Jan 13, 2026

Microneedle patches utilize arrays of microscopic projections, typically 25-2000 micrometers in length, that painlessly penetrate the stratum corneum to deliver peptides directly into the epidermis or dermis where absorption into systemic circulation occurs efficiently.
The technology democratizes peptide access by eliminating injection technique requirements, reducing cold chain dependencies through solid-state formulations, and providing consistent dosing without the variability inherent in self-administered injections.
Understanding microneedle technology
Microneedle technology represents a convergence of materials science, pharmaceutical formulation, and transdermal drug delivery that enables macromolecule transport across the skin barrier without the pain, complexity, or risks associated with conventional hypodermic needles.
Understanding the underlying technology establishes the foundation for appreciating both capabilities and limitations of patch-based peptide delivery.
The skin barrier challenge
Human skin presents a formidable barrier to drug absorption, with the stratum corneum, the outermost 10-20 micrometer layer of dead cells embedded in lipid matrix, blocking passage of most molecules larger than 500 Daltons. Peptides, ranging from several hundred to tens of thousands of Daltons, cannot passively penetrate intact skin regardless of concentration or contact duration.
Traditional transdermal patches work only for small, lipophilic molecules like nicotine, fentanyl, or hormone derivatives that can partition into the lipid matrix and slowly diffuse through. Peptides lack the physicochemical properties enabling this passive absorption, requiring physical disruption of the skin barrier for transdermal delivery.
The stratum corneum thickness varies by body site, with facial skin approximately 10 micrometers thick while palmar and plantar surfaces reach 400-600 micrometers. This variation influences microneedle design requirements and optimal application sites for peptide delivery.
How microneedles work
Microneedles create microscopic pathways through the stratum corneum, bypassing the primary barrier while remaining too short to reach pain-sensing nerve endings concentrated in the deeper dermis. This enables painless penetration that facilitates drug delivery without the sensory experience of conventional needles.
The micropores created by microneedle application provide direct access to the viable epidermis, a metabolically active tissue layer rich in interstitial fluid and capillary networks. Peptides deposited through these channels absorb into local circulation and distribute systemically.
Micropore dimensions, typically 50-200 micrometers in diameter, remain small enough to close within minutes to hours through natural skin healing. This rapid closure minimizes infection risk while the brief window provides sufficient time for peptide absorption from dissolving formulations.
Understanding peptide fundamentals provides context for appreciating delivery method considerations.
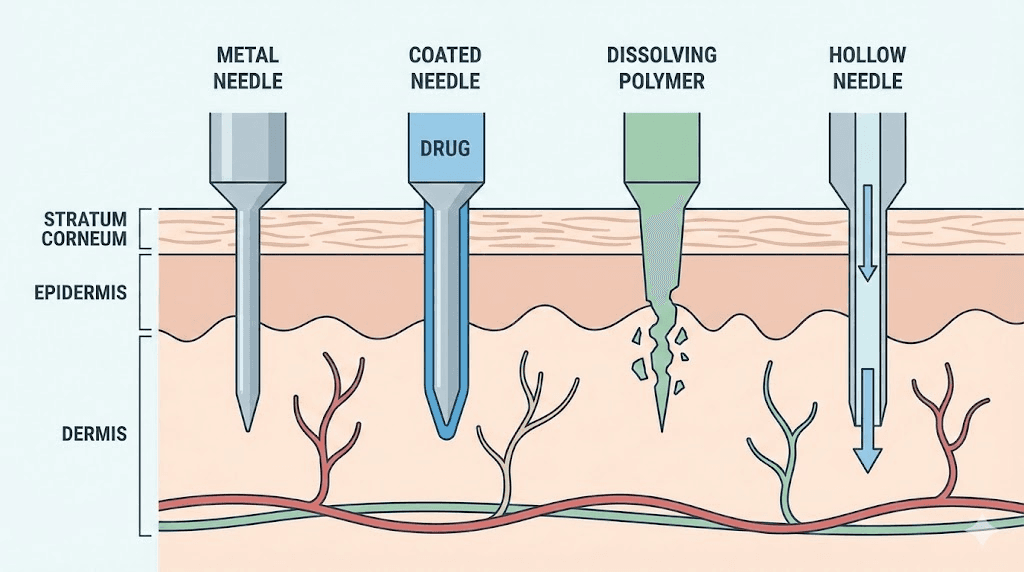
Types of microneedle systems
Solid microneedles create micropores through the skin that allow subsequently applied peptide formulations to absorb. The needles themselves don't contain drug, serving only as penetration enhancers. This approach separates the physical penetration step from drug delivery, allowing flexibility in formulation but requiring multi-step application.
Coated microneedles carry peptide formulations on their external surfaces, depositing drug during insertion. The coating dissolves in skin interstitial fluid, releasing peptide as the needles remain inserted. Rapid dissolution enables short wear times measured in minutes rather than hours.
Dissolving microneedles incorporate peptides directly into the needle matrix, typically composed of water-soluble polymers like hyaluronic acid, polyvinyl alcohol, or carboxymethylcellulose. The entire needle structure dissolves in the skin, leaving no sharps waste and providing complete drug release.
Hollow microneedles function as miniaturized hypodermic needles, injecting liquid formulations through channels within each needle. These systems enable delivery of larger volumes but require more complex manufacturing and application devices.
Hydrogel-forming microneedles swell upon skin insertion, drawing interstitial fluid into the needle structure and simultaneously releasing incorporated drugs. The bidirectional fluid exchange enables both drug delivery and potential biosensing applications.
Advantages of microneedle peptide delivery
Microneedle patches offer compelling advantages over conventional injection for appropriate applications. Understanding these benefits helps identify situations where patch-based delivery provides meaningful value.
Elimination of needle anxiety
Needle phobia affects an estimated 20-25% of adults, representing a significant barrier to peptide adoption regardless of potential benefits. The psychological burden of regular self-injection prevents many individuals from initiating or maintaining peptide protocols even when highly motivated by health goals.
Microneedle patches eliminate the visual and sensory triggers associated with needle anxiety. The microscopic projections are invisible to naked eye examination, and application feels similar to pressing a sticker rather than receiving an injection. Most users report no sensation at all during microneedle application.
The reduced psychological burden extends beyond individual comfort to practical adherence implications. Protocols requiring daily or frequent administration become sustainable when each application involves a simple, painless patch rather than needle insertion. Improved adherence translates directly to better outcomes.
Simplified administration
Traditional peptide injection requires multiple steps: reconstitution with bacteriostatic water, dose calculation and measurement with syringes, proper injection technique, and sharps disposal. Each step introduces potential for error, contamination, or injury.
Microneedle patches reduce administration to pressing a pre-loaded patch against skin for the specified duration. No reconstitution, no calculation, no injection technique, no sharps. The simplicity enables peptide use by individuals who lack the dexterity, vision, or confidence for self-injection.
The standardization of patch-based dosing eliminates variability from injection technique. Each patch delivers a consistent, pre-measured dose regardless of user skill or experience. This consistency supports more predictable outcomes across users.
Those struggling with injection can explore the peptide injections guide for technique improvement, though patches offer an alternative for persistent difficulties.
Improved stability and storage
Liquid peptide formulations require refrigeration after reconstitution, with stability typically limited to 3-4 weeks. This cold chain requirement complicates travel, limits convenience, and creates waste when users cannot complete vials before degradation.
Solid-state microneedle formulations often demonstrate enhanced stability at room temperature. The dry, solid matrix protects peptides from hydrolytic degradation that occurs in aqueous solution. Some dissolving microneedle formulations maintain potency for months without refrigeration.
The stability advantage enables stockpiling of patches without cold storage, simplifies travel with peptide protocols, and reduces waste from unconsumed reconstituted solutions. These practical benefits enhance real-world usability beyond theoretical bioavailability considerations.
Understanding peptide storage requirements provides context for appreciating stability advantages.
Reduced infection risk
Subcutaneous injection creates a direct pathway for pathogens from skin surface to subcutaneous tissue. Improper sterile technique, contaminated vials, or needle reuse can introduce bacteria leading to injection site infections or abscess formation.
Microneedle patches create only superficial micropores that close rapidly, limiting the infection window. The micropore dimensions are too small for most bacteria to enter, and the brief opening duration prevents colonization. Single-use, factory-sterilized patches eliminate contamination risks from multi-dose vials.
No injection site infection cases have been reported in clinical trials of microneedle vaccines and drugs despite thousands of applications. While the peptide research community operates outside formal clinical trial settings, the technology's inherent safety features apply regardless of regulatory context.
Bypass of first-pass metabolism
Oral peptide delivery faces substantial first-pass metabolism in the gastrointestinal tract and liver, destroying most peptide before reaching systemic circulation. This necessitates very high oral doses or specialized formulations to achieve meaningful bioavailability.
Transdermal microneedle delivery bypasses gastrointestinal destruction and hepatic first-pass metabolism entirely. Peptides absorb directly into dermal capillaries and enter systemic circulation without passing through the digestive system. This enables lower total doses compared to oral routes.
The comparison between routes is explored further in injectable versus oral peptides.
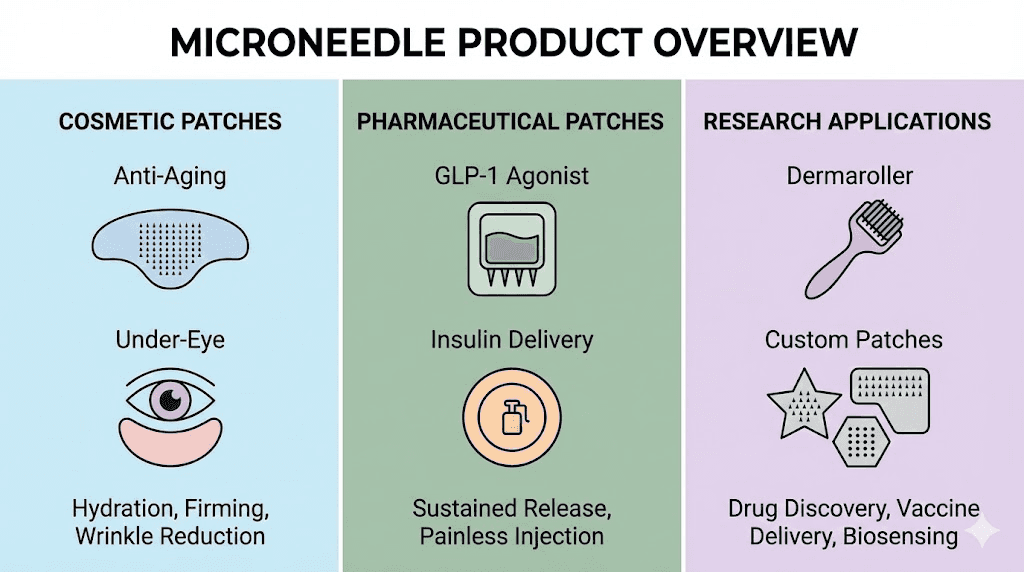
Current microneedle peptide products
The microneedle peptide market has expanded from primarily cosmetic applications toward systemic peptide delivery. Understanding available products helps identify appropriate options for specific goals.
Cosmetic and skincare applications
The most established microneedle peptide applications target local skin effects rather than systemic delivery. These products combine the skin penetration enhancement of microneedles with peptides targeting dermal collagen, elastin, or pigmentation.
Anti-aging patches deliver peptides like GHK-Cu (copper peptide), Matrixyl, Argireline, and similar sequences directly to dermal fibroblasts. The local delivery maximizes peptide concentration at target cells while minimizing systemic exposure and waste.
Hyaluronic acid microneedles combine the dissolving needle matrix with hydrating benefits. The hyaluronic acid constituting the needle structure deposits directly into the dermis upon dissolution, providing deeper hydration than topical application.
Under-eye treatment patches address dark circles, puffiness, and fine lines through targeted peptide delivery to the thin, delicate periorbital skin. The microneedle format enables penetration that topical serums cannot achieve in this challenging area.
Understanding peptides for wrinkles and peptides for dark circles provides context for cosmetic applications.
Emerging systemic delivery applications
Beyond cosmetic applications, microneedle technology increasingly targets systemic peptide delivery for metabolic, regenerative, and hormonal applications. These developments represent the frontier of patch-based peptide administration.
GLP-1 agonist patches are under development by multiple pharmaceutical companies as alternatives to the injectable semaglutide and tirzepatide products dominating the weight loss market. The weekly injection burden of these medications makes them prime candidates for patch conversion.
Insulin microneedle patches have reached clinical trials as painless alternatives to subcutaneous injection for diabetes management. The high-frequency dosing requirement of insulin makes the needle-free advantage particularly valuable.
Vaccine microneedle patches have demonstrated successful immunization in clinical trials, validating the platform's ability to deliver immunogenic peptides and proteins. The cold chain-free stability of these patches is revolutionizing vaccine distribution in resource-limited settings.
While most systemic peptide patches remain in development rather than commercial availability, the progression from cosmetic to systemic applications indicates expanding future options.
Research and custom applications
The research peptide community has begun exploring microneedle delivery for various compounds traditionally administered by injection. Custom formulation and DIY approaches extend patch technology beyond commercial products.
Dermaroller-based delivery uses microneedle rollers to create skin micropores followed by topical peptide application. While less elegant than integrated dissolving patches, this approach enables any peptide formulation to benefit from enhanced transdermal absorption.
Custom dissolving patches can be fabricated using relatively simple equipment by those with formulation expertise. Polymer solutions containing peptides are cast into microneedle molds and dried to create dissolving arrays. This enables experimental application of any peptide in patch format.
Combination approaches use microneedle pretreatment followed by conventional topical or transdermal formulations. The enhanced permeability persists for hours after microneedle application, creating a window for peptide absorption from subsequently applied products.
Peptide compatibility with microneedle delivery
Not all peptides are equally suited for microneedle delivery. Understanding compatibility factors helps identify appropriate candidates and set realistic expectations for patch-based protocols.
Molecular weight considerations
Microneedle delivery works best for peptides in the 500-10,000 Dalton range. Smaller molecules may absorb efficiently without microneedle enhancement, while very large proteins face absorption limitations even through micropore pathways.
Most research peptides fall within the optimal range. BPC-157 at approximately 1,400 Daltons, TB-500 at approximately 4,900 Daltons, and growth hormone releasing peptides in the 800-1,000 Dalton range all represent reasonable candidates for microneedle delivery.
Larger peptides like growth hormone itself (approximately 22,000 Daltons) face greater absorption challenges. While not impossible, achieving adequate bioavailability requires optimized formulations and may not match injection efficiency.
Stability in solid-state formulations
Peptide stability during the manufacturing process and subsequent storage determines practical viability of patch formulations. The drying process used to create solid microneedles can damage sensitive peptides if not carefully controlled.
Peptides containing methionine, tryptophan, or cysteine residues face oxidation risk during processing. Those with asparagine-glycine sequences may undergo deamidation. Formulation with appropriate stabilizers, antioxidants, and controlled drying conditions mitigates these risks.
Peptides demonstrating good lyophilization stability generally translate well to microneedle formulations. Those requiring specific pH ranges or showing sensitivity to drying stress present formulation challenges requiring specialized expertise.
Dose requirements and feasibility
Microneedle patches accommodate limited drug loads compared to injection, typically ranging from micrograms to low milligram quantities depending on patch size and needle density. High-dose peptides may require impractically large patch areas or multiple simultaneous applications.
Peptides dosed in the microgram range, like most research peptides at 100-500 mcg, fit well within patch capacity. Those requiring multi-milligram doses, like some TB-500 protocols at 2-5 mg, challenge patch feasibility without multiple applications or very large patch formats.
Bioavailability differences between injection and patch delivery affect dose translation. Lower patch bioavailability may require higher loaded doses to achieve equivalent systemic exposure, further constraining feasibility for high-dose applications.
Well-suited peptide candidates
Several peptide categories emerge as particularly appropriate for microneedle delivery based on molecular characteristics, dose requirements, and stability profiles.
Cosmetic peptides targeting local skin effects (GHK-Cu, Matrixyl, Argireline) represent ideal candidates. The local delivery maximizes efficiency while avoiding systemic distribution, and the microgram doses fit easily within patch capacity.
Low-dose systemic peptides like BPC-157, epithalon, and similar compounds at 100-500 mcg doses could theoretically work well in patch formats if appropriate formulations were available. The dose range and molecular weights align with patch capabilities.
Frequent-dosing peptides benefit most from the convenience of patch delivery. The value proposition strengthens when daily or multiple-daily administration makes injection burden significant.
The complete peptide list provides overview of various peptides and their characteristics.
Comparison with traditional injection
Understanding the trade-offs between microneedle patches and conventional injection enables informed delivery method selection based on individual priorities and circumstances.
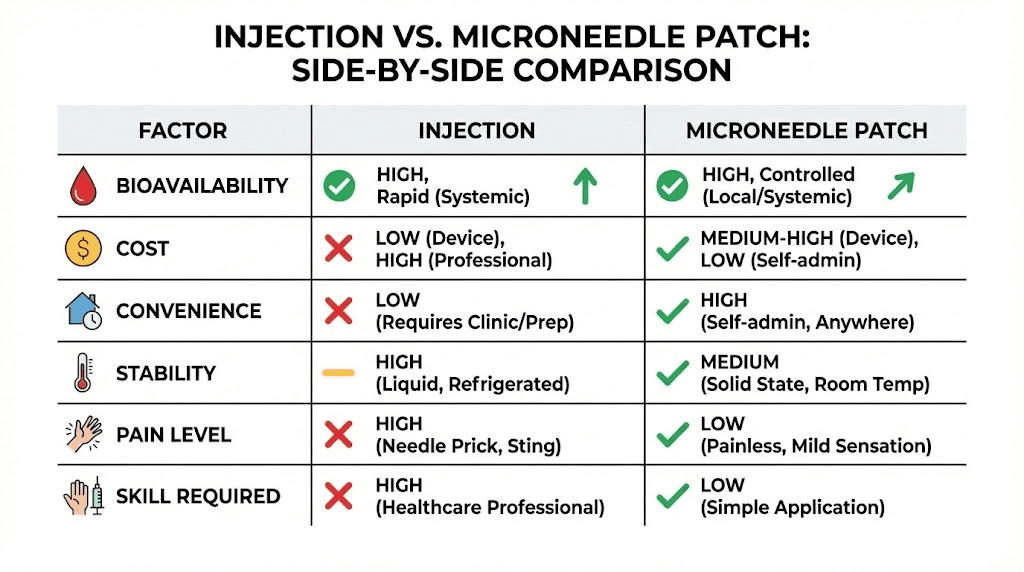
Bioavailability considerations
Subcutaneous injection delivers peptides directly into adipose tissue with predictable absorption kinetics and high bioavailability approaching 100% for most peptides. The established method provides the reference standard for peptide delivery.
Microneedle bioavailability varies significantly with formulation, peptide properties, and application technique. Clinical studies report transdermal bioavailabilities ranging from 30-90% compared to injection depending on the specific system and compound. Lower bioavailability requires dose adjustment to maintain equivalent exposure.
Absorption kinetics differ between methods. Injection provides relatively rapid absorption peaking within 30-60 minutes. Microneedle absorption may be slower or more prolonged depending on formulation dissolution characteristics, potentially affecting time-sensitive applications.
For applications where precise, predictable dosing matters, injection retains advantages. For applications prioritizing convenience and adherence, somewhat lower bioavailability may be acceptable.
Cost comparison
Traditional injection requires initial investment in syringes, bacteriostatic water, and potentially alcohol swabs and sharps containers. Ongoing costs include replacement supplies and potentially professional disposal of sharps waste.
Microneedle patches typically carry higher per-dose costs than injection supplies, though eliminating reconstitution reduces waste from unconsumed vial contents. The cost comparison depends heavily on specific products and peptide utilization patterns.
Currently available cosmetic microneedle patches range from $20-100+ for packs providing 4-8 applications. This substantially exceeds injection supply costs but may provide value for those prioritizing convenience or facing injection barriers.
The peptide cost calculator helps evaluate overall protocol economics.
Practical considerations
Travel: Patches excel for travel applications. No liquids, no needles, no refrigeration requirements for stable formulations simplify transport and eliminate TSA concerns about injectable medications.
Discretion: Patch application attracts less attention than injection, beneficial for those preferring privacy around peptide use. A small adhesive patch resembles common transdermal medications or cosmetic products.
Emergency situations: Stable, pre-loaded patches provide advantages in situations where refrigeration fails or reconstitution isn't possible. Maintaining peptide access during power outages, camping, or other challenging circumstances becomes simpler with solid-state formulations.
Frequency tolerance: The painless nature of microneedle application may enable more frequent dosing without the cumulative discomfort of repeated injections. Protocols requiring multiple daily doses become more tolerable.
The injectable versus oral peptides comparison provides additional delivery method context.
Current limitations
Product availability: Commercial microneedle patches for systemic peptide delivery remain limited. Most available products target cosmetic applications rather than the systemic delivery relevant to research peptide users.
Peptide selection: Only peptides formulated into commercial patches are available in this format. Custom peptide selection remains limited to DIY approaches or dermaroller enhancement methods.
Dose flexibility: Fixed-dose patches lack the flexibility of injection where any dose can be measured with appropriate syringes. Users needing specific doses outside available patch options cannot accommodate this with commercial products.
Bioavailability uncertainty: For many peptides, microneedle bioavailability hasn't been systematically characterized. Users transitioning from injection protocols face uncertainty about dose translation.
Application technique and best practices
Proper application technique maximizes microneedle patch effectiveness. While simpler than injection, attention to application details enhances outcomes.
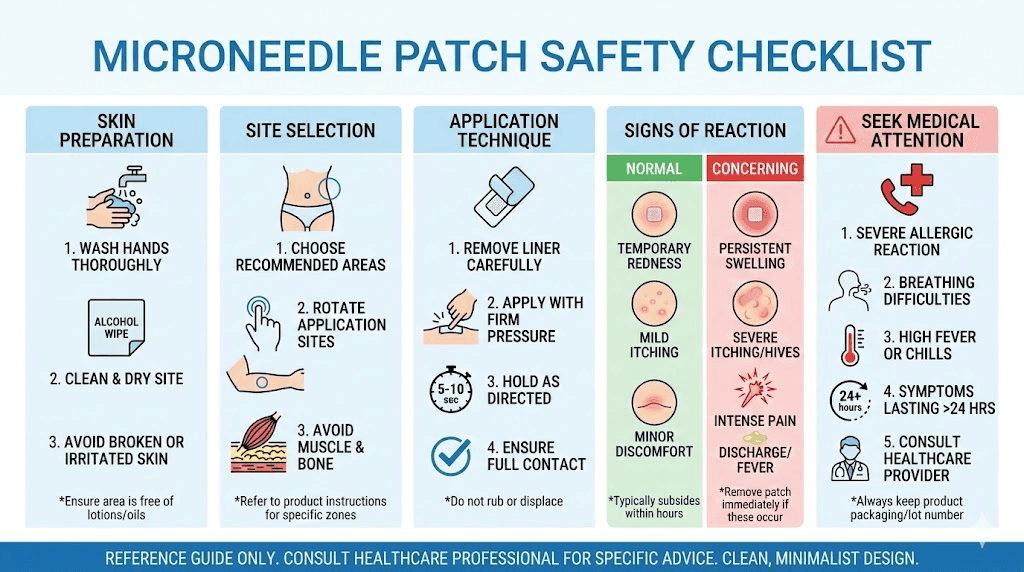
Skin preparation
Clean, dry skin at the application site ensures optimal microneedle penetration and peptide absorption. Wash the area with mild soap and water, then dry completely before application. Avoid oils, lotions, or residues that could interfere with needle insertion or patch adhesion.
Mild exfoliation 24-48 hours before application removes excess stratum corneum buildup that could impede penetration. However, avoid exfoliation immediately before application as fresh exfoliation can increase sensitivity and irritation risk.
Room temperature skin penetrates more consistently than cold skin. If application areas feel cold, allow them to warm before patch application for optimal needle insertion.
Application site selection
Optimal application sites balance accessibility, skin thickness, and vascularization for absorption. Common recommendations include:
Inner forearm: Thin skin with good vascular access, easily visible for proper placement, and accessible for self-application. Commonly used for both cosmetic and systemic patches.
Upper arm: Moderate skin thickness with reliable absorption. Less visible than forearm for those preferring discretion. May require assistance for optimal placement.
Abdomen: Standard injection site that translates well to patch application. Ample surface area accommodates larger patches if needed.
Thigh: Large surface area with moderate skin thickness. Self-accessible and easily concealed by clothing.
Avoid bony prominences, areas with thick stratum corneum (palms, soles), and regions with compromised skin integrity (wounds, rashes, irritation).
Application pressure and duration
Firm, even pressure during initial application ensures complete microneedle insertion. Most patches require 10-30 seconds of sustained pressure to fully penetrate the stratum corneum. Insufficient pressure results in incomplete insertion and reduced drug delivery.
Wear duration depends on formulation type. Dissolving microneedle patches typically require 5-15 minutes for complete needle dissolution. Longer wear doesn't improve drug delivery once needles have dissolved but won't cause harm. Coated microneedles may require shorter contact times.
After the specified wear time, remove the patch and inspect the backing. Dissolved or missing needle arrays indicate successful delivery. Intact needles suggest application failure requiring reapplication.
Site rotation
Like injection sites, microneedle application sites benefit from rotation. Repeated application to identical locations can cause local skin changes, reduced absorption, or irritation. Systematic rotation between multiple sites prevents these issues.
Allow at least 24 hours before reusing an application site. For daily applications, establish a rotation pattern covering 4+ distinct sites. Document application locations to maintain rotation consistency.
Site rotation principles parallel those for injection described in the peptide injections guide.
DIY and enhancement approaches
Beyond commercial products, various approaches extend microneedle benefits to peptides not available in patch format. These methods range from simple enhancement techniques to more complex custom fabrication.
Dermaroller enhancement
Microneedle dermarollers, originally developed for cosmetic skin rejuvenation, create micropore arrays that enhance subsequent peptide absorption. This separates the penetration enhancement from the peptide formulation, enabling any peptide to benefit from improved transdermal delivery.
Procedure: Roll the dermaroller across the target skin area using moderate pressure, covering the region with 4-8 passes in different directions. Immediately apply the peptide solution to the treated area. The micropores remain patent for absorption for approximately 30-60 minutes before closing.
Needle length selection: 0.25-0.5mm needles penetrate the stratum corneum without reaching pain-sensing nerves, enabling painless treatment. Longer needles (1.0mm+) intended for collagen induction therapy aren't necessary or appropriate for drug delivery enhancement.
Limitations: This approach requires liquid peptide formulations rather than utilizing solid-state stability advantages. Sterility concerns arise from multi-use rollers and open vials. The technique introduces additional steps rather than simplifying administration.
Microneedle stamps and pens
Microneedle stamp devices and automated pens provide more controlled penetration than manual rolling. The vertical needle insertion of stamps may create more uniform micropores than the angled insertion from rollers.
Adjustable devices allow needle depth selection, enabling optimization for different skin thicknesses and peptide characteristics. Starting with minimal depth and increasing as needed reduces unnecessary tissue disruption.
Single-use cartridges available for some devices address sterility concerns of reusable rollers. The convenience and safety improvements justify higher per-application costs for regular users.
Custom patch fabrication
Those with appropriate expertise and equipment can fabricate custom dissolving microneedle patches incorporating any peptide. This advanced approach requires understanding of polymer chemistry, sterile technique, and formulation science.
Basic process: Peptide is dissolved in aqueous polymer solution (hyaluronic acid, PVP, or similar), cast into silicone microneedle molds, and dried under controlled conditions. The resulting solid array is transferred to an adhesive backing for application.
Challenges: Maintaining peptide stability during processing requires careful attention to temperature, pH, and drying conditions. Achieving consistent needle geometry affects penetration reliability. Ensuring sterility throughout fabrication prevents contamination risks.
Resources: Academic literature describes fabrication methods in detail for those with appropriate background. However, this approach exceeds casual DIY capabilities and carries risks if executed improperly.
Safety considerations
Microneedle patches demonstrate excellent safety profiles in clinical and commercial use. Understanding potential concerns enables appropriate precautions.
Skin reactions
Transient erythema (redness) at application sites represents the most common observation, occurring in a majority of users. This reflects the normal inflammatory response to stratum corneum disruption and typically resolves within 30-60 minutes. Persistent redness beyond several hours may indicate sensitivity.
Mild itching during or shortly after application occurs occasionally. This typically resolves spontaneously and rarely requires intervention. Antihistamines can address persistent itching if needed.
Allergic reactions to patch components (polymers, adhesives) occur rarely but warrant discontinuation if observed. Patch ingredients should be reviewed by those with known material sensitivities.
Understanding peptide safety and risks provides broader context for supplementation safety.
Infection risk
The micropores created by microneedles theoretically provide pathogen entry routes, though the small diameter and rapid closure minimize practical infection risk. No clinical trial infections have been reported despite thousands of applications across multiple studies.
Proper skin preparation with clean, dry application sites reduces already-low infection risk. Avoiding application to compromised skin (cuts, rashes, active acne) eliminates scenarios where barrier disruption might enable pathogen entry.
Single-use, factory-sterilized patches from reputable manufacturers carry minimal contamination risk. DIY approaches and reused devices require careful attention to sterility.
Contraindications
Certain conditions warrant caution or avoidance of microneedle applications:
Bleeding disorders: While microneedle bleeding is minimal, those with coagulopathies or on anticoagulant therapy should consult healthcare providers before use.
Active skin conditions: Eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, or other active skin conditions affecting potential application sites contraindicate use until resolved. The barrier disruption could exacerbate inflammatory conditions.
Immunocompromised states: Severely immunocompromised individuals face heightened infection risk from any skin penetration. Consultation with healthcare providers is appropriate.
Keloid tendency: Those prone to keloid or hypertrophic scar formation should exercise caution, as repeated microneedle application could theoretically trigger abnormal scarring responses.
Quality and sourcing concerns
Product quality varies significantly across the microneedle market. Lower-quality products may feature dull needles that fail to penetrate, inconsistent needle geometry, unstable peptide formulations, or contamination concerns.
Reputable manufacturers provide documentation of needle specifications, peptide identity and potency, sterility testing, and stability data. Products lacking this documentation warrant skepticism.
The best peptide vendors guide provides sourcing guidance applicable to patch products.
Future developments
Microneedle technology continues advancing rapidly, with developments promising expanded capabilities and availability for peptide delivery applications.
Smart and responsive patches
Next-generation microneedle systems incorporate sensing and responsive drug release capabilities. Glucose-responsive insulin patches that automatically modulate insulin release based on blood sugar levels have reached clinical trials, demonstrating the feasibility of closed-loop transdermal systems.
Similar responsive designs could enable peptide delivery triggered by specific biomarkers, circadian timing, or physiological states. These smart patches would optimize peptide timing beyond what fixed-schedule administration achieves.
Integrated biosensors within microneedle arrays can monitor interstitial fluid biomarkers while simultaneously delivering therapeutics. The bidirectional capability enables both treatment and monitoring from a single patch.
Expanded peptide options
Pharmaceutical development pipelines include multiple peptides in microneedle formulations. GLP-1 agonists for weight management, PTH analogs for osteoporosis, and various vaccines represent active development programs that will expand available patch options upon approval.
As the technology matures, manufacturing costs decrease and formulation expertise expands. This progression will enable microneedle formulations of peptides currently available only as injectables, expanding options for needle-averse users.
The research peptide market may follow pharmaceutical developments, with vendors offering popular peptides in patch formats as demand and manufacturing capabilities align.
Manufacturing and accessibility
Current microneedle manufacturing requires specialized equipment and expertise, limiting production to established companies with significant capital investment. However, manufacturing innovation is reducing barriers to entry.
3D printing of microneedle molds enables smaller-scale production runs and rapid prototyping of new designs. This technology could enable specialty peptide suppliers to offer patch options without pharmaceutical-scale manufacturing.
Home fabrication kits providing molds, polymers, and instructions for creating basic dissolving patches represent a potential future development, though regulatory and safety considerations complicate consumer-level production.
Integrating patches into peptide protocols
For those with access to appropriate microneedle products, thoughtful integration into overall peptide protocols maximizes benefits.
Complementary use with injection
Patches and injection can coexist within protocols, with each method applied to appropriate peptides and situations. Using patches for suitable peptides while maintaining injection for others provides the best of both approaches.
Travel situations represent ideal patch applications even for those who normally inject. Maintaining protocol continuity during trips without carrying injectable supplies, sharps, or requiring refrigeration simplifies travel significantly.
Patches for daily or frequent-dose peptides combined with injection for less frequent compounds balances convenience against practicality. The peptides requiring most frequent administration benefit most from patch convenience.
Transition considerations
Transitioning from injection to patch delivery requires dose adjustment to account for bioavailability differences. Starting conservatively and titrating based on response proves safer than assuming equivalent doses.
Monitoring response during transition identifies whether patch delivery provides equivalent effects to injection. Subjective assessment and objective measurements where applicable confirm successful dose translation.
Maintaining injection capability as backup ensures continuity if patch delivery proves inadequate for specific applications. The transition period may reveal peptides that work well as patches versus those requiring injection.
Protocol tracking and documentation
Documentation of patch applications, including date, time, site, product, and any observations, supports protocol optimization. Tracking enables identification of optimal sites, timing patterns, and any issues requiring adjustment.
Comparing outcomes between patch and injection periods for the same peptides provides personal bioavailability assessment. This data informs future delivery method decisions.
The peptide cycle planning guide provides protocol documentation approaches applicable to any delivery method.
How SeekPeptides supports peptide delivery decisions
SeekPeptides provides resources for understanding peptide delivery options and optimizing administration approaches.
The platform offers evidence-based guidance for navigating the evolving peptide delivery landscape.
It serves as a trusted resource for evidence-based peptide guidance across delivery methods and applications.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your peptides stay stable, your delivery stay painless, and your protocols stay effective. Join SeekPeptides.