Dec 30, 2025

Amylin receptor agonists represent one of the most promising but least understood classes of weight loss peptides. While everyone's heard of GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide and tirzepatide, the amylin pathway remains relatively obscure despite producing comparable weight loss through an entirely different mechanism.
These peptides don't just mimic one hormone - they activate a complex receptor system that controls meal size, gastric emptying, and glucose regulation in ways GLP-1s cannot replicate.
The confusion is understandable. Natural amylin is a pancreatic hormone most people have never heard of.
The first amylin agonist (pramlintide) was approved only for diabetes, requiring multiple daily injections and producing modest weight loss.
Now, next-generation amylin agonists like cagrilintide deliver 10-12% body weight loss with weekly dosing, and when combined with GLP-1s in protocols like CagriSema, produce 15-25% weight loss - approaching bariatric surgery results.
Here's what makes amylin receptor agonists unique: they dramatically slow gastric emptying (stronger than GLP-1s), suppress appetite through brainstem receptors (different pathways than GLP-1), reduce postprandial glucagon secretion, and work synergistically with GLP-1 agonists rather than redundantly.
This complementary mechanism explains why cagrilintide plus semaglutide produces 50% more weight loss than either alone.
This guide covers the complete amylin receptor agonist class including natural amylin's physiological role, how synthetic agonists improve upon nature, cagrilintide vs pramlintide (next-gen vs first-gen), mechanism comparison to GLP-1 and GIP agonists, clinical weight loss data, dosing protocols, side effect profiles, and combination therapy strategies for maximum results.
Understanding amylin agonists reveals why they're becoming the cornerstone of next-generation obesity treatment.
What are amylin receptor agonists
The science behind synthetic amylin peptides.
Natural amylin: the forgotten satiety hormone
What amylin is:
37-amino acid peptide hormone
Co-secreted with insulin from pancreatic beta cells
Released in response to meals (nutrient intake)
Discovered in 1987 (relatively recent)
Named "amylin" for amyloid-like structure
Amylin's natural functions:
Function | Mechanism | Weight Impact |
|---|---|---|
Slows gastric emptying | Delays stomach emptying by 30-50% | Extends fullness, reduces meal size |
Suppresses appetite | Acts on brainstem area postrema | Direct satiety signal to brain |
Reduces glucagon | Inhibits postprandial glucagon secretion | Better glucose control, less hunger |
Limits food intake | Combination of above effects | Natural portion control |
Regulates glucose | Complements insulin action | Metabolic regulation |
Where amylin acts:
Area postrema (brainstem) - primary satiety effect
Nucleus accumbens (brain) - reward/feeding behavior
Stomach smooth muscle - direct gastric slowing
Pancreas alpha cells - glucagon suppression
Amylin vs insulin (complementary hormones):
Both secreted together from beta cells
Insulin: Handles glucose uptake
Amylin: Controls meal size and gastric emptying
Work synergistically to regulate feeding and metabolism
Learn fundamentals at SeekPeptides - explore what are peptides, how peptides work, and peptides for weight loss.
Amylin receptor structure and signaling
The amylin receptor complex:
Not a single receptor
Heterodimer of two proteins:
Calcitonin receptor (CTR)
Receptor activity-modifying protein (RAMP)
Three subtypes: AMY1, AMY2, AMY3 (different RAMP combinations)
How amylin receptor activation works:
Amylin or agonist binds to receptor complex
Activates intracellular signaling cascades
Increases cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate)
Activates protein kinase A (PKA)
Triggers downstream effects (satiety, gastric slowing, etc.)
Receptor distribution:
High density in brainstem (area postrema)
Stomach and GI tract
Central nervous system
Pancreas
Why synthetic agonists needed:
Natural amylin extremely short half-life (5-10 minutes)
Cleared from blood rapidly
Would require constant infusion
Impractical for therapy
Synthetic versions engineered for longer duration
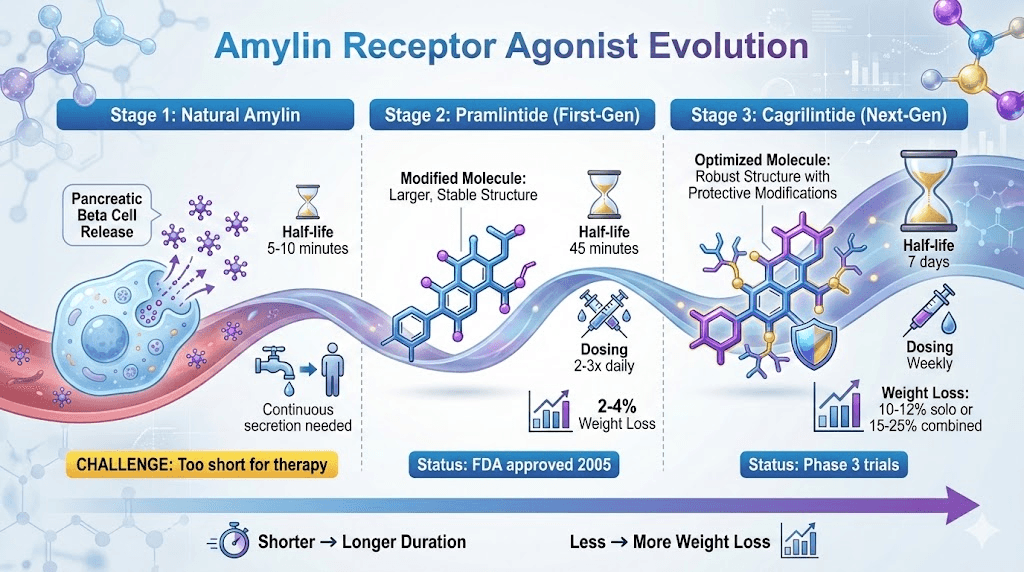
Amylin agonists vs natural amylin
Problems with natural amylin:
Half-life: 5-10 minutes (too short)
Administration: Would need continuous infusion
Forms toxic aggregates (amyloid fibrils)
Difficult to manufacture
Not practical as drug
How synthetic agonists improve:
Modified amino acid sequences
Much longer half-life (hours to days)
Prevent aggregation/amyloid formation
Stable in solution
Practical dosing (daily or weekly injections)
Stronger receptor binding
Better pharmacokinetics
Amylin agonist comparison table:
Drug | Type | Half-Life | Dosing Frequency | Weight Loss | Status | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Natural amylin | Endogenous hormone | 5-10 min | N/A (produced naturally) | N/A | Natural | Too short for therapy |
Pramlintide (Symlin) | First-gen agonist | ~45 minutes | 2-3x daily injection | 2-4% | FDA approved (diabetes) | Short-acting, inconvenient |
Cagrilintide | Next-gen agonist | ~7 days | Weekly injection | 10-12% alone, 15-25% with sema | Phase 3 trials | Long-acting, powerful |
Davalintide | Experimental | ~2-3 hours | Daily | Unknown | Discontinued | Development stopped |
Key innovation: Long-acting formulations
Pramlintide: Incremental improvement (minutes → hours)
Cagrilintide: Breakthrough improvement (minutes → days)
Weekly dosing changes the game for adherence and efficacy
See our cagrilintide weight loss, cagrilintide dosing, and cagrilintide and semaglutide guides.
How amylin receptor agonists work for weight loss
The multiple pathways of appetite suppression.
Gastric emptying delay (primary mechanism)
Most powerful effect of amylin:
Dramatically slows stomach emptying
Food stays in stomach 2-3x longer than normal
Creates mechanical fullness sensation
Strongest gastric slowing of any hormone/drug class
Mechanism of gastric slowing:
Amylin receptors on stomach smooth muscle
Reduces stomach contractions (peristalsis)
Slows pyloric sphincter opening (stomach → intestine)
Extends digestive process significantly
Gastric emptying comparison:
Intervention | Gastric Emptying Delay | Fullness Duration | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Normal (no drug) | Baseline | 2-3 hours post-meal | Standard appetite return |
GLP-1 agonists | Moderate (30-40% slower) | 3-4 hours | Good satiety extension |
Amylin agonists | Strong (50-70% slower) | 5-6+ hours | Very strong satiety |
Both combined | Very strong (70-80%+ slower) | 6-8+ hours | Maximum effect, risk gastroparesis |
Why this matters for weight loss:
Mechanical fullness = can't eat large portions
Extended satiety = skip snacks naturally
Naturally eat less without hunger
Cumulative calorie deficit over time
Potential downside:
Too much slowing = gastroparesis (pathological delay)
Nausea from prolonged fullness
Constipation (entire GI tract slows)
Why titration is critical
Central appetite suppression (brainstem)
Direct brain effects:
Amylin crosses blood-brain barrier
Acts on area postrema (brainstem)
Also affects nucleus accumbens
Different pathways than GLP-1
Area postrema role:
"Vomiting center" of brain
Also integrates satiety signals
Direct feeding behavior control
Why nausea is common side effect (overstimulation)
Amylin vs GLP-1 appetite pathways:
Pathway | Primary Receptor Location | Amylin Effect | GLP-1 Effect | Synergy Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Area postrema | Brainstem | Very strong | Moderate | Yes - different receptor types |
Nucleus accumbens | Brain reward center | Moderate | Strong | Yes - complementary |
Arcuate nucleus | Hypothalamus | Minimal | Very strong | Yes - different sites |
Vagal nerve | GI tract → brain | Moderate | Strong | Yes - both activate |
Why different pathways matter:
GLP-1 primarily hypothalamus (arcuate nucleus)
Amylin primarily brainstem (area postrema)
Combining = two different appetite suppression mechanisms
Synergistic not redundant
Explains CagriSema's superior results
Glucagon suppression and glucose regulation
Amylin's metabolic effects:
Suppresses postprandial glucagon secretion
Glucagon normally raises blood glucose
Inhibiting glucagon = better glucose control
Reduces hepatic glucose output
Why this helps weight loss:
Better glucose control = less insulin spikes
Lower insulin = less fat storage signaling
Reduced postprandial glucose = less hunger rebound
Metabolic optimization
Diabetes benefits (primary FDA indication for pramlintide):
Complements insulin therapy
Reduces mealtime glucose spikes
Lowers HbA1c (long-term glucose marker)
Originally developed for diabetes, not obesity
Weight loss as secondary benefit:
Diabetes patients on pramlintide lost modest weight
Led to investigation of amylin for obesity
Cagrilintide developed specifically for weight loss
Higher doses than needed for glucose alone
Meal frequency and portion size reduction
Real-world eating behavior changes:
Meal frequency:
Normal: 5-6 eating occasions daily (3 meals + snacks)
On amylin agonists: 3-4 eating occasions (meals only, skip snacks)
Natural reduction without conscious effort
Extended satiety eliminates snacking urge
Portion sizes:
Normal: 500-800 calorie meals common
On amylin agonists: 300-500 calorie meals typical
Physical fullness limits consumption
Can't finish normal portions
Example calorie reduction:
Baseline: 2,500 calories daily
On amylin agonist: 1,500-1,800 calories daily
Deficit: 700-1,000 calories daily
Weekly deficit: 4,900-7,000 calories (1.4-2 lbs loss/week)
No conscious restriction needed:
Not "willpower" or "dieting"
Physiological appetite suppression
Eating to comfortable fullness (just reduced capacity)
Sustainable long-term
See our best peptides for weight loss, best peptide stack for weight loss, and peptides for fat loss.
Comparing amylin agonists to other weight loss peptides
How amylin fits in the peptide hierarchy.
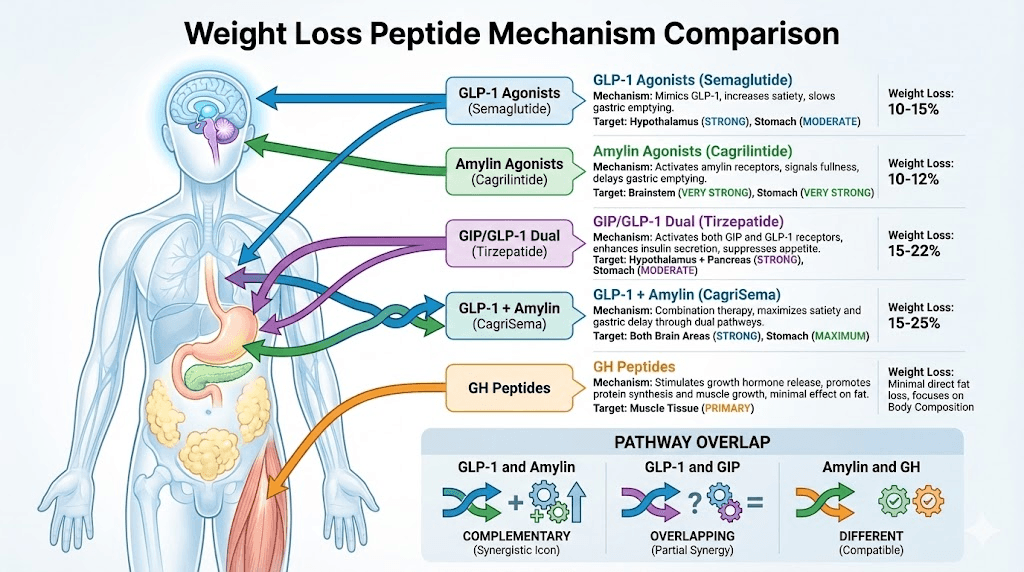
Amylin vs GLP-1 receptor agonists
GLP-1 agonists (semaglutide, liraglutide):
Mechanism: GLP-1 receptor activation
Primary site: Hypothalamus (arcuate nucleus)
Gastric emptying: Moderate delay
Weight loss: 10-15% monotherapy
FDA approved: Yes (Wegovy, Saxenda)
Amylin agonists (cagrilintide):
Mechanism: Amylin receptor activation
Primary site: Brainstem (area postrema)
Gastric emptying: Strong delay (more than GLP-1)
Weight loss: 10-12% monotherapy
FDA approved: Not yet (Phase 3)
Head-to-head comparison:
Factor | GLP-1 Agonists | Amylin Agonists | Winner |
|---|---|---|---|
Weight loss (solo) | 10-15% | 10-12% | Roughly equal |
Gastric emptying | Moderate delay | Strong delay | Amylin stronger |
Central appetite | Strong (hypothalamus) | Strong (brainstem) | Equal, different pathways |
Nausea severity | Moderate (30-40%) | Moderate-high (40-50%) | GLP-1 slightly better tolerated |
FDA approval | Yes (multiple drugs) | No (investigational) | GLP-1 wins availability |
Combination potential | Excellent with amylin | Excellent with GLP-1 | Both benefit from combo |
Dosing | Weekly | Weekly (cagrilintide) | Equal convenience |
Why combine GLP-1 + Amylin:
Different receptor pathways
Different brain sites
Complementary not redundant
Synergistic weight loss (15-25% combined)
CagriSema proves this works
See our semaglutide vs tirzepatide, semaglutide dosage calculator, and tirzepatide dosing guide.
Amylin vs GIP/GLP-1 dual agonists (tirzepatide)
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro/Zepbound):
Dual GIP + GLP-1 receptor agonist
Single molecule, two pathways
15-22% weight loss monotherapy
FDA approved
Superior to semaglutide alone
Tirzepatide vs cagrilintide monotherapy:
Metric | Tirzepatide | Cagrilintide | Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|
Weight loss | 15-22% | 10-12% | Tirzepatide superior as monotherapy |
Mechanisms | GIP + GLP-1 | Amylin | Both multi-pathway approaches |
Side effects | Moderate GI | Moderate-high GI | Tirzepatide better tolerated |
Approval status | FDA approved | Phase 3 | Tirzepatide available now |
Clinical data | Extensive | Growing | Tirzepatide more proven |
Cost (research) | $300-500/month | $800-1,600/month | Tirzepatide more affordable |
Theoretical tirzepatide + cagrilintide combination:
Would add amylin pathway to GIP/GLP-1
Three pathways total
Potential 20-30% weight loss
But no clinical data (unstudied)
Very high GI side effect risk
CagriSema (sema + cagri) safer, proven choice
See our cagrilintide dosage with tirzepatide analysis.
Amylin vs other weight loss peptides
AOD 9604 (HGH fragment):
Mechanism: Fat metabolism stimulation
Weight loss: 5-8% (limited data)
Completely different pathway than amylin
Could theoretically combine
Retatrutide (triple agonist GLP-1/GIP/glucagon):
Mechanism: Three incretin pathways
Weight loss: 20-25% in trials
More powerful than tirzepatide
Also investigational
Different mechanism than amylin
Growth hormone peptides (CJC-1295, Ipamorelin):
Mechanism: GH release, body composition
Weight loss: Minimal direct fat loss
Primarily muscle preservation/growth
Often combined with amylin or GLP-1 for body recomposition
Amylin's unique position:
Only peptide class targeting amylin pathway
Strongest gastric emptying delay
Proven synergy with GLP-1s
Different mechanism than all other weight loss peptides
See our peptide stacks guide, peptide stack calculator, and can you cycle different peptides.
Cagrilintide: the next-generation amylin agonist
Modern long-acting amylin for weight loss.
Cagrilintide development and structure
What cagrilintide is:
Synthetic long-acting amylin analog
Modified 37-amino acid sequence
Developed by Novo Nordisk
Designed specifically for obesity treatment
Based on natural amylin but optimized
Key structural modifications:
Amino acid substitutions for stability
Prevented amyloid aggregation (major improvement)
Extended half-life to ~7 days (vs minutes for natural amylin)
Maintained receptor binding and activity
Better pharmacokinetic profile
Development timeline:
Early 2010s: Initial development
2019-2020: Phase 2 trials (OASIS)
2021-2023: Phase 3 trials (REDEFINE as CagriSema)
2024-2025: FDA submission expected
Likely approval 2025-2026
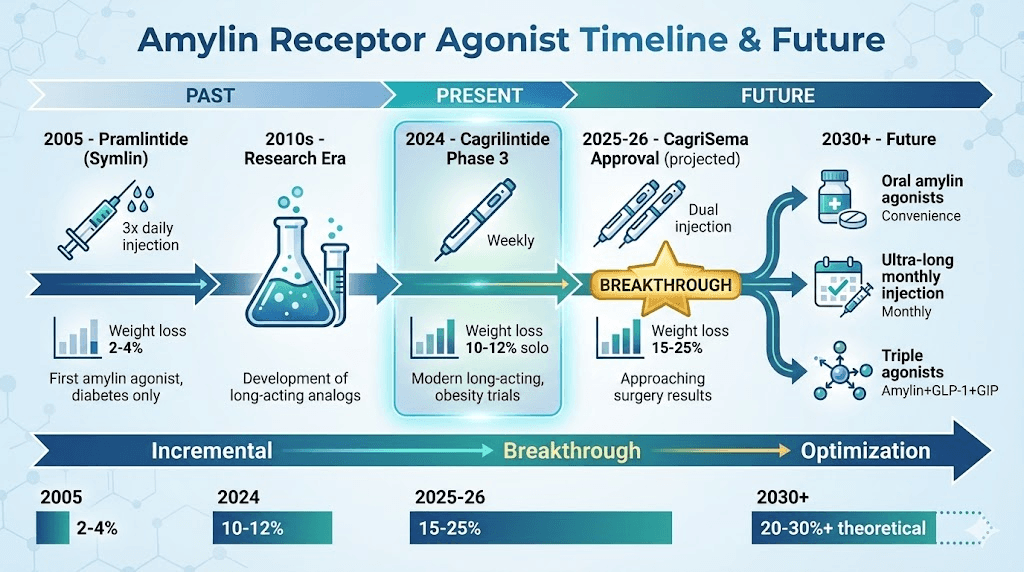
Why cagrilintide is breakthrough:
First truly long-acting amylin agonist
Weekly dosing (vs pramlintide 2-3x daily)
Designed for weight loss (not diabetes adaptation)
Proven synergy with semaglutide (CagriSema)
Approaching availability
Cagrilintide weight loss results
Monotherapy clinical data (OASIS trials):
Duration: 26-68 weeks
Dose: 2.4mg weekly (standard)
Average weight loss: 10-12%
Some participants: 15%+ loss
Well-tolerated at therapeutic dose
Weight loss by dose:
0.6mg weekly: ~6% weight loss
1.2mg weekly: ~8% weight loss
2.4mg weekly: ~10% weight loss
4.5mg weekly: ~12% weight loss (higher side effects)
CagriSema combination (cagrilintide + semaglutide):
Both at 2.4mg weekly
Average weight loss: 15.6% (REDEFINE-1)
Excellent responders: 20-25%
50% more than semaglutide alone
Game-changing results
Real-world expectations:
User Type | Cagrilintide Alone | CagriSema Combo | Example (240 lb person) |
|---|---|---|---|
Poor responder | 8-10% | 12-15% | 19-24 lbs / 29-36 lbs |
Average responder | 10-12% | 15-18% | 24-29 lbs / 36-43 lbs |
Excellent responder | 12-15% | 18-25% | 29-36 lbs / 43-60 lbs |
See our comprehensive cagrilintide weight loss guide.
Cagrilintide dosing protocols
Standard titration (monotherapy):
Weeks 1-4: 0.6mg weekly
Weeks 5-8: 1.2mg weekly
Weeks 9-12: 1.8mg weekly
Week 13+: 2.4mg weekly (maintenance)
Why slow titration critical:
Reduces GI side effects dramatically
Allows body adaptation to gastric slowing
Better long-term adherence
Proven in clinical trials
CagriSema dosing:
Semaglutide: 0.25mg → 2.4mg over 16 weeks
Cagrilintide: 0.6mg → 2.4mg over 12 weeks
Both at maximum by week 17
Continue indefinitely for maintenance
Administration:
Subcutaneous injection
Weekly dosing (same day each week)
Abdomen, thigh, or upper arm
Rotate sites
See our cagrilintide dosing guide for complete protocols.
Cagrilintide side effects
Most common (GI-focused):
Side Effect | Frequency | Severity | Management |
|---|---|---|---|
Nausea | 40-50% | Moderate | Ginger, anti-nausea meds, slow titration |
Constipation | 30-40% | Mild-moderate | Hydration, fiber, magnesium |
Decreased appetite | 80-90% | N/A (intended) | Ensure adequate protein |
Vomiting | 15-20% | Moderate | Reduce dose, smaller meals |
Abdominal discomfort | 25-35% | Mild | Usually resolves with adaptation |
Fatigue | 20-30% | Mild | Often temporary, improves by week 8-12 |
Why GI effects are prominent:
Very strong gastric emptying delay
Stomach stays full longer
Slowed GI transit overall
Adaptation occurs over weeks
Management strategies:
Small frequent meals (5-6 daily)
Avoid fatty/greasy foods
Ginger supplementation
Prescription anti-nausea (Zofran)
Fiber and hydration for constipation
Protein shakes if can't eat solid food
Serious but rare:
Pancreatitis (<1%)
Severe gastroparesis (if not managed)
Gallstones (rapid weight loss)
See our peptide safety and risks guide.
Pramlintide: first-generation amylin agonist
The original amylin drug with limitations.
Pramlintide (Symlin) background
What pramlintide is:
First synthetic amylin analog
FDA approved 2005
Indication: Diabetes (type 1 and type 2)
Brand name: Symlin
Still available by prescription
Structure:
Modified human amylin sequence
Prevents amyloid formation (improvement over natural)
But short half-life (~45 minutes)
Requires frequent dosing
FDA approval details:
Approved as adjunct to insulin therapy
For diabetes patients only
Primary endpoint: Glucose control (HbA1c reduction)
Weight loss noted as secondary benefit
Pramlintide limitations
Why pramlintide didn't revolutionize weight loss:
Short half-life problem:
Half-life only 45 minutes
Requires 2-3 injections daily (before meals)
Inconvenient dosing schedule
Poor adherence
Modest weight loss:
2-4% average body weight loss
Much less than modern options (GLP-1s, cagrilintide)
Not sufficient for obesity treatment
Limited enthusiasm
Diabetes-only indication:
Not approved for weight loss
Only prescribed with insulin
Non-diabetics can't get prescription
Limited accessibility
Dosing complexity:
Must coordinate with meals
Multiple daily injections
Dose adjustments needed
More complex than weekly peptides
Pramlintide vs cagrilintide comparison:
Factor | Pramlintide | Cagrilintide | Improvement Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
Half-life | 45 minutes | 7 days | 224x longer |
Dosing frequency | 2-3x daily | Weekly | 14-21x less frequent |
Weight loss | 2-4% | 10-12% | 3x more effective |
FDA status | Approved (diabetes) | Phase 3 (obesity) | Broader indication |
Convenience | Poor | Excellent | Massive improvement |
Adherence | Low | High | Much better |
Pramlintide's role today:
Still used for diabetes with insulin
Not popular for weight loss
Largely superseded by GLP-1s and coming cagrilintide
Proof-of-concept for amylin pathway
Who still uses pramlintide
Current pramlintide users:
Type 1 diabetics on insulin (primary use)
Type 2 diabetics with difficult glucose control
Some seeking modest weight loss off-label
Relatively small user base
Advantages over nothing:
Better than no amylin agonist
Helps glucose control in diabetes
Some weight loss benefit
FDA approved (accessible)
Why most skip pramlintide:
Better options available (GLP-1s now)
Inconvenient dosing
Modest results
Can't get if not diabetic
Pramlintide cost:
Pharmaceutical: $300-400/month with insurance
Without insurance: $800-1,200/month
Not cost-effective for weight loss
Better to use semaglutide or wait for cagrilintide
Combination therapy: amylin + GLP-1 synergy
Why CagriSema represents the future.
CagriSema (cagrilintide + semaglutide) rationale
Why combine two peptides:
Different receptor pathways (amylin vs GLP-1)
Different brain targets (brainstem vs hypothalamus)
Different primary mechanisms (gastric slowing vs central appetite)
Complementary not redundant
Synergistic weight loss
Physiological rationale:
Amylin and GLP-1 both naturally regulate feeding
Both released in response to meals
Work together in healthy physiology
Replacing both optimizes appetite regulation
Clinical proof of synergy:
Semaglutide alone: 10-15% weight loss
Cagrilintide alone: 10-12% weight loss
Together (CagriSema): 15-25% weight loss
More than additive = true synergy
REDEFINE trial results table:
Treatment Arm | Average Weight Loss | % Losing >10% | % Losing >20% | Side Effect Withdrawals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Placebo | 2.4% | 18% | 2% | 3% |
Semaglutide 2.4mg | 10.2% | 69% | 18% | 9% |
CagriSema (both 2.4mg) | 15.6% | 85% | 43% | 15% |
Improvement over sema | +5.4% (53% more) | +16% | +25% | +6% |
Key findings:
CagriSema 50% more effective than semaglutide
43% achieved >20% weight loss (approaching surgery)
Side effects higher but manageable
Most participants tolerated full doses
See our cagrilintide and semaglutide combination guide and cagrisema dosing protocols.
CagriSema dosing and protocols
Simultaneous start (standard):
Both peptides from week 1
Semaglutide: Standard titration to 2.4mg (16 weeks)
Cagrilintide: Standard titration to 2.4mg (12 weeks)
Both at maximum by week 17
Sequential approach:
Start semaglutide, titrate to 2.4mg
Stabilize 4-8 weeks
Add cagrilintide starting 0.6mg
Titrate cagrilintide to 2.4mg
Both at maximum by week 30-34
Expected timeline (simultaneous):
Month 3: 10-16 lbs lost
Month 6: 22-32 lbs lost
Month 12: 40-55 lbs lost
Month 18: 50-65 lbs lost (15-25% total)
Cost considerations:
Research peptides: $500-900/month combined
Annual cost: $6,000-10,800
Pharmaceutical CagriSema (when approved): $1,200-1,500/month likely
Compare to bariatric surgery: $20,000-25,000 upfront
Use SeekPeptides to plan your CagriSema protocol. Our peptide stack calculator coordinates dual-peptide titration.
Managing combined side effects
Expect amplified GI effects:
Both peptides slow gastric emptying
Synergistic nausea (not just additive)
Constipation very common
Weeks 9-16 most challenging
Nausea management protocol:
Prevention from day 1 (ginger, small meals)
Prescription anti-nausea (Zofran) essential
Liquid nutrition if needed
Slower titration if poorly tolerated
Constipation prevention:
80-100 oz water daily
Fiber 25-30g daily
Magnesium citrate 300-500mg nightly
MiraLAX as needed
Nutrition maintenance:
Protein shakes 2-3 daily (30-40g each)
Target 60-80g protein minimum
Multivitamin daily
B12 supplementation
When to reduce doses:
Severe persistent nausea despite management
Unable to maintain adequate nutrition
Vomiting frequently
Quality of life severely impacted
See our common peptide mistakes beginners make to avoid errors.
Future of amylin receptor agonists
What's coming next in this peptide class.
Pharmaceutical CagriSema approval timeline
Current status (late 2024):
Phase 3 trials completed
REDEFINE-1 results published
Additional Phase 3 trials ongoing
FDA submission expected 2024-2025
Anticipated approval:
FDA decision likely 2025-2026
Similar timeline to semaglutide/tirzepatide
Strong data supporting approval
Obesity indication
What approval means:
Prescription access (with obesity diagnosis)
Insurance coverage potential
Pre-filled combination pens (convenience)
Medical supervision included
Quality guaranteed
Projected pricing:
Likely $1,200-1,500/month without insurance
Similar to Wegovy/Zepbound
Insurance may cover (BMI requirements)
Patient assistance programs likely
Oral amylin agonists in development
Current limitation:
All amylin agonists currently injectable
Peptides break down in stomach (can't absorb orally)
Injection barrier for some patients
Oral formulation research:
Several companies developing oral amylin agonists
Using absorption enhancers
Enteric coating technologies
Still early stage (preclinical/Phase 1)
Challenges:
Peptide degradation in GI tract
Low bioavailability (<5% typical)
Large pill size needed
May never be as effective as injectable
Realistic timeline:
Oral amylin agonists 5-10+ years away
Injectable options remain primary
GLP-1 oral semaglutide showed it's possible
But amylin may be more difficult
Next-generation amylin analogs
Beyond cagrilintide:
Ultra-long-acting formulations (monthly?)
More potent receptor binding
Reduced side effects
Better stability
Dual agonists including amylin:
Amylin + GLP-1 single molecule (instead of two injections)
Amylin + GLP-1 + GIP triple agonist
Other combinations
Challenges:
Creating single molecule with dual activity difficult
Pharmacokinetics complex
CagriSema (two separate injections) works well
May not need single molecule version
Amylin analogs in research:
Several pharmaceutical companies exploring
Academic research ongoing
Market opportunity clear (obesity epidemic)
Expect continued innovation
Track developments at SeekPeptides - we monitor peptide research and FDA approvals.
How you can use SeekPeptides for amylin agonist protocols
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive guidance for amylin receptor agonist therapy. Get personalized protocols for cagrilintide monotherapy or CagriSema combination, titration schedules based on GI tolerance, side effect management strategies, and maintenance dosing after weight loss.
Our platform helps you understand amylin mechanisms, compare to GLP-1 and other peptide classes, decide between monotherapy vs combination approaches, track weight loss and side effects, and optimize dosing for maximum results with manageable side effects.
Access clinical trial data, real-world results, and evidence-based protocols for amylin agonist use. Learn why CagriSema represents the future of medical weight loss and how to implement these protocols safely.
Use our calculators - peptide calculator, peptide cost calculator, peptide stack calculator, semaglutide dosage calculator, peptide reconstitution calculator - for precise amylin agonist protocols.
Learn administration through our guides - peptide injections guide, how to reconstitute peptides, peptide storage guide, getting started with peptides.
Access our best peptide vendors for quality amylin agonist sourcing and peptide safety and risks for comprehensive safety information.
Final thoughts
Amylin receptor agonists represent a distinct peptide class targeting the amylin pathway - a natural satiety hormone that powerfully controls gastric emptying, brainstem appetite signals, and glucose regulation. Unlike GLP-1 agonists that primarily act on the hypothalamus, amylin agonists exert their strongest effects through brainstem area postrema activation and dramatic gastric slowing exceeding that of any other peptide class.
First-generation pramlintide demonstrated proof-of-concept but suffered from short half-life requiring multiple daily injections and producing only 2-4% weight loss.
Cagrilintide represents the breakthrough next-generation amylin agonist with weekly dosing, 10-12% monotherapy weight loss, and proven synergy with GLP-1 agonists when combined.
The CagriSema combination (cagrilintide + semaglutide) delivers 15-25% body weight loss through complementary amylin and GLP-1 pathways - approaching bariatric surgery results without the permanence or surgical risks. Phase 3 REDEFINE trials confirmed 50% greater weight loss compared to semaglutide alone, with 43% of participants achieving over 20% body weight loss.
FDA approval expected 2025-2026 will make pharmaceutical-grade cagrilintide and CagriSema widely accessible, though research peptides currently provide the same compounds for those willing to self-administer. The strong gastric emptying delay produces significant nausea and constipation requiring aggressive management, but most users adapt by weeks 12-16 with proper titration.
Your path to understanding amylin agonists reveals why this peptide class represents the future of obesity pharmacotherapy - not replacing GLP-1s but rather synergizing with them to target multiple appetite and metabolic pathways simultaneously.
The amylin mechanism fills a critical gap in weight loss therapeutics that GLP-1s alone cannot address, explaining the exceptional results seen with dual-pathway combinations.
Helpful resources for amylin receptor agonists
Cagrilintide weight loss - Complete cagrilintide guide
Cagrilintide dosing - Dosing protocols
Cagrilintide and semaglutide - Combination overview
CagriSema dosing - CagriSema protocols
Cagrilintide dosage with tirzepatide - Alternative combo
Peptide calculator - Dose calculator
See you soon, join SeekPeptides