Jan 27, 2026
Seven times more potent than BDNF at promoting synaptogenesis. That is what the research shows for Dihexa.
Not twice as potent. Not three times. Seven times more powerful than the brain growth factor your neurons naturally produce to form new connections. This single data point explains why Dihexa has captured the attention of researchers studying cognitive enhancement, memory formation, and neurodegenerative conditions.
The peptide emerged from Washington State University laboratories where scientists were searching for something specific. They wanted an orally active compound that could cross the blood-brain barrier and enhance cognitive function without the limitations of earlier angiotensin IV analogs. What they created was N-hexanoic-Tyr-Ile-(6) aminohexanoic amide, a small modified peptide with remarkable properties.
Most nootropic peptides work by tweaking neurotransmitter levels. They increase dopamine here, boost serotonin there. Useful approaches, but fundamentally limited. Dihexa operates differently. It promotes the actual structural remodeling of neural circuits, encouraging neurons to sprout new dendritic spines and form fresh synaptic connections. The distinction matters enormously for understanding both potential benefits and risks.
SeekPeptides has compiled this comprehensive analysis drawing from published research, preclinical studies, and documented observations. We will examine exactly how Dihexa works, what the science actually demonstrates, how it compares to other cognitive peptides, and the important safety considerations that anyone researching this compound must understand.
Understanding the science behind Dihexa
Dihexa belongs to a class of compounds derived from angiotensin IV. The original angiotensin IV peptide showed interesting cognitive effects in animal studies but had significant limitations. It degraded rapidly in the bloodstream. It could not effectively cross the blood-brain barrier. Its effects were weak and inconsistent.
Researchers modified the molecular structure systematically. They replaced certain amino acids. They added protective chemical groups. They optimized the compound for stability and brain penetration. The result was Dihexa, a peptide that retained the cognitive-enhancing properties of angiotensin IV while overcoming its practical limitations.
The chemical name, N-hexanoic-Tyr-Ile-(6) aminohexanoic amide, describes the specific modifications made to create this stable, bioavailable compound. Understanding these structural details helps explain why Dihexa behaves differently from its parent molecule and from other peptides in general.
The HGF/c-Met pathway explained
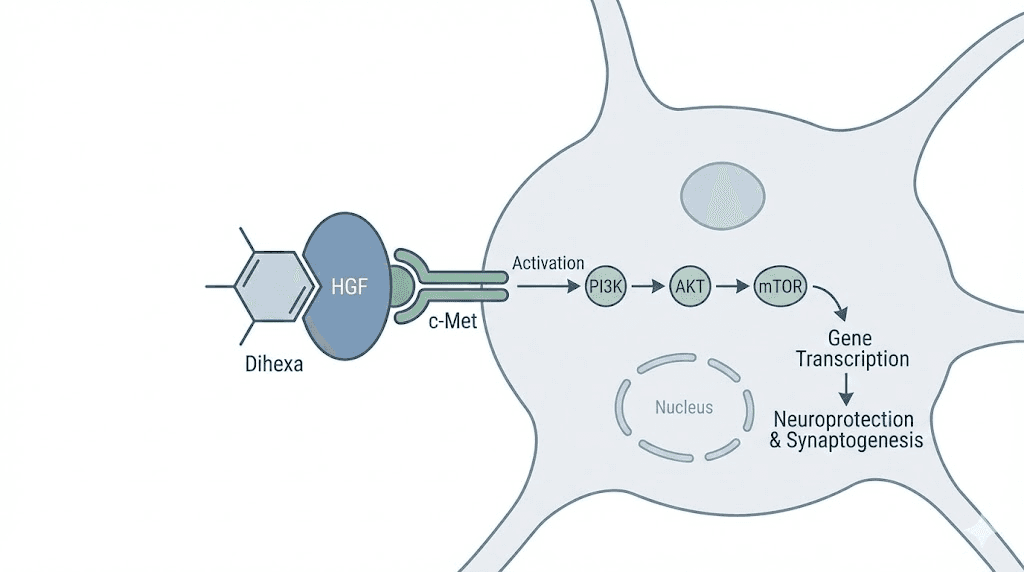
Dihexa exerts its effects primarily through the hepatocyte growth factor system. HGF is a large protein that plays crucial roles in tissue development, wound healing, and importantly, brain function. The receptor for HGF, called c-Met, sits on the surface of many cell types including neurons.
When HGF binds to c-Met, it triggers a cascade of intracellular signals. These signals promote cell survival, encourage cell migration, and stimulate growth. In neurons specifically, this pathway supports the formation of new synaptic connections and the maintenance of existing neural circuits.
Dihexa binds to HGF with remarkably high affinity. Research shows a binding constant of approximately 65 picomolar, which represents extremely tight binding. But Dihexa does not simply block HGF. Instead, it forms a complex with HGF that actually enhances c-Met activation. Think of it as supercharging the natural growth factor signaling system.
This mechanism distinguishes Dihexa from compounds that work by increasing neurotransmitter levels or blocking enzyme activity. By potentiating growth factor signaling, Dihexa promotes structural plasticity, the actual physical remodeling of neural connections that underlies learning and memory.
Why synaptogenesis matters for cognition
Synapses are the connection points between neurons. Information flows through these specialized junctions as electrical signals convert to chemical messages and back again. The density and strength of synaptic connections directly influences cognitive capacity.
Learning involves forming new synapses. Memory consolidation requires strengthening existing connections. Cognitive decline often correlates with synaptic loss. The brain ability to form new synapses throughout life, a property called synaptic plasticity, determines much of cognitive resilience and adaptability.
In laboratory studies, Dihexa dramatically increased dendritic spine density. Dendritic spines are the tiny protrusions on neurons where most excitatory synapses form. After five days of treatment in hippocampal neuron cultures, spine counts nearly tripled. This represents a massive increase in potential synaptic connection points.
The hippocampus plays a central role in memory formation and spatial navigation. Damage to this region causes profound memory deficits. Compounds that enhance hippocampal synaptic density could theoretically improve memory function, which is exactly what animal studies with Dihexa have demonstrated.
What preclinical research actually shows
The evidence base for Dihexa comes entirely from animal studies and cell culture experiments. No human clinical trials have been published. Understanding this limitation is essential for accurately interpreting the research.
Studies in rats have provided the most compelling data. Researchers used several established models of cognitive impairment to test whether Dihexa could restore normal function. The results were consistently positive across multiple experimental paradigms.
Morris water maze performance
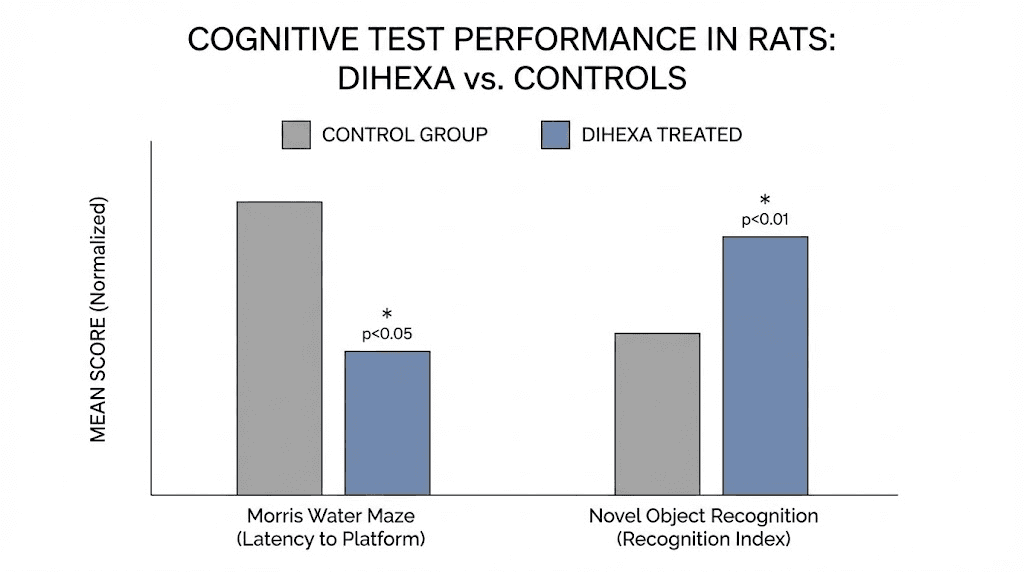
The Morris water maze tests spatial learning and memory in rodents. Animals must learn the location of a hidden platform in a pool of water, using visual cues around the room. Performance on this task depends heavily on hippocampal function.
Rats treated with scopolamine, a drug that impairs memory, showed significant deficits on the water maze. They took longer to find the platform. They made more errors. Their paths were less efficient. This models the kind of cognitive impairment seen in various neurological conditions.
Dihexa reversed these deficits. Treated animals found the platform faster. Their navigation improved. The magnitude of improvement was comparable to or better than other established cognitive enhancers tested in the same paradigm.
Importantly, an HGF antagonist called Hinge blocked Dihexa benefits when administered directly into the brain. This confirmed that Dihexa effects depend on the HGF/c-Met system, not some unrelated mechanism. The specificity of this finding strengthens confidence that the observed cognitive improvements result from enhanced growth factor signaling.
Aged rat studies
Natural aging causes cognitive decline in rats just as it does in humans. Old rats perform worse on memory tasks than young rats. Their brains show reduced synaptic density and decreased growth factor signaling.
When aged rats received Dihexa, their cognitive performance improved toward levels seen in younger animals. The effect was not complete restoration, but the improvement was statistically significant and functionally meaningful. Treated rats made fewer errors and showed better retention of learned information.
These findings suggest potential relevance for age-related cognitive decline. However, extrapolating from aged rats to aging humans requires caution. Rodent and human brains differ in important ways. Effects that appear in one species do not always translate to another.
Alzheimer disease models
Researchers have tested Dihexa in mice genetically engineered to develop Alzheimer-like pathology. The APP/PS1 mouse model accumulates amyloid plaques and shows progressive cognitive decline similar to human Alzheimer disease.
Dihexa treatment improved cognitive function in these animals. Spatial learning recovered. Memory retention improved. Neuronal cell counts in treated animals were higher than in untreated controls, suggesting neuroprotective effects against the disease process.
The research also found that Dihexa reduced inflammatory markers in the brain. Levels of TNF-alpha and IL-1beta, pro-inflammatory cytokines elevated in Alzheimer disease, decreased with treatment. This anti-inflammatory effect could contribute to neuroprotection beyond the direct synaptogenic actions.
A company called M3 Biotechnology has developed a prodrug version of Dihexa called fosgonimeton. This modified compound is currently in clinical trials for Alzheimer and Parkinson disease. The existence of an active clinical development program suggests at least some optimism about translating the animal findings to humans.
Comparing Dihexa to other cognitive peptides
The nootropic peptide field includes several established compounds. Understanding how Dihexa differs from these alternatives helps clarify its unique properties and appropriate applications.
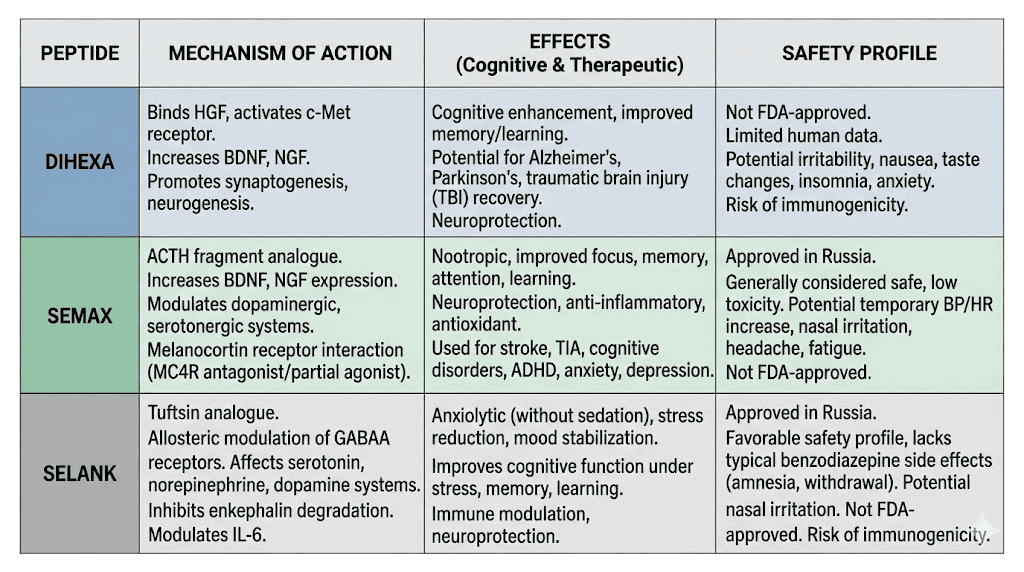
Dihexa versus Semax
Semax is a synthetic analog of ACTH, the adrenocorticotropic hormone. It has a longer history of use, particularly in Russia where it has regulatory approval for certain neurological conditions. The mechanisms and effects differ substantially from Dihexa.
Semax works primarily by increasing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and modulating dopaminergic and serotonergic neurotransmission. Its effects tend to be more immediate and acute. Users often report enhanced focus, improved attention, and faster information processing. The cognitive enhancement feels like optimization of existing capacity rather than structural change.
Dihexa by contrast promotes actual synaptogenesis through HGF/c-Met signaling. Its effects may take longer to manifest but could theoretically produce more lasting changes in neural architecture. The distinction is like the difference between sharpening a tool versus building a better tool from scratch.
Semax has a more established safety record based on broader human exposure. Dihexa remains highly experimental with no published human studies. For researchers prioritizing safety data, Semax offers more reassurance. For those investigating maximal synaptogenic potential, Dihexa presents a more novel approach.
Dihexa versus Selank
Selank derives from the immune-modulating peptide tuftsin. Its primary effects center on anxiety reduction and stress resilience. While cognitive benefits occur, they appear secondary to the anxiolytic properties.
The mechanism involves GABA receptor modulation and serotonin system effects. Selank calms without sedating. It stabilizes mood without blunting cognition. For individuals whose cognitive difficulties stem from anxiety or stress, Selank addresses the underlying problem rather than pushing through it.
Dihexa does not have notable anxiolytic properties. It targets cognition directly through growth factor pathways. Combining the approaches might theoretically yield complementary benefits, though no research has specifically examined this combination.
Dihexa versus PE-22-28
PE-22-28 is another peptide targeting neurogenesis, but through an entirely different mechanism. It blocks the TREK-1 potassium channel, increasing neuronal excitability and serotonin transmission. Like Dihexa, PE-22-28 promotes the birth of new neurons and formation of new synapses.
Research shows PE-22-28 can double neurogenesis rates within just four days of treatment. This timeline is faster than what Dihexa studies have documented. However, the mechanisms differ enough that direct comparison is difficult.
PE-22-28 also appears to function as a BDNF mimetic, activating TrkB receptors that brain-derived neurotrophic factor normally stimulates. This gives it a dual mechanism not present with Dihexa. The peptide choice depends on which signaling pathway a researcher wants to investigate or optimize.
Understanding the landscape
Each cognitive peptide occupies a distinct niche. Nootropic peptides are not interchangeable. Semax for acute cognitive enhancement and neurochemical optimization. Selank for anxiety-driven cognitive difficulties. PE-22-28 for TREK-1 modulation and rapid neurogenesis. Dihexa for maximal HGF/c-Met activation and synaptogenesis.
The right choice depends on research goals, risk tolerance, and which mechanism matches the hypothesis being tested. Dihexa represents the most aggressive approach to structural brain plasticity, but also carries the most uncertainty regarding long-term safety.
Potential benefits based on preclinical evidence
The research suggests several potential benefits of Dihexa, though all findings come from animal studies and require confirmation in humans before clinical relevance can be established.
Enhanced memory formation
The most consistent finding across Dihexa studies is improved memory performance in various animal models. Spatial memory, which depends on hippocampal function, shows particular sensitivity to Dihexa treatment. Animals remember locations better, navigate more efficiently, and retain learned information longer.
This memory enhancement likely results from increased synaptic connectivity. More synapses provide more pathways for encoding and retrieving information. The hippocampus, where neurogenesis and synaptogenesis occur most readily in adults, appears particularly responsive to Dihexa effects.
Whether these improvements would translate to human episodic memory, working memory, or other cognitive domains remains unknown. Animal memory tasks differ substantially from the complex memory challenges humans face. But the consistency of findings across multiple paradigms suggests a robust effect on the underlying neural substrates of memory.
Learning capacity
Closely related to memory is learning, the acquisition of new information and skills. Synaptic plasticity underlies both processes. By promoting new synapse formation, Dihexa could theoretically enhance the speed and efficiency of learning.
Animal studies support this possibility. Treated animals acquired new tasks faster than controls. They made fewer errors during the learning phase. They reached performance criteria in fewer trials. The effect appeared across different types of learning tasks.
For researchers studying cognitive performance optimization, these findings suggest Dihexa might enhance not just retention but also acquisition. The brain ability to form new neural patterns that encode new information could be fundamentally augmented.
Neuroprotection
Dihexa research in disease models suggests potential neuroprotective effects. Treated animals showed less neuronal loss than untreated controls facing the same pathological challenge. Inflammatory markers decreased. Cell survival improved.
The HGF/c-Met pathway naturally promotes cell survival and tissue repair. Potentiating this system could provide protection against various insults, oxidative stress, inflammatory damage, neurodegenerative processes. The signaling cascade activates PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK pathways, both of which support neuronal survival.
This suggests potential relevance beyond cognitive enhancement to actual brain health maintenance. However, the same growth-promoting properties that might protect neurons raise questions about cancer risk, a topic we will address in the safety section.
Potential for neurodegenerative conditions
The Alzheimer mouse model studies have generated interest in Dihexa for neurodegenerative diseases. The combination of cognitive improvement, reduced inflammation, and neuroprotection aligns with therapeutic goals for conditions like Alzheimer and Parkinson disease.
The fosgonimeton clinical trials represent the most advanced effort to test this potential in humans. Results from these trials will provide the first real data on whether preclinical promises translate to clinical benefits. Until then, application to human neurodegenerative conditions remains speculative.
Anti-inflammatory effects observed in research could prove relevant beyond neurodegeneration. Neuroinflammation contributes to many brain conditions. Compounds that reduce inflammatory signaling while promoting repair mechanisms address multiple disease processes simultaneously.
Dosage considerations from research
No established human dosing exists for Dihexa. The compound has not undergone the clinical trials necessary to determine safe and effective doses for humans. What follows reflects only research protocols and anecdotal observations.
Animal study doses
Preclinical studies used doses in the microgram per kilogram range. Typical protocols administered 0.5 mg/kg intraperitoneally or 2.0 mg/kg orally in rats. Higher doses produced better performance on cognitive tests, suggesting dose-dependent effects.
The APP/PS1 mouse studies used doses of 1.44 mg/kg and 2.88 mg/kg, with the higher dose showing greater benefit in some measures. These doses cannot be directly converted to human equivalents without extensive pharmacokinetic studies.
Anecdotal human ranges
Outside of controlled research, reports describe human use in ranges from 1 mg to 20 mg daily. Some sources suggest starting at lower doses around 2-5 mg to assess tolerance before increasing. These numbers lack scientific validation and should not be interpreted as recommendations.
Duration of use varies widely in anecdotal reports. Some describe short courses of days to weeks. Others report longer term use of months. Effects reportedly persist for extended periods after cessation, consistent with the structural nature of synaptogenesis rather than acute neurochemical modulation.
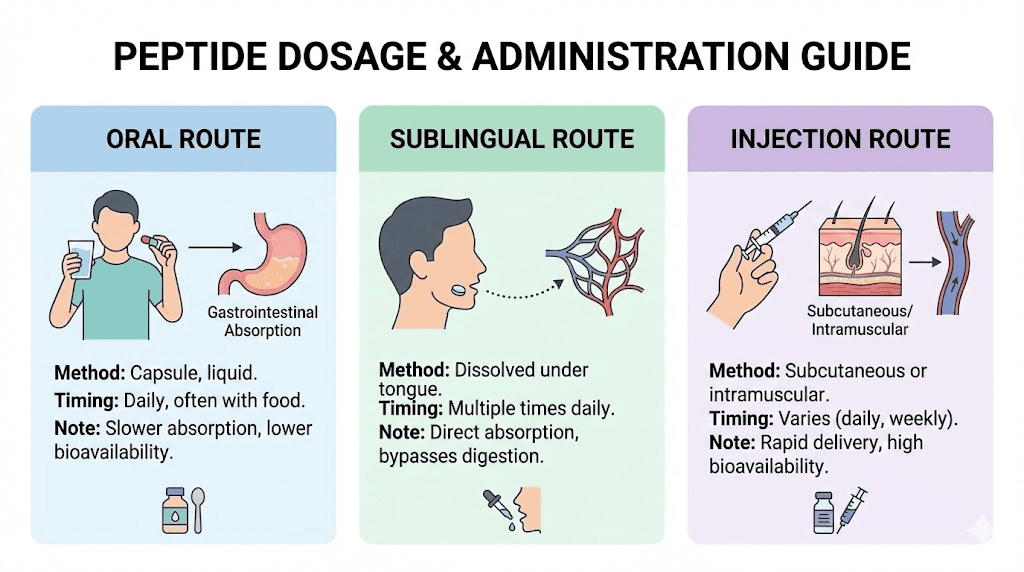
Administration routes
Dihexa stability and lipophilicity allow for oral administration, unusual among peptides. Most peptides degrade in the gastrointestinal tract and require injection. Dihexa metabolic stability appears sufficient to reach the brain after oral dosing.
Sublingual administration may improve bioavailability by avoiding first-pass liver metabolism. Some users report this route as more effective than swallowing capsules. Subcutaneous injection is another option that bypasses gastrointestinal degradation entirely.
The ability to cross the blood-brain barrier orally makes Dihexa more convenient than most cognitive peptides. But convenience should not overshadow the fundamental uncertainty about appropriate dosing in the absence of clinical trials.
Safety considerations and risks
The safety profile of Dihexa remains poorly characterized. Limited short-term studies in animals have not revealed obvious toxicity, but significant concerns exist based on the mechanism of action.
The cancer question
HGF and c-Met signaling promotes cell growth, migration, and survival. These properties make the pathway important for normal development and tissue repair. They also make it relevant to cancer. The HGF/c-Met system is overactive in many tumor types and contributes to cancer progression and metastasis.
Drugs that inhibit c-Met are being developed as cancer treatments. Dihexa does the opposite, it potentiates c-Met signaling. The theoretical concern is obvious. Could enhancing this pathway promote tumor development or accelerate growth of existing cancers?
Short-term animal studies reportedly showed no neoplastic induction. But cancer typically develops over long timeframes. Effects that do not appear in weeks of rodent treatment might manifest after months or years of human use. No long-term safety studies have been conducted.
Researchers at the Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation noted this concern explicitly in their analysis. They characterized the cancer risk as theoretical but significant enough to warrant caution. Anyone considering Dihexa research must weigh potential cognitive benefits against this fundamental uncertainty.
Unknown long-term effects
Beyond cancer specifically, the long-term consequences of enhanced synaptogenesis are unknown. Forming new synapses is generally considered beneficial for cognition. But the brain carefully regulates synaptic density. Too many connections could be as problematic as too few.
Conditions like epilepsy involve excessive neural connectivity. Schizophrenia has been linked to abnormal synaptic pruning. The brain complex balance of connection formation and elimination serves important functions. Artificially driving one side of this equation might have unintended consequences.
There are no studies examining what happens with prolonged Dihexa use. Does the brain adapt by downregulating HGF receptors? Do the newly formed synapses persist or get pruned after treatment stops? How does chronic enhancement of growth factor signaling affect brain development at different ages? These questions remain unanswered.
Reported side effects
Anecdotal reports describe generally mild side effects. Some users report temporary nervousness or restlessness, particularly when starting treatment. Mild mood changes including irritability have been noted. Occasional fatigue or dizziness occurs in some individuals.
These reports cannot be verified and may reflect coincidental symptoms, nocebo effects, or impurities in research products. Without controlled studies, attributing specific effects to Dihexa versus other factors is impossible.
The absence of severe reported side effects provides some reassurance but cannot substitute for systematic safety evaluation. Many adverse effects emerge only with broader use and longer observation periods than currently exist for Dihexa.
Quality and purity concerns
Dihexa is available only from research peptide suppliers. Unlike approved pharmaceuticals, these products do not undergo regulatory quality control. Purity varies between vendors. Contamination is possible. Accurate dosing depends on claimed but unverified product specifications.
Researchers should verify peptide identity and purity through independent testing laboratories before conducting experiments. Certificate of analysis documents from suppliers provide starting assurance but cannot guarantee what is actually in a given vial. Vendor selection matters enormously for research integrity and safety.
Practical research considerations
For researchers choosing to investigate Dihexa, several practical factors require attention.
Reconstitution and handling
Dihexa typically arrives as a lyophilized powder requiring reconstitution before use. Bacteriostatic water serves as the standard diluent for research applications. Sterile technique during reconstitution prevents microbial contamination.
Once reconstituted, Dihexa solutions should be refrigerated at 2-8 degrees Celsius and used within a reasonable timeframe. Most sources suggest two weeks as an upper limit for refrigerated storage. For longer storage, aliquoting and freezing at -20 degrees Celsius preserves stability but requires avoiding repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
Protect solutions from light. Store lyophilized powder in dark, dry conditions at -20 degrees Celsius or colder until ready for use. These storage practices maximize peptide integrity and experimental reproducibility.
Using peptide calculators
Accurate dosing requires understanding the relationship between peptide mass, volume of diluent, and desired concentration. Peptide calculators simplify these conversions. For a 10 mg vial reconstituted with 2 mL of water, the resulting concentration is 5 mg/mL or 0.05 mg per 0.1 mL unit.
Reconstitution calculators help researchers determine exact volumes for specific concentrations. Understanding peptide dosage calculations prevents errors that could invalidate experiments or create safety issues.
Documentation and protocols
Given the experimental nature of Dihexa research, thorough documentation becomes especially important. Record batch numbers, reconstitution dates, storage conditions, and any observed effects. This information helps interpret results and troubleshoot unexpected findings.
Establish clear protocols before beginning experiments. Define dosing schedules, observation timepoints, and outcome measures in advance. Consistent methodology allows meaningful comparison between experiments and with published literature.
How Dihexa fits into peptide research
Dihexa represents one approach within the broader landscape of peptide research. Understanding its place helps researchers select appropriate tools for specific questions.
The growth factor approach
Several strategies exist for enhancing brain plasticity. Direct administration of growth factors like BDNF or NGF is limited by their large size and poor brain penetration. Small molecules that increase endogenous growth factor production offer one alternative. Peptides like Dihexa that potentiate growth factor receptor signaling represent another approach.
The advantage of receptor potentiation is leveraging existing growth factor already present in the brain. Rather than adding exogenous protein that may not reach target tissues, Dihexa amplifies the signal from endogenous HGF. This may produce more physiologically appropriate patterns of receptor activation.
The disadvantage is dependence on baseline HGF levels. If HGF is already deficient, potentiating its activity may have limited effect. Combining Dihexa with strategies to increase HGF expression could theoretically overcome this limitation but adds complexity and unknowns.
Comparing mechanism classes
Different cognitive enhancement strategies target different aspects of brain function. Neurotransmitter modulators like racetams and cholinergics affect acute signaling between neurons. BDNF enhancers like Semax promote neuroplasticity through that particular growth factor. Ion channel modulators like PE-22-28 alter fundamental neuronal excitability.
Dihexa stands somewhat apart by targeting the HGF/c-Met axis specifically. This pathway has received less attention in nootropic contexts than BDNF or acetylcholine systems. Dihexa research may reveal effects and applications that other mechanism classes cannot address.
The diversity of available approaches allows researchers to dissect which aspects of brain function matter most for their questions. Combining multiple mechanisms might produce synergistic effects, though such combinations multiply unknowns and safety concerns.
Integration with other research peptides
Researchers studying brain function often work with multiple compounds. BPC-157 and TB-500 promote tissue healing including neural tissue. Bioregulator peptides like Pinealon target brain function through gene expression modulation. Anti-inflammatory peptides could complement synaptogenic approaches.
Whether these compounds can be combined safely and beneficially remains unstudied. The default assumption should be to investigate single agents before attempting combinations. Each addition multiplies unknowns about interactions, unexpected effects, and long-term consequences.
SeekPeptides provides resources for researchers navigating this complex landscape. Understanding peptide fundamentals and avoiding common mistakes helps build a foundation for more advanced investigations.
The current regulatory landscape
Understanding the legal status of peptides helps researchers operate within appropriate frameworks.
Research compound status
Dihexa has not received FDA approval for any medical indication. It is not a prescription medication, not a dietary supplement, and not approved for human use. The compound exists in regulatory limbo between approved drugs and banned substances.
Possession for research purposes is generally legal in most jurisdictions. Sale for human consumption is not. The practical distinction often depends on labeling and marketing claims rather than the compound itself. Vendors selling Dihexa for research typically include disclaimers about human use.
Clinical development efforts
The fosgonimeton clinical trials represent the formal regulatory pathway for Dihexa-related compounds. If these trials succeed, a modified version of Dihexa could eventually receive approval for specific neurological conditions. This would establish proper dosing, safety monitoring, and quality standards currently lacking.
Trial results will shape the future of this research area. Positive findings could accelerate interest and investment. Negative findings or safety signals could halt development entirely. Researchers should monitor peptide regulation news for updates on these programs.
Self-experimentation concerns
Some individuals obtain Dihexa for personal use despite the absence of clinical guidance. This self-experimentation occurs outside medical supervision and without the safety infrastructure of clinical trials. The risks are borne entirely by the individual.
For researchers whose focus is scientific rather than personal, maintaining appropriate protocols and documentation serves both experimental validity and ethical standards. Research compounds are for research. Personal enhancement decisions fall outside the scope of this analysis.
Frequently asked questions
What is Dihexa peptide?
Dihexa is a synthetic peptide derived from angiotensin IV, developed at Washington State University. Its chemical name is N-hexanoic-Tyr-Ile-(6) aminohexanoic amide. The compound works by potentiating hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) signaling at c-Met receptors, promoting synaptogenesis and neural plasticity.
How does Dihexa differ from other nootropic peptides?
Most nootropic peptides work by modulating neurotransmitter systems or BDNF levels. Dihexa uniquely targets the HGF/c-Met pathway to promote actual structural changes in neural connectivity. This synaptogenic mechanism distinguishes it from compounds like Semax or Selank.
Is Dihexa safe to use?
The safety profile of Dihexa is poorly characterized. Short-term animal studies showed no obvious toxicity, but long-term effects are unknown. The mechanism involves growth pathways potentially relevant to cancer, creating theoretical concerns about chronic use. No human clinical trials have been published.
What dosage is used in research?
Animal studies used doses from 0.5-2.88 mg/kg. Human-equivalent doses cannot be directly calculated without pharmacokinetic studies. Anecdotal reports describe ranges from 1-20 mg daily, but these lack scientific validation and should not be interpreted as recommendations.
Can Dihexa be taken orally?
Yes, unlike most peptides, Dihexa is orally bioavailable. Research showed it maintains stability in the bloodstream and crosses the blood-brain barrier when taken orally. Sublingual administration may offer improved bioavailability by avoiding first-pass metabolism.
How long do Dihexa effects last?
Because Dihexa promotes structural changes rather than acute neurochemical effects, benefits may persist after treatment cessation. Some reports suggest effects lasting days to weeks after stopping. The durability of newly formed synapses has not been systematically studied.
Can Dihexa be combined with other peptides?
Combining peptides multiplies unknowns about interactions and safety. No research has specifically examined Dihexa combinations. The default approach should be single-agent investigation before attempting stacks.
Is Dihexa legal?
Dihexa is not FDA-approved and is not legally available as a medication or supplement. Possession for research purposes is generally permitted in most jurisdictions. Check current regulations for your specific location.
External resources
PMC: The Procognitive and Synaptogenic Effects of Angiotensin IV-Derived Peptides
PMC: AngIV-Analog Dihexa Rescues Cognitive Impairment in APP/PS1 Mouse
For researchers serious about advancing their understanding of cognitive peptides, SeekPeptides offers the most comprehensive resources available. Access detailed protocol guidance, evidence-based analysis, and a community of researchers working at the forefront of this field.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your synapses stay strong, your cognition stay sharp, and your research stay rigorous.



