Jan 10, 2026

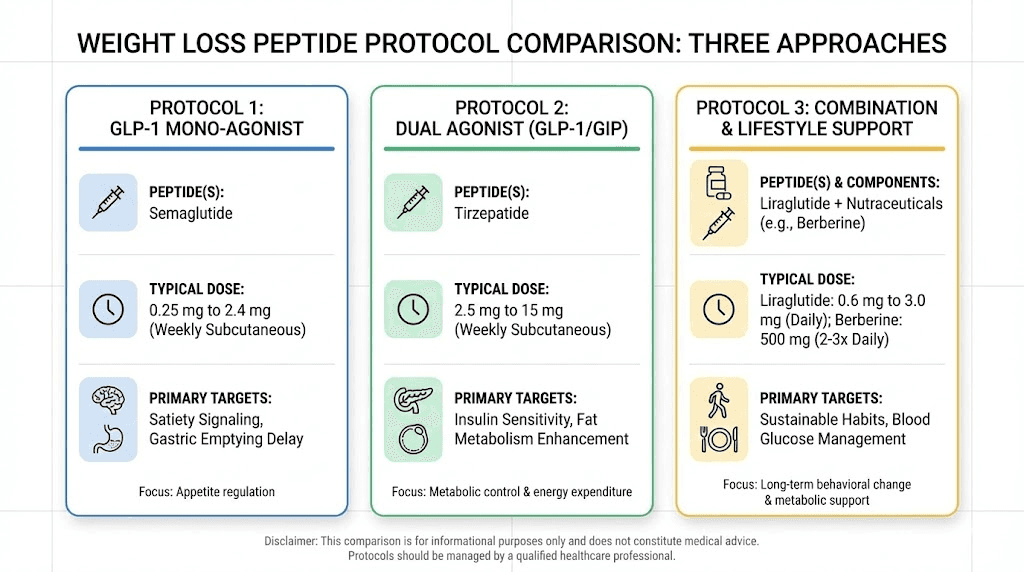
Calculating peptide dosages in milligrams for weight loss requires understanding concentration math, reconstitution volumes, and the specific dosing protocols established through clinical research. The peptide calculator transforms complex calculations into straightforward inputs, converting vial concentrations into precise syringe measurements that deliver exact milligram doses. Weight loss peptides including semaglutide and tirzepatide operate through dose-dependent mechanisms where accuracy directly impacts both efficacy and side effect profiles, making proper mg calculation essential rather than optional. Understanding how to determine the correct milligram dose based on body weight, tolerance, and protocol phase prevents both underdosing that limits results and overdosing that increases adverse effects.
SeekPeptides provides comprehensive dosing calculation resources that support researchers in achieving precise, reproducible protocols for weight loss peptide research.
Understanding peptide concentration and mg dosing
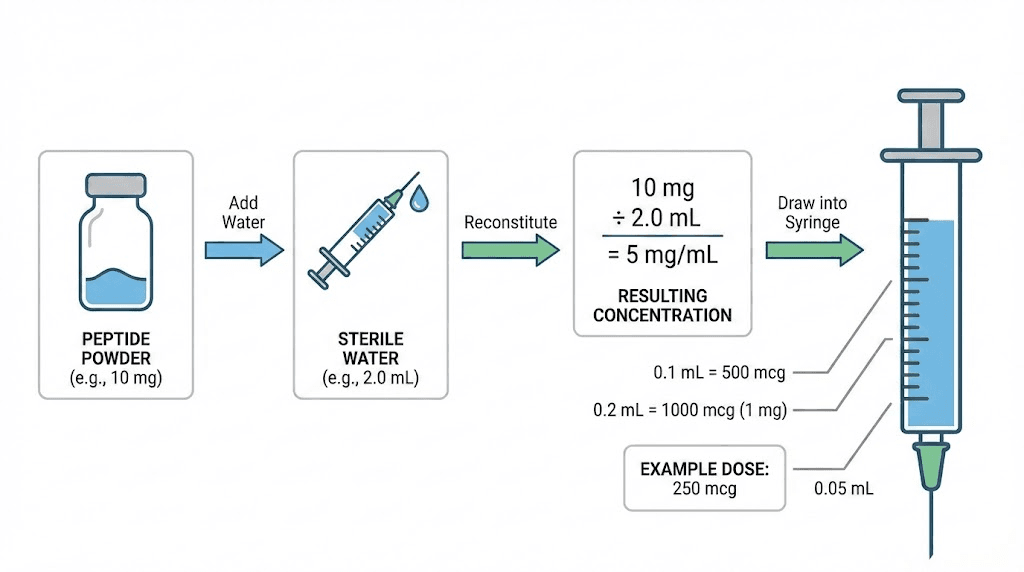
Peptide vials arrive containing a specific mass of lyophilized powder, typically measured in milligrams. When you add bacteriostatic water for reconstitution, you create a solution with a concentration expressed as mg/ml. This concentration determines how many units or milliliters you draw to achieve your target mg dose.
The fundamental calculation follows a simple formula. Divide the total peptide content by the reconstitution volume to find concentration. Then divide your target dose by this concentration to determine injection volume. A 5mg vial reconstituted with 2ml of water creates a 2.5mg/ml solution. To inject 0.25mg, you would draw 0.1ml.
Where confusion arises involves insulin syringe markings. These syringes display units rather than milliliters, with 100 units equaling 1ml. Converting between units and milliliters requires recognizing that 10 units equals 0.1ml. The reconstitution calculator handles these conversions automatically, eliminating manual calculation errors.
Weight loss peptide categories and their dosing ranges
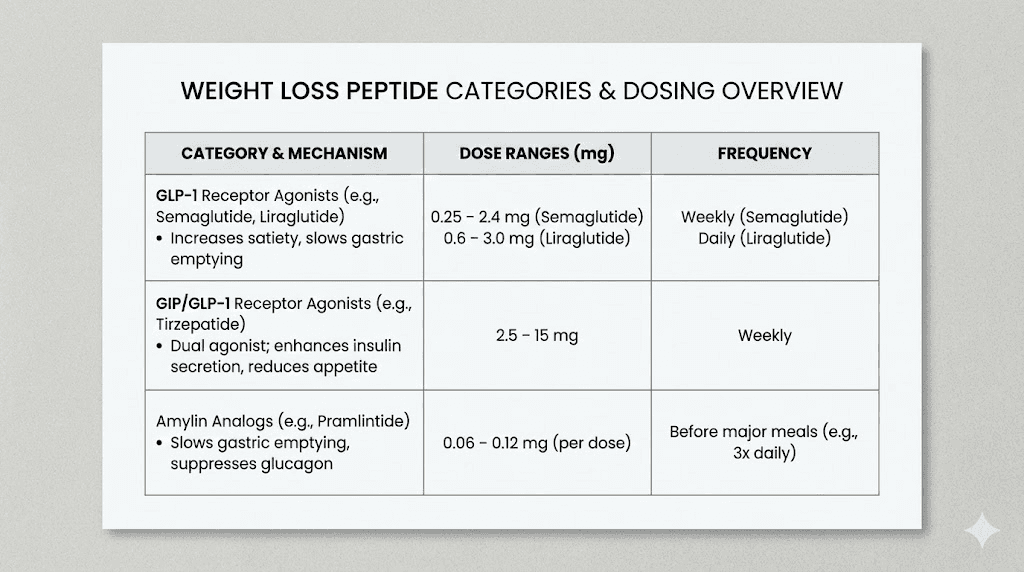
Different fat loss peptides operate through distinct mechanisms with varying effective dose ranges. GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide require microgram to low milligram doses, while growth hormone peptides may use different scales entirely. Understanding these categories prevents dangerous dosing errors when switching between peptide types.
GLP-1 receptor agonists
Semaglutide dosing begins in the microgram range, typically 0.25mg weekly, escalating to maintenance doses of 1.0-2.4mg. The semaglutide dosage calculator accounts for these escalation protocols, providing weekly dose calculations that minimize gastrointestinal side effects through gradual titration.
Tirzepatide follows similar escalation patterns, starting at 2.5mg weekly and increasing to 5mg, 7.5mg, 10mg, 12.5mg, or 15mg based on tolerance and response. These doses might seem small, but GLP-1 agonists possess extraordinary potency at their receptor targets. Even minor calculation errors can significantly impact outcomes.
Both compounds require precise weekly dosing rather than daily administration. Missing doses or doubling up disrupts the steady-state concentrations these peptides need for optimal appetite suppression and metabolic effects. Consistency in both timing and accuracy matters greatly.
Growth hormone secretagogues for fat loss
Peptides that stimulate growth hormone release support fat loss through different mechanisms than GLP-1 agonists. Ipamorelin doses typically range from 100-300mcg per administration, given 1-3 times daily. Converting between mcg and mg requires dividing by 1000, so 200mcg equals 0.2mg.
CJC-1295 dosing varies based on formulation. The DAC version with extended half-life uses doses around 1-2mg weekly, while modified GRF (1-29) without DAC requires more frequent 100-300mcg doses. The CJC-1295 calculator differentiates between these formulations to provide accurate guidance.
Weight loss peptide stacks often combine GH secretagogues with other compounds. Calculating mg doses for multiple peptides requires treating each calculation independently, ensuring accuracy for every component of the protocol.
Fat-specific peptides
AOD-9604 represents a fragment of growth hormone specifically associated with fat metabolism. Typical doses range from 250-500mcg daily, administered once or split into morning and evening doses. This peptide targets visceral fat specifically through lipolytic mechanisms.
Fragment 176-191, closely related to AOD-9604, uses similar dosing ranges. The HGH fragment calculator helps determine precise mcg amounts based on vial concentration and desired dose. These fragments require accurate calculation to achieve the fat-burning threshold without waste.
Tesamorelin, while prescription-only in clinical settings, uses fixed 2mg daily doses in research protocols. Its mechanism involves stimulating natural GH release specifically to reduce visceral adipose tissue, with research originally focused on HIV-associated lipodystrophy.
Using the peptide calculator for weight loss protocols
The peptide calculator streamlines dose determination across all weight loss peptides. Input your vial size, reconstitution volume, and target dose to receive precise syringe measurements. This eliminates manual calculation errors that could compromise your protocol.
Step-by-step calculation process
Begin by identifying your peptide vial content in mg. Semaglutide vials commonly contain 3mg or 5mg, while research peptides may come in 5mg or 10mg sizes. This number serves as your numerator in concentration calculations.
Next, determine your reconstitution volume. Adding more water creates a more dilute solution, requiring larger injection volumes for the same mg dose. Adding less water creates concentrated solutions, allowing smaller injections. Most protocols balance injection volume against precision, using 1-2ml for most reconstitutions.
The calculator divides vial content by water volume automatically. A 5mg vial with 2ml water yields 2.5mg/ml concentration. Enter your target dose, and the calculator determines injection volume in both ml and insulin syringe units.
For weight loss protocols requiring dose escalation, repeat this process for each dose level. The 0.25mg starting dose differs from the 0.5mg week-five dose and the 1.0mg maintenance dose. Preparing a reference chart for your specific reconstitution prevents recalculation each time.
Reconstitution best practices
Proper reconstitution technique ensures your calculations translate into accurate doses. Direct the water stream against the vial wall rather than directly onto the peptide powder. This gentle approach prevents damage to delicate peptide structures.
Allow the powder to dissolve naturally rather than shaking vigorously. Gentle swirling accelerates dissolution without the physical stress that can degrade peptides. Most weight loss peptides dissolve within 1-3 minutes using this technique.
The water type matters for multi-use vials. Bacteriostatic water contains benzyl alcohol preservative that prevents bacterial growth over the vial's use period. Sterile water lacks this protection, requiring single-use or very short storage periods.
Syringe selection and measurement
Insulin syringes provide the precision necessary for peptide dosing. The 0.5ml (50 unit) and 1ml (100 unit) sizes suit most applications. Smaller syringes with finer gradations offer improved accuracy for very small doses.
Reading syringe markings correctly prevents dosing errors. The plunger's rubber stopper has two edges, and the measurement point is the edge closest to the needle. Misreading this reference point can introduce systematic errors across all doses.
For extremely small doses, some researchers use dilution techniques. Adding more reconstitution water creates solutions where larger, more easily measured volumes deliver small mg doses. This approach trades some convenience for improved accuracy in microgram-range dosing.
Weight-based dosing calculations
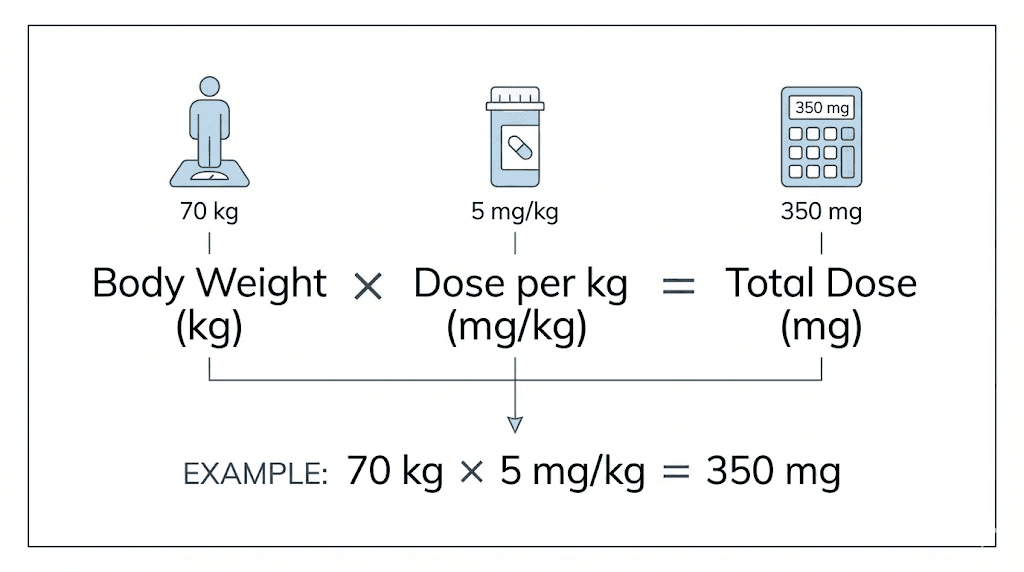
Some peptide protocols adjust doses based on body weight, expressed as mg per kilogram or mcg per kg. These calculations require an additional step, multiplying the per-kg dose by your weight in kilograms to find the total dose.
Converting weight-based protocols
Research studies often report doses in mcg/kg or mg/kg format. If a protocol calls for 5mcg/kg and you weigh 80kg, your dose equals 400mcg or 0.4mg. This personalization accounts for the relationship between body mass and peptide distribution.
Converting pounds to kilograms involves dividing by 2.2. A 180-pound individual weighs approximately 82kg. This conversion must happen before applying weight-based dosing formulas. Errors at this step cascade through all subsequent calculations.
Not all weight loss peptides use weight-based dosing. Semaglutide and tirzepatide employ fixed-dose escalation regardless of body weight, while some research peptides adjust doses to body mass. Following the specific protocol for each peptide ensures appropriate dosing.
Adjusting for body composition goals
Weight loss peptide doses may require adjustment based on individual response and goals. Someone with 100 pounds to lose may eventually require higher maintenance doses than someone fine-tuning the last 15 pounds. These adjustments should occur within established protocol ranges.
Starting doses remain conservative regardless of weight loss goals. The escalation periods built into GLP-1 protocols allow gastrointestinal adaptation that prevents severe nausea and other side effects. Rushing this escalation rarely improves outcomes and often increases adverse events.
For those researching peptide stacks, calculating each component independently prevents confusion. A stack combining ipamorelin at 200mcg with AOD-9604 at 300mcg requires separate calculations for each peptide, even when administered at the same time.
Common weight loss peptides and their specific calculations
Each weight loss peptide has established dosing ranges based on research literature. Applying these ranges through accurate calculation ensures you operate within studied parameters where safety and efficacy data exist.
Semaglutide mg calculations
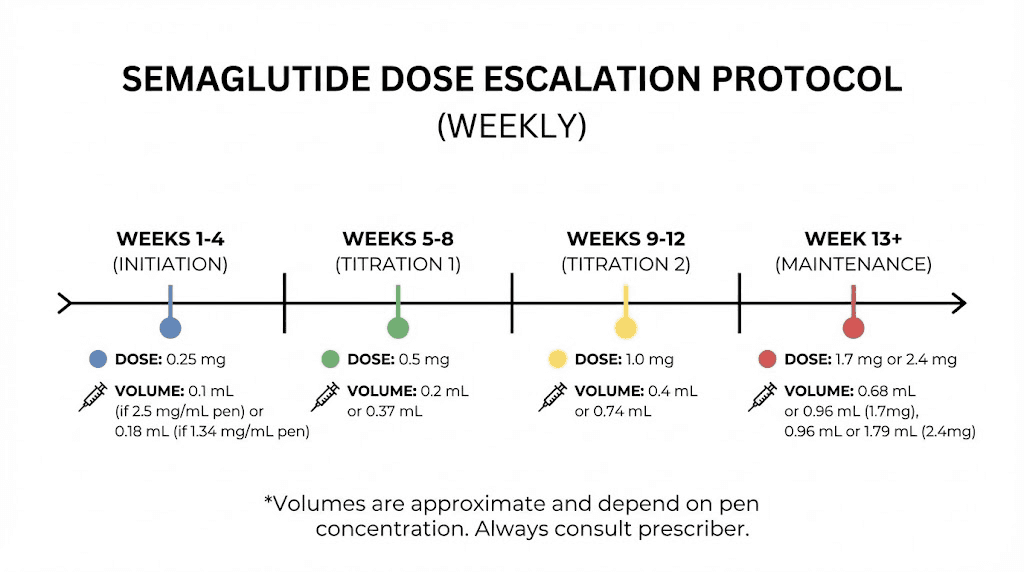
The semaglutide calculator addresses this GLP-1 agonist specifically. Standard escalation follows: 0.25mg weeks 1-4, 0.5mg weeks 5-8, 1.0mg weeks 9-12, with potential further increases to 1.7mg or 2.4mg based on response.
For a 3mg semaglutide vial reconstituted with 1.5ml bacteriostatic water, concentration equals 2mg/ml. The 0.25mg starting dose requires 0.125ml or 12.5 units on an insulin syringe. The 1.0mg maintenance dose requires 0.5ml or 50 units.
Weekly dosing means a 3mg vial provides multiple weeks of treatment at lower doses. At 0.25mg weekly, one vial lasts 12 weeks. At 1.0mg weekly, that same vial lasts only 3 weeks. Planning reconstitution around your protocol phase prevents waste from expired solutions.
Tirzepatide mg calculations
Tirzepatide vials commonly contain 5mg, 10mg, or larger amounts. Escalation typically proceeds: 2.5mg weeks 1-4, 5mg weeks 5-8, 7.5mg weeks 9-12, with potential increases to 10mg, 12.5mg, or 15mg.
A 10mg vial reconstituted with 2ml yields 5mg/ml concentration. The 2.5mg starting dose requires 0.5ml or 50 units. The 5mg dose requires 1ml or 100 units, using the entire syringe. Higher doses may require multiple injections or more concentrated reconstitutions.
The dual GIP/GLP-1 mechanism of tirzepatide means it cannot be directly substituted with semaglutide doses. Each peptide requires independent calculation following its specific protocol, even though both target weight loss.
Growth hormone peptide calculations for fat loss
Ipamorelin at 200mcg from a 5mg vial reconstituted in 2.5ml creates a 2mg/ml or 2000mcg/ml concentration. The 200mcg dose requires 0.1ml or 10 units. Three daily doses means 30 units daily, and the 5mg vial provides approximately 25 days of treatment.
Stacked protocols combining ipamorelin with CJC-1295 or sermorelin require separate vials and calculations for each component. While peptides can be mixed in the same syringe immediately before injection, they should be stored separately to prevent interaction.
Energy-supporting peptides sometimes accompany weight loss protocols. These additional compounds each require independent calculation, expanding the planning needed but not changing the fundamental math for any single peptide.
Escalation protocols and dose adjustments
Weight loss peptide protocols typically begin with lower doses and increase gradually. This escalation approach improves tolerability while identifying the minimum effective dose for each individual. Calculating doses for each escalation phase in advance streamlines the process.
GLP-1 agonist escalation
The escalation schedule for semaglutide and similar compounds exists specifically to minimize gastrointestinal side effects. Starting at full dose would cause severe nausea in most users. The gradual increase allows receptor adaptation and gastrointestinal adjustment.
Each escalation phase requires recalculating injection volume unless you prepare a reference chart. Writing out the ml and unit measurements for each dose level against your specific reconstitution provides a quick reference that prevents calculation errors during the weeks-long escalation period.
Some individuals require slower escalation, extending each phase beyond four weeks if side effects remain problematic. Others tolerate faster increases. The peptide dosing guide provides frameworks for adjusting escalation speed while maintaining safety margins.
Maintenance dose optimization
Once reaching the initial target dose, assessment determines whether further increases benefit the protocol. Some individuals achieve excellent results at 1.0mg semaglutide, while others require 2.4mg for similar effects. This variation reflects individual receptor sensitivity and metabolic differences.
Increasing beyond protocol ranges lacks safety data and increases risk without guaranteed benefit. The established maximum doses represent the upper limits studied in clinical trials, beyond which risk-benefit ratios become unfavorable.
For plateau situations where weight loss stalls, strategies beyond dose escalation often prove more effective. Reviewing diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management frequently identifies addressable factors that dose increases cannot overcome.
Cycle considerations for weight loss peptides
Cycle planning for weight loss peptides differs from other peptide categories. GLP-1 agonists often continue indefinitely for weight maintenance, while GH secretagogues may cycle with periodic breaks. Understanding which approach applies to each peptide prevents inappropriate protocol design.
Long-term GLP-1 use has extensive safety data from diabetes treatment populations. The metabolic benefits persist with continued use, while discontinuation often leads to weight regain. This reality influences decisions about protocol duration.
For peptide cycling approaches, calculating doses for both on and off phases helps maintain protocol structure. Some weight loss stacks include compounds that do require cycling, necessitating periodic recalculation as protocols evolve.
Preventing calculation errors
Dosing errors with weight loss peptides can cause significant problems. Underdosing wastes product and time without delivering results. Overdosing increases side effects and potentially creates safety concerns. Multiple verification steps prevent these outcomes.
Double-checking calculations
Performing calculations twice using different methods catches arithmetic errors. First calculate manually, then verify with the online calculator. Agreement between methods confirms accuracy, while disagreement signals the need for investigation.
Writing calculations down creates a record for future reference and review. This documentation proves especially valuable for complex stacks or when adjusting protocols over time. What seemed clear during initial setup may become confusing weeks later.
Having a knowledgeable second person review calculations provides another error-catching layer. Fresh eyes often spot mistakes that become invisible after staring at numbers repeatedly. This verification step is particularly valuable when working with potent compounds.
Common calculation mistakes
Unit confusion between mcg and mg causes 1000-fold errors. Treating 0.25mg as 0.25mcg would result in massive overdose. Always verify which unit the protocol uses and convert consistently. When in doubt, convert everything to the same unit before calculating.
Reconstitution volume errors cascade through all subsequent calculations. Adding 1ml when you intended 2ml doubles the concentration and halves the volume needed for each dose. Measuring water carefully and recording the actual amount used prevents this error.
Syringe reading mistakes affect every dose from a vial. Misidentifying the measurement edge of the plunger, miscounting gradation marks, or confusing unit and ml scales all introduce systematic errors. Taking time to understand your specific syringe prevents these issues.
Storage and stability considerations
Proper peptide storage maintains the accuracy of your calculations over time. Degraded peptides deliver less active compound than expected, effectively reducing your dose despite correct volume measurement.
Understanding refrigerated shelf life prevents using degraded product. Most reconstituted peptides remain stable 3-4 weeks when properly refrigerated. Planning reconstitution around usage rate ensures fresh product throughout your protocol.
Reconstituted stability varies between peptides. Some remain stable longer than others. Researching your specific peptide's stability profile helps plan appropriate vial sizes and reconstitution frequencies.
Tools and resources for peptide dosing
SeekPeptides offers multiple calculators addressing different aspects of peptide dosing. Using these tools systematically ensures accuracy across all protocol phases and peptide types.
Calculator overview
The general peptide calculator handles any peptide type, accepting vial size, reconstitution volume, and target dose to output injection measurements. This versatility makes it the go-to tool for most calculations.
Peptide-specific calculators like the semaglutide calculator, BPC-157 calculator, and TB-500 calculator incorporate protocol-specific guidance. These tools include escalation schedules and typical dose ranges alongside the core calculations.
The reconstitution calculator focuses specifically on determining appropriate water volumes. It helps balance injection volume convenience against measurement precision, outputting concentration for any given reconstitution.
Stack and cost planning
The stack calculator addresses multi-peptide protocols, helping organize complex regimens with multiple compounds. Weight loss stacks combining fat loss peptides with healing or energy-supporting peptides benefit from this systematic approach.
Cost considerations influence protocol sustainability. The cost calculator estimates expense over protocol duration, helping plan purchases and identify the most cost-effective approaches to achieving weight loss goals.
These tools together support the complete planning process from initial protocol design through daily execution. Bookmarking relevant calculators streamlines ongoing protocol management.
Specific protocols for different weight loss goals
Weight loss encompasses various specific goals requiring tailored approaches. Targeting visceral fat differs from overall weight reduction. Fat loss while preserving muscle requires different peptide selection than simple scale weight reduction.
Maximum fat loss protocols
Aggressive fat loss protocols often combine multiple peptides targeting different mechanisms. GLP-1 agonists reduce appetite and food intake. GH secretagogues increase lipolysis and metabolic rate. Fat-specific fragments directly enhance fat burning. Each component requires independent calculation.
A protocol combining semaglutide, ipamorelin, and AOD-9604 involves three separate calculations. The semaglutide dose follows standard escalation. Ipamorelin doses might be 200mcg twice daily. AOD-9604 might be 300mcg once daily. Each from separate vials, each with unique concentration calculations.
Timing considerations add complexity. GH peptides often perform best before sleep or fasted in the morning. GLP-1 injections are typically weekly. Organizing these schedules while maintaining accurate dosing for each component requires systematic planning.
Muscle-preserving fat loss
Losing fat while maintaining or gaining muscle represents the ideal body composition change. Peptides supporting this goal include GH secretagogues that promote both fat loss and protein synthesis. Muscle-supporting peptides can accompany dedicated fat loss compounds.
Dose calculations for these protocols follow the same principles. The addition of muscle growth peptides means more compounds to calculate, but each individual calculation remains straightforward.
Muscle preservation during aggressive fat loss often requires protein intake attention alongside peptide protocols. The peptides create an anabolic environment, but dietary protein provides the building blocks for muscle maintenance.
Stubborn fat targeting
Some fat deposits resist standard approaches, requiring specialized strategies. Visceral fat around organs and subcutaneous fat in specific areas may respond differently to various peptides. Protocols targeting these stubborn areas may emphasize different compounds.
AOD-9604 and HGH fragment show particular affinity for visceral fat metabolism. Calculating doses for these peptides follows standard procedures, but protocol design might prioritize these compounds for stubborn visceral fat situations.
Local factors including blood flow and receptor density influence fat loss from specific areas. Peptides work systemically rather than locally, but their mechanisms may preferentially affect certain fat deposits based on metabolic characteristics.
Monitoring and adjusting based on results
Weight loss peptide protocols require ongoing assessment and potential adjustment. Tracking progress systematically identifies when dose modifications might help and when other factors need attention.
Progress tracking methods
Scale weight provides one metric but doesn't capture body composition changes. Someone losing fat while gaining muscle might see minimal scale changes despite significant improvements. Body measurements, progress photos, and how clothes fit often prove more informative.
Before and after documentation creates objective comparison points. Weekly photos under consistent lighting reveal changes that daily observation misses. Measurements of waist, hips, and other sites track fat loss from specific areas.
Energy levels, sleep quality, and mood also reflect protocol effectiveness. Energy and focus improvements from GH optimization often accompany the fat loss effects of these peptides. Tracking these subjective measures provides a fuller picture of protocol impact.
When to adjust doses
Inadequate results after sufficient time at a given dose may warrant escalation within established ranges. For semaglutide, this might mean progressing from 1.0mg to 1.7mg or 2.4mg. These adjustments should follow standard escalation timing rather than impulsive changes.
Side effects that remain intolerable despite adaptation time may indicate the need for dose reduction. Finding the balance between effective and tolerable doses often requires some experimentation within protocol guidelines.
Recalculating doses after any protocol change ensures accuracy continues. Adjusting from 1.0mg to 1.7mg semaglutide means new injection volume calculations. Updating reference charts with each change prevents confusion.
Plateau management
Weight loss plateaus occur in virtually all protocols regardless of peptide use. After initial rapid progress, the body adapts to new energy balance. Breaking plateaus often requires addressing factors beyond peptide dosing.
Dietary review frequently identifies plateau causes. Calorie creep, where portions gradually increase, can offset the appetite suppression from GLP-1 agonists. Returning to measured portions often restarts progress without dose changes.
Exercise intensity and variety affect metabolic adaptation. Adding resistance training or changing cardio modalities can overcome plateaus by preventing metabolic efficiency that limits fat loss. Athletic performance peptides might support increased exercise capacity.
Safety considerations for weight loss peptide dosing
Peptide safety depends partly on accurate dosing. Understanding the safety implications of calculation errors reinforces the importance of precision throughout the dosing process.
Overdose risks
GLP-1 agonist overdose primarily causes severe gastrointestinal effects. Nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea beyond normal adaptation responses can occur with excessive doses. While rarely dangerous, these effects significantly impact quality of life and may cause dehydration.
Growth hormone peptide overdose can cause fluid retention, joint pain, and carpal tunnel-like symptoms. These effects resolve with dose reduction but indicate levels beyond physiological optimization. Staying within established dose ranges prevents these issues.
Long-term overdosing carries greater risks than acute errors. Chronically elevated GH signaling might influence cellular growth in unwanted ways. Maintaining physiological rather than supraphysiological levels provides benefits with minimized risks.
Underdose consequences
Underdosing wastes product and time without delivering expected results. Someone calculating their semaglutide dose at half the intended amount would experience reduced appetite suppression and slower weight loss. They might incorrectly conclude the peptide doesn't work.
Systematic underdosing from reconstitution errors affects every dose from a vial. Discovering the error only after finishing the vial means weeks of suboptimal protocol. Verifying calculations early prevents this extended issue.
Inconsistent dosing, varying between under and over, disrupts the steady-state concentrations many peptides require. GLP-1 agonists particularly benefit from consistent weekly dosing. Accuracy matters for every administration, not just occasionally.
Drug interaction considerations
Weight loss peptides may interact with diabetes medications, requiring dose adjustments to prevent hypoglycemia. GLP-1 agonists affect blood glucose through multiple mechanisms. Those using insulin or sulfonylureas need medical guidance when adding these peptides.
Thyroid medications may require monitoring when using GH-stimulating peptides. Growth hormone influences thyroid hormone conversion and metabolism. Changes in thyroid function tests might necessitate medication adjustments.
Blood pressure medications might require adjustment as weight loss progresses. Reduced body mass often improves blood pressure, potentially causing over-medication. Regular monitoring identifies when adjustments become necessary.
Practical workflow for dose preparation
Establishing a consistent workflow for dose preparation minimizes errors and ensures accuracy across every administration. This systematic approach applies whether preparing single doses or organizing a week's worth of injections.
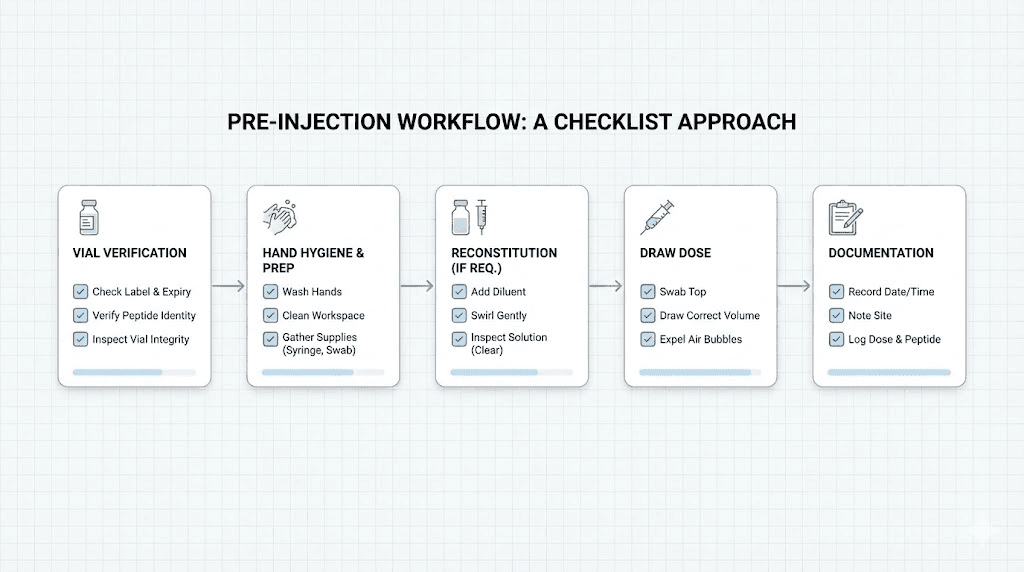
Pre-injection verification
Before drawing any injection, verify the vial contains the expected peptide. When using multiple peptides, similar-looking vials can be confused. Labeling vials clearly and checking labels before each use prevents mix-ups.
Confirm the target dose before calculating injection volume. Escalation protocols mean the dose changes periodically. Checking which phase you're in and what dose applies prevents accidentally using previous phase doses.
Calculate the injection volume fresh or reference your prepared chart. Even with a reference chart, occasional verification against calculator results catches any errors in the original chart preparation.
Drawing and measuring technique
Proper syringe technique ensures the calculated volume translates into accurate dosing. Insert the needle through the vial stopper, invert the vial, and draw slightly more than needed. Then push excess back until the correct volume remains.
Read the syringe at eye level with the measurement markings clearly visible. The curve of liquid in the syringe barrel, called the meniscus, should align with your target marking. Taking time to measure accurately prevents systematic errors.
Remove air bubbles before injection by tapping the syringe with the needle pointed up and pushing bubbles out. While small air bubbles in subcutaneous injections aren't dangerous, they displace product and slightly reduce actual dose delivered.
Documentation and tracking
Recording each injection creates a log for troubleshooting and verification. Date, time, peptide, and dose form the basic record. Adding injection site helps with rotation. Noting any observations helps identify patterns.
This log helps identify missed doses that might otherwise go unnoticed. For weekly GLP-1 injections, seven days between doses can blur together. The record confirms when the last injection actually occurred.
Over longer protocols, documentation reveals compliance patterns. Periods of inconsistency correlate with reduced results. Recognizing these patterns helps maintain the consistency that maximizes peptide benefits.
Frequently asked questions
How do I convert mcg to mg for peptide dosing?
Divide micrograms by 1000 to get milligrams. For example, 250mcg equals 0.25mg. This conversion is essential when protocols use different units than your calculation tools expect. Always verify which unit a protocol uses before calculating.
How much water should I add to reconstitute peptides for weight loss?
Reconstitution volume depends on desired concentration and injection volume preferences. Common choices include 1ml or 2ml of bacteriostatic water. More water means more dilute solution and larger injection volumes. The reconstitution calculator helps determine optimal volumes.
Can I mix different weight loss peptides in the same syringe?
Some peptides can be combined in the same syringe immediately before injection, while others should be administered separately. Research compatibility before mixing. Generally, store peptides in separate vials even if combining for injection.
How long do reconstituted weight loss peptides last?
Most reconstituted peptides remain stable 3-4 weeks when refrigerated properly. Some may last longer, others shorter. Check specific stability data for your peptide. Plan reconstitution around your usage rate to avoid waste from expired solutions.
What if I miss a dose of my weight loss peptide?
For weekly GLP-1 injections, take the missed dose as soon as remembered if within a day or two. If closer to the next scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and resume normal schedule. Never double dose. For daily peptides, resume normal dosing at the next scheduled time.
How SeekPeptides supports weight loss peptide research
SeekPeptides provides essential tools for accurate weight loss peptide dosing. The calculator suite addresses every aspect of dose determination, from initial reconstitution through ongoing protocol adjustments.
The general calculator handles any peptide type, while specialized tools like the semaglutide calculator incorporate protocol-specific guidance. These resources eliminate calculation errors that could compromise weight loss results.
Educational content including the dosage calculation guide and reconstitution instructions build the understanding necessary for confident, accurate peptide use. SeekPeptides supports researchers at every knowledge level.
The cost calculator helps plan sustainable protocols, while the stack calculator organizes complex multi-peptide approaches. Together, these tools enable comprehensive weight loss protocol planning and execution.
Helpful resources
In case I don't see you, good afternoon, good evening, and good night. May your calculations stay accurate, your doses stay precise, and your weight loss stay consistent. Join SeekPeptides.