Jan 31, 2026
Your brain is losing neurons. Right now. Every single day.
That is not fear-mongering. It is biology. After age 25, the average adult loses roughly 0.5% of hippocampal volume per year, and with it goes the capacity for forming new memories, learning new skills, and maintaining the kind of sharp cognition that once felt effortless. Most people accept this decline as inevitable. But what if a peptide could reverse the trend?
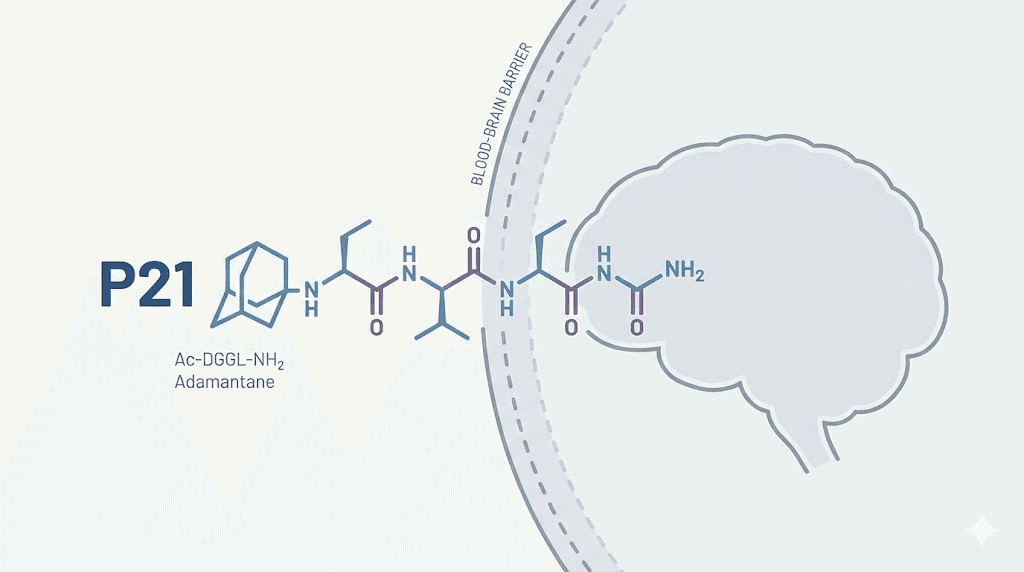
P21, also called P021, is a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the most active region of ciliary neurotrophic factor. It was engineered to do something remarkable. By crossing the blood-brain barrier and boosting brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression, P21 promotes the growth of entirely new neurons in the hippocampus. Not just protecting what you have. Actually building more. In preclinical studies on Alzheimer disease mouse models, this peptide reduced tau pathology, cleared amyloid-beta accumulation, rescued synaptic plasticity, and reversed cognitive impairment. The research team behind it, led by Dr. Khalid Iqbal at the New York State Institute for Basic Research in Developmental Disabilities, has spent over a decade refining this compound.
This guide covers everything researchers need to know about P21. We will walk through the science behind its mechanism of action, the specific benefits demonstrated in published studies, how it compares to related nootropic peptides like Semax and Cerebrolysin, research protocols including both subcutaneous and intranasal delivery, stacking strategies, side effects, and the current state of clinical development. Whether you are new to peptide research or looking to add a targeted neurogenic compound to your protocol, this is the reference you will keep coming back to.
What is P21 and where did it come from?
Understanding P21 requires a brief history lesson. The story begins not with P21 itself, but with Cerebrolysin, a complex mixture of low-molecular-weight peptides and free amino acids derived from porcine brain tissue. Cerebrolysin has been used clinically in Europe and Asia for decades to treat stroke, traumatic brain injury, and dementia. It works. But nobody fully understood why.
Dr. Khalid Iqbal and his colleague Dr. Inge Grundke-Iqbal set out to find the answer. Their laboratory at the New York State Institute for Basic Research had already made groundbreaking discoveries about Alzheimer disease. In 1974, Iqbal was the first to isolate and characterize neurofibrillary tangles from Alzheimer brains. In 1986, the husband-and-wife team discovered that the protein in these tangles was hyperphosphorylated tau. This work established tau pathology as a central feature of Alzheimer disease and laid the groundwork for everything that followed.
Their search for upstream causes of tau pathology led them to neurotrophic factors. In 1999, they discovered that CNTF, ciliary neurotrophic factor, could neutralize FGF-2-mediated tau hyperphosphorylation in adult rat hippocampal neuroprogenitor cells. This was a major finding. But there was a problem.
Full-length CNTF is too large to cross the blood-brain barrier. It has poor plasma stability. And when administered systemically, it triggers the production of anti-CNTF antibodies, essentially causing the immune system to fight the very thing meant to help. Clinical trials using full-length CNTF in ALS patients showed no benefit and produced serious side effects including severe weight loss, anorexia, cramps, and muscle pain.
So Iqbal's team did something clever. They reverse-engineered Cerebrolysin's neurogenic effects, using epitope-mapping strategies to identify the minimal peptide sequence responsible for CNTF-associated signaling. What they found was that just four amino acid residues, positions 148 through 151 of CNTF, could replicate the neurogenic benefits of the full protein. They synthesized this tetrapeptide and added an adamantane moiety at the C-terminal end. The adamantylation increased lipophilicity for better blood-brain barrier penetration, while simultaneously protecting the peptide from degradation by exopeptidases.
The result was P021. A tiny molecule with enormous potential.
How P21 works: mechanism of action explained
P21 does not work the way most people assume. It does not directly bind to CNTF receptors. It does not simply mimic what CNTF does. Instead, P21 takes a more indirect and arguably more elegant approach to boosting neurogenesis and protecting neurons from degeneration.
The LIF inhibition pathway
The primary mechanism involves leukemia inhibitory factor, or LIF. In the brain, LIF acts as a brake on neurogenesis. When LIF signaling is active through the JAK-STAT3 pathway, the production of new neurons in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus slows down. P21 competitively inhibits LIF signaling. By releasing this brake, the peptide allows the brain's natural neurogenic machinery to work more effectively.
Think of it this way. Your brain already has the capacity to generate new neurons. LIF is holding that capacity back. P21 removes the obstruction.
BDNF upregulation
With LIF signaling suppressed, P21 increases CREB activity and the transcription of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. BDNF is perhaps the most important molecule for brain health. It supports the survival of existing neurons, encourages the growth and differentiation of new neurons, and strengthens synaptic connections essential for learning and memory.
The BDNF elevation triggered by P21 sets off a cascade of downstream effects. BDNF binds to its receptor, TrkB, which activates the PI3-Kinase pathway. This leads to activation of Akt, which in turn performs inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3-beta at Serine 9. GSK-3-beta is a major tau kinase, the enzyme responsible for the abnormal hyperphosphorylation of tau protein that drives neurofibrillary tangle formation in Alzheimer disease.
So the chain looks like this: P21 inhibits LIF, which increases BDNF, which activates TrkB-PI3K-Akt signaling, which inhibits GSK-3-beta, which prevents tau hyperphosphorylation.
One compound. Multiple layers of neuroprotection.
CNTF antibody sequestration
There is a third mechanism that adds another dimension. Research suggests P21 may also work by sequestering circulating antibodies that neutralize endogenous CNTF. The body naturally produces some CNTF, but auto-antibodies can reduce its effectiveness. P21 appears to bind these antibodies and help eliminate them, effectively raising the functional concentration of your own CNTF without introducing a foreign protein that triggers further immune reactions.
This is what distinguishes P21 from both full-length CNTF and from Cerebrolysin. It achieves similar neurogenic endpoints without the immunogenicity problems. P21 has not been shown to be antigenic, and it has not been shown to lose efficacy over time, which addresses two of the biggest limitations of its parent compounds.
Synaptic marker changes
Animal studies have documented changes in multiple molecular intermediates downstream of P21 administration. These include altered expression of synaptic markers such as MAP2, synapsin I, GluR1, and NR1. Higher AMPA receptor protein levels, specifically GluR2 and GluR3, have been observed. Higher phosphorylated GSK-3-beta levels confirm the tau-protective mechanism. Changes in these markers indicate that P21 does not just generate new neurons. It helps those neurons integrate functionally into existing circuits and form stronger synaptic connections.
Key benefits of P21 peptide in preclinical research
The published research on P21 spans roughly 10 to 15 peer-reviewed studies from 2010 through 2017, with additional publications extending into 2024. While the body of evidence is still exclusively preclinical, meaning no human clinical trials have been completed, the results across multiple animal models are remarkably consistent and compelling. Here is what the research shows.
Neurogenesis promotion
The most foundational benefit of P21 is its ability to promote the birth of new neurons. This is not a minor effect. In the initial 2010 publication, researchers demonstrated that P21, when administered peripherally to normal adult C57Bl6 mice, enhanced neurogenesis and maturation of newly born neurons in the granular cell layer and subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus.
Experimental observations included increased incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine, a marker used to tag newly divided cells, along with elevated expression of NeuN, a protein that identifies mature neurons. This means P21 was not just stimulating cell division. It was driving those new cells to develop into fully functional neurons.
The dentate gyrus is a well-characterized neurogenic niche, one of the few regions in the adult brain where new neurons continue to be produced throughout life. This region plays a critical role in memory formation, pattern separation, and spatial navigation. Enhancing neurogenesis here has direct implications for cognitive function, and that is exactly what the researchers observed.
Cognitive enhancement in healthy animals
P21 did not just grow new neurons. It made the animals smarter.
The same 2010 study showed that P21-treated mice demonstrated enhanced learning as well as improvements in both short-term and spatial reference memories. These were normal, healthy adult mice, not disease models. The cognitive improvements were measured using validated behavioral assays that test specific aspects of hippocampal function.
This finding has significant implications. If P21 can enhance cognition in healthy brains, not just diseased ones, it suggests a role beyond disease treatment. It points to genuine cognitive enhancement, the kind of effect that has made this peptide attractive to the nootropic research community.
Alzheimer disease pathology reduction
The most extensive body of P21 research has been conducted in the 3xTg-AD mouse model, a transgenic strain that develops both amyloid-beta plaques and tau tangles, closely mimicking human Alzheimer disease pathology. The results in this model are striking.
P21 treatment markedly reduced tau pathology. Significant reductions in abnormal hyperphosphorylation and accumulation of tau at known major Alzheimer neurofibrillary pathology-associated sites were observed. The peptide also attenuated the generation of amyloid-beta, with significant decreases in soluble amyloid-beta levels and a trend towards reduction in plaque load in the CA1 region of the hippocampus.
But here is where it gets truly impressive. When P21 treatment was initiated during the synaptic compensation period, before severe neurodegeneration had set in, it prevented neurodegeneration entirely. It prevented both amyloid-beta and tau pathologies. It rescued episodic memory impairment. And it markedly reduced the mortality rate of the treated animals.
Prevention. Not just treatment.
This is what led Dr. Iqbal to describe P21 as a compound that can "shift the balance from neurodegeneration to neural regeneration." In his 2024 review published in Cytoskeleton, he reaffirmed that development of compounds like P021 represents a novel and promising therapeutic approach for Alzheimer disease and related neurodegenerative conditions.
Neuroprotection against oxidative stress
Beyond growing new neurons and clearing pathological proteins, P21 demonstrated neuroprotective effects against oxidative stress and apoptosis. These are two of the most common mechanisms through which neurons are damaged and lost in aging and neurodegenerative conditions.
Oxidative stress occurs when reactive oxygen species overwhelm the brain's antioxidant defenses. Apoptosis is programmed cell death. Both are accelerated in aging brains and dramatically elevated in conditions like Alzheimer disease, Parkinson disease, and traumatic brain injury. P21's ability to protect against both suggests a broad neuroprotective profile that extends beyond any single disease mechanism.
Synaptic plasticity and dendritic health
One of the most important findings relates to synaptic and dendritic function. In 3xTg-AD mice, P21 rescued deficits in dendritic morphology and synaptic transmission. It promoted the formation of new dendritic spines, the tiny protrusions on neurons where synaptic connections form, and reversed cognitive impairment that had already developed.
This matters because cognitive function depends not just on having enough neurons, but on those neurons being richly connected to each other. The density and health of dendritic spines is one of the strongest correlates of cognitive performance. P21 addresses both sides of the equation, creating new neurons and strengthening the connections between them.
Regenerative medicine potential
By promoting the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, P21 opens possibilities beyond Alzheimer disease. Researchers have speculated about applications in spinal cord injuries, stroke recovery, and other conditions characterized by neuronal damage. The 2024 study by Mottolese and colleagues expanded P21 research into CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder, a severe epileptic encephalopathy. While results in the knockout mouse model were mixed, the in vitro results showed that P21 treatment restored cell proliferation, survival, and neuronal maturation in CDKL5-knockout cells. This suggests the neurogenic properties of P21 may have applications across multiple neurological conditions.
P21 research protocols and dosing
Establishing appropriate protocols for P21 requires understanding that all dosing data comes from animal studies and anecdotal reports from the research community. No human clinical trials have established definitive dosing guidelines. That said, the available information from published research and experienced researchers provides a reasonable framework.
Preclinical dosing from published studies
In the published rodent studies, P21 was typically administered intraperitoneally or subcutaneously at doses ranging from 0.1 to 1 mg per kilogram of body weight daily. The most commonly used effective dose across multiple studies was 0.1 mg per kilogram daily. At this dose, robust effects on neurogenesis, synaptic markers, and cognitive function were consistently observed.
Higher doses of 0.5 to 1.0 mg per kilogram did not appear to provide substantially greater benefits, suggesting a plateau in the dose-response relationship. This is an important detail. More is not always better with P21.
Oral administration was also explored, leveraging P21's impressive stability in gastric environments. The peptide demonstrates approximately 90% stability in gastric juice and greater than 97% stability in intestinal fluid at 37 degrees Celsius, with a plasma half-life exceeding 3 hours. For oral delivery, doses were generally higher, ranging from 1 to 5 mg per kilogram, to account for potential losses during digestion and absorption.
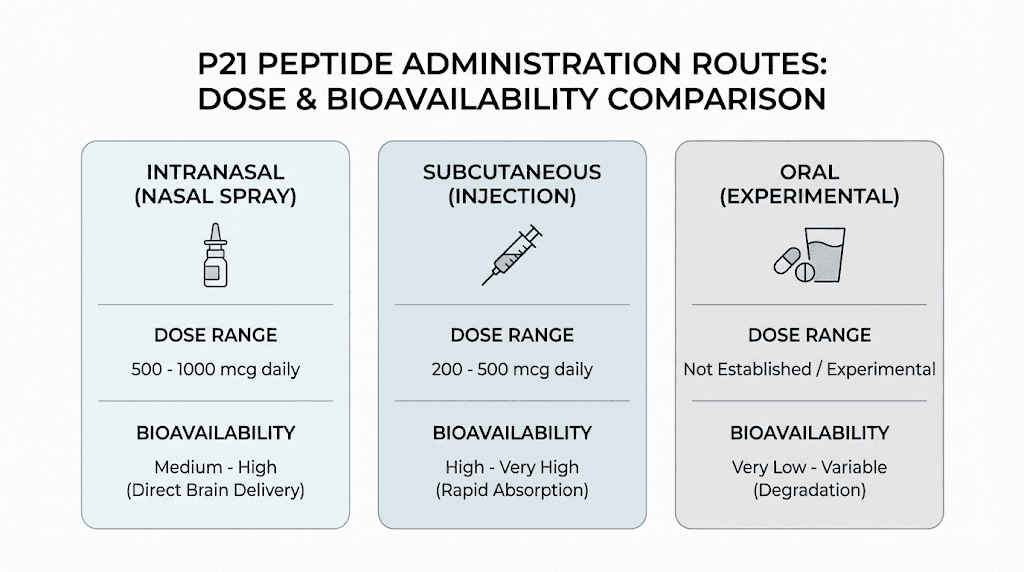
Subcutaneous protocol
According to the International Peptide Society's guidelines, subcutaneous administration of P21 typically follows a protocol of 100 to 500 micrograms daily for 4 to 6 weeks. Many researchers start at the lower end.
Conservative starting protocol:
Weeks 1 through 3: 100 to 250 mcg subcutaneously, once daily
Weeks 4 through 6: Maintain or increase to 250 to 500 mcg based on response
Cycle length: 4 to 6 weeks on, followed by a break to assess lasting effects
One documented protocol involved reconstituting a 5 mg vial with 2.5 mL of bacteriostatic water, then administering 25 IU daily for a 10-day course. This worked out to approximately 500 mcg per day.
For reconstitution, standard peptide handling practices apply. Use bacteriostatic water, inject along the wall of the vial rather than directly onto the lyophilized powder, and store the reconstituted solution in the refrigerator. The SeekPeptides reconstitution calculator can help determine exact concentrations based on the amount of water added.
Intranasal protocol
The intranasal route has gained significant attention in the P21 research community. The top peptide chemist at the now-defunct Ceretropic, a pioneering nootropic vendor, insisted on intranasal administration over subcutaneous injection. His reasoning was practical. He reported being unable to feel increased cognition with subcutaneous dosing, while intranasal delivery produced noticeable effects.
The intranasal route offers direct nose-to-brain transport via olfactory and trigeminal nerve pathways. This bypasses the blood-brain barrier entirely, as well as hepatic first-pass metabolism. Lower doses achieve equivalent central nervous system effects compared to parenteral routes.
Intranasal dosing guidelines:
Starting dose: 500 mcg to 1 mg daily
Maintenance dose: 1 mg daily
Advanced dose: 2 to 4 mg daily for acute cognitive effects
Individual variation: Some researchers find 500 mcg is more than sufficient
The recommendation is to start low and increase gradually. P21 has been described as having a "highly cumulative effect that rewards low, slow dosing." Its full manifestation of effects may not appear until after roughly one month of continual use. Patience matters with this compound.
Oral administration
P21's oral bioavailability is one of its most attractive features from a practical standpoint. Most peptides degrade rapidly in the digestive tract, requiring injection for effective delivery. P21 bucks this trend with its exceptional gastric stability.
Oral protocols from the research literature used doses in the range of 1 to 5 mg per kilogram in animal models. Translating this to human-equivalent doses is not straightforward due to differences in metabolism, body surface area, and pharmacokinetics between species. Researchers who have explored oral P21 have generally used higher absolute doses than those used intranasally or subcutaneously.
P21 versus other nootropic peptides
P21 does not exist in isolation. The peptide research landscape includes several other compounds with nootropic and neuroprotective properties. Understanding how P21 compares helps researchers make informed decisions about which compounds align with their specific research goals.
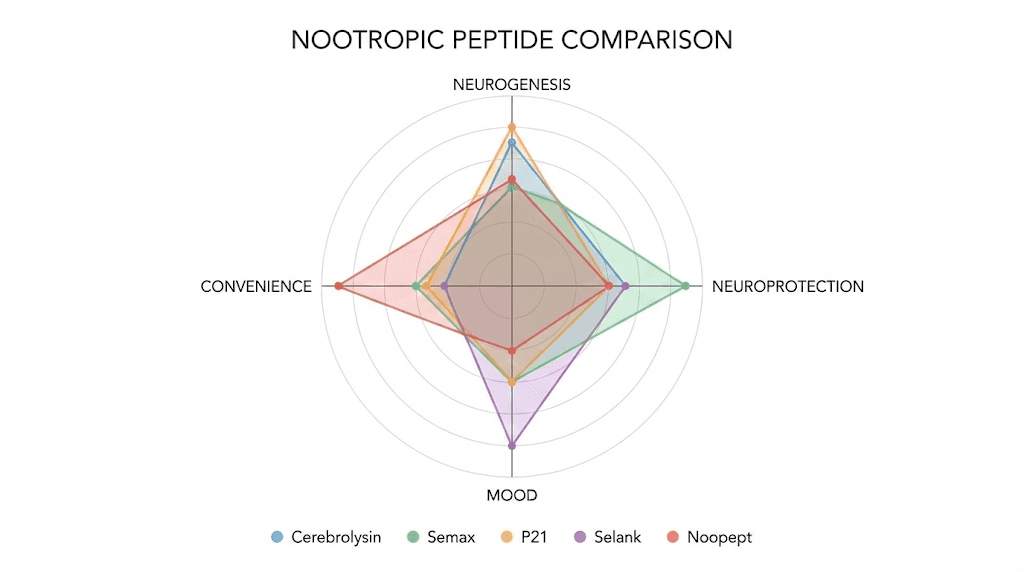
P21 versus Cerebrolysin
This comparison is the most natural starting point since P21 was literally derived from Cerebrolysin. The relationship has been described as "an orchestra versus a soloist." Cerebrolysin provides a complex, holistic approach, delivering a mixture of BDNF, GDNF, NGF, CNTF, and numerous other neurotrophic peptides and amino acids. P21 delivers a precise, focused effect through a single defined pathway.
In user experience reports, Cerebrolysin was described as improving cognition "in almost every manner with evenly distributed benefits." P21 produced similar improvements but localized in fewer cognitive domains. For pure neurogenesis and tau-protective effects, P21 may actually be more potent on a per-pathway basis. For broad-spectrum neural support, Cerebrolysin covers more ground.
There is also a practical consideration. Cerebrolysin requires intramuscular or intravenous injection and typically involves cycles of 5 to 20 daily injections. P21 can be administered intranasally or even orally. This makes P21 considerably more convenient for sustained daily use.
A critical advantage of P21 over Cerebrolysin involves immunogenicity. Cerebrolysin, being a porcine-derived biological, has been noted to potentially promote the production of auto-antibodies against CNTF. While initially effective, this benefit may diminish over time as the immune system fights the very compound being administered. P21 avoids this entirely.
P21 versus Semax
Semax is an analogue of adrenocorticotropic hormone, or ACTH, designed in Russia where it has been on the official List of Vital and Essential Drugs since 2011. It is approved there for stroke, memory disorders, ulcers, optic nerve disease, and immune system support. Unlike P21, Semax has been tested and used clinically in humans, giving it a significantly larger safety and efficacy database.
Both peptides increase BDNF levels, but through different mechanisms. P21 works through LIF inhibition and CNTF pathway modulation. Semax works through ACTH-receptor-mediated pathways, affecting serotonergic and dopaminergic systems. The result is that while both enhance cognition, they produce different cognitive profiles. Semax tends to improve attention, memory retention, and mood, with documented anxiolytic and antidepressant effects. P21 focuses more specifically on neurogenesis and neuroprotection.
Semax also has one practical advantage: established clinical use. It has been through human testing. P21 has not. For researchers prioritizing compounds with human data behind them, Semax is the safer bet.
P21 versus Selank
Selank is another Russian-developed peptide, this one based on the structure of tuftsin, an immunomodulatory peptide. Selank primarily offers anxiolytic and nootropic properties. Where P21 excels at neurogenesis, Selank excels at reducing anxiety while simultaneously enhancing cognitive function.
The two peptides target different aspects of brain health and could be considered complementary rather than competitive.
P21 versus Adamax
Adamax shares interesting similarities with P21. Both incorporate adamantane modifications, both upregulate BDNF, and both were developed to enhance neurotrophin signaling with improved pharmacokinetic profiles. Adamax increases BDNF levels and improves the sensitivity of TrkB receptors in the hippocampus, which is complementary to P21's mechanism of increasing BDNF expression itself.
Biohackers and researchers have noted that combining the two could produce synergistic effects on BDNF-mediated neurogenesis, though this combination has not been studied formally.
P21 versus Dihexa
Dihexa is sometimes mentioned alongside P21 as a cognitive enhancement peptide. Dihexa works through hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor c-Met, promoting synaptogenesis and dendritic branching. It has been described as being millions of times more potent than BDNF at promoting synaptic connections, though this comparison requires context as the peptides work through entirely different mechanisms. Where P21 focuses on growing new neurons, Dihexa focuses on strengthening connections between existing ones.
Comparison table
Feature | P21 | Cerebrolysin | Semax | Selank | Adamax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Origin | Synthetic CNTF mimetic | Porcine brain-derived | Synthetic ACTH analogue | Synthetic tuftsin analogue | Synthetic adamantane peptide |
Primary mechanism | LIF inhibition, BDNF upregulation | Broad neurotrophic support | Serotonin/dopamine modulation | Anxiolytic, immunomodulation | TrkB sensitization, BDNF |
Neurogenesis | Strong | Moderate | Moderate | Mild | Moderate |
Tau protection | Strong | Some evidence | Limited data | Not studied | Not studied |
Administration | Intranasal, SubQ, Oral | IM/IV injection | Intranasal | Intranasal | Intranasal, SubQ |
Human clinical data | None | Extensive | Approved in Russia | Approved in Russia | None |
Immunogenicity risk | Very low | Moderate (anti-CNTF antibodies) | Low | Low | Low |
Best for | Neurogenesis, neuroprotection | Broad neural recovery | Focus, memory, mood | Anxiety, calm focus | BDNF/TrkB optimization |
Stacking P21 with other peptides
For researchers interested in combining P21 with other compounds, several stacking strategies have emerged from the nootropic community. While none of these combinations have been studied in formal research settings, the theoretical rationale based on complementary mechanisms is sound.
P21 plus Semax stack
This is the most frequently discussed combination. The peptide chemist who originally developed the commercial form of P21 stated that it "combines very well with Semax." The rationale is straightforward. P21 primarily drives neurogenesis through LIF inhibition and BDNF upregulation. Semax modulates serotonergic and dopaminergic systems while also increasing BDNF through a different pathway. Together, they may provide both structural brain changes from new neuron growth and immediate neurotransmitter-level cognitive enhancement.
Reported protocol:
P21: 500 mcg to 1 mg intranasal, morning
Semax: 200 to 600 mcg intranasal, morning or split morning and afternoon
Duration: 4 to 6 weeks
Both peptides reward low, slow dosing and have cumulative effects. Starting at the lower ends and gradually increasing is the consistent recommendation from experienced researchers.
P21 plus Selank stack
For researchers dealing with anxiety alongside cognitive goals, adding Selank to P21 could address both concerns simultaneously. Selank provides anxiolytic effects without sedation, while P21 handles the neurogenic heavy lifting. The two work through entirely different pathways and are unlikely to interfere with each other.
P21 plus Adamax stack
Adamax and P21 share structural similarities, both incorporating adamantane modifications, and both increase BDNF through complementary mechanisms. P21 increases BDNF expression at the transcriptional level. Adamax increases the sensitivity of TrkB receptors to BDNF. The theoretical result is more BDNF being produced and the brain being more responsive to it.
This combination has garnered attention specifically because of the dual approach to BDNF optimization. Researchers who pursue this stack typically use modest doses of each to avoid excessive BDNF-pathway stimulation.
P21 plus BPC-157 stack
While BPC-157 is primarily known for its healing properties in connective tissue, it also demonstrates neurotrophic effects. BPC-157 has shown interactions with the dopamine system and potential for protecting against excitotoxicity. Combining it with P21 could provide complementary neuroprotective coverage, with P21 handling BDNF-mediated neurogenesis and BPC-157 providing broad protective and reparative effects through different signaling pathways.
Important stacking considerations
Combining multiple peptides introduces variables that are difficult to control. Without formal drug interaction studies, all stacking recommendations are based on theoretical mechanism compatibility and anecdotal reports. Researchers should start with single compounds to establish baseline responses before adding additional peptides. Keep detailed logs of dosing, timing, and subjective effects. And consult with a qualified healthcare professional before implementing any research protocol.
The SeekPeptides stacking calculator can help plan multi-peptide protocols with appropriate dosing considerations.
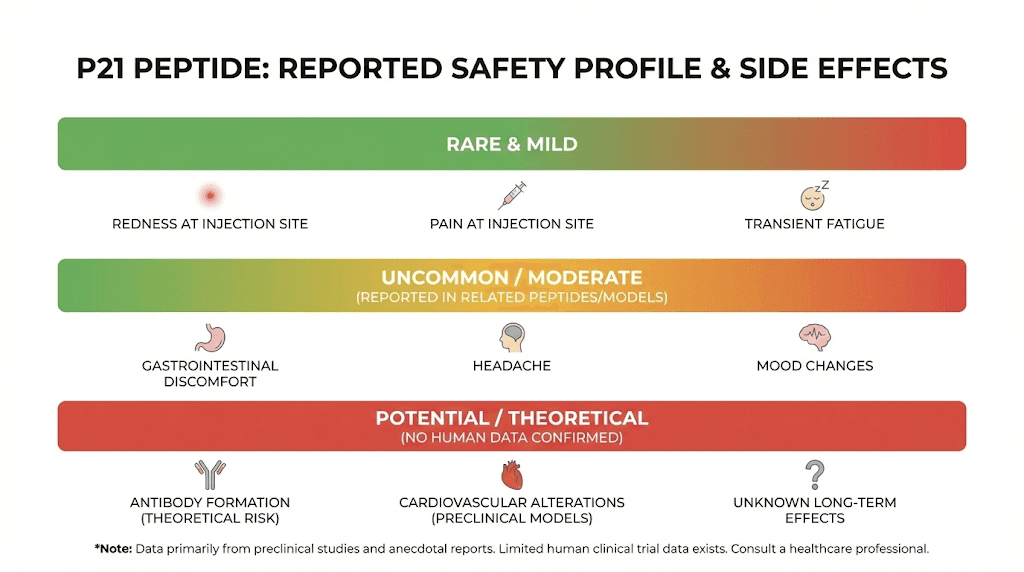
P21 peptide side effects and safety profile
Understanding the safety profile of P21 requires acknowledging a fundamental limitation. There are no published human clinical trials. Everything known about P21 safety comes from animal studies and anecdotal reports from the research community. That said, the available evidence paints a relatively favorable picture.
Reported side effects
Side effects from P21 are described as rare and generally mild. The most commonly reported include:
Injection site reactions: For subcutaneous administration, some redness and mild pain at the injection site may occur. This is common to virtually all injectable peptides and is not specific to P21.
Drowsiness: Some researchers have reported needing to take a nap after administering P21, particularly at higher doses or when first starting the compound. This effect tends to diminish with continued use.
Mild mood changes: Temporary mild depression or mood fluctuation has been reported by some users, which they attribute to the rapid increase in BDNF levels. The brain may need time to adapt to elevated neurotrophin signaling.
Gastrointestinal disturbances: Mild nausea, stomach cramps, or diarrhea have been occasionally reported, particularly with oral administration.
Headache and fatigue: Some researchers note transient headache or fatigue, especially during the first few days of use.
Safety advantages over parent compounds
P21 was specifically engineered to avoid the serious side effects associated with full-length CNTF. Clinical trials using recombinant human CNTF in ALS patients produced significant adverse effects including anorexia, severe cramps, muscle pain, and substantial weight loss. None of these effects have been reported with P21.
The key safety advantage lies in immunogenicity. Full-length CNTF triggers the production of anti-CNTF antibodies when administered systemically. Cerebrolysin, while generally well-tolerated, has also been associated with potential auto-antibody formation against CNTF. P21, being just four amino acids with an adamantane modification, is too small to provoke a significant immune response. No immune reaction to P21 has been documented to date.
Potential concerns and unknowns
Endogenous CNTF interference: There is a theoretical concern that excessive P21 use could interfere with some neuroprotective functions of endogenous CNTF. If the peptide's LIF-inhibiting effects are too pronounced, it could alter the normal balance of neurotrophic signaling in ways that are not yet characterized.
Long-term effects unknown: The longest animal studies ran for several months. Nobody knows what happens with years of P21 use. Given that the peptide promotes neurogenesis, questions about uncontrolled cellular proliferation are reasonable, though no evidence of abnormal growth has been observed in any published study.
Antibody formation possibility: While no immune reaction has been documented, one review of peptide and oligonucleotide drugs targeting abnormal tau suggested that antibody formation against P021 is a theoretical possibility. This remains purely speculative at this point.
Special populations: The International Peptide Society notes that individuals with active malignancies, epilepsy, pregnancy and lactation, and autoimmune conditions require additional safety considerations. These are precautionary recommendations based on the absence of safety data rather than documented adverse events.
Comparison to overall peptide safety
In the context of peptide safety generally, P21 appears to sit on the milder end of the spectrum. It does not directly manipulate growth hormone axes like growth hormone secretagogues. It does not affect metabolic hormones like weight loss peptides. Its primary effects are localized to BDNF-mediated neurotrophin signaling, which, while powerful, is a relatively targeted mechanism. Still, the absence of human clinical data means that true safety characterization awaits further research.
How P21 crosses the blood-brain barrier
One of P21's most remarkable properties is its ability to reach the brain after peripheral administration. Most peptides cannot do this. The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective membrane that keeps the vast majority of circulating molecules out of the central nervous system. Large proteins like full-length CNTF and BDNF cannot cross it effectively, which has been a major obstacle in developing neurotrophic therapies.
P21 overcomes this barrier through two design features. First, its small size. At just four amino acids plus the adamantane modification, it has a molecular weight of 578.3 daltons. This places it well below the approximately 500-dalton threshold that typically limits passive diffusion across the blood-brain barrier. Second, the adamantane moiety increases lipophilicity, the affinity for fatty tissue. Since the blood-brain barrier is composed primarily of lipid-rich cell membranes, a more lipophilic molecule has an easier time slipping through.
Additionally, the adamantylation protects P21 from enzymatic degradation. Exopeptidases in the blood would rapidly chew through an unmodified tetrapeptide. The adamantane group blocks this degradation, giving P21 enough circulating half-life to reach the brain in pharmacologically active concentrations.
For intranasal administration, the blood-brain barrier becomes largely irrelevant. The intranasal route provides direct access to the central nervous system through olfactory and trigeminal nerve pathways. This is why many researchers prefer nasal delivery for P21. It gets to the brain faster, in higher concentrations, and at lower total doses than subcutaneous injection.
The oral bioavailability of P21 is equally impressive. With approximately 90% stability in gastric juice and over 97% stability in intestinal fluid, the peptide survives the digestive tract far better than almost any other oral peptide. Its plasma half-life exceeds 3 hours, providing a reasonable window for brain penetration after oral dosing. This combination of oral stability and blood-brain barrier permeability makes P21 unusually versatile in terms of administration options.
P21 and Alzheimer disease: the detailed science
Alzheimer disease is defined by two pathological hallmarks: extracellular amyloid-beta plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein. Both contribute to neurodegeneration, synaptic loss, and progressive cognitive decline. P21 targets both pathologies through a single upstream mechanism, making it unique among investigational Alzheimer therapies.
The tau connection
Tau is a microtubule-associated protein that normally stabilizes the structural framework of neurons. When tau becomes abnormally hyperphosphorylated, it detaches from microtubules and aggregates into paired helical filaments, which form the neurofibrillary tangles characteristic of Alzheimer disease. These tangles are toxic to neurons and are strongly correlated with cognitive decline.
P21 addresses tau pathology by increasing BDNF expression, which activates the TrkB-PI3K-Akt signaling cascade. Akt phosphorylates GSK-3-beta at Serine 9, which inhibits this kinase. Since GSK-3-beta is one of the primary kinases responsible for tau hyperphosphorylation, inhibiting it prevents the pathological modification that leads to tangle formation.
In the 3xTg-AD mouse model, P21 treatment produced significant reductions in hyperphosphorylated tau at multiple Alzheimer-associated phosphorylation sites. This was not a marginal effect. The reductions were statistically robust and accompanied by functional improvements in cognition.
The amyloid-beta connection
P21 also affected amyloid-beta pathology, though by a somewhat different route. The treatment significantly decreased levels of soluble amyloid-beta and showed a trend toward reduction in plaque load in the hippocampal CA1 region. The mechanism appears to be secondary to the BDNF-GSK-3-beta pathway, as GSK-3-beta is also involved in amyloid precursor protein processing.
The fact that a single compound can address both hallmark pathologies of Alzheimer disease through one upstream mechanism is what makes P21 particularly interesting. Most Alzheimer drug candidates target either amyloid or tau, not both. P21's ability to hit both targets simultaneously, while also promoting neurogenesis to replace lost neurons, represents a truly disease-modifying approach rather than merely symptomatic treatment.
Prevention versus treatment
One of the most compelling findings from the 3xTg-AD studies was that P21 worked best when initiated early, during the synaptic compensation period before severe neurodegeneration had occurred. When treatment began at this stage, P21 prevented neurodegeneration, prevented amyloid-beta and tau pathologies, rescued episodic memory, and markedly reduced mortality.
This suggests that P21 may be most valuable as a preventive intervention rather than a treatment for advanced disease. For longevity-focused researchers, this has obvious implications. Preserving brain health before decline begins may be more effective than trying to restore it afterward.
Clinical development status
P021 is currently under investigation by Phanes Biotech, a company co-founded by Dr. Khalid Iqbal, who serves as Chief Scientific Officer. The company is working to develop P021 as a therapeutic drug for Alzheimer disease and related neurodegenerative conditions. As of the latest available information, no Phase I, II, or III clinical trials have been published, meaning the compound remains in preclinical development. The path from promising animal data to an approved human therapy is long and uncertain, but the scientific foundation laid by over a decade of research is substantial.
Practical guide to P21 reconstitution and storage
Handling P21 correctly ensures that the peptide retains its potency and delivers consistent results. While P21 is more stable than many peptides, proper storage and reconstitution technique still matter.
Reconstitution
P21 typically comes as a lyophilized (freeze-dried) powder in vials of 5 mg or 10 mg. To reconstitute:
Step 1: Allow the vial to reach room temperature naturally. Do not heat it.
Step 2: Using a sterile syringe, draw up the desired amount of bacteriostatic water. For a 5 mg vial, common reconstitution volumes include:
1 mL bacteriostatic water = 5 mg per mL (5000 mcg per mL)
2 mL bacteriostatic water = 2.5 mg per mL (2500 mcg per mL)
2.5 mL bacteriostatic water = 2 mg per mL (2000 mcg per mL)
Step 3: Inject the bacteriostatic water slowly along the inside wall of the vial. Do not spray it directly onto the lyophilized powder. Allow it to trickle down gently.
Step 4: Swirl the vial gently until the powder is fully dissolved. Do not shake vigorously, as this can damage the peptide.
Use the SeekPeptides peptide calculator to determine exactly how many units to draw for your target dose based on your reconstitution volume.
Storage
Before reconstitution: Lyophilized P21 should be stored in a freezer at minus 20 degrees Celsius for long-term storage, or in a refrigerator at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius for shorter periods. Properly stored lyophilized peptide can maintain potency for months to years.
After reconstitution: Store in the refrigerator at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius. Reconstituted peptides generally maintain stability for several weeks when stored properly, though using the solution within 2 to 4 weeks is recommended for optimal potency. The bacteriostatic water contains a preservative (benzyl alcohol) that helps prevent microbial contamination, but it does not prevent peptide degradation indefinitely.
For nasal spray preparation: Researchers preparing P21 for intranasal use typically reconstitute into a sterile nasal spray bottle. The concentration should be calculated so that each spray delivers the desired dose. Nasal spray preparations may have shorter stability than vial-stored solutions due to the delivery mechanism and potential for contamination.
Keep P21 away from direct light, heat, and repeated temperature fluctuations. Proper peptide storage is one of the simplest ways to ensure consistent research results.
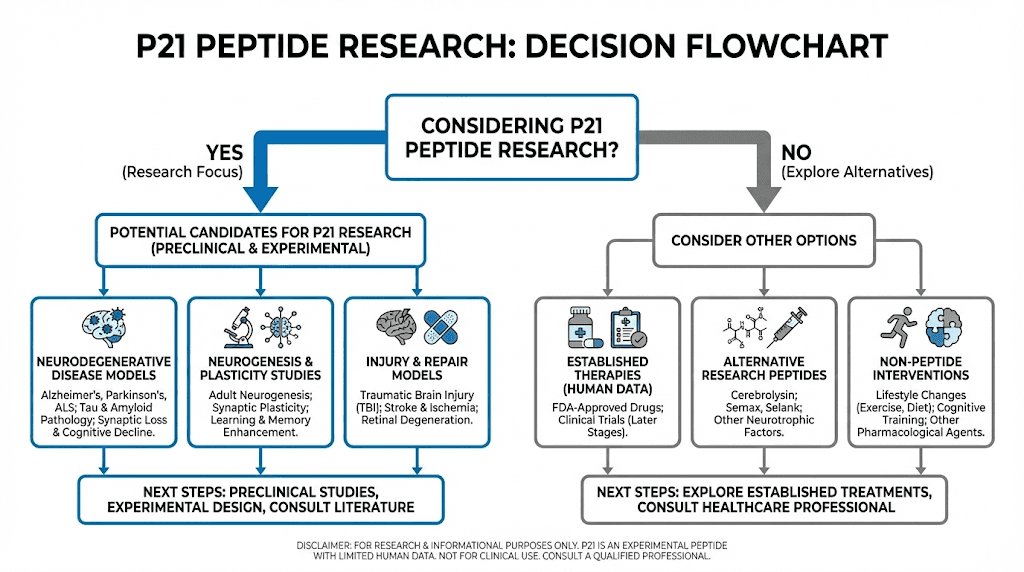
Who should consider P21 research?
P21 is not for everyone. Its research-only status, the absence of human clinical trial data, and its relatively niche mechanism of action mean it appeals to a specific subset of the peptide research community. That said, certain research goals align particularly well with what P21 offers.
Cognitive optimization researchers
Those interested in neurogenesis as a pathway to enhanced cognitive function will find P21 compelling. The peptide directly promotes the growth of new neurons in the hippocampus, the brain region most critical for memory and learning. For researchers who have already explored conventional nootropics and want to investigate structural brain changes rather than just neurotransmitter modulation, P21 represents a fundamentally different approach to cognitive enhancement.
Longevity and anti-aging researchers
Age-related hippocampal volume loss is one of the most consistent biomarkers of brain aging. If P21 can promote neurogenesis in the aging brain, it could address one of the core mechanisms of cognitive decline. Researchers focused on anti-aging protocols and brain health preservation may find P21's neuroprotective and neurogenic properties highly relevant to their work.
Neuroprotection researchers
The dual ability to reduce tau pathology and amyloid-beta accumulation while promoting new neuron growth makes P21 interesting for anyone researching neuroprotection. This includes researchers studying traumatic brain injury recovery, stroke rehabilitation, and neurodegenerative disease mechanisms.
Nootropic stack researchers
For researchers who already use nootropic peptides like Semax, Selank, or Cerebrolysin, P21 offers a complementary mechanism that does not duplicate what those compounds already do. Its specific focus on CNTF-pathway neurogenesis fills a gap that other nootropics do not directly address. The peptide stacking community has shown particular interest in P21 for this reason.
Who should not use P21
Given the lack of human clinical data, several populations should exercise extreme caution or avoid P21 entirely. These include pregnant or breastfeeding individuals, those with active cancer or a history of cancer, given that neurogenesis involves cellular proliferation, individuals with epilepsy or seizure disorders, those with autoimmune conditions, and anyone under 25 whose brain is still developing naturally.
This is not a beginner peptide. Researchers new to peptides should establish familiarity with more extensively studied compounds, build proper handling and dosing skills, and understand their individual responses to neurotrophin modulation before exploring P21.
P21 frequently asked questions
What exactly is P21 peptide?
P21, also known as P021 or Ac-DGGLAG-NH2, is a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from amino acid residues 148 to 151 of ciliary neurotrophic factor. It was developed by Dr. Khalid Iqbal's research team and includes an adamantane modification that improves blood-brain barrier penetration and resistance to enzymatic degradation. Its molecular weight is 578.3 daltons.
Has P21 been tested in humans?
No. As of the latest available information, P21 has not undergone published Phase I, II, or III clinical trials in humans. All efficacy and safety data comes from in vitro and in vivo animal studies. Phanes Biotech is reportedly working toward clinical development, but no human trial results have been published.
How does P21 differ from Cerebrolysin?
P21 was derived from Cerebrolysin through reverse engineering. While Cerebrolysin is a complex mixture of hundreds of peptides and amino acids from porcine brain tissue, P21 is a single defined compound targeting one specific pathway, LIF inhibition leading to BDNF upregulation. Cerebrolysin provides broad neurological support, P21 provides targeted neurogenesis and tau protection. P21 also avoids the immunogenicity risks associated with Cerebrolysin.
Is intranasal or subcutaneous P21 better?
Experienced researchers generally favor intranasal administration for P21. The intranasal route provides direct nose-to-brain transport, bypassing the blood-brain barrier entirely. Lower doses achieve equivalent central nervous system effects compared to subcutaneous injection. The original peptide chemist behind commercial P21 insisted on intranasal delivery based on his inability to detect cognitive effects from subcutaneous dosing.
How long does P21 take to work?
P21 has been described as having a "highly cumulative effect that rewards low, slow dosing." Full manifestation of effects may not appear until after approximately one month of continual use. This makes sense given that neurogenesis is a gradual process, requiring new neurons to be born, mature, and integrate into existing circuits.
Can I stack P21 with Semax?
This is the most commonly discussed P21 stack. The two peptides work through different mechanisms (P21 via CNTF/LIF pathway, Semax via ACTH-receptor pathways) and both increase BDNF, potentially creating complementary effects. The original P21 developer stated it combines well with Semax. Start with low doses of each and build gradually.
What are the main side effects of P21?
Reported side effects are rare and mild. They include drowsiness especially when first starting, mild mood changes potentially related to BDNF fluctuations, injection site reactions with subcutaneous use, mild gastrointestinal disturbance with oral use, and occasional headache or fatigue. P21 does not produce the severe side effects seen with full-length CNTF such as anorexia, weight loss, or muscle pain. See our peptide safety guide for broader context on peptide side effect management.
Is P21 legal?
P21 is sold as a research chemical. It is not FDA-approved for human use. Peptide legality varies by jurisdiction, and researchers should familiarize themselves with local regulations before purchasing or using research peptides.
How should I store P21?
Lyophilized P21 should be stored frozen at minus 20 degrees Celsius for long-term storage. After reconstitution with bacteriostatic water, store refrigerated at 2 to 8 degrees Celsius and use within 2 to 4 weeks. Keep away from light, heat, and temperature fluctuations. See the complete peptide storage guide for detailed recommendations.
Does P21 work for conditions other than Alzheimer disease?
Preliminary research suggests broader applications. A 2024 study explored P21 in CDKL5 Deficiency Disorder with mixed but partially promising results. The neurogenic and neuroprotective mechanisms could theoretically benefit conditions involving neuronal loss including stroke, traumatic brain injury, and other neurodegenerative diseases. However, direct evidence outside Alzheimer models and normal cognition studies is still very limited.
The future of P21 research
P21 sits at an interesting crossroads. The preclinical evidence is robust and consistent. Over a decade of published research from a respected laboratory demonstrates clear benefits for neurogenesis, cognitive function, and Alzheimer pathology in animal models. Yet it remains without human clinical trial data, an essential step before its potential can be fully realized.
Several developments could shape P21's future trajectory. Phanes Biotech's efforts to bring P021 into clinical development represent the most direct path to human data. If the compound enters and progresses through clinical trials, it would provide the safety and efficacy information that the research community currently lacks.
The expansion into non-Alzheimer applications, as seen in the 2024 CDKL5 study, suggests that researchers are beginning to explore P21's broader potential. If neurogenesis-promoting effects are confirmed across multiple pathological contexts, P21 could become relevant to a much wider range of neurological conditions.
The nootropic research community continues to drive grassroots exploration of P21. While anecdotal reports are not a substitute for clinical trials, the collective experience of researchers using P21 provides valuable observational data about dosing, effects, and tolerability that formal studies have not yet generated.
For SeekPeptides members interested in cognitive optimization, P21 represents one of the most scientifically grounded approaches to neurogenesis currently available. The platform provides detailed protocol guides, dosing calculators, and community insights that help researchers navigate compounds like P21 with confidence and safety.
Whether P21 ultimately becomes a clinical therapy or remains a research tool, its contribution to our understanding of neurogenesis and neuroprotection is already significant. The work of Dr. Khalid Iqbal and his team has demonstrated that targeted peptide engineering can achieve what full-length proteins cannot, crossing the blood-brain barrier, avoiding immune reactions, and delivering precise neurogenic effects where they are needed most. For researchers willing to work at the frontier of peptide science, P21 offers a compelling and well-characterized compound to investigate.
For those serious about optimizing their neurological research protocols, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resource available, with evidence-based guides, proven protocols, and a community of thousands who have navigated these exact questions.
External resources
Alzheimer's Drug Discovery Foundation - P021 Cognitive Vitality Report
ScienceDirect - Neurotrophic peptides incorporating adamantane improve learning and memory
PubMed Central - Effects of CNTF small-molecule peptide mimetic in CDKL5 deficiency disorder
Wiley - Tau and Alzheimer disease: Past, present and future (Iqbal, 2024)
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your neurons stay healthy, your BDNF stay elevated, and your cognition stay sharp. Join us here.



