Jan 20, 2026

The nerve pain keeps you awake at night. The tingling in your hands and feet never stops. You've been through the standard treatments, the medications that dull your mind without dulling the pain, and you're still searching for something that actually works.
The frustration is real. So is the exhaustion from fighting your own body.
What if the problem isn't that effective treatments don't exist? What if the real issue is that most approaches target symptoms while ignoring what's actually happening at the cellular level?
ARA-290, also known as cibinetide, represents a fundamentally different approach to neuropathic pain and nerve damage. Rather than masking symptoms or blocking pain signals, this engineered peptide activates your body's own repair mechanisms. It tells damaged nerves to regenerate. It calms inflammation at its source. And unlike many alternatives, it comes with a safety profile that has impressed researchers across multiple clinical trials.
This guide covers everything researchers need to know about ARA-290: how it works at the molecular level, what the clinical studies actually show, proper dosing protocols, storage requirements, and how it compares to other pain-relief peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500. SeekPeptides has compiled the most comprehensive resource available for understanding this promising compound.
What is ARA-290?
ARA-290 is a synthetic 11-amino acid peptide engineered from erythropoietin, the hormone your kidneys produce to stimulate red blood cell production. But here's what makes it different. Scientists identified that EPO does more than just make red blood cells. It protects tissues. It reduces inflammation. It helps damaged cells survive and recover.
The problem with using EPO directly? It creates too many red blood cells. This thickens blood, increases clotting risk, and raises blood pressure. Athletes have died from EPO abuse because of these effects.
ARA-290 solves this problem elegantly.
Researchers isolated the specific portion of the EPO molecule responsible for tissue protection, a region called helix B. They created a small peptide that mimics only this protective function. The result is a compound that provides EPO's healing benefits without affecting red blood cell production at all. Zero erythropoietic activity. Full tissue-protective capacity.
The molecular weight sits at 1257 daltons, making it a relatively small peptide that can reach target tissues effectively. Its sequence, pGlu-Glu-Leu-Glu-Arg-Ala-Leu-Asn-Ser-Ser, was carefully designed to interact with what scientists call the innate repair receptor. More on that mechanism shortly.
Under the research name cibinetide, ARA-290 has completed multiple Phase 2 clinical trials and holds FDA Orphan Drug status for sarcoidosis-associated neuropathy. This designation indicates the FDA recognizes its potential for treating conditions that currently lack adequate treatments. While not yet approved for prescription use, the compound has an extensive research record that researchers continue to build upon.
How ARA-290 works: the innate repair receptor
Understanding ARA-290 requires understanding the innate repair receptor. This receptor system exists throughout your body, lying dormant in healthy tissues but rapidly activating when damage occurs. It's part of your built-in emergency response system.
The innate repair receptor, sometimes called the tissue protective receptor, consists of two protein subunits: the erythropoietin receptor and CD131, also known as the beta-common receptor. These proteins normally exist separately. When tissue injury occurs, when cells experience stress from inflammation, low oxygen, or physical damage, something remarkable happens. The two receptor components move to the cell surface and combine into a functional unit.
This activation is precisely targeted. Healthy tissues don't express the complete receptor. Only damaged or stressed tissues do. It's like having a repair crew that only shows up where repairs are actually needed.
When ARA-290 binds to this assembled receptor, it triggers a cascade of protective effects. The JAK2 signaling pathway activates, leading to suppression of NF-κB, one of the master switches controlling inflammation throughout the body. With NF-κB dialed down, pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha decrease. The inflammatory storm calms.
But inflammation reduction is only part of the story.
ARA-290 also activates survival pathways within cells. It suppresses apoptotic signals, the molecular commands that tell damaged cells to die. While controlled cell death is normally healthy, excessive apoptosis during tissue injury can create more damage than the original insult caused. By keeping borderline cells alive and functioning, ARA-290 preserves tissue that might otherwise be lost.
For nerve cells specifically, ARA-290 appears to do something even more impressive: it stimulates axon regrowth. Research in both animal models and human clinical trials shows that ARA-290 treatment leads to measurable increases in nerve fiber density. Damaged nerves don't just survive, they regenerate.
This mechanism differs fundamentally from traditional pain management approaches. Most analgesics block pain signals or reduce nerve sensitivity. ARA-290 addresses the underlying damage. The distinction matters enormously for conditions where nerve degeneration continues over time.
Interaction with TRPV1 channels
Recent research has uncovered an additional mechanism that helps explain ARA-290's pain-relieving effects. The peptide appears to block TRPV1 channel activity in small nerve fibers. TRPV1, sometimes called the capsaicin receptor because it responds to the compound that makes chili peppers hot, plays a central role in pain sensation.
When TRPV1 channels become overactive, as they often do in neuropathic conditions, they create hypersensitivity. Normal touch becomes painful. Temperature changes feel like burning. By dampening this hyperactivated state, ARA-290 reduces the exaggerated pain responses that make neuropathy so debilitating.
This dual action, reducing inflammation while simultaneously calming overactive pain pathways, may explain why ARA-290 shows effectiveness where other approaches fail. It's working on multiple levels simultaneously.
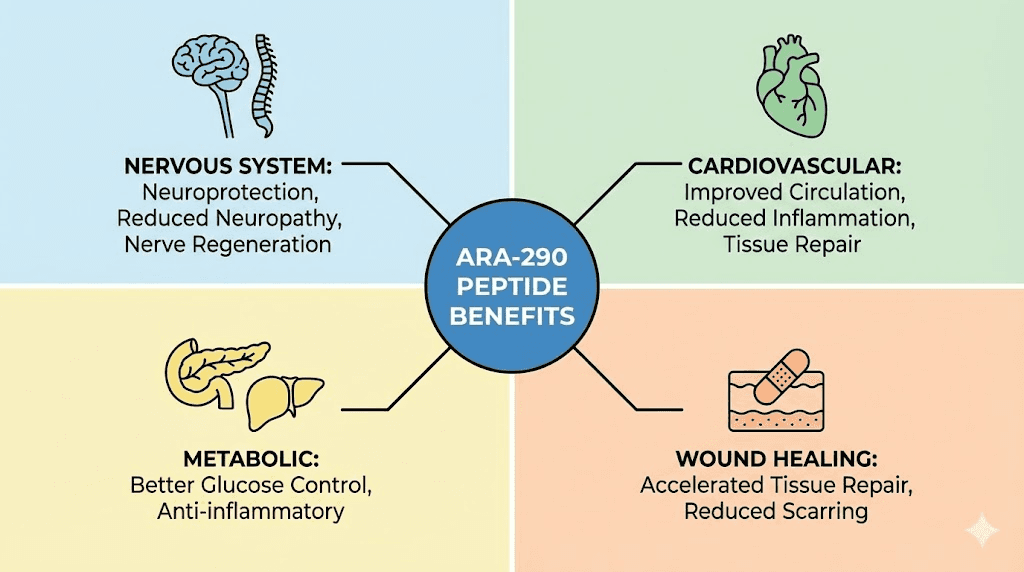
ARA-290 benefits: what the research shows
The benefits of ARA-290 extend across several therapeutic areas. Clinical trials and preclinical studies have examined its effects on neuropathy, metabolic health, cardiovascular function, and wound healing.
The consistency of positive results across different conditions suggests the underlying mechanism, activation of innate repair pathways, has broad applications.
Neuropathy and nerve regeneration
The strongest evidence for ARA-290 comes from studies on small fiber neuropathy. This condition involves damage to the thin nerve fibers responsible for pain sensation, temperature detection, and autonomic functions like sweating and blood pressure regulation. Conventional treatments offer limited relief because they don't address the nerve damage itself.
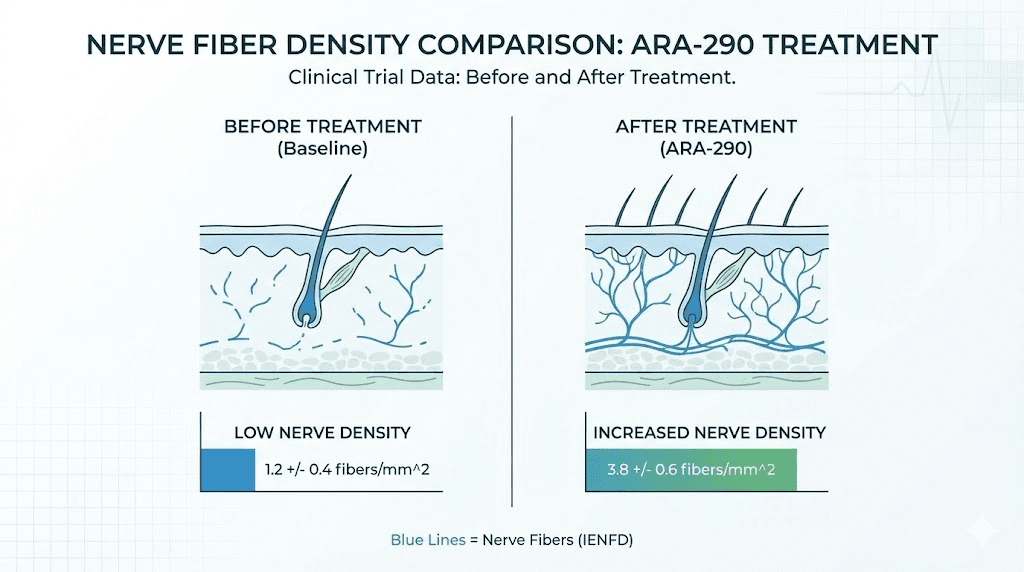
In a randomized, double-blind trial involving 22 patients with sarcoidosis-associated small fiber neuropathy, ARA-290 produced significant improvements. Patients receiving the peptide showed meaningful reductions in their Small Fiber Neuropathy Screening List scores compared to placebo. More impressively, ARA-290 treatment initiated regrowth of small nerve fibers in the cornea, providing objective evidence of nerve regeneration that standard treatments simply cannot achieve.
A subsequent Phase 2b trial built on these findings. Treatment with 4mg daily cibinetide for 28 days produced a 23% increase in corneal nerve fiber abundance compared to placebo. As nerve fibers regenerated, patients reported improved functional activity and reduced symptoms. The correlation between objective nerve measurements and subjective symptom improvement strengthened confidence in the mechanism.
For patients with type 2 diabetes and painful neuropathy, results were similarly encouraging. A 28-day course of ARA-290 improved neuropathic symptoms while also producing metabolic benefits that persisted even after treatment ended. Researchers noted that the beneficial effects appeared to continue beyond the active dosing period, suggesting that ARA-290 initiates repair processes that continue independently.
The response rate in clinical trials hovers around 50% for those with moderate to severe baseline symptoms. While not everyone responds, the magnitude of improvement in responders exceeds what most available treatments can offer. And unlike many analgesics, the improvements appear to reflect actual healing rather than just symptom suppression.
Metabolic improvements
The metabolic benefits observed in diabetes trials deserve attention independent of the neuropathy improvements. Subjects receiving ARA-290 showed reductions in hemoglobin A1c, the marker that reflects average blood sugar over the preceding months. This improvement persisted through a 28-day follow-up period after treatment ended.
Lipid profiles also improved. The cholesterol-to-HDL ratio decreased, partly due to increases in protective HDL cholesterol.
These changes suggest ARA-290 may influence metabolic function through its anti-inflammatory effects, since chronic inflammation contributes significantly to insulin resistance and dyslipidemia.
For researchers interested in metabolic peptides, these findings position ARA-290 as a compound with potential beyond its primary neuropathy indications. The combination of nerve protection and metabolic improvement could prove particularly valuable for the millions dealing with diabetic complications.
Cardiovascular and anti-aging effects
Studies in aged mice have revealed ARA-290's potential for cardiovascular health and longevity. Chronic treatment mitigated age-related changes in cardiac tissue. The ratio of cardiac non-myocytes to myocytes, which typically shifts unfavorably with aging, was preserved. Infiltrating immune cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines decreased. Markers of NF-κB activation, elevated in aging hearts, were reduced.
Perhaps most significantly, ARA-290 treatment blunted age-associated elevations in blood pressure and preserved left ventricular ejection fraction, a measure of how effectively the heart pumps blood. These aren't marginal effects. They represent meaningful preservation of cardiac function that typically declines with age.
The researchers also observed enhanced autophagy in cardiac muscle cells. Autophagy is the cellular recycling process that clears damaged proteins and organelles. Age-related decline in autophagy contributes to cellular dysfunction across multiple organ systems. By supporting this cleanup process, ARA-290 may help maintain cellular health broadly.
Lipofuscin accumulation, often called "aging pigment" because it builds up in cells over time as a marker of oxidative damage, was reduced in ARA-290-treated animals. This finding provides additional evidence that the peptide supports cellular maintenance mechanisms.
For those exploring peptides for anti-aging, ARA-290 represents an interesting option with mechanisms distinct from compounds like Epitalon or GHK-Cu. Its cardiovascular focus may complement other anti-aging strategies.
Wound healing and tissue repair
ARA-290's tissue-protective properties extend to wound healing applications. Research focused on diabetic wound healing, notoriously difficult because diabetes impairs normal repair mechanisms, found that cibinetide treatment improved outcomes in diabetic mice. The peptide enhanced tissue regeneration while reducing the excessive inflammation that slows diabetic wound closure.
The mechanism connects back to the innate repair receptor. Wound sites experience exactly the kind of cellular stress and hypoxia that triggers receptor expression. By activating this system, ARA-290 essentially amplifies the body's natural wound healing response.
This application area overlaps with the benefits offered by other healing peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500, though through different mechanisms.
Later sections will compare these options in detail.
Other research applications
Preclinical studies have evaluated ARA-290 in an impressive range of models: diet-induced insulin resistance, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic autonomic neuropathy, myocardial infarction, chronic heart failure, burns, traumatic brain injury, and shock-induced multi-organ failure. The consistency of tissue-protective effects across such varied conditions reflects the fundamental nature of the innate repair receptor system.
Researchers examining autoimmune neuritis, an inflammatory condition affecting peripheral nerves, found that erythropoietin-derived peptides including ARA-290 reduced inflammation and protected nerve tissue. Studies on colitis, an inflammatory bowel condition, showed that cibinetide dampened immune cell activation and improved outcomes.
These diverse applications don't mean ARA-290 is a cure-all. They indicate that the innate repair receptor system plays a role across multiple types of tissue injury and inflammation. Compounds that activate this system appropriately may benefit a range of conditions characterized by inflammation and tissue damage.
ARA-290 dosage protocols
Dosing information for ARA-290 comes primarily from clinical trials and research protocols. While no standardized prescription guidelines exist since the compound remains investigational, the research record provides useful parameters.
Clinical trial dosing
Phase 2 trials have evaluated several dose levels. The most commonly studied doses range from 1mg to 8mg administered daily for 28 days. The 4mg daily dose emerged as a sweet spot in multiple studies, producing significant benefits with excellent tolerability.
Dose-ranging studies evaluated 1mg, 4mg, and 8mg daily for 28 days in patients with sarcoidosis-related neuropathy. The 4mg group showed the most consistent improvements in both objective measures (corneal nerve fiber density) and subjective symptoms. Some ophthalmic trials extended treatment to 12 weeks at 4mg daily without safety issues.
Research protocols
Outside formal clinical trials, research protocols typically follow similar parameters. A common approach involves 2-4mg administered subcutaneously once daily. Treatment duration varies based on the condition being studied, ranging from 4 weeks to 12 weeks or longer for chronic conditions.
Some protocols use a starting dose of 2mg daily for the first week, allowing assessment of tolerance before increasing to the target dose of 4mg. This graduated approach mirrors standard practices for many peptide protocols.
For reference, here's a typical ARA-290 protocol structure:
Week 1: 2mg once daily (morning administration)
Weeks 2-6: 4mg once daily (morning administration)
Assessment: Evaluate response at week 4, continue if beneficial
Duration: 6-12 weeks depending on indication
The timing of administration may matter less than consistency. Clinical trials typically used morning dosing, though evidence for time-of-day effects remains limited.
Reconstitution calculations
ARA-290 typically comes as a lyophilized powder in 16mg vials. For a practical injection volume, adding 2.0mL of bacteriostatic water creates an 8mg/mL solution. At this concentration:
2mg dose = 0.25mL (25 units on an insulin syringe)
4mg dose = 0.5mL (50 units on an insulin syringe)
Using the peptide reconstitution calculator can help verify calculations for different vial sizes and concentrations. Accurate dosing requires both proper reconstitution and careful measurement, skills covered in guides on how to reconstitute peptides.
The peptide calculator at SeekPeptides can assist with determining exact volumes for your specific vial size and desired dose.
Administration route
Subcutaneous injection is the standard route for ARA-290 research. Early clinical trials used intravenous dosing, but subcutaneous self-administration proved equally effective and more practical for extended protocols.
Standard subcutaneous injection technique applies: pinch a fold of skin, insert the needle at 45-90 degrees, inject slowly, withdraw and apply gentle pressure. Rotating injection sites prevents local tissue changes. The abdomen, thigh, and upper arm all provide suitable locations.
Guides on peptide injections cover proper technique in detail. For those new to injectable peptides, reviewing getting started with peptides provides essential background.
Protocol length considerations
Clinical trial durations of 28 days produced measurable benefits, but the observation that improvements persisted beyond the treatment period suggests ARA-290 initiates repair processes that continue independently. This raises questions about optimal protocol length.
Longer protocols may allow for more complete nerve regeneration in chronic conditions. The 12-week ophthalmic trials showed continued improvement over the extended treatment period. However, data comparing different protocol lengths remains limited.
A reasonable approach mirrors the trial data: run an initial 4-6 week protocol, assess response, and consider extending if benefits are evident and no issues arise. Given the excellent safety profile observed in trials, longer protocols appear well-tolerated.
Reconstitution and storage
Proper handling of ARA-290 requires attention to storage conditions and reconstitution technique. Like most research peptides, the compound is sensitive to temperature and moisture in its reconstituted form.
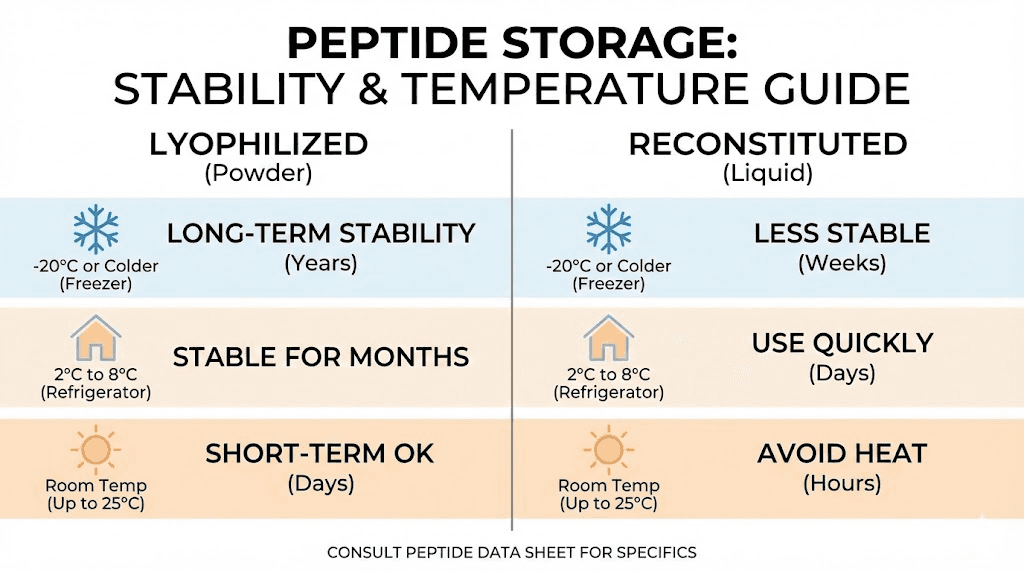
Storage of lyophilized powder
Unreconstituted ARA-290 remains stable under several conditions. Refrigeration at 2-8°C (35-46°F) works well for medium-term storage. Freezing at -20°C (-4°F) extends stability further for long-term storage.
Lyophilized peptides can remain stable at room temperature for days to weeks, which accommodates shipping and brief handling. However, extended room temperature storage accelerates degradation. Once received, moving vials to refrigerated or frozen storage preserves potency.
Light exposure and moisture are the enemies of lyophilized peptides. Keep vials in their original packaging until ready for reconstitution. If storing in a freezer, allow vials to reach room temperature before opening to minimize condensation, which introduces moisture.
For researchers wondering how long peptides last in the fridge or at room temperature, the principle applies broadly: colder is better, and powder form is more stable than solution.
Reconstitution procedure
Before reconstituting, ensure both the peptide vial and bacteriostatic water reach room temperature. Temperature shock from mixing cold solutions can affect peptide structure.
The reconstitution process:
1. Clean the rubber stopper of both vials with an alcohol swab
2. Draw 2.0mL bacteriostatic water into a syringe
3. Insert the needle through the rubber stopper of the peptide vial
4. Direct the water stream against the vial wall, not directly onto the powder
5. Allow the peptide to dissolve naturally, do not shake
6. Gentle swirling is acceptable if dissolution is slow
7. Wait until the solution is completely clear before use
Bacteriostatic water contains 0.9% benzyl alcohol as a preservative, which inhibits bacterial growth and allows multiple uses from a single vial.
Using sterile water for injection instead limits the reconstituted solution to single use.
Storage of reconstituted solution
Once reconstituted, ARA-290 requires refrigeration at 2-8°C and should be used within 28 days. Do not freeze reconstituted peptide solutions, as freezing can damage the peptide structure.
Label vials with the reconstitution date immediately. Store away from light, ideally in a container or wrapped in foil. Check solutions before each use, and discard if any cloudiness, discoloration, or particulate matter appears.
Contamination remains the primary risk with multi-use vials. Using proper sterile technique for each draw minimizes this risk. The peptide storage guide covers additional best practices.
Stability summary
Form | Storage Temperature | Expected Stability |
|---|---|---|
Lyophilized powder | -20°C (freezer) | 1-2+ years |
Lyophilized powder | 2-8°C (refrigerator) | 6-12 months |
Lyophilized powder | Room temperature | Days to weeks |
Reconstituted solution | 2-8°C (refrigerator) | Up to 28 days |
Reconstituted solution | Frozen | Not recommended |
Understanding whether peptides expire helps set realistic expectations. Properly stored lyophilized ARA-290 maintains potency far longer than reconstituted solution, which is why many researchers reconstitute only what they need for 3-4 weeks at a time.
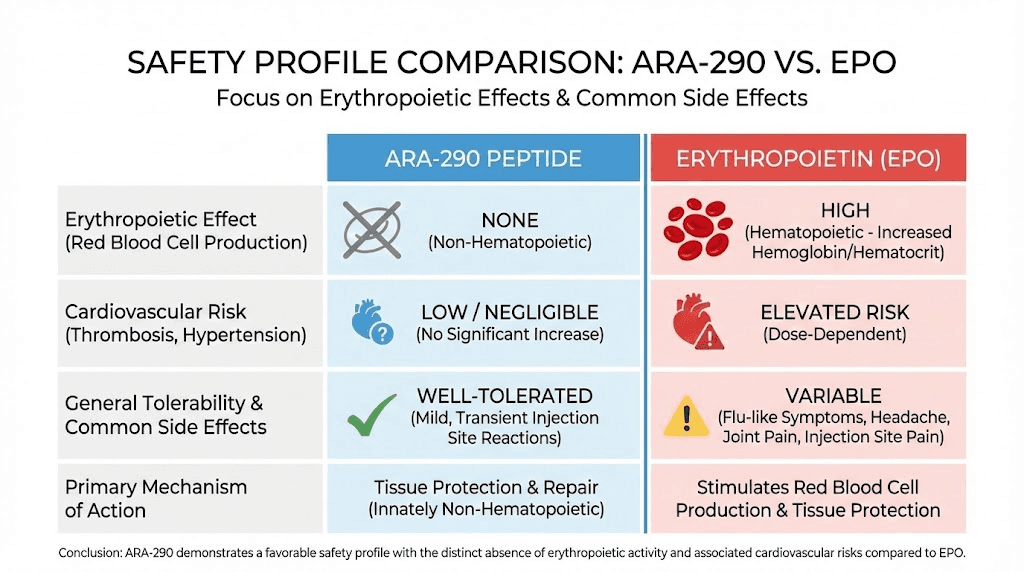
Side effects and safety profile
The safety record of ARA-290 across clinical trials represents one of its strongest attributes. Unlike the erythropoietin it's derived from, ARA-290 avoids the serious cardiovascular risks associated with red blood cell stimulation. And unlike many pain medications, it doesn't produce sedation, addiction, or cognitive impairment.
Clinical trial safety data
Standard toxicity studies in animals revealed no adverse reactions at doses up to 1000 times the initial human dose. This extraordinary therapeutic index provides significant reassurance about basic safety. Similar studies with erythropoietin would show hematological effects at far lower multiples.
In healthy human volunteers receiving supraclinical doses, no safety issues emerged. In patient populations including those with end-stage renal disease, diabetes, and sarcoidosis, therapeutic doses were well tolerated without safety signals.
Across multiple Phase 2 trials, no potential safety issues were identified.
This language, used consistently in published study reports, indicates that researchers specifically looked for problems and didn't find them.
Reported side effects
The side effects reported in trials and research protocols tend to be mild and transient:
Common:
Injection site reactions: redness, swelling, mild irritation at the injection location
Headache: reported in some subjects, typically mild and temporary
Mild gastrointestinal discomfort: occasional reports of nausea or upset stomach
Less common:
Temporary dizziness
Slight increases in heart rate
Minor liver enzyme elevations in some subjects
These effects, when they occur, generally resolve without intervention and don't require discontinuation. The incidence rates compare favorably to placebo groups in controlled trials, indicating that some reported effects may not be causally related to the peptide.
What ARA-290 does not do
Understanding what ARA-290 avoids matters as much as knowing its effects:
No erythropoietic activity: Unlike EPO, ARA-290 does not stimulate red blood cell production. This eliminates risks of polycythemia, increased blood viscosity, and thrombosis that limit EPO use.
No cardiovascular risks: The hypertension and cardiovascular events associated with EPO don't occur with ARA-290 because the pathways responsible aren't activated.
No cognitive impairment: Unlike opioids and many pain medications, ARA-290 doesn't produce sedation or affect mental clarity.
No addiction potential: The mechanism doesn't involve dopamine reward pathways or create physical dependence.
This safety profile makes ARA-290 suitable for extended use in chronic conditions, an important consideration for neuropathy patients who may need ongoing treatment.
Precautions and contraindications
While no absolute contraindications have been established in the research literature, standard precautions apply:
Pregnancy and nursing have not been studied, and ARA-290 should be avoided in these populations until safety data becomes available.
Individuals with active cancer may want to exercise caution. While ARA-290 has shown no tumor-promoting effects in studies, its tissue-protective properties theoretically could affect cancer cells. This remains speculative but warrants consideration.
Those with autoimmune conditions should discuss ARA-290 with their healthcare providers. The immune-modulating effects could theoretically influence autoimmune activity in either direction.
As with all research peptides, sourcing from reputable vendors with verified third-party testing is essential. Impure or contaminated products create risks that properly manufactured peptides don't carry.
ARA-290 vs other healing peptides
Researchers exploring tissue repair and pain relief have several peptide options. Understanding how ARA-290 compares to alternatives like BPC-157 and TB-500 helps with protocol planning.
ARA-290 vs BPC-157
BPC-157, a 15-amino acid peptide derived from human gastric juice, has robust preclinical evidence for musculoskeletal repair, particularly tendons and ligaments. It also shows neuroprotective properties in some models.
Factor | ARA-290 | BPC-157 |
|---|---|---|
Primary focus | Nerve protection, systemic inflammation | Tendon/ligament repair, gut healing |
Clinical trials | Multiple Phase 2 completed | Limited human data |
Mechanism | Innate repair receptor activation | Multiple pathways including VEGF, growth hormone |
Best for | Neuropathy, nerve damage | Soft tissue injuries, gut issues |
Administration | Subcutaneous | Subcutaneous or oral |
Research maturity | More human data | More preclinical data |
BPC-157's mechanisms differ from ARA-290. It works partly through nitric oxide pathways and directly influences growth factor expression.
For localized musculoskeletal injuries, BPC-157's effects may be more targeted. For systemic nerve conditions and inflammation, ARA-290's mechanism may prove more relevant.
Some researchers combine both, hypothesizing that BPC-157's local tissue effects complement ARA-290's systemic nerve and inflammation support. However, combination protocols lack systematic study.
ARA-290 vs TB-500
TB-500, a synthetic version of thymosin beta-4's active fragment, promotes tissue regeneration through effects on cell migration and angiogenesis.
It works more systemically than BPC-157.
Factor | ARA-290 | TB-500 |
|---|---|---|
Primary focus | Nerve protection, anti-inflammation | Whole-tissue regeneration |
Scope | Neurovascular-focused | Systemic, cardiovascular, muscle |
Angiogenesis | Via IRR activation | Directly increases VEGF production |
Best for | Neuropathy, inflammatory conditions | General recovery, muscle injury |
Administration | Subcutaneous daily | Subcutaneous 2x weekly typically |
TB-500's strengths lie in general tissue regeneration and recovery. ARA-290's strengths lie specifically in nerve protection and inflammation control. For conditions involving both nerve damage and tissue injury, using both might provide complementary benefits.
When to choose ARA-290
ARA-290 emerges as the preferred option when:
Neuropathy or nerve damage is the primary concern
Systemic inflammation contributes to symptoms
Previous treatments targeting pain symptoms haven't helped
Nerve regeneration rather than just symptom relief is the goal
Clinical trial evidence matters for decision-making
Cardiovascular protection is also desired
BPC-157 or TB-500 might be preferred when:
Localized soft tissue injury is the focus
Tendon, ligament, or muscle repair is needed
Gut healing is a priority (peptides for gut health)
General recovery and regeneration is the goal
Stacking considerations
Some researchers stack ARA-290 with other peptides targeting different mechanisms. Common combinations discussed in research communities include:
ARA-290 + BPC-157: For conditions involving both nerve damage and tissue injury. ARA-290 addresses systemic inflammation and nerve repair while BPC-157 supports local tissue healing.
ARA-290 + DSIP: For neuropathy with sleep disruption. DSIP's sleep-supporting effects may complement ARA-290's nerve repair while improving recovery.
ARA-290 + KPV: For inflammatory conditions. KPV's anti-inflammatory properties through different pathways may enhance overall inflammation control.
Research on specific stacks remains limited. Understanding how many peptides can be combined safely requires careful consideration. The peptide stacks guide provides framework for thinking through combinations.
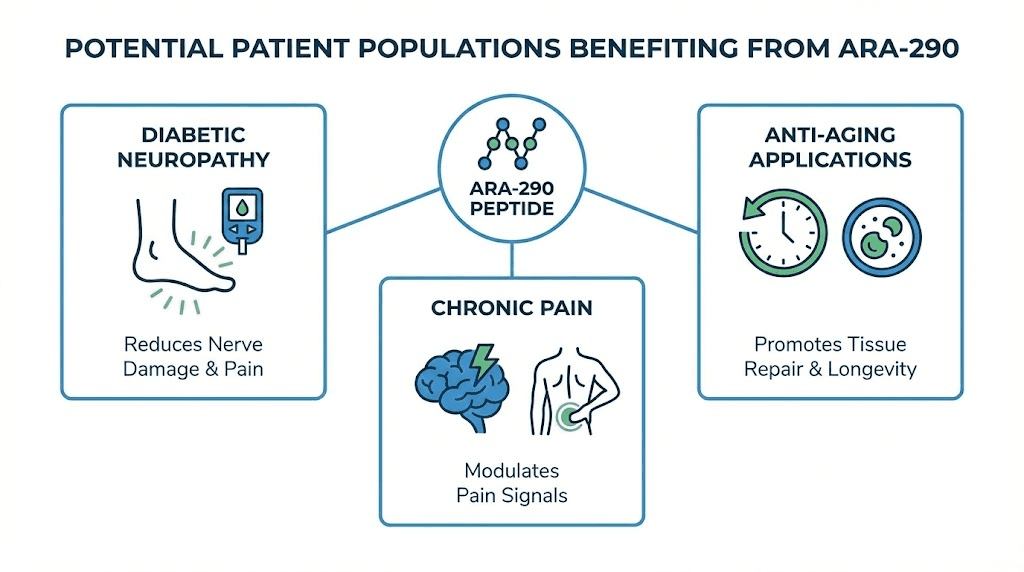
Who can benefit from ARA-290
Based on clinical research and mechanism of action, several populations may find ARA-290 particularly relevant.
Diabetic neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy affects an estimated 50% of people with diabetes over time. The tingling, numbness, and pain in extremities significantly impacts quality of life, and current treatments offer limited relief because they don't address underlying nerve damage.
ARA-290's ability to improve neuropathic symptoms while also benefiting metabolic parameters makes it especially interesting for this population. The persistence of benefits after treatment cessation, observed in trials, suggests the possibility of periodic treatment cycles rather than continuous use.
Those managing diabetes might also explore GLP-1 agonists for blood sugar control alongside ARA-290 for neuropathy. Understanding potential interactions requires consultation with healthcare providers.
Sarcoidosis patients
Sarcoidosis, an inflammatory condition affecting multiple organ systems, frequently involves small fiber neuropathy as a complication. ARA-290's FDA Orphan Drug designation specifically addresses sarcoidosis-associated neuropathy, where the clinical evidence is strongest.
The combination of direct nerve regeneration effects and systemic anti-inflammatory action makes ARA-290 potentially valuable for the complex inflammatory and neurological manifestations of sarcoidosis.
Chronic pain conditions
For those with chronic neuropathic pain that hasn't responded to standard treatments, ARA-290 represents an alternative mechanism.
Rather than blocking pain signals or providing analgesia, it addresses underlying nerve damage and inflammation.
Conditions like fibromyalgia, which involve both pain sensitivity and inflammatory components, might respond to ARA-290's mechanism. Some researchers have explored it alongside other approaches for fibromyalgia.
Athletes and recovery
Nerve injuries in athletics, whether from direct trauma or repetitive strain, can benefit from regenerative support. ARA-290's nerve-specific effects complement the broader tissue healing provided by other injury recovery peptides.
For those focused on athletic performance, ARA-290 fits into recovery protocols rather than performance enhancement directly. Its value lies in supporting return from nerve-involving injuries rather than improving baseline function.
Aging and longevity
The cardiovascular protection and cellular maintenance effects observed in aging studies suggest potential longevity applications. Those building comprehensive anti-aging protocols might consider ARA-290 for its cardiovascular and neuroprotective benefits.
Nerve degeneration occurs naturally with aging, contributing to reduced sensation, coordination, and autonomic function. Supporting nerve health may preserve quality of life into later years.
Current research status and future directions
ARA-290 sits at an interesting position in the pharmaceutical development pipeline.
It has completed multiple Phase 2 clinical trials with positive results and holds FDA Orphan Drug designation, but it's not yet approved for prescription use.
Completed research
The clinical development program has generated substantial human data:
Phase 1 safety studies in healthy volunteers
Phase 2 trials in sarcoidosis with small fiber neuropathy
Phase 2b trials evaluating corneal nerve regeneration
Phase 2 trials in type 2 diabetes with neuropathy
Multiple ophthalmic studies
This represents significantly more human research than most peptides available to researchers. The data supports both efficacy claims and the excellent safety profile.
Ongoing questions
Several questions remain for future research:
Optimal protocol duration: While 28-day protocols showed benefits, the ideal treatment length for different conditions hasn't been established. Can shorter courses achieve similar results? Do longer courses provide additional benefit?
Maintenance protocols: The persistence of benefits after treatment suggests repair processes continue independently. What's the ideal approach for chronic conditions? Periodic treatment cycles? Continuous low-dose maintenance?
Combination approaches: How does ARA-290 interact with other therapies? Can combinations provide additive or synergistic benefits? What combinations should be avoided?
Broader applications: The preclinical evidence spans many conditions. Which other indications merit clinical trials? Traumatic brain injury? Autoimmune neuropathies? Aging-related decline?
Regulatory pathway
The Orphan Drug designation for sarcoidosis-associated neuropathy provides certain advantages for regulatory approval, including extended market exclusivity and potential for accelerated review. However, advancement through Phase 3 trials and approval requires substantial investment.
Staying updated on peptide regulation news helps researchers track the evolving landscape for compounds like ARA-290. The regulatory environment for peptides continues to shift as more research accumulates.
Practical considerations for researchers
For those considering ARA-290 for research purposes, several practical factors deserve attention.
Sourcing
ARA-290 availability varies by supplier. Ensuring pharmaceutical-grade purity requires sourcing from established vendors with verifiable testing. Certificate of Analysis documents should confirm identity, purity, and absence of contaminants.
Third-party testing through independent peptide testing labs provides additional assurance. Given ARA-290's mechanism depends on correct structure, purity matters especially.
Cost considerations
ARA-290 tends to be more expensive than some alternatives like BPC-157. At typical research doses of 4mg daily for 28+ days, total peptide needs can be substantial. The peptide cost calculator helps estimate protocol costs.
Weighing cost against the specific mechanism is important. For neuropathy applications where ARA-290's unique properties matter most, the investment may prove worthwhile. For general tissue repair where alternatives work similarly, other options might provide better value.
Monitoring and assessment
Tracking response helps optimize protocols. Subjective symptom assessment provides one measure, but objective markers can be valuable:
Pain scales: VAS or NRS scores at baseline and regular intervals
Functional measures: activities possible, sleep quality, energy levels
Metabolic markers: if relevant, HbA1c and lipid panels
Nerve function tests: if available, quantitative sensory testing
Understanding how long peptides take to work sets appropriate expectations. ARA-290's nerve regeneration effects may take weeks to manifest fully.
Protocol planning
Proper cycle planning involves considering:
Duration: typically 6-12 weeks for initial protocols
Dose progression: some researchers start lower and titrate up
Assessment points: evaluate at weeks 4, 8, 12
Follow-up: monitor for persistence of benefits after stopping
Subsequent cycles: if benefits fade, when to repeat?
Recording detailed notes supports protocol refinement. What worked, what didn't, what would you change? This information guides future decisions.
Integration with other approaches
ARA-290 works best as part of comprehensive health optimization rather than in isolation. For neuropathy, this might include:
Blood sugar optimization for diabetic neuropathy
Anti-inflammatory nutrition
Exercise appropriate for the condition
Sleep optimization
Stress management
SeekPeptides provides resources for building comprehensive protocols that address multiple factors affecting health outcomes.
Frequently asked questions
What conditions is ARA-290 most studied for?
ARA-290 has been most extensively studied in clinical trials for small fiber neuropathy associated with sarcoidosis and type 2 diabetes. These conditions involve nerve damage and pain that conventional treatments struggle to address. The peptide's ability to regenerate nerve fibers rather than just mask symptoms distinguishes it from standard approaches. Research has also examined its effects in anxiety-related conditions and cardiovascular protection.
How does ARA-290 differ from erythropoietin (EPO)?
While ARA-290 was engineered from a portion of erythropoietin's structure, it completely lacks EPO's red blood cell-stimulating activity. This means ARA-290 provides EPO's tissue-protective benefits without the serious risks of polycythemia, increased blood viscosity, and cardiovascular events that limit EPO use. The difference comes from ARA-290 binding only to the innate repair receptor, not the hematopoietic receptor that EPO activates.
How long does it take to see results from ARA-290?
Clinical trials used 28-day treatment periods and observed measurable improvements within that timeframe.
Some effects on symptoms may appear within 1-2 weeks, while objective measures of nerve regeneration continue improving through week 4 and beyond. Benefits have been observed to persist after treatment stops, suggesting initiated repair processes continue independently. Individual responses vary based on condition severity and other factors.
Can ARA-290 be combined with other peptides?
Researchers sometimes combine ARA-290 with other peptides targeting different mechanisms. Common combinations discussed include pairing it with BPC-157 for tissue repair or KPV for enhanced anti-inflammatory effects. However, systematic research on specific combinations remains limited. Review the stacking guide and consider consulting healthcare providers when combining compounds.
What is the typical dosage for ARA-290?
Clinical trials commonly used 4mg daily administered subcutaneously for 28 days. Dose-ranging studies evaluated 1mg, 4mg, and 8mg, with 4mg emerging as the dose showing consistent benefits. Some research protocols start at 2mg daily for the first week before increasing to the target dose. The peptide calculator can help determine exact volumes for your vial concentration.
Is ARA-290 FDA approved?
ARA-290, also known as cibinetide, holds FDA Orphan Drug designation for sarcoidosis-associated neuropathy, but it is not yet approved as a prescription medication. It remains an investigational compound available for research purposes. The Orphan Drug designation indicates FDA recognition of its potential for conditions lacking adequate treatments. Phase 3 trials and formal approval would require additional development.
What are the main side effects of ARA-290?
Clinical trials reported ARA-290 is generally well tolerated with mild side effects including occasional injection site reactions, headache, and minor gastrointestinal discomfort. Importantly, it does not produce the cardiovascular risks associated with EPO, nor does it cause sedation or addiction like many pain medications. See the peptide safety guide for general safety considerations with research peptides.
How should ARA-290 be stored?
Lyophilized ARA-290 powder should be refrigerated at 2-8°C or frozen at -20°C for long-term storage. Once reconstituted with bacteriostatic water, keep refrigerated and use within 28 days. Do not freeze reconstituted solution. Protect from light and check for clarity before each use. The peptide storage guide covers detailed storage recommendations.
External resources
ARA 290 Improves Metabolic Control and Neuropathic Symptoms in Type 2 Diabetes - PubMed Central
Targeting the Innate Repair Receptor to Treat Neuropathy - PubMed Central
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Join us.