Jan 27, 2026
You have been injecting peptides for months. The syringes, the alcohol swabs, the careful rotation of injection sites, the occasional bruise that forces you to wear long sleeves. It works. The wolverine stack has helped your recovery more than anything else you have tried. But every time you pull out that needle, a part of you wonders if there is a better way.
There is.
The wolverine peptide nasal spray has emerged as a compelling alternative to injections, offering a needle-free method to deliver BPC-157 and TB-500 directly into the bloodstream. The concept is straightforward. Instead of pushing a needle through skin and into subcutaneous tissue, you spray the reconstituted peptide solution into your nasal passages. The rich vascular network lining your nose absorbs the peptides and delivers them systemically within minutes.
But here is where things get complicated. Nasal bioavailability differs significantly from injection bioavailability. The dosing calculations change. The reconstitution process requires different considerations. And the research supporting this delivery method, while promising, comes with important caveats that every informed researcher should understand before making the switch.
This guide covers everything you need to know about wolverine peptide nasal spray. You will learn the exact mechanisms that make intranasal delivery work, the bioavailability comparisons that determine whether this method suits your research goals, step-by-step reconstitution instructions specific to nasal spray preparation, detailed dosing protocols based on current research, and the safety considerations that should inform your decision. SeekPeptides has compiled this information from peer-reviewed research, clinical protocols, and the collective experience of thousands of researchers to give you the most complete resource available on this increasingly popular delivery method.
Understanding the wolverine stack and why nasal delivery matters
The wolverine stack earned its name from the Marvel character known for supernatural healing abilities. Combining BPC-157 and TB-500 creates what researchers describe as a synergistic healing effect that exceeds what either peptide achieves alone. The combination has become one of the most widely used peptide stacks for tissue repair, injury recovery, and systemic healing support.
BPC-157 works locally. It concentrates healing activity at specific injury sites through mechanisms involving angiogenesis, growth factor modulation, and nitric oxide pathway activation. TB-500 works systemically. It circulates throughout the body, promoting cellular migration, reducing inflammation, and supporting repair processes wherever damage exists.
Together, they address healing from two complementary angles.
The question of delivery method becomes relevant when researchers consider their specific goals. Traditional subcutaneous injection provides the highest bioavailability, typically 80-95% of the administered dose reaching systemic circulation. This remains the gold standard for peptide administration. However, injection is not without drawbacks. It requires sterile technique, causes discomfort for needle-averse individuals, creates potential injection site reactions, and demands careful rotation to avoid tissue damage over extended protocols.
Nasal spray offers an alternative that eliminates these concerns while introducing its own set of considerations. The nasal mucosa provides direct access to the bloodstream through a dense network of capillaries. Peptides sprayed into the nose bypass the digestive system entirely, avoiding the enzymatic degradation that destroys oral peptides. Absorption occurs within minutes. And for researchers interested in potential neurological effects, the nasal route offers something injections cannot: a more direct pathway to the central nervous system.
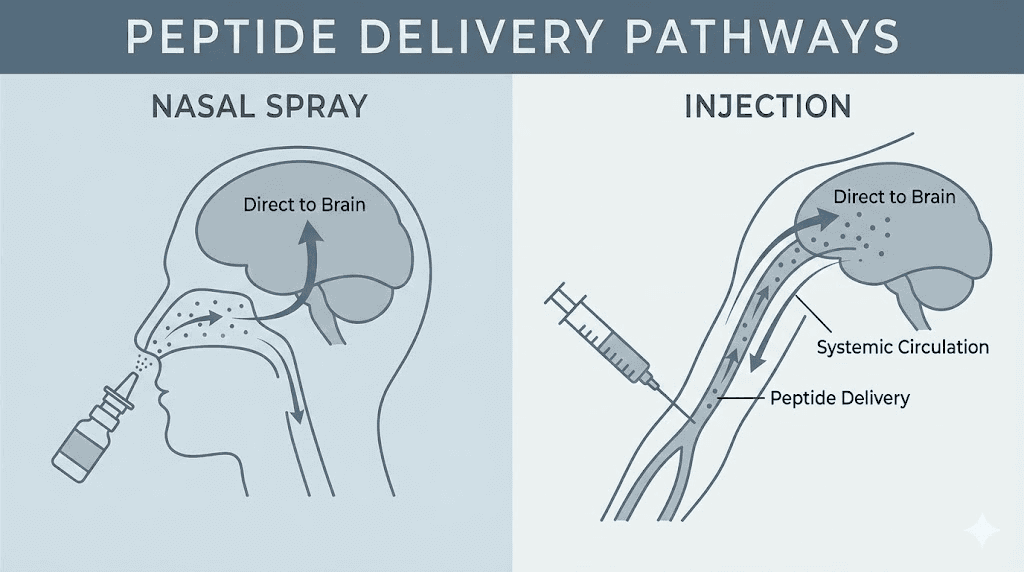
How nasal peptide absorption works
The science behind intranasal peptide delivery involves understanding what happens when a peptide solution contacts your nasal mucosa. This is not simply about getting peptides into your nose. It is about optimizing conditions for maximum absorption while minimizing loss.
Your nasal cavity consists of three main regions. The vestibular region near the nostrils contains hair and filters particles. The respiratory region, which comprises the largest surface area, is lined with ciliated epithelium and rich vasculature. The olfactory region at the top of the nasal cavity connects directly to the brain through the olfactory nerve. Each region plays a different role in peptide absorption.
For systemic absorption, the respiratory region matters most. This area contains extensive blood vessels lying just beneath a thin layer of epithelial cells. When a peptide solution lands on this surface, several things happen simultaneously. The solution spreads across the mucosa. Small peptide molecules begin passing between epithelial cells through paracellular transport. Some molecules cross directly through cells via transcellular transport. Within 10-15 minutes, absorbed peptides enter the bloodstream and begin circulating throughout the body.
The efficiency of this process depends on multiple factors. Molecular size affects absorption, with smaller peptides generally crossing the mucosal barrier more easily than larger ones. BPC-157 contains 15 amino acids with a molecular weight around 1419 Da. TB-500 is larger at 43 amino acids and approximately 4963 Da. Both fall within the range that studies show can be effectively delivered intranasally, though the smaller BPC-157 may achieve somewhat higher bioavailability through this route.
Solution concentration matters significantly. The limited volume that the nasal cavity can accommodate, approximately 100-200 microliters per nostril without runoff, means that higher concentrations deliver more peptide per spray. However, excessively concentrated solutions may cause irritation that paradoxically reduces absorption by triggering protective mucus secretion.
The health of your nasal passages also influences absorption. Inflammation, congestion, or damage to the nasal mucosa can impair peptide uptake. Researchers typically achieve best results when using the spray on clear, healthy nasal passages.
Bioavailability comparison: nasal spray versus injection
Numbers matter when comparing delivery methods. The bioavailability question fundamentally determines whether nasal spray can deliver results comparable to injection.
Research indicates that nasal spray bioavailability for peptides like BPC-157 ranges from 40-60%, depending on formulation and individual factors. Compare this to subcutaneous injection at 80-95% bioavailability. The difference is substantial but not insurmountable.
What does this mean practically? A researcher administering 500mcg of BPC-157 via injection achieves approximately 400-475mcg of systemic absorption. The same 500mcg via nasal spray delivers roughly 200-300mcg systemically. To achieve equivalent systemic levels, nasal spray users need to administer proportionally higher doses.
This calculation becomes important when designing protocols. The convenience of nasal spray comes at the cost of increased peptide consumption. Whether this tradeoff makes sense depends on individual priorities, including needle aversion, convenience requirements, and budget considerations.
TB-500 bioavailability follows similar patterns, though its larger molecular size may result in slightly lower nasal absorption compared to BPC-157. Researchers working with the wolverine stack via nasal spray often adjust their dosing accordingly.
One consideration that partially offsets the bioavailability difference involves absorption kinetics. Nasal spray provides faster absorption than subcutaneous injection in many cases. Peptides reach peak blood levels more quickly, which may be advantageous for certain research applications. The clinical significance of this faster onset remains an area of ongoing investigation.
When nasal delivery may be preferred
Despite lower bioavailability, nasal delivery offers advantages that make it preferable for certain research scenarios. Researchers examining potential neurological or cognitive effects often prefer the nasal route because it provides more direct access to the central nervous system. Some portion of intranasally administered peptides may reach the brain through the olfactory pathway, bypassing the blood-brain barrier that limits systemic delivery to CNS tissues.
The convenience factor should not be underestimated. Nasal spray requires no sterile injection technique. There is no needle disposal concern. Administration takes seconds rather than the minutes required for proper injection protocol. For researchers conducting long-term studies or those with needle aversion, these practical considerations may outweigh the bioavailability difference.
Travel also favors nasal spray. Carrying syringes and vials raises practical and sometimes legal complications that a simple nasal spray bottle avoids.
BPC-157 nasal spray: mechanisms and research
Understanding how BPC-157 works provides context for evaluating nasal delivery. This pentadecapeptide, derived from human gastric juice, demonstrates remarkable healing properties across multiple tissue types in preclinical research.
The primary mechanism involves activation of the VEGFR2-Akt-eNOS pathway. When BPC-157 binds to VEGFR2 receptors, it triggers a cascade that increases nitric oxide production and promotes angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels. This enhanced vascularization brings more oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues, accelerating repair.
Studies show BPC-157 promotes tendon fibroblast outgrowth and migration through FAK-paxillin pathway activation. It demonstrates cytoprotective effects by enhancing eNOS activity through Src kinase-caveolin-1 signaling. It upregulates heme oxygenase-1, reducing oxidative stress that impairs healing. These mechanisms work together to create an environment conducive to tissue repair.
Research specifically examining nasal delivery of BPC-157 remains limited compared to injection studies. However, the peptide characteristics that enable absorption through the gastric mucosa, including its stability in acidic environments and resistance to enzymatic degradation, suggest it should maintain activity when absorbed through nasal mucosa as well.
Preclinical studies demonstrate BPC-157 benefits including accelerated healing of tendons, ligaments, muscles, and bones. The peptide shows gastrointestinal protective effects relevant to gut health. It demonstrates wound healing acceleration in skin injuries. Anti-inflammatory properties reduce swelling and pain associated with injuries. Neuroprotective effects have been observed in certain models of neurological damage.
A 2020 study published in Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology found BPC-157 well-tolerated with no severe toxic effects across multiple animal species, supporting its safety profile for continued research.
TB-500 nasal spray: mechanisms and research
TB-500 operates through fundamentally different mechanisms than BPC-157, which explains why combining them produces synergistic effects. This 43-amino acid peptide derives from thymosin beta-4, a naturally occurring protein that plays crucial roles in cellular organization and tissue repair.
The primary mechanism involves actin regulation. TB-500 binds to G-actin monomers, preventing premature polymerization into filaments. This actin sequestration maintains a pool of mobile actin ready for rapid deployment when cells need to migrate or repair damage. The result is enhanced cellular mobility that allows repair cells to reach injury sites more efficiently.
Beyond actin regulation, TB-500 promotes angiogenesis, reduces inflammation through NF-kB pathway modulation, and enhances stem cell migration and differentiation. Where BPC-157 concentrates effects locally, TB-500 exerts systemic influence that supports whole-body recovery.
Research on TB-500 includes studies showing improved cardiac tissue repair following ischemic damage. Accelerated wound healing through enhanced re-epithelialization has been demonstrated. Anti-inflammatory effects in autoimmune models suggest broader applications. Neurological benefits including improved outcomes in demyelinating disease models point to CNS effects.
For nasal delivery specifically, TB-500 molecular size presents considerations. At nearly 5000 Da, it approaches the upper limit of what intranasal delivery can effectively handle. Research on intranasal peptide delivery indicates that molecules up to approximately 6000 Da can be absorbed, placing TB-500 within range but potentially at lower efficiency than smaller peptides like BPC-157.
This difference has practical implications for dosing. Researchers using nasal spray for TB-500 may need proportionally higher doses compared to BPC-157 to achieve equivalent systemic levels relative to injection administration.
Combining BPC-157 and TB-500 in nasal spray form
The wolverine stack nasal spray combines both peptides in a single delivery system. This combination follows the same synergy principle that makes the injectable wolverine stack popular, applied to intranasal administration.
The rationale for combination is straightforward. BPC-157 provides local healing support, particularly beneficial for specific injury sites. TB-500 provides systemic healing support that circulates throughout the body. Together, they address tissue repair from multiple angles simultaneously.
Commercial preparations typically pair the peptides at ratios reflecting their typical dosing relationships. Common formulations include 5mg BPC-157 with 10mg TB-500 per vial, or 10mg of each peptide. The specific ratio matters less than ensuring adequate amounts of each peptide are delivered per spray.
Researchers preparing their own wolverine stack nasal spray must consider the reconstitution mathematics carefully. Each peptide dissolves in bacteriostatic water. The combined solution goes into a nasal spray bottle calibrated to deliver a known volume per spray. Calculating the final concentration requires accounting for both peptides and the total solution volume.
Stability considerations arise when combining peptides. Both BPC-157 and TB-500 maintain stability in bacteriostatic water when refrigerated properly. Combined solutions follow similar storage requirements, typically remaining stable for 30-60 days when kept cold and protected from light.
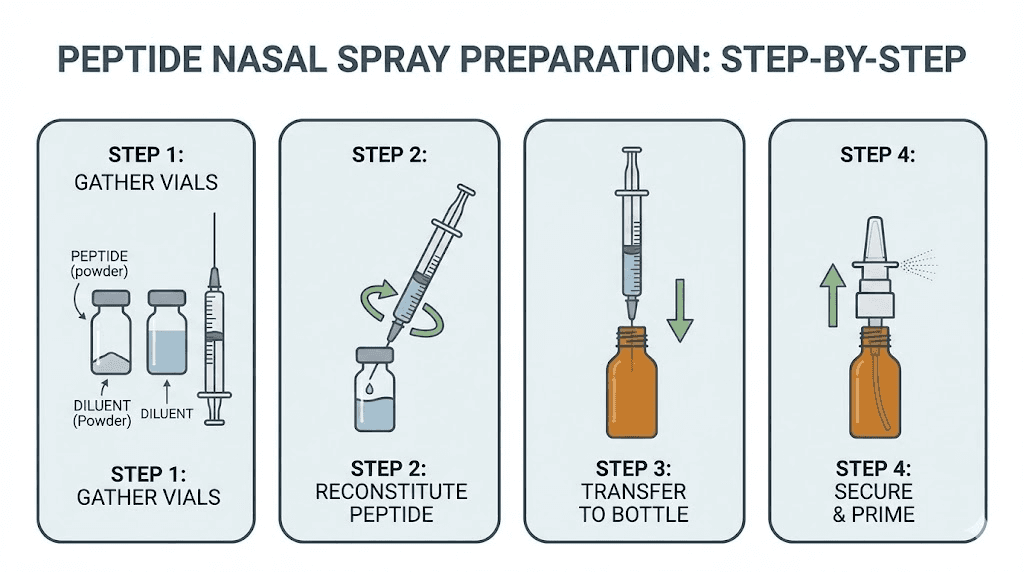
How to prepare wolverine peptide nasal spray
Preparing a nasal spray from lyophilized peptides requires attention to sterile technique and accurate calculations. The process involves more steps than preparing an injectable solution but uses similar principles.
Required supplies
Gather all materials before beginning. You will need lyophilized BPC-157 and TB-500 peptides in sealed vials. Bacteriostatic water serves as the reconstitution medium, with its benzyl alcohol content providing preservation that extends shelf life. Sterile syringes with appropriate gauge needles allow precise water measurement and transfer. A sterile nasal spray bottle, typically with 0.1ml per spray delivery, holds the final solution. Alcohol wipes ensure surfaces and vial tops are properly sterilized.
Reconstitution steps
Begin by cleaning your work surface thoroughly. Wash hands and consider wearing sterile gloves, though this is less critical for nasal spray preparation than for injectables since the solution will not enter sterile tissue.
Calculate your desired concentration first. A typical target provides 250-500mcg of BPC-157 and 250-500mcg of TB-500 per spray. If your nasal bottle delivers 0.1ml per spray and you want 500mcg of each peptide per spray, you need a concentration of 5mg/ml for each peptide.
For a 5mg vial of BPC-157 combined with a 10mg vial of TB-500 in a 15ml nasal spray bottle, you would add bacteriostatic water to create your total volume. The math requires careful attention. With 5mg BPC-157 in 15ml, each ml contains 333mcg, meaning each 0.1ml spray delivers 33mcg. This may be too dilute for typical protocols. Adjusting either the total volume or the peptide amounts changes the final concentration proportionally.
When reconstituting, draw bacteriostatic water into a sterile syringe. Inject slowly down the inside wall of the peptide vial. Never spray water directly onto the lyophilized powder, as this can damage the peptide structure. Allow the peptide to dissolve naturally by gently swirling, never shaking, the vial. Continue until the solution appears completely clear with no visible powder.
Repeat for each peptide vial. Once both are reconstituted, draw up each solution and transfer to your nasal spray bottle. If combining into one bottle, add both solutions together. Attach the spray mechanism and prime by pumping several times until you get consistent spray output.
Label clearly with peptide names, concentrations, reconstitution date, and calculated expiration. Store in the refrigerator when not in use.
Dosing protocols for wolverine nasal spray
Dosing nasal spray peptides requires adjusting for bioavailability differences compared to injection. The goal is achieving systemic peptide levels comparable to established injectable protocols while accounting for the lower absorption efficiency of nasal delivery.
BPC-157 nasal spray dosing
Standard injectable BPC-157 protocols typically use 200-500mcg administered subcutaneously once or twice daily. Given 40-60% nasal bioavailability compared to 80-95% for injection, equivalent nasal doses would be approximately 400-1000mcg to achieve similar systemic levels.
Most nasal spray protocols settle on 500mcg administered 2-3 times daily, totaling 1000-1500mcg per day. This provides adequate systemic exposure while remaining within commonly researched dose ranges. Some researchers use higher doses up to 1000mcg per administration when targeting more aggressive recovery goals.
Splitting doses throughout the day may enhance results. The relatively fast absorption and clearance of nasal peptides means multiple smaller doses can maintain more consistent blood levels than a single large dose.
TB-500 nasal spray dosing
Injectable TB-500 typically follows a loading and maintenance pattern. Loading phases use 2-5mg twice weekly for four weeks. Maintenance uses 1-2mg weekly thereafter. Converting to daily nasal spray requires distributing these weekly amounts across daily administrations and adjusting for bioavailability.
A typical nasal TB-500 protocol might use 500-1000mcg daily during loading phases, dropping to 250-500mcg daily for maintenance. Some protocols advocate higher loading doses up to 2.5mg daily via nasal spray, though this significantly increases peptide consumption.
Combined wolverine stack dosing
When using both peptides together via nasal spray, common protocols include 500mcg BPC-157 combined with 500mcg TB-500 administered 2-3 times daily. This provides roughly 1-1.5mg of each peptide daily during active protocols.
Administration technique affects absorption. Wait at least 30-60 seconds between sprays in the same nostril to avoid oversaturation and runoff. Alternate nostrils with each spray. Avoid blowing your nose for 15-20 minutes after administration. Some researchers tilt their head slightly back during administration to maximize mucosal contact.
Protocol duration
Nasal spray protocols typically follow similar durations to injectable protocols. For acute injuries, 4-6 weeks of active use followed by a break. For chronic conditions or maintenance, 8-12 week protocols are common. Some researchers follow 2-months-on, 1-month-off cycling patterns to prevent potential receptor downregulation.
Safety considerations and potential side effects
Safety evaluation of wolverine peptide nasal spray requires considering both the peptides themselves and the nasal delivery route. Neither BPC-157 nor TB-500 has received FDA approval for human use, placing them in the category of research compounds without official safety data in humans.
Peptide safety profile
Preclinical research on BPC-157 safety is relatively encouraging. Studies in mice, rats, rabbits, and dogs found no severe toxic effects across a wide dose range from 6mcg/kg to 20mg/kg. No lethal dose was established, suggesting a wide safety margin. The peptide consistently demonstrates protective effects against various forms of organ damage in animal models.
TB-500 safety data is less extensive but similarly suggests good tolerability in preclinical models. Animal studies show no major adverse effects at therapeutic doses.
However, preclinical data does not guarantee human safety. The lack of controlled human clinical trials means the full safety profile remains unknown. Long-term effects, potential drug interactions, and effects in specific populations including pregnant women, children, and those with certain medical conditions have not been studied.
Nasal delivery specific concerns
Nasal administration introduces considerations not present with injection. Potential side effects include local irritation of the nasal passages. Sneezing, congestion, or rhinorrhea may occur, particularly with initial use. Some users report headaches associated with nasal peptide administration. These effects are typically mild and transient.
Long-term nasal spray use carries theoretical concerns about mucosal damage. While bacteriostatic water is generally well-tolerated, repeated daily exposure over months could potentially affect the nasal lining. No long-term data specifically addresses this question for peptide nasal sprays.
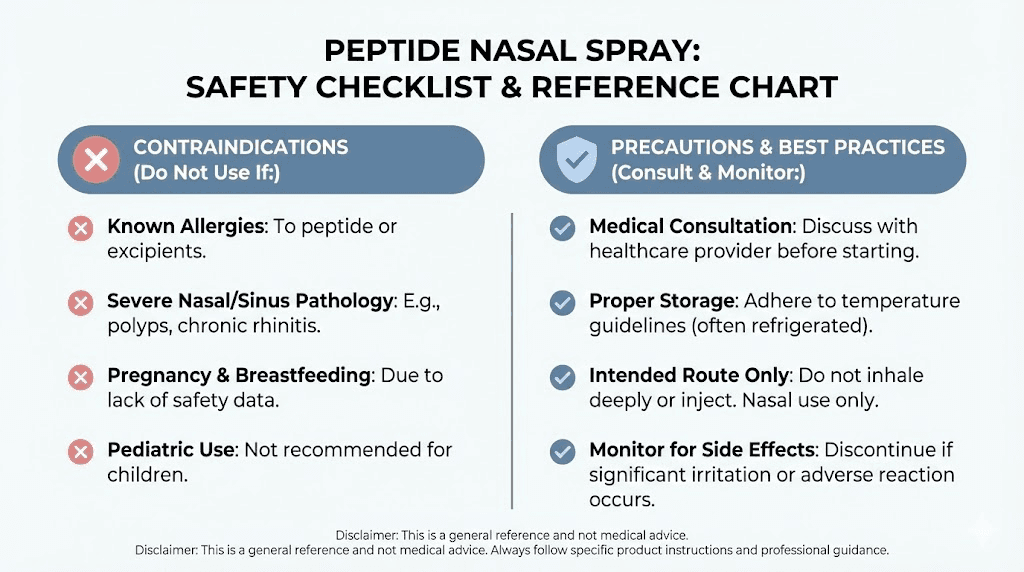
Contraindications and cautions
Researchers should exercise caution in several scenarios. Active nasal infections or significant congestion may impair absorption and potentially worsen nasal conditions. Known allergies to peptide components or benzyl alcohol in bacteriostatic water warrant avoidance. Pregnancy and breastfeeding represent situations where no safety data exists. History of cancer requires careful consideration given the growth-promoting properties of these peptides, though no evidence suggests they promote tumor growth in normal tissue.
Both peptides appear on the World Anti-Doping Agency prohibited substances list. Athletes subject to drug testing should be aware that use of these compounds violates anti-doping rules regardless of delivery method.
Comparing nasal spray to other delivery methods
Understanding how nasal spray fits into the broader landscape of peptide delivery helps researchers choose the optimal method for their specific goals.
Subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous injection remains the reference standard for peptide administration. Bioavailability of 80-95% provides efficient peptide utilization. Technique is straightforward once learned. Injection allows precise dosing with minimal waste. The main drawbacks involve needle discomfort, potential injection site reactions, and the requirement for sterile technique.
For researchers prioritizing maximum bioavailability and established protocol reliability, subcutaneous injection likely remains the preferred method.
Oral administration
Oral peptides face significant bioavailability challenges. Gastric acid and digestive enzymes degrade most peptides before absorption can occur. Estimates suggest oral bioavailability for peptides like BPC-157 may be only 1-2%, meaning massive doses would be required to achieve systemic effects. While some stable peptide formulations exist for oral use, the wolverine stack peptides are not well-suited to this route for systemic goals.
Interestingly, oral BPC-157 may still provide local benefits for gastrointestinal conditions by exerting effects directly on the gut lining before being degraded. This represents a niche application distinct from the systemic effects sought with nasal or injectable administration.
Topical application
Topical peptide delivery works well for local skin effects. Copper peptide serums demonstrate this principle effectively. However, most peptides do not penetrate skin sufficiently to achieve systemic levels. Topical wolverine stack application would likely provide only superficial wound healing benefits at the application site without the broader systemic effects that make this stack valuable.
Transdermal patches
Transdermal delivery systems using microneedles or permeation enhancers show promise for peptide delivery. These methods can achieve bioavailability approaching injection levels while avoiding needle phobia concerns. However, commercial transdermal peptide products remain limited, and preparation requires specialized equipment beyond what typical researchers possess.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Researchers new to nasal peptide delivery often make errors that reduce effectiveness or compromise safety. Learning from common mistakes saves time and peptide waste.
Reconstitution errors
Using the wrong diluent ranks among the most serious errors. Sterile water without bacteriostatic preservative shortens shelf life dramatically and risks bacterial contamination with repeated use. Saline solutions may affect peptide stability differently than bacteriostatic water. Always use pharmaceutical-grade bacteriostatic water for nasal spray preparation.
Shaking the vial during reconstitution can denature peptides. The agitation creates shear forces that damage the delicate molecular structure. Always swirl gently instead.
Calculating concentrations incorrectly results in either underdosing or overdosing. Double-check math before reconstituting. Write down calculations and verify before proceeding.
Storage mistakes
Leaving reconstituted nasal spray at room temperature accelerates peptide degradation. Always refrigerate when not actively using. Never freeze, as this can damage peptide structure. Keep away from light, which can degrade some peptides over time.
Using reconstituted solution beyond its stability window wastes effort on degraded peptides. Most bacteriostatic water reconstitutions remain stable 30-60 days when properly refrigerated. Mark your bottle with the reconstitution date and discard after this period.
Administration technique errors
Spraying too rapidly without allowing absorption time leads to solution dripping down the throat and being swallowed rather than absorbed. Wait between sprays. Tilting the head too far back causes the same problem. A slight backward tilt is sufficient.
Blowing your nose immediately after administration removes solution before absorption completes. Wait at least 15-20 minutes.
Using nasal spray during severe congestion dramatically reduces absorption. Clear nasal passages before administration when possible. If you have an active sinus infection, consider postponing nasal peptide use until it resolves.
What to expect: timelines and results
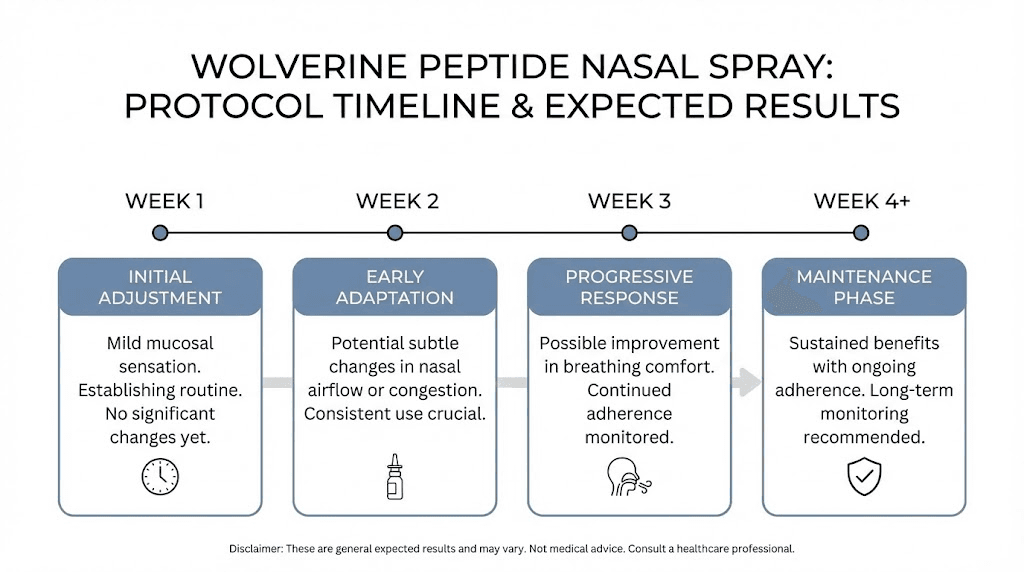
Setting realistic expectations for wolverine peptide nasal spray helps researchers evaluate their protocols objectively. Results develop gradually rather than appearing overnight.
Early phase: weeks one through two
During the initial period, most researchers notice subtle changes at most. Some report mild sensations at injury sites, possibly indicating increased activity. Sleep quality may improve for some, potentially related to recovery support. Energy levels sometimes increase. These early signs are encouraging but not universal.
Many researchers notice nothing definitive during the first two weeks. This does not indicate failure. Tissue healing takes time regardless of intervention support.
Intermediate phase: weeks two through four
More noticeable changes typically emerge during weeks two through four. Pain levels at injury sites often decrease measurably. Mobility and function improvements become apparent. Recovery from exercise or activity often accelerates noticeably. Inflammation reduction becomes visible in some cases.
This phase typically provides the clearest indication of whether the protocol is working for a given individual and condition.
Extended phase: weeks four through eight
By weeks four through eight, substantial healing progress is often evident for responding individuals. Chronic conditions that have resisted other interventions sometimes show significant improvement. Tissue that was clearly damaged may demonstrate functional recovery. The full extent of benefits often becomes clear during this phase.
Researchers should evaluate their results around the four to six week mark to determine whether to continue, adjust, or discontinue their protocol.
Factors affecting results
Individual variation in response is substantial. Age, overall health, injury severity and chronicity, concurrent therapies, nutrition, sleep, and activity levels all influence outcomes. The same protocol that produces dramatic results for one researcher may show modest effects for another.
Acute injuries typically respond faster than chronic degenerative conditions. Recent injuries from weeks to months old often show faster improvement than problems persisting for years.
When to choose injection instead
Despite the convenience of nasal delivery, certain situations favor traditional injection. Understanding when to use each method helps optimize results.
Local injuries benefit most from local injection. When treating a specific tendon, ligament, or muscle injury, injecting BPC-157 near the injury site concentrates the peptide where it is needed most. Nasal spray provides systemic distribution that may dilute effects at a specific location.
Maximum potency requirements favor injection. When optimal results matter more than convenience, the higher bioavailability of injection delivers more peptide per dose. For serious injuries or aggressive recovery goals, this efficiency may be important.
Cost sensitivity points toward injection. Since nasal spray requires higher doses to achieve equivalent systemic levels, peptide consumption increases. Researchers on limited budgets may find injection more economical despite the additional supplies required.
Research consistency benefits from established injection protocols. Most published research uses injection. Researchers wanting to replicate established protocols precisely should use the same delivery method.
Combining nasal and injectable approaches
Some researchers use both delivery methods strategically. This hybrid approach attempts to capture benefits of each route.
A common pattern involves using nasal spray for TB-500 systemic delivery while injecting BPC-157 locally at specific injury sites. This provides the convenience of nasal administration for the systemically-acting peptide while maintaining local concentration of BPC-157 where targeted healing is desired.
Another approach uses nasal spray for maintenance phases after an initial injection loading phase. The intensive early protocol uses injection for maximum initial impact. Once healing is established, nasal spray maintains support more conveniently.
Travel situations often prompt temporary switches from injection to nasal spray. Researchers maintaining ongoing protocols may prefer nasal spray during travel periods when carrying injection supplies is inconvenient, returning to injection when practical logistics allow.
Quality and sourcing considerations
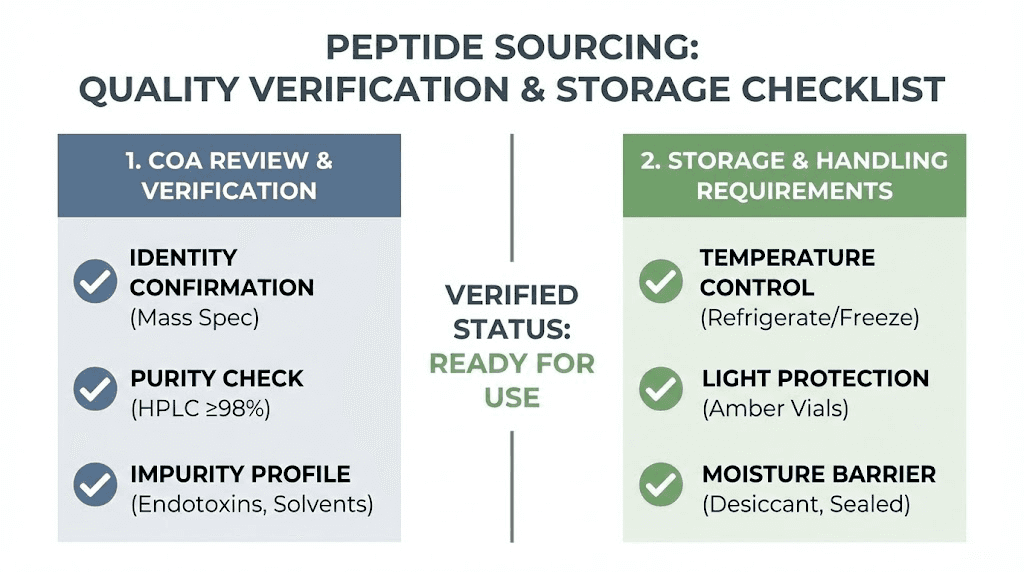
Peptide quality directly impacts results regardless of delivery method. Nasal administration may actually require higher quality standards since contamination would contact sensitive nasal mucosa rather than subcutaneous tissue that handles minor contamination more readily.
Purity verification matters significantly. Third-party testing confirming peptide identity and purity provides assurance that the product contains what it claims. Certificates of analysis from reputable testing laboratories should accompany purchases. Testing labs can verify both identity through mass spectrometry and purity through HPLC analysis.
Vendor reputation requires research. Established vendors with track records of consistent quality and transparent practices reduce risk of receiving substandard or adulterated products. Community feedback from other researchers provides valuable insight into vendor reliability.
Proper peptide handling during shipping affects quality. Peptides should ship cold with appropriate packaging. Receiving peptides that were exposed to elevated temperatures during transit may result in degradation before reconstitution.
Storage upon receipt maintains quality. Lyophilized peptides remain stable at room temperature for short periods but should be refrigerated for long-term storage. Freezing is acceptable for long-term storage of unreconstituted peptides. Once reconstituted, always refrigerate and use within the recommended timeframe.
Frequently asked questions
Does wolverine peptide nasal spray work as well as injection?
Nasal spray delivers lower bioavailability than injection, typically 40-60% compared to 80-95% for subcutaneous administration. This means you need proportionally higher doses via nasal spray to achieve similar systemic peptide levels. Whether this translates to equivalent results depends on individual factors and goals. Many researchers report satisfactory outcomes with properly dosed nasal spray protocols, though those seeking maximum potency often prefer injection.
How long does reconstituted nasal spray last?
When prepared with bacteriostatic water and stored refrigerated, reconstituted wolverine peptide nasal spray typically remains stable for 30-60 days. The benzyl alcohol in bacteriostatic water provides antimicrobial preservation that extends usability. Always label your spray with the reconstitution date and discard after 60 days regardless of remaining volume. If the solution becomes cloudy or develops particles, discard immediately.
Can I use regular saline for nasal spray?
Using regular saline instead of bacteriostatic water is not recommended for peptide nasal spray. Saline lacks the preservative necessary to prevent bacterial growth with repeated use. While a single-use preparation with sterile saline might be acceptable, multi-use bottles like nasal sprays require the antimicrobial protection of bacteriostatic water. Additionally, the peptide stability profile may differ in saline solutions.
How many sprays should I take per day?
Typical protocols involve 2-4 sprays per nostril, 2-3 times daily, depending on your concentration and target dose. Most researchers aim for 500-1000mcg of BPC-157 and 500-1000mcg of TB-500 daily during active protocols. Calculate your spray volume and concentration to determine how many sprays achieve your target dose. Always wait 30-60 seconds between sprays in the same nostril to maximize absorption.
Can nasal spray reach the brain directly?
Some portion of intranasally administered peptides may reach the central nervous system through the olfactory pathway, bypassing the blood-brain barrier. This nose-to-brain delivery is an area of active research for various therapeutic applications. For researchers interested in potential cognitive or neurological effects, nasal delivery may offer advantages over systemic injection. However, the extent and clinical significance of direct brain delivery for wolverine stack peptides requires further study.
Will the nasal spray cause irritation?
Some users experience mild nasal irritation, particularly with initial use. This typically manifests as slight tingling, increased mucus production, or occasional sneezing. These effects are usually mild and transient. If irritation is persistent or severe, reducing dose or frequency may help. Ensuring your solution is properly prepared at appropriate concentration reduces irritation risk. Significant ongoing irritation warrants discontinuing use.
Making the decision: is nasal spray right for you?
Choosing between nasal spray and injection for your wolverine stack protocol requires weighing multiple factors specific to your situation.
Nasal spray makes sense if needle aversion significantly impacts your ability to maintain consistent protocols. The best protocol is one you actually follow. If needles prevent consistency, lower bioavailability with reliable adherence beats higher bioavailability with sporadic use.
Nasal spray suits researchers interested in potential neurological effects who want the potential nose-to-brain delivery pathway. While systemic injection also delivers peptides to the brain via blood circulation, nasal delivery may provide more direct CNS access for some portion of the dose.
Nasal spray works well for maintenance phases after initial intensive treatment. Once you have seen results from a loading phase, nasal spray can conveniently maintain benefits without ongoing injection.
Nasal spray accommodates travel and lifestyle factors that make injection impractical. If your schedule or travel patterns make maintaining injection protocol difficult, nasal spray provides a workable alternative.
Injection likely remains preferable if you are treating specific local injuries and want maximum peptide concentration at the injury site. If maximum potency matters for your research goals. If peptide budget is a significant constraint. If you want to replicate established injection-based protocols precisely.
Many researchers ultimately use both methods at different times depending on circumstances. Building familiarity with both options provides flexibility to adapt your approach as situations change.
For researchers serious about understanding peptide protocols in depth, SeekPeptides provides comprehensive resources including dosing calculators, reconstitution guides, and protocol recommendations based on research evidence and community experience.
In case I do not see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your nasal passages stay clear, your peptides stay potent, and your recovery stay consistent. Join us today.



