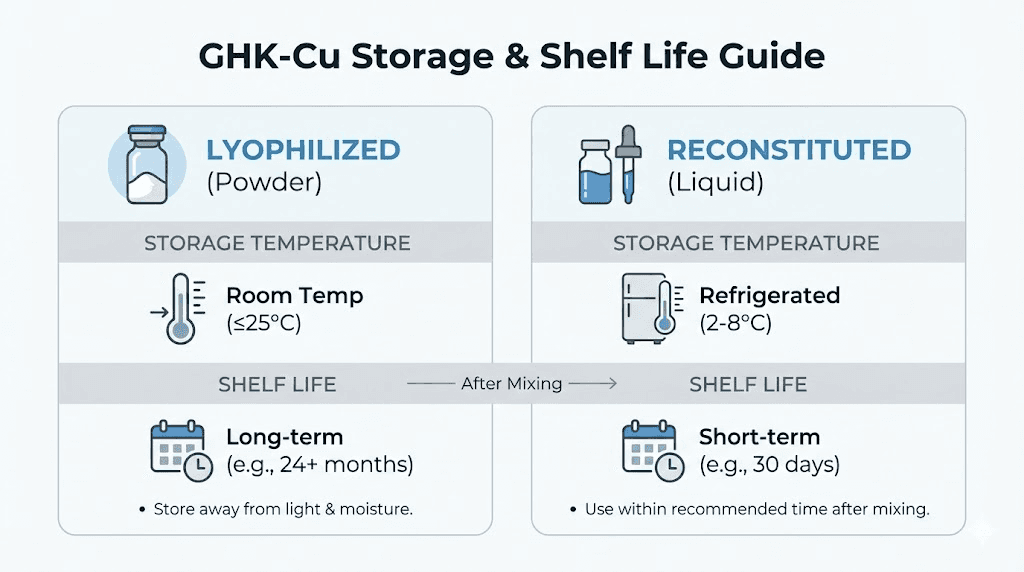
Freezer storage (-20°C / -4°F): Optimal for long-term preservation. Lyophilized GHK-Cu maintains potency for 18-24 months or longer when frozen. Store the sealed vial in a consistent location away from the door where temperature fluctuates.
Refrigerator storage (2-8°C / 35-46°F): Acceptable for medium-term storage. Expect 12-18 months of stability. Fine if you plan to use the peptide within a year of purchase.
Room temperature: Avoid if possible. Stability drops to 2-4 months maximum. Only acceptable for very short-term holding before reconstitution.
Keep the vial tightly sealed until ready for reconstitution. Moisture exposure accelerates degradation even in powder form. Some suppliers include desiccant packets, which help maintain dryness. The copper peptide storage guide covers additional considerations specific to copper-containing peptides.
Reconstituted solution storage
Once you add water, storage requirements become more stringent and the clock starts ticking.
Refrigeration is mandatory. Store reconstituted GHK-Cu at 2-8°C (35-46°F) constantly. Every hour at room temperature reduces remaining potency and lifespan.
Protect from light. UV and visible light can accelerate copper oxidation.
Keep the vial in its box or wrap in foil if your refrigerator has bright lighting.
Use within 21-30 days. The shorter estimate (21 days) provides safety margin. The longer estimate (30 days) represents the outer limit. Most protocols recommend splitting the difference at 28 days maximum.
Never freeze reconstituted solution intended for continued use. Ice crystals physically damage peptide structures. If you must freeze (to preserve excess), accept that some potency loss will occur and that portion should be used more quickly once thawed.
The reconstituted peptide shelf life article covers general principles applicable to all peptide solutions.
Practical storage tips
Label everything with reconstitution date. Memory fails. Writing "reconstituted 1/17" on the vial takes seconds and prevents using expired solution weeks later.
Store in the main refrigerator body, not the door. Door shelves experience temperature swings every time you open the fridge. Interior shelves maintain more consistent temperature.
Keep away from produce drawers where humidity tends to be higher. The crisper drawer's moisture isn't ideal for peptide storage.
Consider a dedicated mini-fridge for research materials if you use peptides regularly. This eliminates temperature fluctuations from frequent kitchen fridge access and keeps your materials organized.
The comprehensive storage guide addresses these points in greater detail with specific recommendations for various peptide types.
Cost efficiency: maximizing your 100mg investment
A 100mg GHK-Cu vial represents a meaningful investment. Understanding how to maximize value while maintaining protocol effectiveness helps justify the expense and avoid waste.
Cost per dose calculations
GHK-Cu pricing varies significantly between suppliers, but let's work with typical market ranges for a 100mg vial.
If your 100mg vial costs $80-150 (common retail range):
At 1mg daily: $0.80-1.50 per dose
At 2mg daily: $1.60-3.00 per dose
At 3mg daily: $2.40-4.50 per dose
At 5mg daily: $4.00-7.50 per dose
Compared to clinic-administered GHK-Cu treatments costing $50-200+ per session, self-administered research protocols offer substantial cost advantages. The peptide cost calculator helps compare expenses across different suppliers and protocols.
Avoiding waste
The biggest cost inefficiency comes from peptide going unused before expiration. Several strategies minimize waste:
Match reconstitution to usage rate. If you're using 2mg daily for a 30-day period, reconstitute only enough for that period (60mg). Keep remaining powder frozen for later.
But account for reconstitution limitations. Most 100mg vials can't be easily subdivided while maintaining sterility. You may need to reconstitute the full amount and accept some efficiency loss.
Consider protocol intensity. Using a higher dose to finish the vial within stability windows may be more cost-effective than losing 30-40% to expiration. Running a 3mg daily protocol for 33 days uses everything vs. running 1mg daily and discarding 70mg when it expires.
Coordinate with cycle length. Plan your protocol so vial supply aligns with intended cycle duration. Starting a 100mg vial at 2mg daily when you only intend to run a 4-week cycle guarantees significant waste.
Bulk purchasing considerations
Larger quantities often offer per-milligram savings, but require consideration of shelf life.
Buying multiple 100mg vials makes sense if you plan extended research, expect to run multiple cycles annually, or have reliable freezer storage for long-term powder preservation.
Buying excessive quantities that sit for years before use risks degradation even in ideal storage. The savings from bulk pricing can be offset by potency loss in aging inventory.
The vendor comparison guide discusses how to evaluate suppliers on both price and quality factors.
Planning your 100mg protocol
Now let's put everything together into practical protocol planning. How do you structure a research protocol around a 100mg GHK-Cu vial?
Protocol planning framework
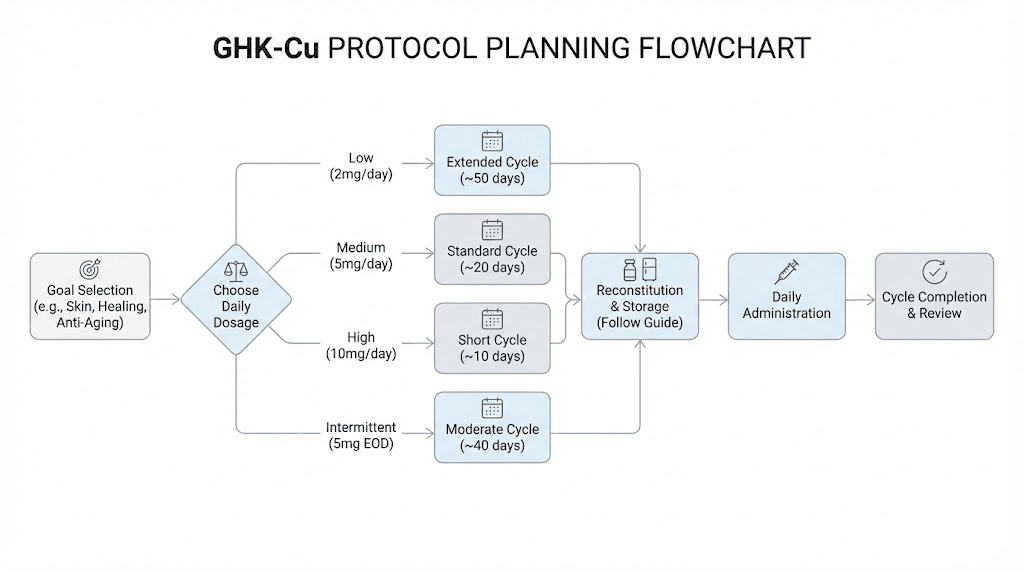
Step 1: Define your goals
What are you hoping to achieve? Skin rejuvenation typically requires 8-12 weeks. Hair growth support needs 3-6 months minimum. Wound healing support may need only 4-6 weeks. Your goal determines appropriate cycle length. The comprehensive GHK-Cu guide discusses applications and expected outcomes.
Step 2: Select your dosing schedule
Based on goal intensity and budget, choose a dose and frequency. Standard recommendations use 2mg administered 3-7 times weekly. More aggressive protocols may use 3-5mg. Conservative maintenance may use 1mg. The dosing principles guide helps match dose to application.
Step 3: Calculate supply requirements
How much GHK-Cu do you need for your intended cycle? Multiply daily dose by days per week by number of weeks.
Example: 2mg × 5 days/week × 12 weeks = 120mg needed
This tells you whether 100mg suffices (need to adjust protocol) or whether you need additional supply.
Step 4: Plan reconstitution batches
Given the 30-day stability limit, how will you handle reconstitution?
If your weekly usage is 10mg (2mg × 5 days), you'll use 40mg per month. Reconstituting all 100mg means 60mg might expire before use. Options include higher dosing to finish faster, freezing portions (accepting some potency loss), or accepting the waste as acceptable cost of the protocol.
Step 5: Schedule cycle and recovery
Plan your on-cycle period and subsequent off-cycle recovery. An 8-week on, 4-week off schedule provides predictable timing. The cycling guide discusses how to structure breaks appropriately.
Example protocols with 100mg
Skin rejuvenation protocol:
Goal: Improved skin texture, reduced fine lines, enhanced collagen
Dose: 2mg subcutaneously, 5 days/week
Duration: 10 weeks
Total peptide: 100mg exactly
Reconstitution: Full vial at start, use within 30 days for first 60mg, freeze remainder in sterile vial, thaw at day 28
Recovery: 6 weeks off before considering second cycle
Intensive hair support protocol:
Goal: Hair follicle stimulation, reduced shedding, improved density
Dose: 2mg daily, 7 days/week
Duration: 7 weeks (one vial), then reassess
Total peptide: 98mg (leaves tiny remainder)
Reconstitution: Full vial, use 60mg in first 30 days, frozen portion for remaining 38mg
Recovery: 4-8 weeks off, then evaluate need for second vial
Conservative longevity protocol:
Goal: General anti-aging, skin health maintenance, systemic benefits
Dose: 1mg daily, 5 days/week
Duration: 20 weeks (two 10-week blocks with reconstitution in between)
Total peptide: 100mg
Reconstitution: 50mg initially, frozen 50mg for second batch
Recovery: 8-12 weeks off annually
The getting started guide covers fundamentals for those new to peptide research.
Comparing 100mg to other vial sizes
Is 100mg the right vial size for your needs? Understanding how it compares to alternatives helps make informed purchasing decisions.
50mg vials
Smaller vials offer advantages for certain situations:
Lower entry cost. Half the peptide means roughly half the price, making initial experimentation more accessible.
Better stability management. At 2mg daily, 50mg lasts 25 days, fitting comfortably within the reconstitution stability window. No waste from expiration.
Flexibility for shorter cycles. If running 4-6 week protocols, 50mg may provide exactly what you need without excess.
The drawback is cost efficiency. Per-milligram pricing is typically 10-20% higher for smaller vials. If you're committed to longer protocols, buying larger makes economic sense.
The 50mg dosage guide provides specific protocols optimized for smaller vials.
200mg+ vials
Larger vials appear in the market occasionally:
Best per-milligram value. Bulk quantities offer the lowest cost per dose.
Requires careful planning. Unless you're running high-dose protocols or have multiple cycles planned, much may expire before use.
Storage considerations increase. Managing larger quantities requires more attention to stability and portion management.
Larger vials suit experienced researchers with established protocols who know exactly how much they'll use over extended periods.
Pre-reconstituted solutions
Some suppliers offer GHK-Cu already reconstituted. While convenient, these products have limitations:
Shorter usable lifespan. The stability clock started at manufacturing, not when you received it. Your actual usage window may be much shorter than you expect.
Shipping concerns. Temperature control during shipping is critical but variable. Peptide may arrive partially degraded.
Verification challenges. Harder to assess quality when you can't see the original powder form and dissolution behavior.
For most researchers, lyophilized powder offers better value and quality control despite the inconvenience of reconstitution.
Administration considerations
How you administer GHK-Cu affects how quickly you use your 100mg supply and how effectively the peptide works.
Subcutaneous injection
The most common administration route for research applications. Subcutaneous injection places the peptide in the fat layer just beneath the skin, where it absorbs gradually into systemic circulation.
Typical injection sites include the abdomen (avoiding the navel area), outer thigh, and upper arm. Rotating between sites prevents localized tissue irritation from repeated injection. The injection guide covers proper technique.
GHK-Cu is noted to cause more injection site reactions than many other peptides. The copper component can cause localized burning, redness, or irritation in some individuals. This isn't universal, but awareness helps manage expectations.
Topical application
Topical use doesn't consume reconstituted injectable solution but rather uses dedicated topical preparations. However, some researchers apply small amounts of reconstituted GHK-Cu topically to targeted areas.
Topical absorption is significantly lower than injection. The hydrophilic peptide doesn't penetrate skin efficiently on its own. Microneedling dramatically improves topical absorption by creating channels through the skin barrier. The topical application guide discusses effective approaches.
If adding topical to injectable protocols, account for the additional peptide use in your supply calculations.
Dosing frequency options
Daily dosing provides consistent peptide levels but uses supply faster and requires more frequent injections. At 2mg daily, 100mg lasts about 7 weeks.
Five-times-weekly dosing (weekdays on, weekends off) reduces total usage by about 30% while maintaining most benefits. This extends 100mg to roughly 10 weeks at 2mg per dose.
Three-times-weekly dosing (often Monday, Wednesday, Friday) further reduces usage and extends supply to approximately 16 weeks at 2mg per dose. Some research suggests this frequency maintains effectiveness for many applications.
The optimal frequency depends on your goals, schedule, and tolerance for injection frequency. The dosing frequency guide discusses the tradeoffs in detail.
Combining GHK-Cu with other peptides
Many researchers use GHK-Cu alongside other peptides. This affects protocol planning and total peptide management.
Common combinations
GHK-Cu + BPC-157 + TB-500: The "healing stack" combines GHK-Cu's regenerative signaling with BPC-157's tissue repair and TB-500's systemic healing support. This combination targets injury recovery, joint health, and overall tissue repair from multiple mechanisms. The stacking guide provides detailed protocols.
GHK-Cu + growth hormone secretagogues: Combining with compounds like Ipamorelin or CJC-1295 addresses both regenerative signaling and growth hormone optimization. Synergistic effects may enhance skin, hair, and overall anti-aging outcomes.
GHK-Cu + anti-inflammatory peptides: For hair and skin applications, adding KPV peptide provides anti-inflammatory support that may enhance GHK-Cu's effectiveness by reducing inflammatory interference with regenerative processes.
Impact on supply planning
Multi-peptide protocols increase complexity. Each peptide has its own dosing, reconstitution, and stability considerations. Budget, storage space, and protocol management all expand.
However, combining peptides doesn't necessarily increase GHK-Cu consumption. You still use the same amount of GHK-Cu. The addition simply adds other compounds to your regimen.
Where combinations affect planning is in overall budget and protocol length decisions. You might choose to run a shorter, more intensive multi-peptide protocol rather than a longer GHK-Cu-only approach. The combination guide and stack calculator help plan multi-peptide protocols.
Troubleshooting common issues
Even with careful planning, problems arise. Here's how to address common issues with 100mg GHK-Cu protocols.
Running out before cycle completion
If your supply runs short before reaching intended cycle duration:
Option 1: End cycle early. If you're already 6+ weeks in, you've likely received meaningful benefit. Ending slightly early is better than running out mid-protocol next time.
Option 2: Reduce frequency. Dropping from daily to three-times-weekly extends remaining supply while maintaining some benefit.
Option 3: Reduce dose. Cutting from 2mg to 1mg doubles remaining supply. Lower dosing may maintain results even if it won't produce new gains.
Option 4: Purchase additional supply. If continuing at full dose matters for your goals, obtaining another vial may be worthwhile.
Solution appearing cloudy or discolored
Discard immediately. Don't attempt to filter or salvage. Cloudiness indicates contamination or degradation that compromises both safety and effectiveness.
Review what went wrong. Did you use sterile technique during reconstitution? Was bacteriostatic water fresh and sterile? Has storage temperature been consistent? Has the vial been exposed to light or contamination? Identifying the cause prevents recurrence with future vials.
The common mistakes guide covers frequent errors that lead to these problems.
Injection site reactions
GHK-Cu is known for more injection site reactions than many peptides. The copper component can cause localized burning, redness, swelling, or itching. These reactions are generally harmless but uncomfortable.
Strategies to minimize reactions include rotating injection sites consistently to avoid repeated trauma to the same area, ensuring the solution is at room temperature before injection (cold injections can increase irritation), injecting slowly rather than quickly, and using a smaller gauge needle for less tissue trauma.
If reactions are severe or don't resolve within hours, discontinue use and consult appropriate medical guidance.
The side effects guide discusses GHK-Cu reactions in more detail.
Uncertain whether peptide is still potent
If you're unsure whether your reconstituted GHK-Cu is still effective:
Visual assessment: Should be clear with blue tint. Any cloudiness, particles, or color change suggests problems.
Time assessment: If over 30 days since reconstitution, potency is likely compromised regardless of appearance.
Storage assessment: If the vial has been left at room temperature for extended periods, degradation has accelerated.
When in doubt, starting fresh with new reconstitution or a new vial is safer than continuing with potentially degraded peptide. Using ineffective peptide wastes time more than money.
Frequently asked questions
How many doses are in a 100mg GHK-Cu vial?
At the standard 2mg dose, a 100mg vial contains 50 doses. At 1mg, you get 100 doses. At 3mg, approximately 33 doses.
The peptide calculator provides exact calculations for any dose amount.
Will one 100mg vial last a full cycle?
Typically yes for standard 8-12 week cycles at moderate dosing. At 2mg five times weekly, 100mg lasts about 10 weeks, covering most protocols. Daily dosing at higher amounts may require additional supply for longer cycles.
How long does reconstituted GHK-Cu stay good?
Reconstituted GHK-Cu should be used within 21-30 days when refrigerated at 2-8°C. The copper component creates oxidation vulnerabilities that limit stability compared to other peptides. The shelf life guide covers stability in detail.
Should I reconstitute the whole 100mg at once?
Only if you'll use it within 30 days. Otherwise, you'll waste what expires. Options include partial reconstitution (if feasible with your vial format), freezing portions of reconstituted solution (accepting some potency loss), or adjusting your dose higher to use everything before expiration.
What concentration should I mix 100mg GHK-Cu at?
Standard reconstitution uses 3mL of bacteriostatic water creating ~33.3mg/mL. This provides convenient injection volumes (0.06mL for 2mg dose). The reconstitution calculator determines volumes for custom concentrations.
Can I use GHK-Cu continuously or do I need breaks?
Cycling is recommended. Standard protocols suggest 8-12 weeks on followed by 4-8 weeks off. Breaks maintain receptor sensitivity and allow copper levels to normalize. The cycling guide discusses optimal on/off patterns.
Is 100mg enough for hair growth support?
For one cycle, yes. Hair restoration typically requires 3-6 months of sustained effort, which may span 2-3 cycles with breaks. Plan for multiple 100mg vials if pursuing long-term hair protocols. The copper peptides for hair guide covers application specifics.
How does 100mg compare to 50mg vials?
100mg offers better per-milligram value but creates potential waste if you can't use everything before stability expires. 50mg aligns better with 30-day stability windows at standard dosing. The right choice depends on your planned protocol intensity and length.
For researchers looking to optimize their GHK-Cu protocols and maximize results from every vial, SeekPeptides provides detailed dosing calculators, personalized protocol guidance, and a community of experienced researchers who've navigated these exact planning challenges.