Jan 9, 2026

Memory represents the foundation of human experience. Every skill you possess, every relationship you maintain, every piece of knowledge you draw upon exists because your brain successfully encoded, stored, and retrieved that information. When memory falters, whether through age, stress, injury, or disease, the impact extends far beyond simple forgetfulness into the core of who you are and what you can accomplish.
Peptides offer a fundamentally different approach to memory enhancement than traditional nootropics. Where stimulants and racetams work by temporarily modifying neurotransmitter activity, memory-enhancing peptides target the underlying biological infrastructure that determines your brain's capacity to form and retain memories. They influence neurotrophic factors that govern neuron health. They promote synaptogenesis, the creation of new connections between brain cells. They protect existing neural architecture from damage while encouraging plasticity that enables learning.
The difference matters enormously for anyone serious about cognitive optimization. Temporary neurochemical boosts fade when the compound clears your system. Structural improvements to brain architecture, the kind memory peptides can produce, persist far longer and compound over time. This guide covers everything researchers need to know about peptides for memory enhancement, from mechanism breakdowns to practical protocols to stacking strategies that maximize results.
SeekPeptides provides personalized protocols for cognitive enhancement peptides tailored to individual goals and circumstances.
Understanding memory and how peptides enhance it
Memory formation involves multiple stages that peptides can influence at various points. Understanding these stages helps explain why different peptides suit different memory goals.
Encoding represents the first stage. When you experience something worth remembering, your brain must convert that experience into a neural pattern. This involves activating specific neurons in patterns that represent the information. Strong encoding requires attention, emotional engagement, and sufficient neurochemical support. Peptides that enhance dopamine signaling or reduce anxiety can improve encoding by increasing focus and reducing interference.
Consolidation follows encoding. The initial neural pattern must stabilize into a lasting memory trace. This process requires protein synthesis, structural changes at synapses, and often sleep for optimal completion. Peptides that enhance brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression directly support consolidation by promoting the synaptic strengthening that makes memories stick.
Storage involves maintaining memory traces over time. Memories don't simply persist passively. They require ongoing maintenance as neural connections naturally turn over. Neuroprotective peptides help preserve stored memories by protecting the neurons and synapses that hold them.
Retrieval is accessing stored memories when needed. Even perfectly encoded and consolidated memories prove useless if you cannot retrieve them on demand. Certain peptides improve retrieval by enhancing the neural signaling pathways involved in memory access.
The getting started with peptides guide provides foundational context for newcomers. Understanding basic peptide concepts makes the specific memory applications clearer.
Semax: the gold standard for memory enhancement
Semax stands as the most thoroughly researched memory-enhancing peptide, with decades of clinical use in Russia where it holds regulatory approval for cognitive and neurological applications. Derived from a fragment of adrenocorticotropic hormone with stabilizing modifications, Semax demonstrates remarkable memory-enhancing properties without hormonal side effects.
How Semax improves memory
BDNF modulation represents Semax's primary memory mechanism. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor functions as a master regulator of neuroplasticity, directly controlling the brain's ability to form new synaptic connections and strengthen existing ones. Semax significantly increases BDNF expression in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex, the brain regions most critical for memory formation and working memory respectively.
Higher BDNF levels translate directly to enhanced memory capacity. The protein promotes synaptogenesis, meaning more connection points between neurons where memories can be encoded. It supports long-term potentiation, the cellular mechanism underlying learning. It protects existing neurons from damage that would otherwise degrade memory function over time.
Beyond BDNF, Semax influences multiple neurotransmitter systems relevant to memory. Dopaminergic enhancement improves the motivation and reward signaling that marks experiences as worth remembering. Cholinergic modulation supports the acetylcholine signaling critical for memory encoding. These effects complement the structural BDNF benefits with acute neurochemical enhancement.
Gene expression studies reveal Semax activates transcription of numerous neuroplasticity-related genes beyond BDNF alone. This broad genomic influence suggests the peptide works through multiple parallel pathways rather than a single mechanism, potentially explaining its robust and consistent effects across different users and conditions.
The Semax peptide dosage guide covers administration details. The nasal spray peptides guide explains intranasal delivery technique that provides the most practical Semax administration.
Semax clinical evidence for memory
Russian clinical research provides substantial evidence for Semax's memory effects. Studies in healthy individuals demonstrate improved performance on memory tasks within days of starting treatment. Working memory, the ability to hold and manipulate information temporarily, shows particularly consistent improvement. This type of memory underlies everything from following conversations to solving complex problems.
Long-term memory also benefits. Research subjects show improved recall of learned information days and weeks after encoding while using Semax. This suggests the peptide enhances consolidation and storage, not just temporary retrieval.
Clinical applications extend to pathological memory loss. Semax holds approval in Russia for stroke recovery, where it accelerates return of cognitive function including memory. Research in mild cognitive impairment shows slowed progression and maintained function. While not reversing established dementia, Semax appears to support remaining memory capacity.
The evidence quality for Semax exceeds most other nootropic compounds. Decades of clinical use, multiple controlled trials, and regulatory approval provide confidence that effects observed in research translate to real-world benefits.
Semax dosing for memory enhancement
Standard memory protocol:
200-600mcg intranasally, administered one to three times daily. Most users begin with 200mcg twice daily and adjust based on response. Effects typically appear within 30-60 minutes and persist for 4-6 hours, making morning and early afternoon dosing ideal for daytime cognitive demands.
Intensive learning periods:
600-900mcg daily, divided across two to three doses, during periods requiring maximum memory function. Exam preparation, intensive training, or demanding professional projects suit this higher dosing tier.
Long-term memory maintenance:
200-400mcg daily for ongoing memory support and brain health preservation. Lower doses suffice for maintenance once acute enhancement goals are achieved.
Cycling recommendations:
Most protocols suggest 2-4 week cycles followed by 1-2 week breaks. Some researchers use continuous low-dose Semax without apparent tolerance, though cycling remains the conservative approach given limited data on very long-term continuous use.
The peptide calculator helps determine appropriate dosing. The peptide reconstitution calculator ensures accurate preparation of nasal spray solutions.
Selank: memory enhancement through stress reduction
Selank offers a unique approach to memory enhancement by combining direct cognitive effects with potent anxiolytic properties. For the many people whose memory suffers under stress, Selank addresses both the symptom and a major underlying cause simultaneously.
The stress-memory connection
Chronic stress devastates memory function through multiple mechanisms. Elevated cortisol damages hippocampal neurons directly, shrinking the brain region most critical for memory formation. Stress hormones impair long-term potentiation, making new memory formation harder. Anxiety consumes working memory capacity that would otherwise process and encode new information.
Selank breaks this cycle. The peptide reduces anxiety through GABA system modulation, lowering the stress response that impairs memory. Simultaneously, it enhances BDNF expression like Semax, providing direct memory support independent of stress effects. This dual action produces greater memory improvement in anxious individuals than either mechanism alone would predict.
The peptides for anxiety complete guide details Selank's anxiolytic mechanisms. Understanding the anxiety component helps appreciate why Selank sometimes outperforms Semax for memory in stressed populations.
Selank memory mechanisms
Beyond stress reduction, Selank influences memory through several direct pathways. Enkephalin metabolism modulation affects endogenous opioid systems in ways that support learning without the cognitive impairment typical of opioid agonists. Serotonergic effects enhance cognitive flexibility, the ability to update mental models based on new information.
BDNF elevation, though perhaps less pronounced than with Semax, still provides meaningful neuroplasticity support. The combined effect of reduced anxiety plus enhanced plasticity plus improved cognitive flexibility produces comprehensive memory benefits.
Research evidence supports these mechanisms. Studies show Selank improves memory performance in anxious patients beyond what anxiety reduction alone would predict. Healthy individuals under stress also show memory improvements with Selank treatment, maintaining cognitive function under pressure that would otherwise impair it.
The Selank peptide injection dosage guide covers administration options. Both intranasal and subcutaneous routes work effectively.
Selank protocols for memory
Standard cognitive enhancement:
200-400mcg per nostril, two to three times daily. Intranasal delivery provides rapid onset, useful when you need quick memory support for imminent cognitive demands.
Subcutaneous administration:
250-500mcg daily or every other day for more consistent systemic levels. Some users prefer injection for reliable dosing compared to nasal spray variability.
Acute stress situations:
400-600mcg intranasally 30-60 minutes before anticipated stressful events requiring good memory function. Presentations, exams, and high-pressure meetings all suit this acute approach.
Cycling:
2-4 week cycles with equal break periods prevent potential receptor adaptations and allow assessment of baseline changes.
Dihexa: extreme potency neurogenesis
Dihexa represents the most potent memory-enhancing compound ever studied, active at picomolar concentrations that dwarf traditional nootropics by seven orders of magnitude. Originally developed for Alzheimer's disease research, Dihexa demonstrates remarkable neurogenic properties that have attracted intense interest despite limited human data.
Mechanism of extraordinary potency
Dihexa works through the hepatocyte growth factor system and its c-Met receptor. This signaling pathway governs neurogenesis, synaptogenesis, and neuroprotection through mechanisms distinct from the BDNF pathways Semax and Selank primarily influence. By potentiating HGF/c-Met signaling, Dihexa dramatically enhances the brain's capacity to form new synaptic connections.
The synaptogenic effects appear particularly pronounced for memory. Research shows Dihexa increases dendritic spine density, the physical protrusions where synaptic connections form. More spines mean more potential connections, directly expanding memory storage and processing capacity at the structural level.
The HGF system normally shows greatest activity during brain development, then diminishes with age. Dihexa essentially reactivates developmental neuroplasticity mechanisms in adult brains, potentially explaining why animal studies show it can reverse age-related cognitive decline rather than merely slow progression.
Research evidence for memory
Animal research provides striking evidence for Dihexa's memory effects. Rats treated with Dihexa show dramatically improved performance on spatial memory tasks, with some studies suggesting effects comparable to reversing years of age-related decline. Both acquisition of new memories and retention of existing ones improve significantly.
Microscopy studies confirm the proposed mechanism. Dihexa-treated animals show increased dendritic spine density, providing structural evidence that explains the functional improvements. More synaptic connections correlate with better memory capacity in dose-dependent fashion.
Alzheimer's disease models show perhaps the most impressive results. Dihexa can reverse cognitive deficits even after significant disease progression, recovering lost function rather than merely stabilizing decline. This distinguishes Dihexa from compounds that only slow deterioration.
Human evidence remains limited to anecdotal reports from researchers. Users describe significant improvements in memory formation and recall, particularly for complex information and spatial memory. However, controlled human trials have not been published, making evidence quality substantially lower than for Semax or Selank.
Dihexa considerations and dosing
Typical research doses:
0.5-2mg daily, administered orally or subcutaneously. The extreme potency means even small doses produce significant effects. Most researchers start at 0.5mg and carefully assess response before any increase.
Duration:
Short cycles of 2-4 weeks with extended breaks of 4-8 weeks represent the conservative approach. The potentially permanent synaptic changes Dihexa induces warrant caution about extended continuous use.
Safety considerations:
Limited human safety data means Dihexa carries more uncertainty than established peptides. Theoretical concerns about excessive uncontrolled neuroplasticity or growth factor signaling remain unresolved. The HGF pathway's involvement in tissue growth raises theoretical questions about interactions with cancer biology, though no direct evidence supports this concern.
Users should approach Dihexa more cautiously than compounds with decades of clinical use. Starting doses should be minimal, observation periods should be extended, and any unusual effects should prompt discontinuation pending evaluation.
The how long do peptides take to work article helps set realistic timeline expectations for any peptide protocol.
P21: targeted hippocampal neurogenesis
P21, derived from Cerebrolysin research, offers a cleaner single-peptide approach to neurogenesis compared to complex mixtures. The peptide specifically targets hippocampal neurogenesis, the creation of new neurons in the brain region most critical for memory formation.
Neurogenesis for memory
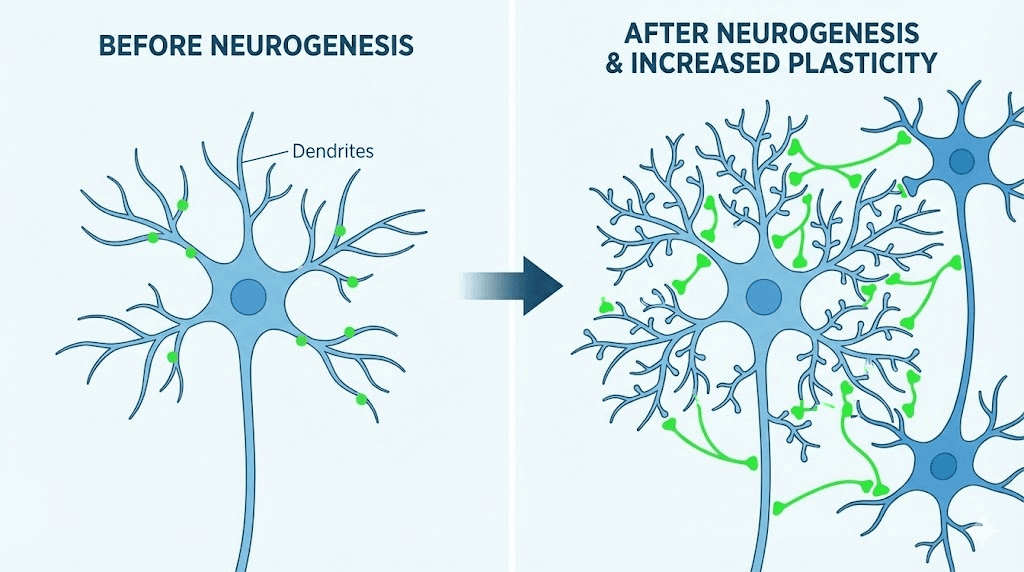
The adult brain can create new neurons, contrary to older scientific beliefs. This neurogenesis occurs primarily in the hippocampus, specifically the dentate gyrus subregion. New neurons integrate into existing memory circuits, enhancing capacity for learning and memory formation.
Neurogenesis rates decline with age, stress, and various pathological conditions. This decline correlates with age-related memory impairment. Compounds that enhance neurogenesis offer potential to reverse rather than merely slow memory decline by restoring the cellular substrate for memory formation.
P21 enhances hippocampal neurogenesis through BDNF pathway activation and GSK-3β inhibition. The combination promotes both new neuron production and survival of newly created neurons. More new neurons that successfully integrate means greater memory capacity.
P21 research and application
Animal studies demonstrate P21 enhances memory task performance, particularly on tests that depend on hippocampal function. Spatial memory and contextual memory both improve following P21 administration. Histological confirmation shows increased neurogenesis correlating with functional improvements.
Depression models show relevant effects as well. Depression involves hippocampal volume reduction partly due to reduced neurogenesis. P21's antidepressant-like effects in animal models may relate to restoring hippocampal neurogenesis, which would also support memory function impaired by depression.
Human evidence remains anecdotal but consistent with animal findings. Users report memory improvements alongside mood enhancement, suggesting the neurogenesis mechanism translates from animal models.
P21 dosing:
1-2mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously daily for cycles of 2-4 weeks. Some protocols use every-other-day dosing. Extended breaks of 4-8 weeks between cycles allow assessment of lasting effects and neurogenesis completion.
The peptide injection sites guide covers proper subcutaneous administration technique.
Cerebrolysin: the clinical neurotrophic mixture
Cerebrolysin consists of low-molecular-weight peptides derived from porcine brain tissue. Though a complex mixture rather than single defined peptide, Cerebrolysin has accumulated substantial clinical evidence for cognitive and memory applications, particularly in neurological recovery contexts.
Broad neurotrophic support
The mixture's effects arise from multiple peptide components acting on various growth factor pathways simultaneously. Components mimic or enhance BDNF, NGF, CNTF and other neurotrophic factors, producing comprehensive support for neuronal health and plasticity.
This broad approach has advantages and disadvantages. Multiple mechanisms provide redundancy, multiple pathways to benefit. But the complexity makes precise mechanism attribution difficult and batch-to-batch consistency potentially variable.
Clinical evidence base
Stroke recovery:
Multiple controlled trials demonstrate Cerebrolysin accelerates cognitive and motor recovery following stroke. Memory function specifically improves faster with Cerebrolysin treatment. Effects appear strongest when treatment begins early after stroke.
Traumatic brain injury:
Research supports Cerebrolysin for TBI recovery, where neurotrophic support aids healing and functional restoration including memory.
Alzheimer's disease:
Clinical trials show modest benefits for Alzheimer's patients, with some studies demonstrating slowed cognitive decline. Memory preservation appears among the benefits, though effects are more pronounced in earlier disease stages.
Healthy cognition:
Limited research in healthy individuals suggests cognitive enhancement, though evidence is less robust than for neurological conditions.
Administration:
Cerebrolysin requires intramuscular or intravenous injection, typically 5-30ml depending on indication. Treatment protocols often involve daily injections for 10-20 days. The injection requirements and clinical setting associations make Cerebrolysin less practical than intranasal peptides for routine cognitive enhancement.
BPC-157: supporting memory through healing
While primarily known for tissue healing, BPC-157 offers memory benefits through multiple indirect and some direct mechanisms. The body protection compound demonstrates neuroprotective properties that support cognitive function as part of its broad systemic effects.
Gut-brain axis effects
The gut-brain axis connects intestinal health directly to brain function through neural, hormonal, and immune pathways. Gut inflammation correlates with cognitive impairment including memory deficits. BPC-157's profound gut-healing effects may improve memory function by reducing this inflammatory burden.
The peptides for gut health page details BPC-157's intestinal applications. Understanding the gut connection illuminates why a healing peptide might enhance memory.
Direct neuroprotective mechanisms
BPC-157 demonstrates neuroprotective effects independent of gut healing. Research shows the peptide protects dopaminergic neurons against various toxic insults. Since dopamine signaling supports memory encoding through attention and reward marking, protecting these systems supports memory function.
Serotonergic modulation also occurs. The peptide influences serotonin systems relevant to cognitive flexibility and mood, both of which impact memory performance.
The BPC-157 dosage calculator helps determine appropriate dosing. Standard protocols of 250-500mcg twice daily support both healing and potential cognitive benefits. The BPC-157 vs TB-500 comparison helps select appropriate healing peptides when cognitive support is part of broader goals.
Pinealon: sleep and memory connection
Pinealon represents a tripeptide influencing pineal gland function and circadian rhythm regulation. Since sleep proves critical for memory consolidation, compounds that optimize sleep architecture indirectly enhance memory substantially.
Sleep for memory
Memory consolidation depends heavily on sleep. During sleep, particularly slow-wave and REM stages, the brain transfers memories from temporary hippocampal storage to permanent cortical storage. Sleep deprivation dramatically impairs memory formation, while optimized sleep enhances it.
Pinealon influences melatonin synthesis and circadian rhythm regulation. Better circadian alignment means better sleep timing and architecture. Improved sleep means better memory consolidation and next-day encoding capacity.
Pinealon applications
Sleep optimization:
100-200mcg daily, particularly evening administration, supports circadian regulation.
Memory support:
Higher doses up to 400mcg daily may provide direct cognitive effects beyond sleep improvement.
The Pinealon peptide benefits article covers this peptide more comprehensively.

Comparing peptides for different memory goals
Different memory concerns call for different peptide selections. This comparison helps match peptides to specific needs.
Peptide | Primary Memory Mechanism | Best Application | Evidence Level | Administration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Semax | BDNF enhancement | General memory enhancement | Strong clinical | Intranasal |
Selank | Anxiolysis + BDNF | Stress-impaired memory | Strong clinical | Intranasal/SC |
Dihexa | HGF synaptogenesis | Age-related decline | Strong preclinical | Oral/SC |
P21 | Hippocampal neurogenesis | Learning capacity | Moderate preclinical | SC/IM |
Cerebrolysin | Multi-neurotrophic | Injury recovery | Strong clinical | IM/IV |
BPC-157 | Neuroprotection | Supporting factor | Strong preclinical | SC/Oral |
Pinealon | Sleep optimization | Consolidation support | Moderate | Oral/SC |
Selection by situation
General memory enhancement in healthy individuals:
Semax represents the first choice due to strong evidence, easy administration, and reliable effects. Start here unless specific circumstances suggest otherwise.
Memory impaired by anxiety or stress:
Selank addresses both the stress cause and memory symptom simultaneously. Often outperforms Semax when anxiety is a significant factor.
Age-related memory decline:
Dihexa offers the most potent intervention for age-related changes, potentially reversing rather than merely slowing decline. The limited safety data requires careful consideration of risk tolerance.
Learning new skills or information:
P21's hippocampal neurogenesis focus specifically supports new memory formation. Good choice for periods of intensive learning.
Recovery from brain injury or stroke:
Cerebrolysin has the strongest clinical evidence for neurological recovery contexts.
Comprehensive cognitive support:
Stacking multiple peptides with complementary mechanisms provides broader benefits than any single agent.
Stacking strategies for memory optimization
Combining peptides with complementary mechanisms can produce effects exceeding any single compound. Careful stack design matches peptides to goals while managing complexity.
Foundational memory stack
This beginner-friendly combination provides comprehensive memory support:
Semax: 400mcg intranasal, twice daily morning and early afternoon
BPC-157: 250mcg subcutaneous, twice daily
Rationale: Semax provides direct BDNF-mediated memory enhancement. BPC-157 offers neuroprotection and gut-brain axis support. The combination addresses memory enhancement and protective factors.
Run for 4-6 weeks, then assess before continuing or modifying.
Stress-adapted memory stack
For those whose memory suffers under chronic stress:
Selank: 400mcg intranasal, twice daily
BPC-157: 300mcg subcutaneous, twice daily
Pinealon: 200mcg evening
Rationale: Selank addresses anxiety impacting memory while providing direct cognitive enhancement. BPC-157 supports gut health often compromised by stress. Pinealon optimizes sleep frequently disrupted by stress. The combination attacks stress-related memory impairment from multiple angles.
Maximum neuroplasticity stack
For aggressive memory enhancement:
Semax: 600mcg intranasal, twice daily
Dihexa: 1mg oral or subcutaneous, once daily
P21: 1mg subcutaneous, every other day
Rationale: Multiple neuroplasticity pathways activated simultaneously. Semax elevates BDNF. Dihexa potentiates HGF signaling. P21 promotes hippocampal neurogenesis. Together they maximize the brain's capacity for structural adaptation.
This aggressive approach should be reserved for those with previous peptide experience and higher risk tolerance. Shorter cycles of 2-3 weeks with extended breaks are appropriate.
The peptide stack calculator helps design multi-peptide protocols. The how many peptides can you take at once article discusses combination principles.
Recovery and protection stack
For those recovering from injury, illness, or cognitive insult:
BPC-157: 500mcg subcutaneous, twice daily
Semax: 400mcg intranasal, twice daily
TB-500: 2mg subcutaneous, twice weekly
Rationale: Heavy emphasis on healing and protection. BPC-157 and TB-500 provide systemic healing support. Semax offers neuroprotection and cognitive enhancement. Appropriate for recovery periods where protection matters as much as enhancement.
The TB-500 dosage calculator helps with dosing for the healing component.
Practical protocols for memory enhancement
Theory requires practical implementation. These protocols translate peptide science into actionable approaches.
Protocol 1: conservative memory enhancement
Goal: Reliable memory improvement with minimal risk
Peptide: Semax only
Dose: 200mcg intranasal twice daily, morning and early afternoon
Duration: 4 weeks on, 2 weeks off
Assessment: Track memory performance on standardized tasks or real-world metrics before starting and weekly during protocol
This conservative approach suits first-time peptide users or those prioritizing safety. Semax's decades of clinical use provide confidence in the risk profile. Effects should be noticeable within the first week.
Protocol 2: comprehensive cognitive optimization
Goal: Broad cognitive enhancement including memory
Peptides: Semax + Selank (alternating or combined)
Approach:
Week 1-2: Semax 400mcg twice daily, establish baseline response
Week 3-4: Add Selank 300mcg twice daily, assess combination
Week 5-6: Continue combination or adjust ratios based on response
Week 7-8: Break period, assess retained benefits
This protocol provides both BDNF enhancement and anxiolytic benefits, covering multiple cognitive domains beyond memory alone.
Protocol 3: intensive learning support
Goal: Maximum memory enhancement for intensive learning periods
Peptides: Semax + P21
Approach:
Semax: 600mcg intranasal, twice daily throughout
P21: 1.5mg subcutaneous, every other day
Duration: 3-4 weeks covering intensive learning period
Extended break: 6-8 weeks after protocol completion
This aggressive approach suits specific periods like exam preparation, professional certification study, or intensive skill acquisition. Not appropriate for indefinite use.
Protocol 4: age-related memory support
Goal: Address age-related memory decline
Peptides: Dihexa + Semax + BPC-157
Approach:
Dihexa: 1mg daily for 3 weeks
Semax: 400mcg twice daily ongoing with cycling
BPC-157: 300mcg twice daily for systemic support
Repeat Dihexa courses quarterly with ongoing Semax between
This approach uses Dihexa's potent neurogenic effects periodically while maintaining enhancement and protection between courses. Appropriate for older individuals with noticeable memory decline and higher risk tolerance given Dihexa's limited human data.
Supporting memory enhancement with lifestyle factors
Peptides work best alongside lifestyle factors that support brain health. Neglecting fundamentals limits what peptides can achieve.
Sleep optimization
Memory consolidation requires quality sleep. No peptide fully compensates for chronic sleep deprivation. Prioritize 7-9 hours nightly with consistent timing. Address sleep disorders if present. Consider Pinealon if circadian rhythm disruption impairs sleep quality.
Exercise
Physical exercise powerfully enhances BDNF production, synergizing with peptide effects. Aerobic exercise in particular boosts hippocampal neurogenesis. Aim for regular cardiovascular activity alongside peptide protocols.
Cognitive engagement
Use enhanced plasticity productively. Peptides increase the brain's capacity for learning but cannot create memories of experiences you do not have. Engage in challenging cognitive activities, learn new skills, and provide the brain with material worth remembering.
Nutrition
Brain function requires adequate nutrition. Omega-3 fatty acids support neuronal membrane health. B vitamins enable neurotransmitter synthesis. Adequate protein provides amino acids for neurotransmitter and peptide production. Address any nutritional deficiencies that might limit cognitive potential.
Stress management
Chronic stress impairs memory through multiple mechanisms. While Selank addresses stress pharmacologically, behavioral stress management remains valuable. Meditation, nature exposure, and social connection all support cognitive health.
Sourcing and quality considerations
Peptide quality varies dramatically between suppliers. Memory-enhancing effects depend on receiving actual peptides at stated concentrations.
Verification importance
Third-party testing verifies peptide identity and purity. Request certificates of analysis from suppliers. Legitimate suppliers provide testing documentation readily. Absence of testing should prompt skepticism.
The are research peptides safe article covers safety verification in detail.
Supplier research
Research supplier reputation before purchasing. Community reviews indicate consistency and quality over time. The best place to buy BPC-157 article discusses supplier evaluation principles applicable to all peptides.
Storage requirements
Proper storage preserves peptide integrity. Most peptides require refrigeration after reconstitution. Lyophilized peptides generally remain stable at room temperature but last longer refrigerated. The how to store peptides guide covers storage requirements comprehensively.

Frequently asked questions
Which peptide works fastest for memory?
Semax typically shows noticeable effects within 30-60 minutes of intranasal administration and accumulating benefits within days of starting. The rapid onset makes it practical for acute memory demands while providing lasting benefits with continued use. Dihexa also works relatively quickly but structural changes from neurogenesis take weeks to fully manifest.
Can peptides reverse memory loss?
Some evidence suggests peptides can partially reverse memory loss, not merely prevent further decline. Dihexa shows the strongest evidence for reversal in animal models, recovering function lost to age or pathology. Semax and Cerebrolysin show recovery effects in stroke and injury contexts. However, severe degenerative conditions like advanced Alzheimer's are unlikely to reverse substantially with any current intervention.
Are memory peptides safe long term?
Semax and Selank have decades of clinical use in Russia without major safety concerns emerging. These represent the safest options for long-term use. Newer peptides like Dihexa and P21 lack long-term human data, making extended use more uncertain. Cycling protocols and conservative dosing help manage risk for peptides with limited long-term information.
Do memory peptides cause dependence?
Memory-enhancing peptides do not appear to cause physical dependence in the manner of stimulants or benzodiazepines. Stopping peptides does not produce withdrawal symptoms. Some cognitive benefits may persist after discontinuation due to structural changes like increased synaptic density. However, acute cognitive enhancement from mechanisms like enhanced neurotransmission will fade when peptides are stopped.
Can I combine memory peptides with other nootropics?
Memory peptides often combine well with other nootropics. Racetams, choline sources, and adaptogenic herbs generally do not conflict with peptide mechanisms. However, combining multiple powerful neuroplasticity enhancers requires caution. Start with peptides alone, then add other compounds individually to assess interactions.
How long until I notice memory improvement?
Semax users often notice effects within days, with full benefits developing over 2-4 weeks. Selank similarly shows rapid effects particularly on anxiety-related memory impairment. Neurogenesis-promoting peptides like Dihexa and P21 may require several weeks for structural changes to translate into noticeable functional improvement. Individual response varies based on baseline, dosing, and what aspects of memory are being assessed.
Will memory improvements persist after stopping peptides?
Some improvements likely persist, particularly those arising from structural changes like increased synaptic density or neurogenesis. Memories formed during enhanced plasticity remain even after peptides are discontinued. However, the ongoing enhancement of plasticity and neurochemistry will fade, potentially reducing the rate of new learning compared to active peptide use. Periodic peptide courses may maintain benefits better than single courses followed by indefinite discontinuation.
How SeekPeptides supports your memory optimization goals
Memory enhancement through peptides requires navigating complex decisions. Which peptides suit your specific goals? What dosing optimizes benefits while managing risks? How should protocols evolve as you progress? SeekPeptides provides personalized guidance for these decisions.
The platform offers customized peptide protocols tailored to individual cognitive enhancement goals. Rather than generic recommendations, you receive protocols designed for your specific situation, whether that involves general memory enhancement, recovery from cognitive insult, preparation for intensive learning demands, or addressing age-related decline.
Access to comprehensive research libraries helps you understand the science behind recommendations. The AI peptide advisor provides 24/7 support for questions that arise during your protocol. Progress tracking tools help assess what works and guide protocol refinement over time.
Memory matters too much to approach casually. Get personalized guidance for your cognitive enhancement journey with SeekPeptides.
Helpful resources and tools
These tools support memory peptide protocols:
Peptide calculator for general dosing guidance
Peptide reconstitution calculator for accurate preparation
Peptide stack calculator for multi-peptide protocol design
Peptide cost calculator for budget planning
BPC-157 dosage calculator for neuroprotective support
TB-500 dosage calculator for recovery protocol
Final thoughts
Memory defines capability more than any other cognitive function. What you can learn, what skills you can develop, what knowledge you can apply, all depend on memory working well. Peptides offer tools for enhancing memory that work through fundamentally different mechanisms than traditional approaches.
The evidence supports real effects. Semax and Selank have decades of clinical use. Newer compounds show striking results in research settings. The mechanisms are understood well enough to design rational protocols. Memory enhancement through peptides represents an area where the science has matured sufficiently for practical application.
Start conservatively with well-established peptides. Build understanding through direct experience. Expand protocols as familiarity and risk tolerance allow. Support peptides with lifestyle factors that enable optimal brain function.
Memory is not fixed. The brain retains plasticity throughout life. Peptides can enhance that plasticity, making memory formation more efficient and memory retention more durable. The opportunity exists to improve one of the most fundamental aspects of human cognition.
Your next step: explore the calculators, read the related guides, and consider how personalized peptide protocols through SeekPeptides might support your memory optimization goals.