Dec 27, 2025

Pure collagen peptides typically don't cause acne directly, but many collagen supplements contain additives, sweeteners, fillers, or are combined with biotin (which commonly causes breakouts). Marine collagen and bovine collagen affect skin differently.
Additionally, people with specific skin conditions or hormonal issues may experience breakouts from increased protein intake. The solution is choosing pure, unflavored collagen, avoiding biotin-containing formulas, and starting with lower doses.
This guide breaks down exactly why some people break out from collagen, which ingredients in collagen supplements trigger acne, how to choose acne-safe collagen, alternative peptides for skin without breakout risk, troubleshooting strategies if collagen causes your acne, and complete protocols for clear skin while taking collagen.
Let's start with understanding the relationship between collagen and acne.
Can collagen peptides actually cause acne?
The relationship between collagen and acne is complex, not straightforward.
Pure collagen peptides: Unlikely to cause acne directly
What pure collagen is:
Hydrolyzed protein from animal sources
Amino acids: Glycine, proline, hydroxyproline
No hormones when properly processed
Minimal impact on insulin or androgens
Why pure collagen usually doesn't cause acne:
Doesn't contain hormones
Doesn't significantly spike insulin (in moderate amounts)
Doesn't directly increase sebum production
Most people tolerate it without breakouts
The reality:
Pure, unflavored collagen peptides are generally acne-safe
Problems usually come from additives or individual reactions
Small percentage of people may still break out
Learn about peptides in our what are peptides guide and how peptides work.
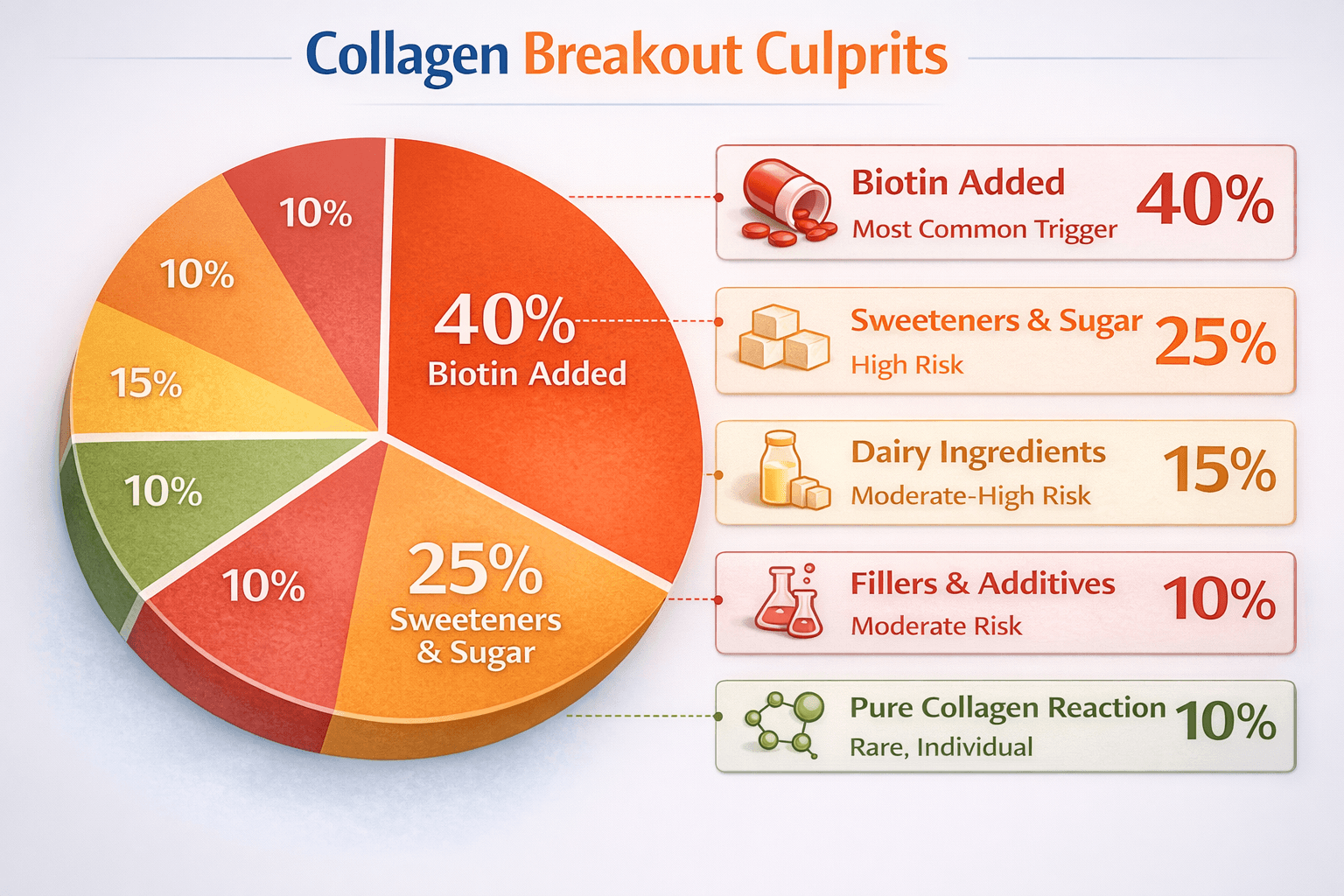
Common culprits in collagen supplements that cause acne
The real acne triggers in collagen products:
1. Biotin (Vitamin B7) - #1 acne trigger
Often added to collagen for "hair, skin, nails"
High doses (5,000-10,000mcg) commonly cause breakouts
Interferes with skin barrier function
Increases sebum production in some people
2. Sweeteners and sugar
Flavored collagen contains sugars or artificial sweeteners
Sugar spikes insulin → increases androgens → acne
Even natural sweeteners can trigger breakouts in sensitive individuals
3. Dairy-derived ingredients
Some collagen blends contain whey or casein
Dairy is highly comedogenic (pore-clogging)
Triggers acne in dairy-sensitive people
4. Fillers and additives
Maltodextrin, xanthan gum, other fillers
Can cause inflammation in sensitive individuals
Quality control issues in cheap supplements
5. Excess protein/amino acids
Very high doses (50g+ daily) may increase IGF-1
IGF-1 linked to acne in some studies
Most people don't take this much
Individual factors that increase breakout risk
You're more likely to break out from collagen if you:
Hormonal acne prone:
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome)
Hormonal imbalances
Already dealing with hormonal breakouts
Insulin sensitive:
Protein can spike insulin in insulin-resistant people
Insulin increases androgens
Androgens increase sebum and acne
Inflammatory skin conditions:
Rosacea
Seborrheic dermatitis
Eczema
May react to collagen protein
Gut issues:
Leaky gut or dysbiosis
May react to protein supplements differently
Gut-skin axis problems
See our copper peptides ruined my skin guide for other peptide skin issues.
Why some people break out from collagen (mechanisms)
Understanding the biological pathways helps prevent breakouts.
IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor) pathway
How this works:
High protein intake can increase IGF-1
IGF-1 stimulates sebaceous glands
More sebum = more acne potential
Especially problematic in acne-prone people
When collagen triggers this:
Very high doses (30g+ daily)
Combined with other protein sources
In insulin-resistant individuals
Already elevated IGF-1 levels
How significant is this:
Moderate collagen doses (10-20g) unlikely to cause issues
More relevant with whey protein (higher leucine)
Individual variation exists
mTOR activation and sebum production
What is mTOR:
Cellular growth pathway
Activated by protein, especially leucine
Stimulates sebaceous gland activity
Linked to acne in research
Collagen's mTOR impact:
Lower in leucine than whey protein
Moderate mTOR activation
Less problematic than other proteins
But can still affect sensitive individuals
Biotin interference with skin barrier
Why biotin causes breakouts:
Competes with pantothenic acid (B5) absorption
B5 deficiency impairs skin barrier
Weakened barrier = more acne
Increased sebum production
Biotin in collagen products:
Many brands add 5,000-10,000mcg biotin
Far exceeds nutritional needs (30mcg daily)
Primary cause of "collagen acne"
Easily avoided by choosing biotin-free collagen
Detox response and initial breakouts
"Purging" vs true acne:
Some people experience temporary breakouts starting collagen
May be detox response or skin adjustment
Usually clears within 2-4 weeks
Different from ongoing acne caused by product
How to tell the difference:
Purging: Temporary, improves after 2-4 weeks
True acne: Persists or worsens over time
Purging: Usually in areas you normally break out
True acne: New areas or pattern
Types of collagen and acne risk
Different collagen sources affect skin differently.
Marine (fish) collagen vs bovine (beef) collagen
Marine collagen:
Type I collagen primarily
Smaller peptides, better absorption
May be less likely to cause breakouts
Cleaner source (less processing)
More expensive
Bovine collagen:
Types I and III collagen
Larger peptides
More common in supplements
Cheaper
May contain more impurities if low quality
For acne-prone skin:
Marine collagen generally safer choice
Bovine collagen fine if pure and high-quality
Source matters less than purity and additives
Hydrolyzed collagen vs gelatin
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides:
Broken down into small amino acids
Easily absorbed
Room temperature soluble
Better bioavailability
Gelatin:
Partially hydrolyzed collagen
Requires hot liquid to dissolve
Lower bioavailability
Less convenient
Acne considerations:
Both similar acne risk if pure
Hydrolyzed collagen preferred for skin benefits
Neither inherently acne-causing
Collagen Types I, II, III and skin effects
Type I collagen:
Most abundant in skin
Best for anti-aging and skin health
Unlikely to cause acne when pure
Type II collagen:
Primarily for joints, not skin
Less relevant for skin benefits
No specific acne concerns
Type III collagen:
Supports skin elasticity
Often combined with Type I
Safe for acne-prone skin
Multi-collagen blends:
Contain Types I, II, III, V, X
More ingredients = more potential reactions
Not necessary for skin - Type I sufficient
How to choose acne-safe collagen supplements
Selecting the right product prevents breakouts.
Look for these characteristics
Must-haves for acne-prone skin:
Pure, unflavored (no sweeteners or flavors)
Biotin-free (check label carefully)
No added vitamins/supplements (simple is better)
Grass-fed/wild-caught (cleaner source)
Third-party tested (quality control)
Minimal ingredients (ideally just collagen)
Ideal ingredient list: "Hydrolyzed collagen peptides (bovine or marine). That's it."
Red flags to avoid:
Contains biotin or B-complex
Sweetened or flavored
"Beauty blend" with multiple ingredients
Contains hyaluronic acid, vitamin C, etc. (get separately)
Very cheap (quality concerns)
Best collagen for acne-prone skin
Recommended characteristics:
Pure marine or grass-fed bovine collagen
Unflavored and unsweetened
Single ingredient
10-20g collagen per serving
No biotin or added vitamins
Starting protocol:
Begin with 5-10g daily
Increase slowly to 15-20g if tolerated
Monitor skin for 2-4 weeks
Stop immediately if breakouts occur
Timing and dosing to minimize breakouts
Best practices:
Take collagen with meals (slows absorption, gentler on system)
Start low (5-10g) and increase gradually
Don't exceed 20g daily unless needed
Consider every-other-day dosing if sensitive
Take morning or early afternoon (not before bed)
What to avoid:
Taking collagen on empty stomach (can spike insulin in sensitive people)
Very high doses (30g+) especially if acne-prone
Combining with other high-protein supplements
See our bone broth vs collagen peptides comparison for alternatives.
What to do if collagen is causing your acne
Troubleshooting strategies for breakouts.
Step 1: Identify if it's really the collagen
Elimination test:
Stop collagen completely for 2-4 weeks
Document skin changes
If acne clears = collagen is culprit
If acne persists = something else causing it
Check these factors:
Started any other new supplements?
Changed diet or skincare?
Hormonal cycle changes (women)?
Stress levels increased?
New medications?
Step 2: Check your collagen product
Investigate the ingredient list:
Does it contain biotin? (Most common cause)
Any sweeteners or flavors?
Multiple ingredients or "blends"?
Dairy-derived components?
Try switching brands:
Choose pure, unflavored, biotin-free version
Preferably marine collagen
Single-ingredient product
Monitor for 3-4 weeks
Step 3: Adjust dosing
Reduce amount:
Cut dose in half (if taking 20g, try 10g)
Take every other day instead of daily
Split dose (10g morning, 10g evening)
Change timing:
Take with largest meal (not on empty stomach)
Morning instead of evening
With fat source (may slow absorption)
Step 4: Support skin health while taking collagen
Add these to prevent breakouts:
Zinc: 30-50mg daily (reduces inflammation, controls sebum)
Pantothenic acid (B5): 1-2g daily (counters biotin interference)
Probiotics: Support gut-skin axis
Omega-3s: Reduce inflammation
Skincare adjustments:
Use gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser
Add salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide spot treatment
Don't over-cleanse (strips barrier)
Use lightweight, oil-free moisturizer
Step 5: Try alternative collagen sources
Bone broth:
Natural collagen source
Contains gelatin (partially hydrolyzed)
Easier on some people's systems
Homemade or high-quality store-bought
Collagen-boosting foods:
Vitamin C-rich foods (stimulates collagen production)
Copper-rich foods (nuts, shellfish)
Amino acid-rich foods (chicken, fish, eggs)
May work better than supplements for some
Topical collagen peptides:
Applied to skin directly
Won't cause acne from internal mechanisms
Limited absorption but may help
See our glow peptides guide for topical options.
Alternative peptides for skin that don't cause acne
Other peptides offer skin benefits without breakout risk.
GHK-Cu (copper peptides) for skin
Why GHK-Cu is better for acne-prone skin:
Doesn't contain biotin or additives
Applied topically (not ingested)
Promotes collagen synthesis without increasing protein intake
Anti-inflammatory properties
Improves skin without acne risk
Benefits:
Stimulates natural collagen production
Reduces wrinkles and fine lines
Improves skin texture and tone
Enhances wound healing
Works for acne-prone skin
Dosing:
Topical serum: 1-2% GHK-Cu applied daily
Injectable: 1-2mg, 3-5x weekly subcutaneous
Timeline:
4-6 weeks: Initial improvements
8-12 weeks: Visible skin transformation
See our complete copper peptides GHK-Cu guide and can you use peptides and retinol together.
BPC-157 for skin and gut health
Why BPC-157 helps without causing acne:
Injectable (bypasses gut, no digestive issues)
Heals gut lining (improves gut-skin axis)
Reduces inflammation systemically
Doesn't spike insulin or IGF-1 significantly
No biotin or additives
Skin benefits:
Wound healing and scar reduction
Reduces inflammation (helps inflammatory acne)
Improves gut health (clearer skin via gut-skin connection)
Supports collagen synthesis indirectly
Dosing:
250-500mcg twice daily injectable
8-12 weeks for skin benefits
Can use long-term safely
See our BPC-157 guide, how to take BPC-157, and is BPC-157 banned.
Matrixyl (palmitoyl peptides) for topical use
Why Matrixyl is acne-safe:
Topical application only
Stimulates collagen without oral supplementation
No systemic effects
Well-tolerated by acne-prone skin
Benefits:
Increases collagen Types I, III, IV production
Reduces wrinkles
Improves skin firmness
Lightweight, non-comedogenic
How to use:
Apply serum with Matrixyl peptides
Use morning and/or evening
Combine with vitamin C for enhanced results
Hyaluronic acid for hydration without breakouts
Why HA is safe for acne-prone skin:
Not a protein (glycosaminoglycan)
Holds water, doesn't trigger acne pathways
Topical or oral both safe
Improves skin hydration
Benefits:
Plumps skin and reduces fine lines
Improves moisture retention
Works immediately (topical)
Safe for all skin types
See our hyaluronic acid peptide guide for combining with peptides.
Collagen and acne: Complete comparison table
Here's how different collagen options compare for acne-prone skin:
Collagen Type/Source | Acne Risk | Why | Best For | Avoid If | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Pure unflavored marine collagen | Low | No additives, clean source | Acne-prone skin wanting collagen | Shellfish allergy | Choose biotin-free |
Pure unflavored bovine collagen | Low-Moderate | May contain impurities if low quality | Most people | Very sensitive skin | Get grass-fed, high quality |
Flavored/sweetened collagen | High | Sugar triggers insulin/acne | Non-acne-prone | Acne-prone skin | Switch to unflavored |
Collagen + biotin blends | Very High | Biotin commonly causes breakouts | Those not acne-prone | Acne-prone skin | Biggest acne trigger |
Multi-collagen complex | Moderate | More ingredients = more reactions | Joint health | Sensitive acne-prone | Simple better for skin |
Bone broth (homemade) | Low | Natural, no additives | Sensitive individuals | None (unless meat allergy) | Gentler than supplements |
Gelatin powder | Low-Moderate | Less bioavailable, natural | Gut health + collagen | None specific | Similar to collagen |
Topical collagen | Very Low | Not ingested, no systemic effects | Acne-prone wanting topical benefits | None | Limited absorption though |
GHK-Cu (alternative) | Very Low | Topical or injectable, no acne pathway | Acne-prone wanting skin benefits | None | Better choice for acne-prone |
Collagen from diet | Low | Whole foods, gentle on system | Everyone | Strict vegans/vegetarians | No supplementation issues |
Key takeaways:
Pure, unflavored collagen = lowest risk
Biotin-containing products = highest risk
Marine collagen generally safer than bovine
Topical alternatives (GHK-Cu) best for very acne-prone skin
Real-world case studies: Collagen and acne
Learning from actual experiences.
Case 1: Biotin was the culprit
Scenario:
28-year-old woman started "beauty collagen" with 10,000mcg biotin
Developed cystic acne within 2 weeks
Acne persisted for 6 weeks while taking it
Solution:
Stopped beauty collagen
Switched to pure, biotin-free marine collagen
Acne cleared within 3 weeks
No breakouts on pure collagen
Lesson: Check for biotin first - it's the most common cause.
Case 2: Dosing was too high
Scenario:
35-year-old man taking 40g collagen daily for joint health
Developed inflammatory acne on back and shoulders
Never had acne issues before
Solution:
Reduced dose to 15g daily
Acne gradually improved over 4-6 weeks
Maintained clear skin on lower dose
Lesson: More isn't always better - moderate doses work fine.
Case 3: Gut health was the issue
Scenario:
32-year-old woman with IBS and acne-prone skin
Collagen supplement worsened both gut and skin
Digestive distress and breakouts
Solution:
Stopped oral collagen
Started BPC-157 injectable for gut healing
Used topical GHK-Cu for skin
Both gut and skin improved
Lesson: If you have gut issues, injectable peptides may work better than oral supplements.
Case 4: It wasn't the collagen
Scenario:
Started collagen same time as new skincare product
Blamed collagen for breakouts
Stopped collagen, acne continued
Solution:
Eliminated new skincare product
Reintroduced collagen
Skin cleared, no issues with collagen
Lesson: Correlation doesn't equal causation - look at all changes.
How you can use SeekPeptides for acne-safe skin peptides
SeekPeptides helps you optimize skin health with peptides that won't trigger breakouts. Get personalized recommendations for collagen alternatives like GHK-Cu, BPC-157, and Matrixyl that provide skin benefits without acne risk.
Learn which peptides are safe for acne-prone skin and which to avoid.
Our AI advisor provides guidance on choosing pure collagen without biotin, transitioning from problematic products to acne-safe options, and combining peptides with acne treatments safely.
Access our research library covering peptide effects on skin health, acne mechanisms, and proven protocols for clear skin. Use our calculators - peptide calculator, BPC-157 dosage calculator, peptide cost calculator - for precise skin-focused peptide protocols.
So, can collagen peptides cause acne?
Pure collagen peptides rarely cause acne directly, but collagen supplements containing biotin, sweeteners, dairy, or fillers frequently trigger breakouts. The #1 culprit is biotin added to "beauty collagen" formulas.
If you're breaking out from collagen, first check if your product contains biotin (most common cause). Switch to pure, unflavored, biotin-free marine or bovine collagen. Start with lower doses (10g daily) and monitor your skin for 2-4 weeks.
For acne-prone skin, topical peptides like GHK-Cu or injectable peptides like BPC-157 offer better alternatives. These provide skin benefits without triggering the insulin, IGF-1, or biotin pathways that can cause acne.
Your skin sensitivity, the quality of your collagen product, and any additives matter far more than the collagen itself.
Pure collagen is generally safe for most people, but individual reactions vary. Listen to your skin and adjust accordingly.
The path to clear skin while taking collagen requires choosing high-quality, pure products, avoiding biotin-containing formulas, starting with conservative doses, and having backup alternatives ready if collagen doesn't work for your skin.
Helpful resources for skin peptides
Peptide calculator - Calculate doses
BPC-157 dosage calculator - BPC-157 skin protocols