Dec 30, 2025
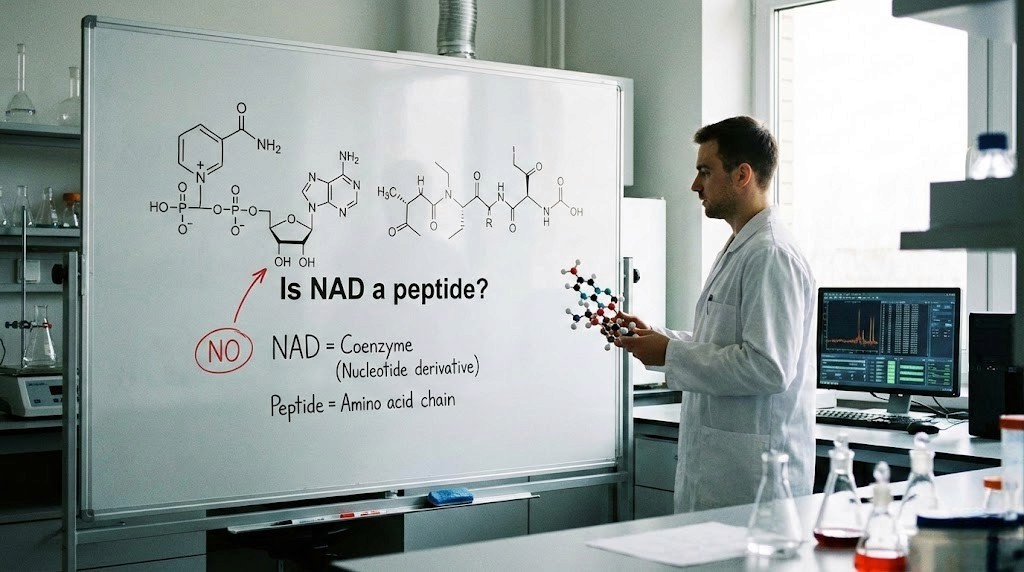
No, NAD is not a peptide. NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is a coenzyme - a small organic molecule composed of nucleotides, not amino acids.
The confusion arises because NAD frequently appears alongside peptide therapy discussions, NAD-boosting compounds are sometimes called "NAD peptides," and wellness clinics often offer both NAD IV therapy and peptide treatments together, creating association despite their fundamentally different chemical structures.
The critical distinction lies in building blocks - peptides are chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds (like proteins but shorter), while NAD is a dinucleotide consisting of two nucleotides (adenine and nicotinamide) joined together through phosphate groups. NAD functions as an electron carrier in cellular metabolism, shuttling electrons in redox reactions critical for energy production, whereas peptides act as signaling molecules that trigger specific biological responses by binding to receptors.
The "NAD peptide" terminology actually refers to peptides that boost NAD+ levels indirectly - compounds that enhance NAD+ biosynthesis, improve mitochondrial function, or support cellular energy metabolism. These include SS-31 (Elamipretide) which optimizes mitochondrial function where NAD+ operates, Epithalon which may influence cellular metabolism and NAD+-dependent processes, MOTS-c which regulates mitochondrial metabolism, and Humanin which supports mitochondrial health. None of these are NAD itself, but they work synergistically with NAD+-dependent pathways.
Direct NAD+ supplementation faces challenges - oral NAD+ pills poorly absorbed due to molecular size and instability, IV NAD+ therapy expensive ($500-1,500 per session) and requires clinical setting, NAD+ precursors like NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) or NR (nicotinamide riboside) more practical oral options, and true peptide therapies offer complementary but distinct mechanisms from direct NAD+ supplementation.
This guide examines NAD+ chemical structure and why it's not a peptide, peptides vs coenzymes fundamental differences, why "NAD peptides" terminology creates confusion, actual peptides that support NAD+ pathways, comparing NAD+ precursors to mitochondrial peptides, whether NAD+ and peptide therapy should be combined, and clarifying optimal strategies for cellular energy optimization.
Understanding the NAD-peptide distinction prevents confusion about what you're actually taking and helps optimize anti-aging and energy enhancement strategies.
NAD+ chemical structure explained
What NAD actually is (not a peptide).
NAD is a coenzyme, not a peptide
Chemical classification:
NAD+ = Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Class: Coenzyme (helper molecule for enzymes)
Structure: Two nucleotides joined together
NOT amino acid-based
NOT a peptide
What "dinucleotide" means:
"Di" = two
"Nucleotide" = basic building block of DNA/RNA
Two nucleotides connected: Nicotinamide + Adenine
Linked by phosphate groups (not peptide bonds)
Completely different from peptide structure
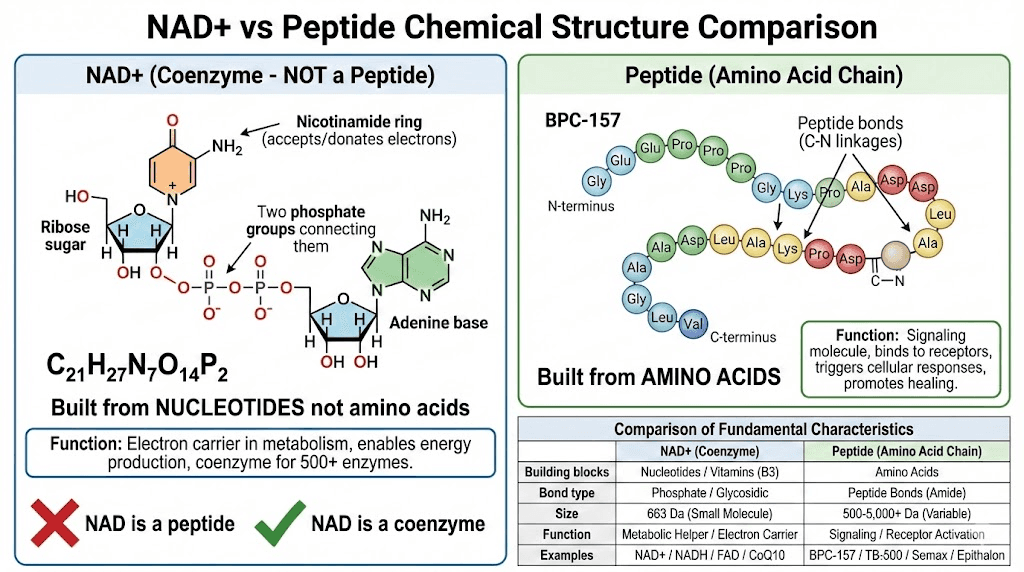
NAD+ structural components:
Component | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|
Nicotinamide | Pyridine nucleotide | Accepts/donates electrons (redox) |
Adenine | Purine nucleotide | Structural support, recognition |
Ribose sugars (2x) | Five-carbon sugars | Connect components |
Phosphate groups (2x) | Phosphate bridges | Link nucleotides together |
Chemical formula:
C₂₁H₂₇N₇O₁₄P₂
Molecular weight: ~663 Da
Contains: Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus
NO amino acids present
Completely distinct from peptide chemistry
NAD+ vs NADH:
NAD+ = Oxidized form (electron acceptor)
NADH = Reduced form (electron donor)
Constantly interconverting in cells
Critical for energy metabolism
The "+" indicates oxidized state
Learn about what peptides are and how they work at SeekPeptides.
Peptides vs coenzymes: fundamental differences
What peptides are:
Chains of amino acids (2-50 amino acids typically)
Connected by peptide bonds (C-N linkages)
Building blocks: 20 standard amino acids
Function: Signaling molecules, hormone mimics
What coenzymes are:
Small organic molecules (not amino acid chains)
Help enzymes catalyze reactions
Examples: NAD+, FAD, Coenzyme Q10
Building blocks: Various (nucleotides, vitamins)
Function: Metabolic helpers, electron carriers
Structural comparison:
Feature | Peptides | Coenzymes (NAD+) |
|---|---|---|
Building blocks | Amino acids | Nucleotides, vitamins, other |
Bond type | Peptide bonds (C-N) | Various (phosphate, glycosidic) |
Size | 2-50+ amino acids | Small molecules |
Function | Signaling, receptor binding | Metabolic helper, electron carrier |
Examples | NAD+, NADH, FAD, CoQ10 |
How they work differently:
Peptides:
Bind to specific receptors (like hormones)
Trigger signaling cascades
Cause cells to change behavior
Example: BPC-157 binds receptors → angiogenesis
Coenzymes (NAD+):
Assist enzyme function directly
Carry electrons/chemical groups
Enable metabolic reactions
Example: NAD+ accepts electrons → NADH in glycolysis
Metabolic roles:
Peptides: Regulate what cells do (signaling)
NAD+: Enable how cells make energy (metabolism)
Complementary but distinct mechanisms
Can work together in comprehensive protocols
Why the confusion exists
Reasons NAD gets called a "peptide":
1. Marketing association:
Wellness clinics offer both
"NAD + Peptide Therapy" packages
Listed together creates association
Easier to group under "peptide clinic"
Technically incorrect but convenient
2. "NAD peptides" terminology:
Really means "NAD-boosting peptides"
Shortened to "NAD peptides"
Misleading but widespread
Not NAD itself
3. Similar goals:
Both target anti-aging
Both enhance energy
Both support mitochondrial function
Used in similar contexts
Easy to conflate
4. Complexity:
NAD+ chemistry complex
Peptide is more familiar term
People default to "peptide" label
Simplifies communication (incorrectly)
5. Vendor confusion:
Some peptide vendors list "NAD+"
Mixed with actual peptides
Blurs distinction
Consumers don't know difference
The truth:
NAD+ is NOT a peptide chemically
They're different molecule types
They work through different mechanisms
Can be used together (synergistic)
But fundamentally distinct
What are "NAD peptides" actually?
Clarifying the misleading terminology.
Peptides that boost NAD+ levels
"NAD peptides" = NAD-boosting peptides
NOT NAD itself
Peptides that enhance NAD+ pathways
Support mitochondrial function
Optimize cellular metabolism
Indirect NAD+ benefits
Main NAD-supporting peptides:
1. SS-31 (Elamipretide, Bendavia):
Mechanism: Mitochondrial-targeted peptide
Optimizes mitochondrial function
Enhances ATP production (where NAD+ works)
Improves electron transport chain efficiency
Dose: 5-10mg daily
See SS-31 peptide benefits guide
2. Epithalon (Epitalon):
Mechanism: Telomerase activator, cellular metabolism
May influence NAD+-dependent pathways
Supports mitochondrial health
Anti-aging through multiple pathways
Dose: 10mg daily × 10-20 days cyclic
See Epithalon guide
3. MOTS-c:
Mechanism: Mitochondrial-derived peptide
Regulates mitochondrial metabolism
Improves metabolic flexibility
Enhances energy production
Dose: 5-15mg 2-3x weekly
4. Humanin:
Mechanism: Mitochondrial peptide
Protects against mitochondrial dysfunction
Anti-apoptotic (prevents cell death)
Supports cellular energy systems
Dose: 1-5mg daily
How they relate to NAD+:
Peptide | NAD+ Connection | Primary Benefit | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|
Optimizes mitochondria where NAD+ functions | Enhanced energy, reduced fatigue | Research vendors | |
Supports cellular metabolism, NAD+-dependent processes | Longevity, sleep, overall health | Common | |
MOTS-c | Mitochondrial metabolic regulation | Metabolic health, fat loss | Limited vendors |
Humanin | Mitochondrial protection | Neuroprotection, metabolic support | Limited vendors |
Why called "NAD peptides":
All support mitochondrial/metabolic function
NAD+ critical for mitochondria
Synergistic effects with NAD+
Similar anti-aging goals
Convenient (if inaccurate) grouping
Mitochondrial peptides explained
What mitochondrial peptides are:
Peptides that target mitochondria
Optimize cellular energy production
Support metabolic function
Often work where NAD+ operates
Complementary to NAD+ supplementation
SS-31 (most studied):
Tetrapeptide: D-Arg-Dmt-Lys-Phe-NH₂
Concentrates in mitochondrial inner membrane
Stabilizes cardiolipin (critical lipid)
Improves electron transport chain
Reduces reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Clinical trials for heart failure, mitochondrial diseases
MOTS-c mechanism:
16-amino acid peptide
Encoded by mitochondrial DNA
Regulates nuclear gene expression
Improves insulin sensitivity
Enhances exercise capacity
Humanin mechanism:
24-amino acid peptide
Mitochondrial-derived
Protects against various stresses
Anti-apoptotic signaling
Neuroprotective properties
Benefits of mitochondrial peptides:
Enhanced energy levels
Reduced fatigue
Better exercise capacity
Metabolic improvements
Complementary to NAD+
Learn about mitochondrial peptides and energy peptides at SeekPeptides.
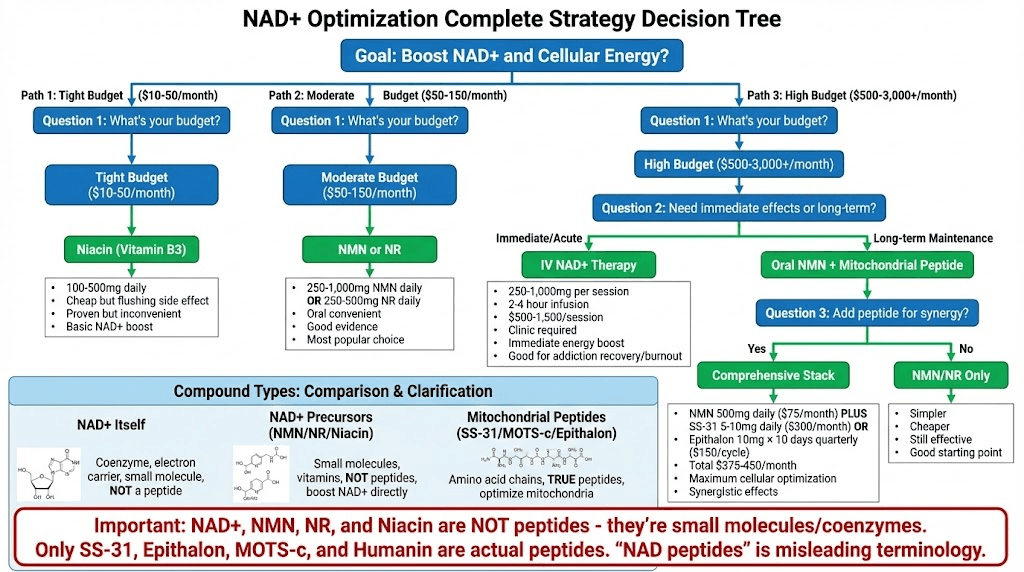
NAD+ precursors vs peptides
Direct NAD+ boosting approaches:
NAD+ precursors (not peptides):
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)
Niacin (Nicotinic Acid, Vitamin B3)
Directly convert to NAD+ in body
Oral supplementation works
Not peptides - small molecules
NAD+ precursor comparison:
Precursor | Mechanism | Dose | Cost/Month | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NMN | Direct conversion to NAD+ | 250-1,000mg daily | $50-150 | Good evidence, popular |
NR | Converts to NMN then NAD+ | 250-500mg daily | $40-100 | Good evidence, well-studied |
Niacin | NAD+ precursor (ancient) | 100-500mg daily | $10-20 | Proven but causes flushing |
Peptides vs NAD+ precursors:
NAD+ precursors (NMN/NR):
Directly boost NAD+ levels
Measurable NAD+ increase in blood
Oral supplementation convenient
Well-tolerated (minimal sides)
Affordable ($40-150/month)
Evidence: Moderate to good
Mitochondrial peptides (SS-31, etc.):
Optimize mitochondrial function
Don't directly increase NAD+ (work with existing)
Require injection
Generally well-tolerated
Expensive ($200-400/month)
Evidence: Limited human data
Which approach better?
Goal | Best Approach | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
Directly boost NAD+ | NMN or NR | Direct precursors increase levels |
Optimize mitochondria | SS-31 or MOTS-c | Peptides target mitochondrial function |
Budget-friendly | NMN/NR | Much cheaper than peptides |
Maximum effect | Combine both | Synergistic (NMN + SS-31) |
Convenient | NMN/NR | Oral vs injection |
Combining NAD+ precursors + peptides:
NMN provides NAD+ building blocks
SS-31 optimizes mitochondria to use NAD+
Potentially synergistic
Comprehensive energy optimization
Expensive but thorough
NAD+ supplementation methods
How to actually boost NAD+ levels.
Oral NAD+ precursors (NMN, NR, Niacin)
Most practical NAD+ boosting:
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
NR (Nicotinamide Riboside)
Niacin (Vitamin B3)
All convert to NAD+ in body
Oral supplementation effective
NOT peptides - small molecules
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide):
Dose: 250-1,000mg daily (typical 500mg)
Timing: Morning on empty stomach
Cost: $50-150/month
Evidence: Animal studies strong, human studies emerging
Absorption: Sublingual may be better
Direct NAD+ precursor (one step conversion)
NR (Nicotinamide Riboside):
Dose: 250-500mg daily (typical 300mg)
Timing: Morning with or without food
Cost: $40-100/month
Evidence: Good human trials showing NAD+ increase
Brands: TruNiagen, Tru Niagen (established)
Converts to NMN, then NAD+ (two steps)
Niacin (Vitamin B3):
Dose: 100-500mg daily
Timing: With food (reduces flushing)
Cost: $10-20/month (very cheap)
Side effect: Flushing (red face, warmth) common
Evidence: Oldest NAD+ precursor, proven
Time-release reduces flushing
Comparison:
Precursor | NAD+ Boost | Tolerability | Cost | Evidence | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
NMN | Strong | Excellent | $$ | Emerging | Popular, effective |
NR | Moderate-strong | Excellent | $$ | Good | Well-studied, reliable |
Niacin | Moderate | Flushing issue | $ | Proven | Cheap but side effects |
How they work:
Take NMN/NR orally
Absorbed in gut
Enters bloodstream
Cells convert to NAD+
NAD+ levels increase 50-100%+
Enhanced cellular energy and function
IV NAD+ therapy
Direct NAD+ infusion:
NAD+ solution injected intravenously
Bypasses digestion
Direct bloodstream delivery
100% bioavailability (vs oral ~30-50%)
Offered at wellness clinics
Typical IV NAD+ protocol:
Dose: 250-1,000mg NAD+ per session
Duration: 2-4 hours (slow infusion)
Frequency: 1-2x weekly initially, then monthly maintenance
Cost: $500-1,500 per session
Location: Requires clinic visit
IV NAD+ benefits (claimed):
Immediate energy boost
Mental clarity enhancement
Addiction recovery support
Anti-aging effects
Detoxification support
Athletic recovery
IV NAD+ challenges:
Expensive: $2,000-6,000/month if weekly
Time-consuming: 2-4 hours per session
Clinic requirement: Can't do at home
Side effects: Nausea, cramping during infusion
Evidence: Limited controlled trials
IV vs oral comparison:
Factor | IV NAD+ | Oral NMN/NR |
|---|---|---|
Bioavailability | 100% | 30-50% |
Cost per month | $2,000-6,000 | $50-150 |
Convenience | Clinic visits, 2-4 hours | Take pill at home |
Evidence | Limited | Moderate |
Immediate effect | Strong (hours) | Gradual (weeks) |
When IV NAD+ makes sense:
Acute needs (addiction recovery, burnout)
Money no object
Want immediate effects
Supervised medical setting preferred
Special occasions (events, competitions)
When oral better:
Budget-conscious
Long-term consistent use
Convenience priority
Daily maintenance approach
Similar long-term benefits
Combining NAD+ with peptide therapy
NAD+ + Peptides synergistic?
Yes, complementary mechanisms
NAD+ provides cellular energy
Peptides provide signaling
Work together for comprehensive benefits
Common in wellness protocols
Effective combinations:
1. NMN + SS-31:
NMN: Boosts NAD+ levels
SS-31: Optimizes mitochondria
Synergy: More fuel + better engine
Energy enhancement profound
Cost: $250-550/month combined
2. NMN + Epithalon:
NMN: Cellular energy
Epithalon: Telomeres, metabolism
Synergy: Comprehensive anti-aging
Epithalon cyclic (10-20 days), NMN continuous
Cost: $50-150/month NMN + $100-200 per Epithalon cycle
3. NAD+ IV + Peptide injections:
IV NAD+: Immediate energy boost
Peptides (various): Targeted effects
Often done together at clinics
Comprehensive wellness protocols
Cost: $1,000-3,000+ per session
Stacking recommendations:
Goal | NAD+ Approach | Peptide Addition | Why This Works |
|---|---|---|---|
NMN 500mg daily | SS-31 5-10mg daily | Fuel + optimization | |
NMN 500mg daily | Epithalon 10mg × 10 days quarterly | NAD+ + telomeres | |
Athletic performance | NMN 500mg daily | CJC/Ipamorelin 300mcg 5x weekly | Energy + recovery |
Cognitive enhancement | NMN 500mg daily | Semax 200-600mcg daily | Brain energy + nootropic |
Safety of combining:
Generally safe (different mechanisms)
No known negative interactions
Both well-tolerated independently
Monitor for side effects
Work with knowledgeable practitioner
See peptide stacking guide and NAD peptides guide for protocols.
How you can use SeekPeptides for energy and anti-aging
SeekPeptides clarifies the NAD-peptide distinction while providing comprehensive guidance on actual peptides and NAD-boosting strategies. Learn about SS-31 for mitochondrial optimization, Epithalon for longevity, and NAD peptides that actually boost cellular energy.
Use our calculators - peptide calculator, cost calculator, stack calculator - for protocol planning.
Access comprehensive guides - best peptide for energy, peptides for anti-aging, peptide stacks guide, what are peptides.
Find peptide therapy clinics offering NAD+ and peptide combinations, and best vendors for quality peptide sourcing.
Final thoughts
NAD is definitively not a peptide - it's a coenzyme (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) built from nucleotides rather than amino acids, functioning as an electron carrier in cellular metabolism rather than a signaling molecule that binds receptors. The confusion stems from "NAD peptides" terminology describing mitochondrial peptides like SS-31 and Epithalon that support NAD+-dependent pathways, not NAD itself.
Direct NAD+ optimization uses oral precursors (NMN, NR, niacin) that convert to NAD+ in cells, providing practical and affordable supplementation at $50-150 monthly. IV NAD+ therapy delivers immediate effects but costs $500-1,500 per session, making it impractical for most long-term use. True mitochondrial peptides like SS-31 optimize how mitochondria utilize existing NAD+ rather than boosting levels directly.
Combining oral NAD+ precursors with mitochondrial peptides creates synergistic cellular energy optimization - NMN provides fuel while SS-31 optimizes the engine. This comprehensive approach costs $250-550 monthly but addresses both NAD+ availability and mitochondrial efficiency for maximum anti-aging and energy benefits.
Your cellular optimization strategy should distinguish between NAD+ supplementation (coenzyme, not peptide, taken orally) and mitochondrial peptide therapy (true amino acid peptides, requiring injection), selecting approaches based on goals, budget, and understanding of fundamental chemical differences.
Helpful resources for NAD and energy
NAD peptides guide - Complete NAD overview
SS-31 peptide benefits - Mitochondrial peptide
Best peptide for energy - Energy optimization
Epithalon peptide benefits - Longevity peptide
Peptides for anti-aging - Anti-aging category
In case I don’t see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. Take care of yourself.