Jan 23, 2026
You have been taking collagen for three weeks. Maybe four. The container sits on your counter, that familiar blue label staring back at you every morning. And yet you wonder if anything is actually happening. Is this powder doing what it promised? Are you using it correctly? These questions haunt thousands of people who start collagen supplementation without understanding what collagen peptides actually do inside the body.
The confusion runs deeper than most realize. Vital Proteins has become one of the most recognized peptide supplement brands globally, yet many users cannot articulate exactly what their daily scoop accomplishes. They add it to coffee. They mix it into smoothies. They trust the process without understanding the mechanism. That changes today.
This guide breaks down everything Vital Proteins collagen peptides are used for, backed by research rather than marketing claims. You will learn the specific benefits, the optimal dosing strategies, which forms work best for different goals, and how to tell if your supplementation is actually working. SeekPeptides provides the evidence-based protocols that transform guesswork into results. By the end, you will know exactly para que sirve, what it serves, and whether it deserves a permanent spot in your daily routine.
What are Vital Proteins collagen peptides
Vital Proteins collagen peptides represent a specific form of bioactive peptides derived from bovine or marine sources through a process called enzymatic hydrolysis. This process breaks down the large collagen protein molecules into smaller chains of amino acids called peptides, typically ranging from 3 to 6 kilodaltons in molecular weight. The smaller size matters tremendously because it determines how efficiently your body can absorb and utilize the supplement.
Collagen itself serves as the most abundant protein in the human body, comprising roughly 30 percent of total protein content. It provides structural support to skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and connective tissue throughout your entire system. Think of collagen as the scaffolding that holds everything together, from the firmness of your skin to the cushioning in your joints.
The problem begins around age 25 to 30. Natural collagen production starts declining by approximately 1 to 1.5 percent annually. By age 50, you have lost a significant portion of your body natural collagen-producing capacity. This decline manifests visibly as wrinkles, sagging skin, and fine lines. Less visibly, it contributes to joint stiffness, reduced bone density, weaker hair and nails, and slower recovery from injuries.
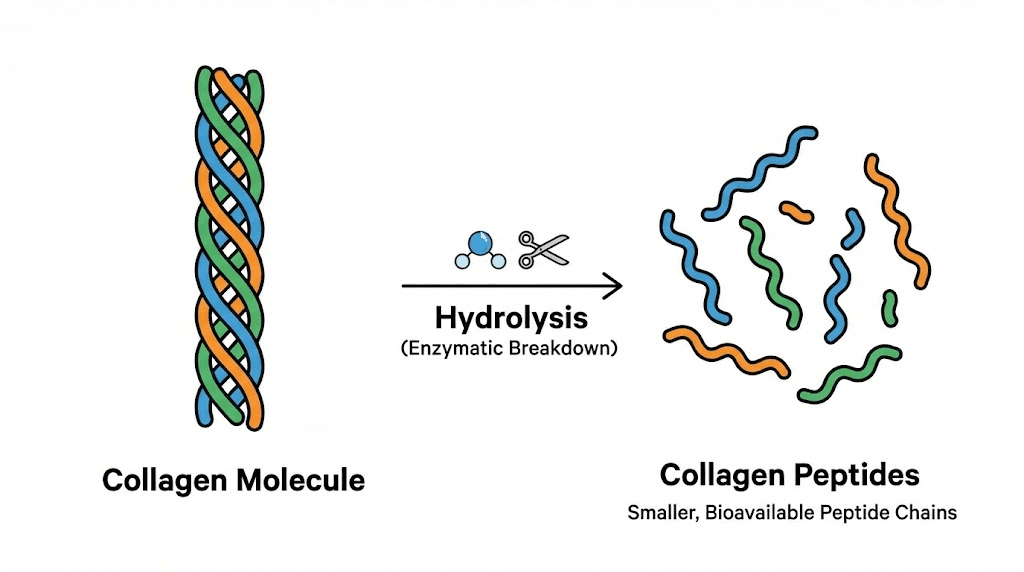
Vital Proteins sources their collagen primarily from grass-fed, pasture-raised bovine hides or wild-caught fish depending on the product line. The marine collagen version comes from fish scales and skin, offering type I collagen predominantly. The bovine version provides both type I and type III collagen, which together account for roughly 90 percent of the collagen found in human tissue.
Understanding the terminology helps avoid confusion. Collagen peptides, hydrolyzed collagen, and collagen hydrolysate all refer to the same thing. The different names simply reflect whether manufacturers emphasize the process (hydrolysis) or the end product (peptides). Vital Proteins uses the term collagen peptides on their flagship products, but the mechanism remains identical regardless of labeling.
The science behind collagen peptide absorption
When you consume Vital Proteins collagen peptides, your digestive system does not simply absorb whole collagen molecules and deposit them directly into your skin or joints. The reality involves a more complex and fascinating process that determines whether supplementation actually delivers results.
Your gastrointestinal tract breaks down ingested collagen peptides into even smaller units, primarily dipeptides and tripeptides along with individual amino acids. These small peptide fragments, particularly those containing hydroxyproline (a signature amino acid found almost exclusively in collagen), enter your bloodstream through specialized transporters in the intestinal lining. Research shows that peptides smaller than 1 kilodalton demonstrate superior absorption efficiency and prolonged blood retention compared to larger fragments.
Once absorbed, these collagen-derived peptides and amino acids circulate throughout your body. They serve two primary functions. First, they provide raw building blocks, the specific amino acids your body needs to synthesize new collagen. Second, and perhaps more importantly, certain bioactive peptides act as signaling molecules that stimulate your own fibroblasts, the cells responsible for producing collagen, to increase their output.
This signaling function explains why collagen supplementation can theoretically boost collagen production beyond simply providing raw materials. Studies have shown that specific collagen peptides can trigger fibroblasts to produce more type I collagen, hyaluronic acid, and elastin. They may also inhibit enzymes called matrix metalloproteinases that break down existing collagen in the skin.
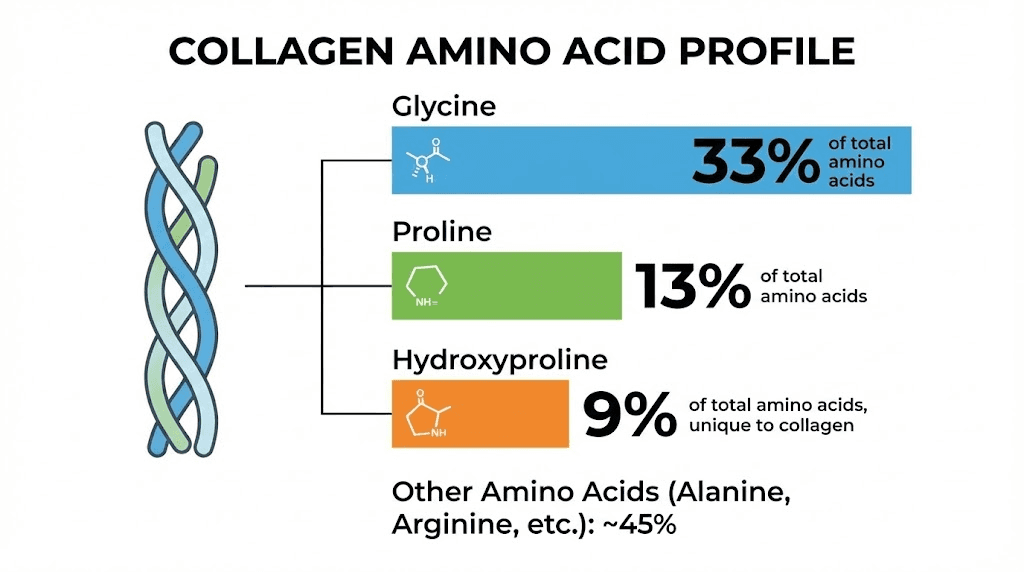
The key amino acids in collagen peptides include glycine (comprising about 33 percent of collagen), proline, hydroxyproline, and leucine. Vital Proteins products contain 18 different amino acids in total, with this specific profile distinguishing collagen from other protein sources. The high glycine content supports detoxification, sleep quality, and gut health while proline and hydroxyproline provide the unique structural properties that support skin and joint tissue.
Skin health benefits and research evidence
Skin health represents the most extensively studied application for collagen peptides, and the evidence has grown substantially stronger in recent years. Multiple randomized controlled trials now support the use of oral collagen supplementation for improving various markers of skin aging.
A 2023 meta-analysis published in a peer-reviewed dermatology journal examined 26 randomized controlled trials involving over 1,700 participants. The analysis found that collagen supplementation significantly improved skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkle depth compared to placebo. Participants taking collagen showed measurable improvements in as little as 4 to 12 weeks, with benefits continuing to accumulate with longer supplementation periods.
The mechanism works on multiple levels. Collagen peptides stimulate fibroblast proliferation and migration while increasing production of type I collagen and glycosaminoglycans in the dermal layer. Ultrasound imaging studies have documented increased dermal density in collagen users compared to control groups, indicating actual structural changes in the skin rather than superficial moisture retention alone.
A particularly compelling 2025 Korean study examined 70 healthy adults aged 20 to 59 taking 1,650 milligrams of low-molecular-weight collagen peptides daily for eight weeks. Researchers found significant improvements in dermal density visible on ultrasound scans by day 10, with continued gains through week eight. Skin elasticity improved substantially by weeks four and eight, particularly in the cheek area where age-related changes typically appear first.

However, critical evaluation of the evidence reveals important nuances. A separate meta-analysis specifically examining study quality and funding sources found that trials funded by supplement companies showed significant benefits while non-industry-funded studies showed no effect. This discrepancy raises questions about publication bias and suggests consumers should maintain realistic expectations while the independent research base continues developing.
For those specifically interested in reducing wrinkles, combining collagen peptides with other evidence-based ingredients may enhance results. Vitamin C plays an essential role in collagen synthesis, and the Vital Proteins Advanced formula includes 100 percent of the daily value. Hyaluronic acid, also included in some Vital Proteins formulations, supports skin hydration from within. These synergistic combinations address multiple aspects of skin aging simultaneously.
Joint health and mobility support
Beyond aesthetics, collagen peptides show considerable promise for supporting joint health and reducing discomfort associated with osteoarthritis and exercise-induced joint stress. This application matters particularly for active individuals and aging populations experiencing cartilage degradation.
Collagen comprises approximately 60 percent of cartilage, the firm tissue that cushions bones at joint surfaces and absorbs shock during movement. Type II collagen specifically concentrates in articular cartilage, though supplementation with type I collagen peptides may still provide benefits through shared amino acid profiles and signaling effects.
A 2025 randomized controlled trial published in Frontiers in Nutrition examined low-molecular-weight collagen peptides in participants with knee osteoarthritis. The study found that collagen supplementation improved joint function scores and reduced pain compared to placebo over the treatment period. Researchers proposed that collagen peptides may increase synthesis of type I, II, and IV collagen along with proteoglycans and elastin in articular cartilage, potentially reducing tissue damage and associated pain signals.
For athletes and physically active individuals, collagen supplementation may support recovery from exercise-induced joint stress and reduce activity-related joint pain. Studies examining athletes with functional knee problems found that 5 grams of collagen peptides daily for 12 weeks significantly reduced joint pain during movement compared to placebo. The benefits appeared most pronounced during activities that stressed the joints, such as running, jumping, and changing direction.
A systematic review examining collagen effects on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury found that supplementation promoted recovery, decreased pain, improved strength outcomes, and potentially improved the fat-to-lean body mass ratio when paired with resistance exercise. These findings suggest benefits extending beyond joint health alone into broader athletic performance and body composition contexts.
The timeline for joint benefits differs from skin effects. While some skin improvements appear within weeks, joint health benefits typically require 3 to 5 months of consistent daily supplementation before becoming noticeable. This longer timeframe reflects the slower turnover rate of cartilage compared to skin cells, requiring patience and consistent use to see meaningful changes.
Hair, nail, and bone benefits
Marketing claims frequently highlight hair growth and nail strength as collagen benefits, but the evidence base here remains thinner than for skin and joints. Understanding what research actually supports helps set appropriate expectations.
For nails, one small study examined 25 participants with brittle nails taking 2.5 grams of bioactive collagen peptides daily for 24 weeks. Results showed 12 percent increased nail growth rate and 42 percent decreased frequency of broken nails. However, this study lacked a placebo control group, limiting the ability to attribute improvements specifically to collagen rather than other factors or placebo effect.
Hair benefits remain even less supported by clinical evidence. Currently, no human studies have demonstrated that collagen supplementation directly improves hair growth, thickness, shine, or volume. The theoretical basis rests on collagen providing amino acids that support keratin production and maintaining the collagen-rich dermis layer where hair follicles anchor. While this mechanism seems plausible, clinical validation is still lacking.
The copper peptide GHK-Cu has considerably more evidence supporting hair benefits than oral collagen peptides. For those specifically targeting hair concerns, exploring topical or injectable peptide options may yield better results than relying on oral collagen alone.
Bone health represents a more promising area. Collagen comprises approximately 90 percent of the organic matrix of bone, providing the framework upon which minerals deposit to create strong, resilient skeletal tissue. A 2025 meta-analysis examining collagen peptide effects on bone and muscle health found that supplementation, particularly when combined with calcium and vitamin D, showed promise for enhancing bone mineral density and bone turnover markers.
Studies in postmenopausal women, a population at elevated risk for osteoporosis, found that 5 grams of collagen peptides daily for 12 months increased bone mineral density at the spine and femoral neck compared to controls. The combination of collagen with resistance exercise appeared particularly effective for maintaining bone health during aging.
Muscle mass and body composition
Collagen peptides have emerged as a potential tool for supporting muscle mass and improving body composition, particularly when combined with resistance training. This application interests athletes, aging adults concerned about sarcopenia, and anyone pursuing body recomposition goals.
A frequently cited study examined elderly men with sarcopenia performing resistance training three times weekly while supplementing with either 15 grams of collagen peptides or a placebo. After 12 weeks, the collagen group gained significantly more fat-free mass and muscle strength while losing more fat mass compared to the control group.
The mechanism likely involves collagen specific amino acid profile. Collagen provides substantial glycine and proline, amino acids that support connective tissue in and around muscles. While collagen is not a complete protein for muscle protein synthesis (it lacks sufficient leucine and other essential amino acids), it may support the tendons, fascia, and structural components that allow muscles to function optimally and recover from training.
For individuals focused primarily on weight loss and muscle gain, collagen peptides work best as a complement to adequate total protein intake rather than a replacement for complete protein sources. The recommended approach involves meeting overall protein goals through whole foods and complete protein supplements while adding collagen peptides specifically for connective tissue support and potential body composition benefits.
The satiety effects of collagen peptides may also support weight management goals. Protein generally increases feelings of fullness compared to carbohydrates or fats, and some research suggests collagen may be particularly satiating. One study found that collagen supplementation reduced appetite and subsequent food intake more than other protein sources tested, though more research is needed to confirm this effect.
Gut health and digestive benefits
The gut health connection represents one of the more interesting emerging applications for collagen peptides, though research remains preliminary. The high glycine content in collagen has drawn particular attention for its potential anti-inflammatory and gut-protective properties.
Glycine helps maintain the mucous membrane lining the digestive tract and may support the integrity of tight junctions between intestinal cells. These tight junctions prevent undigested food particles and bacteria from crossing into the bloodstream, a phenomenon sometimes called intestinal permeability or leaky gut when function becomes compromised.
One study examining collagen peptide supplementation in healthy women with mild digestive symptoms found that 20 grams daily (split into two servings) over 8 weeks significantly reduced bloating compared to placebo. Participants also reported improved overall digestive comfort, though the mechanisms remain unclear.
The KPV peptide and BPC-157 have more robust evidence supporting gut health benefits than oral collagen peptides. However, for those seeking a food-grade supplement with potential digestive support, collagen peptides offer a well-tolerated option with minimal side effect risk.
Collagen peptides may also support the gut-skin axis, the bidirectional communication pathway between intestinal health and skin condition. Improving gut barrier function and reducing systemic inflammation may indirectly benefit skin health beyond the direct effects of collagen on dermal tissue.
How to use Vital Proteins collagen peptides
Proper usage maximizes the potential benefits of collagen peptide supplementation. Understanding optimal dosing, timing, and preparation methods helps ensure you get the most from your investment.
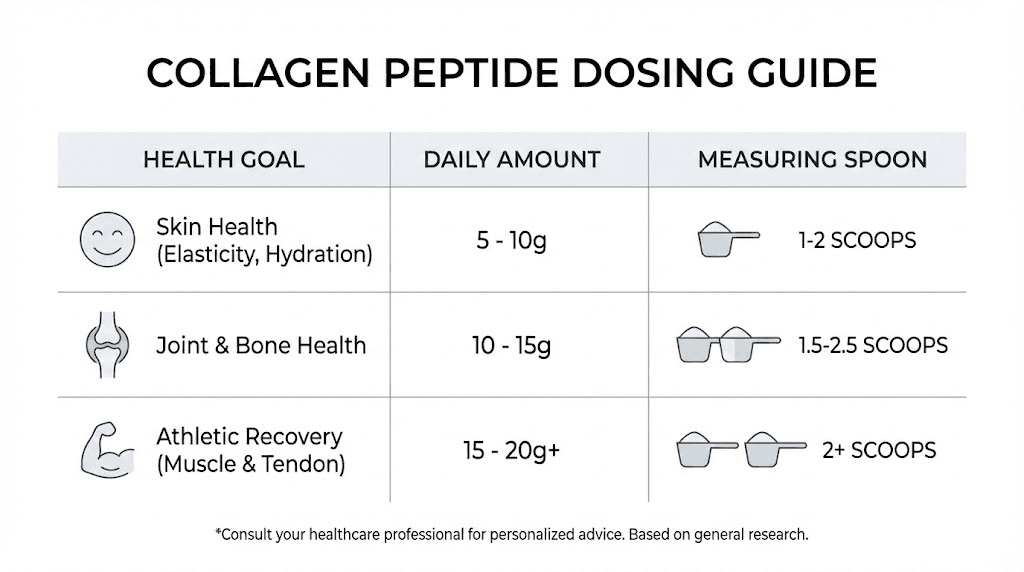
The standard serving size for Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides is 20 grams (approximately two scoops or four tablespoons), providing 18 grams of collagen protein. This dose aligns with the higher end of research protocols examining skin, joint, and body composition benefits. However, studies have shown benefits across a wide dosing range from as little as 2.5 grams to 15 grams or more daily.
Dosing by goal
For skin health improvements including hydration, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction, research supports doses between 2.5 and 10 grams daily. The Korean study showing significant skin benefits used just 1.65 grams daily, suggesting that lower doses may suffice for cosmetic goals. Starting with one scoop (10 grams) daily represents a reasonable middle-ground approach.
For joint health and osteoarthritis symptom management, most successful studies used approximately 10 grams daily. This dose appears sufficient to support cartilage health and reduce activity-related joint discomfort in physically active individuals. Those with significant joint concerns may benefit from the full 20-gram serving.
For muscle mass and body composition goals, higher doses around 15 grams daily showed the most promising results in studies, particularly when combined with resistance training. Athletes and those pursuing lean muscle gains may want to use the full recommended serving.
Timing considerations
Unlike some supplements with specific timing requirements, collagen peptides can be taken at any time of day. The most important factor is consistency, taking it daily over an extended period rather than focusing on precise timing.
Some practitioners recommend taking collagen on an empty stomach to maximize absorption, though research has not definitively established that timing matters significantly. Others suggest taking collagen with vitamin C to support collagen synthesis, which the body requires vitamin C to perform efficiently.
Many users find it most convenient to add collagen peptides to their morning coffee or smoothie, making it an easy habit to maintain. The unflavored Vital Proteins formula dissolves completely in hot or cold liquids without affecting taste, making it versatile for various applications.
Preparation methods
Vital Proteins collagen peptides dissolve readily in both hot and cold liquids. Popular preparation methods include adding to coffee, tea, smoothies, oatmeal, soups, and baked goods. The heat from cooking does not destroy collagen peptides, as they are already hydrolyzed into stable small peptide fragments.
For best dissolution in cold liquids, add the powder to the liquid first, then stir or blend thoroughly. In hot beverages like coffee, the peptides typically dissolve within seconds with minimal stirring. Using a blender or shaker bottle ensures complete mixing in thicker preparations like smoothies or protein shakes.
Different Vital Proteins products and their uses
Vital Proteins offers multiple collagen product variations, each formulated for slightly different applications. Understanding the differences helps you select the right product for your specific goals.
Collagen Peptides (original unflavored)
The flagship product contains hydrolyzed bovine collagen providing type I and type III collagen. This versatile unflavored formula works in any beverage or food application. It contains 18 grams of collagen protein per serving along with 18 amino acids. This product suits those wanting a clean, foundational collagen supplement without additional ingredients.
Collagen Peptides Advanced
The advanced formula includes 100 percent daily value of vitamin C to support the body natural collagen synthesis process, plus 120 milligrams of hyaluronic acid for additional skin hydration support. This combination addresses multiple aspects of skin aging in a single product. Those specifically targeting skin tightening and hydration may prefer this formulation.
Marine Collagen
Sourced from wild-caught white fish, marine collagen provides primarily type I collagen. Some research suggests marine collagen may have higher bioavailability due to its smaller peptide size and molecular structure. The marine collagen option suits those who prefer fish-derived products or want to avoid bovine sources for dietary, religious, or environmental reasons.
Flavored varieties
Vital Proteins offers flavored options including chocolate, vanilla, and various seasonal flavors. These contain additional ingredients for taste and may include added sugars or sweeteners depending on the specific product. Flavored options work well for those who find the unflavored version unpalatable or want a standalone collagen beverage.
Collagen Creamers
These products combine collagen peptides with coconut milk powder, medium-chain triglycerides, and flavoring to create a coffee creamer alternative. They provide a convenient way to add collagen to morning coffee while replacing conventional creamers. The added fats may enhance absorption of fat-soluble nutrients consumed alongside the collagen.
Setting realistic expectations and timeline
Understanding what to realistically expect, and when, prevents disappointment and helps you evaluate whether collagen supplementation is working for you. The timeline for results varies significantly by application and individual factors.
Skin benefits timeline
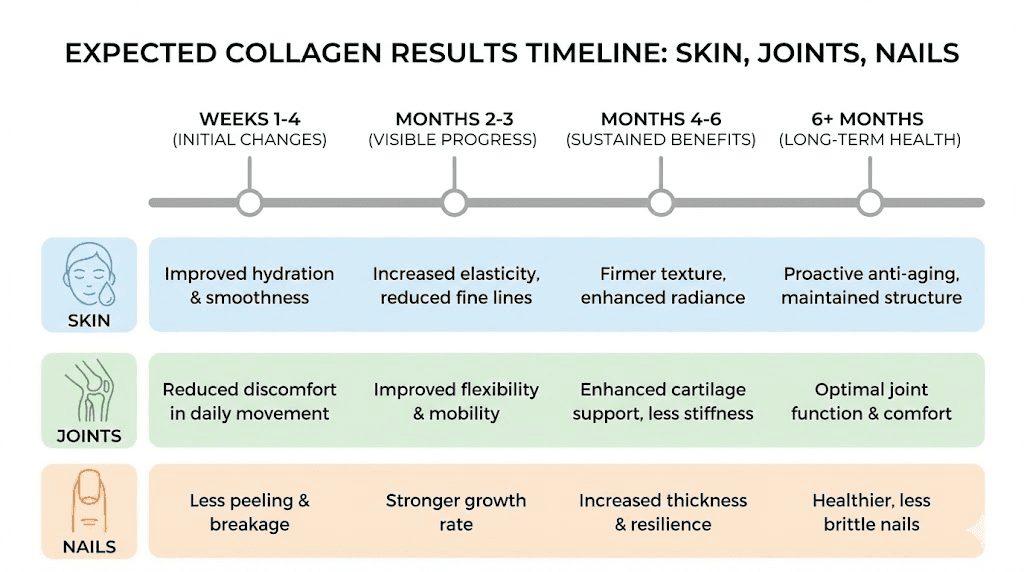
Initial improvements in skin hydration may become noticeable within 4 to 6 weeks of consistent daily use. Some studies have documented increased dermal density as early as day 10 using ultrasound imaging, though these changes may not be visible to the naked eye initially.
Visible improvements in skin elasticity and fine lines typically require 8 to 12 weeks of supplementation. More substantial changes in wrinkle depth and overall skin quality may take 12 to 24 weeks to become apparent. Patience matters here, as skin cell turnover cycles take time, and collagen deposits in the dermis build gradually.
Joint benefits timeline
Joint health improvements generally require longer supplementation periods than skin benefits. Most studies showing significant effects used treatment periods of 3 to 6 months. Some individuals report noticing reduced joint stiffness or discomfort earlier, but meaningful cartilage support takes time to develop.
For those with existing joint issues like osteoarthritis, consistent use for 5 to 6 months provides the best evaluation window. If no improvements occur after 6 months of proper supplementation, collagen may not be the most effective intervention for your specific situation.
Hair and nail timeline
Nail benefits in the available research appeared after 24 weeks (6 months) of supplementation. This extended timeline reflects the slow growth rate of nails and the time required for supplementation to influence the nail matrix where new growth originates.
Hair benefits lack sufficient research to establish a reliable timeline. Those expecting dramatic hair improvements from collagen peptides alone should moderate their expectations or explore other peptides for hair health with stronger evidence bases.
Potential side effects and safety considerations
Collagen peptides have an excellent safety profile overall, with most research documenting few or no adverse effects. However, understanding potential issues helps you make informed decisions and recognize problems if they occur.
Common mild effects
Digestive symptoms represent the most frequently reported side effects, typically including mild bloating, feelings of heaviness, or gastrointestinal discomfort. These effects usually diminish after the first few days of supplementation as the digestive system adjusts. Starting with a smaller dose and gradually increasing may minimize initial digestive upset.
Some individuals report a lingering aftertaste with certain collagen products, though the unflavored Vital Proteins formula typically dissolves without affecting the taste of beverages significantly. Those sensitive to taste may prefer adding collagen to strongly flavored smoothies or coffee rather than plain water.
Allergic reactions
Bovine collagen may cause reactions in individuals with beef allergies, though this is uncommon. Marine collagen poses risks for those with fish or shellfish allergies and should be avoided by anyone with known sensitivities to seafood. Symptoms of allergic reaction may include itching, hives, swelling, or in severe cases, difficulty breathing.
A 2022 case report documented Stevens-Johnson syndrome, a severe skin reaction, in a previously healthy patient following collagen supplement consumption. While extremely rare, this case demonstrates that severe reactions can occur with any supplement, including those considered generally safe.
Contamination concerns
A 2025 study examining marine collagen supplements found detectable levels of toxic metals including lead, cadmium, chromium, mercury, and arsenic in tested products. However, none exceeded European Union regulatory limits, and calculated daily intakes remained below tolerable daily intake thresholds at recommended serving sizes.
Choosing products from reputable manufacturers with third-party testing helps minimize contamination risks. Vital Proteins products undergo quality testing, though consumers should verify current certifications and testing protocols as these may change over time.
Special populations
Limited research exists on collagen supplementation during pregnancy or breastfeeding. While collagen is a natural protein found in foods, concentrated supplementation has not been extensively studied in these populations. Pregnant or nursing women should consult healthcare providers before starting collagen supplements.
Those with kidney disease should approach collagen supplementation cautiously, as high protein intake can stress compromised kidney function. The peptide safety considerations that apply to other supplements apply here as well, emphasizing consultation with healthcare providers for individuals with existing health conditions.
Comparing collagen peptides to other peptides
Understanding how collagen peptides fit within the broader peptide landscape helps contextualize their benefits and limitations. Collagen peptides differ fundamentally from bioactive signaling peptides like BPC-157, GHK-Cu, or TB-500 in both their mechanism and application.
Collagen peptides function primarily as nutritional supplements providing amino acid building blocks and potentially acting as weak signaling molecules. They require consistent daily intake over extended periods to accumulate benefits. Their effects are subtle, systemic, and build gradually over weeks to months.
Bioactive signaling peptides like GHK-Cu demonstrate more potent and specific effects through direct receptor interactions and cellular signaling. For example, GHK-Cu has considerably stronger evidence supporting hair growth and wound healing benefits than oral collagen peptides. These peptides typically require different delivery methods (topical, injectable, intranasal) and may produce faster, more pronounced results.
For anti-aging and skin health, combining oral collagen peptides with topical GHK-Cu or other copper peptides addresses the issue from both internal and external angles. The oral supplement supports collagen synthesis from within while topical application directly stimulates skin cells at the surface.
For joint health specifically, peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500 demonstrate stronger tissue-healing properties than oral collagen. Those with significant joint injuries or damage may find these peptides for tendon repair more effective than collagen supplementation alone, though the approaches can complement each other.
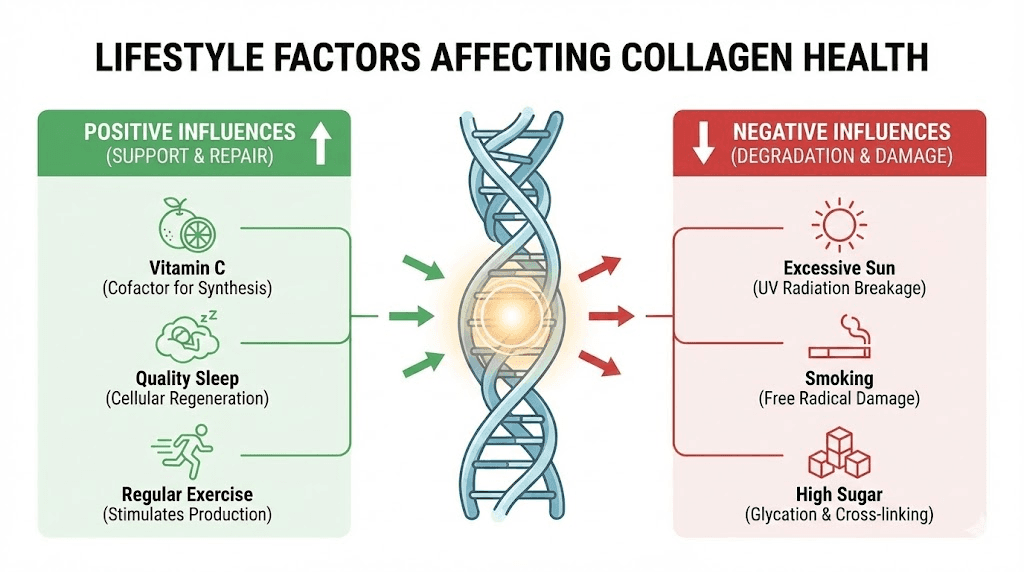
Maximizing results with lifestyle factors
Collagen supplementation works best as part of a comprehensive approach to skin, joint, and overall health. Several lifestyle factors significantly influence collagen synthesis and the effectiveness of supplementation.
Vitamin C intake
Vitamin C serves as an essential cofactor for collagen synthesis enzymes. Without adequate vitamin C, the body cannot properly cross-link collagen fibers, resulting in weaker, less functional collagen even with sufficient amino acid availability. Consuming vitamin C from foods (citrus fruits, bell peppers, berries, leafy greens) or supplements alongside collagen optimizes synthesis.
The Vital Proteins Advanced formula includes vitamin C for this reason. Those using the standard unflavored formula should ensure adequate vitamin C intake from other sources, aiming for at least the recommended daily allowance of 75 to 90 milligrams, though some evidence suggests higher intakes around 200 milligrams may better support collagen production.
Sun protection
Ultraviolet radiation from sunlight dramatically accelerates collagen breakdown in the skin through a process called photoaging. Sun exposure activates matrix metalloproteinases, enzymes that degrade collagen and elastin fibers. Supplementing with collagen while continuing unprotected sun exposure works against your goals.
Consistent sunscreen use, seeking shade during peak UV hours, and wearing protective clothing all help preserve existing collagen while giving supplements the best chance to rebuild damaged tissue. This combination of protection and supplementation yields better results than either approach alone.
Sleep quality
Growth hormone, released primarily during deep sleep, plays important roles in tissue repair and collagen synthesis. Chronic sleep deprivation impairs the body ability to rebuild and maintain collagen-rich tissues. Prioritizing 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep supports natural collagen production and allows supplements to work more effectively.
Interestingly, the glycine in collagen peptides may itself support sleep quality. Some research suggests glycine supplementation improves subjective sleep quality and reduces daytime sleepiness. Taking collagen peptides in the evening could theoretically provide modest sleep support while also supplying amino acids during the overnight repair window.
Exercise and movement
Mechanical loading through exercise stimulates collagen synthesis in tendons, cartilage, and bone. Studies have shown that collagen supplementation combined with resistance training produces greater improvements in connective tissue health and body composition than either intervention alone.
For joint health specifically, low-impact movement like walking, swimming, or cycling helps maintain cartilage health by promoting nutrient exchange within the joint. Pairing collagen supplementation with regular physical activity optimizes benefits for both joint function and overall musculoskeletal health.
Avoiding collagen destroyers
Certain lifestyle factors actively break down collagen and work against supplementation efforts. Smoking dramatically accelerates skin aging by generating free radicals and reducing blood flow to skin tissue. Excessive alcohol consumption impairs collagen synthesis and contributes to dehydration. High sugar intake promotes glycation, a process where sugars bind to collagen fibers and make them stiff and dysfunctional.
Reducing or eliminating these factors while supplementing with collagen creates a more favorable environment for results. The combination of adding beneficial inputs (collagen, vitamin C, sleep, exercise) while removing harmful factors (UV exposure, smoking, excess sugar) produces the best outcomes.
Evaluating product quality and authenticity
Not all collagen supplements deliver equal quality despite similar-sounding label claims. Understanding how to evaluate products helps ensure you get genuine benefits from your supplementation investment.
Third-party testing
Independent laboratory testing verifies that products contain what labels claim and screens for contaminants like heavy metals, pathogens, and adulterants. Look for certifications from organizations like NSF International, Informed Sport, or USP that indicate third-party verification. Peptide testing labs provide additional resources for verifying supplement quality.
Source transparency
Reputable manufacturers clearly disclose collagen sources, including the animal species, body part (hide, bone, scale), and geographic origin. Vital Proteins specifies grass-fed, pasture-raised bovine sources or wild-caught fish depending on the product line. This transparency allows consumers to make informed decisions based on quality, sustainability, and dietary preferences.
Processing methods
The hydrolysis process that creates collagen peptides can use enzymatic, acid, or alkali methods. Enzymatic hydrolysis generally produces higher-quality peptides with better-preserved bioactivity. While consumers cannot always determine processing methods from labels, choosing established brands with quality reputations increases the likelihood of proper manufacturing practices.
Molecular weight
Optimal collagen peptide molecular weight ranges from approximately 2 to 5 kilodaltons for absorption. Some products specify molecular weight or describe peptides as low molecular weight, indicating smaller, more absorbable fragments. Very large peptides or whole collagen proteins absorb poorly compared to properly hydrolyzed peptides.
Frequently asked questions
Can collagen peptides cause weight gain?
Collagen peptides are unlikely to cause weight gain when used as directed. A 20-gram serving provides approximately 70 calories with negligible fat and carbohydrates. The protein content may actually support satiety and help maintain lean muscle mass. Studies examining collagen for body composition found improvements in the fat-to-lean mass ratio rather than weight gain.
Do collagen peptides break intermittent fasting?
Yes, collagen peptides technically break a fast as they contain calories and protein that stimulate metabolic processes. However, the impact depends on your fasting goals. For autophagy benefits, any caloric intake disrupts the fasted state. For weight management fasting, the minimal calories and appetite-suppressing effects may be acceptable to some practitioners. See our guide on whether collagen breaks a fast for detailed analysis.
Can I take collagen peptides with other supplements?
Collagen peptides combine safely with most supplements. Taking them with vitamin C enhances collagen synthesis. They can be used alongside other peptide stacks for complementary benefits. However, those taking multiple supplements should be mindful of total protein intake and any interactions with medications. Consulting a healthcare provider helps ensure safe combinations.
Are collagen peptides safe for daily long-term use?
Studies examining collagen supplementation for up to 12 months have not identified significant safety concerns with daily use. The amino acids in collagen are found naturally in foods, suggesting the body handles them well over extended periods. However, taking periodic breaks or varying doses seasonally may be reasonable approaches for long-term supplementation.
What is the difference between collagen peptides and gelatin?
Both derive from collagen through hydrolysis, but the process differs in extent. Gelatin results from partial hydrolysis and retains larger molecular fragments that form gels when cooled. Collagen peptides undergo more complete hydrolysis into smaller fragments that dissolve in both hot and cold liquids without gelling. Collagen peptides absorb more readily than gelatin, making them preferable for supplementation.
Can vegetarians or vegans use collagen peptides?
No, authentic collagen peptides always derive from animal sources, as collagen is an animal-specific protein. No plant sources produce true collagen. So-called vegan collagen products contain amino acids and cofactors that may support the body own collagen production but are not actual collagen. Vegetarians and vegans seeking similar benefits may focus on vitamin C, proline-rich foods, and plant-based peptides for skin.
How do I know if collagen is working?
Signs that collagen supplementation is working include improved skin hydration and texture (skin feels softer, more supple), reduced joint stiffness or discomfort during movement, stronger and faster-growing nails, and potentially improved hair texture. Taking photos monthly and tracking joint comfort during activities provides objective measures to evaluate progress over the multi-month timeline required for visible results.
External resources
National Institutes of Health - Collagen Peptides Research Review
Harvard Health - Collagen Supplements Guide
For those seeking comprehensive guidance on optimizing collagen supplementation and exploring complementary peptides, SeekPeptides offers detailed protocols, dosing calculators, and expert resources to help you achieve your health and wellness goals with evidence-based approaches.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your collagen stay abundant, your skin stay supple, and your joints stay flexible.



