Dec 30, 2025

Walk into any health food store or scroll through Instagram wellness accounts, and you'll encounter Vital Proteins everywhere - particularly their chocolate-flavored collagen peptides powder that promises to dissolve into coffee, smoothies, or even water while delivering 20g of collagen per serving. The brand has become synonymous with collagen supplementation thanks to celebrity endorsements, attractive packaging, and aggressive marketing claiming benefits for skin, hair, nails, joints, and gut health.
But does Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides Chocolate actually work?
Is the premium price justified compared to generic collagen supplements?
Does the chocolate flavor compromise effectiveness or add unwanted ingredients?
And perhaps most importantly for peptide enthusiasts - how does this grass-fed bovine collagen powder compare to targeted collagen-boosting peptides like GHK-Cu that actively stimulate your body's own collagen production?
The chocolate flavor makes Vital Proteins more palatable than unflavored collagen, but adds cocoa powder, natural flavors, and stevia - ingredients some prefer to avoid.
The 20g collagen dose per serving provides Types I and III collagen (the main types in skin, bones, and connective tissue), making it theoretically effective for anti-aging and joint support. However, at $43+ for 567g (about 28 servings), you're paying premium prices when generic collagen peptides offer identical benefits at half the cost.
This guide examines what Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides Chocolate contains and how it works, documented benefits for skin, hair, joints, and overall health, optimal dosing and usage strategies, taste and mixability analysis, comparing to generic collagen and collagen-stimulating peptides, whether the chocolate flavor compromises effectiveness, and value analysis versus alternatives.
Understanding what you're actually getting helps determine if Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides Chocolate merits the premium or if better collagen optimization strategies exist.
What is Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides Chocolate
Product composition and sourcing.
Ingredient breakdown and analysis
Primary ingredient:
Collagen peptides (20g per serving)
Source: Grass-fed, pasture-raised bovine (cow hide and bones)
Types: I and III collagen (most abundant in humans)
Hydrolyzed for better absorption
Standard collagen peptide formulation
Flavoring ingredients:
Cocoa powder: Provides chocolate flavor, some antioxidants
Natural flavors: Undefined proprietary blend (concerning for some)
Stevia leaf extract: Zero-calorie sweetener (some dislike taste)
These additions distinguish from unflavored collagen
Complete ingredient list analysis:
Ingredient | Amount/Serving | Purpose | Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|
Collagen peptides | 20g | Primary active ingredient | None - standard dose |
Cocoa powder | ~2-3g (estimated) | Flavor, antioxidants | Minimal, actually beneficial |
Natural flavors | Not disclosed | Enhance chocolate taste | Vague, proprietary |
Stevia | Small amount | Sweetness without calories | Some dislike stevia aftertaste |
What's NOT in it (important):
No added sugars (major plus)
No artificial sweeteners beyond stevia
No dairy (just bovine collagen, which is protein not dairy)
No gluten
No soy
Whole30 approved, Paleo-friendly
Nutritional profile per serving (2 scoops, ~20g):
Calories: 70
Protein: 18g (from collagen)
Carbohydrates: 1g
Fat: 0g
Sodium: 90mg
Essentially a pure protein supplement with minimal extras
Learn about collagen vs other peptides and what peptides are at SeekPeptides.
Grass-fed bovine sourcing claims
What "grass-fed, pasture-raised" means:
Cows raised primarily on pasture (not feedlots)
Diet of grass vs grain (more natural)
No antibiotics or hormones (Vital Proteins claims)
More humane and sustainable
Potentially higher quality collagen
Does sourcing matter for collagen?
Minimal difference in amino acid profile (collagen is collagen)
Grass-fed may have fewer contaminants
Environmental and ethical benefits
Mostly marketing advantage
Generic collagen works identically for skin/joint benefits
Vital Proteins sourcing transparency:
Sources from Brazil primarily
Third-party testing for heavy metals
Non-GMO verified
More transparent than many brands
But still expensive for what you get
Reality check:
Grass-fed bovine collagen ≈ conventional collagen for effectiveness
You're paying 2-3x for sourcing claims
If budget-conscious, generic works fine
If values-driven (ethical, environmental), may be worth premium
Compare to other collagen sources and cost-effective alternatives.
Hydrolyzed collagen vs gelatin
What hydrolyzation means:
Collagen broken into smaller peptides
Molecular weight: 2,000-5,000 Daltons (small)
Dissolves in cold water (vs gelatin needs hot)
Better absorption in digestive system
Standard for collagen supplements
Hydrolyzed collagen (Vital Proteins) vs gelatin:
Property | Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides | Gelatin |
|---|---|---|
Solubility | Dissolves cold or hot water | Only dissolves in hot, gels when cool |
Molecular size | Small peptides (2-5kDa) | Larger molecules |
Absorption | Better/faster absorbed | Slower absorption |
Use cases | Drinks, smoothies, coffee | Gummies, jello, bone broth |
Convenience | Mix into anything | Requires cooking/heating |
Effectiveness | Same benefits once absorbed | Same benefits |
Why Vital Proteins uses hydrolyzed:
Convenience (mix into cold drinks)
Better absorption claims
Premium positioning
Industry standard for collagen powders
Absorption and bioavailability:
Hydrolyzed collagen: ~90% absorbed
Broken into di- and tri-peptides in gut
These small peptides enter bloodstream
Similar to other peptide supplements
See how peptides work and bone broth vs collagen peptides comparison.
Types I and III collagen explained
What collagen types mean:
28 types of collagen in human body
Types I and III most abundant (90%+ of total)
Different types in different tissues
Vital Proteins provides Types I and III
Type I collagen:
Most abundant (90% of body's collagen)
Found in: Skin, bones, tendons, ligaments, organs
Provides: Structure, firmness, elasticity
Anti-aging benefits primarily from Type I
Critical for skin health
Type III collagen:
Second most abundant
Found in: Skin (alongside Type I), blood vessels, hollow organs
Provides: Elasticity, support for organs
Works synergistically with Type I
Important for vascular health
Types I and III distribution:
Tissue | Type I | Type III | Importance for Supplementation |
|---|---|---|---|
Skin | 80-85% | 10-15% | Both types for skin elasticity and firmness |
Bones | 90%+ | Minor | Type I critical for bone strength |
Tendons/Ligaments | 95%+ | Minor | Type I for connective tissue |
Blood vessels | 60-70% | 30-40% | Both types for vascular integrity |
Joints | High | Moderate | Both for joint health |
Why not Type II collagen?
Type II found in cartilage primarily
Requires chicken sternum or shark cartilage (different source)
Some products add Type II separately
Vital Proteins chocolate doesn't include it
If targeting joint cartilage specifically, Type II beneficial
Does the type source matter?
Bovine (cow) = Types I and III naturally
Marine (fish) = Types I and III
Chicken = Type II
Your body doesn't use them as-is - breaks down then rebuilds
Providing building blocks is what matters
Learn about collagen production and peptides for skin.
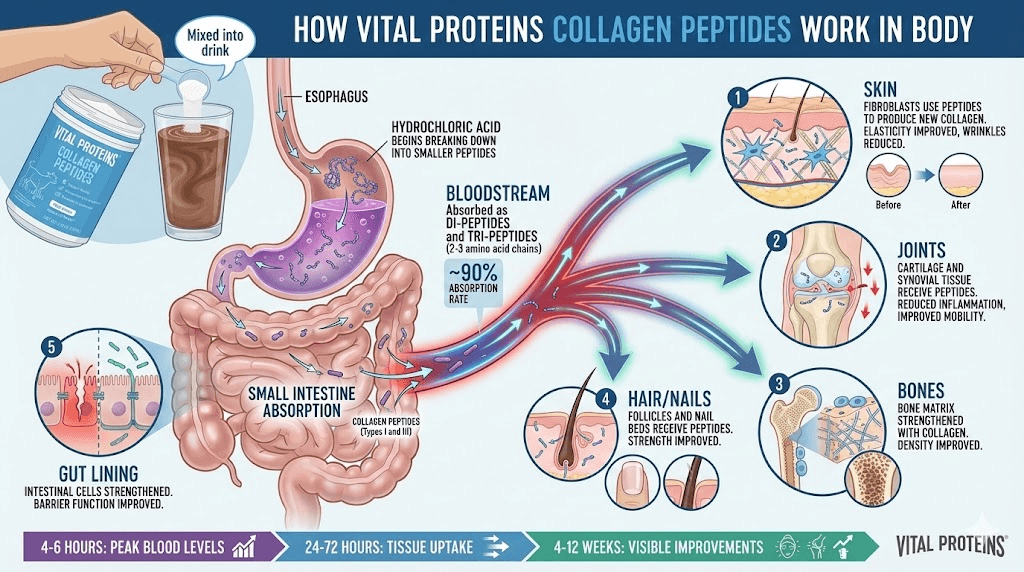
Documented benefits of collagen supplementation
What research actually shows (not just marketing).
Skin anti-aging effects
Clinical evidence for collagen and skin:
Multiple studies show skin elasticity improvements
Wrinkle depth reduction in several trials
Hydration and firmness increases
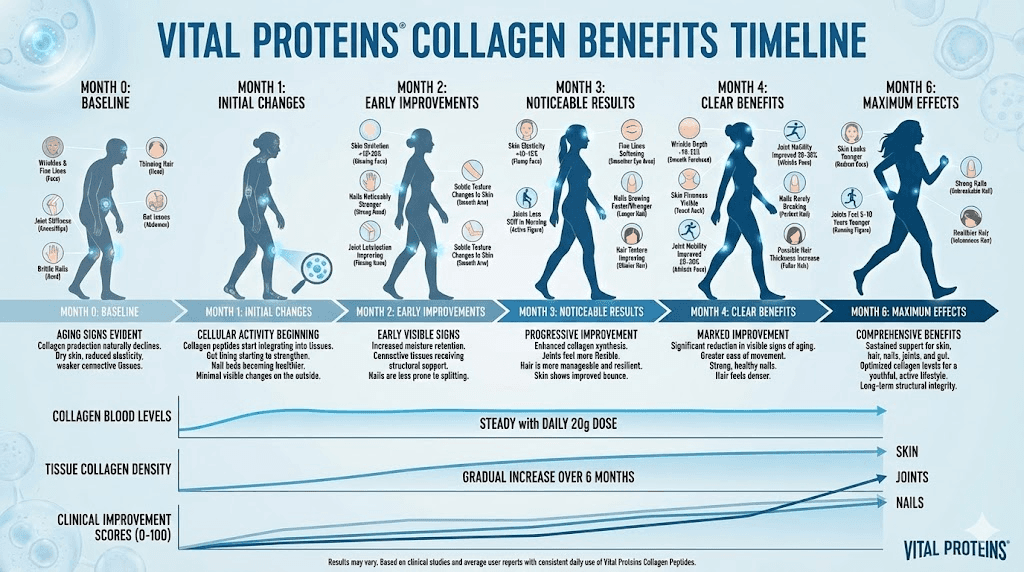
Takes 4-12 weeks for visible results
Dose: 2.5-15g daily (Vital Proteins 20g exceeds this)
Study results summary:
Study | Duration | Dose | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
German study (2014) | 8 weeks | 2.5g or 5g daily | Skin elasticity +20%, more in older women |
Japanese study (2017) | 12 weeks | 5g daily | Wrinkle depth -17%, moisture +28% |
Korean study (2019) | 12 weeks | 10g daily | Firmness improved, photo-aging reduced |
Meta-analysis (2021) | Multiple studies | 2.5-15g range | Consistent benefits for skin aging markers |
Mechanism for skin benefits:
Collagen peptides absorbed into bloodstream
Trigger fibroblasts (skin cells) to produce more collagen
Also stimulate elastin and hyaluronic acid
Provide amino acid building blocks
Similar to GHK-Cu but different pathway
Realistic expectations:
Subtle improvements (not dramatic transformation)
Better than placebo, less than injectable peptides
Preventive benefits likely strongest
Works best combined with other interventions
Requires consistent daily use
Timeline for skin results:
Weeks 1-4: No visible changes, cellular preparation
Weeks 4-8: Subtle hydration improvement
Weeks 8-12: Elasticity and firmness increase noticeable
Month 4-6: Maximum benefits, wrinkle reduction visible
Ongoing: Maintenance of improvements
Compare to GHK-Cu for stronger skin rejuvenation and glow peptides.
Joint pain and mobility improvements
Collagen for joint health:
Type I collagen in tendons and ligaments
Type III in connective tissue
Reduces joint pain in several studies
Improves mobility and stiffness
Supports cartilage (though Type II better for this)
Clinical evidence:
Study Population | Duration | Dose | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
Athletes (Penn State) | 24 weeks | 10g daily | Joint pain reduced during activity |
Osteoarthritis patients | 70 days | 10g daily | Pain -26%, stiffness improved |
Rheumatoid arthritis | 3 months | 10g daily | Tender joint count decreased |
Elderly (joint pain) | 6 months | 8g daily | Improved mobility, less pain medication |
Mechanism:
Provides building blocks for cartilage repair
Reduces inflammation in joints
Supports connective tissue integrity
May stimulate chondrocytes (cartilage cells)
Different from BPC-157 (direct healing) but complementary
Best for:
Age-related joint stiffness
Athletic wear and tear
Mild-moderate osteoarthritis
Prevention of joint degeneration
Not a substitute for:
Severe arthritis treatment
Acute injury repair (use BPC-157, TB-500)
Medical joint treatments
See best peptides for joint pain and injury recovery.
Hair and nail strength
Evidence for hair:
Limited direct studies on collagen for hair growth
Anecdotal reports of thicker, stronger hair
Mechanism: Provides amino acids for hair proteins
Less proven than skin benefits
Takes 3-6 months to notice
Evidence for nails:
One study: 24 weeks collagen → 12% faster nail growth, 42% decrease in broken nails
Improved nail quality reported commonly
Mechanism: Keratin production support
Faster results than hair (weeks vs months)
Hair and nail timeline:
Timeframe | Hair Changes | Nail Changes |
|---|---|---|
Weeks 1-4 | None visible | Slight strength improvement |
Weeks 4-12 | Possible texture improvement | Noticeably stronger, less brittle |
Month 3-6 | Thickness may increase, less shedding | Continued improvement, faster growth |
Reality check:
Hair/nail benefits weaker evidence than skin
Many factors affect hair health
Collagen one piece of puzzle
Protein intake overall critical
Dedicated hair peptides may work better
Gut health and digestion
Collagen for gut lining:
Glycine (amino acid in collagen) supports gut integrity
May help leaky gut (increased permeability)
Reduces inflammation in GI tract
Supports mucosal lining
Less studied than skin/joint benefits
Proposed mechanisms:
Provides glycine, proline, glutamine
These amino acids crucial for intestinal cells
May reduce gut inflammation
Supports tight junction integrity
Similar to BPC-157's gut benefits but milder
Evidence level:
Mostly theoretical and anecdotal
No large-scale gut studies on collagen
Biological plausibility exists
Likely beneficial but not proven
BPC-157 has better gut healing evidence
Who might benefit:
IBS or digestive issues
General gut health optimization
Combined with other interventions
Learn about peptides for gut health and BPC-157 for targeted digestive support.
Optimal dosing and usage
Getting the most from Vital Proteins Chocolate.
Recommended daily serving
Vital Proteins serving size:
2 scoops = 20g collagen
Exceeds clinical study doses (2.5-15g range)
Provides substantial amino acids
Standard for collagen supplements
Can split into 10g twice daily
Is 20g necessary?
Most studies used 5-15g successfully
20g may provide faster/stronger results
Or simply marketing (bigger number looks better)
10-15g likely sufficient for most
Dosing strategies:
Approach | Daily Dose | Timing | Best For | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Full serving | 20g (2 scoops) | Once daily, morning | Maximum results, budget allows | $1.50/day |
Half serving | 10g (1 scoop) | Once daily | Budget-conscious, maintenance | $0.75/day |
Split dose | 10g twice | Morning + evening | Consistent blood levels | $1.50/day |
Loading phase | 20g daily × 12 weeks, then 10g maintenance | Front-loaded | Faster initial results | Variable |
When to take:
Morning with coffee: Most popular, convenient
Pre-workout: Supports joints during exercise
Post-workout: Recovery support
Before bed: Overnight repair
Consistency matters more than timing
Best mixing methods and recipes
How to mix:
Blender or shaker bottle: Best results, smooth
Spoon stirring: Works but may clump
Hot coffee: Dissolves well (heat helps)
Cold drinks: Dissolves okay, slower
Does NOT gel (unlike gelatin)
Popular mixing options:
In coffee:
Add to hot coffee, stir well
Creates creamy texture
Chocolate flavor complements coffee
Most common use
In smoothies:
Blends perfectly
Adds protein without flavor change (chocolate masked by fruits)
Nutrient-dense meal
Can combine with other supplements
In protein shakes:
Boosts total protein
Chocolate on chocolate common
Post-workout option
In baking:
Can bake with collagen (heat-stable)
Protein brownies, muffins, pancakes
Doesn't affect rising/texture much
Way to incorporate without drinking
Simple recipes:
Chocolate Collagen Coffee:
1 cup hot coffee
2 scoops Vital Proteins Chocolate
1 tbsp MCT oil or coconut oil
Blend for 30 seconds = frothy mocha
Chocolate Collagen Smoothie:
1 banana
1 cup almond milk
2 scoops collagen
1 tbsp almond butter
Ice, blend
Tips for best mixing:
Warm liquids dissolve better
Blend for smoothest texture
Add liquid first, then powder
Shake vigorously if no blender
Small clumps harmless (just texture)
Cycling vs continuous use
Should you cycle collagen?
Most take continuously (not cycled like some peptides)
Collagen provides building blocks (not hormonal)
Benefits accumulate with consistent use
Stopping = gradual return to baseline
Continuous use rationale:
Daily collagen breakdown needs replenishment
Studies used continuous supplementation
Results from sustained intake
Unlike bioregulator peptides (cyclic)
More like daily vitamins
What happens if you stop:
Benefits gradually fade over 2-4 months
Collagen production returns to normal
Not harmful to stop
Can restart anytime
Similar to stopping any supplement
Budget-friendly cycling:
Full dose (20g) for 3 months, then maintenance dose
On/off months (less ideal but saves money)
Continuous half-dose instead of full dose
Your call based on budget
See our peptide cycle planning guide and cost calculator at SeekPeptides.
Does it break a fast?
Technical answer: Yes, collagen breaks a fast
Contains protein (18g per serving)
Triggers insulin response (moderate)
Activates mTOR (protein synthesis pathway)
Provides calories (70 per serving)
Not "fasted state" technically
Practical answer: Depends on fasting goals
Fasting Type | Collagen Compatible? | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
Autophagy-focused | NO | Protein stops autophagy via mTOR |
Weight loss/calorie restriction | YES | 70 calories minimal impact on deficit |
Metabolic health | MAYBE | Small insulin response, probably fine |
Gut rest | NO | Digestive system processes it |
Intermittent fasting (loose) | YES | Many include it without issue |
Collagen and autophagy:
Autophagy (cellular cleanup) requires true fast
Protein intake stops autophagy
If autophagy is goal, avoid collagen during fast
Take during eating window
Compromise approaches:
Use collagen to break fast (first thing eaten)
Save for eating window
Accept "dirty fasting" with collagen
Your fasting, your rules
See our complete does collagen peptides break a fast analysis.
Taste, mixability and user experience
Real-world usability assessment.
Chocolate flavor analysis
Taste profile:
Mild chocolate flavor (not intense)
Slight cocoa bitterness
Stevia sweetness (not sugar-sweet)
Some detect stevia aftertaste
Not as sweet as hot chocolate
Compared to unflavored:
Much more palatable than unflavored
Unflavored has slight beef taste
Chocolate masks collagen taste completely
Worth it if you find unflavored unpleasant
User reviews (common feedback):
"Tastes like watered-down cocoa" - common
"Stevia aftertaste bothers me" - stevia-sensitive people
"Love it in coffee!" - most popular use
"Decent but not amazing flavor" - honest
"Kids will drink it" - family-friendly
Stevia controversy:
Zero-calorie sweetener from plant
Some love it, some hate bitter aftertaste
Individual taste perception varies
If you dislike stevia, this isn't for you
Alternative: Unflavored collagen + your own sweetener
Mixability and texture
How well it dissolves:
Hot liquids: Excellent, fully dissolves
Warm liquids: Very good
Room temperature: Good with stirring
Cold liquids: Fair, needs vigorous mixing
Overall: Better than many collagen brands
Texture in drinks:
Slightly thickens (minimal)
Adds body to coffee (some like this)
No grittiness when properly mixed
Occasional small clumps if poorly stirred
Not slimy or gel-like
Common mixing issues:
Clumping if added to cold liquid too fast
Floats on top if not stirred immediately
Needs shaker bottle or blender for cold drinks
Hot coffee = easiest, smoothest
Tips for perfect mixing:
Add liquid first, then powder
Stir/shake immediately
Use warm or hot liquids
Frother makes it extra smooth
Blender bottle for cold drinks
Value for money assessment
Cost breakdown:
Vital Proteins Chocolate: $43 for 567g (28 servings at 20g)
Per serving: $1.54
Per gram collagen: $0.077
Monthly (daily use): ~$46
Price comparison:
Product | Cost | Servings | Per Serving | Per Gram | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Vital Proteins Chocolate | $43 | 28 | $1.54 | $0.077 | $46 |
Generic unflavored | $20 | 28 | $0.71 | $0.036 | $22 |
Marine collagen | $35 | 20 | $1.75 | $0.12 | $53 |
Collagen gummies | $25 | 30 | $0.83 | $0.28 | $25 |
Bone broth | $30 | 20 | $1.50 | Variable | $45 |
Is it worth the premium?
No if purely cost-focused (generic works same)
Maybe if you value grass-fed sourcing
Yes if chocolate flavor critical for adherence
Depends on your priorities (cost vs convenience)
Cost-saving alternatives:
Generic collagen: 50% cheaper
Buy unflavored, add your own cocoa
Split servings (10g vs 20g)
Shop sales or subscribe-and-save
Consider collagen-boosting peptides instead
Use our peptide cost calculator to compare options at SeekPeptides.
Vital Proteins vs alternatives
Better options for different goals.
Generic collagen peptides comparison
Generic vs Vital Proteins:
Collagen content: Identical (Types I & III bovine)
Effectiveness: No difference for skin/joint benefits
Sourcing: Generic may be conventional vs grass-fed
Cost: Generic 50% cheaper
Brand trust: Vital Proteins more recognized
When generic is better:
Budget is priority
Don't care about sourcing claims
Want unflavored versatility
Buying in bulk
Value-focused approach
When Vital Proteins is better:
Prefer chocolate flavor
Value grass-fed sourcing
Like established brand
Gift-worthy packaging
Willing to pay for convenience
See best peptide vendors and bone broth vs collagen peptides comparison.
GHK-Cu and collagen-boosting peptides
Different approach: Stimulate your own collagen
GHK-Cu activates genes for collagen production
Your body makes its own collagen
Providing building blocks (Vital Proteins) vs signaling production (GHK-Cu)
Different mechanisms, potentially synergistic
GHK-Cu advantages:
More targeted skin anti-aging
Stimulates your own collagen (better quality?)
Additional benefits (wound healing, antioxidant)
Stronger clinical evidence for skin
Can use topically or inject
GHK-Cu disadvantages:
Requires injection or reconstitution
Higher per-dose cost
More complex to use
Primarily skin-focused (less for joints)
Combining both:
Collagen provides building blocks
Potentially synergistic
Expensive but comprehensive
See GHK-Cu 50mg dosage guide, copper peptides guide, and how long GHK-Cu lasts.
Marine vs bovine collagen
Marine (fish) collagen:
Types I and III (same as bovine)
Smaller molecular weight (claimed better absorption)
More sustainable sourcing
Usually more expensive
Bovine (cow) collagen (Vital Proteins):
Types I and III
Standard molecular weight
More affordable
No fishy issues
Grass-fed options available
Does source matter?
Absorption: Probably no significant difference
Effectiveness: Equivalent for skin/joints
Sustainability: Marine potentially better
Allergens: Fish allergy vs beef allergy consideration
Cost: Bovine usually cheaper
Recommendation:
Choose based on values/preferences not efficacy
Both work equally well
Bovine (Vital Proteins) better value
Marine if you prefer fish sourcing
How you can use SeekPeptides for collagen optimization
SeekPeptides helps you optimize collagen strategies beyond simple supplementation. Compare oral collagen to collagen-stimulating peptides like GHK-Cu for targeted skin rejuvenation.
Use our calculators - peptide cost calculator to compare Vital Proteins to alternatives, peptide stack calculator to combine collagen with other anti-aging peptides.
Learn about comprehensive approaches - peptides for anti-aging, glow peptides, best peptides for women, peptide stacks guide.
Access guides on specific collagen peptides, bone broth vs collagen, does collagen break a fast, can collagen cause acne.
Final thoughts
Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides Chocolate delivers a convenient, palatable way to supplement 20g daily collagen for skin, joint, and overall health benefits. The grass-fed bovine sourcing, Types I and III collagen, and chocolate flavor make it a premium option backed by decent clinical evidence for anti-aging effects.
However, the $43 price tag ($1.54 per serving) represents a 2x premium over generic collagen that works identically. You're paying for sourcing claims, brand recognition, and chocolate convenience - valid if those matter to you, but unnecessary if results are your only concern.
The chocolate flavor uses cocoa and stevia, making it far more palatable than unflavored collagen without adding sugar. This improves adherence, potentially making the premium worthwhile if flavor prevents you from using cheaper alternatives. The mild chocolate taste works well in coffee, smoothies, and shakes.
For maximum skin anti-aging, consider collagen-stimulating peptides like GHK-Cu that activate your body's own collagen production genes rather than just providing building blocks. Combining both approaches may offer synergistic benefits.
Your collagen strategy depends on priorities - if convenience and taste justify premium pricing, Vital Proteins Chocolate delivers. If budget matters most, generic collagen works identically. For targeted anti-aging, injectable peptides may prove more effective despite higher complexity.
Helpful resources for collagen
Bone broth vs collagen peptides - Complete comparison
Does collagen peptides break a fast - Fasting guide
Can collagen peptides cause acne - Skin concerns
Peptide cost calculator - Compare costs
Peptide stack calculator - Plan combinations
In case I don’t see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Take care of yourself.