Jan 9, 2026

The research peptide marketplace has expanded dramatically over recent years, with dozens of vendors competing for researchers seeking quality compounds for scientific investigation. Klow Peptides has emerged as one supplier within this growing landscape, positioning themselves among vendors serving the research community with compounds ranging from metabolic peptides to healing compounds like BPC-157 and growth hormone secretagogues. The proliferation of peptide suppliers creates both opportunity and challenge for researchers, as quality varies dramatically across vendors while marketing claims often prove difficult to verify independently.
Navigating vendor selection requires systematic evaluation across multiple dimensions including testing documentation, pricing structures, product availability, shipping logistics, and customer service responsiveness. The research versus pharmaceutical peptides distinction matters significantly here, as research peptide vendors operate outside pharmaceutical regulatory frameworks while still needing to deliver products suitable for scientific investigation. Understanding where Klow Peptides fits within this market landscape helps researchers make informed sourcing decisions based on evidence rather than marketing claims alone.
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive vendor evaluation resources helping researchers assess suppliers objectively. This guide examines Klow Peptides thoroughly, covering their product offerings, quality verification practices, pricing structures, ordering experience, and how they compare to alternative vendors in the research peptide space.
The analysis draws on available documentation, community reports, and systematic evaluation criteria applicable to any peptide supplier.
Understanding the research peptide vendor landscape
Before examining any specific vendor, understanding the broader market context provides essential perspective for evaluation.
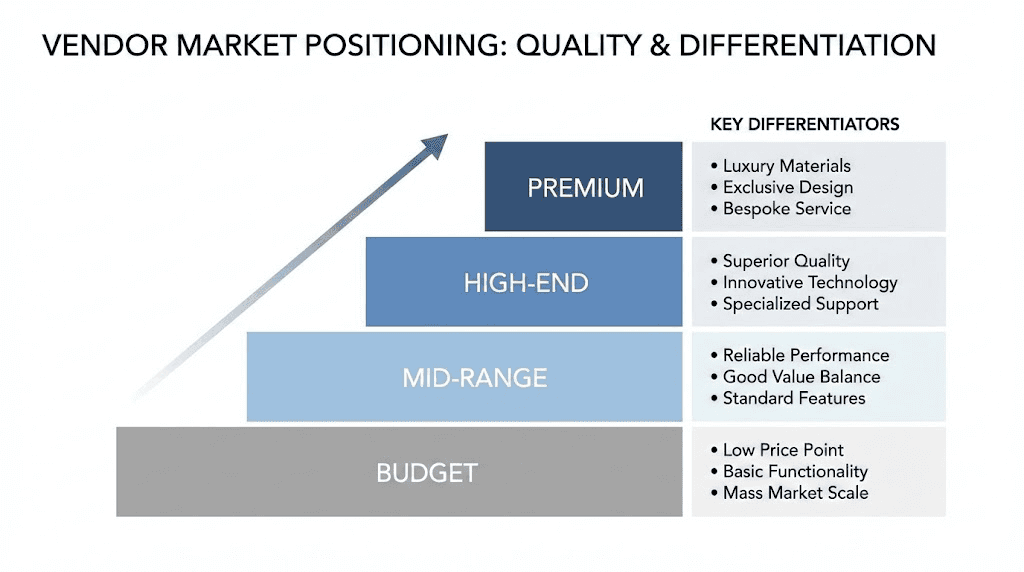
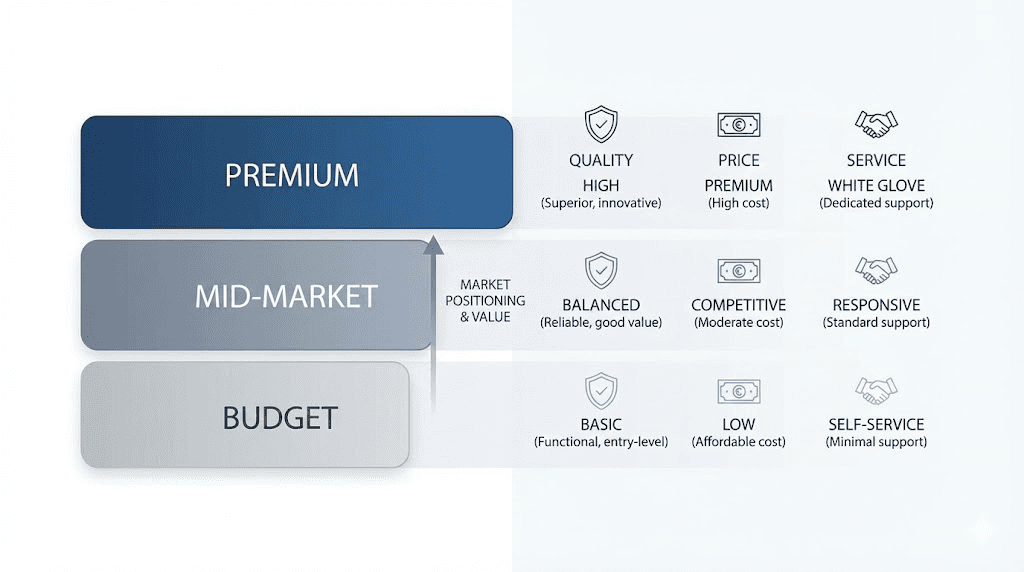
Market structure and vendor categories
Premium tier vendors:
Premium vendors emphasize quality verification, comprehensive testing documentation, and customer service excellence. These suppliers typically charge higher prices reflecting their investment in quality systems. Products often include detailed certificates of analysis from third-party laboratories, and customer support responds promptly to inquiries. The best peptide vendors generally fall within this category, prioritizing quality over lowest-price competition.
Mid-market suppliers:
Mid-market vendors balance quality and affordability, offering testing documentation while maintaining competitive pricing. These suppliers may provide less comprehensive COAs or use less well-known testing laboratories. Product quality often proves adequate for many research applications while costs remain accessible for budget-conscious researchers. Klow Peptides positions within this mid-market segment based on available information.
Budget vendors:
Budget-focused suppliers prioritize lowest possible pricing, sometimes sacrificing testing depth or customer service. Quality verification may prove limited or absent, requiring researchers to conduct independent testing for critical applications. While some budget vendors deliver adequate products, the category carries higher risk of quality issues requiring careful evaluation.
Quality verification importance
Why testing matters:
Peptide quality directly impacts research outcomes. Impure compounds introduce variables that confound results, while degraded products may produce no effects or unexpected responses. The peptide research and studies guide emphasizes quality verification as foundational to meaningful research. Without confirmed purity and identity, researchers cannot draw valid conclusions from their investigations.
Certificate of analysis standards:
Quality COAs include multiple analytical methods confirming both identity and purity. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) provides purity percentage, while mass spectrometry confirms molecular identity. The peptide elution time and intensity heatmap guide helps researchers interpret these analytical results. Complete COAs include laboratory identification, batch numbers, testing dates, and methodology details.
Third-party versus in-house testing:
Third-party laboratory testing provides stronger verification than in-house analysis. Independent laboratories have no financial incentive to report favorable results, making their findings more credible. Vendors providing only in-house testing require greater scrutiny, as conflicts of interest may influence reported results.
Evaluating vendor claims critically
Marketing versus reality:
Vendor marketing often emphasizes quality claims that prove difficult to verify. Phrases like "pharmaceutical grade," "highest purity," and "laboratory tested" appear frequently without supporting documentation. Critical evaluation requires looking beyond marketing language to actual evidence including verifiable COAs, laboratory accreditation, and community verification reports.
Red flags to watch:
Warning signs include vendors unable to provide COAs upon request, generic certificates without batch-specific information, unrealistically low pricing suggesting quality compromises, and limited or absent customer service. The peptide safety and risks guide covers quality-related concerns affecting research safety.
Community intelligence:
Research communities share vendor experiences providing insight beyond marketing claims. Forum discussions, review aggregators, and community testing initiatives reveal patterns invisible from vendor websites alone. While individual reports require critical evaluation, consistent themes across multiple sources prove informative.
Klow Peptides company overview
Examining Klow Peptides specifically requires assessing their business practices, product offerings, and market positioning.
Business background and positioning
Company establishment:
Klow Peptides operates as a research peptide supplier serving the scientific community. The company positions within the mid-market vendor segment, emphasizing product availability and competitive pricing. Their catalog spans multiple peptide categories serving various research applications from metabolic studies to tissue repair investigations.
Market approach:
The vendor targets researchers seeking accessible pricing without completely sacrificing quality verification. This positioning attracts budget-conscious researchers while distinguishing from the lowest-cost suppliers through basic quality documentation. Understanding this market position helps calibrate expectations appropriately.
Geographic operations:
Operational details including manufacturing relationships, inventory locations, and shipping origins affect delivery timelines and product handling. Domestic inventory enables faster shipping compared to international fulfillment, while manufacturing source locations may influence quality consistency.
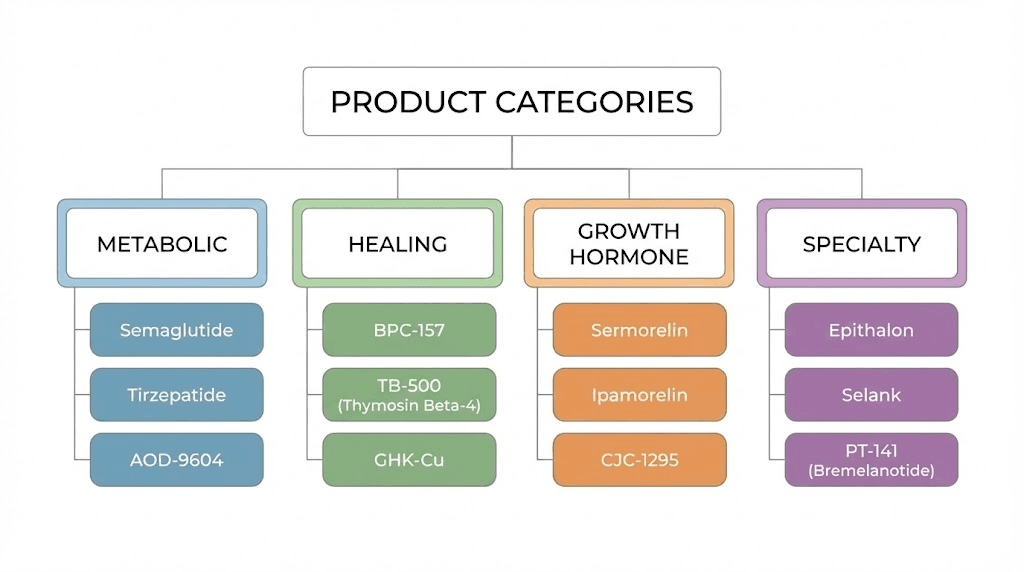
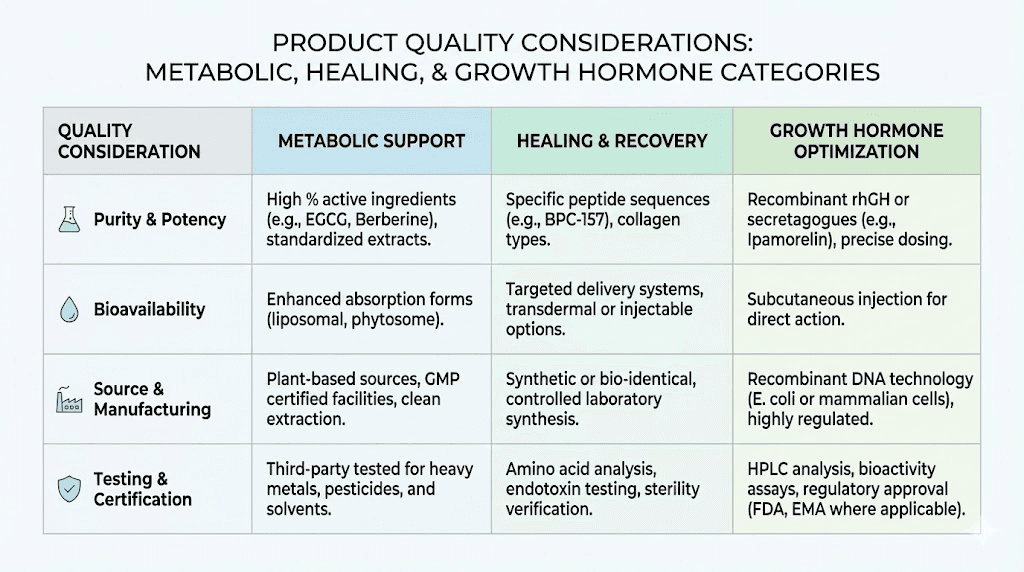
Product catalog overview
Metabolic research peptides:
The catalog includes compounds relevant to metabolic research including GLP-1 analogs and related peptides. Semaglutide, tirzepatide, and similar compounds serve weight loss research applications. The fat loss peptide category represents significant demand within the research community.
Healing and recovery compounds:
BPC-157, TB-500, and related peptides support injury healing research. These popular compounds maintain steady demand, and vendor quality consistency for these established products provides insight into overall reliability. The BPC-157 versus TB-500 comparison helps researchers select appropriate compounds.
Growth hormone secretagogues:
CJC-1295, ipamorelin, and growth hormone releasing peptides round out typical offerings. The ipamorelin versus CJC-1295 comparison guides research protocol selection. These compounds serve muscle growth and anti-aging research applications.
Specialty and emerging compounds:
Newer compounds including retatrutide and other emerging peptides may appear in vendor catalogs as market demand develops. Availability of cutting-edge compounds indicates vendor market awareness and supply chain capabilities.
Quality claims and documentation
Stated purity standards:
Vendors typically claim 98%+ purity for research peptide products. Evaluating these claims requires examining supporting documentation rather than accepting stated percentages at face value. Actual COAs should match label claims with appropriate analytical methodology supporting the stated purity.
Testing documentation availability:
Quality vendors provide COAs readily upon request or include them with shipments. Difficulty obtaining testing documentation suggests quality verification gaps. Researchers should request COAs before purchasing to evaluate documentation quality and verify testing claims.
Laboratory relationships:
Understanding which laboratories perform testing helps assess result credibility. Accredited laboratories following standardized methods provide more trustworthy results than unknown testing sources. Vendor transparency about laboratory relationships indicates quality commitment.
Evaluating Klow Peptides quality systems
Quality assessment requires examining multiple verification dimensions beyond marketing claims.
Certificate of analysis evaluation
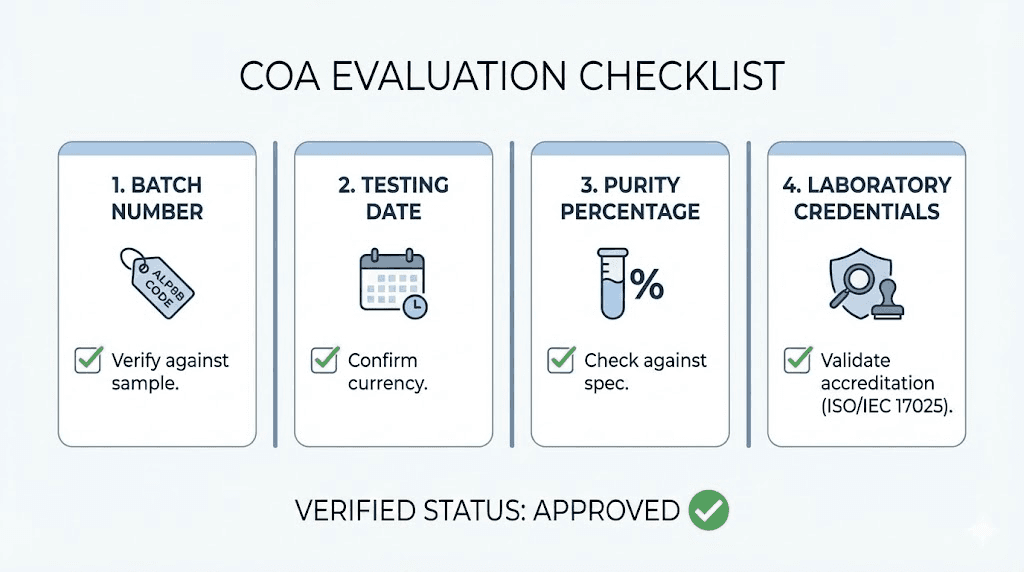
COA completeness:
Complete certificates include peptide identification, batch number, testing date, purity percentage, analytical method, and laboratory identification. Missing elements reduce document usefulness for quality verification. The research standards guide covers documentation expectations.
Analytical methods used:
HPLC remains the standard purity assessment method, providing percentage purity through peak area analysis. Mass spectrometry confirms molecular identity through mass measurement. Amino acid analysis verifies sequence accuracy. Multiple analytical methods provide stronger verification than single-method testing.
Batch specificity:
COAs should reference specific production batches matching product labels. Generic certificates without batch information suggest template documents rather than actual testing. Batch-specific documentation enables tracking quality consistency across purchases.
HPLC interpretation specifics
Chromatogram elements:
HPLC produces chromatograms showing peaks corresponding to different compounds. The main peak represents the target peptide, while additional peaks indicate impurities. Peak area ratios yield purity percentages. Understanding chromatogram interpretation helps researchers evaluate COA validity.
Retention time consistency:
Specific peptides produce characteristic retention times under standardized analysis conditions. Consistent retention times across batches indicate reliable identification. Significant variation suggests different compounds or analytical inconsistency.
Peak quality indicators:
Sharp, symmetrical peaks indicate clean separation and compound purity. Broad, tailing, or shouldered peaks suggest contamination or degradation. Visual chromatogram assessment provides quality insight beyond stated purity percentages.
Mass spectrometry verification
Molecular weight confirmation:
Mass spectrometry measures molecular weight, confirming compound identity. Each peptide has a specific expected mass based on amino acid composition. Matching expected mass provides identity verification complementing purity assessment.
Fragmentation analysis:
Advanced mass spectrometry analysis can confirm peptide sequences through characteristic fragmentation patterns. This deeper analysis provides stronger identity confirmation than molecular weight alone. Not all vendor COAs include fragmentation data.
Result interpretation:
Mass spectrometry results should closely match theoretical values for the target peptide. Small deviations may reflect measurement precision, while significant differences indicate identity problems or modifications.
Pricing analysis and value assessment
Cost considerations factor into vendor evaluation while avoiding overemphasis on price alone.
Klow Peptides pricing structure
Competitive positioning:
Pricing typically falls within the mid-market range, below premium vendors while above the cheapest suppliers. This positioning reflects the quality-price balance characterizing mid-market vendors. Researchers should evaluate whether pricing aligns with quality verification depth.
Volume considerations:
Bulk purchasing often provides per-unit cost reductions. Understanding volume discount structures helps optimize purchasing for extended research protocols. The peptide cost calculator assists with total protocol budgeting.
Promotional opportunities:
Periodic sales and promotions may provide purchasing opportunities below standard rates. Timing purchases around promotional periods can reduce costs significantly when protocol timelines allow flexibility.
Value equation beyond price
Quality-adjusted cost:
True value considers cost per unit of verified pure compound rather than nominal product pricing. Lower-priced products with lower actual purity may deliver less active compound per dollar. This calculation requires honest quality assessment.
Reliability premium:
Consistent quality from reliable vendors may justify modest price premiums over less predictable sources. Research disruption from quality issues costs more than small per-unit savings. The vendor comparison guide helps evaluate reliability factors.
Service value:
Customer service responsiveness, shipping reliability, and problem resolution contribute to overall value beyond product pricing. Vendors with strong service may warrant premium consideration for critical research applications.
Comparison to alternatives
Premium vendor comparison:
Premium vendors typically charge more while providing more comprehensive quality verification. The Prime Peptides comparison examines one premium alternative. Price differences should reflect quality verification depth.
Budget alternatives:
Lower-priced vendors exist with varying quality consistency. Cost savings must be weighed against verification uncertainty. Budget sourcing may suit non-critical applications while critical research warrants quality investment.
Value optimization:
Optimal value often comes from mid-market vendors providing adequate quality verification at reasonable prices. Matching vendor selection to research criticality optimizes budget allocation across different application needs.
Ordering process and customer experience
Practical purchasing considerations affect research convenience and timeline.
Website and ordering interface
Navigation experience:
Website organization affects product discovery and ordering efficiency. Clear category structures and search functionality help researchers locate specific compounds. Product pages should include relevant specifications, pricing, and availability information.
Account features:
Account creation enables order tracking, purchase history, and potentially loyalty benefits. Guest checkout options accommodate privacy preferences. Account features providing research protocol support add value beyond basic ordering.
Payment processing:
Payment options including credit cards, cryptocurrency, and alternative methods accommodate different preferences. Processing security and privacy protection matter given research compound purchasing sensitivity.
Shipping and delivery
Shipping options:
Standard and expedited shipping options accommodate different timeline requirements. Shipping cost structures affect total purchase expense. The peptide storage guide covers shipping-related stability considerations.
Packaging quality:
Appropriate packaging protects temperature-sensitive peptides during transit. Insulated packaging with cooling elements maintains stability. Arrival condition reflects shipping practice quality. Understanding room temperature stability helps evaluate shipping risk.
Delivery reliability:
Consistent delivery within stated timeframes enables research planning. Tracking information provides shipment visibility. Delivery reliability patterns emerge from community experience reports.
Customer service quality
Pre-purchase support:
Responsive customer service for product questions and COA requests indicates vendor commitment. Testing service responsiveness before purchasing reveals support quality. Knowledgeable support staff add value for protocol questions.
Issue resolution:
Problems including shipping delays, quality concerns, or order errors require resolution processes. Understanding policies before purchasing sets appropriate expectations. Effective resolution processes build vendor confidence.
Communication quality:
Clear, timely communication throughout the purchasing process reflects operational professionalism. Response times and communication helpfulness indicate service priority.
Quality verification beyond vendor documentation
Independent verification provides confidence beyond vendor-supplied information.
Independent testing options
Third-party laboratory analysis:
Submitting samples to independent laboratories provides verification beyond vendor COAs. Analytical laboratories accept peptide samples for purity and identity testing. Testing costs add to research expenses but provide certainty for critical applications.
Testing strategy:
Strategic testing of initial orders from new vendors or periodic verification of ongoing suppliers balances cost against verification value. Testing every purchase proves cost-prohibitive, while never testing accepts unnecessary risk.
Laboratory selection:
Accredited laboratories with peptide analysis experience provide reliable results. Testing methodology should match vendor COA methods for direct comparison. Turnaround time affects research timeline planning.
Community verification resources
Forum discussions:
Research communities share vendor experiences including quality reports and concerns. These crowdsourced assessments provide insight beyond marketing. Forum reports require critical evaluation as manipulation occurs, but patterns across multiple sources prove informative.
Testing initiatives:
Community-organized testing where samples undergo independent analysis with shared results provides valuable data. Participating in or benefiting from community testing enhances purchasing decisions for all members.
Experience aggregation:
Tracking reported experiences across time reveals vendor consistency patterns. Isolated issues among positive reports may reflect individual circumstances, while consistent concerns warrant attention.
Practical quality indicators
Physical characteristics:
Quality lyophilized peptides appear as fine, uniform powder. Discoloration, clumping, or unusual appearance may indicate problems. While appearance alone cannot confirm quality, obvious abnormalities warrant concern.
Reconstitution behavior:
Pure peptides dissolve readily without residue. Difficulty dissolving, cloudiness, or particulates suggest issues. The reconstitution calculator helps with proper preparation. Understanding reconstitution procedures ensures proper technique.
Research outcomes:
Ultimately, consistent expected results provide the most relevant quality indicator. The results tracking guide helps establish outcome expectations. Unexpected results warrant quality investigation.
Product-specific considerations
Different peptide categories present unique quality and sourcing considerations.
Metabolic peptides from Klow
GLP-1 receptor agonists:
Semaglutide and related compounds represent significant investment, making quality verification particularly important. The semaglutide calculator helps with protocol planning. Comparing semaglutide versus tirzepatide guides compound selection.
Newer metabolic compounds:
Emerging compounds like retatrutide may have less established quality benchmarks. The retatrutide buying guide covers sourcing considerations. Quality verification becomes more important for newer compounds with limited community experience.
Dosing considerations:
Metabolic peptide protocols require accurate dosing for meaningful results. The tirzepatide dosing guide provides protocol frameworks. Quality inconsistency undermines dosing accuracy and research validity.
Healing peptides assessment
BPC-157 quality factors:
BPC-157 represents one of the most popular research peptides with well-established quality expectations. The BPC-157 calculator assists with dosing. Understanding BPC-157 administration ensures proper use.
TB-500 considerations:
TB-500 serves healing research applications with specific quality requirements. The TB-500 calculator helps with protocol planning. The TB-500 benefits guide covers research applications.
Combination protocols:
Researchers often combine healing peptides, making quality consistency across compounds important. The stack calculator assists with combination planning. The stacking guide covers combination strategies.
Growth hormone peptides evaluation
CJC-1295 quality:
CJC-1295 requires proper handling to maintain the DAC modification. The CJC-1295 calculator helps with dosing. Storage stability affects product integrity over time.
Ipamorelin assessment:
Ipamorelin quality affects growth hormone release research outcomes. Comparing ipamorelin versus CJC-1295 helps with compound selection. The ipamorelin benefits guide covers research applications.
HGH fragment considerations:
HGH Fragment 176-191 has specific stability requirements. The HGH fragment calculator assists with protocol planning. Smaller peptides may have different stability profiles requiring careful handling.
Safety and responsible research practices
Quality sourcing supports research safety alongside proper protocols.
Quality-related safety considerations
Contamination risks:
Impure peptides may contain contaminants affecting research safety. The safety guide covers quality-related risks. Endotoxin testing on COAs indicates bacterial contamination screening.
Identity verification importance:
Receiving the wrong compound poses significant risks. Mass spectrometry confirmation on COAs provides identity verification. Unexpected research responses warrant quality investigation.
Degradation product concerns:
Degraded peptides may contain breakdown products with unknown effects. Proper storage practices minimize degradation. Understanding refrigerated storage duration helps maintain quality.
Protocol safety fundamentals
Dosing accuracy:
Quality peptides enable accurate dosing for safe protocols. The peptide calculator assists with dose calculations. The dosing guide covers protocol fundamentals.
Administration safety:
Proper injection technique minimizes administration risks. The injection guide covers technique fundamentals. Understanding reconstitution water requirements ensures proper preparation.
Monitoring practices:
Tracking responses helps identify quality or safety concerns early. The benefits and risks guide covers monitoring approaches. Unexpected responses warrant investigation including quality verification.
Research best practices
Documentation importance:
Recording vendor, batch, and protocol details enables quality correlation with outcomes. The cycle planning guide covers documentation approaches. Thorough records support troubleshooting if issues arise.
Starting conservatively:
New vendor relationships warrant conservative initial protocols. The getting started guide covers fundamental practices. Understanding peptide timelines sets realistic expectations.
Ongoing evaluation:
Monitoring vendor quality over time protects against degradation in previously reliable sources. Community engagement provides early warning of quality changes. Regular quality verification maintains research integrity.
Comparing Klow Peptides to alternatives
Contextualizing one vendor requires understanding alternatives.
Premium vendor comparison
Quality verification depth:
Premium vendors typically provide more comprehensive testing documentation including multiple analytical methods and detailed laboratory information. The quality premium reflects investment in verification systems that mid-market vendors may not match.
Service differences:
Premium vendors often provide superior customer service with faster response times and more knowledgeable support. Research guidance may accompany basic order support. Service quality differences affect researcher experience beyond product quality.
Price-quality tradeoffs:
Premium pricing should reflect genuine quality advantages rather than marketing positioning alone. Evaluating whether quality differences justify price premiums requires examining actual documentation and verification depth.
Mid-market alternatives
Comparable vendors:
Multiple mid-market vendors compete with similar positioning. Direct comparison requires evaluating testing documentation, pricing, service quality, and community reputation across candidates. Building relationships with multiple vendors provides sourcing flexibility.
Differentiation factors:
Product availability, specific compound specialization, and service elements differentiate similarly-positioned vendors. Researchers may prefer different vendors for different compounds based on these factors.
Quality consistency:
Mid-market vendor quality may prove more variable than premium suppliers. Ongoing monitoring and periodic verification protect against quality degradation over time.
Budget vendor considerations
Cost-quality tradeoffs:
Budget vendors sacrifice quality verification depth for lower pricing. Some deliver adequate products despite limited documentation, while others provide substandard materials. Risk tolerance affects appropriate selection.
Verification requirements:
Budget sourcing increases independent verification importance. Researchers unable to verify independently face greater uncertainty with low-cost sources. The common mistakes guide covers sourcing pitfalls.
Appropriate applications:
Non-critical applications may justify budget vendor selection where quality uncertainty proves acceptable. Critical research warrants quality investment regardless of budget constraints.
Long-term vendor relationship considerations
Extended research benefits from stable, reliable sourcing relationships.
Relationship development
Initial evaluation period:
New vendor relationships warrant careful evaluation over initial purchases. Quality consistency across multiple orders provides reliability evidence. Service quality patterns emerge through repeated interactions.
Building vendor familiarity:
Familiar vendors reduce verification burden over time as quality consistency establishes confidence. Account history may provide loyalty benefits or service advantages. Relationship investment pays dividends for extended research programs.
Diversification value:
Maintaining relationships with multiple quality vendors provides sourcing flexibility. Supply disruptions, quality changes, or pricing shifts affect individual vendors unpredictably. Diversification protects research continuity.
Quality monitoring over time
Consistency tracking:
Monitoring quality across purchases reveals consistency patterns. Declining quality warrants attention and potential vendor change. Improving quality may indicate operational investments worth recognizing.
Periodic verification:
Occasional independent testing maintains quality confidence even with established vendors. Testing frequency depends on research criticality and vendor track record. Verification provides ongoing quality assurance.
Community monitoring:
Staying engaged with research communities provides early warning of vendor quality changes. Shared experiences benefit the entire research community. Contributing observations helps others while gaining access to broader intelligence.
Vendor change considerations
When to consider alternatives:
Quality inconsistency, service degradation, or pricing changes may warrant exploring alternatives. New vendors entering the market may offer improved value propositions. Regular market monitoring identifies opportunities.
Transition planning:
Changing vendors requires evaluation effort and potential research disruption during transition. Planning transitions between protocol phases minimizes disruption. Testing new vendor products before committing substantial orders reduces risk.
Maintaining options:
Even with satisfactory primary vendors, maintaining awareness of alternatives provides insurance against future changes. Market evolution may shift optimal vendor selection over time.
How SeekPeptides supports vendor evaluation
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources supporting informed vendor selection and peptide research success.
The peptide calculator helps researchers plan protocols regardless of vendor selection. For reconstitution needs, the reconstitution calculator ensures accurate preparation. Budget planning benefits from the cost calculator projecting total research expenses across vendor options.
Educational resources covering peptide fundamentals, mechanisms of action, and getting started guidance support researchers at all experience levels. Quality evaluation resources including the analytical interpretation guide help assess vendor documentation.
SeekPeptides serves as a trusted resource for evidence-based peptide information, helping researchers make informed decisions about vendors, compounds, and protocols through comprehensive educational content and practical tools.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your vendors stay reliable, your peptides stay pure, and your research outcomes stay consistent. Join SeekPeptides.